Proteolytically released Lasso/teneurin-2 induces axonal attraction by interacting with latrophilin-1 on axonal growth cones
Figures
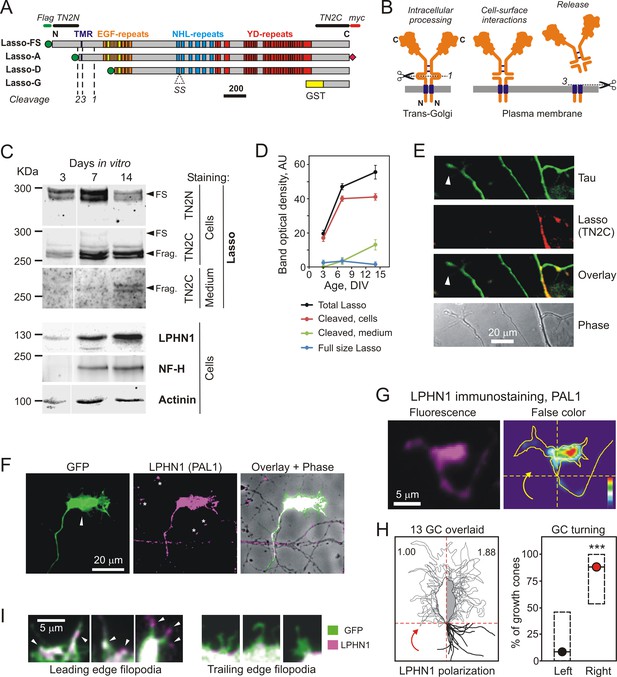
Lasso is cleaved and released into the medium during neuronal development.
(A) Recombinant Lasso constructs used in this work (FS, full size). The three proteolytic cleavage sites and the SS splice site are indicated. The antibody recognition sites/epitopes are shown by bars above the structure. Scale bar, 200 amino acids. (B) Intracellular processing and release of TENs. Left, TEN2 is constitutively cleaved in the trans-Golgi vesicles by furin at site 1. Middle, when delivered to the cell surface, the ECD remains tethered to the membrane and functions as a cell-surface receptor. Right, regulated cleavage at site 3 releases the ECD into the medium. (C) Expression of Lasso and release of its ECD fragment in hippocampal neurons in culture. Rat hippocampal neurons were cultured for 3, 7 and 14 days, and proportionate amounts of the conditioned media and cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE. A Western blot (representative of three independent experiments, which all gave similar results) was stained for Lasso, LPHN1, neurofilament-H (NF-H), and actinin. The doublet bands corresponding to splice variants of full-size Lasso (FS) and the fragment of ECD (Frag.) cleaved at site 1 are indicated by arrowheads. (D) Quantification of Western blots (as in C), using Lasso C-terminus staining data. (E) Axonal growth cones (white arrowheads) do not express Lasso/teneurin-2. Neurons in a 9 DIV hippocampal culture were permeabilized and stained for the axonal protein Tau (green) and Lasso (TN2C, red) (representative image from n = 5 experiments). (F) A detailed study of growth cones. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with a vector encoding GFP, then, after 14 DIV, stained for LPHN1 (PAL1 and Alexa 647-conjugated secondary antibody, magenta), and axonal growth cones were visualized by GFP fluorescence (green). (G, H) Correlation of LPHN1 polarization within a growth cone with its recent travel trajectory. G left, a fluorescent image of a growth cone stained for LPHN1 (magenta). G right, the same image in false color (contour based on GFP staining), demonstrating LPHN1 polarization on the right side. H left, the contours of 13 roughly symmetrical growth cones and their preceding axons were aligned to locate the stronger LPHN1 staining on the right. Note, that all axons approach growth cones from the right low quadrant. H right, the proportion of right- and left-turning growth cones plotted with Jeffreys 99.73% confidence intervals for a binomial parameter; ***, p<0.001; n = 13. (I). LPHN1 is found within filopodia and lamellipodia on the leading edge (left, arrowheads), but not on the trailing edge (right) of a growth cone. Green, GFP fluorescence; magenta, PAL1 staining for LPHN1.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1, Panels D and H.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.004
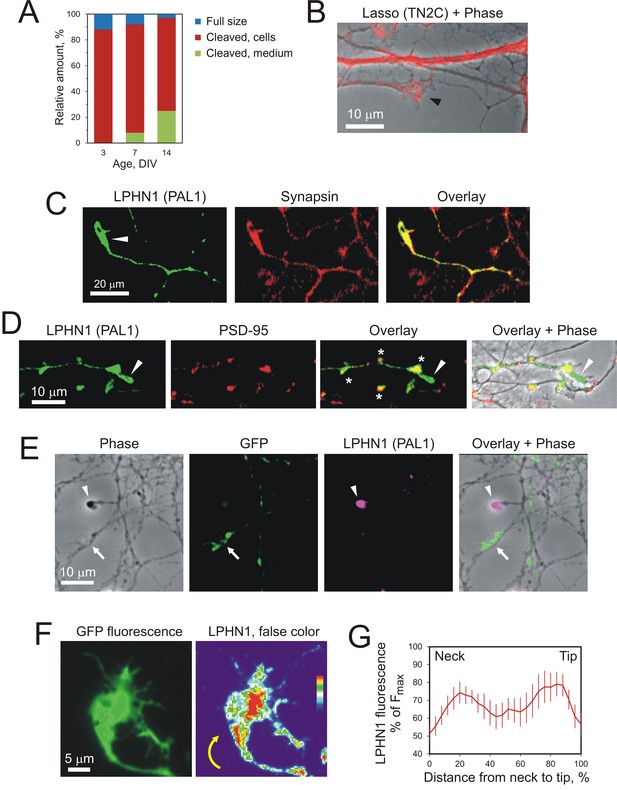
Lasso is expressed on dendrites and LPHN1 on axonal growth cones in developing neurons.
(A) Proportional expression of full-size Lasso and its fragments in hippocampal neurons in culture. The data are from Western blots (as in Figure 1C, n = 3), stained using the TN2C antibody. (B) Lasso (red) is strongly expressed on dendritic shafts and dendritic growth cones (black arrowhead). Neurons in 7–9 DIV hippocampal cultures were stained for Lasso/teneurin-2 using TN2C antibody. (C) LPHN1 is expressed in axons and axonal growth cones (white arrow) in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. 7–9 DIV neuronal cultures were permeabilized and stained for LPHN1 (green) and synapsin (red). A growth cone is indicated by the white arrow. (D) LPHN1 is enriched in en passant synapses. A 9 DIV hippocampal culture was stained for Lasso (TN2C, green) and postsynaptic structural protein, PSD-95 (red). Synapses are indicated by asterisks; the growth cone, by a white arrowhead. (E) Knockdown of LPHN1. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with a bicistronic vector, encoding GFP and an shRNA against LPHN1, then at 14 DIV stained for LPHN1 (magenta) and imaged. Note that the growth cone of a knockdown neuron (green, arrow) lacks LPHN1, while the growth cone of an uninfected neuron (magenta, arrowhead) expresses LPHN1. (F) LPHN1 is expressed near the leading edge of turning growth cones. Left, GFP fluorescence of a growth cone. Right, the same growth cone stained for LPHN1 and rendered in false color. Note two peaks of LPHN1 quantity (red): in the central region (immediately above the ‘neck’, i.e. the end of axon shaft), and near the actively growing side of the growth cone. (G) An average profile of LPHN1 expression within turning growth cones. LPHN1 fluorescence was quantified along the median line of turning growth cones, expressed as % of maximal fluorescence and plotted against the normalized length of growth cones (distance expressed as %). The data are the mean values ± SEM; n = 9. Note the bimodal distribution of LPHN1 expression.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1—figure supplement 1, Panels A and G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.006
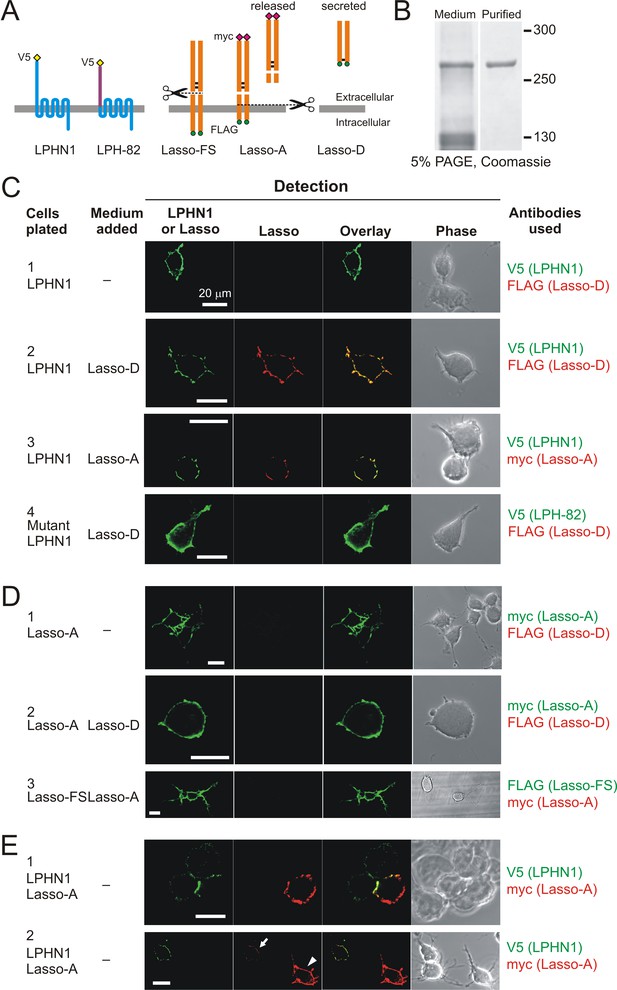
Soluble Lasso binds to LPHN1 on other cells.
(A) A scheme of LPHN and Lasso constructs used in this experiment. LPH-82 is LPHN1 with the ECD from another adhesion G-protein-coupled receptor, EMR2, used as a negative control. (B) Purification of Lasso-D. Lasso-D was expressed in stably transfected HEK293 cells, then purified on a column with anti-FLAG Ab and analyzed by SDS-PAGE in a 5% gel, stained with Coomassie R250. (C–E) Interaction between the soluble Lasso species and NB2a cells expressing LPHN1, LPH-82, or Lasso-A. Cells expressing LPHN1 (C, panels 2, 3), but not Lasso-A or Lasso-FS (D) or mutant LPH-82 (C, panel 4) are able to interact with Lasso-D or Lasso-A. E, panel 1. Short-term, high-density incubation of cells expressing LPHN1 and membrane-anchored Lasso-A allows these proteins to form inter-cellular contacts. E, panel 2. After a 48 hr co-culture, a sufficient amount of Lasso-A is released into the medium, diffuses away from Lasso-A expressing cells (arrowhead) and can be detected interacting with distant LPHN1-expressing cells (arrow). Images are representative of n = 6–7 independent experiments.
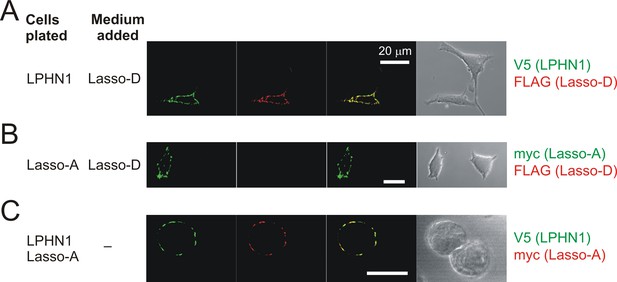
Soluble Lasso specifically binds to LPHN1-expressing cells.
Interaction between the soluble Lasso species and NB2a cells expressing LPHN1 or Lasso-A. Cells expressing LPHN1 (A), but not Lasso-A (B), are able to bind the soluble Lasso-D. (C) Binding of the soluble Lasso ECD released by the cells expressing the full-size Lasso-A to the surface of cells expressing LPHN1, after 48 hr in co-culture. Note the lack of Lasso-D binding to cells not expressing LPHN1 (A–C) and the clumping of both proteins (C). Images are representative of n = 7 independent experiments.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2—figure supplement 2, Panel C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.009
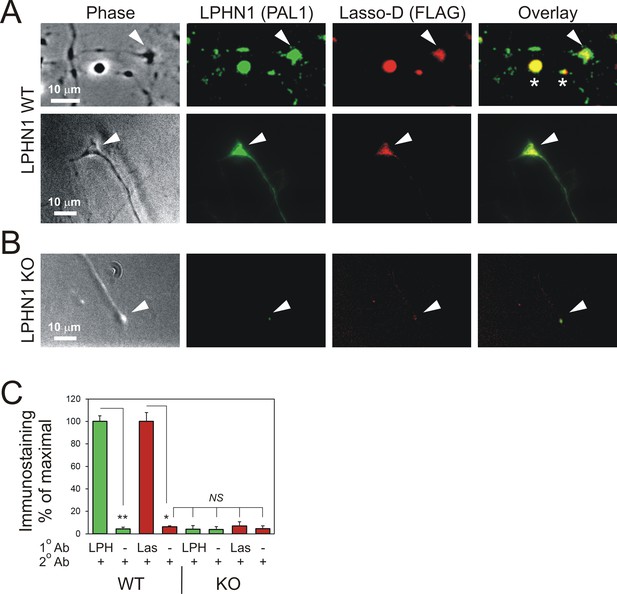
Soluble Lasso specifically binds to LPHN1 on axonal growth cones.
Hippocampal neurons from LPHN1 WT or KO newborn mice were grown in culture for 14 days and then incubated with the medium from NB2a cells stably expressing Lasso-D. The cultures were fixed and stained for LPHN1 (PAL1, green) and exogenous Lasso-D (FLAG, red). (A) Two examples of LPHN1 WT axonal growth cones. (B) An example of LPHN KO growth cones. Asterisks, axonal varicosities; arrowheads, axonal growth cones. The images are representative of 5–7 independent measurements, which all gave similar results. Note that LPHN1 KO neurons do not exhibit LPHN1 staining (green), only showing autofluorescence, and do not appreciably bind Lasso-D (red). (C) Quantification of the immunostaining data from n = 3 independent experiments. In control experiments, only secondary antibodies were used. Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction: *, p=0.031; **, p=0.009.
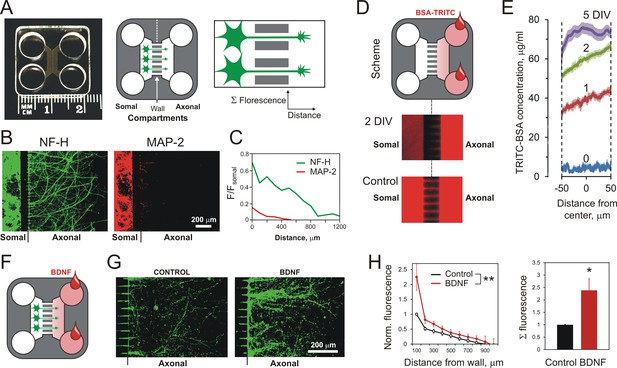
Using MAIDs to study axonal attraction by soluble chemoattractants.
(A) Left, a photograph of a MAID. Center, a scheme of the experiment: neurons are seeded into the Somal Compartment and their neurites grow into the Axonal Compartment; both compartments are then stained for NF-H (axons) and MAP-2 (dendrites). Right, an enlarged portion of the separating wall showing the principles of fluorescence measurements in the Axonal Compartment. (B) Fluorescent images from the same MAID stained for NF-H (green) and MAP-2 (red) showing that axons penetrate into the Axonal Compartment significantly more readily than dendrites. (C) Profiles of NF-H and MAP-2 fluorescence in the Axonal Compartment, normalized to respective fluorescence in the Somal Compartment show that the relative degree of penetration of axons is ~5 fold higher compared to dendrites. (D) Gradients of soluble proteins can be established within microchannels and maintained for several days. Top, a scheme of the experiment: TRITC-conjugated BSA was added to the Axonal Compartment and monitored using time-lapse fluorescent microscopy. Middle, fluorescence distribution 2 days after TRITC-BSA addition. Bottom, fluorescence distribution after filling the whole MAID with TRITC-BSA. (E) Quantification of the TRITC-BSA gradient within microchannels (normalized to 100 µg/ml TRITC-BSA). The mean values are shown ±SEM; n = 4. (F–H) A gradient of BDNF in MAIDs acts as an axonal attractant. (F) A scheme of the experiment. (G) Representative images of NF-H-positive axons in the Axonal Compartment exposed to control conditions (left) or to a BDNF gradient in the microchannels (right). H. Left, Average profiles of normalized NF-H fluorescence in the presence or absence of BDNF (2-way ANOVA: **, p=0.002; F1,84 = 10.15). Right, integrated NF-H fluorescence between 0 and 500 μm from the separating wall (t-test: *, p=0.04; n = 5).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3, Panels C, E, and H.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.012
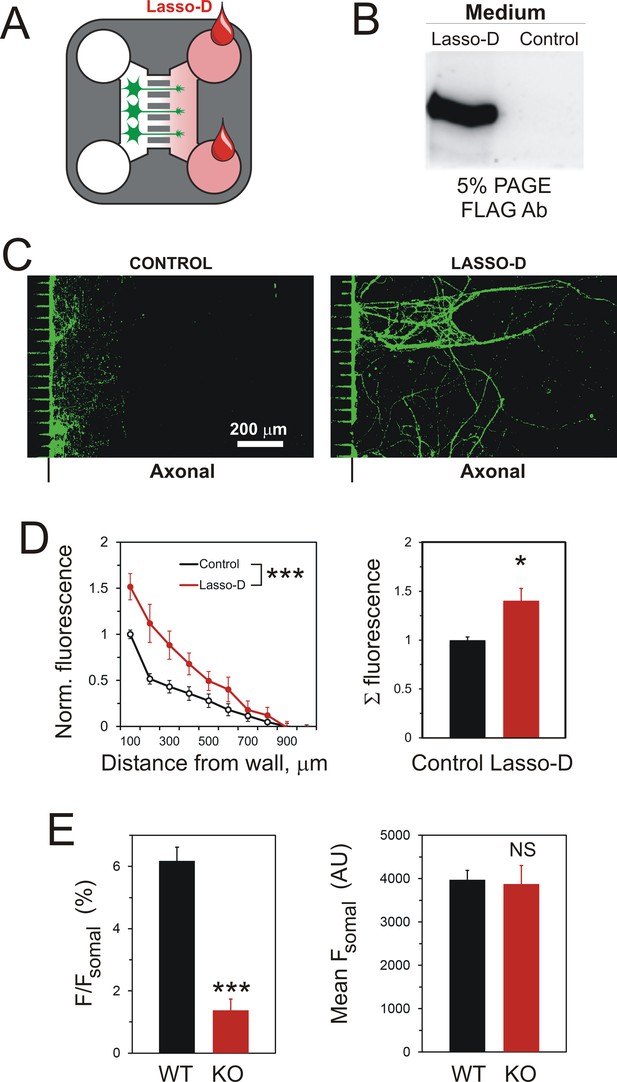
A gradient of soluble Lasso-D induces axonal attraction via LPHN1.
(A) A scheme of the experiment: hippocampal neurons were cultured in Somal Compartments, purified Lasso was added to Axonal Compartments at 3 DIV. (B) Lasso remains intact in the Axonal Compartment. The media from Axonal Compartments were collected at 8 DIV and analyzed by Western blotting. (C). Images of NF-H-positive axons in the Axonal Compartment exposed to control medium (left) or Lasso-D (right). (D) Analysis of axonal growth in Axonal Compartments. Left, profiles of NF-H immunofluorescence with and without Lasso-D (3-way ANOVA: ***, p<0.001; F1,144 = 12.92). Right, average integrated immunofluorescence at 0–500 μm from the wall, with and without Lasso-D (t-test: *, p=0.027; n = 7). (E) Knockout of LPHN1 blocks axonal attraction by soluble Lasso. Hippocampal neurons from Adgrl1-/- (LPHN1 KO) and Adgrl1+/+ (LPHN1 WT) mice were cultured in MAIDs and exposed to Lasso-D gradient. The amount of cellular material in each compartment was quantified by DiO labeling at 8 DIV. E. Left, LPHN1 KO cultures sent significantly fewer neurites to Lasso-containing Axonal Compartments compared to WT cultures (t-test: ***, p<0.001, n = 3). Right, there was no difference in the number of cells, dendrites and axons in the Somal Compartments between the two types of cultures (t-test: N.S., p=0.4, n = 3).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1—figure supplement 1, Panels D and E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.014
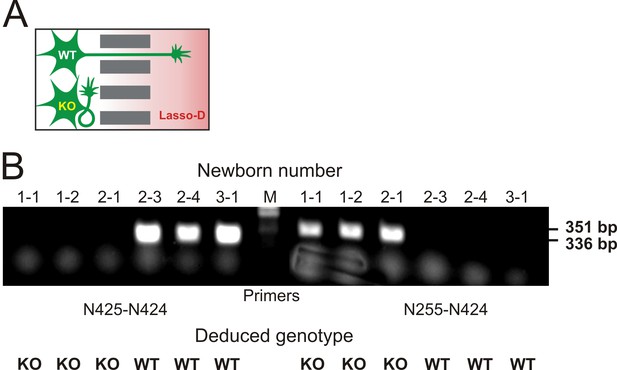
Knockout of LPHN1 prevents axonal attraction by soluble Lasso.
(A) Experimental hypothesis: predicted behavior of LPHN1 KO axons in response to a gradient of soluble Lasso. (B) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based genotyping of 6 newborn pups from three mothers used to prepare hippocampal cultures in MAIDs. The PCR primers used are indicated below and the sizes of amplified fragments are shown on the right; the deduced genotypes are indicated at the bottom.
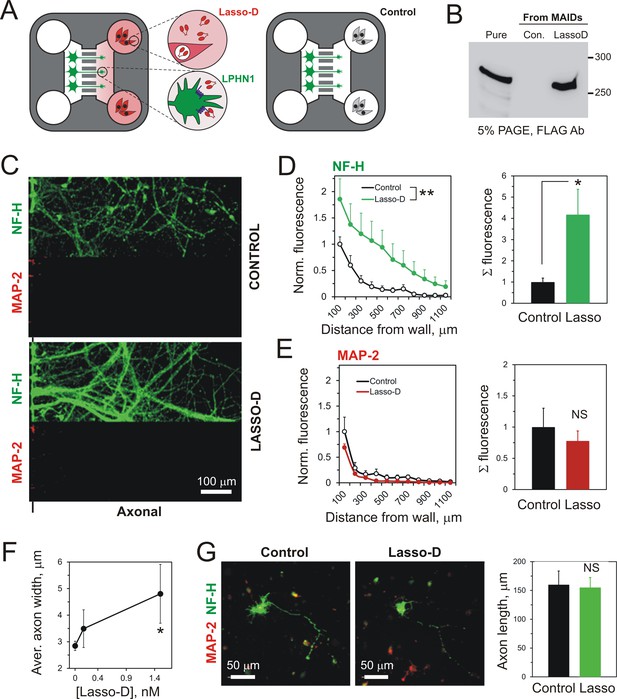
A spatio-temporal gradient of soluble Lasso induces axonal attraction and fasciculation, but does not increase axonal length.
(A) A scheme of the experiment: HEK293A cells stably transfected with Lasso-D were cultured in the wells of Axonal Compartments; untransfected cells were used as a control. (B) A representative Western blot of the media from Axonal Compartments; Lasso-D is secreted by transfected HEK293A cells only and is stable. (C) Images of NF-H-positive axons (green) and MAP-2-positive dendrites (red) in the Axonal Compartment exposed to temporal gradients formed by control cells (top) or Lasso-D-expressing cells (bottom). (D) Left, profiles of axons in Axonal Compartments, identified by NF-H immunofluorescence, exposing a difference between control and Lasso-secreting cells (3-way ANOVA: **, p=0.006; n = 7, F1,84 = 7.89). Right, average integrated axonal fluorescence at 0–500 μm from the wall, with control or Lasso-secreting cells (t-test: *, p=0.045; n = 7). (E) Left, profiles of dendrites in Axonal Compartments, identified by MAP-2 immunofluorescence, with control or Lasso-secreting cells (3-way ANOVA: non-significant, p=0.23; F1,84 = 1.46). Right, average integrated dendritic fluorescence at 0–500 μm from the wall, with control or Lasso-secreting cells (t-test: non-significant, p=0.54; n = 7). (F) Soluble released Lasso-D induces axonal fasciculation. The width of all NF-H-positive axonal bundles was measured at 100 µm from the separating wall. The degree of fasciculation correlates with Lasso concentration (Pearson’s correlation: R2 = 0.43, p=0.041). (G) Soluble Lasso has no effect on axon length in cultured hippocampal cells. Left. Representative images of GFP-positive neurons immunostained for GAP-43 (red); after treatment with control medium (left) or with Lasso-D (right). Right. Quantification of the total neurite length in GFP-expressing neurons after the treatment (t-test: non-significant, p>0.05, n = 30 cells without Lasso-D and 61 cells with Lasso-D from three independent cultures).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5, Panels D-G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.017
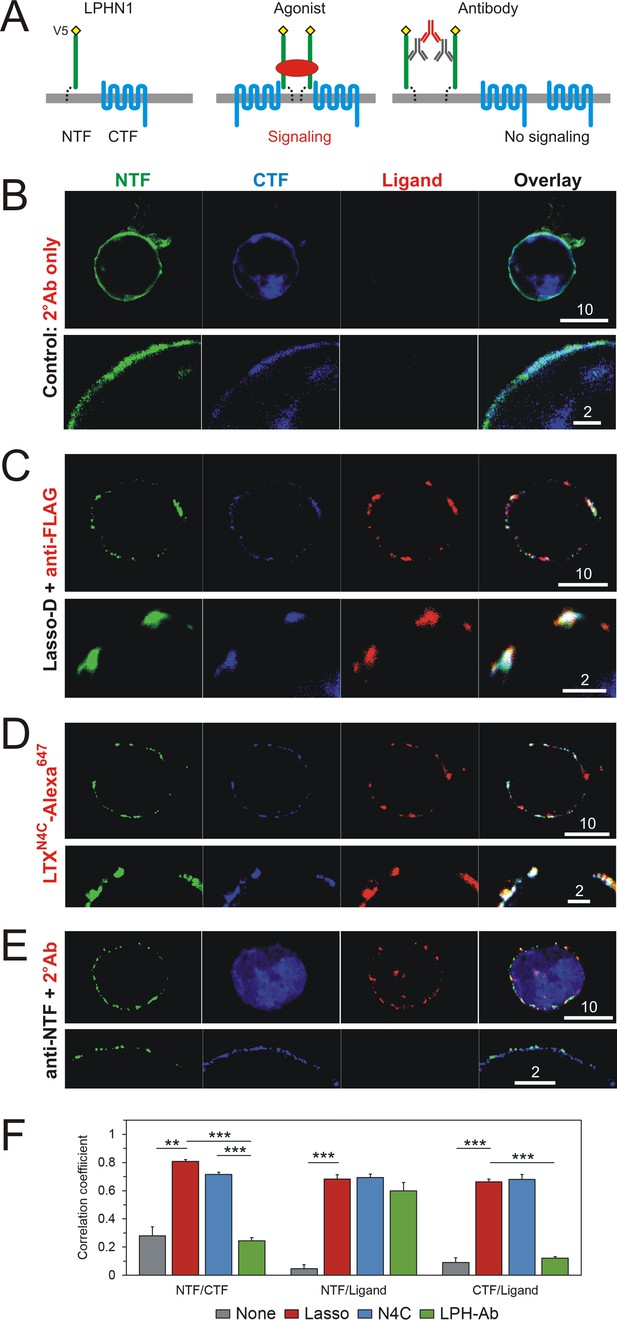
Interaction of LPHN1 with soluble Lasso causes LPHN1 aggregation.
(A) A scheme of behavior of LPHN1 fragments at rest (left) and after binding an active agonist (middle) or a non-agonistic antibody (right). (B–D) Distribution of NTF and CTF in NB2a cells stably expressing LPHN1 and treated with control buffer (B), Lasso-D (C) or LTXN4C (D). (E) The binding of a non-agonistic antibody against NTF of LPHN1 does not cause an association of the NTF and CTF of LPHN1. Images shown are representative of 4 independent experiments (n = 4–7). All scale bars are in μm. (F) Quantitative analysis of correlation between the ligand-induced redistribution of NTF, CTF and ligand. T-test with Bonferroni correction: **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; n = 4–7 independent experiments.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Source data for Figure 6, Panel F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.019
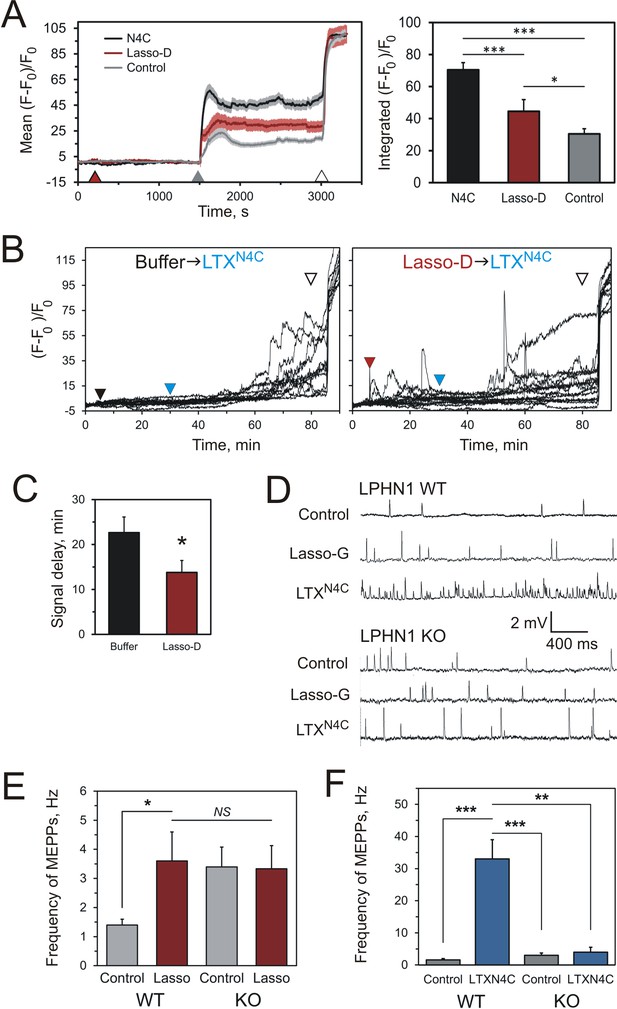
Soluble Lasso induces Ca2+signaling in LPHN1-expressing cells and enhances spontaneous exocytosis at neuromuscular junctions.
(A) Changes in intracellular Ca2+ concentration in neuroblastoma cells stably expressing LPHN1 were monitored using a Ca2+ indicator dye, Fluo-4. The scheme of the experiment is shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 1A. After 5 min recording of baseline fluorescence, the cells were treated (maroon arrowhead) with control buffer, 1 nM LTXN4C or 360 nM Lasso-D. 20 min later, 2 mM Ca2+ was added (gray arrowhead) to synchronize the intracellular Ca2+ signaling, followed by 1 nM wild-type α-latrotoxin (open arrowhead) to measure Fmax, for normalization. Left, profiles of normalized Fluo-4-Ca2+ fluorescence over time for the three conditions used (mean values ± SEM are shown; the data are from 80 to 120 individual cells from n = 4 independent experiments). Right, integration of Fluo-4-Ca2+ fluorescence over time (from B). Pre-treatment with Lasso-D potentiates intracellular Ca2+ signaling. T-test with Bonferroni correction: *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001. (B) Experiments testing the effect of Lasso-D on the time-course of LTXN4C-induced LPHN1-dependent Ca2+ signaling. Cells expressing LPHN1 were loaded with Fluo-4 and stimulated first with control buffer (black arrowhead, left) or 1.5 nM Lasso-D (maroon arrowhead, right), and then with 2 nM LTXN4C (blue arrowhead). 1 nM wild-type LTX was added at the end (open arrowhead). Ca2+ fluorescence measurements were obtained as in A. Representative normalized Ca2+ fluorescence profiles are shown. (C) Time delay before the onset of LTXN4C-induced signaling in cells pretreated with control buffer or Lasso-D determined from traces in B. T-test: *, p<0.05; the data are from 166 buffer-LTXN4C-treated cells and from 144 Lasso-LTXN4C-treated cells, from n = 5 independent experiments. (D) Representative raw recordings of MEPPs in neuromuscular preparations from LPHN1 WT and KO mice, in buffer containing 2 mM Ca2+ without any agonists or in the presence of 20 nM Lasso-G or 1 nM LTXN4C. (E) The frequency of MEPPs in the absence or presence of 20 nM Lasso-G, as in D. Lasso-G significantly increases the frequency of MEPPs at neuromuscular junctions from WT mice, but has no effect on exocytosis in LPHN1 KO synapses. The data shown are the means ± SEM from 21 (control) and 23 (Lasso-G) individual muscle fibers from 5 WT preparations and 36 and 26 muscle fibers from 6 KO preparations. (F) Positive control: 1 nM LTXN4C increases the frequency of MEPPs in WT, but not in LPHN1 KO neuromuscular junctions. The data are the means ± SEM from 21 and 32 individual muscle fibers from 6 WT preparations and 36 and 12 muscle fibers from 6 KO preparations. Mann-Whitney test with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons: *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; NS, non-significant.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Source data for Figure 7, Panels A-C, E, and F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.021
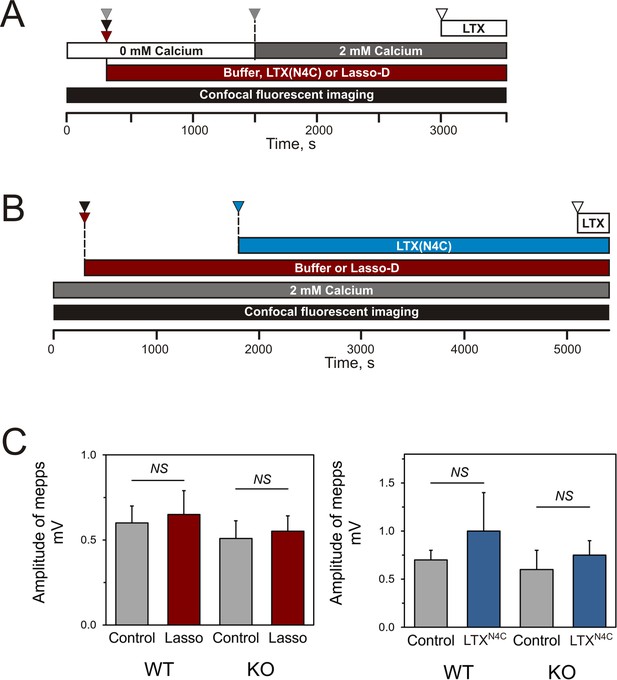
Design of the experiments testing Lasso induced Ca2+signaling in LPHN1-expressing cells and its presynaptic action at mouse neuromuscular junctions.
(A) Experimental paradigm for testing the effect of Lasso-D on LPHN1-dependent Ca2+ signaling. After 5 min recording of baseline fluorescence of neuroblastoma cells expressing LPHN1, the cells were treated with control buffer (gray arrowhead), 1 nM LTXN4C (black arrowhead) or 360 nM Lasso-D (maroon arrowhead). 20 min later 2 mM Ca2+ was added (gray arrowhead) to synchronize the intracellular Ca2+ signaling, followed by 1 nM wild-type α-latrotoxin (open arrowhead) to induce maximal Ca2+ influx through the LTX pore. (B) Experimental paradigm for testing the effect of Lasso-D on the time-course of LTXN4C-induced LPHN1-dependent Ca2+ signaling. Cells expressing LPHN1 were loaded with Fluo-4 and stimulated first with control buffer (black arrowhead) or 1.5 nM Lasso-D (maroon arrowhead), and then with 2 nM LTXN4C (blue arrowhead). 1 nM wild-type LTX was added at the end (open arrowhead). (C) Analysis of the amplitudes of MEPPs recorded at neuromuscular junctions from WT and KO mice, indicating a lack of postsynaptic effects of Lasso-G or LTXN4C. Left, the mean amplitudes of MEPPs in the absence or presence of Lasso-G. The data are the means ± SEM from 21 (control) and 23 (Lasso-G) individual muscle fibers from 5 WT preparations and 36 and 26 muscle fibers from 6 KO preparations. Right, the mean amplitudes of MEPPs in the absence or presence of 1 nM LTXN4C. The data are the means ± SEM from 21 and 32 individual muscle fibers from 6 WT preparations and 36 and 12 muscle fibers from 6 KO preparations. Mann-Whitney test with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons: NS, non-significant.
-
Figure 7—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 7—figure supplement 1, Panel C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.023
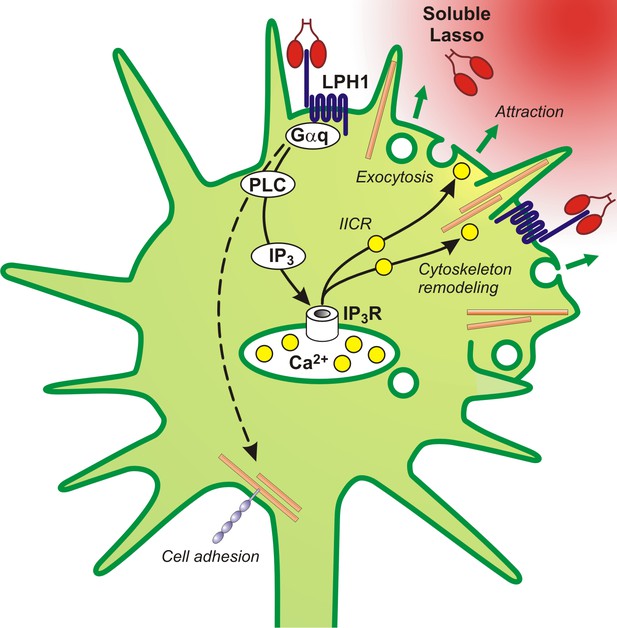
A proposed scheme of the mechanism of axonal attraction by released Lasso ECD.
When Lasso binds the NTF of LPHN1, it causes its re-association with the CTF. This activates Gαq/11 and triggers the PLC signaling cascade. Downstream of this cascade, the local IP3-induced calcium release (IICR) from intracellular stores stimulates exocytosis and may also stimulate reorganization of actin through Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), thus mediating axonal attraction. The dashed line represents LPHN1-mediated activation of neuronal adhesion molecules via an unknown mechanism that may lead to axonal fasciculation observed in the presence of soluble Lasso (Figure 5C, F).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel | Sigma-Aldrich | A2220 | |
| Antibody | Chicken anti-myc | Millipore | AB3252 RRID:AB_2235702 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-actinin | Sigma-Aldrich | A7811 | (Western blot 1:1,500) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-FLAG M2 | Sigma-Aldrich | F3165 RRID:AB_259529 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-Lasso/ teneurin-2 C-terminus | (Silva et al., 2011) | dmAb | TN2C (Immunocytochemistry 1:300; Western blot 1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-MAP-2 | Neuromics | MO22116 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-synapsin | Santa-Cruz Biotechnology | sc-376623 RRID:AB_11150313 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-myc | Millipore | 05–419 RRID:AB_309725 | clone 9E10 (Immunocytochemistry 1:1000; Western blot 1:) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-V5 | AbD Serotec/Bio-Rad | MCA1360 | clone SV5-Pk1 (Immunocytochemistry 1:2,000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-GFP | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11122 RRID: AB_221569 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-NF-H | Neuromics | RA22116 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:1,000; Western blot 1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-PSD-95 | Millipore | AB9708 RRID:AB_11212529 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:2,000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-Tau | Synaptic Systems | 314 002 RRID:AB_993042 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-V5 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PA1-29324 RRID:AB_1961277 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:2,000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-LPHN1 NTF | (Davletov et al., 1998) | RL1 | (Immunocytochemistry 1:1,000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-LPHN1-peptide | (Davydov et al., 2009) | PAL1 | (Immunocytochemistry; Western blot 3 ng/mL) |
| Antibody | Sheep anti-teneurin-2 N-terminus | R and D systems | AF4578 RRID:AB_10719438 | TN2N (Western blot 1 μg/mL) |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293A | ECCC | RRID:CVCL_6910 | |
| Cell line (Mus musculus) | Neuroblastoma 2a | ATCC | RRID:CVCL_0470 | |
| Chemical compound | B27 Supplement | Life Technologies | 17504044 | |
| Chemical compound | Ca-free Hibernate-A medium | BrainBits UK | HE-Ca | |
| Chemical compound | Fluo-4 acetomethoxy ester | Thermo Fisher Scientific | F14201 | |
| Chemical compound | Insulin Transferrin Selenium Supplement | Life Technologies | 41400045 | |
| Chemical compound | Neurobasal-A medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 21103049 | |
| Chemical compound | Purified protein: BSA-TRITC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A23016 | |
| Chemical compound | Vybrant DiO | Thermo Fisher Scientific | V22886 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Amaxa Rat Neuron Nucleofector Kit | Lonza | VAPG-1003 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 34094 | |
| Other | Microfluidic Axon Isolation Devices (MAIDs) | Xona Microfluidics | SND150 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | BLOCK-iT Lentiviral Pol II miR RNAi Expression System pLenti6/V5-GW/ EmGFP-miR | Life Technologies | K4938-00 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Bottom pre-miRNA oligo targeting LPHN1 mRNA | This paper | LPHN1miR14B | Sequence provided under Methods |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Lasso-A | (Silva et al., 2011) | GenBank: JF784341 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Lasso-D | (Silva et al., 2011) | GenBank: JF784344 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Lasso-FS | (Silva et al., 2011) | GenBank: JF784340 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Lasso-G | (Silva et al., 2011) | GenBank: JF784347 | GST-Lasso |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | LPH-42 | (Volynski et al., 2004) | GenBank:MF966512 | V5-LPH-A |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pLenti6.2-GW/EmGFP-miR negative control | Thermo Fisher Scientific | K4938-00 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Primer: N255: Neo Forward | This paper | Sequence provided under Methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Primer: N424: Neo/ LPHN1 Reverse | This paper | Sequence provided under Methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Primer: N425: LPHN1 Forward | This paper | Sequence provided under Methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Top pre-miRNA oligo targeting LPHN1 mRNA | This paper | LPHN1miR14T | Sequence provided under Methods |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Purified protein: Alexa Fluor 647-labeled LTXN4C | (Volynski et al., 2004) | N/A | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Purified protein: Human BDNF | R and D Systems | 248-BD | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Purified protein: Lasso-D | (Silva et al., 2011) | N/A | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Purified protein: Lasso-G | (Silva et al., 2011) | N/A | GST-Lasso |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Purified protein: LTXN4C | (Volynski et al., 2003) | N/A | |
| Software | AxoScope 10 | Axon Instruments | ||
| Software | FIJI, ImageJ | NIMH, Bethesda, Maryland, USA | RRID:SCR_002285 RRID:SCR_003070 | |
| Software | LSM 510 Software (for image acquisition) | Carl Zeiss Microimaging GmbH | LSM 510 | |
| Software | LSM Image Browser (for image archiving and measurements) | Carl Zeiss Microimaging GmbH | RRID:SCR_014344 | |
| Software | MATLAB | Mathworks | RRID:SCR_001622 | |
| Software, algorithm | MATLAB | Mathworks | https://github.com/artificialbrain-tech/Axon-Guidance-Scripts | Axonal guidance scripts |
| Software | MiniAnalysis | Synaptosoft | ||
| Software | Volocity (for image acquisition and stitching) | Perkin-Elmer | RRID:SCR_002668 | |
| Strain (Escherichia coli) | E. coli: K12 JM109 | Promega Corporation | L2005 | |
| Strain (Mus musculus) | Mouse: C57BL/6J, Adgrl1-/-, LPHN1 KO | This paper | AG148/2 | P0 hippocampus |
| Strain (Mus musculus) | Mouse: C57BL/6J, Adgrl1-/-, LPHN1 KO | This paper | AG148/2 | P21 flexor digitorum brevis muscle |
| Strain (Rattus norvegicus) | Rat: E18 hippocampus | BrainBits UK | Rhp |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37935.025





