A tRNA modification balances carbon and nitrogen metabolism by regulating phosphate homeostasis
Figures
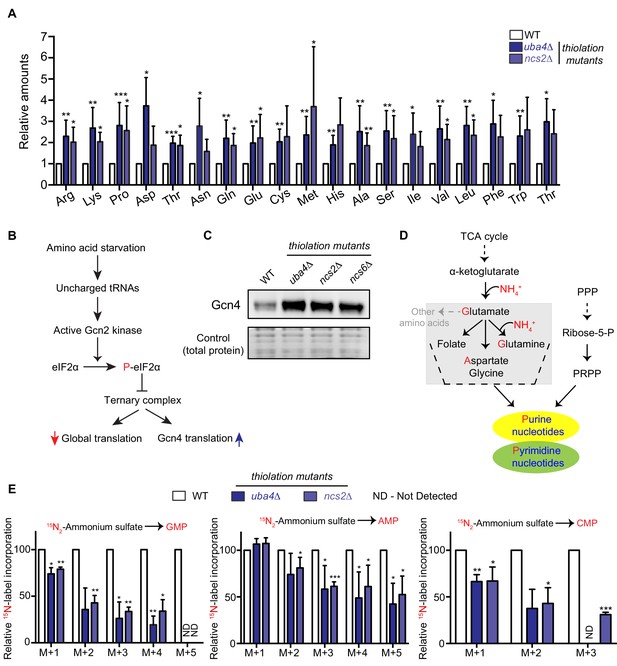
Amino acid and nucleotide metabolism are decoupled in tRNA thiolation deficient cells.
(A) Intracellular pools of amino acids are increased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Steady-state amino acid amounts were measured in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media by targeted liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Amino acid levels in tRNA thiolation mutant cells relative to WT are plotted, where levels in WT were set to 1. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) to WT. Data are displayed as mean ± SD, n >= 3. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (B) A schematic representation illustrating the induction of Gcn4 translational upon amino acid starvation, as mediated by the Gcn2 kinase, and phosphorylation of the eIF2α initiation factor. (C) Gcn4 protein is increased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Western blots indicating Gcn4 protein levels (Gcn4 tagged with HA epitope at the endogenous locus) in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ, ncs2Δ and ncs6Δ) grown in minimal media, as detected using an anti-HA antibody. A representative blot obtained from three biological replicates (n = 3) is shown. Also see Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (D) A schematic representation of de novo nucleotide (purine and pyrimidine) biosynthesis from its precursors- amino acids, the pentose phosphate pathway and PRPP (5-Phopsphoribosyl-1-Pyrophosphate), and the folate/one-carbon pathway. (E) Nucleotide synthesis is decreased in tRNA thiolation mutants (nitrogen label). WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were pulse-labelled with 15N2-labelled ammonium sulfate for 90 min to measure newly synthesized nucleotides (GMP, AMP and CMP) using targeted LC-MS/MS. The incorporation of 15N atoms from 15N2-labelled ammonium sulfate into nucleotides is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 15N-labelled atoms. Label incorporation in tRNA thiolation mutant cells relative to WT is plotted, where label incorporation in WT was set to 100. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) to WT. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3 for AMP and CMP, n = 2 for GMP. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Also see Figure 1—figure supplement 2A,B and D.
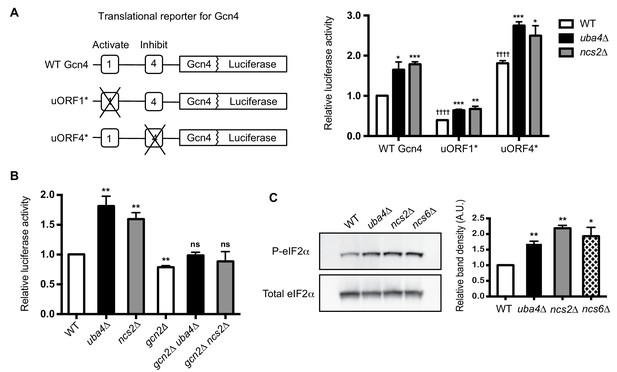
Gcn2-dependent translational induction of Gcn4 in tRNA thiolation deficient cells.
(A) GCN4 translation is increased in tRNA thiolation mutants. A schematic representation of different Gcn4-luciferase (Gcn4-luc) translational reporter constructs. Two upstream ORFs in the 5’ UTR of Gcn4, uORF1 and uORF4, which activate and inhibit GCN4 translation respectively are highlighted. This 5’ UTR is fused to first 55 amino acids of Gcn4, followed by luciferase cDNA. Wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) transformed with different Gcn4-luciferase translational reporter constructs were grown in minimal media and luciferase assay was performed. Relative luciferase activity is plotted, where luciferase activity in WT transformed with WT Gcn4-luc construct was set to 1. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) to WT. † denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing WT transformed with uORF1* and uORF4* constructs to WT transformed with WT Gcn4-luc construct. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 4. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ††††p<0.0001. (B) GCN4 translation is Gcn2-dependent in tRNA thiolation mutants. Wild-type (WT), tRNA thiolation mutants (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ), gcn2Δ, gcn2Δ uba4Δ and gcn2Δ ncs2Δ cells transformed with WT Gcn4-luc construct were grown in minimal media and luciferase assay was performed. Relative luciferase activity is plotted, where luciferase activity in WT was set to 1. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3. ns denotes non-significant difference. **p<0.01, Student’s t-test, comparing all samples to WT. (C) Phosphorylated eIF2α (P-eIF2α) protein levels are increased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Western blots indicating P-eIF2α and total eIF2α (Sui2 tagged with FLAG epitope at the endogenous locus) protein levels in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ, ncs2Δ and ncs6Δ) grown in minimal media, as detected using anti-phospho eIF2α and anti-FLAG antibodies respectively. A representative blot obtained from three biological replicates (n = 3) is shown. Relative band density in arbitrary units (A.U.) is plotted. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
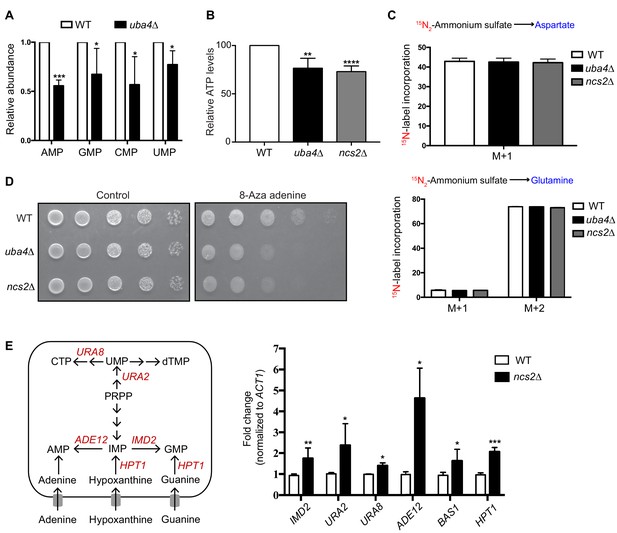
Amino acid and nucleotide measurements in tRNA thiolation deficient cells.
(A) Intracellular levels of nucleotides are decreased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Steady-state nucleotide (AMP, GMP, CMP and UMP) amounts were measured in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant (uba4Δ) grown in minimal media using targeted LC-MS/MS. Relative nucleotide levels are plotted, where levels in WT were set to 1. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n >= 3. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, Student’s t-test, comparing all samples to WT. (B) Total cellular ATP levels are decreased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Steady-state ATP levels were measured in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ). Relative ATP levels are plotted, where levels in WT were set to 100. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 4. **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001, Student’s t-test, comparing all samples to WT. (C) Amino acid synthesis is unaffected in tRNA thiolation mutants. Wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were pulse-labelled with 15N2-labelled ammonium sulfate, and labelled (newly synthesized amino acids- aspartate and glutamine) were measured using targeted LC-MS/MS. Percent label incorporation in wild-type and tRNA thiolation mutant cells was plotted. The incorporation of 15N atoms from 15N2-labelled ammonium sulfate into amino acids is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 15N-labelled atoms. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3 for aspartate and n = 2 for glutamine. (D) tRNA thiolation mutants exhibit increased sensitivity to 8-azaadenine. Wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were spotted on minimal media agar plates containing 300 μg/ml 8-Aza adenine. (E) Expression of nucleotide biosynthetic genes is increased in thiolation mutants. A schematic representation of nucleotide biosynthesis-related genes, and their roles. Fold change in expression of genes associated with nucleotide biosynthetic pathway (IMD2, URA2, URA8, ADE12, BAS1 and HPT1) in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ) is plotted. In general, these genes were upregulated in tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ).
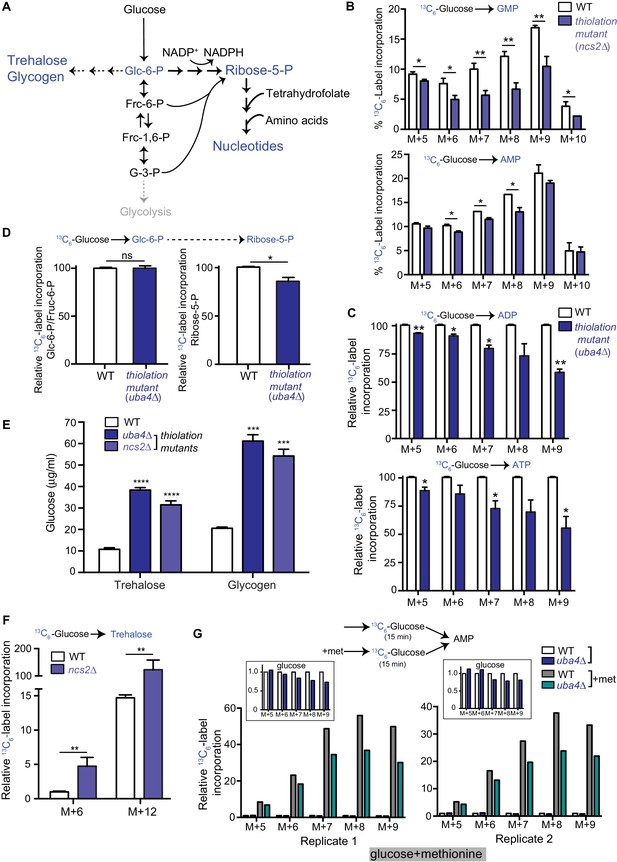
Carbon flux is routed towards storage carbohydrates in thiolation mutants.
(A) Schematic representation depicting nucleotide and storage carbohydrates (trehalose and glycogen) biosynthesis, starting from a common precursor, glucose-6-phosphate. In normal conditions where carbon and nitrogen are not limiting, flux is typically higher towards the pentose phosphate pathway (ribose-5-phosphate), and eventually nucleotides. (B) Nucleotide synthesis is decreased in tRNA thiolation mutant (carbon label). WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were pulse-labelled with [U-13C6]-labelled glucose for 10 min, and quenched, and newly synthesized nucleotides (GMP, AMP) were measured, using LC-MS/MS. Percent label incorporation in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells was plotted. The incorporation of 13C atoms from [U-13C6]-labelled glucose into nucleotides is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 13C-labelled atoms (with all five carbons labelled in the ribose sugar). * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test) of relevant data comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ) to WT. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3 for GMP and n = 2 for AMP. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Also see Figure 2—figure supplement 1A. (C) ADP and ATP synthesis is decreased in the thiolation mutant. WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ) grown in minimal media were pulse-labelled with [U-13C6]-labelled glucose for 10 min, quenched, and newly synthesized ADP and ATP were measured, using LC-MS/MS. Relative label incorporation in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells are shown, where label amounts in WT cells is set to 1. The incorporation of 13C atoms from [U-13C6]-labelled glucose into nucleotides is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 13C-labelled atoms (with all five carbons labelled in the ribose sugar). * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test) of relevant data comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ) to WT. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (D) PPP flux is decreased in the tRNA thiolation mutant. WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ) grown in minimal media were pulse-labelled with [U-13C6]-labelled glucose for 2 min, quenched and collected, and early (glucose-6-phosphate) and late (ribose-5-phosphate) PPP intermediates were measured by LC-MS/MS. Relative 13C6-label incorporation into these metabolites are shown. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 2. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Student’s t-test. Also see Figure 2—figure supplement 1B. (E) Steady-state trehalose and glycogen amounts are increased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Trehalose and glycogen content of WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media was plotted. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) to WT. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 4 biological replicates with two technical replicates each for trehalose, and n = 3 biological replicates with two technical replicates each for glycogen. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Also see Figure 2—figure supplement 1C. (F) Trehalose synthesis is increased in tRNA thiolation mutant. WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were pulse-labelled with [U-13C6]-labelled glucose for 5 min, quenched, and label incorporation into newly synthesized trehalose was measured using targeted LC-MS/MS. Relative label incorporation into trehalose in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells is shown, where label in WT M + 6 is set to 1. The incorporation of 13C atoms from [U-13C6]-labelled glucose into trehalose is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 13C-labelled atoms. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ) to WT. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (G) Thiolation mutants exhibit reduced methionine-induced carbon incorporation into nucleotides. WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ) were grown in standard minimal media, 2% glucose, with or without 2 mM methionine (met) supplemented. Cells were pulse-labelled with [U-13C6]-labelled glucose for 15 min, and metabolites extracted. Here, carbon incorporation into newly synthesized nucleotides (AMP) was measured, using LC-MS/MS. The relative label incorporation in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells with or without methionine is shown, where label in WT in the absence of methionine is set to 1. Two independent biological replicates (replicate 1 and 2) are shown. The relative label incorporation in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells growing in standard minimum medium (without methionine supplementation) is shown as an inset, to suitably illustrate the strong induction in nucleotide synthesis due to methionine supplementation. The incorporation of 13C atoms from [U-13C6]-labelled glucose into nucleotides is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 13C-labelled atoms (with all five carbons labelled in the ribose sugar). Also see Figure 2—figure supplement 2D.

Carbon flux is routed away from nucleotides and towards storage carbohydrates in tRNA thiolation deficient cells.
(A) Nucleotide synthesis is decreased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were pulse-labelled with [U-13C6]-labelled glucose for 5 min to measure newly synthesized nucleotides (GMP and AMP) using targeted LC-MS/MS. Percent label incorporation in wild-type and tRNA thiolation mutant cells was plotted. The incorporation of 13C atoms from [U-13C6]-labelled glucose into nucleotides is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 13C-labelled atoms (with all five carbons labelled in the ribose sugar). Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 4 for GMP and n = 2 for AMP. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, Student’s t-test, comparing all samples to WT. (B) Glycolytic and pentose phosphate pathway intermediates are unchanged in thiolation mutant cells. Wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were pulse-labelled with [U-13C6]-labelled glucose for 5 min to measure newly synthesized glycolytic and pentose phosphate pathway intermediates (2/3-phosphoglycerate, 6-phosphogluconate, ribose-5-P/ribulose-5-P, sedoheptulose-7-P) using targeted LC-MS/MS. Percent label incorporation in wild-type and tRNA thiolation mutant cells was plotted. The incorporation of 13C atoms from [U-13C6]-labelled glucose into these sugar phosphates is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 13C-labelled atoms. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3. (C) Steady-state trehalose and glycogen amounts are increased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Colorimetric assay 96-well images for trehalose and glycogen content of wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media is shown. Images are shown for n = 3 biological replicates. (D) Thiolation mutants exhibit reduced methionine-induced carbon incorporation into nucleotides. WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ) grown in standard minimal medium (2% glucose), with or without 2 mM methionine (met) supplementation, were pulse-labelled with [U-13C6]-labelled glucose for 15 min and metabolites extracted. Here, newly synthesized nucleotides (GMP) were measured, using LC-MS/MS. The relative label incorporation in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells with or without methionine is shown, where label in WT in the absence of methionine is set to 1. Two independent biological replicates (replicate 1 and 2) are shown. The incorporation of 13C atoms from [U-13C6]-labelled glucose into nucleotides is represented as M + n, where n is the number of 13C-labelled atoms (with all five carbons labelled in the ribose sugar).

Sulfur starvation phenocopies the metabolic state of thiolation mutants.
(A) A schematic representation illustrating the experimental design for sulfur starvation. Wild type cells growing in standard glucose medium were shifted to sulfur-rich and sulfur-starved/sulfur amino acid limited conditions. From appropriate cell extracts, metabolites were analyzed by LC/MS/MS or enzyme assays, to estimate amino acids, nucleotides (AMP), or, trehalose, and luciferase assays were performed to measure GCN4 translation. (B) Intracellular levels of sulfur amino acid metabolites decrease in the sulfur-starved condition. Steady-state amounts of sulfur-containing metabolites (methionine, cysteine, SAM and SAH) were measured in wild-type (WT) grown in sulfur-rich and sulfur-starved media using targeted LC-MS/MS. Relative metabolite levels are plotted, where levels in sulfur-rich condition was set to 1. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 4. ****p<0.0001, Student’s t-test, comparing sulfur limited to sulfur-rich condition. (C) In WT cells, intracellular pools of amino acids increase in the sulfur-starved condition, similar to tRNA thiolation mutants. Steady-state amino acid amounts were measured in wild-type (WT) grown in sulfur-rich and sulfur-starved media using targeted LC-MS/MS. Relative amino acids are plotted, where level in sulfur-rich condition was set to 1. Data are displayed as mean ± SD, n >= 3. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, Student’s t-test, comparing sulfur limited to sulfur-rich condition. Amino acid amounts in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant were re-plotted from Figure 1A for comparison. (D) In WT cells, intracellular levels of nucleotides decrease in the sulfur-starved similar to tRNA thiolation mutants. Steady-state nucleotide (AMP) amounts were measured in wild-type (WT) grown in sulfur rich and sulfur-starved media using targeted LC-MS/MS. Relative nucleotide levels are plotted, where levels in sulfur-rich condition was set to 1. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 2. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, Student’s t-test, comparing sulfur limited to sulfur-rich condition. Nucleotide amounts in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant were re-plotted from Figure 1—figure supplement 2A for comparison. (E) In WT cells, steady-state trehalose amounts increase in the sulfur-starved condition, similar to tRNA thiolation mutants. Trehalose content of WT grown in sulfur-rich and sulfur-starved medium was plotted. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3 biological replicates with three technical replicates. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, Student’s t-test, comparing sulfur limited to sulfur-rich condition. Trehalose amounts in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant were re-plotted from Figure 2E for comparison. (F) In WT cells, GCN4 translation increases in sulfur amino acid (methionine and cysteine) limited conditions similar to tRNA thiolation mutants. Wild-type (WT) transformed with Gcn4-luciferase translational reporter construct was grown in sulfur amino acid replete media and subsequently shifted to sulfur amino acid limited media for 1 hr and luciferase assay was performed. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 4. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, Student’s t-test. GCN4 translation in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant were re-plotted from Figure 1—figure supplement 1A for comparison.
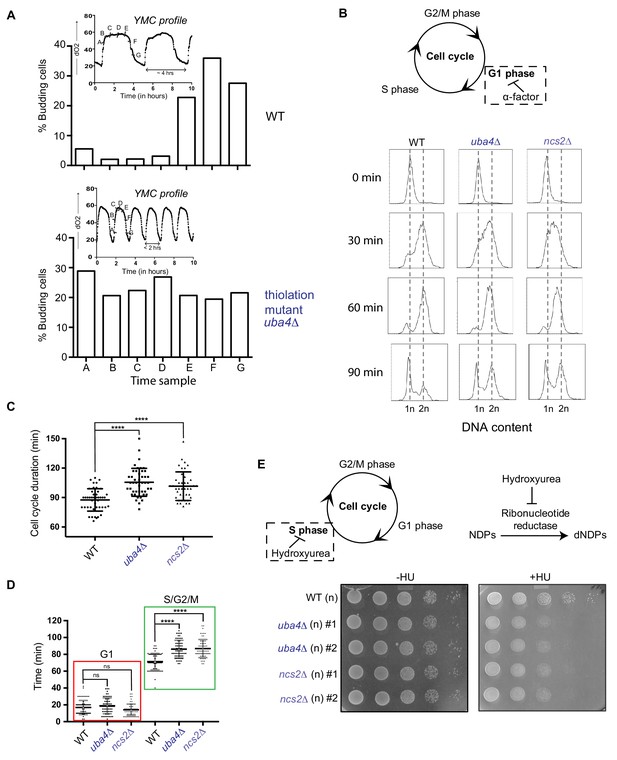
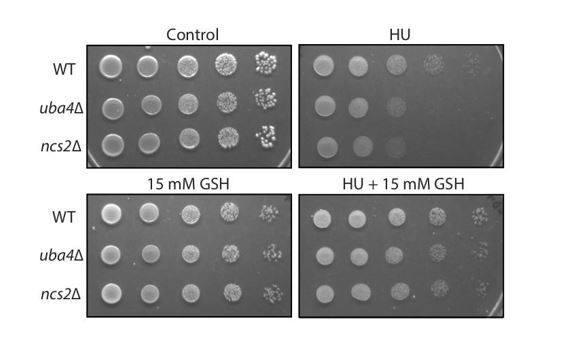
tRNA thiolation couples cellular metabolic state with normal cell cycle progression.
(A) tRNA thiolation mutants exhibit asynchronous cell division and disrupted yeast metabolic cycles. WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ) growing in chemostat cultures under conditions of normal yeast metabolic cycles, were sampled at 20 min time intervals. Percentage of budded cells represents the fraction of cells in S/G2/M phases of the cell cycle. At least 200 cells were analysed for each time point, for the respective strains. Inset: the oxygen consumption profiles of WT and tRNA thiolation mutant metabolic cycles are represented. Note that the metabolic cycles of thiolation mutants are disrupted. (B) tRNA thiolation mutants show delayed cell cycle progression. The DNA content of WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media, during G1 arrest (0 min) and after release from G1 arrest (30, 60 and 90 min) was determined by flow cytometry analysis, and is presented. (C and D) Cell cycle duration, distribution of G1 phase duration (red) and S/G2/M phase durations (green) for WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) were measured in single cells using time lapse live-cell microscopy. The G1 duration (starting from the time of complete division of mother and daughter cells to bud emergence), and S/G2/M durations (from the time of bud emergence to complete division of mother and daughter cells) were determined for only first generation mother cells. At least 100 cells were analysed for each strain. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) to WT. ns denotes non-significant difference. ****p<0.0001. (E) tRNA thiolation mutants exhibit increased HU sensitivity. WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were spotted on minimal media agar plates containing 150 mM HU. Also see Figure 3—figure supplement 1A and B.
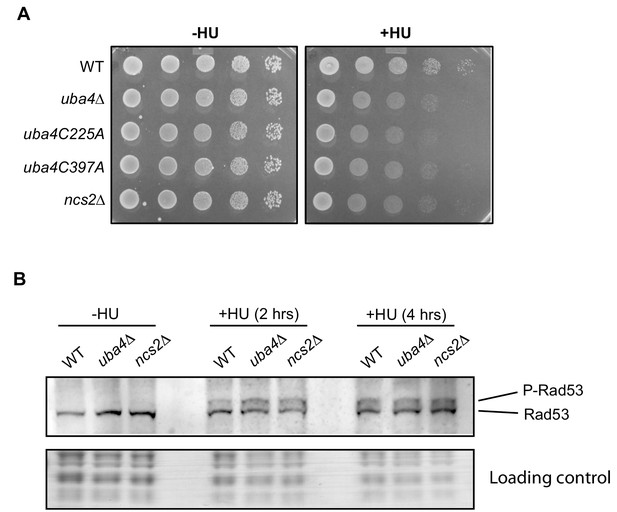
HU sensitivity in tRNA thiolation deficient cells is independent of the Rad53 checkpoint pathway.
(A) Catalytically dead uba4 mutants (C225A and C397A) exhibit increased HU sensitivity. Wild-type (WT), tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) and catalytically dead uba4 mutant (C225A and C397A) grown in minimal media were spotted on minimal media agar plates containing 150 mM HU. (B) Rad53 activation is not perturbed in tRNA thiolation mutants. Western blots indicating Rad53 phosphorylation levels (P-Rad53) in wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media in the presence or absence of 150 mM HU for 2 and 4 hr, as detected using anti-Rad53 antibody. A representative blot obtained from two biological replicates (n = 2) is shown.
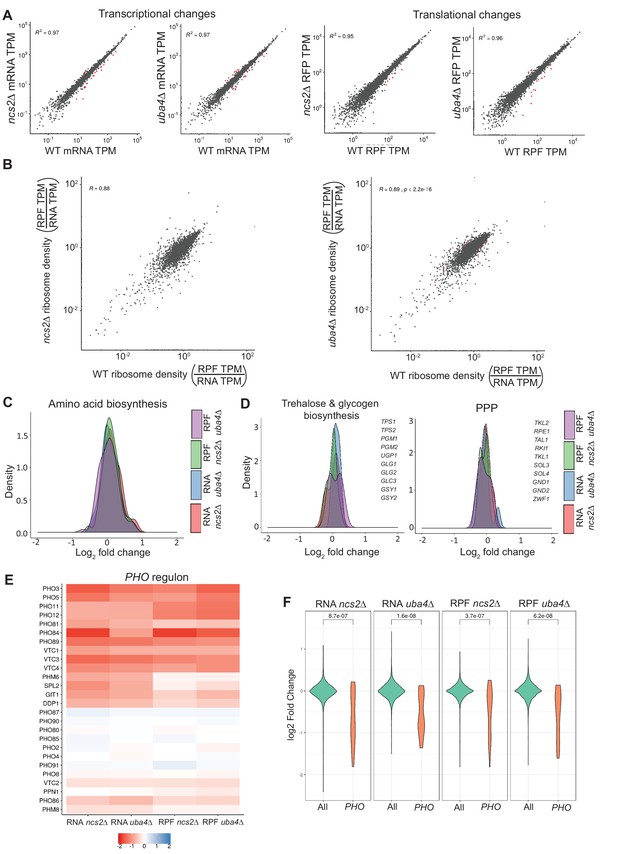
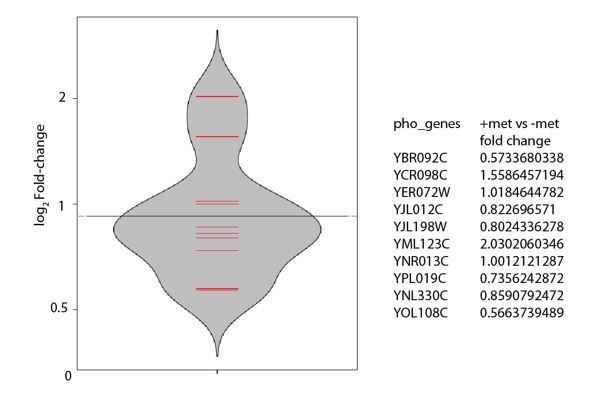
Loss of tRNA thiolation results in reduced phosphate homeostasis (PHO)-related transcripts and ribosome-footprints.
(A) Correlation plots are shown, for WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (ncs2Δ and uba4Δ), for both gene expression (transcript) and ribosome footprint (translation) changes. The coefficients of determination (R2) values are indicated, along with their significance (p values). Note: Very few differentially regulated genes were observed, and these are indicated as red points. Also see Figure 4—figure supplement 1. (B) Correlation plots comparing ribosome densities (RPF TPM/RNA TPM) for the thiolation mutants (ncs2Δ or uba4Δ respectively) with WT cells. Note: overall ribosome densities for thiolation mutants correlate exceptionally well with ribosome densities in WT cells, with the correlation coefficients (R) > 0.88 in both comparisons. Also see Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for correlations between biological replicates of the same genetic background. (C) A density plot, representing changes in expression (transcript and ribosome footprints) of genes associated with amino acid biosynthetic pathways. In general, amino acid biosynthesis genes were upregulated in tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ). Also see Figure 4—figure supplement 3C. (D) A density plot, representing changes in expression (transcript and ribosome footprints) of genes associated with trehalose and glycogen biosynthetic pathways, and the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). In general, trehalose, glycogen biosynthesis and PPP genes were unchanged in tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ), compared to WT cells. Also see Figure 4—figure supplement 3C (E) Heat map depicting changes in expression (transcript and ribosome footprints) of genes associated with the phosphate (PHO) regulon, in the tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ), compared to WT cells, at the transcript and ribosome-footprint levels (log2 2-fold changes). (F) A density plot with a statistical comparison between WT and tRNA thiolation mutants, for changes in transcript or ribosome footprints of all genes in the genome, or only the PHO regulon. Note: p<10−7 for all the comparison datasets. Also see Figure 4—figure supplement 3C.
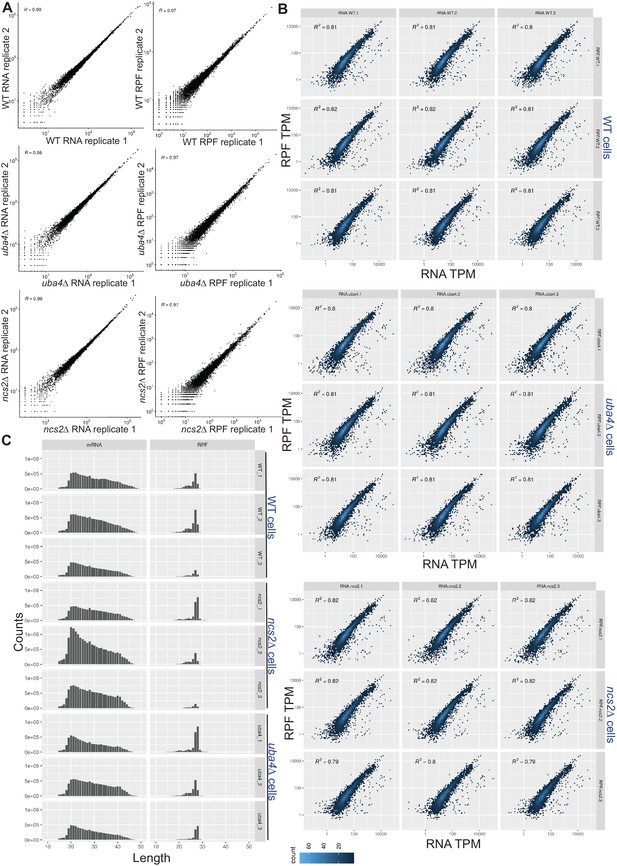
Transcript and ribosome footprint profiles in wild-type and tRNA thiolation mutant cells.
(A) Correlation plots, for RNA (transcript) or ribosome footprint (RPF), between biological replicates, of WT, or thiolation mutant cells. Note, correlation coefficients (R) for any replicate of the same genetic background was >0.97. (B) Correlation plots, for gene expression (transcript) and ribosome footprint (translation) changes for wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) are shown. The plots with R2 values are shown for n = 3 biological replicates for each strain. R2 values were all >0.8 for any sample. (C) The frequency distribution of mRNA and ribosome-protected fragment (RPF) lengths (nt) for wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) are shown for n = 3 biological replicates for each strain.

Gene expression (transcript) and ribosome footprint (translation) changes for wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells.
(A) Changes in the ribosome density based on codon occupancy are shown at A, P, and E sites. Different codons are highlighted in both plots. n = 3 biological replicates for each strain are plotted. (B) Gcn4 translation is increased in tRNA thiolation mutant cells. Ribosome occupancy for the GCN4 ORF and its four upstream ORFs (uORFs) (represented by grey boxes) present in the 5’ UTR are shown. (C) Gcn4 mRNA is unchanged in tRNA thiolation mutant cells. mRNA reads for the GCN4 ORF and its four upstream ORFs (uORFs) (represented by grey boxes) present in the 5’ UTR are shown.

Gene expression and ribosome footprint changes for wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells in PHO regulon, ribosomal subunits, PPP, trehalose/glycogen, nucleotide and amino acid synthesis genes.
(A) Heat maps representing changes in expression (transcript and ribosome footprints) of genes involved in nucleotide biosynthesis, for wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ). (B) Heat maps representing changes in expression (transcript and ribosome footprints) of genes involved in ribosomal large and small subunit genes, for wild-type (WT) and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ). (C) A composite violin plot, for all changes in transcript or ribosome footprints, for groups of genes in the PHO regulon, ribosomal subunits, genes in the PPP or trehalose/glycogen synthesis, nucleotide synthesis, and amino acid synthesis, comparing tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) with WT cells.
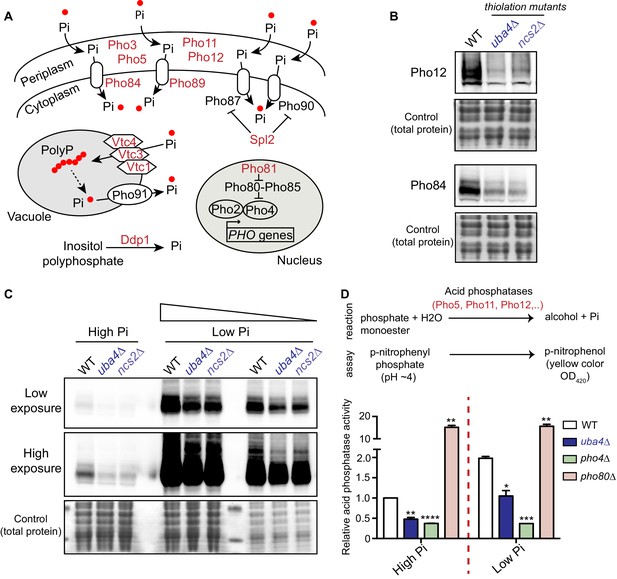
tRNA thiolation mutants exhibit a dampened PHO response.
(A) A schematic representation of PHO regulon-related genes, and their roles. Pho84 and Pho89 are high affinity phosphate transporters, Pho87 and Pho90 are low affinity phosphate transporters, Spl2 is a negative regulator of low affinity phosphate transporters, Pho3, Pho5, Pho11 and Pho12 are secreted acid phosphatases, Pho80-Pho85 is a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) complex, Pho81 is a CDK inhibitor, Pho2 and Pho4 are transcription factors, Vtc1, Vtc3 and Vtc4 are involved in vacuolar polyphosphate accumulation, Pho91 is a vacuolar phosphate transporter, Ddp1 and Ppn1 are polyphosphatases. Proteins highlighted in red are down-regulated in tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ). (B) Pho12 and Pho84 proteins are decreased in tRNA thiolation mutants. Pho12 and Pho84 protein levels (Pho12 and Pho84 tagged with FLAG epitope at their endogenous loci) in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in minimal media were detected by Western blot analysis using an anti- FLAG antibody. A representative blot is shown (n = 3). (C) Pho84 protein is decreased in tRNA thiolation mutants in both high and low Pi conditions. Pho84 protein levels (the carboxy-terminus of Pho84 tagged with a FLAG epitope at its endogenous locus) in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in high and low Pi media were detected and compared by Western blot analysis using an anti- FLAG antibody. For high and low Pi condition comparisons, the same amount of total protein was loaded in each lane of the SDS-PAGE gel. For low Pi, two different concentrations of total protein (undiluted and 1:3 diluted) were loaded, since the PHO-related proteins are strongly induced in this condition, and hence a dilution is required to visualize a non-saturated image. A representative blot is shown (n = 2). Also see Figure 5—figure supplement 1A. (D) Acid phosphatase activity is decreased in tRNA thiolation mutants. A schematic representation of the acid phosphatase reaction, and the colorimetric assay used to study this reaction, is shown. This quantitatively measures the collective intracellular activity of the PHO acid phosphatases Pho5, Pho11, Pho12 and Pho3. Acid phosphatase activity was determined in WT, tRNA thiolation mutant (uba4Δ), pho4Δ and pho80Δ in both high and low Pi media conditions, using this assay. Acid phosphatase activity was plotted relative to WT grown in high Pi, which was set to 1. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing all samples to WT in both high and low Pi condition. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 2 biological replicates with three technical replicates each. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
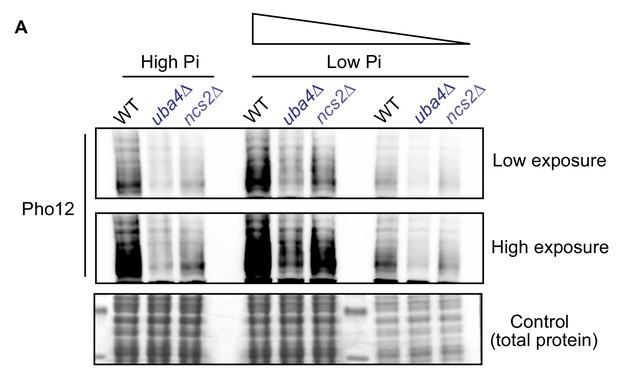
tRNA thiolation mutants exhibit a dampened PHO response.
(A) Pho12 protein is decreased in tRNA thiolation mutants in high and low Pi conditions. Using cells expressing endogenous Pho12 with a FLAG epitope at its carboxy-terminus, Pho12 protein levels in WT and tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) grown in high and low Pi media were detected and compared by Western blot analysis using an anti- FLAG antibody. For high and low Pi condition comparisons, the same amount of total protein was loaded in each lane of the SDS-PAGE gel. For low Pi, two different concentrations of total protein (undiluted and 1:3 diluted) were loaded, since the PHO-related proteins are strongly induced in this condition, and hence a dilution is required to visualize a non-saturated image. A representative blot is shown (n = 2).
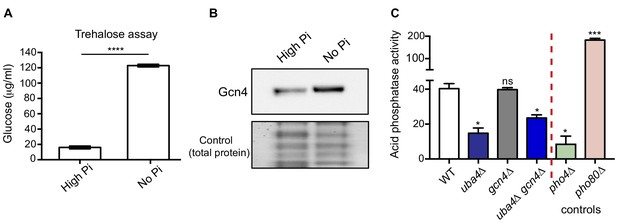
Phosphate depletion in wild-type cells phenocopies tRNA thiolation mutants.
(A) Trehalose amounts are increased upon phosphate starvation. Trehalose content of WT cells grown in high and no Pi media was plotted. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3. ****p<0.0001. (B) Gcn4 protein is increased upon phosphate starvation. Gcn4 protein levels (Gcn4 tagged with HA epitope at the endogenous locus) in WT grown in high and no Pi media were detected by Western blot analysis using an anti-HA antibody. A representative blot is shown (n = 3). (C) Cells lacking Uba4 and Gcn4 (uba4Δ gcn4Δ) also show decreased acid phosphatase activity. Acid phosphatase activity was determined in WT, tRNA thiolation mutant (uba4Δ), gcn4Δ, uba4Δ gcn4Δ, pho4Δ and pho80Δ grown in high Pi media conditions supplemented with amino acids, by a colorimetric assay. Note that loss of Gcn4 alone has no effect on acid phosphatase activity. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing all samples to WT. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n = 3 biological replicates (with three technical replicates each). ns denotes non-significant difference. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.
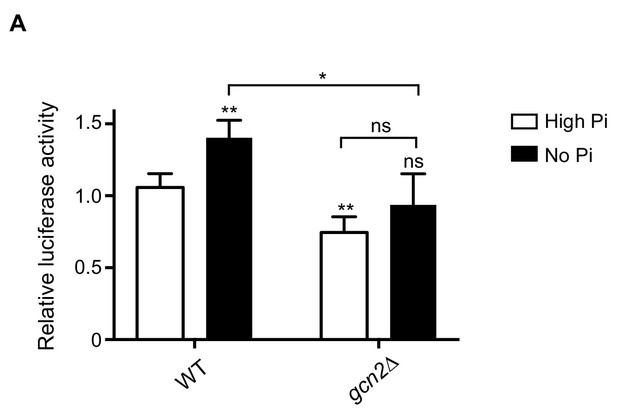
Gcn2-dependent translational induction of Gcn4 during phosphate starvation.
(A) GCN4 translation is Gcn2-dependent in phosphate-starved wild-type cells. Wild-type (WT) and gcn2Δ cells transformed with the WT Gcn4-luc construct were grown in high and no phosphate medium supplemented with amino acids and 2% glucose. Luciferase activity was measured, to estimate Gcn4 translation. Relative luciferase activity is plotted, where luciferase activity in WT in high Pi media was set to 1. Data are displayed as means ± SD, n >= 3. ns denotes non-significant difference. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Student’s t-test, comparing all samples to WT in high Pi media, or as indicated.
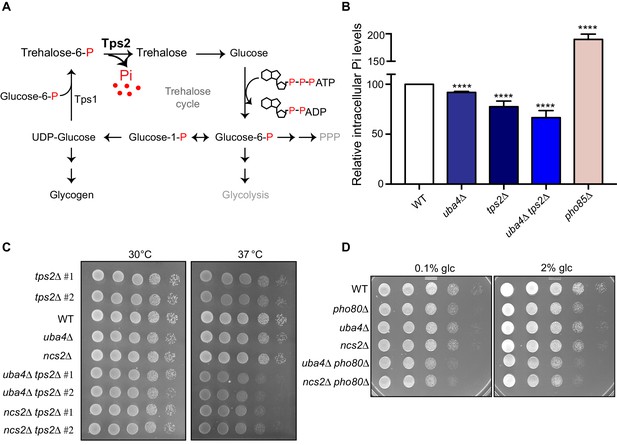
Trehalose synthesis associated phosphate release enables cells to maintain phosphate balance.
(A) A schematic representation of the trehalose cycle, showing the routing of glucose-6-phospate towards trehalose and glycogen biosynthesis. Trehalose synthesis requires two glucose molecules, catalysed by the Tps1 and Tps2 enzymes. The Tps2-mediated reaction synthesizes trehalose, and notably releases free Pi. (B) Intracellular Pi levels are maintained in tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ) by Tps2 activity. Free intracellular Pi levels were determined in WT, tRNA thiolation mutant (uba4Δ), tps2Δ, uba4Δ tps2Δ and pho85Δ cells grown in minimal media, by a colorimetric assay. Intracellular Pi levels in mutant cells relative to WT are plotted, where WT was set to 100. Data are displayed as means ± SD, at least n = 2 biological replicates with three technical replicates each. ****p<0.0001, Student’s t-test, comparing all samples to WT. Also see Figure 7—figure supplement 1A. (C) Synthetic genetic interaction between TPS2 and tRNA thiolation genes (UBA4 and NCS2) at 37° C. WT, tRNA thiolation mutants (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ), tps2Δ, uba4Δ tps2Δ and ncs2Δ tps2Δ double mutant cells grown in minimal media were spotted on low Pi media agar plates with 2% glucose and incubated at 30° C and 37° C. Also see Figure 7—figure supplement 1B. (D) Synthetic genetic interaction between PHO80 and tRNA thiolation genes (UBA4 and NCS2). WT, tRNA thiolation mutants (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ), pho80Δ, uba4Δ pho80Δ and ncs2Δ pho80Δ double mutant cells grown in minimal media (0.1% glucose) were spotted on minimal media agar plates (0.1% and 2% glucose) and incubated at 30° C.
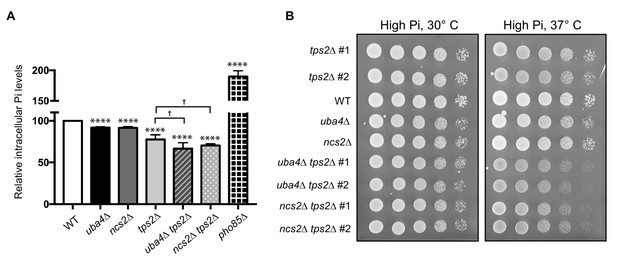
Tps2 maintains phosphate balance in tRNA thiolation deficient cells.
(A) Intracellular Pi levels are maintained in tRNA thiolation mutant cells (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ) by Tps2 activity. Free intracellular Pi levels were determined in wild-type (WT), tRNA thiolation mutants (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ), tps2Δ, uba4Δ tps2Δ, ncs2Δ tps2Δ and pho85Δ cells grown in minimal media, by a colorimetric assay. Intracellular Pi levels in mutant cells relative to wild-type are plotted, where wild-type was set to 100. * denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing mutant cells to WT. † denotes statistical significance (Student’s t-test), comparing tps2Δ to double mutants (uba4Δ tps2Δ, ncs2Δ tps2Δ). Data are displayed as means ± SD, at least n = 2 biological replicates with three technical replicates each. †p<0.05, ****p<0.0001. (B) Synthetic genetic interaction between TPS2 and tRNA thiolation genes (UBA4 and NCS2). Wild-type (WT), tRNA thiolation mutants (uba4Δ and ncs2Δ), tps2Δ, uba4Δ tps2Δ and ncs2Δ tps2Δ double mutant cells grown in minimal media till OD600 - 0.8–1.0 were spotted on high Pi media agar plates and incubated at 30° C and 37° C.
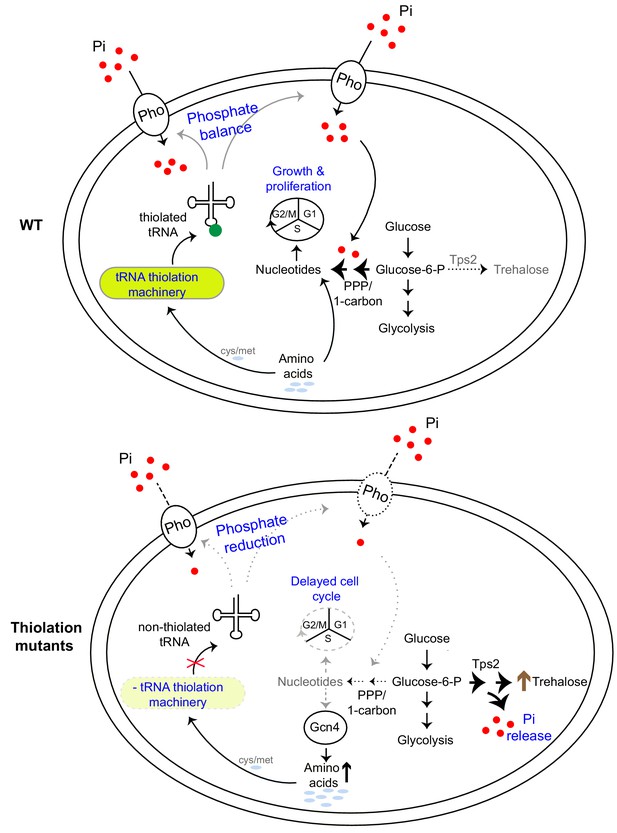
A model illustrating how tRNA thiolation regulates the metabolic state of the cell.
WT cells (which have a functional tRNA thiolation machinery) in amino acid (methionine and cysteine) replete conditions have high amounts of thiolated tRNAs. In these cells, carbon flux coupled with amino acid utilization is towards nucleotide biosynthesis. Sufficient nucleotide levels support growth, and proper cell cycle progression, and reflect an overall ‘growth’ metabolic state. The absence of the tRNA thiolation machinery results in non-thiolated tRNAs, and here carbon flux is driven away from nucleotide synthesis and towards storage carbohydrates, with a concurrent accumulation of amino acids. This metabolic rewiring in these mutants is due to reduced expression of genes involved in phosphate-responsive signalling pathway (a dampened PHO response), which results in a phosphate-limited state. Due to this restricted phosphate availability in the thiolation mutants, these cells attempt to restore intracellular phosphate levels through a metabolic rewiring, via Tps2-dependent trehalose synthesis, accompanied by phosphate release. Thus, despite the absence of carbon or nitrogen (amino acid) starvation, the tRNA thiolation mutants exhibit an overall metabolic signature of a ‘starved state’, with decreased nucleotide synthesis and delayed cell cycle progression. Key: Pho: phosphate transporters, Pi: inorganic phosphate, PPP: Pentose Phosphate Pathway, cys: cysteine, met: methionine.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | anti-HA | Roche | Cat# 12CA5 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | anti-phospho eIF2a (Ser51) | Cell Signalling Technology | Cat# 9721S | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-FLAG | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat # F1804-5MG | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | anti-Rad53 yC-19 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat # sc-6749 | WB (>1:1000) |
| Antibody | HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (anti-mouse, anti-rabbit) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat # 7076S Cat # 7074S | WB (1:5000) |
| HPLC column | Synergi 4µ Fusion-RP 80A column (100 × 4.6 mm) | Phenomenex | Cat # 00D-4424-E0 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gcn4-luciferase translation reporters | this study | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein | trehalase | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat # T8778 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | amyloglucosidase | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat # 10115 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | RNAse A | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat # R4875 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | protease solution | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat # P6887 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Glucose estimation kit | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat # GAGO20 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RiboZero | Epicenter | Cat # MRZH116 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | luciferase assay kit | Promega | Cat # E1500 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Maxima SYBRGreen/ROX qPCR Master Mix | Thermo Scientific | Cat # K0222 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ATP estimation kit | Thermo Scientific | Cat # A22066 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SYTOX green | Thermo Scientific (Invitrogen) | Cat # S7020 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | p-nitrophenyl phosphate | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat # N4645 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | bicinchoninic acid assay | Thermo Scientific | Cat # 23225 | |
| Software, algorithm | Prism 7 | Graphpad |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Strains used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44795.022
-
Supplementary file 2
Plasmids used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44795.023
-
Supplementary file 3
Mass transitions for detection of metabolites.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44795.024
-
Supplementary file 4
RNA-RFP changes (mutant-WT).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44795.025
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44795.026