Evoked transients of pH-sensitive fluorescent false neurotransmitter reveal dopamine hot spots in the globus pallidus
Figures
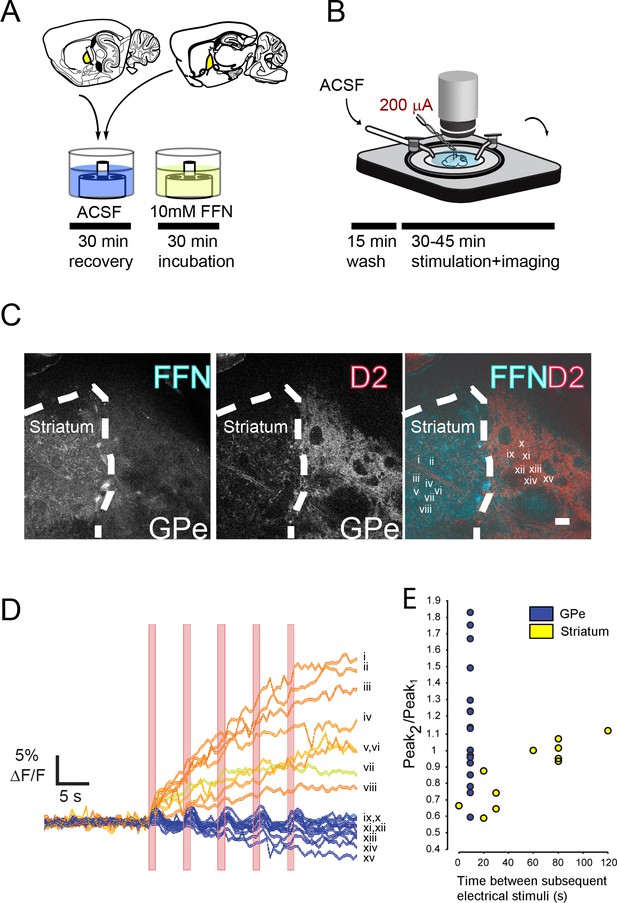
Electrical stimulation of GPe evokes FFN102 transients.
(A, B) Preparation of GPe brain slice. (C) In BAC-D2 GFP mice, the striatum and GPe are distinguishable, as the GPe receives a thick plexus of D2-positive terminals, while the striatum is rich in FFN labeled processes. Scale bar = 50 μM. (D) In response to 1 s long electrical stimulation at 10 Hz frequency, FFN fluorescence corresponding to regions in panel C) show a ‘flashing’ pattern of transients in the GPe (inset Roman numerals for traces ix-xv) and a prolonged and sustained increase in fluorescence in the striatum (inset Roman numerals for traces i-viii). Bars indicate the period of each stimulus (1 s). (E) Signal amplitude of stimuli at one interval in the GPe (from data in panel D), and a range of intervals in the striatum (from a different experiment): note the high variability of signal in GPe.
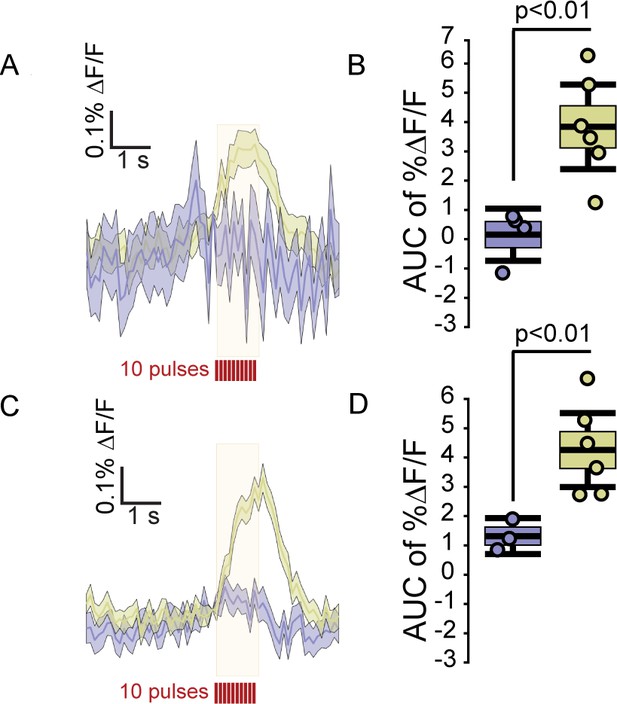
FFN102 and DAT dependence of fluorescence transients.
(A) Averaged traces of electrically evoked fluorescence from slices incubated with FFN, gold, or ACSF alone, blue. Traces reflect the average %ΔF/F, shading reflects ±SEM (n = 4 slices for ACSF, n = 6 slices for 10 μM FFN). (B) Box-and-whisker plot showing the AUC %ΔF/F evoked in the FFN and ACSF conditions. The edges of the boxes are 1 SEM from the mean, and the whiskers indicate ±2 SEM. Each point represents the average of images from one slice. ACSF slices were significantly different from FFN slices (two-tailed unpaired t-test, p < 0.01). For ACSF slices, the AUC %ΔF/F was 0.1 (CI95=[−0.78,0.98]) compared to 3.8 for FFN slices (CI95=[2.31,5.29]). (C) Transients from slices that were either incubated with FFN, gold, or FFN with 10 μM nomifensine, blue (n = 3 slices for FFN with nomifensine and n = 6 slices for FFN alone). (D) FFN102 transients evoked by electrical stimulation were strongly decreased by nomifensine (two-tailed unpaired t-test, p < 0.01; FFN, mean AUC %ΔF/F = 1.3 (CI95 = [0.61,1.99]) FFN with nomifensine, mean AUC %ΔF/F = 4.12 (CI95 = [2.97,5.27]).
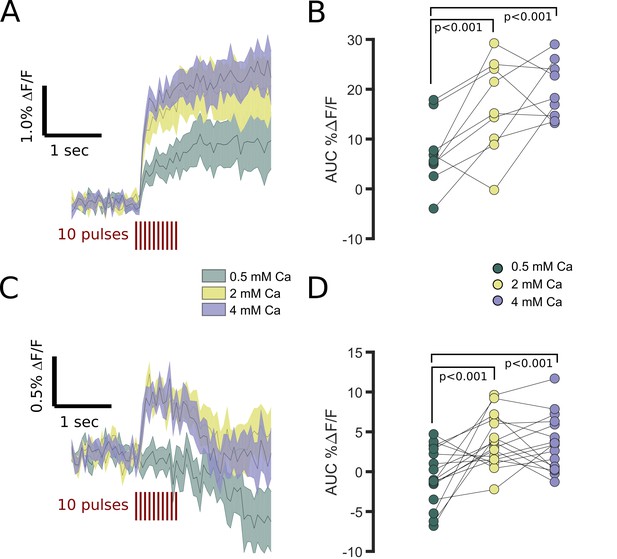
FFN102 transients are regulated by extracellular calcium.
(A) Average processed transients of electrically evoked transients from striatal areas in slices perfused with 0.5, 2, and 4 mM Ca2+ (n = 9 slices). (B) There was a main effect of calcium-level on AUC %ΔF/F (repeated measures ANOVA, p < 0.001). The AUC %ΔF/F was higher in 2 and 4 mM than 0.5 mM Ca2+ (two-tailed paired t-test, p < 0.001). (C) Average processed transients of electrically evoked transients from GPe in slices perfused with 0.5, 2, and 4 mM Ca2+ (n = 16 slices). (D) The AUC %ΔF/F was higher in 2 and 4 mM than 0.5 mM Ca2+ (two-tailed paired t-test, p < 0.001). Additionally, there was a significant interaction between calcium levels and region (p<0.05).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Fluorescence time courses for FFN transients evoked under varying calcium levels.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.005
-
Figure 3—source code 1
Analysis and figures for FFN102 transients under varying calcium levels.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.006
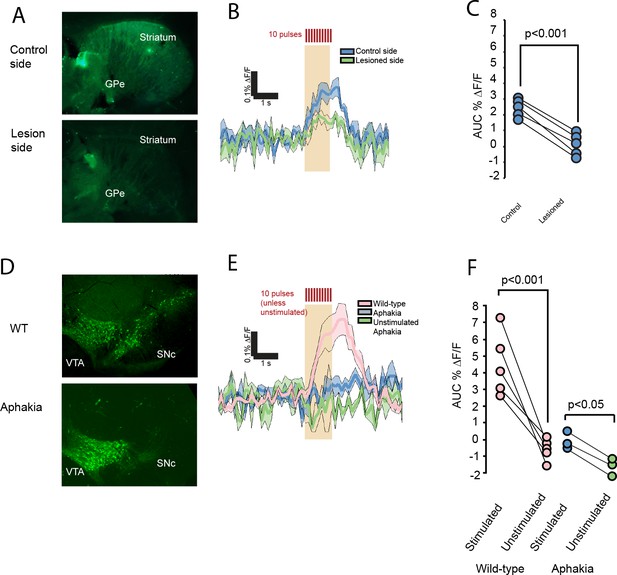
FFN102 transients are ablated in dopamine depleted mice.
(A) Representative images of slices in 6-OHDA experiments, post-fixed after imaging and immunolabeled for tyrosine hydroxylase. (B) Evoked transients from control side, blue, or lesioned side, green (n = 5 slices from five mice for each condition; shading represents SEM). (C) The lesioned hemispheres show decreased transients (average difference of 2.46, CI95 = [2.10, 2.82], two-tailed paired t-test p < 0.001). (D) Representative immunolabel for tyrosine hydroxylase in wild-type and aphakia mice shows a decreased label in the SNc, but not VTA. (E) Evoked transients wild-type mice of the same background, pink, aphakia mice, blue, and unstimulated aphakia mice, green (shading represents SEM). (F) Comparison of stimulation-evoked fluorescence changes in aphakia and wild-type mice (average difference in AUC %ΔF/F = 4.54 (CI95 = [3.05, 6.03], n = 5 slices from five mice for WT experiments, p < 0.001); between stimulated and unstimulated slices from aphakia mice, the average difference in the AUC %ΔF/F = 1.46 (CI95 of difference = [1.00, 1.91]; n = 3 slices from three mice for aphakia experiments; p < 0.05).
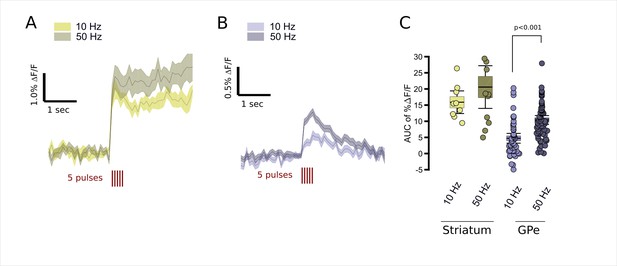
Modulation of FFN102 transients by stimulus frequency.
(A) FFN transients evoked in the striatum by five pulses (red lines) at 10 Hz, gold traces, or 50 Hz, dark gray traces (N = 9 slices for 10 Hz stimuli, N = 12 slices for 50 Hz stimuli; shading represents SEM). (B) FFN transients evoked in the GPe by five pulses at either 10 Hz, bright blue traces, or 50 Hz, dark blue traces (N = 52 slices for 10 Hz stimulation, N = 68 slices for 50 Hz stimulation). (C) The AUC %ΔF/F for the period from 0 to 300 ms from stimulus onset. Striatal responses were not significantly different at higher frequencies (CI95 of %ΔF/F at 10 Hz = [12.6,19.1] versus at 50 Hz = [14.7,26.5]), whereas GPe showed significantly higher AUC %ΔF/F at 50 Hz than 10 Hz (CI95 of %ΔF/F at 10 Hz = [3.46, 5.99] versus at 50 Hz = [9.28, 11.5]), significance assessed using two-tailed unpaired t-test, p < 0.001).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Fluorescence time courses for FFN transients evoked by 10 Hz and 50 Hz stimulation.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.009
-
Figure 5—source code 1
Analysis and figures for FFN102 transients evoked by 10 Hz and 50 Hz stimulation.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.010
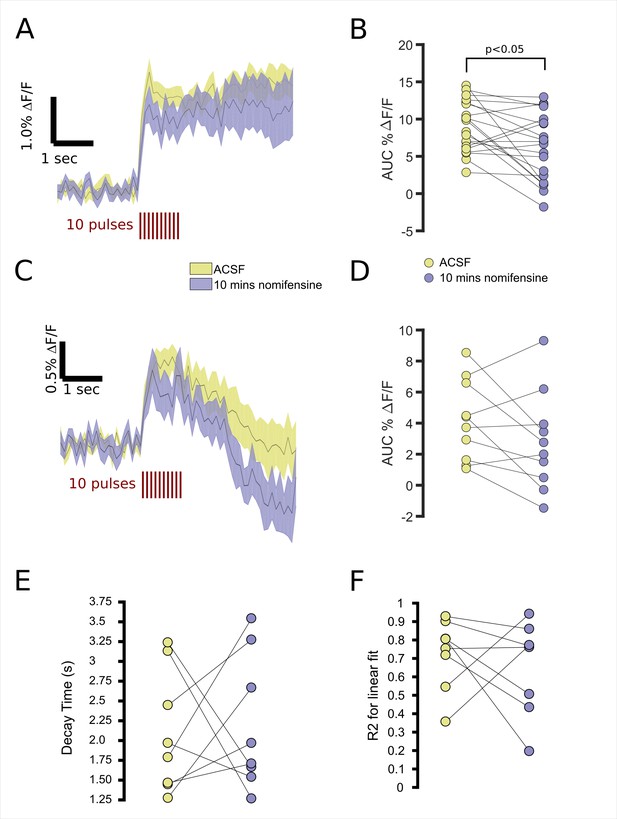
Differences in FFN102 transients in striatum and GPe are unrelated to reuptake.
(A) FFN transients imaged in the striatum for slices perfused first with ACSF alone followed by ten minutes with nomifensine. (B) The average AUC during the stimulus was 8.56 for control slices with a CI95 = [6.92,10.20], and for nomifensine, the average AUC was 5.90 with a CI95 = [3.94, 7.85] (paired t-test, p < 0.05). (C) FFN transients imaged in the GPe for slices similarly treated. (D) The average AUC during the stimulation time period was 4.16 with a CI95 = [2.56, 5.75], and for nomifensine, the average AUC was 2.78 with a CI95 = [0.81, 4.75] (paired t-test, p > 0.05). (E) Decay constants of log-transformed GPe traces show the time for the transient to decay to 10% of its initial value. Treated slices had an average decay time of 2.09 s, CI95= [1.56, 2.62], and untreated slices had an average of 2.20 s, CI95= [1.61, 2.79]. (F) Goodness-of-fit measurements for log-transformed traces.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Fluorescence time courses for FFN transients evoked under nomifensine block.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.012
-
Figure 6—source code 1
Analysis and figures for FFN102 transients during nomifensine block.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.013
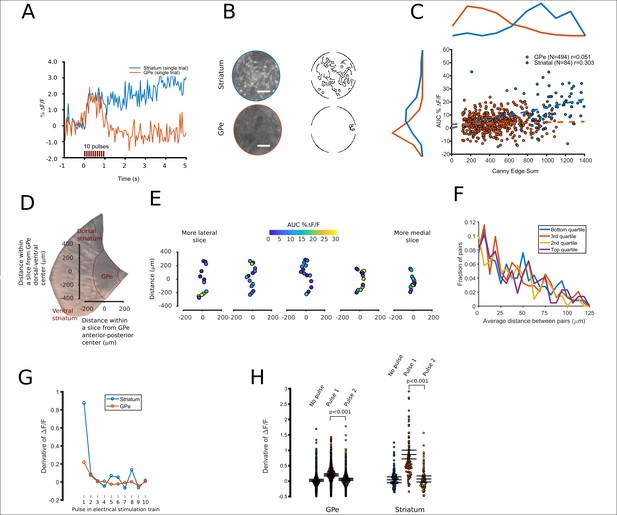
Spatial and temporal characterization of FFN102 transients.
(A) A representative FFN transient from striatum, blue, and a ‘hotspot’ within the GPe, red. (B) Canny filtered masks were calculated from the average of each field of view’s baseline images, returning a pixel value of ‘1’ if the area has a high contrast and otherwise ‘0’. The fields of view that produced these transients are shown, both in their raw form and as a Canny edge filtered image. White scale bar = 10 µm. (C) For each field of view, the Canny edge sum (x axis) is displayed with the amplitude of its FFN transient (y axis). Correlation values are shown for GPe (n = 494 fields of view) and striatum (n = 84 fields of view). (D) An area of a representative brain slice containing the GPe. The two axes display distance in µm along the long axis of the GPe. (E) Points oriented to show imaging locations along the long axis of the GPe, with colors corresponding to their AUCs. Slices are shown from left to right, from more lateral to more medial slices. (F) Histograms showing the distance between pairs of all fields of view imaged within a slice. The distributions are split into four quartiles, where pairs in the top quartile both had the largest FFN transients compared to other pairs in the same slice. Similarly, pairs in the bottom quartile both had smaller FFN transients compared to the other 75% of pairs. (G) A plot of the derivative of the fluorescence intensity over time, averaged over the fields of view for each region (N = 84 for striatum, N = 494 for GPe). (H) Values of the derivative of the fluorescence intensity over time, for three intervals: 100 ms prior to stimulation, 100 ms after the first pulse, and 100 ms after the second pulse. Error bars represent the mean with CI95. All non-overlapping error bars were significant at p < 0.001. The mean value for the derivative at the first pulse was 0.86% for the striatum and 0.20% for the GPe.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Fluorescence time courses for spatial and temporal analysis.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.015
-
Figure 7—source code 1
Analysis and figures for FFN102 transients used for spatial and temporal analysis.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.016
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | Male and female C57BL/6J mice | The Jackson Laboratory | RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664 | |
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | Male Drd2- BAC-GFP mice | MMRC | MGI:3843608 | |
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | Male and female aphakia mice | Provided by Dr. Un Kang (doi:10.1111/gbb.12210; doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006511108) | ||
| Antibody | mouse monoclonal anti-tyrosine hydroxylase | Millipore | RRID:AB_390204 | (1:750) |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42383.017





