Factors affecting template switch recombination associated with restarted DNA replication
Figures
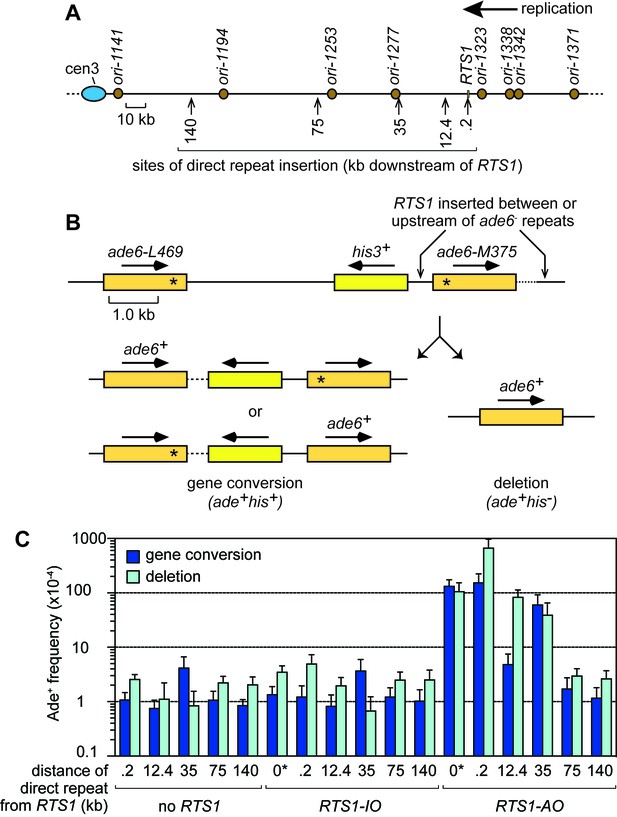
TS downstream of RTS1.
(A) Map showing sites of insertion for the direct repeat recombination reporter on chromosome 3. (B) Schematic of the direct repeat recombination reporter showing the position of RTS1 insertion and two types of Ade+ recombinant. Asterisks indicate the position of point mutations in ade6-L469 and ade6-M375. (C) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW429, MCW7229, MCW7429, MCW7430, MCW7297, MCW4712, MCW7131, MCW7257, MCW7565, MCW7614, MCW7326, MCW4713, MCW7133, MCW7259, MCW7567, MCW7616 and MCW7328. ‘0*’ indicates that RTS1 is positioned between the ade6- repeats. Data are mean values ± SD. Ade+ recombinant frequencies with statistical analysis are also shown in Supplementary file 1.
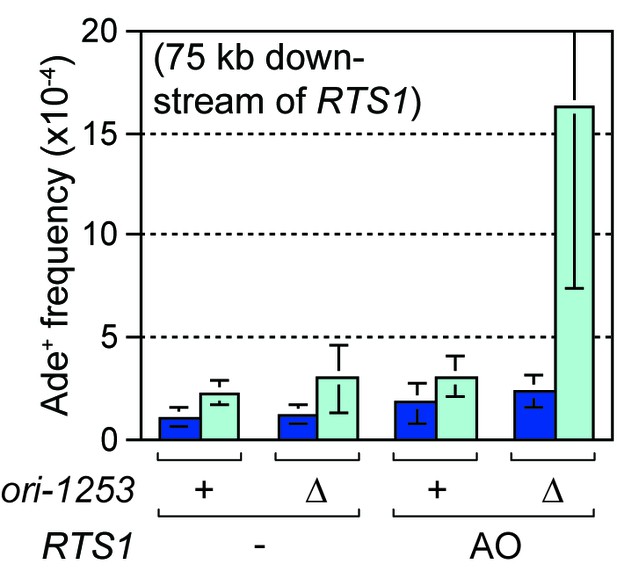
Effect of ori1253∆ on the frequency of TS recombination 75 kb downstream of RTS1.
Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW7430, MCW7987, MCW7616 and MCW7620. Data are mean values ± SD. Ade+ recombinant frequencies with statistical analysis are also shown in Supplementary file 1.
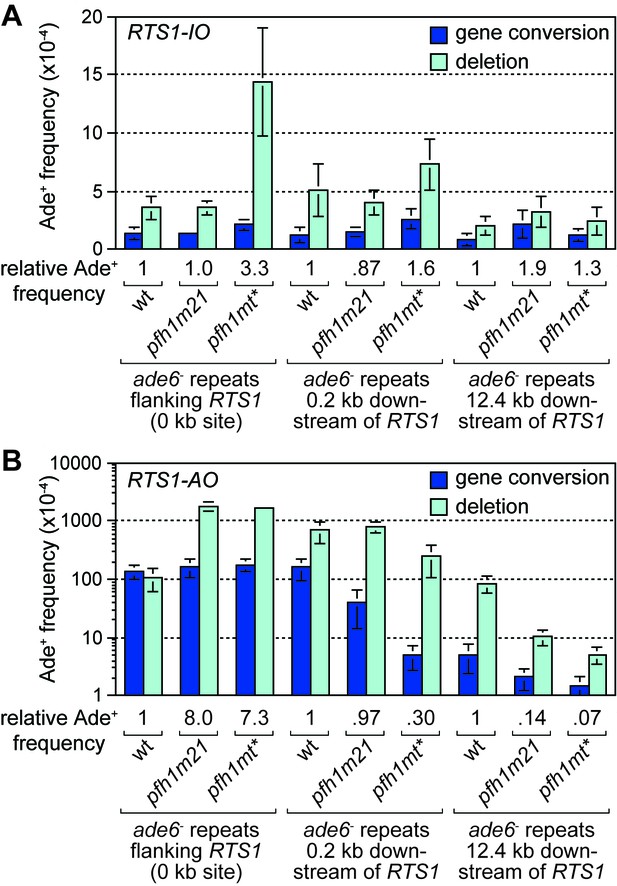
Effect of pfh1-m21 and pfh1-mt* mutations on TS recombination at and downstream of RTS1.
(A) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW4712, MCW4940, MCW4954, MCW7131, MCW7599, MCW7603, MCW7257, MCW7421 and MCW7425. (B) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW4713, MCW4942, MCW4956, MCW7133, MCW7601, MCW7605, MCW7259, MCW7422 and MCW7426. Data are mean values ± SD. Ade+ recombinant frequencies with statistical analysis are also shown in Supplementary file 1.
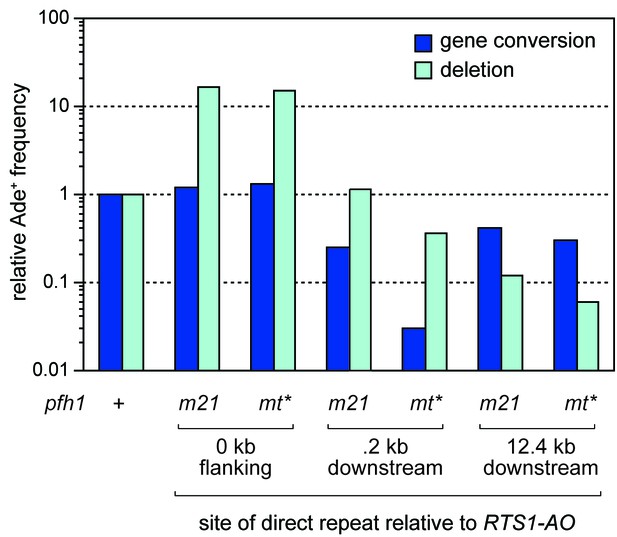
Relative Ade+ recombinant frequencies for the pfh1-m21 and pfh1-mt* strains shown in Figure 2B.
Values are relative to wild-type.
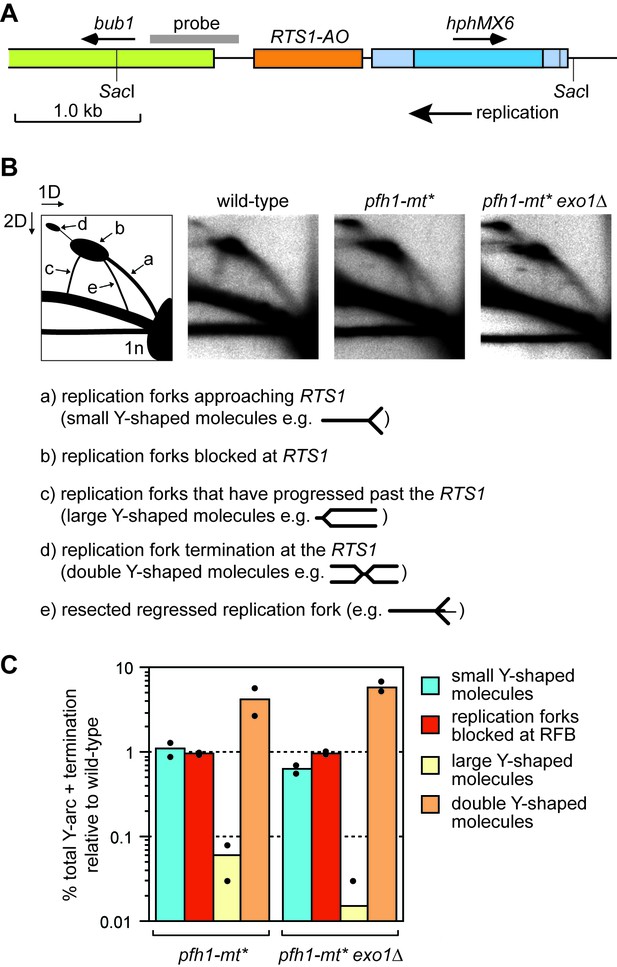
Pfh1 is needed for replication past RTS1-AO.
(A) Schematic showing location of RTS1-AO and hphMX6 adjacent to bub1 on chromosome 3. The position of the probe used for the 2DGE analysis in B) is also shown. (B) 2DGE of replication intermediates in the SacI fragment shown in A). The DNA was extracted from strains MCW7223, MCW8587 and MCW8605. (C) Quantification of 2DGE. Values are relative to wild-type and are based on two independent experiments with each value represented by a dot around the mean.
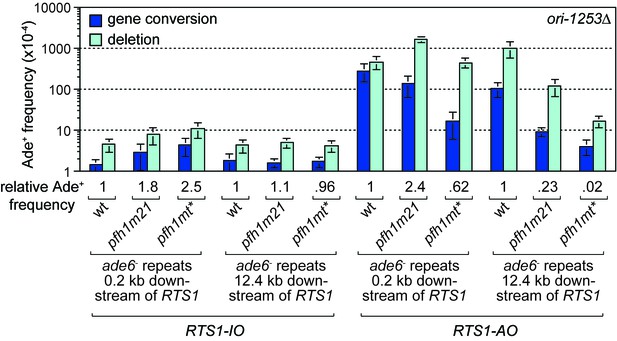
Effect of ori1253∆ on the frequency of TS recombination downstream of RTS1 in wild-type and pfh1 mutants.
The strains are MCW7414, MCW7598, MCW7602, MCW7293, MCW7423, MCW7427, MCW7416, MCW7600, MCW7604, MCW7295, MCW7424, MCW7428. Data are mean values ± SD. Ade+ recombinant frequencies with statistical analysis are also shown in Supplementary file 1.
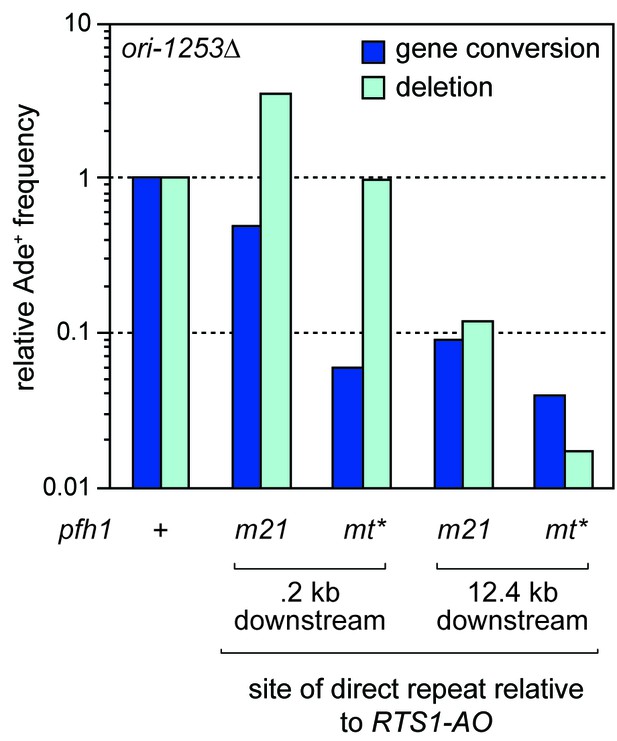
Relative Ade+ recombinant frequencies for the pfh1-m21 and pfh1-mt* strains shown in Figure 4.
Values are relative to wild-type.
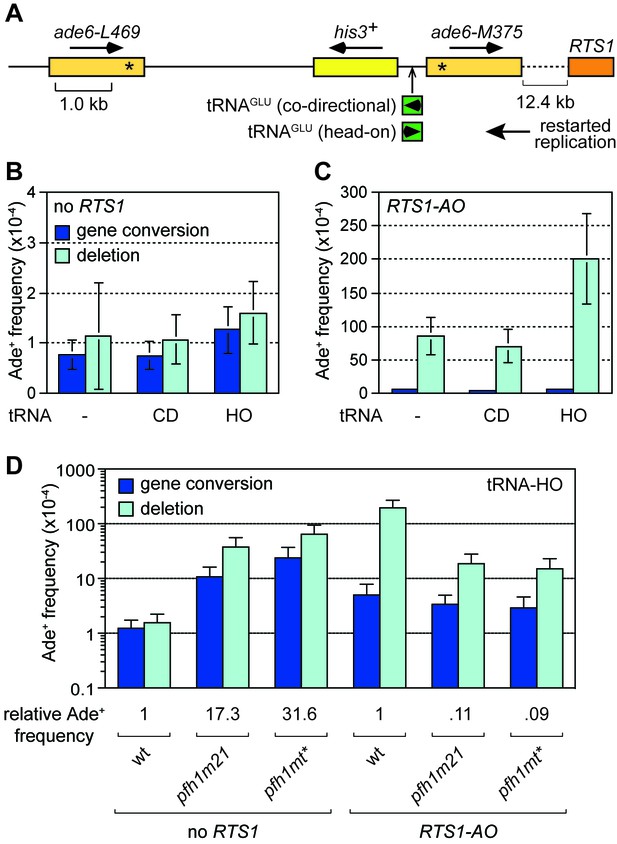
Effect of tRNAGLU08CD and tRNAGLU08HO on TS downstream of RTS1.
(A) Schematic showing the position of tRNAGLU08CD/HO within the direct repeat recombination reporter 12.4 kb downstream of RTS1. (B) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW7229, MCW7434 and MCW7433. (C) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW7259, MCW7521 and MCW7517. (D) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW7433, MCW9381, MCW9383, MCW7517, MCW9360 and MCW9361. Data are mean values ± SD. Ade+ recombinant frequencies with statistical analysis are also shown in Supplementary file 1.
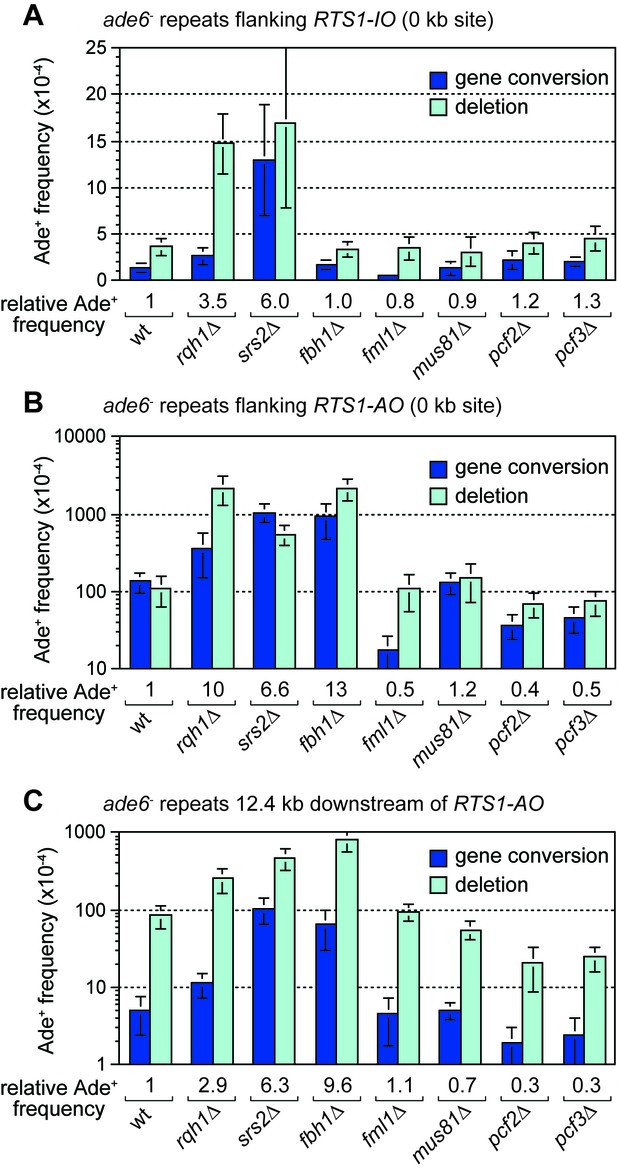
Effect of rqh1∆, srs2∆, fbh1∆, fml1∆, mus81∆, pcf1∆ and pcf2∆ on TS recombination at and downstream of RTS1.
(A) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW4712, MCW1443, FO1748, FO1814, MCW3059, MCW1451, MCW6972 and MCW7147. (B) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW4713, MCW1447, FO1750, FO1816, MCW3061, MCW1452, MCW7213 and MCW7149. (C) Ade+ recombinant frequencies for strains MCW7259, MCW8201, MCW8200, MCW8227, MCW8193, MCW8195, MCW8359 and MCW8360. Data are mean values ± SD. Ade+ recombinant frequencies with statistical analysis are also shown in Supplementary file 1.
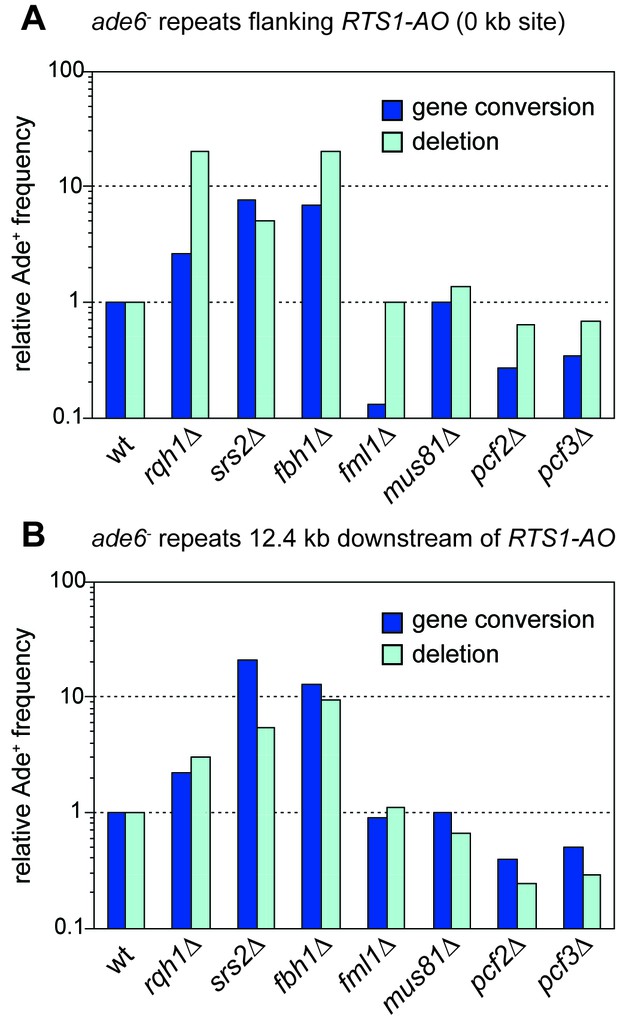
Relative Ade+ recombinant frequencies for the RTS1-AO containing strains shown in Figure 5.
Values are relative to wild-type.
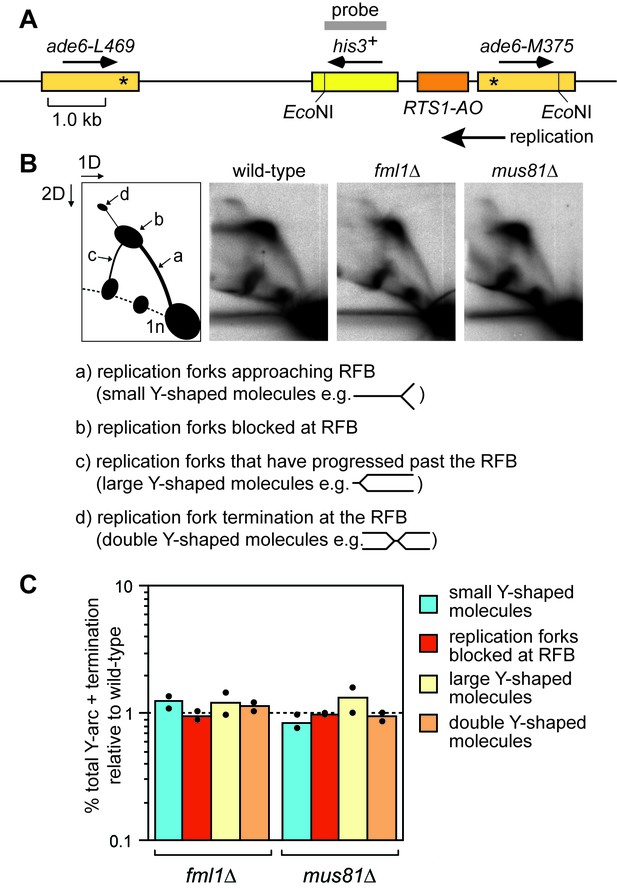
Fml1 and Mus81 are not needed for replication past RTS1-AO.
(A) Schematic showing location of RTS1-AO between ade6 heteroalleles on chromosome 3. The position of the probe used for the 2DGE analysis in (B) is also shown. (B) 2DGE of replication intermediates in the EcoNI fragment shown in (A). The DNA was extracted from strains MCW4713, MCW3061 and MCW1452. (C) Quantification of 2DGE. Values are relative to wild-type and are based on two independent experiments with each value represented by a dot around the mean.
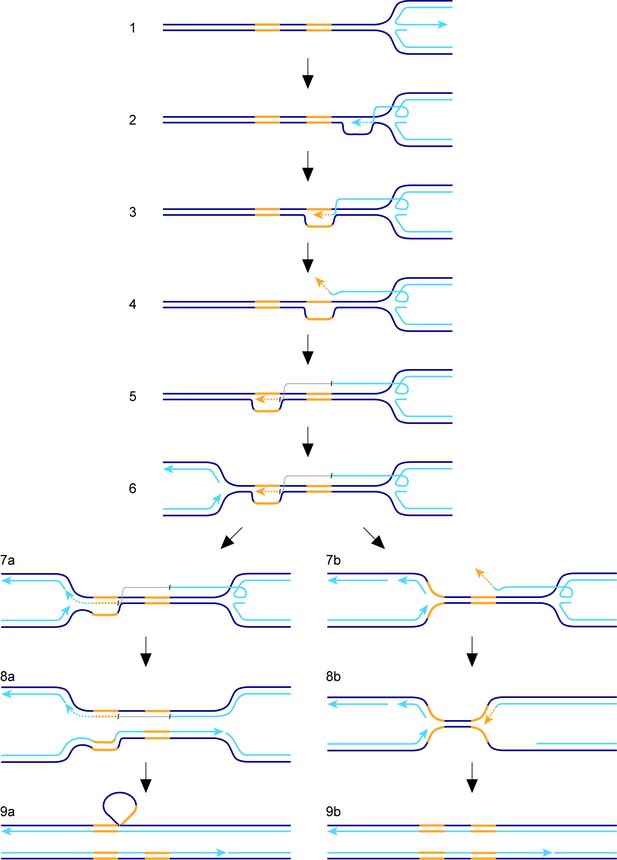
Model for TS between direct repeats.
Parental DNA strands are dark blue, nascent DNA strands are light blue and DNA repeats are yellow. The grey line in steps 5, 6, 7a and 8a indicates that the light blue and yellow lines, which it connects, are continuous. See main text for a step-by-step description of the model.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (S. pombe) | various strains | PMID: 15889146 | standard laboratory strain (972) derivatives; see Supplementary file 2 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. pombe) | various strains | PMID: 25806683 | standard laboratory strain (972) derivatives; see Supplementary file 2 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. pombe) | various strains | this paper | standard laboratory strain (972) derivatives; see Supplementary file 2 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. pombe) | MCW4956 | PMID: 22426535 | standard laboratory strain (972) derivatives; see Supplementary file 2 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. pombe) | various strains | PMID: 19546232 | standard laboratory strain (972) derivatives; see Supplementary file 2 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. pombe) | MCW3059 | PMID: 18851838 | standard laboratory strain (972) derivatives; see Supplementary file 2 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. pombe) | MCW3061 | PMID: 18851838 | standard laboratory strain (972) derivatives; see Supplementary file 2 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMJ33 | this paper | plasmid; see Materials and methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMJ34 | this paper | plasmid; see Materials and methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCB44 | this paper | plasmid; see Materials and methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMW899 | PMID: 22426535 | plasmid | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMW905 | PMID: 22426535 | plasmid | |
| Sequence-based reagent | various oligonucleotides | this paper | see Supplementary file 3 (oligonucleotides) |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Direct repeat recombinant frequencies.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41697.014
-
Supplementary file 2
Schizosaccharomyces pombe strains.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41697.015
-
Supplementary file 3
Oligonucleotides.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41697.016
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41697.017





