CCL5 promotes breast cancer recurrence through macrophage recruitment in residual tumors
Figures
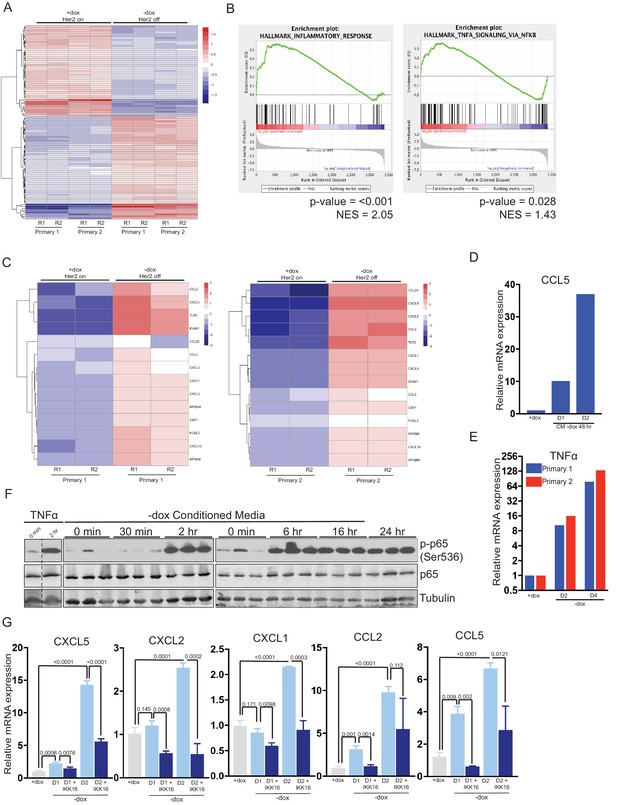
Her2 downregulation induces an inflammatory gene expression program driven by the TNFα/IKK pathway.
(a) RNA-seq analysis of two independent primary Her2-driven tumor cell lines in the presence of Her2 expression (+dox) or 2 days following Her2 downregulation (-dox). The heatmap shows the top 100 differentially expressed genes between +dox and -dox conditions. R1 and R2 are biological replicates. (b) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of RNA-seq data showing enrichment of an inflammatory response signature and a TNFα/NF-κB signature in cells following Her2 downregulation. p-Values and normalized enrichment scores (NES) are shown. (c) Heatmap showing expression of select genes from the TNFα/NF-κB signature in the presence of Her2 expression (+dox) or following Her2 deinduction (-dox). (d) qRT-PCR analysis of CCL5 expression following 1- or 2-day treatment with conditioned media harvested from primary cells following Her2 downregulation. Dox was added to conditioned media prior to treatment to maintain Her2 expression in target cells. Results shown are representative of two independent experiments. (e) qRT-PCR of TNFα expression in primary cells in the presence of Her2 expression (+dox) or 2 and 4 days following Her2 downregulation. Results shown are representative of two independent experiments. (f) Primary tumor cells were treated with conditioned media as described in (d), and activation of the NF-κB pathway was assessed by Western blot analysis of total and phospho-p65. Results show three biological replicates per time point. (g) qRT-PCR analysis of the indicated genes in primary tumor cells in the presence of Her2 expression (+dox) or 1 and 2 days following Her2 downregulation (-dox). At the time of Her2 downregulation, cells were treated with the pan-IKK inhibitor IKK16 (100 nM) or vehicle control. Results show the average of 3 biological replicates per condition. Error bars denote mean ± SEM. Significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t-test.
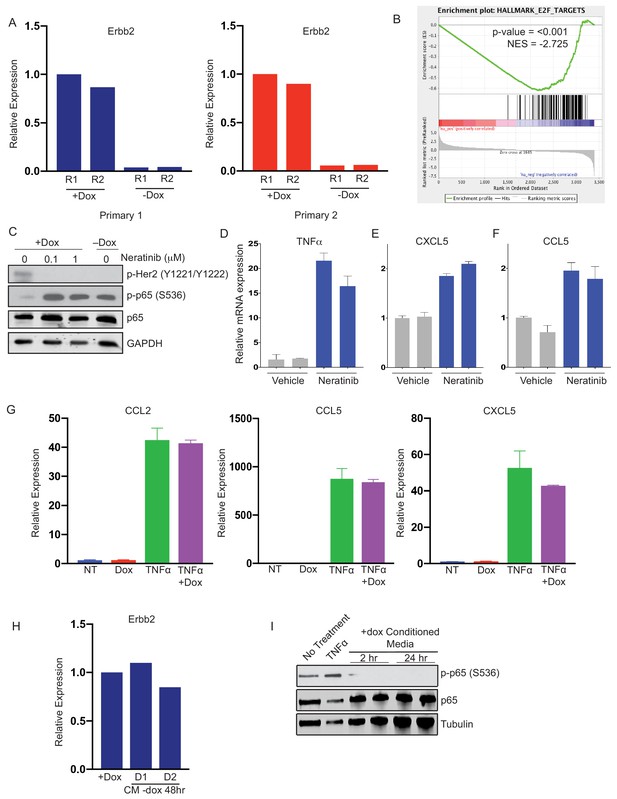
Gene expression changes following Her2 inhibition.
(a) qRT-PCR analysis of Erbb2 expression in primary cells with Her2 on (+dox) or Her2 off (-dox). (b) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of RNA-seq data showing an E2F gene signature is enriched in cells with Her2 signaling on. p-Values and normalized enrichment scores (NES) are shown. (c) Western blot showing p65 phosphorylation in primary tumor cells treated with the indicated concentration of Neratinib for 24 hr, or 24 hr following dox withdrawal. (d–f) qRT-PCR analysis of TNFα, CCL5, and CXCL5 expression 24 hr after treatment with 0.1 μM Neratinib. (g) qRT-PCR analysis of CCL2, CCL5, and CXCL5 expression in NIH-3T3 treated with 2 μg/mL dox, 10 ng/mL TNFα, or both for 24 hr. (h) qRT-PCR analysis of Erbb2 expression of cells treated with -dox conditioned media with dox supplementation. (i) Primary tumor cells were treated with +dox conditioned media and activation of the NF-κB pathway was assessed by Western blot analysis of total and phospho-p65. Results show two biological replicates per time point.
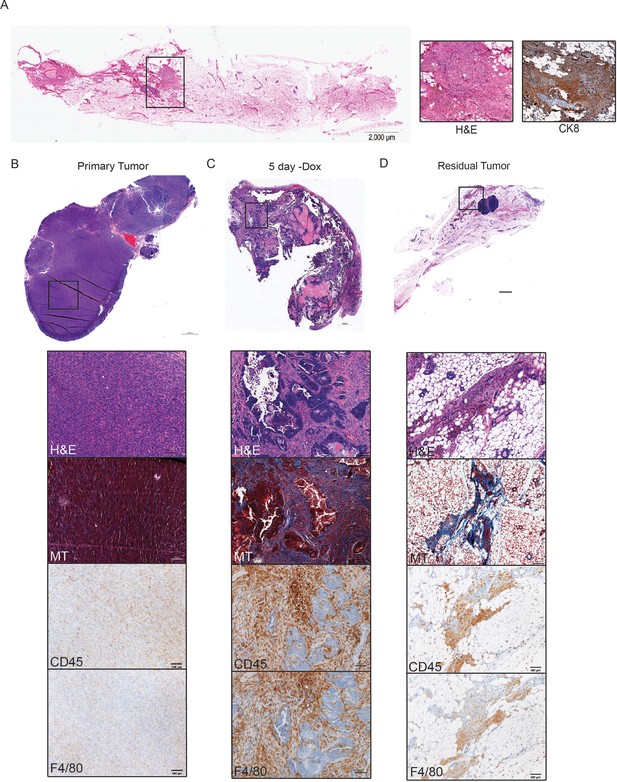
Immune cell infiltration during tumor regression and residual disease.
(a) H and E-stained section of a representative residual tumor from a previously tumor-bearing MTB/TAN mouse. Insets show higher magnification view of residual tumor cells (left) and staining for CK8 (right). (b–d) Representative images of a primary tumor (b), regressing tumor (5 days -dox) (c), and residual tumor (d), stained with H and E, Masson’s Trichome (MT), CD45, or F4/80. Primary tumors show little collagen deposition and only modest leukocyte infiltration. Her2 downregulation leads to infiltration of CD45+ cells, predominantly F4/80+ macrophages. Residual tumors have abundant collagen deposition and leukocyte infiltration.
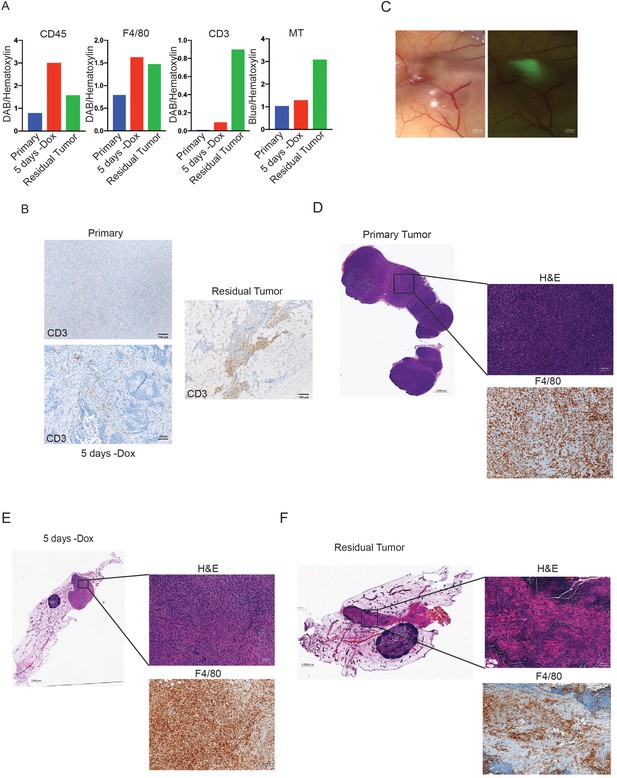
Immune cell infiltration inautochthonousand orthotopic tumors following Her2 downregulation.
(a) CD3 staining of representative MTB;TAN primary, 5 days -dox, and residual tumors. (b) Bright-field and fluorescent images of a representative GFP-labeled orthotopic residual tumor in the context of a non-fluorescent mammary gland. (c) Quantification of IHC and MT staining of primary, regressing, and residual tumors from the MTB;TAN model. (d–f) F4/80 staining of representative orthotopic primary, 5 days -dox, and residual tumors showing macrophage infiltration.
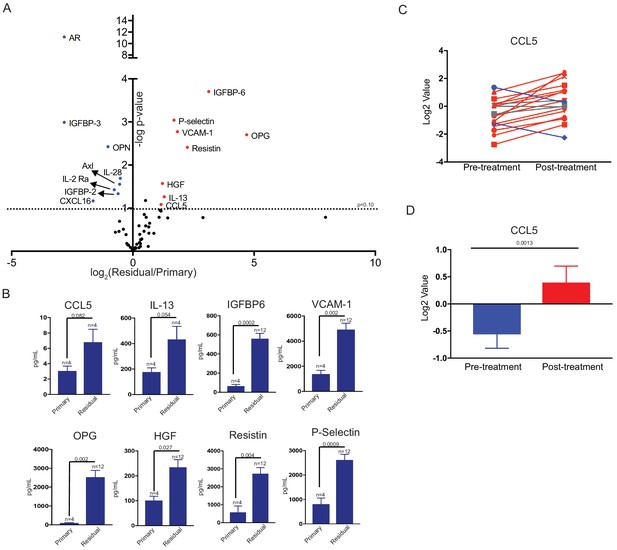
Differential cytokine expression in residual tumors.
(a) Volcano plot showing differential cytokine expression between primary and residual tumors. Antibody-based cytokine arrays were used to measure cytokine expression in orthotopic primary tumors or microdissected residual tumors. Cytokines that are upregulated (fold change >2, p-value < 0.1) in dormant tumors are in red, and downregulated cytokines (fold change <-2, p-value < 0.1) are in blue. Significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. (b) Quantification of CCL5, IL-13, IGFBP6, VCAM-1, OPG, HGF, Resistin, and P-Selectin expression in primary tumors and residual tumors. Values were derived from the cytokine arrays shown in (a). Significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. (c) CCL5 expression in 18 matched pre- and post-treatment samples from GSE10281. Red lines show tumors in which CCL5 expression increased following treatment (>1.5 fold change), and blue lines show tumors with decreased CCL5 expression (<1.5 fold change). (d) Average CCL5 expression in pre- and post-treatment samples from (e). Significance was determined using a two-tailed paired Student’s t-test. Error bars denote mean ± SEM.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Cytokine array expression data analysis from arrays Q1 and Q4.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43653.009
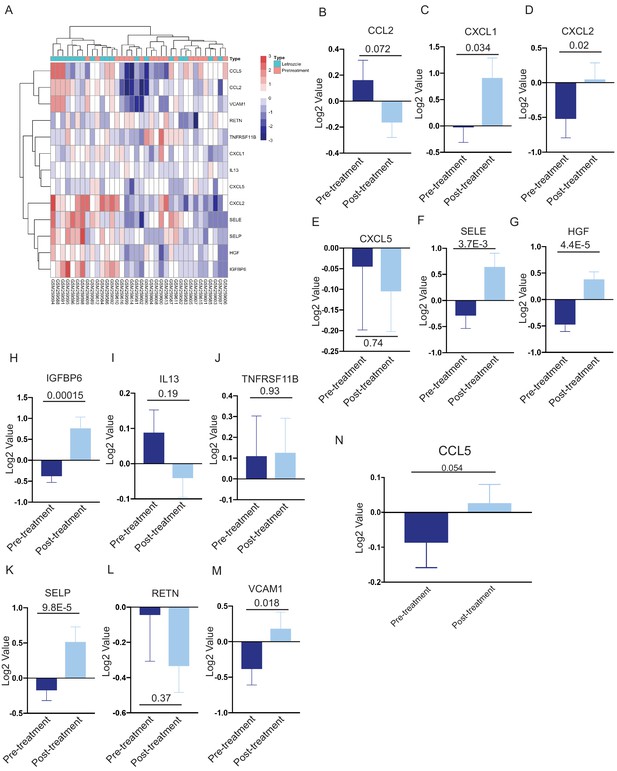
Cytokine gene expression in human breast cancers following neoadjuvant therapy.
(a) Heatmap showing expression of selected cytokine and chemokine genes from 18 matched human breast tumors prior to treatment, or in residual tumors following neoadjuvant Letrozole treatment (GSE10281). Gene expression values were log2 transformed and median centered. (b–m) Average expression of CCL2, CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL5, SELE, HGF, IGFBP6, IL-13, TNFRSF11B, SELP, RETN, and VCAM-1 in 18 matched pre- and post-treatment samples following neoadjuvant Letrozole treatment (GSE10281). Two-tailed paired t-test was performed between pre- and post-treatment samples. (n) Average CCL5 expression in 25 matched pre- and post-treatment samples from human breast tumors treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (GSE21974). Two-tailed paired t-test was performed between pre- and post-treatment samples.
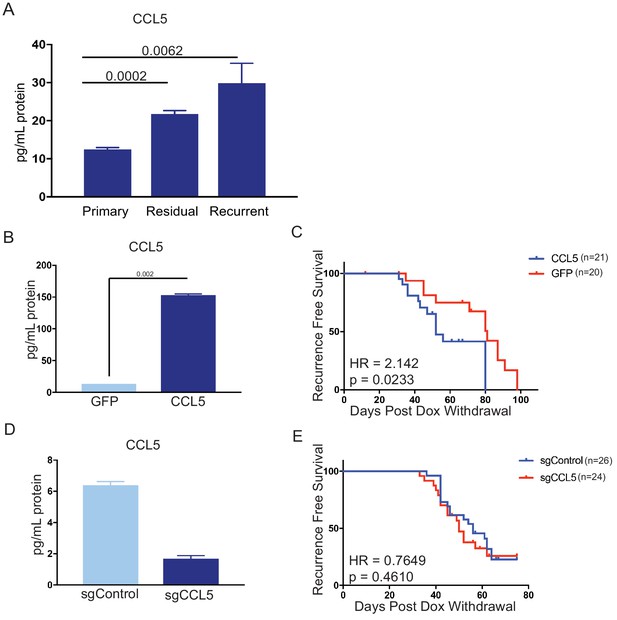
CCL5 expression promotes tumor recurrence following Her2 downregulation.
(a) CCL5 protein levels in orthotopic primary (n = 4), residual (n = 3), and recurrent (n = 2) tumors as determined by ELISA. (b) CCL5 protein levels in primary tumor cells engineered to express CCL5. Results show the mean ± SEM for two independent experiments. Significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. (c) Recurrence-free survival for mice with control tumors or tumors expressing CCL5. CCL5 expression significantly accelerated recurrence (Hazards Ratio (HR) = 2.1, p=0.02). Results are from a single experiment with 20 control tumors and 21 CCL5 tumors. p-Values and hazards ratios are indicated. Statistical significance was determined by Mantel-Cox log rank test. (d) CCL5 expression as determined by ELISA in primary tumor cells expressing a control sgRNA or a sgRNA targeting CCL5. Results show the mean ± SEM for a single representative experiment. (e) Recurrence-free survival of mice with control tumors or CCL5 knockout tumors. CCL5 knockout in tumor cells did not significantly delay tumor recurrence (HR = 0.76, p = 0.46). Results are from a single experiment with 26 control tumors (sgControl) and 24 sgCCL5 tumors. Statistical significance was determined by Mantel-Cox log rank test. Error bars denote mean ± SEM.
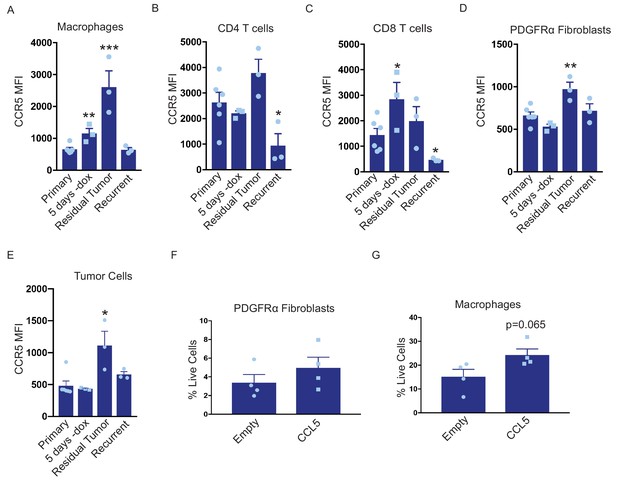
CCL5 promotes macrophage infiltration in residual tumors.
(a–d) Flow cytometry of immune cells in primary (n = 6), regressing (5 days -dox; n = 3), residual (n = 3), and recurrent (n = 3) tumors from autochthonous MTB;TAN mice. Immune cell populations analyzed include CD11b+/F4/80+ macrophages (a), CD4+ T cells (b), CD8+ T cells (c), PDGFRα fibroblasts (d), and tumor cells (e). Each immune cell population was divided into CCR5- or CCR5+ cells, and the median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the CCR5+ population was calculated. (f) Flow cytometry of CD45-/PDGFRα+ fibroblasts in control residual tumors (n = 4) or residual tumors expressing CCL5 (n = 4). (g) Flow cytometry of CD11b+/F4/80+ macrophages in control residual tumors (n = 4) or residual tumors expressing CCL5 (n = 4). Error bars denote mean ± SEM. Significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
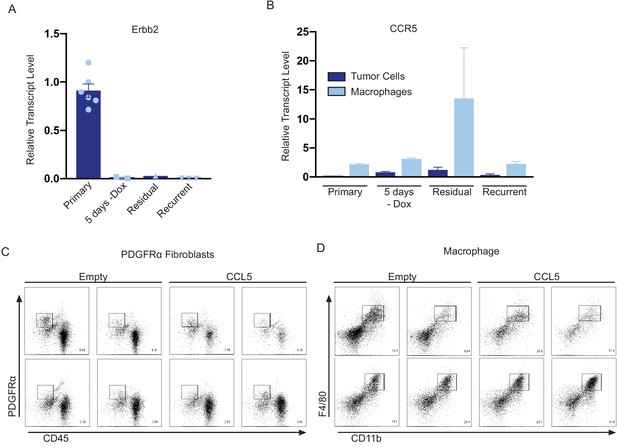
CCL5 recruits CCR5+ macrophages to residual tumors.
(a) qRT-PCR analysis of Erbb2 in primary, 5 days – dox, residual, and recurrent tumors from the MTB;TAN model cohort used for flow cytometry analysis of CCR5 expression. (b) qRT-PCR analysis of CCR5 on sorted tumor cells and macrophages from primary, 5 days -dox, residual, and recurrent tumors from the MTB;TAN model. (c) Flow plots of CD45-/PDGFRα+ fibroblasts in control (n = 4) and CCL5-expressing (n = 4) residual tumors (d) Flow plots of CD11b+/F4/80+ macrophages in control (n = 4) and CCL5-expressing (n = 4) residual tumors.
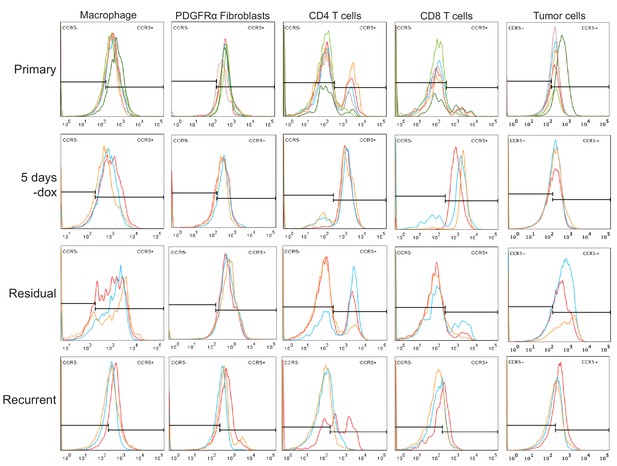
CCR5 staining on immune cell populations in primary, regressing, residual, and recurrent tumors.
Histograms showing CCR5 staining in macrophages, PDGFRα fibroblasts, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and tumor cells from primary tumors (n = 6), regressing tumors (5 days -dox; n = 3), residual tumors (n = 3), and recurrent tumors (n = 3).
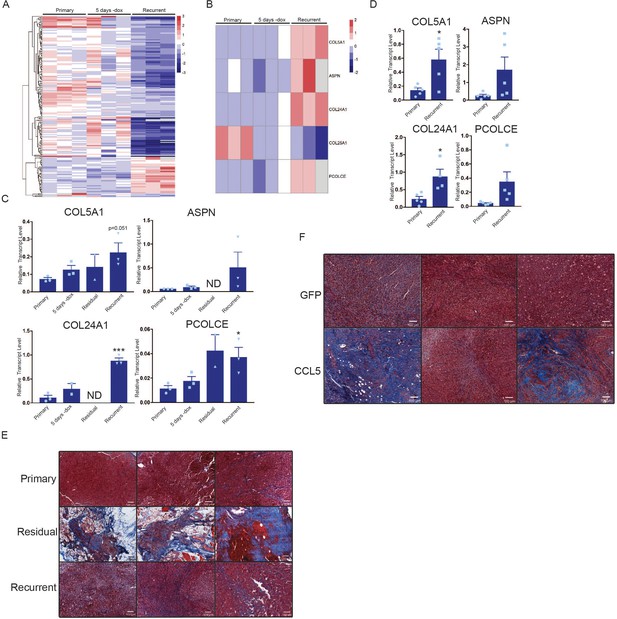
Macrophages express collagen and collagen deposition factors.
(a) RNA-seq analysis of tumor-associated macrophages from primary (n = 3), regressing (5 days -dox; n = 3), and recurrent (n = 3) tumors. The heatmap shows differentially expressed genes (p<0.01, Student’s t-test) between primary and recurrent TAMs. (b) Heatmap showing expression of specific collagen genes from RNA-seq analysis in (a). (c) qRT-PCR analysis of COL5A1, ASPN, COL24A1, and PCOLCE expression in the cohort in (a) along with sorted macrophages from residual tumors. ND = not detected (d) qRT-PCR analysis of COL5A1, ASPN, COL24A1, and PCOLCE expression in unsorted MTB;TAN primary (n = 5) and recurrent (n = 5) tumors. (e) Masson’s trichrome staining showing collagen deposition in primary (n = 3), residual (n = 3), and recurrent (n = 3) tumors from the MTB;TAN model. Collagen is stained in blue, and higher collagen staining is present in residual and recurrent tumors. (f) Masson’s trichrome staining in a subset of control and CCL5-expressing orthotopic recurrent tumors. The entire cohort of tumors is shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Error bars denote mean ± SEM. Significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq from primary and recurrent tumor cell lines used to clear contaminates from TAM RNA-seq.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43653.016
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Candidate list of differnetially expressed genes between primary and recurrent TAMs after filtering.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43653.017
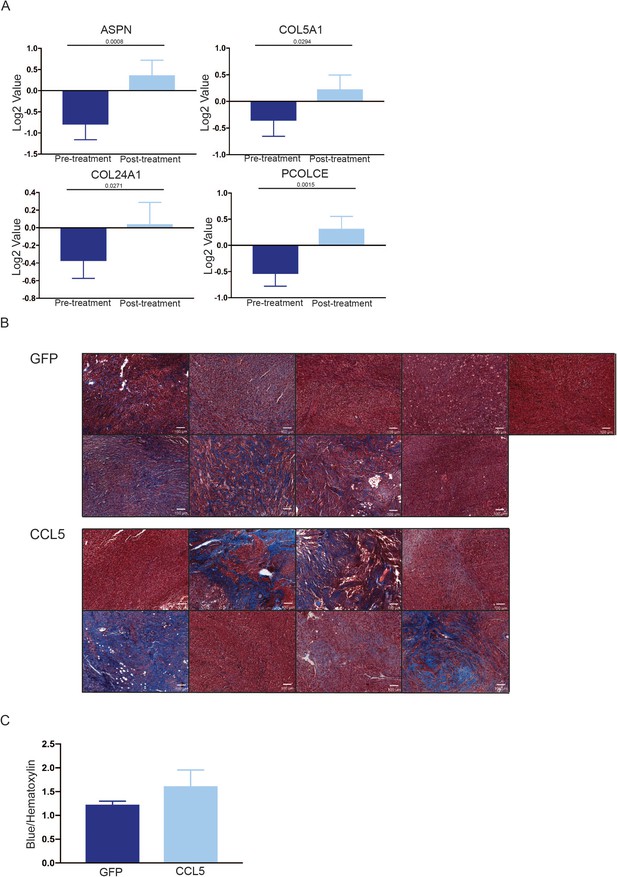
Collagen gene expression and deposition in residual and recurrent tumors.
(a) Average expression of ASPN, COL5A1, COL24A1, and PCOLCE in 18 matched pre- and post-treatment samples from human breast tumors treated with neoadjuvant Letrozole (GSE10281). Two-tailed paired t-test was performed between pre- and post-treatment samples. (b) Masson’s trichrome staining showing collagen deposition in control (n = 4) and CCL5-expressing (n = 4) recurrent tumors. (c) Quantification of (b).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Souce or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pLenti CMV GFP Neo | Addgene | Plasmid # 17447 RRID:Addgene_17447 | Campeau et al., 2009 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | lentiCas9- Blast | Addgene | Plasmid # 52962 RRID:Addgene_ 52962 | Sanjana et al., 2014 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | lentiGuide- Puro | Addgene | Plasmid # 52963 RRID:Addgene_ 52963 | Sanjana et al., 2014 |
| RecombinantDNA reagent | psPAX2 | Addgene | Plasmid # 12260 RRID:Addgene_ 12260 | Trono Lab Packing and Envelope Plasmids |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMD2.G | Addgene | Plasmid# 12259 RRID:Addgene_ 12259 | Trono Lab Packing and Envelope Plasmids |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | NIH-3T3 | American Type Culture Collection | Cat# CRL-1658 RRID:CVCL_0594 | |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | 54074 | This paper | Derived from MTB;TAN model | |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | 99142 | This paper | Derived from MTB;TAN model | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 293T Ampho | American Type Culture Collection | Cat# CRL-3213 RRID:CVCL_ H716 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 293T Eco | American Type Culture Collection | Cat# CRL-3214 RRID:CVCL_ H717 | |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti- NFκB p65 | Cell Signaling | D14E12 RRID:AB_ 10859369 | 1:1000 (WB) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-p- NFκB p65 | Cell Signaling | 93H1 RRID:AB_ 10827881 | 1:1000 (WB) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti- Tubulin | Santa Cruz | TU-02 RRID:AB_ 628408 | 1:1000 (WB) |
| Antibody | Goat anti-rabbit HRP | Cell Signaling | Cat# 7074 RRID:AB_ 2099233 | 1:5000 (WB) |
| Antibody | Goat anti-mouse HRP | Cell Signaling | Cat# 7076 RRID:AB_ 330924 | 1:5000 (WB) |
| Antibody | Goat anti-rabbit Alexa Flour 680 | Life Technologies | Cat# A21076 RRID:AB_141386 | 1:5000 (WB) |
| Antibody | IRDYE 800CW Goat anti-mouse | LI-COR | Cat# 926–32210 RRID:AB_ 621842 | 1:5000 (WB) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CD45R/B220, APC conjugated | Invitrogen/ eBioscience (Carlsbad, CA) | RA3-6B2 RRID:AB_ 469395 | 1:50 (FC) |
| Antibody | Hamster monoclonal anti-CD49b, AF488 conjugated | BioLegend | HMα2 RRID:AB_ 492851 | 1:200 (FC) |
| Antibody | Hamster monoclonal anti-FcεRIα, PE conjugated | BioLegend | 1-Mar RRID:AB_ 1626104 | 1:50 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-Siglec-F/CD170, PE conjugated | BD | E50-2440 RRID:AB_ 10896143 | 1:200 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-PDGFRα/CD140a, PE conjugated | Invitrogen/ eBioscience | APA5 RRID:AB_ 657615 | 1:100 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CD45, PECy5 conjugated | BD | 30-F11 RRID:AB_ 394612 | 1:200 (FC) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-CD45, APC conjugated | BD | 30-F11 RRID:AB_ 1645215 | 1:200 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat anti-CD45, V50 conjugated | BD | 30-F11 RRID:AB_ 1645275 | 1:200 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-F4/80, AF647 conjugated | BD | T45-2342 RRID:AB_ 2744474 | 1:50 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CD11b, PE conjugated | BD | M1/70 RRID:AB_ 394775 | 1:50 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CD11b, PECy7 conjugated | BD | M1/70 RRID:AB_ 2033994 | 1:100 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-Ly6G, APC conjugated | BD | 1A8 RRID:AB_ 1727560 | 1:200 (FC) |
| Antibody | Hamster monoclonal anti-CD3e, PE conjugated | BD | 145–2 C11 RRID:AB_ 394460 | 1:100 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CD4, APCC7y conjugated | BD | GK1.5 RRID:AB_ 394331 | 1:100 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CD8a, APC conjugated | BD | 53–6.7 RRID:AB_ 398527 | 1:200 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CD16/CD32 Fc Blocker | BD | 2.4G2 RRID:AB_ 394659 | 1:50 (FC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CCR5/CD195, BV421 conjugated | BD | C34-3448 RRID:AB_ 2741677 | 1:100 (FC) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Cytokertin 8 | Troma 1, Brulet, P, Kemler, R Institut Pasteur, Paris, France | Troma 1 RRID:AB_ 531826 | 1:50 (IHC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-CD45 | BD Biosciences | 30-F11 RRID:AB_ 394606 | 1:200 (IHC) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-CD3 | Themo | SP7 RRID:AB_ 1956722 | 1:100 (IHC) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-F4/80 | Bio-Rad | Cl:A3-1 RRID:AB_ 1102558 | 1:1000 (IHC) |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | TNFα, mouse | BioLegend | Cat# 575202 | 10 ng/mL |
| Commercial assay or kit | Trichrome stain | Abcam | ab150686 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Vectastain ABC Kit (Rabbit IgG) | Vector Labs | Cat# PK-6101 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Vectastain ABC Kit (Rat IgG) | Vector Labs | Cat# PK-4004 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNeasy Mini Kit | Qiagen | Qiagen:74106 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | QIAshredder | Qiagen | Qiagen:79656 | |
| Commerical assay or kit | Quantibody Mouse Cytokine Array Q1 | RayBiotech | Cat# QAM-CYT-1–1 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Quantibody Mouse Cytokine Array Q4 | RayBiotech | Cat# QAM-CYT-4 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | IKK16 | Selleckchem | Cat# S2882 | 100 nM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamine 2000 | Life Technologies | Cat# 11668019 | 60 µL per reaction |
| Chemical compound, drug | Polybrene | Sigma | Cat# 107689 | 6 µg/mL |
| Chemical compound, drug | 2x Cell Lysis Buffer | RayBiotech | Cat# AA-LYS | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Luminata Classico/Crescendo Western HRP Substrate | Millipore | Cat#WBLUC0500 Cat# WBLUR0500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Doxycycline | RPI | Cat# D43020-100.0 | 2 mg/kg in vivo and 2 µg/mL in vitro |
| Sequence-based reagent | RT-PCR primers | This paper | CCL5 cDNA into pK1 plasmid | Forward: TAACCTCGAGATGAAGATCTCTGCAGCTG, Reverse: TAACGCGGCCGCCAGGGTCAGAATCAAGAAACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | RT-PCR primers | This paper | CCL5 cDNA into pLenti CMV plasmid | Forward: TAACTCTAGAATGAAGATCTCTGCAGCTG, Reverse: TAACGTCGACCAGGGTCAGAATCAAGAAACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | gRNAs | This paper | Targeting CCL5 | CCL5_1 (TGTAGAAATACTCCTTGACG), CCL5_2 (TACTCCTTGACGTGGGCACG), CCL5_3 (TGCAGAGGGCGGCTGCAGTG) |
| Sequence-based reagent | CCL5 | Thermo | Mm01302427_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | CXCL1 | Thermo | Mm04207460_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | CXCL2 | Thermo | Mm00436450_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | CXCL5 | Thermo | Mm00436451_g1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | CCL2 | Thermo | Mm00441242_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Actin | Thermo | Mm02619580_g1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | ASPN | Thermo | Mm00445945_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | PCOLCE | Thermo | Mm00476608_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | COL5A1 | Thermo | Mm00489299_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | COL24A1 | Thermo | Mm01323744_m1 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Prism (https://graphpad.com) | RRID:SCR_002798 | Version 8 |
| Software, algorithm | JMP Pro | SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC | ||
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo | TreeStar | RRID:SCR_008520 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | Fiji (http://fiji.nih.gov/ | RRID:SCR_002285 | Schindelin et al., 2012 |
-
WB = Western blot, FC = flow cytometry, IHC = immunohistochemistry
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.43653.019





