Hedgehog signaling patterns the oral-aboral axis of the mandibular arch
Figures
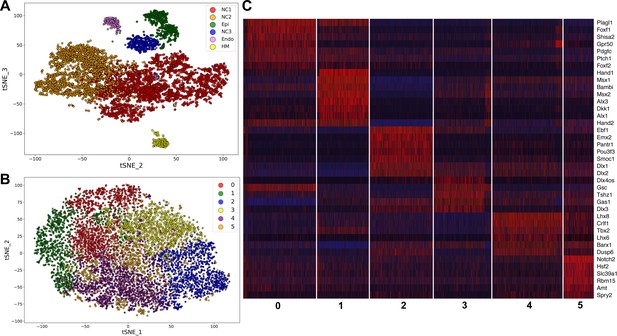
Analysis of scRNA-seq data of E10.5 mouse mandibular arch.
(A) tSNE plot of all cells with high quality RNA-seq results shows clustering of the major cell types. (B) Unsupervised clustering of the neural crest-derived mandibular mesenchyme cells shows six identifiable subgroups. (C) Heat map showing distribution of cells in the six subgroups shown in B, with selected marker genes exhibiting more than 1.3-fold difference in expression levels across all six subgroups. The cluster numbers are marked at the bottom of Panel C and correspond to the cluster numbers in Panel B. The expression level for each marker gene in the individual cells is reflected by color of the vertical bars, with bright blue being lowest and bright red being highest.
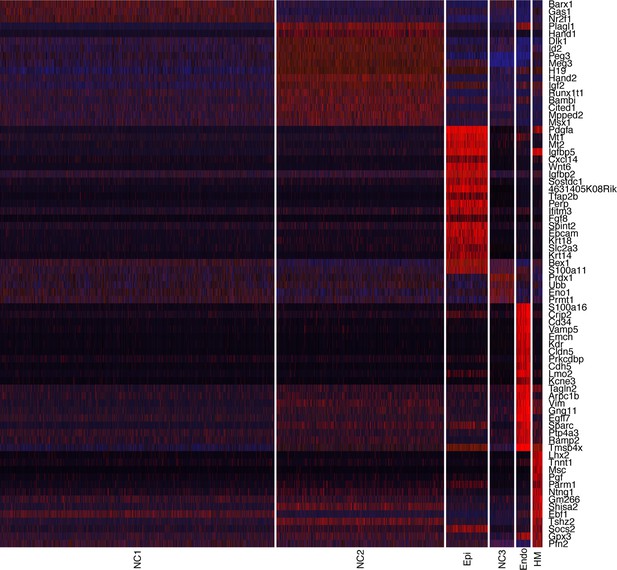
Heatmap showing transcriptome profiles of the major cell types in the E10.5 mouse mandibular arch, with select marker genes exhibiting more than 1.5-fold difference in expression levels across all clusters.
NC1 – NC3, neural crest derived mesenchyme cells; Epi, epithelial cells; Endo, endothelial cells; HM, head mesoderm cells. Each row shows the pattern of expression of one marker gene in all cells of all six clusters, with gene names labeled at the right side. The level of expression in the individual cells is reflected by the color of the vertical bar, with brightest blue being the lowest and the brightest red being highest.
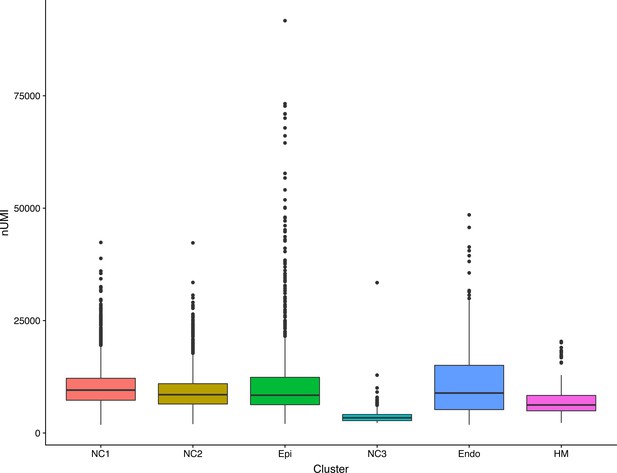
Dot plot showing the number of unique genes whose expression was detected in the single cells in the six different clusters.
NC1 – NC3, neural crest derived mesenchyme cells; Epi, epithelial cells; Endo, endothelial cells; HM, head mesoderm cells. The box marks the number of genes detected in 25% to 75% of the cells in that cluster, with the median gene number marked by the horizontal bar inside the box.
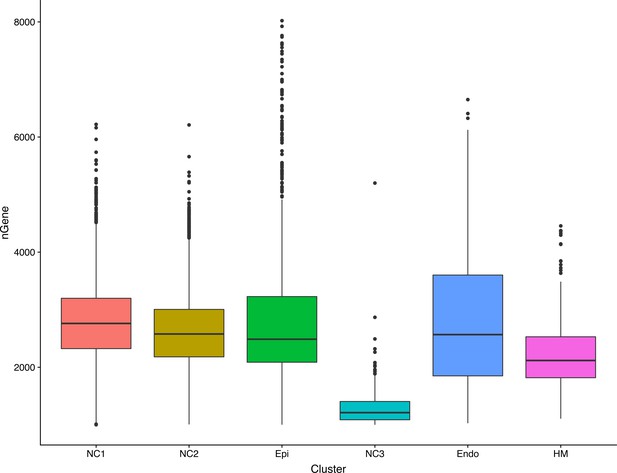
Dot plot showing the number of transcripts detected in the single cells in the six different clusters.
NC1 – NC3, neural crest derived mesenchyme cells; Epi, epithelial cells; Endo, endothelial cells; HM, head mesoderm cells. The box marks the number of transcripts detected in 25% to 75% of the cells in that cluster, with the median number of transcripts marked by the horizontal bar inside the box.
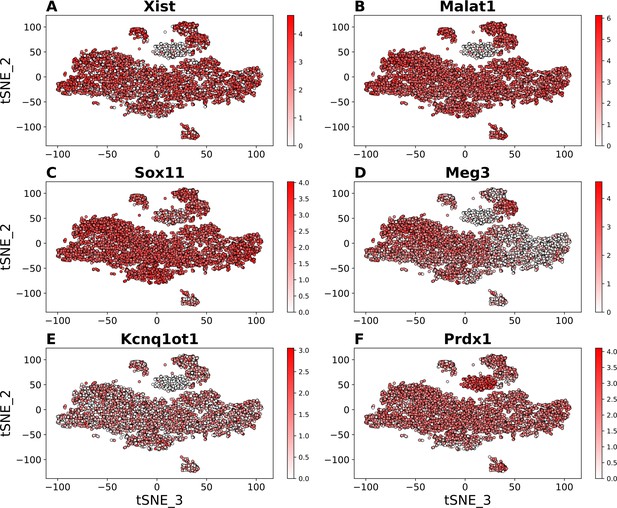
Comparison of the levels of transcripts for selected marker genes in tSNE maps of the E10.5 mandibular arch scRNA-seq data.
The tSNE cluster map as shown in Figure 1A in the manuscript is used to show the marker gene expression in the individual cells, with transcript levels shown in red color (darker color indicating higher level of transcripts detected). (A) Xist lncRNAs. (B) Malat1 LncRNAs. (C) Sox11 mRNAs. (D) Meg3 lncRNAs. (E) Kcnq1ot1 lncRNAs. (F) Prdx1 mRNAs. The NC3 cluster showed dramatically reduced expression of most transcripts, including the Xist, Malat1, Meg3, Kcnq1ot1 lncRNAs and Sox11 mRNAs. Prdx1 was among very few genes whose transcripts were detected at higher levels in NC3 than in the other clusters.
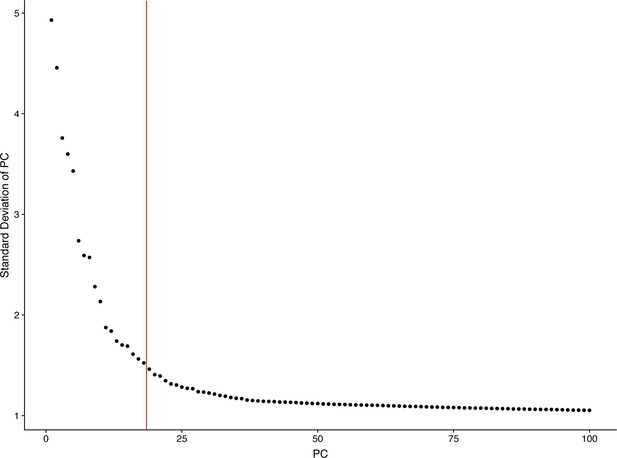
Distribution of the principal components by JackStraw plot.
The red line marks the cutoff for identifying the most significant PCs used for tSNE implementation.
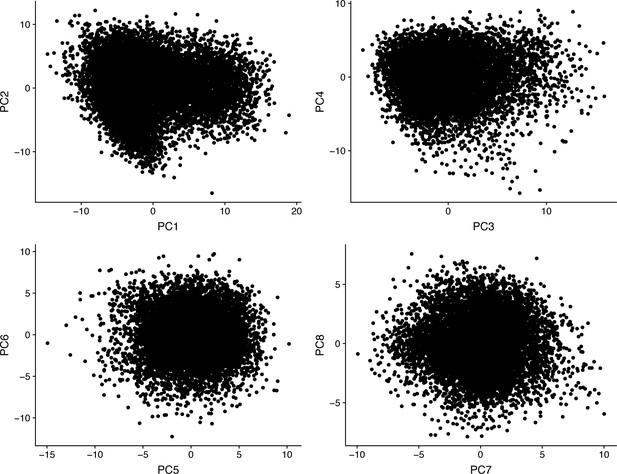
Analysis of the top eight principal components identified in the scRNA-seq data.
Most of the cells showed similar distribution by principal component analysis, with no apparent spatial segregation.
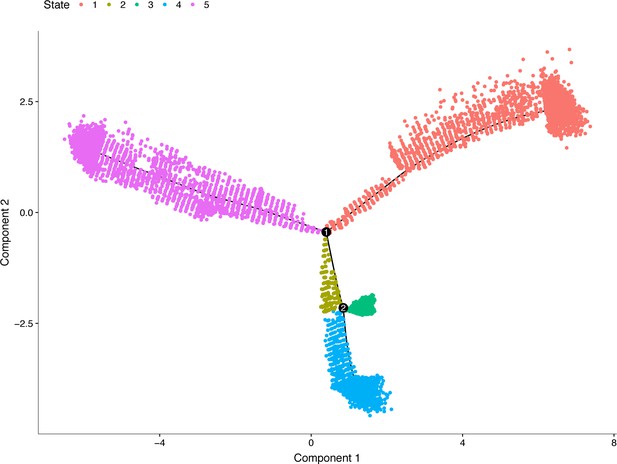
Developmental trajectories of all of the neural crest cells derived from analysis of the E10.5 mandibular arch scRNA-seq data using Monocle-2.
The cellular states are color coded. Two branch points were identified. Gene ontology analysis showed that States 3 and 4 were enriched with the cell differentiation terms ‘osteoblast differentiation’ and ‘neuron differentiation’, respectively (top enriched gene ontology terms for States 3 and 4 are provided in Supplementary file 6 and 7).
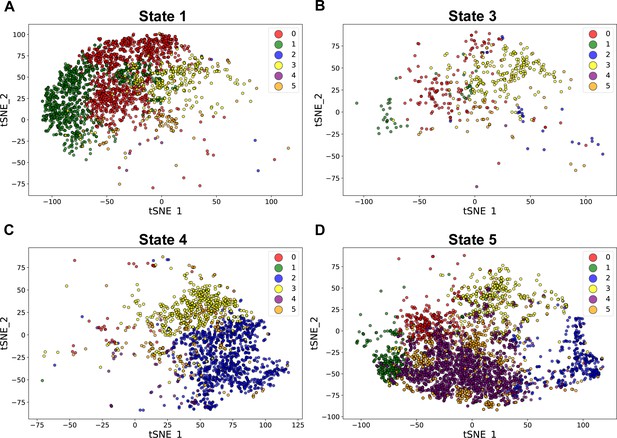
Distribution of the five cellular states from the developmental trajectory analysis of the neural crest cells in the E10.5 mandibular arch on tSNE plot of the six subgroups derived from iterative clustering.
The color code for the cell subgroups is the same as shown in Figure 1B in the manuscript. The developmental trajectories did not correlate with obvious spatial axis.
A .mov file showing three dimensional tSNE projection of the six subgroups of neural crest derived mandibular arch mesenchyme cells.
The color codes for the six subgroups are the same as in Figure 1B (Cluster 0, red; Cluster 1, green; Cluster 2, blue; Cluster 3, yellow; Cluster 4, purple; Cluster 5, orange).
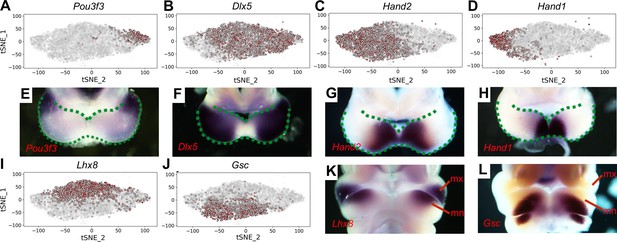
Distribution of E10.5 mandibular arch cells expressing select marker genes in the neural crest compartments in tSNE maps.
(A–D) Cells expressing Pou3f3 (A), Dlx5 (B), Hand2 (C), and Hand1 (D) in the neural crest cell population, detected by scRNA-seq, are shown in red color in tSNE plot, with the brightness of the red color corresponding to levels of transcripts detected. (E–H) Rostral views of the mandibular arches of E10.5 mouse embryos showing patterns of expression of Pou3f3 (E), Dlx5 (F), Hand2 (G), and Hand1 (H) mRNAs detected by whole mount in situ hybridization. Green dots mark the oropharyngeal and aboral sides of the mandibular arches, with the distal caps of the paired mandibular arches meeting at the midline. (I, J) Cells expressing Lhx8 (I), and Gsc (J) in the neural crest cell population, detected by scRNA-seq, are shown in red color in tSNE plot. (K, L) Frontal views of the mandibular arches of E10.5 mouse embryos showing patterns of expression of Lhx8 (K) and Gsc (L) mRNAs detected by whole mount in situ hybridization. mn, mandibular process; mx, maxillary process.
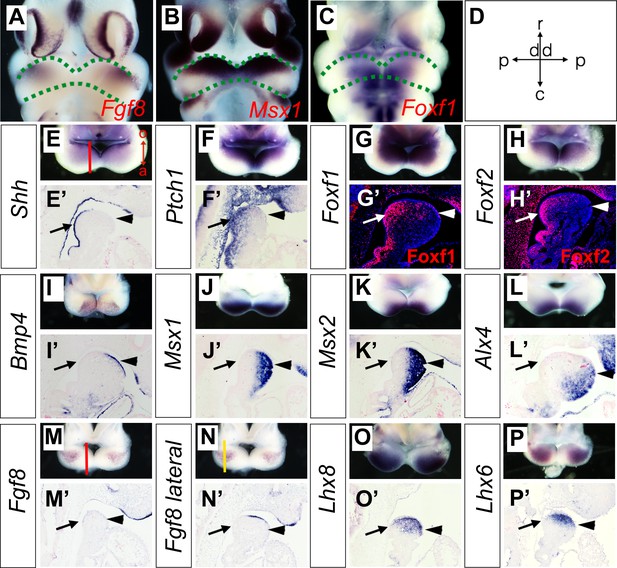
Expression of Shh, Bmp4, Fgf8, and their target genes in the developing mandibular arch.
(A–C) Frontal views of E10.5 embryonic mouse heads after whole mount in situ hybridization detecting Fgf8 (A), Msx1 (B) and Foxf1 (C). Green dashed lines mark the rostral and caudal sides of the embryonic mandibular arch. (D) A schematic indication of the proximal-distal and rostral-caudal axis of developing mandibular arch in the frontal view. (E–P) Rostral views of the mandibular arches in E10.5 mouse embryos showing patterns of expression of Shh (E), Ptch1 (F), Foxf1 (G), Foxf2 (H), Bmp4 (I), Msx1 (J), Msx2 (K), Alx4 (L), Fgf8 (M, N), Lhx8 (O), and Lhx6 (P) mRNAs. The red vertical line in Panel E shows approximate position of sagittal sections selected for in situ hybridization detection on sections. The orientation of the oral (o) and aboral (a) axis is also indicated in Panel E. Note the complementary pattern of Foxf1 and Msx1 expression along the oral-aboral axis in G and K that could not be distinguished on the frontal views in B and C. (E’–P’) Sagittal sections showing expression of Shh (E’), Ptch1 (F’), Bmp4 (I’), Msx1 (J’), Msx2 (K’), Alx4 (L’), Fgf8 (M’, N’), Lhx8 (O’), Lhx6 (P’) mRNAs, and Foxf1 (G’) and Foxf2 (H’) proteins in the distal mandibular arch in E10.5 mouse embryos. Protein immunofluorescence is shown in red color in G’ and H’, whereas mRNA signals in all other panels are shown in purple/blue color. Arrow points to oropharyngeal endoderm, and arrowhead points to aboral ectoderm. The red and yellow lines in (M) and (N), respectively, indicate the different positions corresponding to the sections in (M’) and (N’).
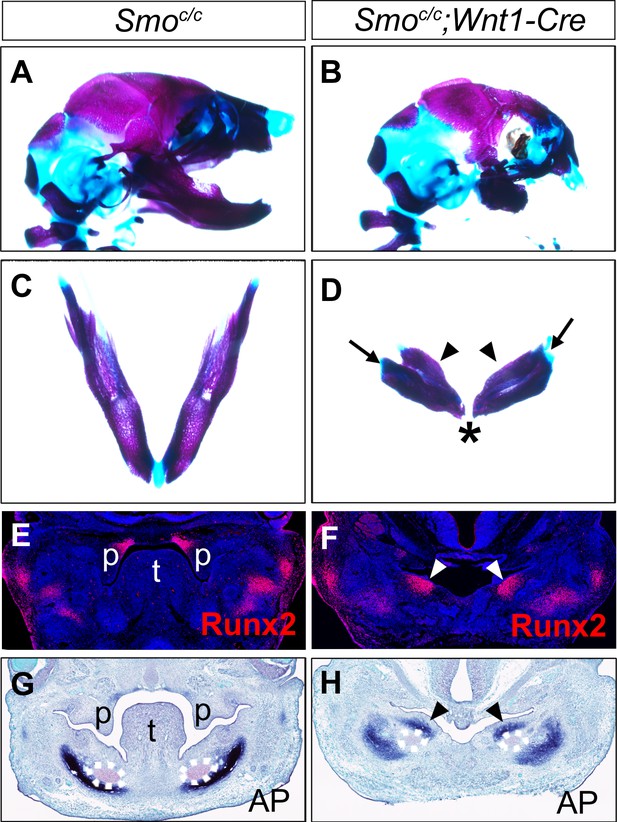
Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre embryos display tongue agenesis and ectopic ossification.
(A, B) Lateral view of skeletal preparations of heads of E18.5 Smoc/c (A) and Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre (B) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). (C, D) Comparison of the mandibular skeletons of E18.5 Smoc/c (C) and Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre (D) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Arrows in D point to condylar cartilage and the arrowheads point to the duplicated dentary bone. Asterisk in D indicates truncation of the distal mandible in Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre embryos. (E, F) Immunofluorescent detection of Runx2 protein (red) on frontal sections of E12.5 Smoc/c (E), and Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre (F) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Sections were counterstained with DAPI. (G, H) Detection of alkaline phosphatase activity (blue) on frontal sections of E13.5 Smoc/c (G) and Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre (H) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Arrowheads in F and H point to the ectopic ossification at the oral side of mandibular mesenchyme. The condensed Meckel’s cartilage primordia are outlined using dashed lines in G and H. p, palate; t, tongue.
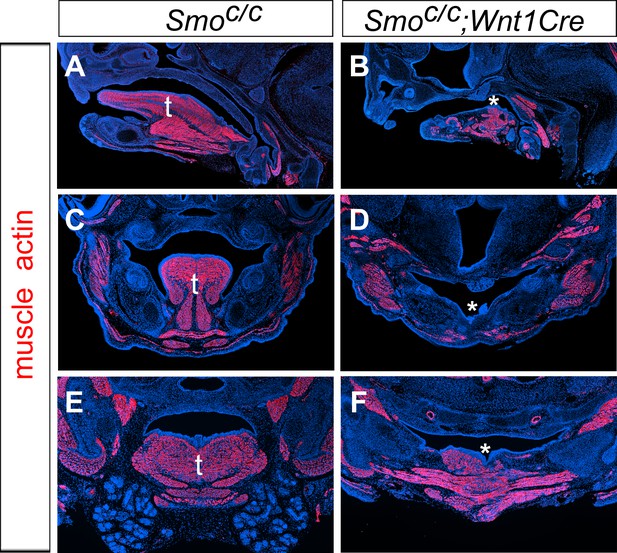
Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre display agenesis of the oral tongue structure.
(A–F) Immunofluorescent detection of muscle actin (red) on sagittal sections (A–B), and frontal sections (C–F) of E15.5 Smoc/c (A, C, E) and Smoc/cWnt1-Cre (B, D, F) embryos. Sections were counterstained with DAPI. t, tongue, * shows disrupted tongue structures in Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre (B, D, F) embryos.
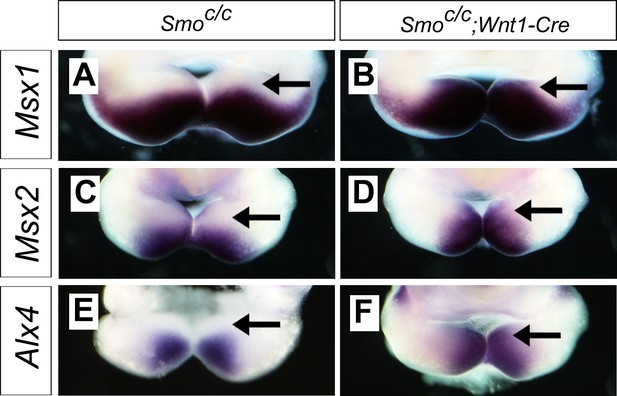
Mouse embryos with tissue-specific inactivation of Smo signaling in the neural crest lineage exhibit altered pattern of expression of BMP target genes in the mandibular arch.
(A–F) Rostral views of microdissected E10.5 mandibles from Smoc/c control (A, C, E) and Smoc/c;Wnt1-Cre (B, D, F) embryos showing differential expression of Msx1 (A, B), Msx2 (C, D), and Alx4 (E, F) mRNA expression along the oral-aboral axis. Arrow points to the oropharyngeal side of the mandibular arch.
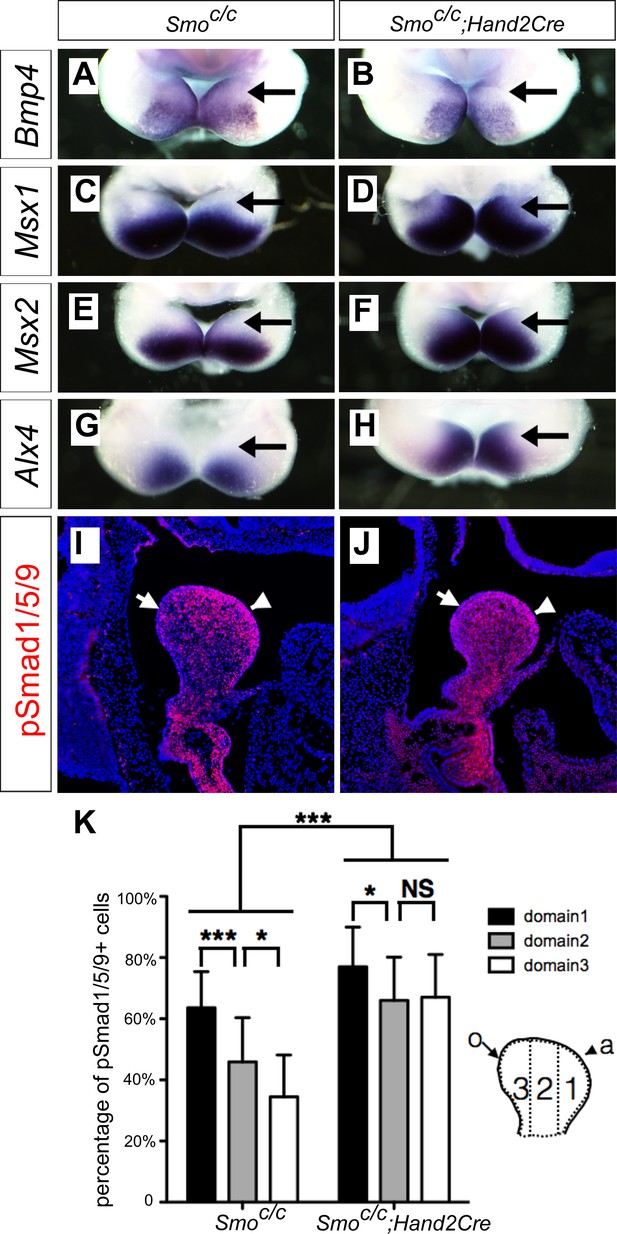
Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre embryos exhibit oropharyngeally expanded BMP signaling activity in the developing mandibular arch.
(A–H) Whole mount in situ hybridization detection of Bmp4 (A, B), Msx1 (C, D), Msx2 (E, F), and Alx4 (G, H) mRNAs in the mandibular arches in E10.5 Smoc/c (A, C, E, G), and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (B, D, F, H) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). (I, J) Immunofluorescent detection of phospho-Smad1/5/9 (pSmad1/5/9, red) on sagittal sections through the distal region of the mandibular arches in E10.5 Smoc/c (I) and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (J) embryos . Arrow points to oropharyngeal side and arrowhead points to aboral side of the mandibular arch. (K) Quantification of percentage of pSmad1/5/9 positive nuclei in the three domains along the aboral-oral axis of mandibular mesenchyme (domain1, domain2, domain3). Statistical analysis was performed on data from 22 sections of 4 embryos of each genotype by using two-way ANOVA. a, aboral, o, oral. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.
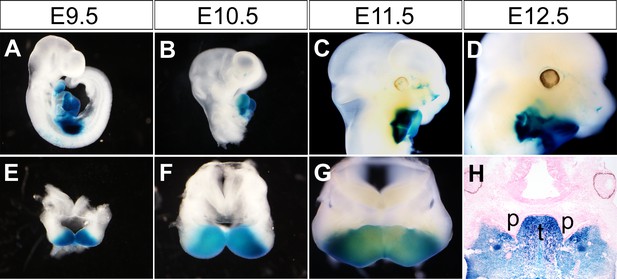
Tissue specificity of Cre-mediated activation of lacZ expression in the developing craniofacial complex of Hand2-Cre;R26R-LacZ embryos from E9.5 to E12.5.
(A–G) X-gal staining of whole mount heads of Hand2-Cre;R26R-LacZ embryos at E9.5 (A, E), E10.5 (B, F), E11.5 (C, G) and E12.5 (D). (H) X-gal staining on frontal sections from the middle region of Hand2-Cre;R26R-LacZ embryos at E12.5. p, palatal shelf; t, tongue.
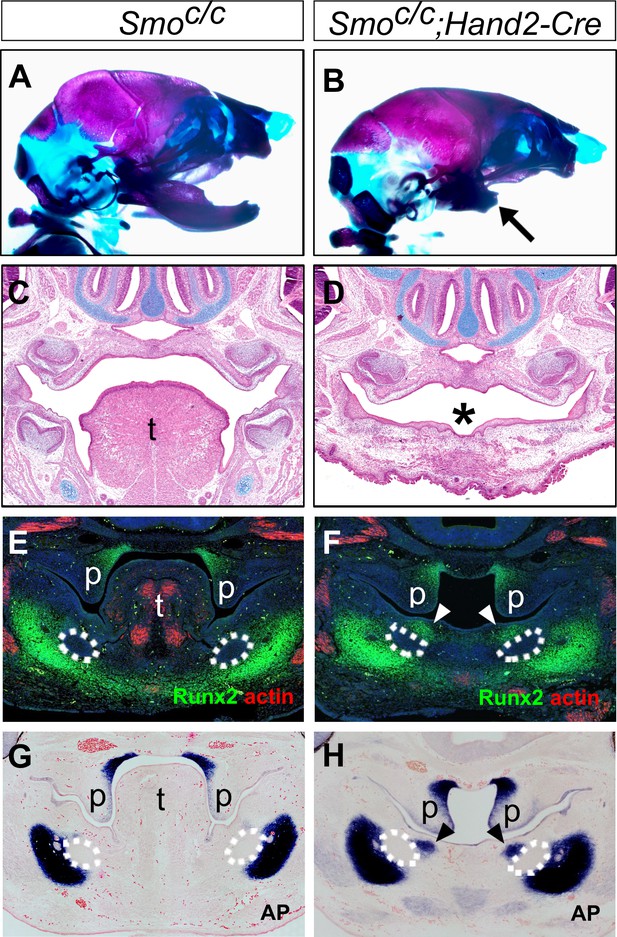
Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre embryos display tongue agenesis and ectopic ossification.
(A, B) Skeletal preparations of heads of E18.5 Smoc/c (A) and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (B) embryos (n = 5 for each genotype). Arrow in B indicates the shortened mandible in the Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre embryo. (C, D) HE staining of frontal sections of E16.5 Smoc/c (C) and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (D) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Asterisk in D marks absence of tongue in the Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre embryo. (E, F) Immunofluorescent detection of Runx2 (green) and muscle alpha-actin (red) on frontal sections of E12.5 Smoc/c (E) and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (F) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Sections were counterstained with DAPI. (G, H) Detection of alkaline phosphatase activity (blue) on frontal sections of E12.5 Smoc/c (G) and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (H) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Sections were counterstained with eosin. Arrowheads in F and H indicate the ectopic ossification at the oral side of the developing mandible. The condensed Meckel’s cartilage primordia are outlined using dashed lines in E-H. p, palate; t, tongue.
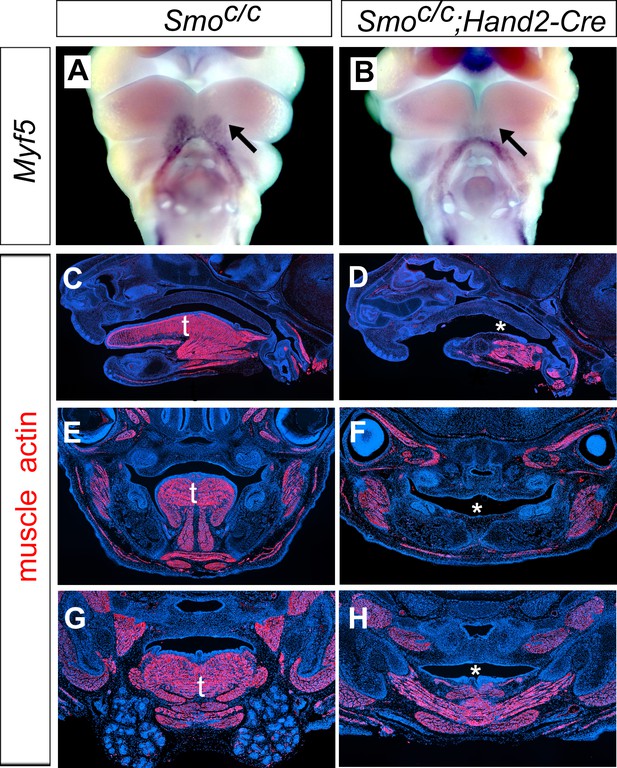
Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre display agenesis of the oral tongue structure.
(A–B) Frontal views of E10.5 embryos from Smoc/c control (A) and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (B) embryos showing expression of Myf5. Arrows show the Myf5 positive tongue muscle precursor cells. (C–H) Immunofluorescent detection of muscle actin (red) on sagittal sections (C–D), and frontal sections (E–H) of E15.5 Smoc/c (C, E, G) and Smoc/cWnt1-Cre (D, F, H) embryos. Sections were counterstained with DAPI. t, tongue, * shows disrupted tongue structures in Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (D, F, H) embryos.
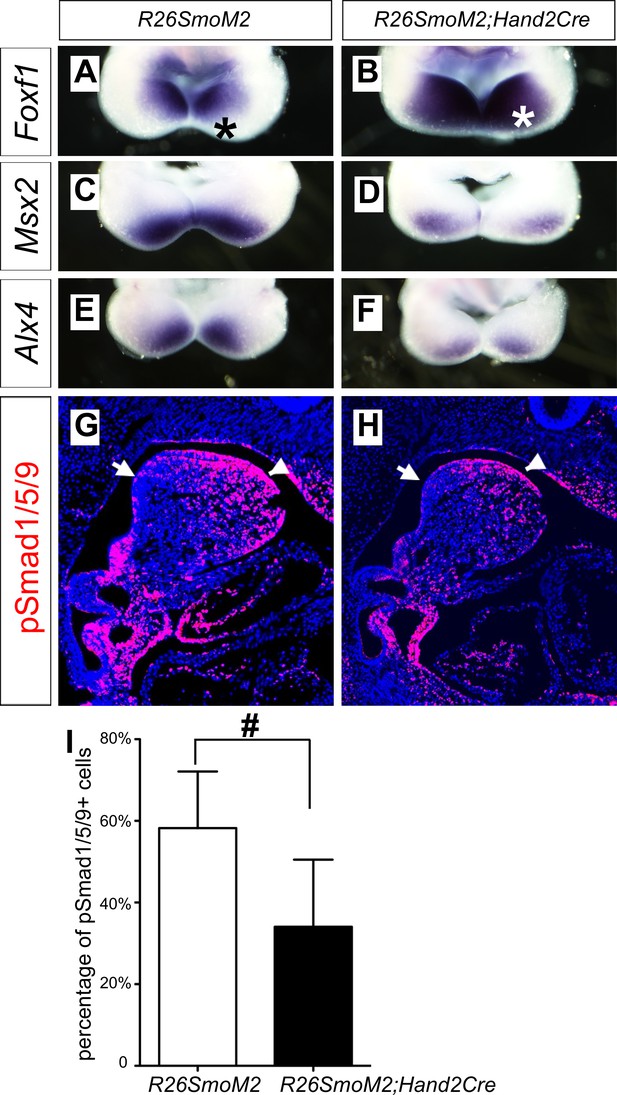
Ectopic activation of Smo signaling inhibits BMP signaling activity in the mandibular arch mesenchyme.
(A–F) Rostral views of the mandibular arches following whole mount in situ hybridization detection of Foxf1 (A, B), Msx2 (C, D), and Alx4 (E, F) mRNAs in the E10.5 R26SmoM2 (A, C, E), and R26SmoM2;Hand2-Cre (B, D, F) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Asterisks in A and B mark the aboral side of the mandibular arch. (G, H) Immunofluorescent detection of phospho-Smad1/5/9 (pSmad1/5/9, red) on sagittal sections through the distal regions of E10.5 R26SmoM2 (G) and R26SmoM2;Hand2-Cre (H) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Arrow points to oropharyngeal endoderm, and arrowhead points to mandibular ectoderm. (I) Quantification of the percentage of pSmad1/5/9 positive nuclei in the mandibular arch mesenchyme. Statistical analysis was performed on data from 18 sections of three embryos for each genotype by using Student’s t-test. #, p<0.001.
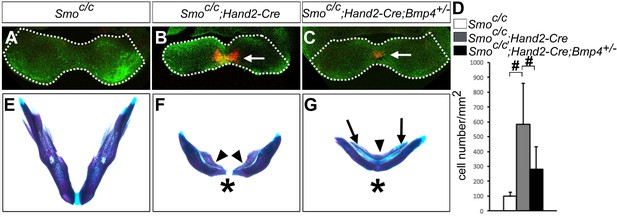
Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre embryos showed Bmp4-dependent increase in apoptosis of distal mandibular mesenchyme.
(A–C) Immunofluorescent detection of active-Caspase3 (red) in E10.5 Smoc/c (A), Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (B), and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre;Bmp4+/- (C) embryos. Mandibles are outlined with white dash lines. (D) Quantification of active-Caspase3 positive cell density in the Smoc/c, Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre;Bmp4+/- samples. The results were presented as mean ± SD. Smoc/c (98.96 ± 28.21 cells/mm2); Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (584.12 ± 275.20 cells/mm2); Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre;Bmp4+/- (280.45 ± 153.23 cells/mm2). Analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test to compare all pairs. #, p<0.001. (E–G) Skeletal preparations showing mandibles of E18.5 Smoc/c (E), Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (F), and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre;Bmp4+/- (G) embryos (n = 5 for each genotype). Arrowheads in F and G point to duplicated dentary bone. Asterisks in F and G mark differences in the morphology of the distal mandibular structure in Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (F) and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre;Bmp4+/- (G) embryos. Arrows in G point to the Meckel’s cartilage.
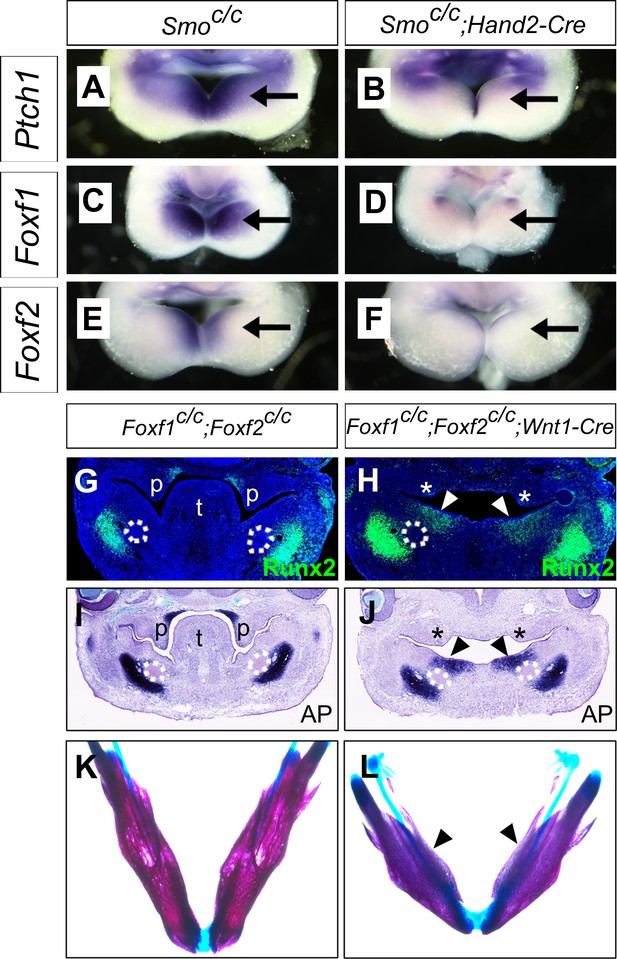
Foxf1 and Fox2 mediate Shh-Smo signaling function in mandible and tongue development.
(A–F) Rostral views of the mandibular arches of E10.5 Smoc/c (A, C, E) and Smoc/c;Hand2-Cre (B, D, F) embryos following whole mount in situ hybridization detection of Ptch1 (A, B), Foxf1 (C, D), and Foxf2 (E, F) mRNAs (n = 3 for each genotype). Arrow points to the mRNA signals in the oral side of the mandibular arch. (G, H) Immunofluorescent detection of Runx2 (green) on frontal sections of E12.5 Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c (G) and Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre (H) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). Sections were counterstained with DAPI. (I, J) Detection of alkaline phosphatase activity (blue) on frontal sections of E12.5 Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c (I) and Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre (J) embryos (n = 3 for each genotype). (K, L) Skeletal preparations showing mandibles of E18.5 Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c (K) and Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre (L) embryos. Arrowheads in H, J, and L point to ectopic ossification at the oral side of the mandible (n = 3 for each genotype). Asterisks in H and J mark the defective palatal shelves in Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre embryos. The Meckel’s cartilage primordia are indicated by white dashed circles in G-J. p, palate; t, tongue.
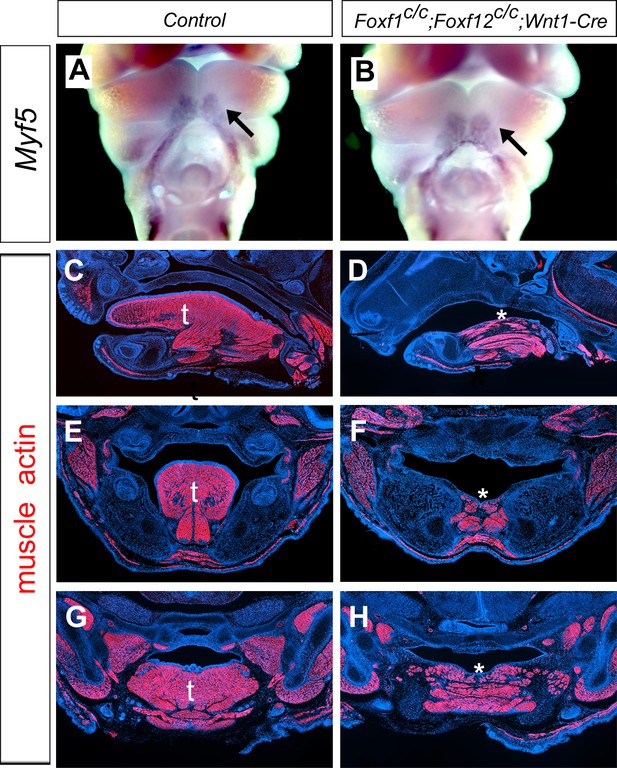
Foxf1c/c; Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre display agenesis of the oral tongue structure.
(A–B) Frontal views of E10.5 embryos from control (littermates that are Cre negative) (A) and Foxf1c/c; Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre (B) embryos showing expression of Myf5. Arrows show the Myf5 positive tongue muscle precursor cells. (C–H) Immunofluorescent detection of muscle actin (red) on sagittal sections (C–D), and frontal sections (E–H) of E16.5 control (C, E, G) and Foxf1c/c; Foxf2c/c;Wnt1Cre (D, F, H) embryos. Sections were counterstained with DAPI. t, tongue, * shows disrupted tongue structures in Foxf1c/c; Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre (D, F, H) embryos.
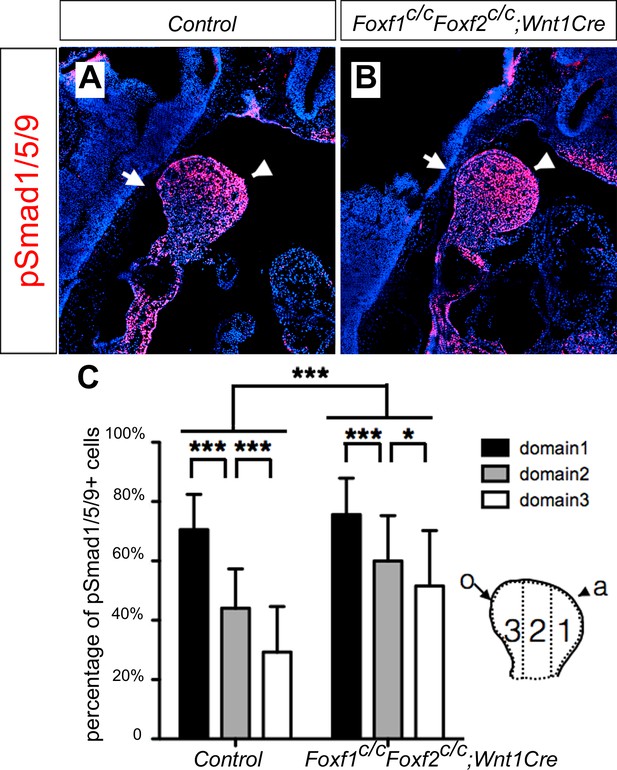
Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre embryos exhibit oropharyngeally expanded BMP signaling activity in the developing mandibular arch.
(A, B) Immunofluorescent detection of phospho-Smad1/5/9 (pSmad1/5/9, red) on sagittal sections through the distal region of the mandibular arches in E10.5 control (littermates that are Cre negative) (A) and Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre (B) embryos. Arrow points to oropharyngeal side and arrowhead points to aboral side of the mandibular arch. (C) Quantification of the percentage of pSmad1/5/9 positive nuclei in the three domains along aboral-oral axis of mandibular arch mesenchyme (domain1, domain2, domain3). Statistical analysis was performed on data from 28 sections of 5 control embryos and 33 sections of 5 Foxf1c/c;Foxf2c/c;Wnt1-Cre embryos by using two-way ANOVA. a, aboral, o, oral. ***p<0.001.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of marker genes with more than 1.5-fold enrichment in the individual clusters.
Column A lists gene name. Column B lists p value of differential expression. Column C lists average fold change over all other clusters. Column D list the percentage of cells in the corresponding cluster expressing the marker gene. Column E list the percentage of cells in all other clusters combined expressing the marker gene. Column F list the Bonferroni corrected p value. Column G lists the cluster name. NC1 – NC2, neural crest derived mesenchyme cells; Epi, epithelial cells; Endo, endothelial cells; HM, head mesoderm cells.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40315.026
-
Supplementary file 2
List of marker genes exhibiting differential expression (at least 1.3-fold) between cells in the NC3 cluster and cells in the NC1 and NC2 clusters.
Column A list gene name. Column B list p value of differential expression. Column C lists average fold change of expression of the marker gene in NC1/2 cells over NC3 cells. Positive value in Column C indicates higher levels of expression in NC1/2 than in NC3. Column D lists percentage of cells in NC1/2 clusters expressing the gene. Column E list percentage of cells in NC3 cluster expressing the gene. Column F list Bonferroni corrected p value of differentiation expression. Genes whose expression pattern is shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 4 are highlighted in yellow.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40315.027
-
Supplementary file 3
List of marker genes exhibiting more than 1.3-fold enrichment in expression levels in a specific neural crest subgroup over all other five subgroups.
Genes that are shown in Figure 1B are highlighted in yellow color. Column A lists gene name. Column B lists p value of differential expression. Column C lists average fold change over all other subgroups. Column D list the percentage of cells in the corresponding subgroup expressing the marker gene. Column E list the percentage of cells in all other subgroups combined expressing the marker gene. Column F list the Bonferroni corrected p value of differential expression. Column G lists the subgroup number corresponding to Figure 1B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40315.028
-
Supplementary file 4
Top 50 hits from gene ontology (GO) analyses of marker genes of Subgroup 0 of the neural crest cells shown in Figure 1B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40315.029
-
Supplementary file 5
Top 100 hits from gene ontology (GO) analyses of marker genes of Subgroup 1 of neural crest cells shown in Figure 1B.
GO analysis was performed using Toppgene (https://toppgene.cchmc.org/enrichment.jsp).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40315.030
-
Supplementary file 6
Top 50 hits from gene ontology (GO) analyses of marker genes of State three from developmental trajectory analysis shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 7.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40315.031
-
Supplementary file 7
Top 20 hits from gene ontology (GO) analyses of marker genes of State four from developmental trajectory analysis shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 7.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40315.032
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40315.033





