Neuronal reactivation during post-learning sleep consolidates long-term memory in Drosophila
Figures
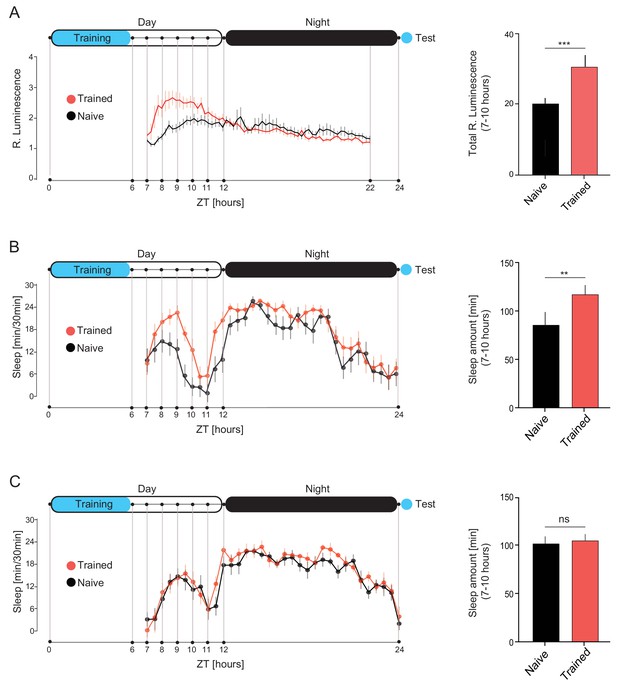
DAN-aSP13 neurons are activated during sleep.
(A) (left) Luminescence of DAN-aSP13 neurons expressing Lola-LUC reporter (MB315B-GAL4>UAS-FLP; Lola>stop>LUC) normalized to luminescence of the genetic control (UAS-FLP; Lola>stop> LUC). Mean luminescence of the wild-type males trained with mated female in single pair assays as indicated (red, n = 42) and naïve males (black, n = 40) is shown as a solid line with SEM indicated as thin vertical lines. (right) Total luminescence in experienced and naïve males between 7–10 hr. P value is for Ho Lucexp = Lucnaive; ***p<0.001. Student T-test. (B) (left) Sleep profile of the wild-type males that were trained for 6 hr with mated females (red, n = 16) and naïve males (black, n = 16). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. (right) Total sleep of the experienced and naïve males between 7–10 hr. P value is for Ho Sleepexp = Sleepnaive; **p<0.01. Student T-test. (C)(left) Sleep profile of the dopR1 mutants that were trained for 6 hr with mated females (red, n = 16) and naïve males (black, n = 16). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. (right) Total sleep of the experienced and naïve males between 7–10 hr. P value is for Ho Sleepexp = Sleepnaive; ns p>0.05. Student T-test. Schematic of the experimental set-up in A, B and C indicates 12 hr light and dark periods (white and black areas) and time of training and test (blue shading).
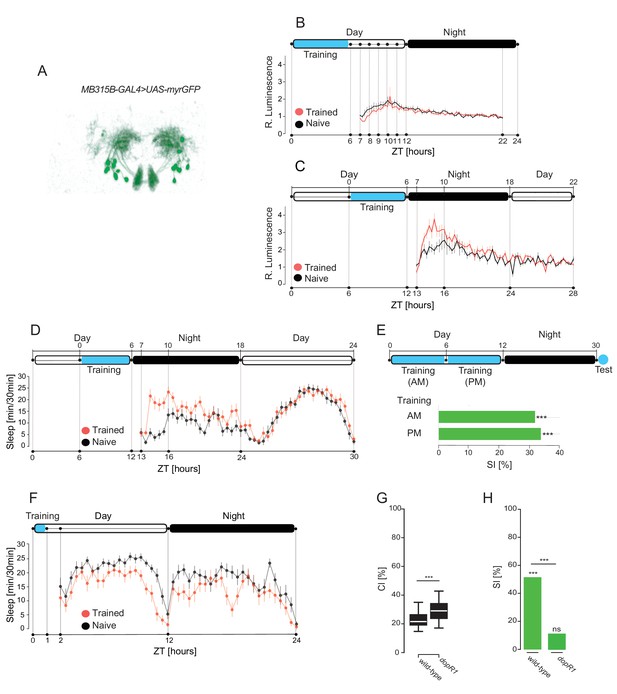
Learning sufficient to induce LTM leads to the enhencement of the post-learning sleep and activation of DAN-aSP13 in the specific time window.
(A) Expression pattern of MB315B-GAL4 line. (B) Luminescence of DAN-aSP13 neurons expressing Lola-LUC reporter (MB315B-GAL4>UAS-FLP; Lola>stop>-LUC) normalized to luminescence of the genetic control (UAS-FLP; Lola>stop>LUC). Mean luminescence of the wild-type males trained in single pair assays as indicated with virgin female (red, n = 24) or naïve males (black, n = 20) shown as a solid line with SEM indicated as thin vertical lines. (C) Luminescence of DAN-aSP13 neurons expressing Lola-LUC reporter (MB315B-GAL4 > UAS FLP; Lola > stop > LUC) normalized to luminescence of the genetic control (UAS-FLP; Lola>stop>LUC). Mean luminescence of the wild-type males trained in single pair assays as indicated with mated female (red, n = 22) and naïve males (black, n = 19) is shown as a solid line with SEM indicated as thin vertical lines. (D) Sleep profile of the wild-type males that were trained for 6 hr with mated females as indicated (red, n = 16) and naïve males (black, n = 16). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. (E) SIs of wild type males trained as indicated with a mated female in single pair assays and tested 24 hr later. P value is for Ho SI = 0; ***p<0.001, ns p>0.05. Permutation test. (F) Sleep profile of the wild-type males that were trained for 1 hr with mated females (red, n = 16) and naïve males (black, n = 16). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. (G) CIs of the wild-type or dopR1 mutant males during 6 hr training in single pair assay w a mated female. P value is for Ho CIwild-type = CIDopR1; ***p<0.001. Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test. (H) SIs of the wild-type or dopR1 mutant males tested 24 hr after training for 6 hr with mated females. P value is for Ho SI = 0; ***p<0.001, ns p>0.05. Permutation test.
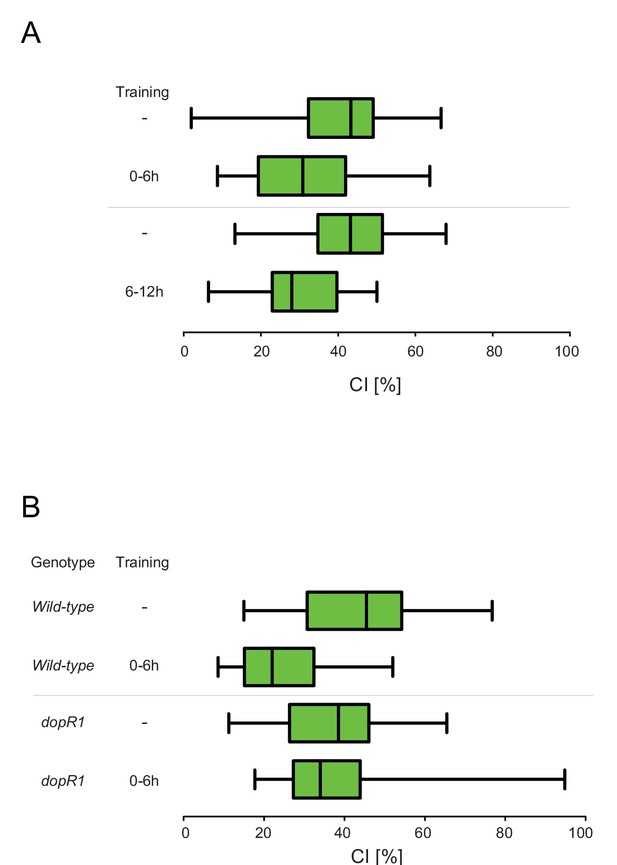
Courtship Indices (CIs) of males that had undrgone treatment according to Figure 1—figure supplement 1E and H.
(A) Courtship indices (CIs) of the wild-type males trained in single pair assays with a mated female as indicated in Figure 1—figure supplement 1E and Table S1. (B) Courtship indices (CIs) of males of the indicated genotypes trained in single pair assays with a mated female as indicated in Figure 1—figure supplement 1H and Table S3.
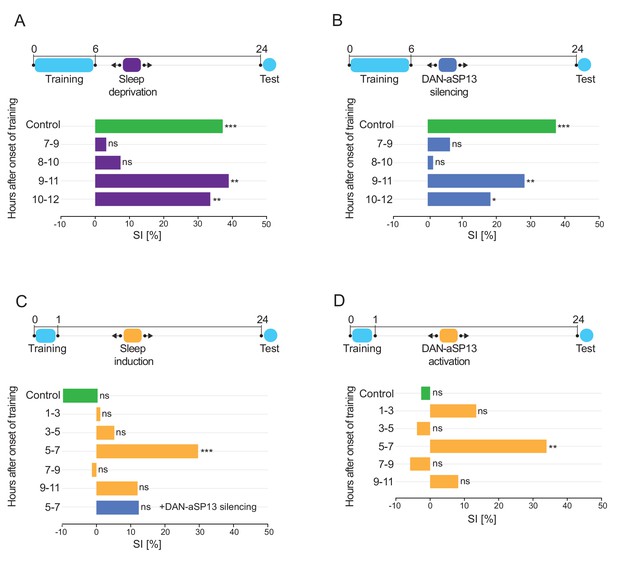
Sleep after learning is necessary and sufficient for LTM consolidation.
(A) SIs of the wild-type males tested 24 hr after training for 6 hr with a mated female and sleep deprived at indicated time periods after training (dark purple bars). SI of the wild-type control males that were allowed to sleep (green bar). P value is for Ho SI = 0; ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, ns p>0.05. Permutation test. (B) SIs of males after training for 6 hr with a mated female and DAN-aSP13s silenced with shits at indicated time periods (dark blue bars). SI of the control males with DAN-aSP13s active (green bar). P value is for Ho SI = 0; ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns p>0.05. Permutation test. (C) SIs of males after training for 1 hr with a mated female and 104y neurons activated with csChrimson at indicated time periods (orange bars). SI of the control males with 104y neurons not activated (green bar). SI of the wild-type males with 104y neurons activated and DAN-aSP13s silenced between 5–7 hr after training (blue bar). P value is for Ho SI = 0; ***p<0.001, ns p>0.05. Permutation test. (D) SIs of males after training for 1 hr with a mated female and DAN-aSP13 neurons activated with csChrimson at indicated time periods (orange bars). SI of the control males with DAN-aSP13 not activated (green bar). P value is for Ho SI = 0; **p<0.01, ns p>0.05. Permutation test.
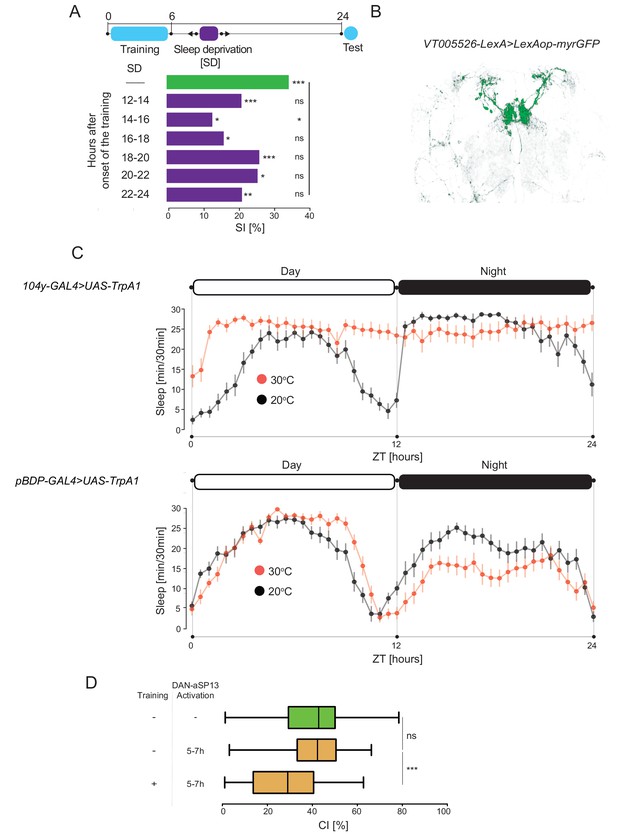
Activation of FB neurons induces sleep.
(A) SIs of the wild-type males after 6 hr training with a mated female and sleep deprived during night at indicated time periods (dark purple bars). SI of the control males which were not deprived of sleep (green bar). P value is for Ho SI = 0; ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns p>0.05. Permutation test. (B) Expression pattern of VT005526-LexA line (C) (upper panel) Sleep profile of males (104y-GAL4 > UAS-TrpA1) with 104y neurons activated (30°C, red, n = 16) and not activated (20°C, black, n = 16). (lower panel) Sleep profile of the genetic control males (pBDP-GAL4 > UAS-TrpA1) at 30°C (red, n = 32) and 20°C (black, n = 32). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. White and black areas indicate 12 hr light and dark periods, respectively. (D) CIs of the naïve and experienced males trained for 1 hr with mated female and DAN-aSP13 activated as indicated. Ho CIcontrol = CInaiveact ns p>0.05; Ho CInaiveact = CItrainedact ***p<0.001. Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test.
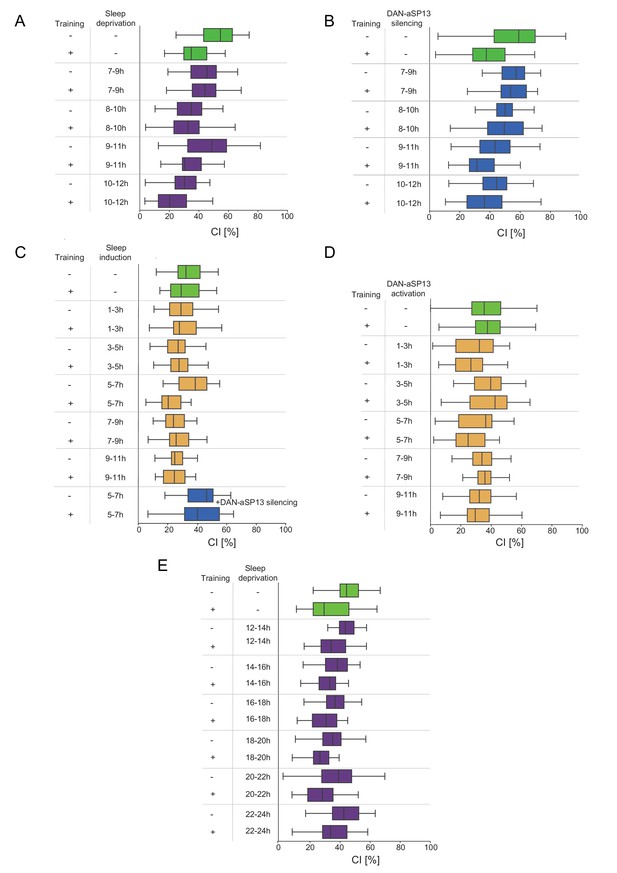
Courtship Indices (CIs) of males that had undergone treatment according to Figure 2 and Figure 2—figure supplement 1A.
(A) Courtship indices (CIs) of the wild-type males trained in single pair assays with a mated female and sleep deprived as indicated in Figure 2A and Table S4. (B) Courtship indices (CIs) of males trained in single pair assays with a mated female and DAN-aSP13s silenced as indicated in Figure 2B and Table S6. (C) Courtship indices (CIs) of males trained in single pair assays with a mated female and sleep induced as indicated in Figure 2C and Table S7. (D) Courtship indices (CIs) of males trained in single pair assays with a mated female and DAN-aSP13s activated as indicated in Figure 2D and Table S8. (E) Courtship indices (CIs) of males trained in single pair assays with a mated female and sleep deprived as indicated in Figure 2—figure supplement 1A and Table S5.
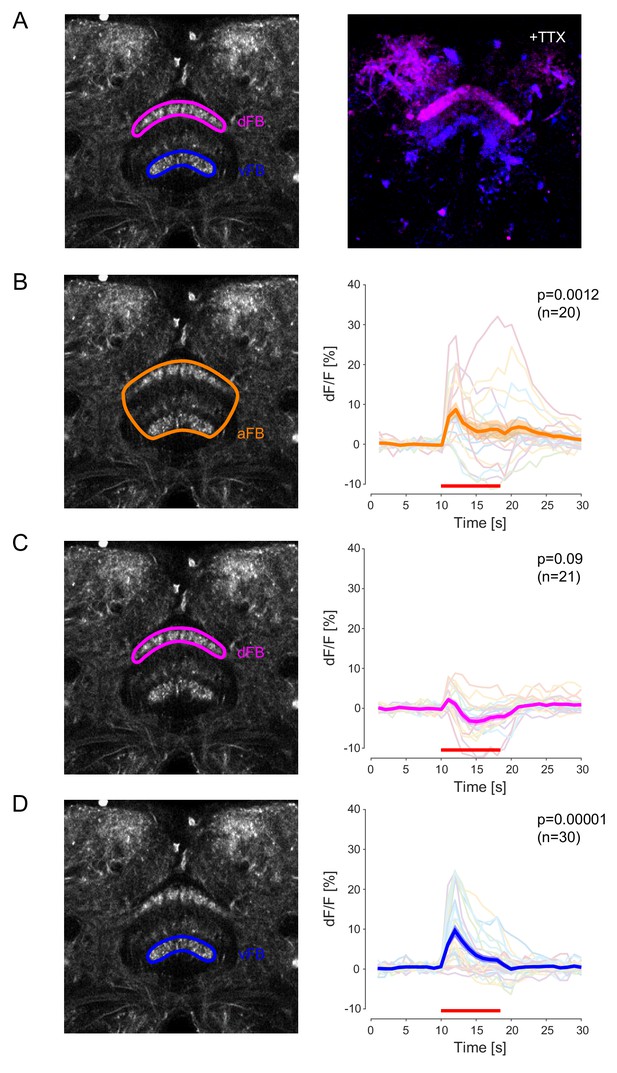
FB neurons provide an excitatory input to DAN-aSP13.
(A) (left) Expression pattern of 104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato with depicted dFB (magenta) and vFB (blue) layers for local activation with DMD. (right) Excitatory response of dFB (magenta) or vFB (blue) layers in the presence of 20 uM tetradotoxin (TTX) upon activation of dFB or vFB, respectively. The calcium response pattern evoked by stimuli was calculated by the correlation of determination. (B) (left) Expression pattern of 104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato with depicted 104y FB neurons (orange) for local activation with DMD. (right) Normalized calcium levels (dF/F) in DAN-aSP13 upon local activation of 104y FB neurons (104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato, R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCamP6s). DAN-aSP13 activity in individual flies is shown in colored thin lines and the mean trace is shown in a thick orange line with SEM indicated by shaded area. (C) (left) Expression pattern of 104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato with depicted dFB layer (magenta) for local activation with DMD. (right) Normalized calcium levels (dF/F) in DAN-aSP13 upon local activation of dFB (104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato, R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCamP6s). DAN-aSP13 activity in individual flies is shown in colored thin lines and the mean trace is shown in a thick magenta line with SEM indicated by shaded area. (D) (left) Expression pattern of 104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato with depicted vFB layer (blue) for local activation with DMD. (right) Normalized calcium levels (dF/F) in DAN-aSP13 upon local activation of vFB (104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato, R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCamP6s). DAN-aSP13 activity in individual flies is shown in colored thin lines and the mean trace is shown in a thick blue line with SEM indicated by shaded area. (B, C, D): Red line indicates the time of the light stimulus. P value in all panels represents the probability that the mean dF/F of pre-stimulation (10 s) and the mean dF/F during stimulation has the same median across flies (tested by Wilcoxon rank sum test, sample size indicated with n value).
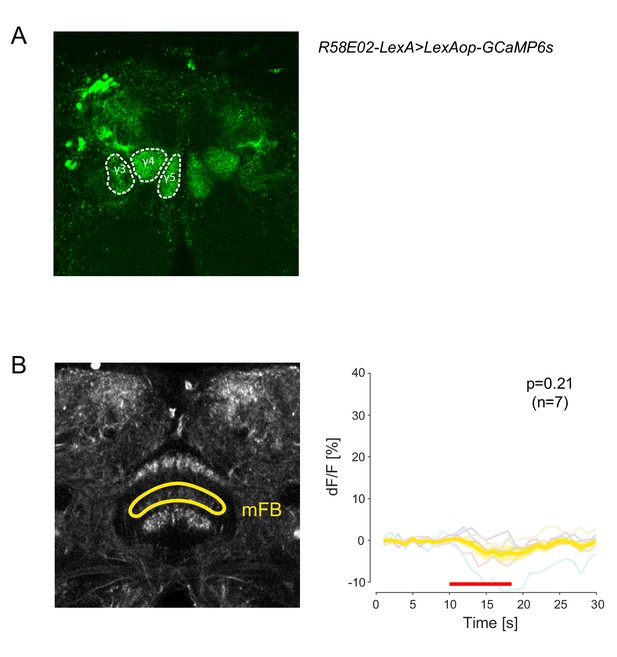
Activation of the mFB has no effect on DAN-aSP13 activity.
(A) Expression pattern of the broad PAM-DANs driver (R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCaMP6s). Manually defined DAN-γ5 (DAN-aSP13), DAN-γ4 and DAN-γ3 are depicted in white dashed circles. (B) (left) Expression pattern of 104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato with depicted mFB layer for local activation with DMD (yellow). (right) Normalized calcium levels (dF/F) in DAN-aSP13 upon local activation of mFB (104y-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato, R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCamP6s). DAN-aSP13 activity in individual flies is shown in colored thin lines and the mean trace is shown in a thick yellow line with SEM indicated by shaded area. Red line indicates the time of the light stimulus. P value represents the probability that the mean dF/F of pre-stimulation (10 s) and the mean dF/F during stimulation has the same median across flies (tested by Wilcoxon rank sum test, sample size indicated with n value).
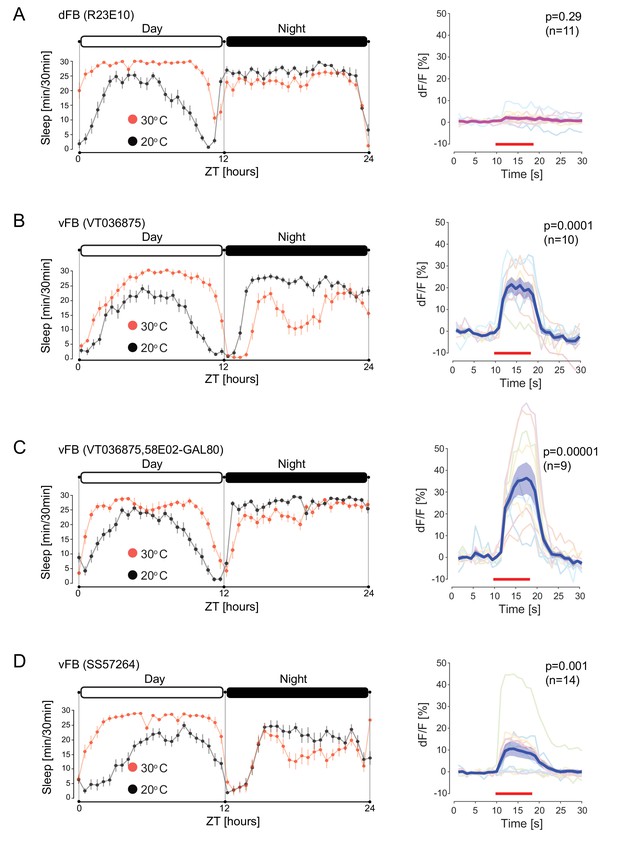
Sleep promoting vFB neurons activate DAN-aSP13.
(A) (left) Sleep profile of males (R23E10-GAL4 > UAS-TrpA1) upon activation of dFB neurons (red, n = 16) and control males with dFB neurons not activated (black, n = 16). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. White and black areas indicate 12 hr light and dark periods, respectively. (right) Normalized calcium levels (dF/F) in DAN-aSP13 upon activation of dFB (R23E10-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88, R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCamP6s). DAN-aSP13 activity in individual flies is shown in colored thin lines, and the mean trace is shown in thick magenta line with SEM indicated by shaded area. (B) (left) Sleep profile of males (VT03687-GAL4 > UAS-TrpA1) upon activation of vFB neurons (red, n = 16) and control males with vFB neurons not activated (black, n = 16). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. White and black areas indicate 12 hr light and dark periods, respectively. (right) Normalized calcium levels (dF/F) in DAN-aSP13 upon activation of vFB (VT036875-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88, R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCamP6s). DAN-aSP13 activity in individual flies is shown in colored thin lines, and the mean trace is shown in thick blue line with SEM indicated by shaded area. (C) (left) Sleep profile of males (VT036875-GAL4 > UAS-TrpA1, R58E02-GAL80) upon activation of vFB neurons (red, n = 16) and control males with vFB neurons not activated (black, n = 16). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. White and black areas indicate 12 hr light and dark periods, respectively. (right) Normalized calcium levels (dF/F) in DAN-aSP13 upon activation of vFB (VT036875-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88, R58E02-GAL80, R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCamP6s). DAN-aSP13 activity in individual flies is shown in colored thin lines, and the mean trace is shown in thick blue line with SEM indicated by shaded area. (D) (left) Sleep profile of (SS57264-GAL4 > UAS-TrpA1) males upon activation of vFB neurons (red, n = 16) and control males with vFB neurons not activated (black, n = 16). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. White and black areas indicate 12 hr light and dark periods, respectively. (right) Normalized calcium levels (dF/F) in DAN-aSP13 upon activation of vFB (SS57264-GAL4 > UAS-Chrimson88, R58E02-LexA > LexAop-GCamP6s). DAN-aSP13 activity in individual flies is shown in colored thin lines, and the mean trace is shown in thick blue line with SEM indicated by shaded area. (A–D) (right panels) Red line indicates the time window of the light stimulus. P value represents the probability that the mean dF/F of pre-stimulation (10 s) and the mean dF/F during stimulation has the same median across flies (tested by Wilcoxon rank sum test, sample size indicated with n value).
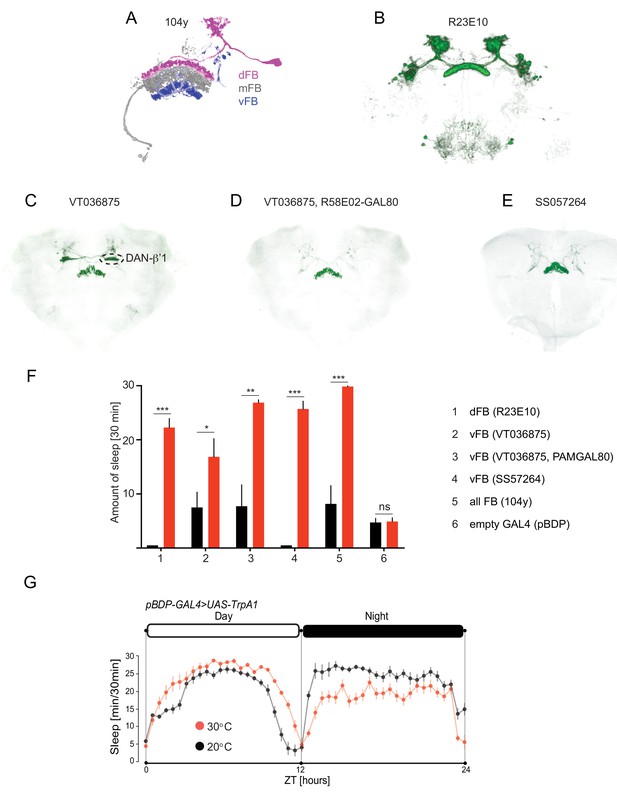
Specific class of vFB neurons acutely induces sleep.
(A) Three single FB neural cell types were manually traced in MCFO data: dFB (magenta), vFB (blue) and mFB (grey). Confocal images registered to standard brain of four FB lines in Figure 4 and superimposed on the standard brain. (B) R23E10-GAL4 (C) VT036875-GAL4 (D) VT036875-GAL4, 58E02-GAL80 (E)SS57264 driving UAS-myrGFP or UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato. (F) Total amount of sleep of the experienced and naïve males quantified per 30 min time period upon activation with CsChrimson (activated, red, n = 8–9 and not activated, black, n = 8–9). (G) Sleep profile of the genetic control males (pBDP-GAL4 > UAS-TrpA1) (30°C, red, n = 48) and (20°C, black, n = 48). Sleep time was plotted in 30 min bins. White and black areas indicate 12 hr light and dark periods, respectively.
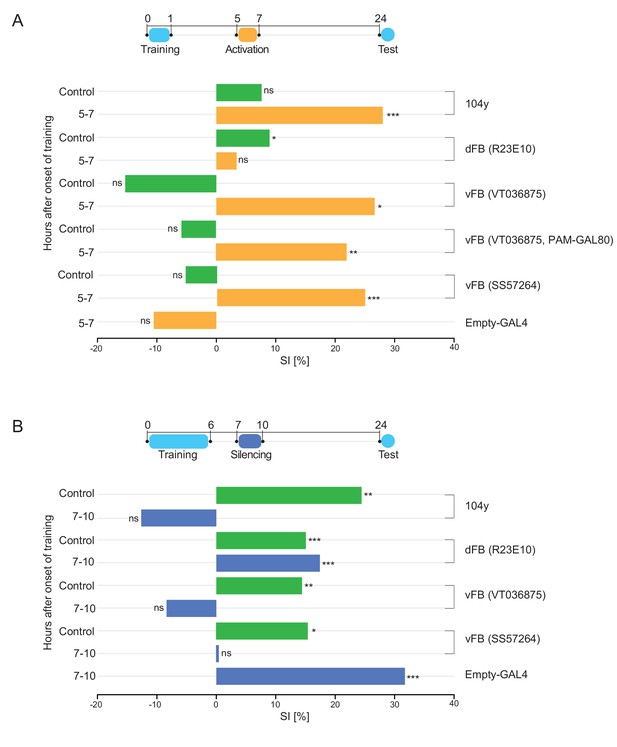
Sleep promoting vFB neurons are sufficient and necessary for LTM consolidation.
(A) SIs of males of indicated genotypes tested 24 hr after 1 hr training with a mated female and activation at the specific time interval with CsChrimson (orange bars). SI of control males with relevant neurons not activated (green bar). P value is for Ho SI = 0; ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns p>0.05. Permutation test. (B) SIs of males of indicated genotypes tested 24 hr after training for 6 hr with a mated female and silencing with shits at the specific time interval (dark blue bars). SI of wild type control males with DAN-aSP13 active (green bar). P value is for Ho SI = 0; ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns p>0.05. Permutation test.
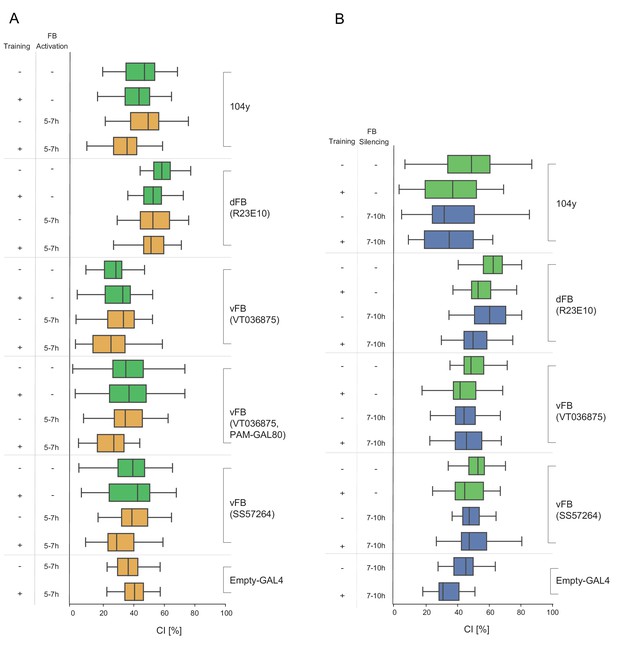
Courtship Indices (CIs) of males that had undergone treatment according to Figure 5A and B.
(A) Courtship indices (CIs) of males trained in single pair assays with a mated female and with FB neurons activated as indicated in Figure 5A and Table S9. (B) Courtship indices (CIs) of males trained in single pair assays with a mated female and with FB neurons silenced as indicated in Figure 5B and Table S10.
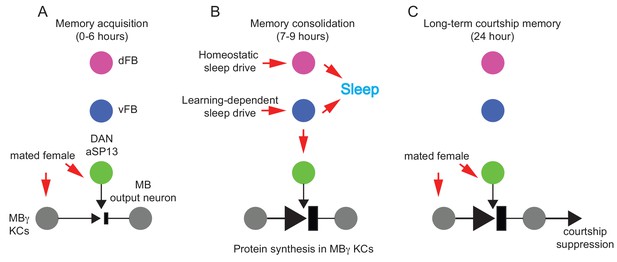
Post-learning activation of DAN-aSP13 neurons mediates LTM consolidation.
(A) The MBγ and DAN-aSP13s are repetitively activated during 6 hr training by the olfactory and behavioral cues presented by a mated female, respectively. (B) Males display an enhanced amount of sleep after training for LTM. Enhanced sleep is mediated by the vFB neurons in response to a learning induced sleep drive while the remaining amount of sleep is regulated by dFB neurons in response to homeostatic sleep drive. Only vFB neurons activate DAN-aSP13s. Dopamine released as a result of DAN-aSP13s activation stimulates molecular processes in the γKCs neurons that involve synthesis of new proteins essential for LTM memory persistence. (C) Subsequently, experienced males suppress their courtship towards mated females for 24 hr or longer.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-FLP.PEST; lola >> luc | DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1706608114 | Obtained from Michael Rosbash lab | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MB315B-GAL4 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.04577 | Obtained from Gerry Rubin lab | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster | UAS-myr::smGFP | DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.119917 | BDSC ID: #32197 | Obtained from Gerry Rubin lab |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Dopr1(attP) | DOI: 10.1038/nature11345 | Obtained from Barry Dickson lab | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | VT005526-LexA | DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.05.037 | ||
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 104y-GAL4 | DOI: 10.1126/science.1202249 | FlyBase ID: FBti0072312 | Bloomington Stock Center |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-CsChrimson-mVenus | DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2836 | BDSC ID: #55134, #55136 | Obtained from Vivek Jayaraman lab |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | LexAop2-CsChrimson-mVenus | DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2836 | BDSC ID: #55139 | Obtained from Vivek Jayaraman lab |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | pBDP-GAL4 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.04577 | Obtained from Gerry Rubin lab | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-TrpA1 | DOI: 10.1101/gad.1278205 | ||
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | LexAop-Shits | PMID: 12745632 | ||
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | LexAop-myr::smGFP | DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.119917 | BDSC ID: #32203 | Obtained from Gerry Rubin lab |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-GCaMP6s | DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1703090115 | Obtained from David Anderson lab | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | R58E02-LexA | DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0803697105 | BDSC ID: #52740 | Obtained from Gerry Rubin lab |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster | UAS-Chrimson88-tdTomato | DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1703090115 | Obtained from David Anderson lab | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | LexAop2-Syn21-opGCaMP6s | DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1703090115 | Obtained from David Anderson lab | |
Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | R23E10-GAL4 | DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0803697105 | BDSC ID: 49032 | Obtained from Gerry Rubin lab |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | VT036875-GAL4 | DOI: 10.1101/198648 | VDRC ID: 203402 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | R58E02-Gal80 | DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1703090115 | Flybase ID FBtp0097258 | Obtained from Glenn Turner lab |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Shits | PMID: 12745632 | ||
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | SS57264-GAL4 | This paper | generated by combining the VT045282-GAL4p65adz(attP40) and VT020829-ZpGAL4dbd(attP2) lines. | |
| Chemical Compund, drug | Luciferin | GOLDBIO | Cat. LUCK | |
| Chemical Compund, drug | Tetradotoxin | abcam | Cat. ab120054 | |
| Software, algorithm | Permutation Test | PMID: 10355520 | ||
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Prism (https://graphpad.com) | Version 7 | RRID:SCR_015807 |
| Software, algorithm | FIJI | FIJI (https://imagej.net/Fij) | RRID:SCR_002285 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary Tables.
Table S1. LTM does not depend on the circadian time of training Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes according to Figure 1—figure supplement 1E, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc). Table S2. dopR1 mutant court mated females more than wild-type males Courtship indices (CIs) of naïve males of the indicated genotypes according to Figure 1—figure supplement 1G during 6 hr training with mated female are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that CIs of both groups are equal (H0: CIwt = CIDopR1). Table S3. dopR1 mutant males do not learn Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes according to Figure 1—figure supplement 1H, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc). Table S4. Day-time sleep deprivation between 7–9 hr impairs LTM Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes, sleep deprived as denoted in Figure 2A, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc). Table S5. Night-time sleep deprivation does not impair LTM Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes, sleep deprived as denoted in Figure 2-figure supplement A, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc). Table S6. Silencing of DAN-aSP13 between 7–9 hr impairs LTM Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes with DAN-aSP13 silenced as denoted in Figure 2B, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc). Table S7. Sleep induction between 5–7 hr consolidates STM to LTM Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes and sleep induced as denoted in Figure 2C, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc). Table S8. DAN-aSP13 activation between 5–7 hr consolidates LTM Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes with DAN-aSP13 activated as denoted in Figure 2D, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc). Table S9. Activation of vFB neurons between 5–7 hr consolidates LTM Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes with vFB activated as denoted in Figure 5A, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc). Table S10. Silencing of vFB neurons between 7–10 hr impairs LTM Suppression indices (SIs) of naïve (train-) and experienced (train+) males of the indicated genotypes with vFB silenced as denoted in Figure 5B, tested in single-pair assays with mated females as trainers and testers. Courtship indices (CIs) are shown as median of n males and dispersion of the data as interquartile range (IQR). P values determined by permutation test for the null hypothesis that learning equals 0 (H0: SI = 0) or for the null hypothesis that experimental and control males learn equally well (H0: SI = SIc).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42786.016
-
Supplementary file 2
Fly genotypes.
Specific fly genotypes used in all main and supplementary figures.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42786.017
-
Source code 1
Source code for analysis of calcium traces.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42786.018
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42786.019





