Evolution of empathetic moral evaluation
Figures
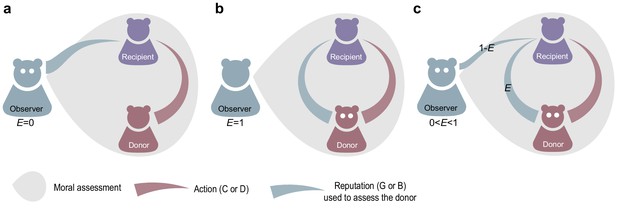
Empathetic and egocentric modes of moral assessment.
An observer updates the reputation of a donor based on the donor’s action towards a recipient and the recipient’s reputation. (a) An egocentric observer () forms a moral judgment based on the recipient’s reputation as seen from her own perspective. (b) An empathetic observer makes a judgment based on the recipient’s reputation in the eyes of the donor (). (c) More generally the empathy parameter corresponds to the probability that observer will assess the donor using the donor’s – not the observer’s – perspective of the recipient’s reputation.
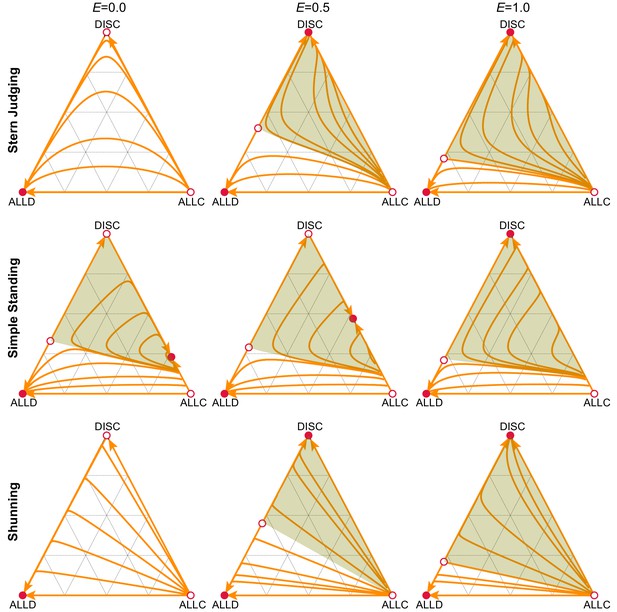
Empathetic moral evaluation facilitates the evolution of cooperation.
We analyzed strategy evolution in the donation game under different social norms of moral assessment. Triangles describe the frequencies of three alternative strategies: unconditional defectors (ALLD), unconditional cooperators (ALLC), and discriminators (DISC) who cooperate with good recipients and defect against bad recipients. Red circles indicate the stable (filled) and unstable (open) strategic equilibria under replicator dynamics. The basin of attraction towards a stable equilibrium that supports cooperation (green) is larger as empathy, , increases, for all three social norms shown. Orange curves illustrate sample trajectories towards stable equilibria. Costs and benefits are , , and error rates are .

Cooperation rates at the cooperative equilibria of strategy evolution.
For Stern Judging (SJ) and Shunning (SH) norms the cooperative equilibrium (when it exists) corresponds to a homogeneous population of DISC players, while for Simple Standing (SS) and Scoring (SC) it consists of a mixture of ALLC and DISC strategists. , .
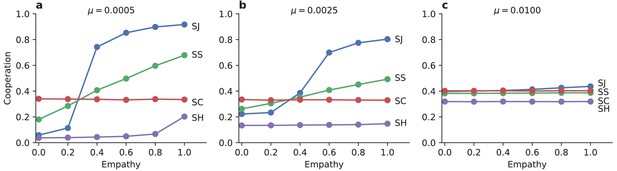
Empathetic moral judgment facilitates cooperation.
The degree of empathy, , determines which social norms of moral assessment produce the most cooperation and thus the greatest social benefit. (a) The Stern Judging (SJ) norm supports the highest rate of cooperation when empathy is high. But Stern Judging performs poorly under egocentric moral judgment, where Scoring (SC) and Simple Standing (SS) produce greater levels cooperation. The scoring norm (SC) does not depend on reputations, and so it shows cooperation levels that are insensitive to the level of empathy. The Shunning norm (SH) always produces the lowest level of cooperation. (b, c) As the strategy exploration rate increases, Stern Judging and Simple Standing become less efficient at promoting cooperation under highly empathetic moral evaluation, but they perform better under egocentric evaluation. All panels show ensemble mean cooperation levels in replicate Monte Carlo simulations of individuals. Similar results hold in a continuous strategy space (see Figure 3—figure supplement 1).

Mean cooperation rates with continuous strategies.
The figure shows results of Monte Carlo simulations assuming a continuous strategy space , with mutations sampled uniformly. The qualitative results agree with those reported in Figure 3 for discrete strategies: Stern Judging (SJ) produces the highest rates of cooperation when empathy is high, but it performs poorly under non-empathetic moral evaluation. , , .
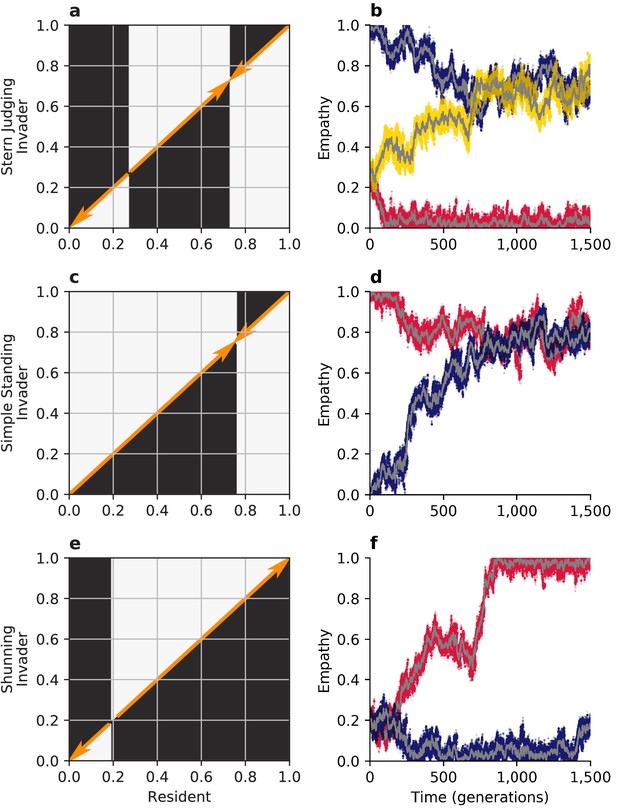
Evolution of empathy.
The figure summarizes analytical predictions for empathy evolution under three different social norms, using adaptive dynamics in a population of discriminators, compared to Monte Carlo simulations in finite populations. (a, c, e) White areas in the pairwise invasibility plots show values of for which the invader’s expected payoff exceeds the mean payoff of the resident population. Orange arrows indicate the direction of predicted evolution. (b, d, f) Monte Carlo simulations in small populations of 100 individuals with recurring mutations to reflect the predictions of adaptive-dynamics analysis. For each norm, sample trajectories showing all values in three independent populations are show in colors (red, blue, yellow), with the population means shown in gray.
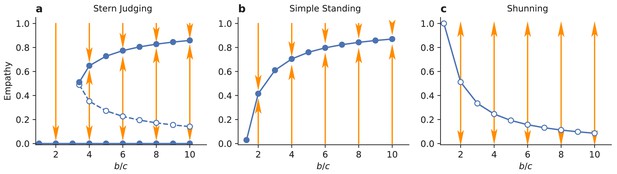
Evolutionary stability of empathy.
Circles indicate evolutionarily stable (solid) and unstable (open) singular values of empathy, , in an infinite population of discriminator strategists. (a) Above a critical benefit-cost ratio , increasing the benefit of cooperation promotes the evolution of high levels of empathy under Stern Judging norm. (b) Under Simple Standing there is a single ESS value for empathy. The highest levels of empathy evolve with high benefits and low costs of cooperation. However, in this case the monomorphic discriminator equilibrium is not stable at the ESS value of empathy. (c) In populations governed by the Shunning norm there are no stable internal equilibria for , and empathy will evolve to either one or zero.
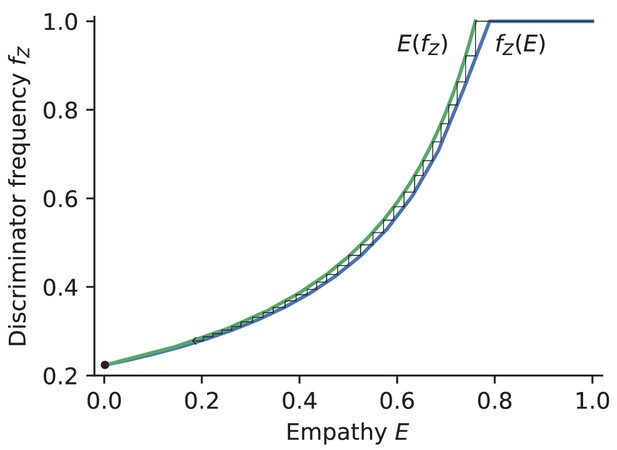
Empathy-strategy co-evolution in an infinite population under Simple Standing norm.
The figure combines the equilibria analysis in the replicator dynamics for strategy evolution given fixed empathy, ; and singular-point analysis in pairwise invasibility plots for empathy evolution, . We make no assumption about the timescales of the two mutational processes. The only fixed point across the two models is .
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44269.011
-
Source data 1
Zip folder with data for all figures, code to produce the figures from these data, and the simulation code that generated the data.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44269.012





