Multi-protein bridging factor 1(Mbf1), Rps3 and Asc1 prevent stalled ribosomes from frameshifting
Figures
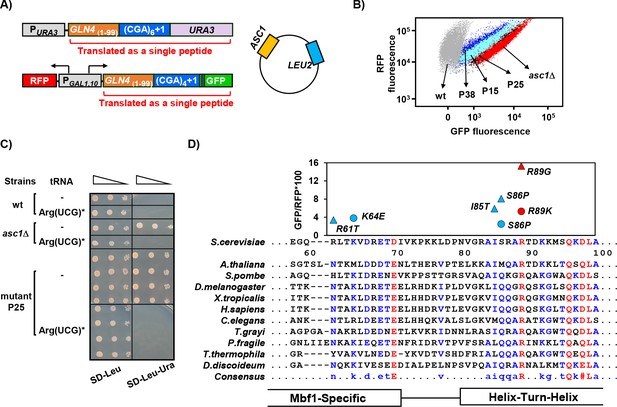
MBF1 (Multi-protein Bridging Factor 1) prevents frameshifting at CGA codon repeats.
(A) Schematic of selection for mutants that frameshift at CGA codon repeats. The indicated CGA codon repeats plus one extra nucleotide were inserted upstream of the URA3 and GFP coding region (with an upstream HA tag shown in purple), resulting in an Ura- GFP- parent strain. Additional copies of the ASC1 gene were introduced on a LEU2 plasmid to avoid recessive mutations in the native ASC1 gene. To obtain mutants with increased frameshifting efficiency, Ura+ mutants were selected and screened for increased GFP/RFP. (B) Expression of GLN4(1-99)-(CGA)4+1-GFP is increased in the MATa Ura+ mutants from this selection. Flow cytometry scatter plot showing GFP fluorescence versus RFP fluorescence for three mutants from this selection (P15: mbf1-R89K, light blue; P25: mbf1Δ125–151, black; P38: mbf1-K64E, dark blue), for the asc1Δ mutant (red) and for the wild-type parent strain (gray). (C) Expression of the non-native tRNAArg(UCG)* suppressed the Ura+ phenotype of mutant P25 at 30°C. Serial dilutions of the indicated strains with empty vector or expressing the mutant tRNAArg(UCG)* were grown on the indicated media. (D) Mutations in the MBF1 mutants map in conserved amino acids in both the MBF1-specific domain and the Helix-Turn-Helix (HTH) domain of Mbf1 protein. Alignment of yeast Mbf1 amino acids 60–100 with other eukaryotic species is shown (full alignment see Figure 1—figure supplement 3A). GFP/RFP of frameshifted (CGA)4+1 reporter is shown for mutants obtained from MATa (circles) and MATα (triangles) strains, with the color of markers corresponding to the consensus level of this residue (Blue: 50–90%, Red: >90%), however the conserved residue for R61 is N, and for S86 is Q, with all others identical to yeast.
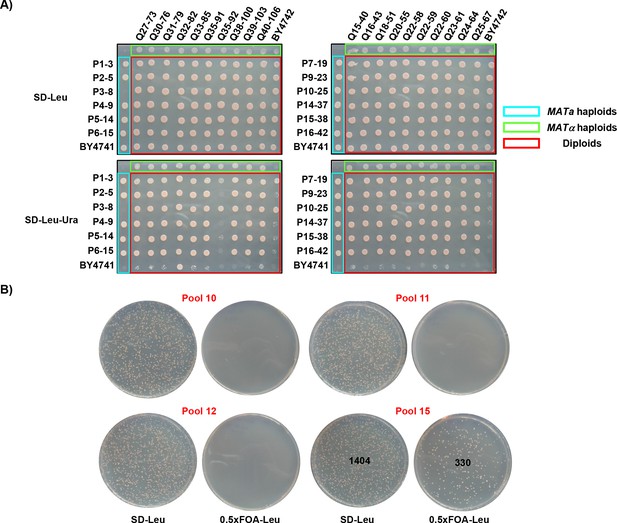
Classification of dominant and recessive mutations and complementation of a recessive mutation.
(A) Analysis of complementation and dominant/recessive nature of mutations. Twelve MATa mutants were crossed with 20 MATα mutants, as well as with the wild type strains. An Ura+ phenotype of resulting diploids with the wild type strain indicated that three mutants were dominant while the Ura+ phenotype of mutants crossed with each other indicated one major complementation group among recessive mutants. (B) Introduction of the Prelich library pool 15 DNA resulted in FOA-resistant cells (Ura-) which indicated suppression of the frameshifting phenotype.
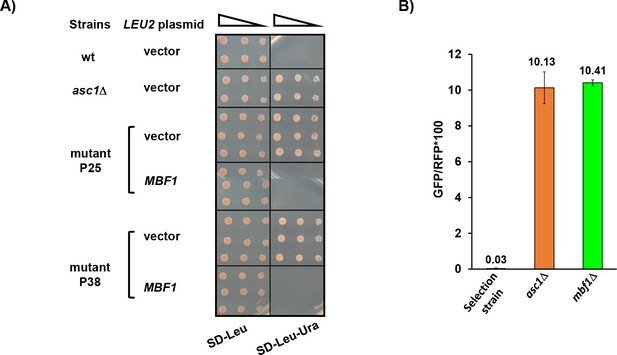
Confirmation that mutations in MBF1 are responsible for frameshifting.
(A) Plasmid-borne MBF1 gene suppressed the Ura+ phenotype of mutants P25 and P38 at 30°C. (B) Deletion of the MBF1 coding sequence in the parent GFP- strain resulted in GFP+ phenotype.
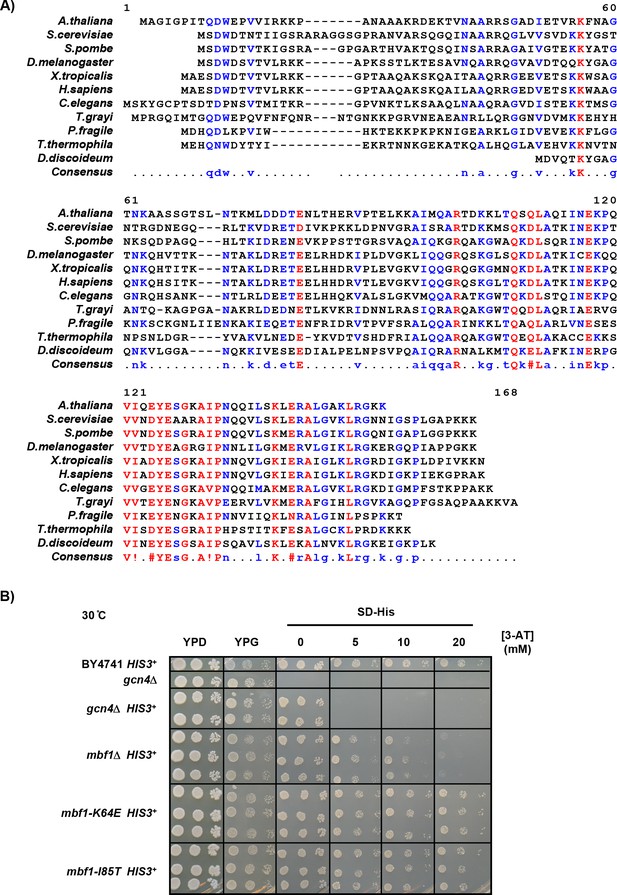
Mbf1 is conserved and frameshifting mutations do not exhibit sensitivity to 3-AT.
(A) Amino acid sequence alignment of Mbf1 protein from 11 eukaryotic species using MultAlin (http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/) (Corpet, 1988). The color of text corresponds to the consensus level of this residue (Blue: 50–90%, Red: >90%) (B) Frameshifting mbf1-K64E and I85T mutants grow like wild type on plates with 3-aminotriazole at 30°C and do not display a gcn4Δ phenotype. The mbf1Δ strains are more resistant to 3-AT than gcn4Δ strains.
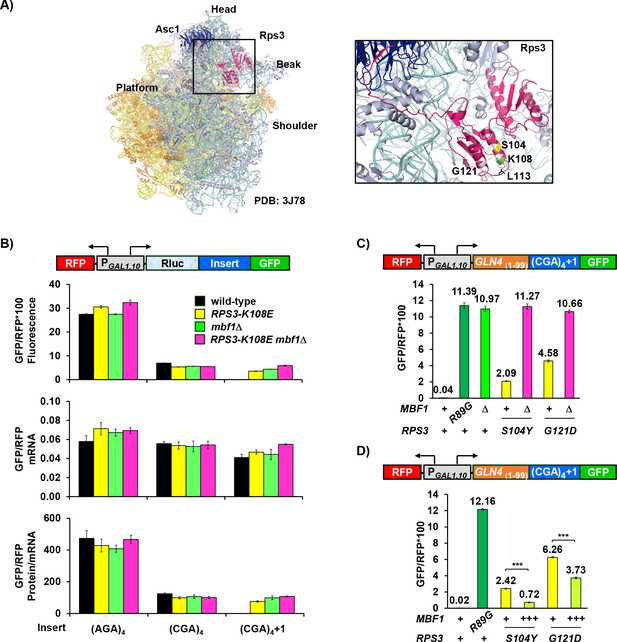
Ribosomal protein Rps3 mediates reading frame maintenance with Mbf1 at CGA codon repeats.
(A) Left: Yeast ribosome from PDB: 3J78 (Svidritskiy et al., 2014) (light blue: small subunit; yellow: large subunit) showing Asc1/RACK1 (dark blue) and Rps3 (pink). Right: Residues of Rps3 in which mutations cause frameshifting are marked- S104 (yellow), K108 (green), L113 (black), G121 (gray). (B) Analysis of effects of RPS3-K108E, mbf1Δ and RPS3-K108E mbf1Δ mutations on expression of GFP/RFP protein (fluorescence), mRNA and protein/mRNA from reporters containing four Arg codons (AGA versus CGA) in-frame and in the +1 frame. (C) Assay for epistatic relationship between RPS3 mutations from this selection and the mbf1Δ mutation. (D) Overproduction of Mbf1 protein in indicated RPS3 mutants significantly decreased expression of frameshifted Gln4(1-99)-GFP fusion protein (***p < 0.001) analyzed by flow cytometry.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
(Source data file for Figure 2B–D).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.009
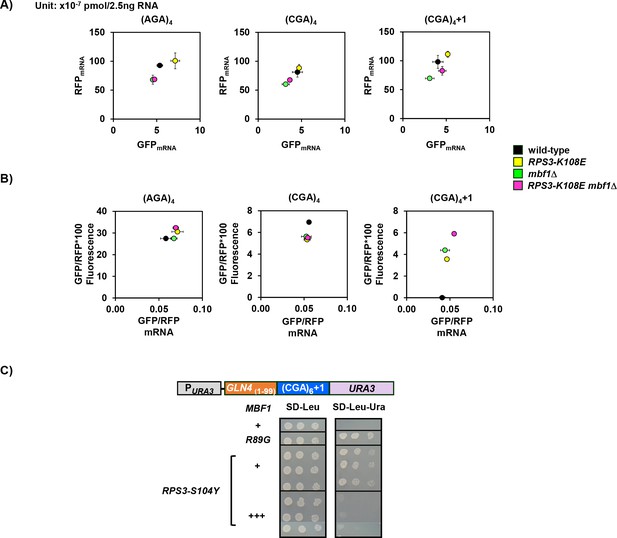
RPS3 and mbf1Δ mutants do not affect mRNA levels of CGA-containing reporters.
(A) Scatter plot of RFP mRNA versus GFP mRNA of Rluc-GFP reporters containing in-frame or out-of-frame four Arg codons (AGA versus CGA) in wild-type (black), RPS3-K108E (yellow), mbf1Δ (green) and RPS3-K108E mbf1Δ (pink) mutants. (B) Scatter plot of GFP/RFP*100 fluorescence versus GFP/RFP mRNA of Rluc-GFP reporters containing in-frame or out-of-frame four Arg codons (AGA versus CGA) in the same strains as in (A). (C) Overproduction of Mbf1 protein in the RPS3-S104Y mutant reduced frameshifting-dependent growth on -Ura media, shown by a spot test assay at 30°C.
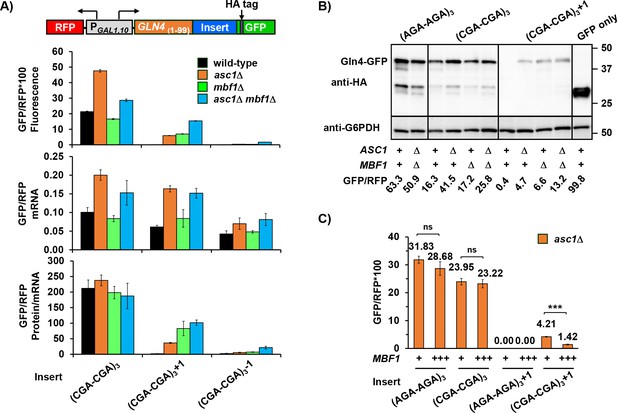
Mbf1 and Asc1 play distinct, but related, roles at CGA codon pairs.
(A) Analysis of effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on protein expression (fluorescence), mRNA levels and protein/mRNA of GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters containing three CGA-CGA codon pairs in the 0, +1, and −1 reading frames. GFP/RFP values are reported in all cases. (B) Western analysis of Gln4(1-99)-GFP fusion protein in yeast strains from (A) indicates the expression of frameshifted Gln4(1-99)-GFP full-length protein in all three mutants. The protein was detected by anti-HA antibody recognizing the HA epitope between the codon insert and GFP. The GFP and RFP values were measured by flow cytometry while harvesting for cell lysis. (C) Overproduction of Mbf1 suppressed frameshifting at CGA-CGA codon pairs in the asc1Δ mutant, but did not affect the in-frame expression, based on GFP/RFP expression from the indicated reporters shown in (A). ns: p > 0.05, ***p < 0.001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data file for Figure 3A and C).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.013
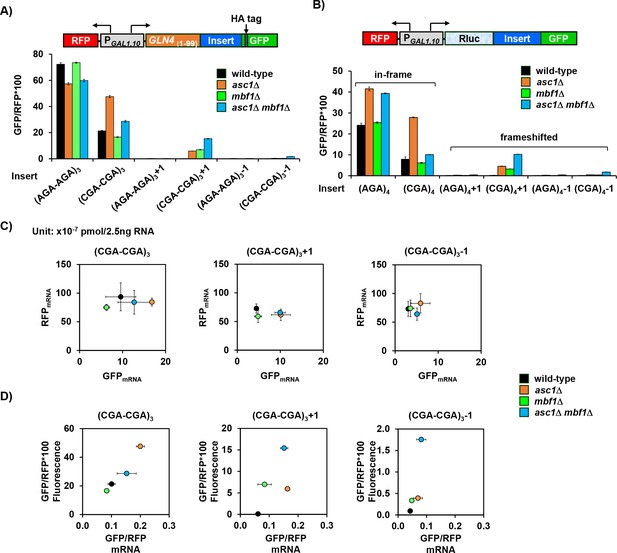
Analysis of effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on protein and mRNA expression of GFP reporters.
(A) Analysis of effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on protein expression of GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters containing three Arg-Arg codon pairs (AGA-AGA versus CGA-CGA) in 0, +1, and −1 reading frames. (B) Analysis of effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on protein expression of Rluc-GFP reporters containing four adjacent Arg codons (AGA versus CGA) in 0, +1, and −1 reading frames. (C) Scatter plot of RFP mRNA versus GFP mRNA of GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters containing three CGA-CGA codon pairs (0, +1, or −1 frame) in the indicated strains. (D) Scatter plot of GFP/RFP*100 fluorescence versus GFP/RFP mRNA of GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters containing three CGA-CGA codon pairs (0, +1, or −1 frame) in the same strains as in (C).
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data file for Figure 3—figure supplement 1B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.014
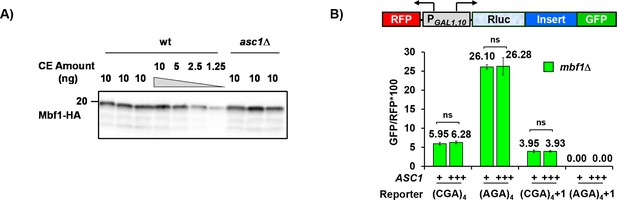
Frameshifting is likely not due to reduction in Mbf1 protein in the asc1Δ mutant nor to limiting Asc1 protein in the mbf1Δ mutant.
(A) Western analysis of HA tagged Mbf1 in the asc1Δ mutant (three independent isolates shown) compared to the wild-type strain (four independent isolates shown) indicates that Mbf1 levels were similar in both strains. (B) Overexpression of Asc1 does not affect either in-frame read-through or frameshifting at CGA codon repeats in the mbf1Δ strain. ns: p > 0.05.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 2
Source data file for Figure 3—figure supplement 2B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.015
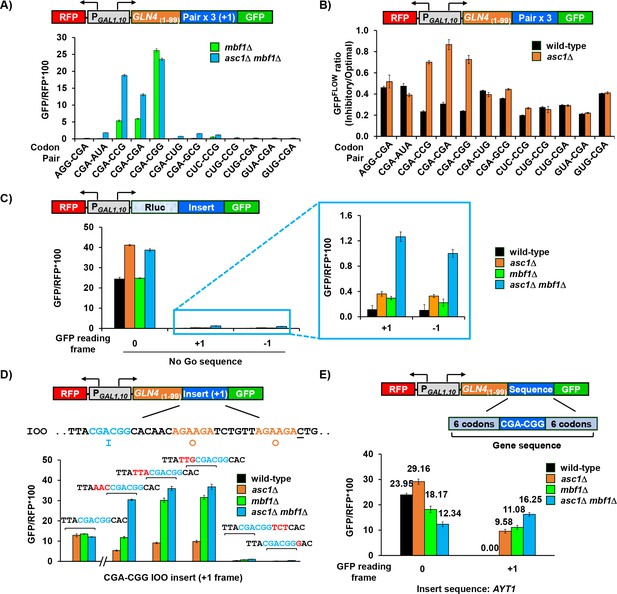
Mbf1 and Asc1 work at a common subset of inhibitory codon pairs and at a single inhibitory codon pair in a context-dependent manner.
(A) Frameshifted GFP/RFP fluorescence was detected at three inhibitory codon pairs (Gamble et al., 2016) in the mbf1Δ mutant, and at seven codon pairs in the asc1Δ mbf1Δ double mutant. Frameshifting was assayed from reporters bearing 3 copies of the indicated inhibitory codon pair and a +1 nucleotide to place GFP in the +1 frame. (B) In-frame expression downstream of three inhibitory codon pairs (CGA-CGA; CGA-CCG; CGA-CGG) was improved by the deletion of ASC1. The GFPFLOW ratio is the ratio of GFP/RFP from reporters with three copies of an inhibitory pair relative to GFP/RFP from synonymous reporters with three copies of the optimized pair. (C) Mutation of either ASC1 or MBF1 allowed frameshifting at no-go sequences in the GFP reporter, and mutation of both ASC1 and MBF1 resulted in significantly more frameshifted GFP/RFP. (D) Variation of the sequences surrounding a single CGA-CGG inhibitory codon pair indicated that the 3’ nucleotide downstream of the pair was required for efficient frameshifting. Frameshifted GFP/RFP from GLN4(1-99)-insert-+1 GFP reporters with a single CGA-CGG inhibitory codon pair was analyzed in the four indicated strains. Variations in the sequences surrounding this pair are shown in red. The construct, IOO contains the inhibitory CGA-CGG pair in position 1(I) and synonymous optimal pairs (AGA-AGA) in the positions 2 and 3 (OO) sites. The original IOO construct was measured separately (hash marks) and also reported in Figure 4—figure supplement 2B. (E) Analysis of effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on expression of GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters containing the native yeast AYT1 sequence with a single CGA-CGG codon pair in 0 and +1 reading frames. This native yeast sequence provoked significant amount of frameshifting.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source data file for Figure 4A–E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.019
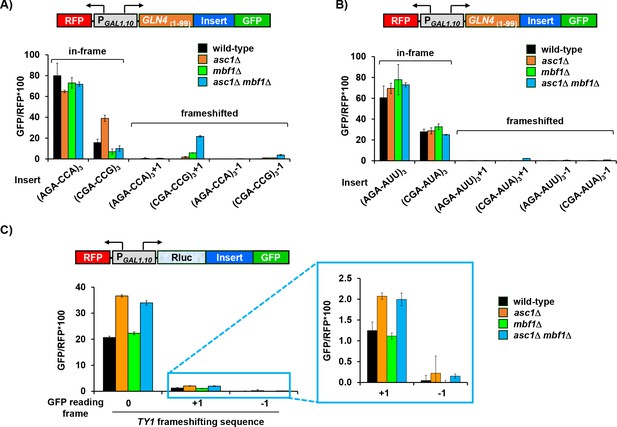
Analysis of effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on expression of different GFP reporters containing two sets of inhibitory codon pairs and programmed frameshifting site in TY1.
(A, B) Analysis of effects of the indicated mutations on expression of Gln4(1-99)-GFP reporters containing three copies of either (A) the Arg-Pro (AGA-CCA or CGA-CCG) codon pairs or (B) the Arg-Ile (AGA-AUU or CGA-AUA) codon pairs in 0, +1, and −1 reading frames. Mutation of either ASC1 or MBF1 allowed frameshifting in the (CGA-CCG)3+1 reporter, but not in the (CGA-AUA)3+1 reporter, while mutations of both ASC1 and MBF1 resulted in significantly more frameshifted GFP/RFP in both reporters. (C) Analysis of effects of the indicated mutations on expression of Gln4(1-99)-GFP reporters containing the yeast TY1 programmed frameshift site (Belcourt and Farabaugh, 1990). Deletion of MBF1 and/or ASC1 did not affect the efficiency of programmed frameshifting in the TY1 transposon.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data file for Figure 4—figure supplement 1A-C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.020
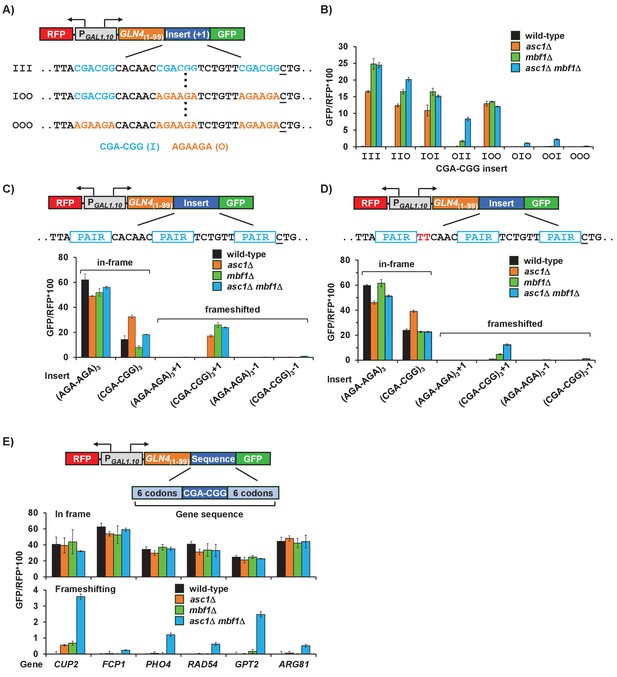
Efficient frameshifting occurs at a single CGA-CGG pair in a particular context.
(A) Schematic of inserts in +1 frame in GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters used to identify the contributions of individual CGA-CGG pairs to frameshifting. Sequences with all possible combinations of zero, one, two or three inhibitory CGA-CGG pairs (I, shown in cyan) [substituting the synonymous optimal pair AGA-AGA (O, shown in orange) at other positions] were assayed. (B) All constructs with an inhibitory codon pair at the first position (III, IIO, IOI, IOO) showed high levels of frameshifting in all three mutants. Analysis of effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on expression of GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters with the indicated position and number of inhibitory codon pairs. (C, D) Analysis of effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on expression of GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters containing three Arg-Arg codon pairs (AGA-AGA versus CGA-CGG) in 0, +1, and −1 reading frames. In (C), the first codon pair is followed by CAC, while in (D) the first codon pair is followed by TTC. (E) Analysis of effects of native yeast gene sequences containing a single CGA-CGG codon pair on in-frame and frameshifted expression of GFP. In each case, six codons upstream and downstream of the CGA-CGG were inserted into the GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporter in-frame and with a +1 frameshift after the inserted sequence. Expression of GFP/RFP was measured in wild type, asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutants.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 2
Source data file for Figure 4—figure supplement 2B-E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.021
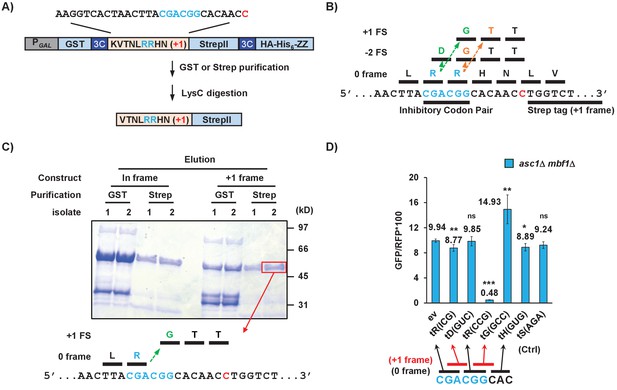
Frameshifting occurs in the +1 direction with the CGA codon in the P site and is modulated by tRNA competition at the A site.
(A) Schematic of the purification construct for the frameshifted peptide. An eight amino acid sequence with a single CGA-CGG pair from the RNA-ID reporter was inserted between a GST tag and an out-of-frame StrepII tag. LysC treatment of purified frameshifted protein yields a 16 or 17 amino acid peptide. The red nucleotide indicates the extra nucleotide in the +1 frame construct. (B) Schematic of four possible frameshifting events at the inhibitory CGA-CGG codon pair, each of which can be distinguished by one or two amino acids in the resulting peptide. Ribosomes can frameshift either in the forward direction (+1) or in the reverse direction (−2) when the P site is occupied by either the CGA codon (first amino acid in the out-of-frame peptide shown in green) or the CGG codon (the first amino acid in the out-of-frame peptide shown in orange). (C) Purified protein products of both in-frame and +1 frame constructs were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, stained with Coomassie Blue. The frameshifted protein of +1 frame construct from Strep purification (in red box) was excised, cleaved with LysC and analyzed by Mass Spectrometry, resulting in identification of the peptide shown below the figure. This peptide corresponds to that expected of a +1 frameshift occurring when the CGA codon occupies the P site. (D) Overexpression of tRNA corresponding to +1 frame codon improved frameshifting efficiency, while overexpression of tRNA corresponding to the next in-frame codon significantly reduced frameshifting. ns: p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
(Source data file for 5D).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.023
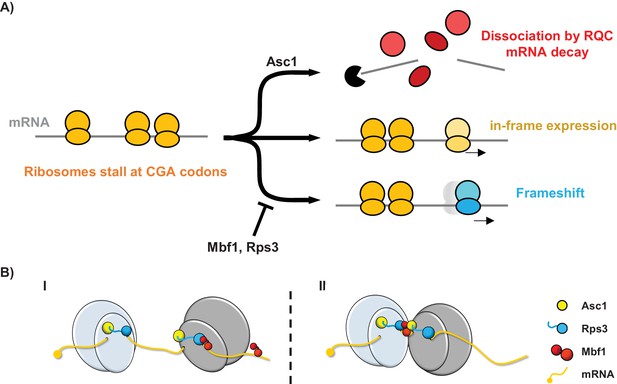
Models for the interplay between the Mbf1/Rps3 and Asc1-mediated RQC pathways and for the role of Mbf1 in reading frame maintenance.
(A) Model of the two pathways that maintain reading frames of stalled ribosomes at CGA codons. Mbf1 and Rps3 act on stalled ribosomes to prevent frameshifting while Asc1 causes removal of many of these ribosome from the translating pool and destroys the mRNA with the stall sequence. (B) Two models of roles of Mbf1 and Rps3 in reading frame maintenance. In model I, Mbf1 (two domains shown in red) interacts with mRNA, and is recruited through an interaction with Rps3 (blue) to the leading stalled ribosome (gray) to restrict mRNA movement. The interaction must be transient, with removal of Mbf1 when the ribosome translocates. In model II, Mbf1 is recruited to the colliding ribosomes (light blue) possibly by both Asc1 (yellow) and Rps3. We postulate that again an interaction with mRNA could buffer the effects of ribosome collision.
Tables
| Reagent type | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | MBF1/ YOR298C-A | SGD:S000007253 | ||
| Gene (S. cerevisiae) | ASC1/ YMR116C | SGD:S000004722 | ||
| Gene (S. cerevisiae) | RPS3/ YNL178W | SGD:S000005122 | ||
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae, MATa) | BY4741 | Open Biosystems | ||
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae, MATα) | BY4742 | Open Biosystems | ||
| Genetic reagent (S. cerevisiae) | See Supplementary table 1 in Supplementary file 3 | this paper | ||
| Antibody | anti-HA High Affinity (Rat monoclonal) | Roche | 3F10, catalog# 11867423001; RRID:AB_10094468 | 1:3000 dilution |
| Antibody | Goat anti-Rat IgG-HRP conjugate | Jackson Immuno Research | catalog# 112-035-003; RRID:AB_2338128 | 1:5000 dilution |
| Antibody | anti-G-6-PDH (Rabbit monoclonal) | Sigma | catalog# A9521; RRID: AB_258454 | 1:5000 dilution |
| Antibody | Goat anti- Rabbit IgG- HRP conjugate | Biorad | catalog# 1706515; RRID:AB_11125142 | 1:10000 dilution |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | See Supplementary table 2 in Supplementary file 3 | this paper | ||
| Sequence- based reagent | See Supplementary table 3 in Supplementary file 3 | this paper | ||
| Sequence -based reagent | Random Primers | Invitrogen | catalog# 48190011 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | T4 DNA Polymerase, LIC-qualified | Novagen | catalog# 70099 | Used for ligation- independent cloning |
| Commercial assay or kit | Super Script II Reverse Transcriptase | Invitrogen | catalog# 18064014 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RQ1 Rnase- Free Dnase | Promega | catalog# M6101 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RiboMAX Large Scale RNA Production System-T7 | Promega | catalog# P1300 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | MicroSpin G-25 columns | GE | catalog# 27-5325-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Fast SYBR Green Master Mix | Applied Biosystems | catalog# 4385612 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Glutathione sepharose-4B | GE | catalog# 17-0756-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | MagStrep ‘type3’ XT beads | IBA | catalog# 2-4090-002 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 5-FOA | USBiological | catalog# F5050 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Complete mini EDTA-free protease inhibitor | Roche | catalog# 11836170001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | leupeptin | Roche | catalog# 11017128001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | pepstatin | Roche | catalog# 11359053001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glutathione | Sigma | catalog# G4251 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Biotin | IBA | catalog# 2-1016-002 | |
| Software, algorithm | MultAlin | (Corpet, 1988) | http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/ |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Related to Figure 2.
Effects of RPS3-K108E, mbf1Δ and RPS3-K108E mbf1Δ mutants on GFP/RFP protein, mRNA and protein/mRNA from in-frame and frameshifted RLuc-Arg4-GFP/RFP.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.025
-
Supplementary file 2
Related to Figure 3.
Effects of asc1Δ, mbf1Δ and asc1Δ mbf1Δ mutations on GFP/RFP protein, mRNA and protein/mRNA from GLN4(1-99)-GFP reporters with three CGA-CGA codon pairs in the 0, +1, and −1 reading frames.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.026
-
Supplementary file 3
Related to Key Resources Table in Materials and methods Strains, plasmids and oligonucleotides used in these studies.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.027
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39637.028





