The elemental mechanism of transcriptional pausing
Figures
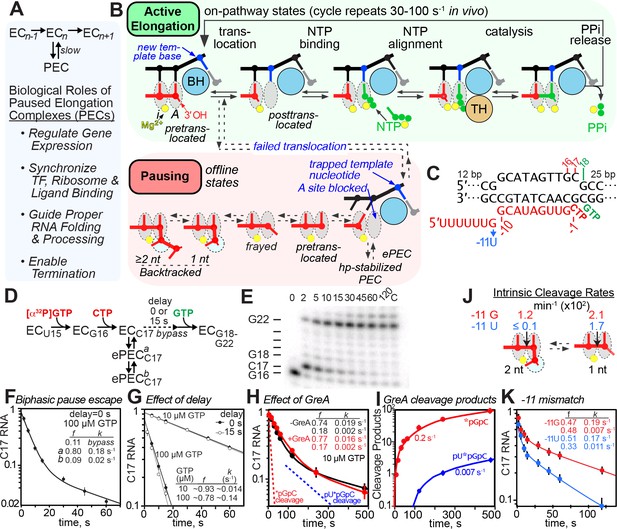
The consensus elemental pause signal.
(A) The simplest elemental pause kinetic scheme and the biological roles of pausing. (B) Model of RNAP active site during the normal nucleotide addition cycle (green) consisting of RNA-DNA translocation, NTP substrate binding, active-site closing and NTP alignment (mediated by the trigger loop [TL] and bridge helix [BH]), phosphoryl transfer (catalysis), and PPi release. Catalysis is reversible when PPi remains present. Pausing (red) occurs when altered RNAP-DNA-RNA interactions create a barrier to completion of translocation that blocks entry of the next template nucleotide into the active site, creating the elemental pause state. The elemental pause state can rearrange further into backtracked or hairpin-stabilized pauses depending on other RNA-DNA sequences. (C) Central region of the RNA:DNA scaffold used for pause assays (complete scaffold is in Figure 1—figure supplement 1A). The −11U mismatch substitution was used to test possible contributions of backtracking (see panels J and K). (D) Pause assay and kinetic scheme consistent with biphasic pause escape intermediates. (E) Example of pause assay products separated by denaturing gel electrophoresis (radiolabeled by 32P-G16 incorporation; C17 is the pause RNA). (F) Observed levels of C17 RNA as a function of time in a simple elemental pause assay at 37°C and 100 µM GTP. Pause fractions (f) and apparent escape rates (k) are shown for the pause and slow pause species. (G) Effect of delayed addition of 10 µM or 100 µM GTP after formation of C17 PECs. Additional data documenting the offline elemental pause states are in Figure 1—figure supplement 1B–G and Figure 1—figure supplement 2. (H) Effect of GreA (1 µM) on elemental pausing at 10 µM GTP. The dotted lines indicate the rates of 2-nt or 3-nt cleavage in the presence of GreA based on appearance of cleavage products (see panel I). (I) Rate of appearance of GreA-induced cleavage products during pause assay in panel H. (see Figure 1—figure supplement 3A,B,C,D for measurements of GreA/B cleavage rates and effects on pausing). (J) Rates of intrinsic cleavage of C17 halted ePECs matched with pause assays shown in panel (K). The −11U substitution reduced intrinsic cleavage in the −1 backtrack register by a factor of >50 (see Figure 1—figure supplement 3E,F for measurement of intrinsic cleavage rates). (K) Effect of −11 U mismatch on the elemental pause at 100 µM GTP with pause prone-RNAP.
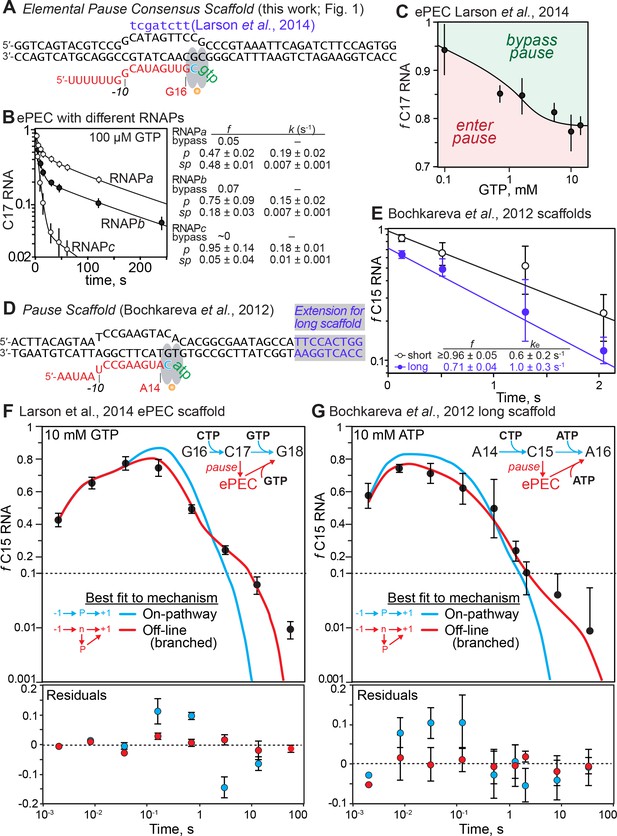
The elemental pause is a distinct offline state, not an on-pathway elongation intermediate.
(A) The complete consensus elemental pause scaffold (ntDNA #9563, tDNA #8334, RNA #8342; Supplementary file 1), identical to that used in Larson et al. (2014), except the template and nontemplate DNA strands are fully complementary (the noncomplementary, nontemplate strand bases in the Larson et al. scaffold are indicated in purple; ntDNA #8333). (B) Pause RNA as a function of time and kinetic fractions for three different RNAP preparations. (C) Effect of GTP concentration on partition of C17 between bypass and pause states in experiments also reported in Larson et al. (2014). (D) The pause scaffold defined by Bochkareva et al. (2012) (black; ntDNA #8195, tDNA #8196, RNA, #7974; Supplementary file 1) and the 10 bp downstream duplex extension to move the duplex end outside the RNAP footprint (purple on gray background; black; ntDNA #8289, tDNA #8196). Steps in a minimal pause assay and the constrained offline pause pathway (red) are shown on the right. (E) Estimation of pause fractions and apparent pause escape rates at 10 mM ATP for the Bochkareva et al. scaffold with (long) and without (short) the additional 10 bp downstream duplex. (F) Best fit by numerical integration and residuals for on-pathway (unbranched) and off-line mechanisms for the consensus ePEC scaffold (panel A) at 10 mM GTP. The fits shown were calculated using the average of data from three experimental repeats, including error (SD) in the fitting. The residuals were calculating by performing individual fits to the three replicate datasets and then averaging and calculating SD for the residuals for each fit. The sinusoidally varying residuals for the unbranched mechanism vs. their random and within-error variation for the branched mechanism establishes that pausing occurs by the branched mechanism. (G) Best fit by numerical integration and residuals for on-pathway (unbranched) and off-line (distinct pause species at C15) mechanisms for the Bochkareva et al. (2012) ePEC scaffold (panel B) at 10 mM ATP. The fits and residuals were calculated as described for panel E, except that data from six experimental repeats were used, and by the same reasoning establish that pausing occurs by the branched mechanism.
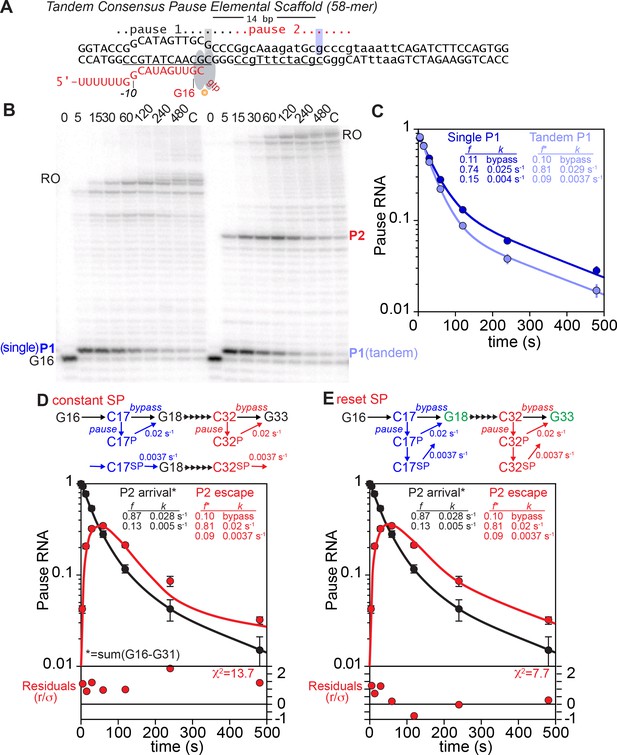
(A) Scaffold used to probe for biphasic escape kinetics at two sequential elemental pause sites (Tandem Consensus Elemental Pause Scaffold; tDNA #12623, ntDNA #12624, RNA #8342; Supplementary file 1).
(B) Pause assays on single or tandem consensus pause scaffold (Single Pause; left time course) or Tandem Pause Scaffold (right time course). Transcription was initiated by addition of NTPs to 100 µM each ATP, UTP, and CTP, and 10 µM GTP. The gel image is representative of triplicate assays. (C) Quantitation of the C17 pause band (P1) on the single or tandem pause scaffold. (D) Tandem scaffold pause P2 fit to a kinetic model with a single pause species (constant EC fraction in slow pause, SP, state). The fit was calculated by first modeling the arrival of ECs at the second pause, plotted as escape from the region before the pause (red line). This flux of ECs arriving at the second pause was subjected to least-squares fitting using numerical integration to a model of pausing involving only a single pause species. Residuals show the difference between the actual and predicted P2 pause RNA amounts. (E) Tandem scaffold pause P2 fit to a kinetic model with two pause species (EC resets so SP reforms at second site). Fitting was conducted as described for panel E, except the pause model included two pause species, with a slow pause arising from the faster pause.
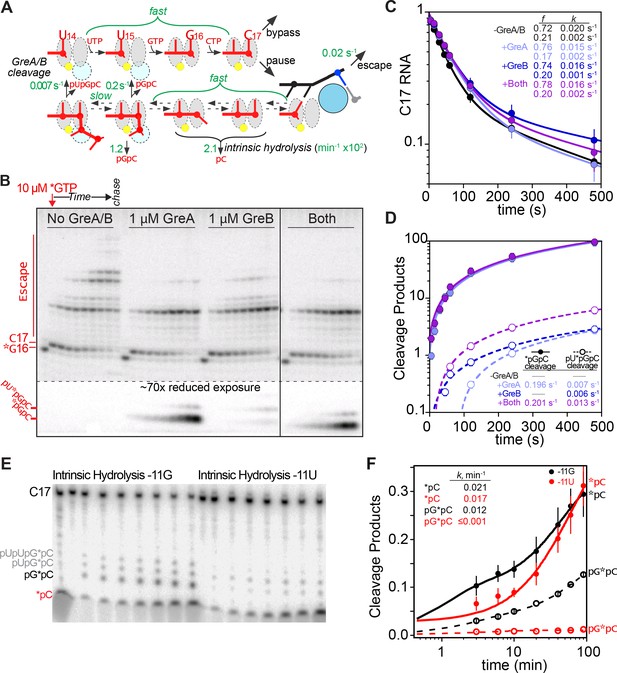
(A) Model for RNA cleavage in pre-translocated or backtracked states following entry into the elemental pause.
Fast extension of ECsU14-G16 and fast interchange of half-translocated, pre-translocated, frayed, and 1 bp backtracked ePECs enables generation of 2-nt cleavage products even when the half-translocated ePEC (in which the block to pause escape is manifest) is the predominant species. Observed rates of GreA cleavage and intrinsic cleavage are indicated in green (from panels D and F). (B) Pause assays to test the effect of Gre factors. The RNA was 3′ end-labeled with 10 µM [α-32P]GTP (constant specific activity throughout the experiment; * indicates 32P label). Transcription was initiated by addition of NTPs (final concentration of 100 µM CTP, 100 µM UTP, – or +Gre factors (1 µM final of each), as indicated). The gel image is representative of results obtained in at least triplicate assays. (C) Quantitation of pause fraction in B as a function of time. Error bars are SD of at least triplicates. (D) Quantitation of cleavage products in B as a function of time. Error bars are SD of at least triplicates. Cleavage rates too slow to measure (<0.005 s−1) are indicated in the table as dashes. (E) Intrinsic exo- and endonuclease activity on consensus pause scaffolds with −11G or −11U RNA (related to Figure 1J,K). After forming ECs and 3′-end labeling with [α-32P]CMP, the ECs were simultaneously used for pause assays (Figure 1K) and the intrinsic cleavage assays shown here. See Materials and methods for experimental details. (F) Quantitation of cleavage products in panel E as a function of time. The data were fitted to a double-exponential function. The rate constants for the major kinetic fractions are shown in the inset table.
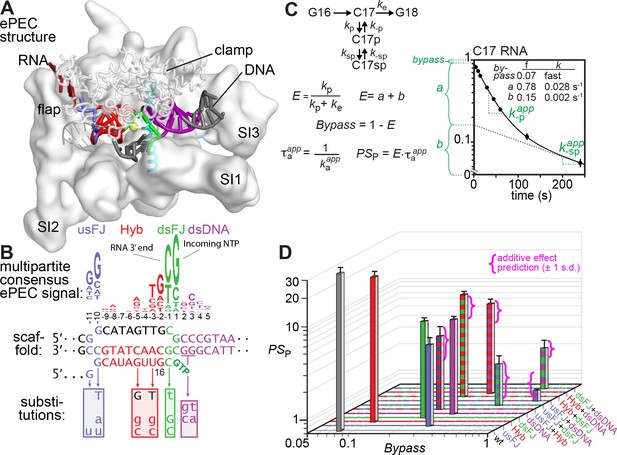
The elemental pause signal is multipartite.
(A,B) The consensus ePEC. The ePEC structure (pdb 6bjs; Kang et al., 2018a) is shown above the consensus pause sequence (Larson et al., 2014) color-coded as usFJ (blue), Hyb (red), dsFJ (green), and dsDNA (purple). Scaffold substitutions tested for effects on pausing are shown below the location of the changes. (C) Two-component pause mechanism, equations used to calculate pause efficiencies and pause strengths, and example plot of pause assay data. The pause assay data shown are for the ‘wild-type’ (unsubstituted) consensus pause scaffold at 37°C and 10 µM GTP. Pause fractions (fast fraction a, slow fraction b) and escape rates k-p,app and k-sp,app were obtained by nonlinear regression using a double-exponential equation (see Materials and methods). (D) Plot of pause strength (PSP) vs. bypass for each scaffold variant. Combinations are indicated by ‘+” (e.g., usFJ + Hyb). The magenta brackets show the predicted range of PSP values (95% confidence interval) for combinations of substitutions in individual pause signal elements assuming the pause signal elements additively and independently affect a single energy barrier to pause escape (additive effects on ∆G‡ are multiplicative in PSP). Additional data for the wild-type and mutant pause signals are in Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Fraction C17 pause RNA for wild-type and mutant pause signals.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40981.009
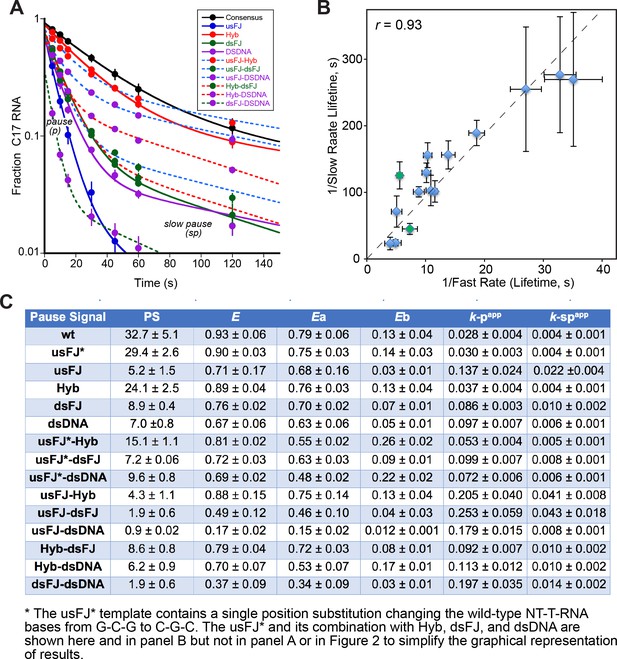
(A) Quantitation of pause assays with scaffold variants described in Figure 2.
All pause assays were performed with the same RNAP preparation. (B) Plot of fast species lifetime (1/k-p, app) vs. slow species life (1/k-sp, app) for each scaffold variant. The high positive correlation between the two species rates is consistent with a model in which a single kinetic barrier limits escape from either pause species. (C) Summary table of pause strength (PS), efficiency (E), fast species fraction (Ea), slow species fraction (Eb), fast species rate (k-p, app), and slow species rate (k-sp, app).
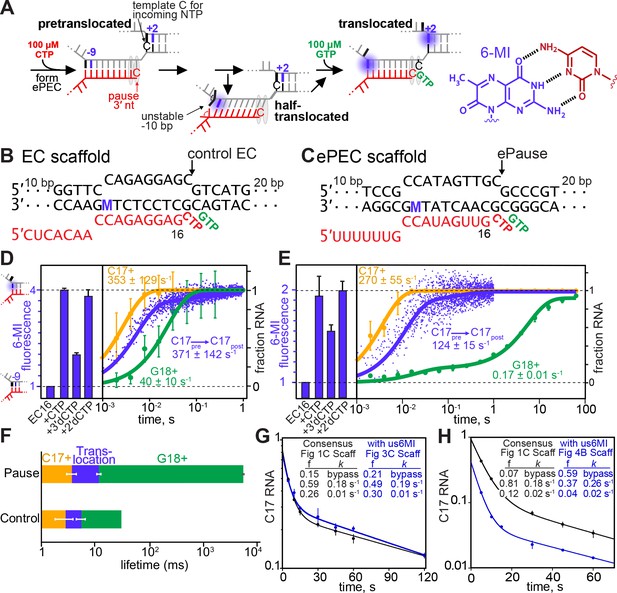
Translocation of the RNA:DNA hybrid is not rate-limiting for elemental pause escape.
(A) Scheme for translocation following CTP addition to control EC or ePEC scaffolds. The locations of 6-MI for both usFJ and dsFJ probes are indicated, but a probe was present in only one location in the scaffolds used (see panels B and C and Figure 4A and B). 6-MI is a GMP base analog that fluoresces unless quenched by stacking with an adjacent GMP. (B and C) Scaffolds used to reconstitute control EC and ePEC for fluorescence experiments. M, position of 6-MI. Full scaffold sequences and additional data characterizing pause behaviors of these scaffolds are in Figure 3—figure supplement 1 and Figure 3—figure supplement 2. (D) Equilibrium fluorescence changes (blue bars) upon addition of incoming NTP or NTP analog to the non-pausing EC scaffold measured at 37°C. Nucleotide addition (orange and green traces) and translocation (blue trace) rates were determined using KinTek quenched-flow (RQF-3) or stopped-flow (SF-300X) instruments, respectively. C17+ represents the fraction of RNA at or beyond C17. G18+ represents the fraction of RNA at or beyond G18. 6-MI fluorescence was normalized to that observed after 2′dCMP addition to G16. (E) Experiments performed as in D but on an ePEC scaffold. (F) Data from (D) and (E). Mean times for CMP addition, translocation, and subsequent GMP addition for the ePEC and control EC. (G,H) Pause kinetics at 100 µM GTP for the 6-MI-containing ePEC scaffolds (G), us6MI; (H), ds6MI) compared to the consensus pause scaffold. f, kinetic fractions. k, rate constants for pause fractions.

Control EC scaffold used for 6-MI translocation assays in Figures 3 and 4.
Full sequences of oligonucleotides are given in Supplementary file 1. 6-MI is present at the locations indicated in Figures 3 and 4.
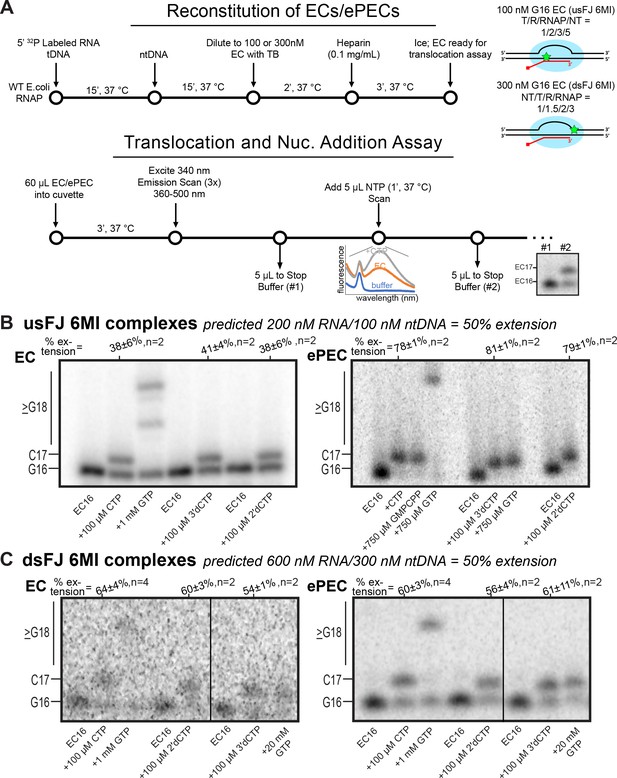
Reconstitution of ECs and PECs for 6-MI translocation assays.
(A) Experimental schematic for the assay of translocation and nucleotide addition. (B) Nucleotide addition for samples used in translocation assays of usFJ 6MI complexes (EC, left; ePEC, right). Percentages above extension lanes indicate the fraction of RNA extended (vs. the prediction of 50% based on reconstitution ratios). Error is range for n = 2 or SD for n ≥ 3. (C) Nucleotide addition for samples used in translocation assays of dsFJ 6MI complexes (EC, left; ePEC, right). Percentages above extension lanes indicate the fraction of RNA extended (vs. the prediction of 50% based on reconstitution ratios). Error is range for n = 2 or SD for n ≥ 3.
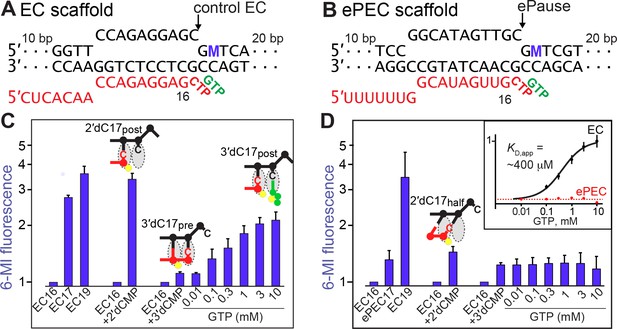
Translocation of the incoming template DNA limits elemental pause escape.
(A and B) Scaffolds used to reconstitute control EC and ePEC for fluorescence experiments. M, position of 6-MI. (C and D) Equilibrium fluorescence changes of control EC and ePEC, respectively, upon reaction with NTP or NTP analog or binding of GTP to 3′deoxyC-containing complexes. RNA extension was verified by quantifying radiolabeled RNAs (see Figure 3—figure supplement 2). Inset, GTP-binding curve fit for the 3′dC17 EC (black line) and the 3′dC-ePEC (dotted red line; no binding evident). Error bars are SD of triplicate measurements.
NTP binding but not TL folding is inhibited in the ePEC.
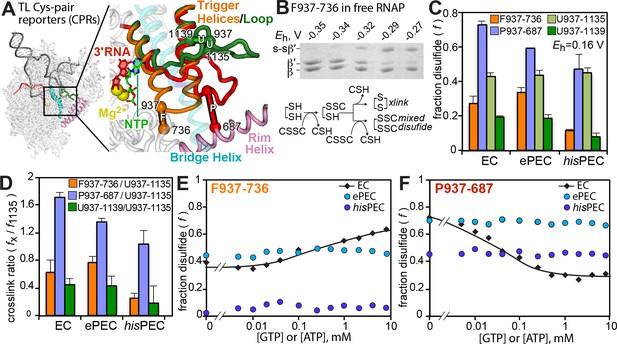
Scaffolds used for these experiments are shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 1. (A) Location of F937-736, P937-687, U937-1137, and U937-1139 Cys-pair reporters to test various conformations of the TL. The SI3 domain inserted in the EcoRNAP TL is not shown. A complete description of these reporters is published elsewhere (Nayak et al., 2013; Windgassen et al., 2014). (B) Example CPR reaction showing SDS-PAGE mobility of uncrosslinked and crosslinked β′ as a function of redox potential generated by increasing concentrations of cystamine. Reaction scheme for crosslink generation by cystamine. (C) Fraction crosslink formed by CPRs for the EC, ePEC, and hairpin-stabilized hisPEC in which TL mobility is restricted. Data are mean ± range from two replicates. (D) Ratio of crosslinks to the U1135 crosslink. A high ratio indicates a greater degree of crosslinking (E) F937-736 crosslink as a function of GTP or ATP concentration in 3′dC- or 3′dU-containing EC, ePEC, and hisPEC. (F) P937-687 crosslink as a function of GTP or ATP concentration in 3′dC- or 3′dU-containing EC, ePEC, and hisPEC.
Scaffolds used for disulfide bond assays of trigger loop position shown in Figure 5.
Full sequences of oligonucleotides are given in Supplementary file 1. (A–C) For experiments on RNA 3′ OH-containing EC and PECs (Figure 5B–D), the full-length RNAs were used. For experiments on 3′deoxyEC and 3′deoxyPECs (Figure 5E,F), RNAs lacking the 3′ nucleotide were used for reconstitution and then extended with a 3′dNMP by RNAP-mediated catalysis. (D) hisPEC scaffold used in Figure 5C (ntDNA#10924, tDNA #10919, RNA #6593+#6594). In this scaffold, the his pause hairpin is mimicked by a 8 bp duplex that stabilizes the pause indistinguishably from the natural his pause hairpin (Hein et al., 2014).
Restriction of clamp movement has less effect on ePEC than on hairpin-stabilized PEC.
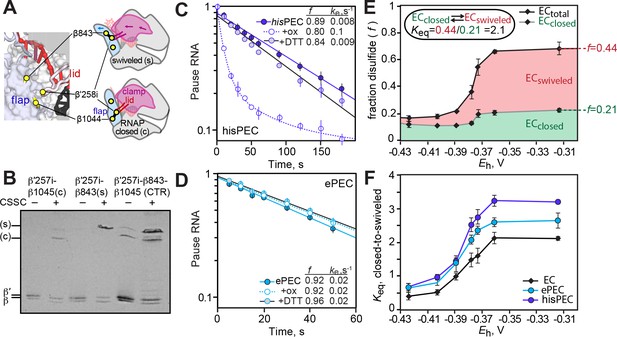
(A) Location of disulfides used to restrict clamp movement or generate the Cys-triplet reporter (CTR; described in Hein et al., 2014; Kang et al., 2018b). (B) Example β-β′ disulfide mobilities during SDS-PAGE illustrating the identification of the closed (β1044-β′258i, (c) or swiveled (β843-β′258i, (s) disulfides. (C) Effect of the closed clamp crosslink on pausing by the hairpin-stabilized hisPEC (scaffold shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1A). (D) Effect of the closed clamp crosslink on pausing by the ePEC (scaffold shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 1A). (E) CTR assay on an EC scaffold illustrating the formation of the closed and swiveled crosslinks as a function of redox potential generated by increasing concentrations of cystamine (Figure 6—figure supplement 1F). (F) CTR assay of clamp swiveling in EC, ePEC, and hisPEC (scaffolds shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1B,C,D, respectively).
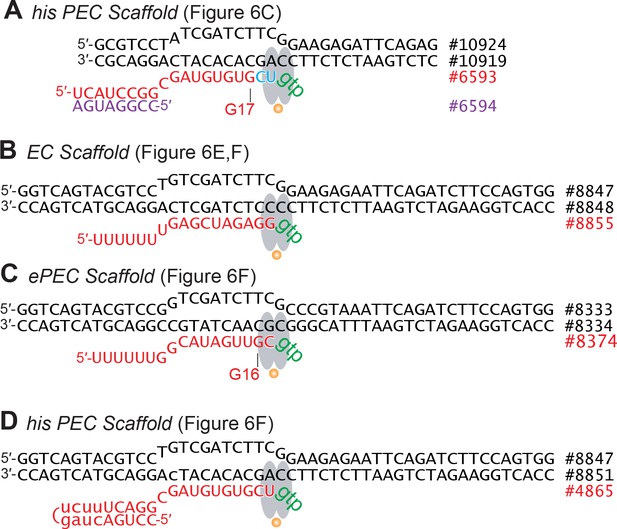
Scaffolds used for CPR and CTR clamp-position assays shown in Figure 6.
Full sequences of oligonucleotides are given in Supplementary file 1. (A) Control EC scaffold used in Figure 6E,F (ntDNA#8847, tDNA #8848, RNA #8855). (B) ePEC scaffold used in Figure 6F (ntDNA#8833, tDNA #8834, RNA #8374). (C) hisPEC scaffold used in Figure 6F (ntDNA#8847, tDNA #8851, RNA #4865).
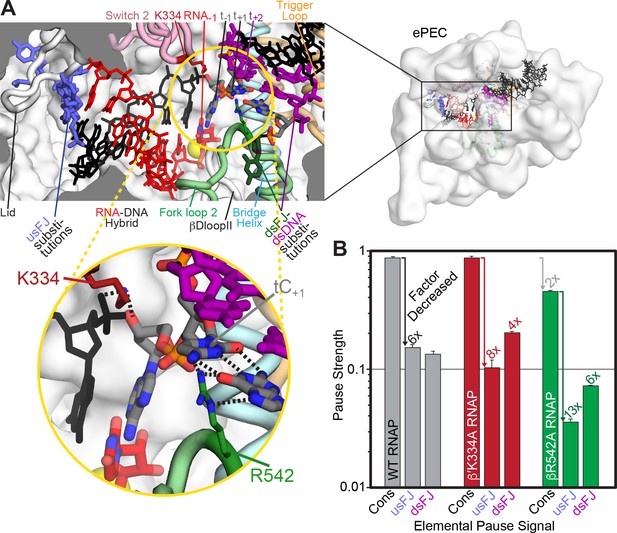
β R542 in fork-loop two may contribute to a template base loading barrier in ePEC.
(A) Locations of β′K334 and βR542 in the ePEC. Relevant components of the ePEC are colored and labeled in a cutaway view of the active-site region of the ePEC. (B) Relative pause strength (PSP, Figure 2B) for wild type, β′K334A, and βR542A RNAPs on the consensus pause scaffold (Cons), the usFJ mutant scaffold, and the dsFJ mutant scaffold (see Figure 2A). The factor decrease relative to the wild-type RNAP on the consensus pause scaffold or relative to the consensus pause for the different RNAPs is given above the bars and depicted using colored arrows. Error is SD from ≥3 replicates.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Fraction C17 pause RNA for wild-type and mutant pause signals.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40981.019
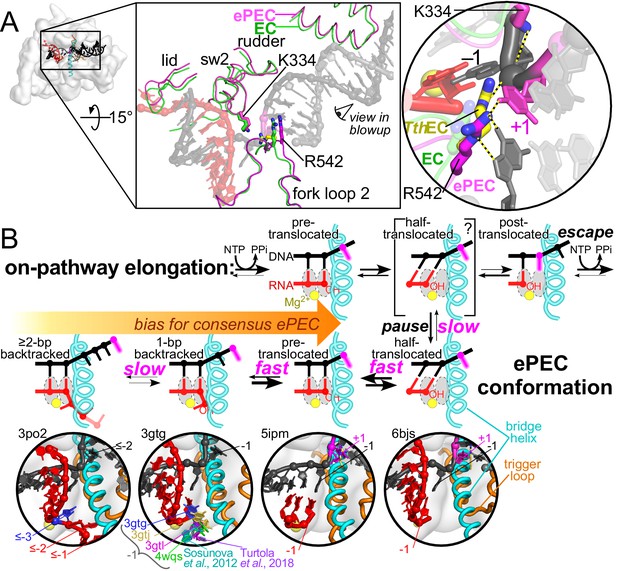
Multistate model of elemental pausing.
(A) The small shift in RNAP modules observed in the ePEC (pdb 6bjs; magenta) relative to an EC (pdb 6alf; green) is depicted in the top central panel (Kang et al., 2018a; Kang et al., 2017). The locations of K334 in the EC (faint green) and ePEC (magenta) and the locations of R542 in a TthRNAP EC (pdb 2o5i, yellow; Vassylyev et al., 2007), EC, and ePEC are shown in expanded view on the right. The +1 dC nucleotide trapped in the downstream DNA is magenta. (B) Discrete states present during formation of and escape from an elemental pause. The kinetic block is the loading of the template base, but the ePEC can assume other translocation registers depending on the sequences surrounding the pause. Examples of structures occupying the different translocation registers are shown in the close-ups below the active-site schematics (Ó Maoiléidigh et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2009; Sosunova et al., 2013; Sekine et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2016; Kang et al., 2018a; Turtola et al., 2018).
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Oligonucleotides and plasmids used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40981.022
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40981.023





