The Toll pathway inhibits tissue growth and regulates cell fitness in an infection-dependent manner
Figures
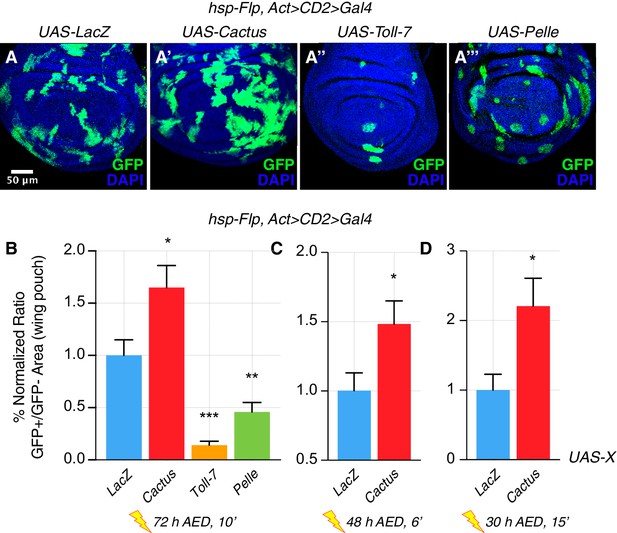
The Toll pathway negatively regulates clonal growth.
When compared to LacZ overexpressing (OE) clones, here used as a control (A), clonal inhibition of the Toll pathway via the overexpression of the NFkB inhibitor Cactus (IkB) causes overgrowth (A’). Pathway activation via the overexpression of Toll-7 (A’’) or Pelle (A’’’) causes growth reduction. Clones are induced 72 hr AED with a 10’ heat shock. Data are quantified as the percentage of the normalized ratio between GFP+ and GFP- tissue areas in the wing pouch (B). Similarly, Cactus OE clones grow larger when the heat shock is performed at different developmental stages and for different durations, respectively for 6’ 48 hr AED (C) and for 15’ 30 hr AED (D). ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, t-test. Bars represent SEM.
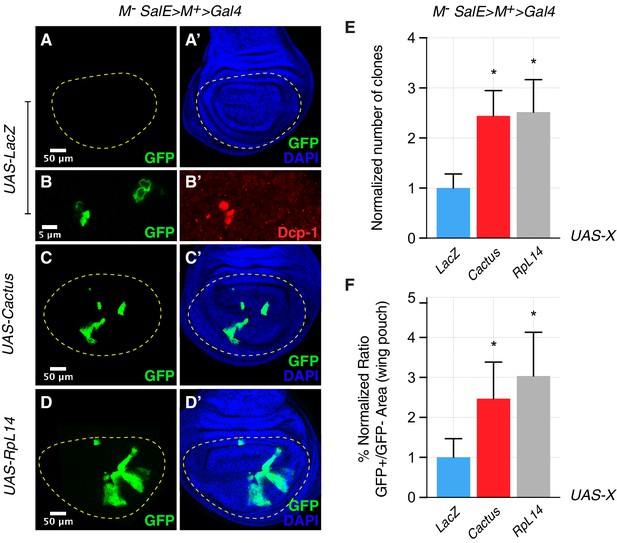
Toll pathway inhibition rescues cell competition-driven elimination of minute clones.
Clones lacking a copy of a ribosomal protein gene, here RpL14, are eliminated from the tissue (A, A’) via the induction of apoptosis, as shown with a Dcp-1 staining (B, B’). The overexpression in these clones of the Toll pathway inhibitor Cactus/IkB rescues their elimination (C, C’), similarly to the rescue generated by overexpressing RpL14, used here as a positive control (D, D’). Normalized number of clones (E) and the percentage of the normalized ratio between GFP+ and GFP- tissue areas in the wing pouch (F) are quantified. *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test. Bars represent SEM.
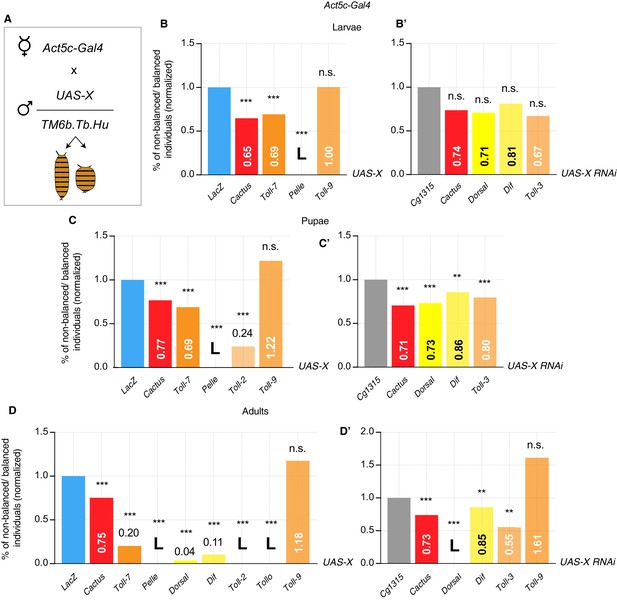
Viability assay identifies lethal and partially lethal Toll pathway alterations.
Act5c-Gal4/TM6b female flies are crossed with males carrying UAS-X either balanced or not. The progeny is either wild-type or TM6b (Tubby larvae and pupae, Humerals adults). Phenotypes are counted and impact of different Toll pathway modifications is assessed by comparison with UAS-LacZ for overexpression constructs or with UAS-Cg1315 for RNAi constructs (A). Viability assay in larvae. Overexpression of Pelle is lethal, whereas Cactus and Toll-7 OE is partially lethal. No effect on viability is obtained with other modifications (B–B’). Viability assay in pupae. Pelle OE is lethal; overexpression of Cactus, Toll-7 and Toll-2 is partially lethal. Knock-down of Cactus, Dorsal, Dif and Toll-3 RNAi is partially lethal. No effect is obtained with Toll-9 OE (C–C’). Viability assay in adults. Overexpression of Pelle, Toll-2 and Tollo is lethal. Knock-down of Dorsal is lethal. Partial lethality is obtained by overexpressing Cactus, Toll-7, Dorsal and Dif or by knocking-down Cactus, Dif and Toll-3. No effect is observed when Toll-9 is either overexpressed or down-regulated (D–D’). ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, chi-square test.
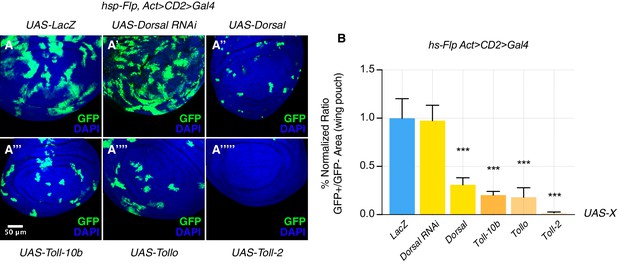
The Toll pathway negatively regulates growth.
When compared to LacZ OE clones, here used as a control (A), clonal inhibition of the Toll pathway via the down-regulation of the NFkB transcription factor Dorsal has no effect on growth, but clones appear more fragmented such that they possess a larger surface of contact with surrounding tissues (A’). Pathway activation via the overexpression of either Dorsal (A’’), the constitutively active form of the Toll-1 receptor (Toll-10b) (A’’’), Tollo (A’’’’) or Toll-2 (A’’’’’) causes growth reduction and rounded-up shapes of clones. Clones are induced 72 hr AED with a 10’ heat shock. Data are quantified as the percentage of the normalized ratio between GFP+ and GFP- tissue areas in the wing pouch (B). ***p<0.001, t-test. Bars represent SEM.
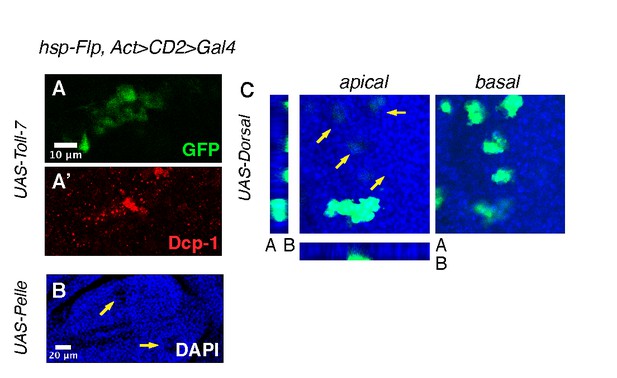
The Toll pathway induces delamination and apoptosis.
Toll-7 overexpressing clones, used as an example, round-up and are highly apoptotic, as observed with anti-Dcp-1 staining (A–A’). Pelle overexpressing clones, for example seen in the DAPI channel, are pushed out of the tissue at the basal surface of the disc and form a visible apical hole in the epithelium (B). Dorsal overexpressing clones are delaminated from the tissue at the basal surface (C). Heat shock was performed 72 hr AED for 6 min.
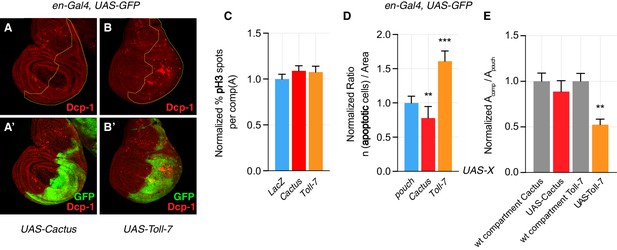
Compartmentally induced Toll pathway causes apoptosis.
Cactus and Toll-7 are overexpressed in the posterior compartment of wing discs (en-Gal4). Cactus OE compartments show less apoptosis when compared to control anterior compartments (A–A’), quantified in D). Toll-7 compartments are massively apoptotic, when compared to wild-type anterior compartments (B–B’). Data are quantified as follows: the ratio between the number of apoptotic cells in the posterior compartment and the area of the compartment is compared, and normalized to, the ratio between the number of apoptotic cells in the pouch and the area of the pouch. (D). No difference is detected in the number of proliferative cells (pH3 staining) across compartments. Data are quantified by calculating the percentage, in each condition, of pH3 spots in the posterior compartment normalized for the area of the compartment (C). Toll-7 compartments are smaller than wild-type compartments, whereas Cactus compartments show a similar size when compared to their wild-type counterparts. Data are quantified by calculating the ratio between compartments of each condition and the area of the wing pouch, and normalized to the ratio between the area of wild-type compartments and the area of the wing pouch (E). Apoptotic spots, pH3 spots and compartment areas are calculated using FIJI. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, t-test (paired t-test in (D)). Bars represent SEM.
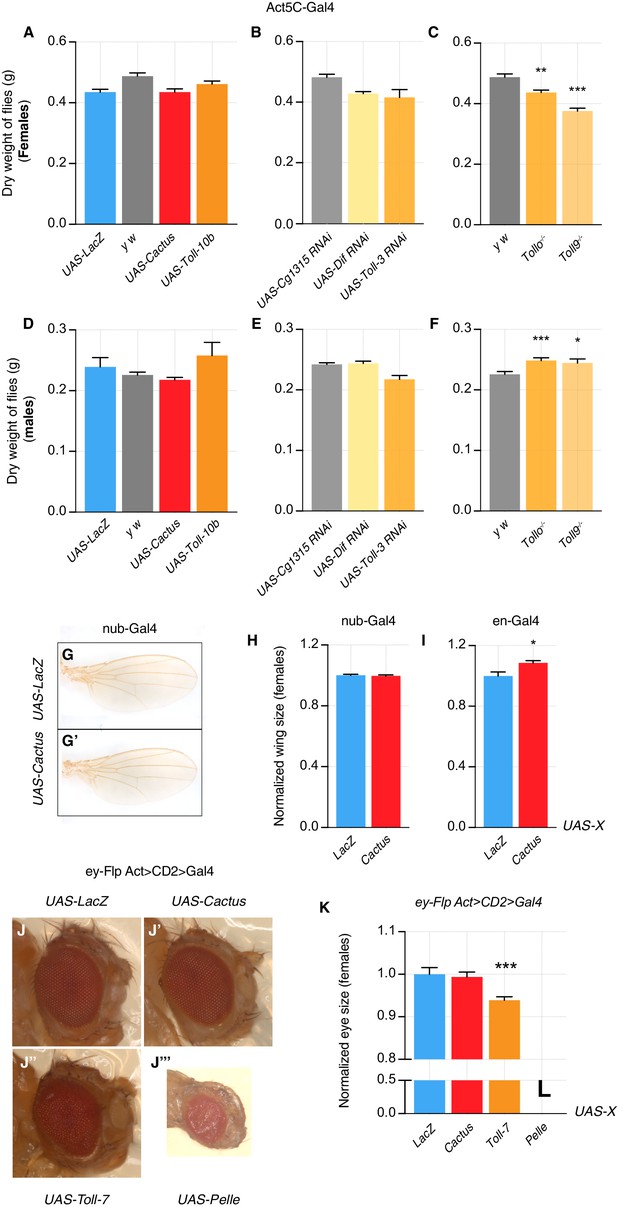
Toll pathway modifications have no or little effect on organismal and organ growth.
Dry weight of Cactus and Toll-10b overexpressing female flies (Actin driver) does not differ from LacZ control flies (A). Dry weight of Dif and Toll-3 knock-down flies does not differ from Cg1315 RNAi control flies (B). Tollo-/- and Toll9-/- female flies have a slightly reduced weight when compared with y w flies (C). Similarly, male flies overexpressing Cactus and Toll-10 or downregulating Dif and Toll-3 do not show effects on dry weight when compared to LacZ and Cg1315 RNAi flies (D–E). Tollo-/- and Toll9-/- male flies have a slightly increased weight when compared with y w flies (F). No effect on wing size is detected when Cactus is overexpressed using nub-Gal4, compared to LacZ OE animals (G–H). Wings are slightly bigger when engrailed is used as a Gal4 driver to drive Cactus overexpression (I). No effect is detected on eye size when Cactus is overexpressed and a small reduction in size is seen when Toll-7 is overexpressed. Pelle OE is lethal and pharate eyes appear smaller but fully developed (J–K). ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, t-test. Bars represent SEM.
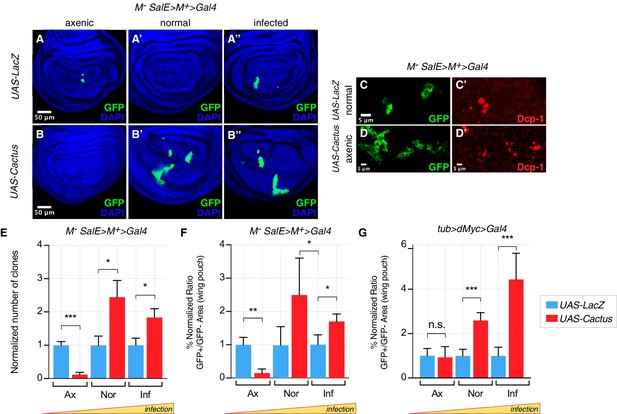
Toll pathway inhibition rescues cell competition-driven elimination of loser clones in an infection-dependent manner.
Minute clones, which lack a functional copy of the RpL14 gene, are eliminated via cell competition under axenic (A), normal (A’), and infected conditions (A’’). LacZ overexpression in loser cells is used as a negative control. Toll pathway inhibition via Cactus OE fails to rescue cell competition-driven elimination of minute clones under axenic conditions (B), whereas elimination is rescued under both normal (B’) and infected (B’’) conditions. Loser clones are highly apoptotic, as shown with a Dcp-1 staining (C, C’). and Cactus OE escaper clones under axenic conditions are extremely fragmented and apoptotic (Dcp-1 staining, (D, D’) Data are quantified by scoring the number of clones in the wing pouch (E), and by calculating the percentage of the normalized ratio between GFP+ and GFP- tissue areas in the wing pouch (F). Similarly, the elimination of loser clones with a single copy of dMyc in a background with two copies of dMyc is rescued specifically under normal or, even more efficiently, under infected conditions, but not under axenic conditions, as quantified in (G). ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, n.s. not significant, Mann-Whitney test. Bars represent SEM.
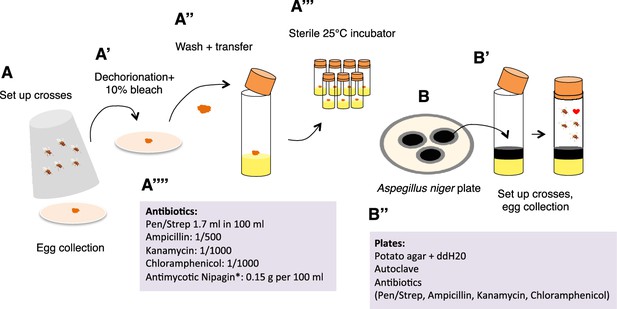
Methods to grow axenic or infected animals.
In order to develop axenic animals, crosses were set up in cages and eggs were collected onto agar plates (A). Embryos were dechorionated in 10% bleach (A’), washed and transferred into tubes containing axenic food (A’’). Tubes and plugs were previously autoclaved. Larvae were grown at 25°C in a sterile incubator (A’’’). Food was prepared with a cocktail of antibiotics and antifungal agents, as listed in (A’’’’). In order to develop infected animals, A. niger was cultivated onto potato agar plates (B) and then added to the food, where crosses were set up and eggs collected (B’). Food was prepared with a mix of antibiotics to avoid bacterial growth, listed in (B’’).
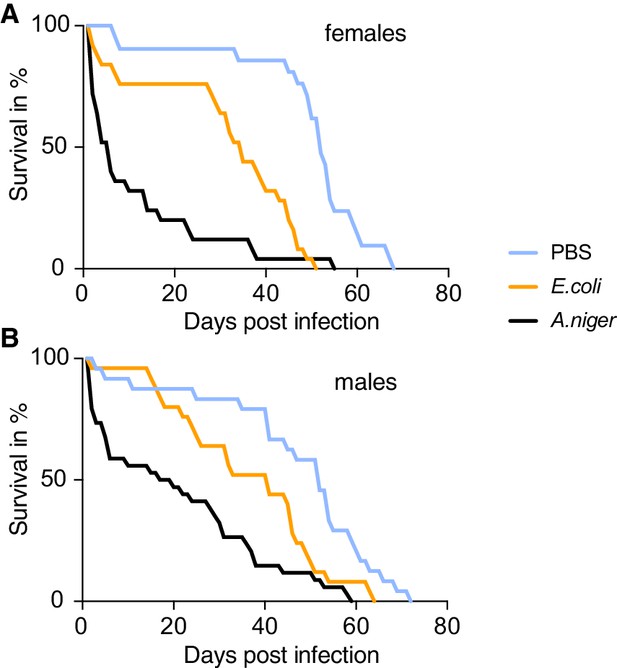
Flies infected with A.niger have a reduced life span.
Flies are infected with either a PBS control solution, a E. coli solution or a solution of A. niger. Life span was measured. Female flies infected with E. coli and, to a larger extent, flies infected with fungi, die earlier than control animals (A). A similar trend is observed for males (B).
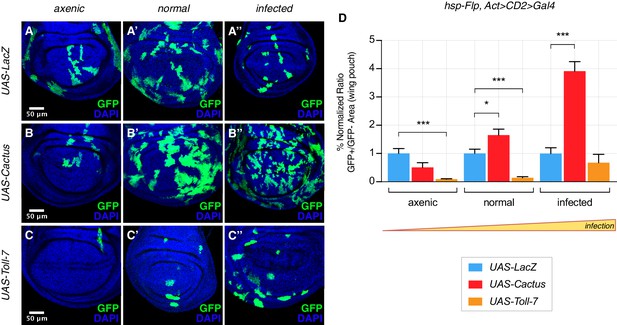
The Toll pathway negatively regulates clonal growth in an infection-dependent manner.
Under normal laboratory conditions, when compared to LacZ OE clones (A’), clonal inhibition of the Toll pathway with Cactus OE causes overgrowth in a wild-type background (B’). When the pathway is activated via the overexpression of Toll-7, clones are instead reduced in size (C’). The growth advantage provided by the inhibition of the pathway is further enlarged under infected conditions (B’’) compared to (A’’). Inhibition of the pathway under axenic conditions does not provide a growth advantage over the surrounding cells (B) compared to (A). On the contrary, pathway activation enhances the growth-defective phenotype in axenic conditions (C) and the effect is no longer evident when larvae develop under infected conditions (C’’). Data are quantified in (D) as the percentage of the normalized ratio between GFP+ and GFP- tissue areas in the wing pouch. ***p<0.001, *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test. Bars represent SEM.
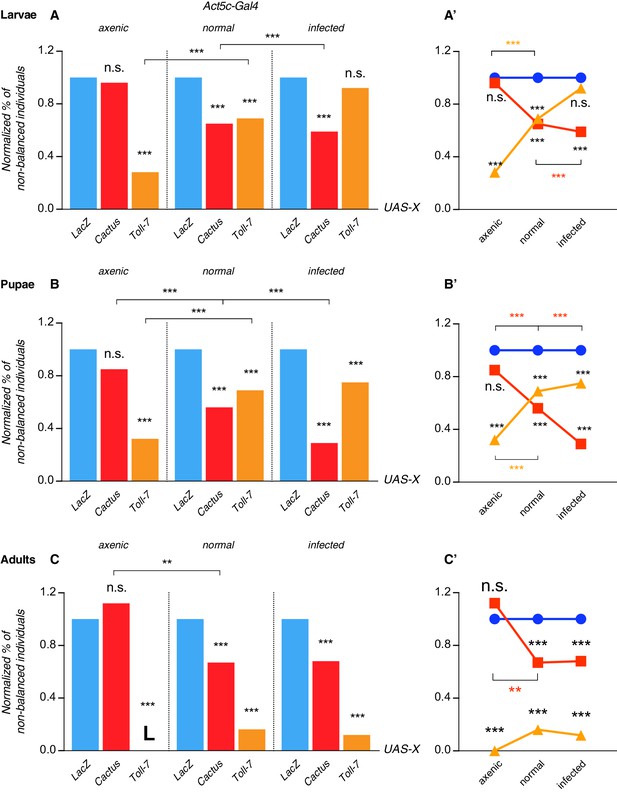
Pathway activation-induced lethality is partially rescued under infected conditions and pathway suppression-induced lethality is rescued under axenic conditions.
Lethality is scored as a normalized percentage of non-balanced individuals, since progeny can either inherit either the Act-Gal4 that drives the overexpression of our genes of interest or a TM6b balancer chromosome. In larvae and in normal conditions Cactus and Toll-7 overexpression is partially lethal. Under axenic conditions Cactus OE fully rescues larval lethality, whereas Toll-7 OE lethality is further increased. Infected larvae that overexpress Toll-7 rescue lethality observed under normal and, even more, axenic conditions (A). Lethality trend is shown in (A’). In pupae, similarly to larvae, Cactus OE shows no effect on viability, whereas its impact increases with increased infection. The opposite can be seen with Toll-7 OE pupae (B–B’). In adults the situation resembles the one described for larvae and pupae, although Toll-7 OE is lethal under axenic conditions and no rescue of the partial lethality seen under normal conditions is observed under infected conditions (C–C’). ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, chi-square test.
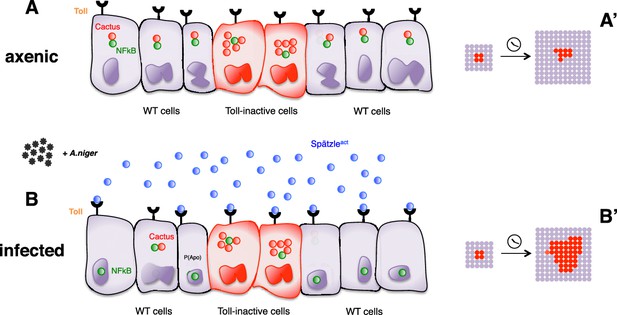
Infection-dependent role of the Toll pathway in cell growth (pathway inhibition scenario).
The cartoon shows wild-type cells, colored in violet, that surround red-Cactus overexpressing cells. Toll receptors are present on cell membranes. Spätzle cytokines are drawn as blue circles, Cactus as red circles and NFkB as green circles. Infection with A. niger is depicted with black symbols. Nuclear shapes indicate either a dividing or a static cell (A and B). Under axenic condition, no pathogens are present in the extracellular environment and, independently of the amount of IkB inhibitor in the cytoplasm, the NFkB transcription factors are unable to translocate to the nucleus. The outcome is a leveled and uniform growth between wild-type and Cactus OE cells (A). When cells are naturally or artificially exposed to infectious agents, Toll pathway activation in wild-type cells causes NFkB nuclear translocation. On the contrary, Cactus OE cells remain unresponsive, with NFkB confined to the cytoplasm. This generates a strong growth advantage over the surrounding wild-type cells (B). After developmental time, indicated in the cartoon with a clock, clones of red Cactus OE cells are growing over a larger percentage of the tissue upon infection (A’ and B’). The source of active Spätzle may be both systemic, as suggested by our experiments, and local (Alpar et al., 2018).
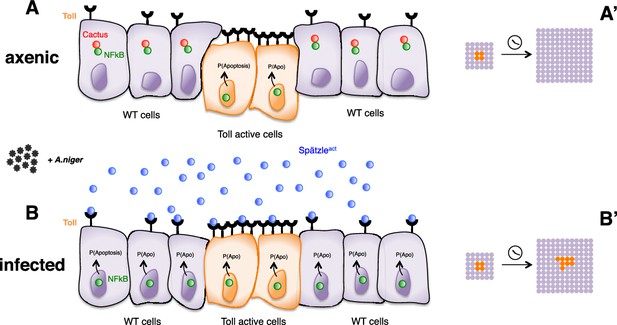
Infection-dependent role of the Toll pathway in cell growth (pathway activation scenario).
The cartoon shows wild-type cells, colored in violet, that surround orange Toll-7 overexpressing cells, as indicated by the increased number of receptors on the surface of the cells. Spätzle cytokines are drawn as blue circles, Cactus as red circles and NFkB as green circles. Infection with A. niger is depicted with black symbols. Nuclear shapes indicate either a dividing or a static cell (A and B). Under either axenic or normal conditions, no or ‘natural’ amounts of pathogens are present in the environment. Cells with higher numbers of receptors have presumably higher chances to sense the infection via Spätzle and to therefore activate the Toll pathway, leading to cell death and delamination. Surrounding wild-type cells therefore gain a growth advantage over Toll overexpressing cells (A). When a large amount of pathogen is present, activation of the pathway presumably reaches saturation levels in all cells, irrespectively of the number of exposed receptors. Cell growth is therefore leveled among wild-type and Toll overexpressing cells (B). After developmental time, indicated in the cartoon with a clock, clones of orange Toll OE cells are growing over a larger percentage of the tissue upon infection (A’ and B’). The source of active Spätzle may be both systemic, as suggested by our experiments, and local (Alpar et al., 2018).
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39939.016





