Changes to social feeding behaviors are not sufficient for fitness gains of the Caenorhabditis elegans N2 reference strain
Figures
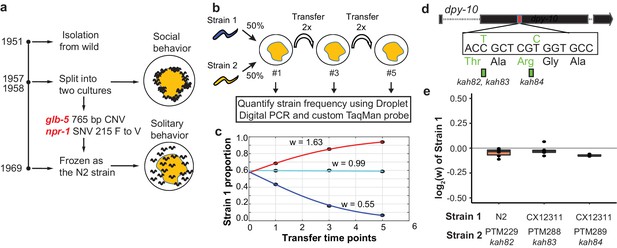
Schematic of competition assays used to measure relative fitness levels between two strains.
(a) Overview of life history of the standard reference N2 strain since its isolation from the wild. Derived alleles in npr-1 and glb-5 arose and fixed after 1957 and before 1969 when methods for cryopreservation were developed. These two alleles were identified for their role in changing foraging behavior on bacterial lawns from social to solitary behavior. (b) Schematic of pairwise competition experiments used throughout the paper to quantify fitness differences between two strains. (c) Relative proportion of each strain as ascertained by Droplet Digital PCR using a custom TaqMan probe (dots) is used to estimate the relative fitness between the two strains (line). (d) Silent mutations were edited into the 90th or 92nd amino acid of the dpy-10 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 to create a common SNV for Droplet Digital PCR. We refer to these as barcoded strains. (e) Competition experiments between the parent strain (top) and the same strain containing one of the silent mutations. We display the result from each competition experiment as a single dot overlaid on top of a boxplot showing the mean, first, and third quartiles of all replicates.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Relative proportion of each strain as ascertained by Droplet Digital PCR shown in Figure 1c.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.004
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Competition experiment using indicated barcoded strains carry the dpy-10 silent mutation shown in Figure 1e.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.005
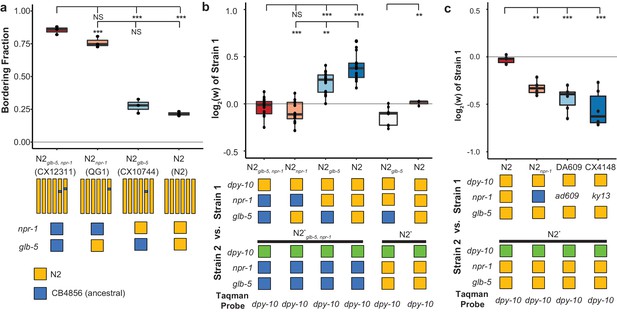
Derived alleles of npr-1 and glb-5 are beneficial.
(a) The bordering rate of the N2 reference strain compared to three near isogenic lines (NILs) containing ancestral alleles of npr-1 and/or glb-5 introgressed from the CB4856 wild strain. Bordering rate is defined as the fraction of animals on the edge of the bacterial lawn at a single timepoint. Schematic of each NIL shown below along with the allele of npr-1 and glb-5 they contain. Orange represents N2-derived DNA and blue represents CB4856-derived DNA. These strains are referred to by the ancestral alleles they contain (e.g. N2glb-5=CX10744, which is an introgression surrounding glb-5). To ascertain statistical significance, ANOVA was used followed by a Tukey's Honest Significant Difference test for multiple comparison tests. NS, not significant, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (b) Competition experiments between NILs shown in panel a against barcoded strains shown in Figure 1d,e. Green box indicates the strain contains the barcoded allele of dpy-10. Positive values indicate Strain one is more fit; negative values indicate Strain two is more fit. NS not significant, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test or Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (c) Competition experiments between strains containing two loss-of-function alleles of npr-1 (ad609 and ky13) along with controls. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
The bordering rate of the N2 compared to three near isogenic lines (NILs) containing ancestral alleles of npr-1 and/or glb-5 introgressed from the CB4856 wild strain shown in Figure 2a.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.007
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Competition experiments between N2 and NILs shown in Figure 2b.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.008
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Competition experiments between strains containing two loss-of-function alleles of npr-1 (ad609 and ky13) along with N2 shown in Figure 2c.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.009
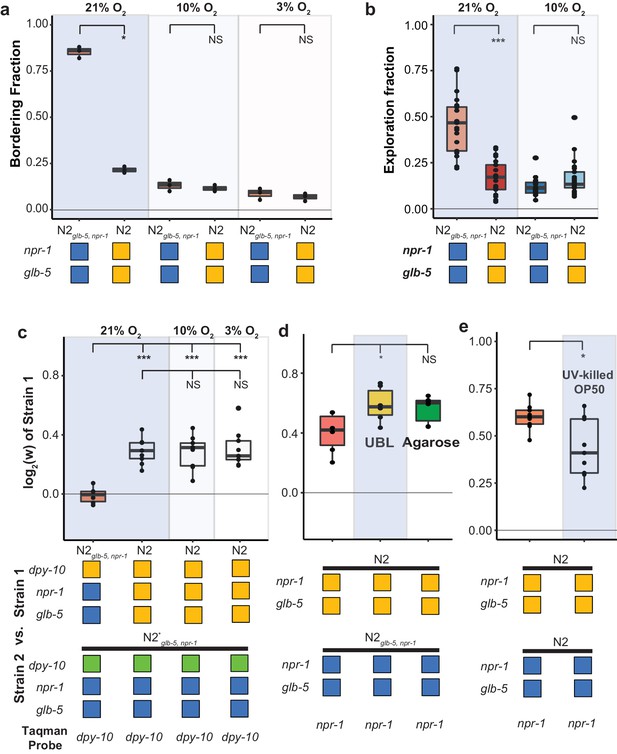
Fitness advantage of N2 is independent of foraging behavior.
(a and b). Environmental O2 levels were manipulated using a Biospherix chamber. Differences in (a) bordering behavior and (b) roaming and dwelling behavior were suppressed in N2glb-5, npr-1 at lower environmental O2 levels. NS not significant, *p<0.05 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (c). Fitness advantage of N2 over the barcoded N2glb-5, npr-1 strain was independent of environmental O2. NS, not significant, ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test. (d and e) Fitness differences of N2 and N2glb-5, npr-1 on (d) uniform bacterial lawns (UBL) where animals were unable to border, on plates containing agarose to prevent burrowing behaviors (NS, not significant, *p<0.05 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test), and (e) on UV-killed bacteria (*p<0.05 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Bordering rate at ambient (21%) and lower environmental (10%) O2 levels shown in Figure 3a.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.011
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Roaming and dwelling behavioral assay in ambient (21%) and lower environmental (10%) O2 levels shown in Figure 3b.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.012
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Fitness advantage of N2 over the barcoded N2glb-5, npr-1 strain was independent of environmental O2 shown in Figure 3c.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.013
-
Figure 3—source data 4
Fitness differences of N2 and N2glb-5, npr-1 on uniform bacterial lawns (UBL) and on plates containing agarose shown in Figure 3d.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.014
-
Figure 3—source data 5
Fitness differences of N2 and N2glb-5, npr-1 on UV-killed bacteria shown in Figure 3e.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.015
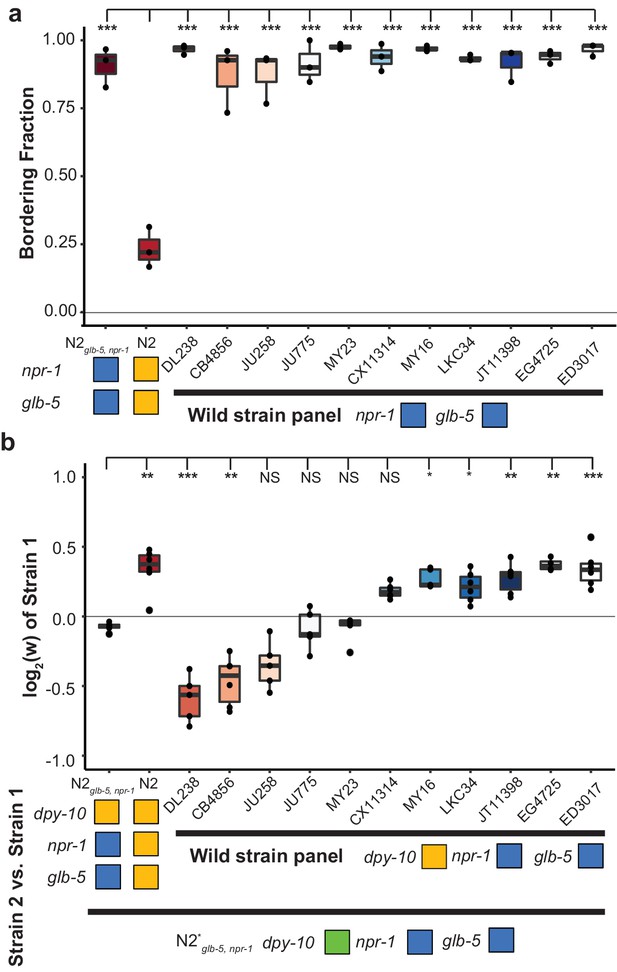
Bordering rate and relative differences between wild C.elegans strains.
(a) A panel of 11 wild strains was tested for bordering behavior. Each of these wild strains contains ancestral alleles of glb-5 and npr-1. ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test. (b) Competition experiments between 11 wild strains and barcoded N2glb-5, npr-1 animals. Despite the similarity of bordering behavior, these wild strains displayed a range of relative fitness. NS, not significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Bordering rate of 11 wild strains shown in Figure 4a.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.021
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Competition experiments between 11 wild strains and barcoded N2glb-5, npr-1 animals shown in Figure 4b.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.022
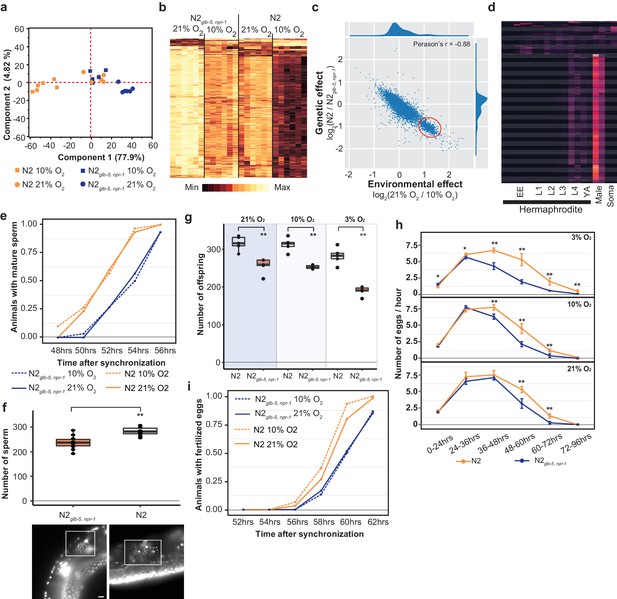
Reproductive timing in N2 occurs earlier than the N2glb-5,npr-1 strain.
(a) PCA analysis of transcriptional profiles of bleach-synchronized N2 and N2glb-5,npr-1 animals grown in 10% or 21% environmental O2 (six replicates per strain/condition). The largest two eigenvectors are shown, along with the amount of variance they explain. Developmental age of animals is approximately L4 stage. (b) Hierarchical clustering of normalized, differentially expressed genes. Columns show strain and conditions; rows show gene expression. (c) Averaged effect of genotype (y-axis) vs environment (x-axis) for each gene (Supplementary file 1). A small cluster of 652 genes with similar changes is circled in red. (d) The developmental expression of these 652 genes was further investigated using a previously published dataset. Columns show developmental stage and rows show each gene. Most of these gene peaked in expression in L4 hermaphrodite animals and was further enriched in male L4 animals (Male). Soma indicates expression levels from somatic cells, suggesting this cluster is enriched in germline cells. (e) Animals identified with mature sperm. x-axis indicates time since synchronization using hatch-off. Strain/condition shown in legend. p=0.0076 by Friedman test. (f) Number of sperm produced by each strain as determined by DAPI straining. Representative images are shown below. Scale bar = 10 μm. **p<0.01 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (g) Averaged total number of offspring produced by each strain when grown in different environmental O2 levels. **p<0.01 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (h) Averaged egg-laying rate of L4-synchronized N2 and N2glb-5,npr-1 animals when grown at different O2 levels. x-axis indicates time since L4 stage. NS, not significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (i) Number of animals observed with fertilized eggs in their uterus. x-axis indicates time from synchronized egg-lay. p=0.0109 by Friedman test.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
List of normalized differentially expressed genes for PCA analysis and Hierarchical clustering.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.024
-
Figure 5—source data 2
List of the relative expression levels of protein coding genes across all of the developmental stages highlighted in Figure 5c.
The dataset is used to show Figure 5d. The soruce of the gene expression data across all of the developmental stages is from previous research: Boeck et al. (2016) .
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.025
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Number of animals identified with mature sperm at indicated timepoint shown in Figure 5e.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.026
-
Figure 5—source data 4
Number of sperm produced by each strain as determined by DAPI straining shown in Figure 5f.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.027
-
Figure 5—source data 5
Mean number of offspring produced by each strain when grown in different environmental O2 levels shown in Figure 5g.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.028
-
Figure 5—source data 6
Mean egg-laying rate of L4-synchronized N2 and N2glb-5,npr-1 animals when grown at different O2 levels shown in Figure 5h.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.029
-
Figure 5—source data 7
Number of animals observed with fertilized eggs in their uterus at indicated timepoint shown in Figure 5i.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.030
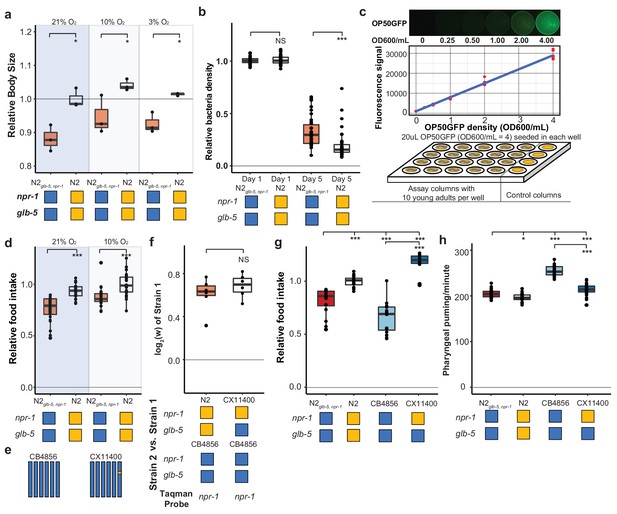
Feeding differences of strains containing derived alleles.
(a) N2 and N2glb-5,npr-1 animals were synchronized by hatch-off and allowed to grow at the indicated O2 levels for 72 hr. Video recordings were used to estimate the size of the animals. *p<0.05 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (b) A previously published liquid, bacterial clearing assay was used to estimate food consumption for the N2glb-5,npr-1 and N2 animals. On day 4, N2 animals had consumed more bacteria than N2glb-5,npr-1animals. NS, not significant, ***p<0.001 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (c). To test food consumption on agar plates, we developed a new assay by seeding 24-well agar plates with defined amounts of OP50-GFP bacteria. The number of bacteria on the plate could be estimated using a microplate reader. (d) N2 animals consumed more food than N2glb-5,npr-1 regardless of foraging behaviors. ***p<0.001 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (e) Schematic of CB4856 wild strain (blue) and a NIL (CX11400) containing the N2 allele of npr-1 from N2 (orange). (f) We tested the fitness effect of the N2 allele of npr-1 in the CB4856 wild strain using the CX11400 NIL strain. NS, not significant by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (g) Food consumption assays between CB4856 and N2 strains or CB4856 and the CX11400 NIL. ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test. (h) Pharyngeal pumping rates of N2, CB4856 and two NIL strains. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Growth rates of N2 and N2glb-5,npr-1 shown in Figure 6a.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.034
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Food consumption in liquid S media shown in Figure 6b.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.035
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Food consumption assay setup using OP50 GFP on 24-well agar plate shown in Figure 6c.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.036
-
Figure 6—source data 4
N2 animals consume more food in O2 independent manner shown in Figure 6d.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.037
-
Figure 6—source data 5
Fitness effect of the N2 allele of npr-1 in the CB4856 wild strain shown in Figure 6f.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.038
-
Figure 6—source data 6
Food consumption assays between CB4856 and N2 strains or CB4856 and the CX11400 NIL shown in Figure 6g.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.039
-
Figure 6—source data 7
Pharyngeal pumping rates of N2, CB4856 and two NIL strains shown in Figure 6h.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.040
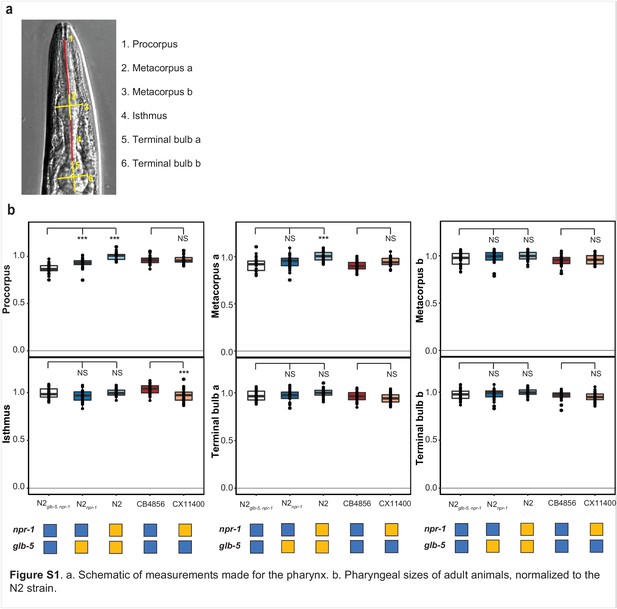
Measurement of pharyngeal sizes of adult animals.
(a) Schematic of measurements made for the pharynx. (b) Pharyngeal sizes of adult animals, normalized to the N2 strain. ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Measurement of pharyngeal sizes of adult animals shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1b.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.033
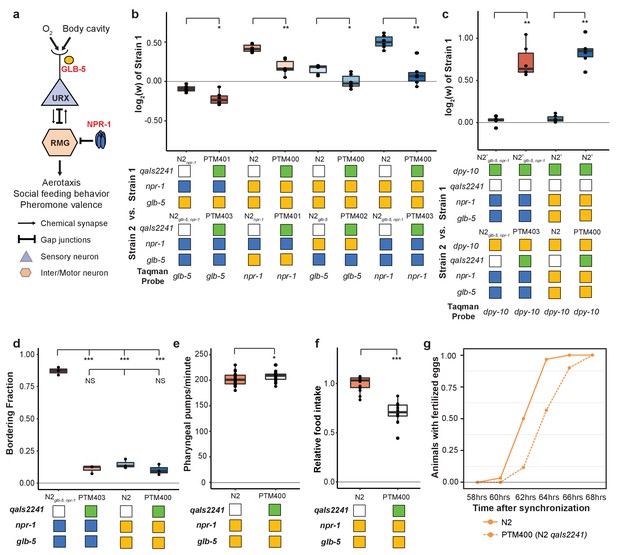
O2-sensing neurons contribute to fitness differences of N2 and N2glb-5,npr-1.
(a) Schematic showing putative cellular sites of action for glb-5 and npr-1. glb-5 modulates O2 responses in the URX body cavity neurons. npr-1 is thought to modulate electrical signaling in the RMG hub-and-spoke neuron which forms gap junctions onto URX. (b and c) Competition experiments between indicated strains. qaIs2241 is an integrated genetic cassette that ablates the URX, AQR, and PQR neurons. Green indicates the presence of the cassette (and loss of URX, AQR, and PQR neurons). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (d) Bordering rates of indicated strains. The qaIs2241 cassette suppresses bordering of the N2glb-5,npr-1 strains. NS not significant, *p<0.05 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (e) Pharyngeal pumping rates of N2, and N2 strains carrying the qaIs2241 cassette. *p<0.05 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (f) Relative food consumption rates between the indicated strains. ***p<0.001 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (g) Number of animals observed with fertilized eggs in their uterus. x-axis indicates time from synchronized egg-lay. p=0.0455 by Friedman test.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Competition experiments between indicated strains carry qaIs2241 cassette shown in Figure 7b.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.042
-
Figure 7—source data 2
Competition experiments between indicated strains carry qaIs2241 cassette shown in Figure 7c.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.043
-
Figure 7—source data 3
Bordering fraction of indicated strains shown in Figure 7d.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.044
-
Figure 7—source data 4
Pharyngeal pumping rates of N2 and N2 carries qaIs2241 cassette shown in Figure 7e.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.045
-
Figure 7—source data 5
Food consumption assay of N2 and N2 carries qaIs2241 cassette shown in Figure 7f.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.046
-
Figure 7—source data 6
Number of animals observed with fertilized eggs in their uterus shown in Figure 7g.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.047
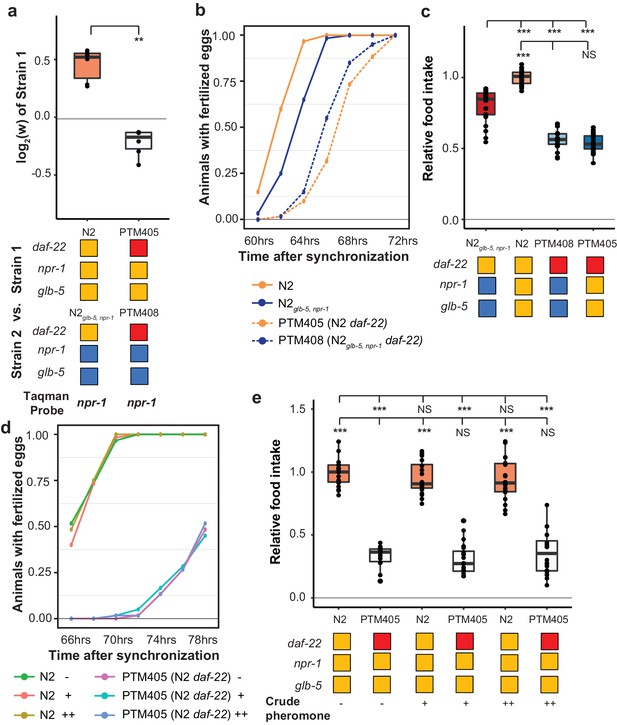
daf-22 is required for fitness differences of N2 and N2glb-5,npr-1.
(a) Competition experiments between indicated strains. daf-22 encodes a sterol carrier protein, which is required for biosynthesis of most ascaroside pheromones. Red indicates the strain contain a deletion that spans the gene. **p<0.01 by Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney nonparametric test. (b) Number of animals that carry fertilized eggs at the indicated timepoints. p=6.61×10−4 by Friedman test. (c) On plate feeding assays of the indicated strains. NS, not significant, ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test. (d and e) Attempts to rescue the relative food intake and reproductive timing defects of the daf-22 strain using crude pheromone. Neither of two concentrations of crude pheromone isolated from animals grown in liquid cultures had a significant effect on the two traits. NS, not significant, ***p<0.001 by ANOVA with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test. p=7.45×10−6 by Friedman test.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Competition experiment between indicated strains shown in Figure 8a.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.049
-
Figure 8—source data 2
Number of animals observed with fertilized eggs in their uterus shown in Figure 8b.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.050
-
Figure 8—source data 3
Food consumption assay of indicated strains shown in Figure 8c.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.051
-
Figure 8—source data 4
Number of animals observed with fertilized eggs in their uterus in different pheromone concentration shown in Figure 8d.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.052
-
Figure 8—source data 5
Food consumption assay in different pheromone concentration shown in Figure 8e.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.053
Videos
N2glb-5, npr-1 animal’s behavior in 10% O2 level.
A single generation (3 days) of growth of the N2glb-5, npr-1 strain in the presence of 10% environmental O2.
N2glb-5, npr-1 animal’s behavior in 21% O2 level.
A single generation (3 days) of growth of the N2glb-5, npr-1 strain in the presence of 21% environmental O2.
N2 animal’s behavior in 10% O2 level.
A single generation (3 days) of growth of the N2 strain in the presence of 10% environmental O2.
N2 animal’s behavior in 21% O2 level.
A single generation (3 days) of growth of the N2 strain in the presence of 21% environmental O2.
Tables
| Reagent type or resource | Designation | Source of reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (C. elegans) | npr-1 | Worm base | Wormbase ID: WBGene00003807 | Sequence: C39E6.6 |
| Gene (C. elegans) | glb-5 | Worm base | Wormbase ID: WBGene00015964 | Sequence: C18C4.1 |
| Gene (C. elegans) | dpy-10 | Worm base | Wormbase ID: WBGene00001072 | Sequence: T14B4.7 |
| Gene (C. elegans) | daf-22 | Worm base | Wormbase ID: WBGene00013284 | Sequence: Y57A10C.6 |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | OP50 | Caenorhabditis genetics center (CGC) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:OP50 | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | OP50 GFP | Caenorhabditis genetics center (CGC) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:OP50-GFP | with pFPV25.1 express GFP. |
| Strain (C. elegans) | N2 | Cori Bargmann Lab (The Rockefeller University) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:N2 | |
| Strain (C. elegans) | CB4856 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:CB4856 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | DL238 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:DL238 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | JU258 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:JU258 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | JU775 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:JU775 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | MY16 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:MY16 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | MY23 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:MY23 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | CX11314 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:CX11314 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | LKC34 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:LKC34 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | ED3017 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:ED3017 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | JT11398 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:JT11398 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | EG4725 | Caenorhabditis elegans Natural Diversity Resource (CeNDR) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:EG4725 | Website: https://www.elegansvariation.org/ |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM229 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM229 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM288 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM288 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM289 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM289 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM95 | PMID: 27467070 | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM95 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | CX12311 | PMID: 21849976 | RRID:WB-STRAIN:CX12311 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | QG1 | PMID: 27172189 | RRID:WB-STRAIN:QG1 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | CX10774 | PMID: 19285466 | RRID:WB-STRAIN:CX10774 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | CX11400 | PMID: 23284308 | RRID:WB-STRAIN:CX11400 | Strain Background: CB4856 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | CX4148 | PMID: 9741632 | RRID:WB-STRAIN:CX4148 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | DA609 | PMID: 9741632 | RRID:WB-STRAIN:DA609 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | CX7102 | PMID: 16903785 | RRID:WB-STRAIN:CX7102 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM400 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM400 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM401 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM401 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM402 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM402 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM403 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM403 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM404 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM404 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM405 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM405 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Strain (C. elegans) | PTM408 | This paper | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PTM408 | Strain Background: N2 |
| Sequence-based reagents (Plasmid) | Plasmid: pDD162 PrU6::dpy-10_sgRNA | PMID: 27467070 | CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing sgRNA | |
| Sequence-based reagents (Plasmid) | Plasmid: pDD162 Preft3::Cas9 | PMID: 27467070 | CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing Cas9 | |
| Sequence-based reagents (Oligonucleotide) | dpy-10 (cn64) | PMID: 25161212 | CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing DNA repair oligo for inducing dpy-10 cn64 mutation | |
| Sequence-based reagents (Oligonucleotide) | dpy-10 (kah82/kah83) | This paper | CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing DNA repair oligo for inducing dpy-10 Thr90 slient mutation | |
| Sequence-based reagents (Oligonucleotide) | dpy-10 (kah84) | This paper | CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing DNA repair oligo for inducing dpy-10 Arg92 slient mutation | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 1x Antibiotic-Antimycotic | ThermoFisher | Cat. No.: 15240062 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FUDR | Sigma | Cat. No.: F0503 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Taqman probe: dpy-10 (kah82/kah83) | ThermoFisher: Custom TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays | PTM09 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Taqman probe: dpy-10 (kah84) | ThermoFisher: Custom TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays | PTM10 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Taqman probe: npr-1(g320) | ThermoFisher: Custom TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays | PTM08 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Taqman probe: WBVar00209467 | ThermoFisher: Custom TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays | PTM11 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | TruSeq Stranded mRNA kit | Illumina | Cat. No.: 20020595 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Zymo DNA isolation kit | Zymo | Cat. No.: D4071 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Zymo DNA cleanup kit | Zymo | Cat. No.: D4064 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | ddPCR Supermix for Probes | BIORAD | Cat. No.: 1863010 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Droplet Generation Oils | BIORAD | Cat. No.: 1863005 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | ddPCR Droplet Reader Oil | BIORAD | Cat. No.: 1863004 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | VECTASHIELD antifade Mounting Medium with DAPI | VECTOR | Cat. No.: H-1200 | |
| Software, Algorithm | edgeR | PMID: 19910308 | RRID:SCR_012802 | Opensource: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/edgeR.html |
| Software, Algorithm | SARTools | PMID: 27280887 | RRID:SCR_016533 | Opensource: https://github.com/PF2-pasteur-fr/SARTools |
| Software, Algorithm | MATLAB | MathWorks | RRID:SCR_001622 | |
| Software, Algorithm | Rstudio | Rstudio | RRID:SCR_000432 | https://www.rstudio.com/ |
| Software, Algorithm | JMP12 | SAS JMP | RRID:SCR_014242 | |
| Software, Algorithm | Image J | NIH | RRID:SCR_003070 | Opensource: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ |
| Software, Algorithm | MetaMorph | Molecular Devices | RRID:SCR_002368 | |
| Software, Algorithm | Custom TaqMan Assay Design Tool | ThermoFisher | https://www.thermofisher.com/order/custom-genomic-products/tools/genotyping/ |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Full list of average read count per gene of each strain in 10% O2 or 21% O2 level.
The table contains the full list of average read count per gene. Each gene count number per strain/condition is the average of 6 replicates.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.054
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38675.055





