Two-step regulation of trachealess ensures tight coupling of cell fate with morphogenesis in the Drosophila trachea
Figures
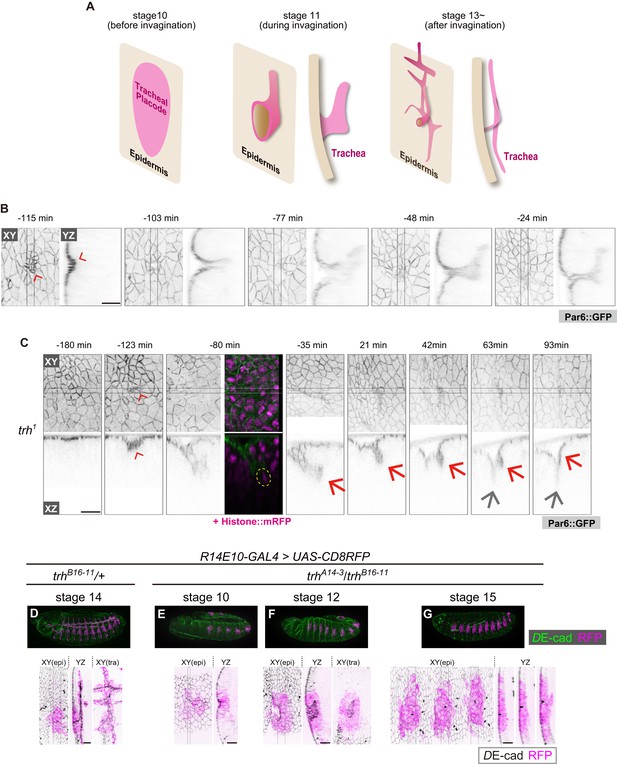
trh is essential for maintaining the invaginated tracheal structures.
(A) Schematic of the tracheal morphogenesis process. For clarity, only apical surfaces are shown. (B, C) Live imaging of tracheal invagination in a control embryo (B) and a trh mutant (C). Red arrowheads: apical constriction forming a tracheal pit. Yellow circle: a mitotic cell associated with accelerated invagination, distinguished by condensed histone. Red arrows: transient invagination and return to epidermis in a trh1 mutant. Gray arrows: segmental groove, which is not a tracheal structure. Par-6::GFP indicates the apical cell side, and His2Av::mRFP indicates chromosomes. Time point zero is set to the onset of germband retraction. (D) Activity of R14E10-GAL4 in a control embryo monitored using UAS-mCD8RFP. (E–G) Activity of R14E10-GAL4 in trhA14-3/B16-11 mutant embryos monitored using UAS-mCD8RFP. Green: DE-cad, Magenta: mCD8RFP driven by R14E10-GAL4. Cells expressing RFP initiated invagination at stage 10 (E), and invaginated structures formed within the RFP-positive cell cluster at stage 12 (F). However, these invaginated structures were not observed at stage 16, and RFP-positive cells were observed in the surface epidermis (G). Scale bars, 10 μm.
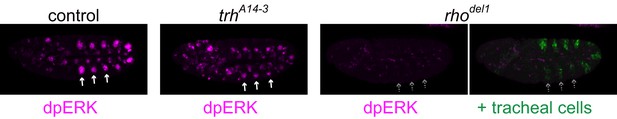
Activation pattern of EGFR signaling before invagination.
Activation pattern of ERK (di-phosphorylated ERK) in a control, a trhA14-3 mutant, and a rhodel1 mutant embryo at stage 10 before invagination. Before invagination, ERK was phosphorylated in the tracheal placodes of the control and trh mutant but not in those of the rho mutant. tracheal placodes were labeled by using trh66-lacZ.
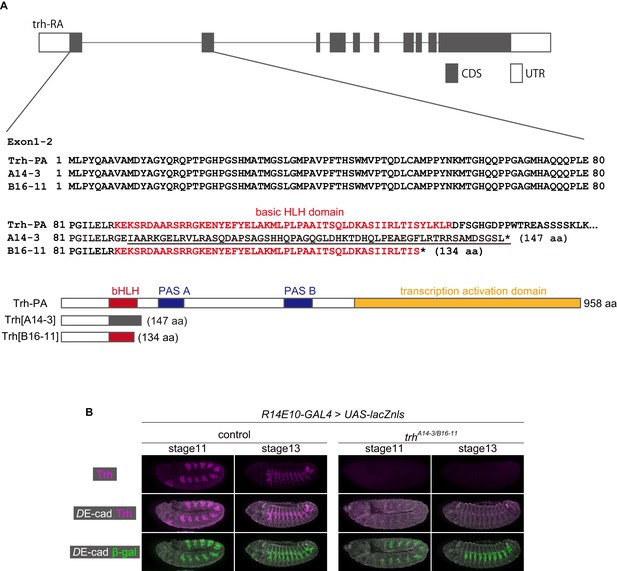
Characterization of TALEN-induced trh mutants.
(A) Predicted amino acid sequences of trhA14-3 and trhB16-11 TALEN mutant proteins. Each allele has a frameshift mutation on the most upstream common exon among all isoforms. Both frameshift mutations lead to premature translational termination and the loss of the PAS A, PAS B and transcription activation domains. The trhA14-3 allele also loses the bHLH domain. The changes in the predicted amino acid sequences of the Trh-PA isoform are shown as an example. (B) No Trh protein expression was detected in trhA14-3/B16-11 mutant embryos. β-gal driven by R14E10-GAL4 labels would-be tracheal cells.
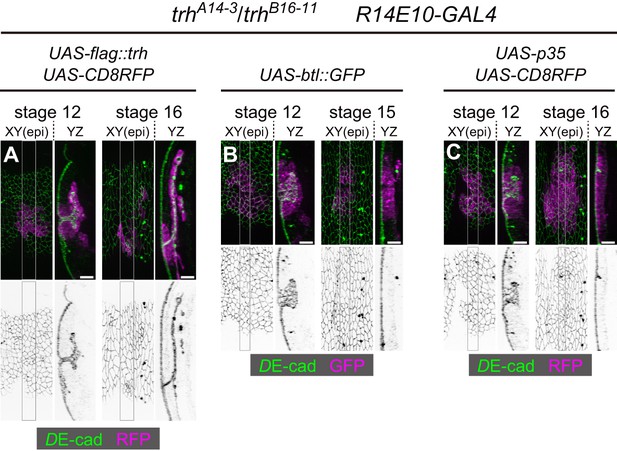
The trh mutant phenotype was not rescued by btl overexpression or the inhibition of apoptosis.
(A–D) Phenotypes resulting from gene overexpression in the tracheal placodes of trhA14-3/B16-11 mutants. Each gene was overexpressed using R14E10-GAL4. (A) trh overexpression, (B) btl:GFP overexpression, (C) p35 overexpression. Scale bars, 10 μm.
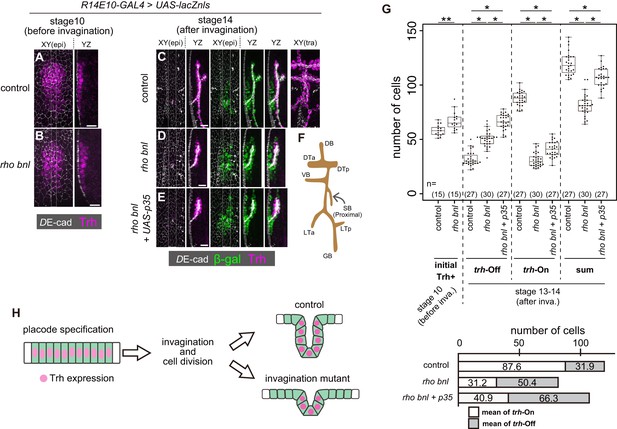
Trh expression is maintained only in invaginated tracheal cells.
(A, B) Trh expression in a tracheal placode of a control (rhodel1 bnlP1 /+) (a) and a rhodel1 bnlP1 mutant (B) embryo at stage 10 before invagination. (C–E) Trh and β-gal expression in a control embryo (C), a rhodel1 bnlP1 mutant (D), and a rhodel1 bnlP1 mutant with p35 overexpression (E) at stage 14 after invagination. β-gal and p35 expression were driven by R14E10-GAL4. (F) Schematic of the tracheal branching pattern after invagination. (G) Upper: Boxplot of cell numbers. Initial Trh+: the number of Trh-expressing cells before invagination, trh-Off: the number of cells expressing β-gal driven by R14E10-GAL4 in the epidermis (Trh-negative) after invagination (stage 13–14), trh-On: the number of invaginated tracheal cells expressing Trh after invagination (stage 13–14), sum: the sum of trh-Off and trh-On. **: Exact Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney Test, p=0.001331, *: Steel-Dwass test, p<0.001 (for trh-Off, control vs rho bnl: p=5.3 × 10−9, control vs rho bnl +p35: p=8.3 × 10−10, rho bnl vs rho bnl +p35: p=3.9 × 10−8; for trh-On, control vs rho bnl: p=5.28 × 10−10, control vs rho bnl +p35: p=8.4 × 10−10, rho bnl vs rho bnl +p35: p=2.8 × 10−10; for sum, control vs rho bnl: p=3.1 × 10−10, control vs rho bnl +p35: p=2.0 × 10−4, rho bnl vs rho bnl +p35: p=3.2 × 10−9). Lower: mean numbers of trh-On cells and trh-Off cells at stages 13–14 after invagination. (H) Schematic of the dynamics of Trh expression during invagination. Scale bars, 10 μm.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2G and Figure 2—figure supplement 1B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45145.009
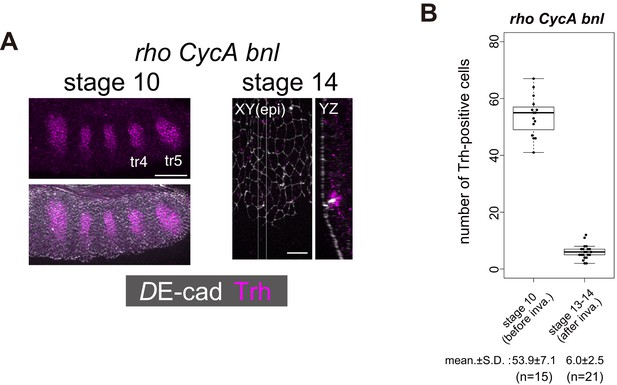
Only a few invaginated cells maintain Trh expression in rho CycA bnl mutants.
(A) Trh expression in the tracheal cells of a rhodel1 CycAC8LR1 bnlP1 mutant at stage 10 before invagination and stage 14 after invagination. Although Trh expression was almost normal at stage 10, only a few invaginated cells were Trh-positive after invagination. Scale bars, (stage 10) 50 μm, (stage 14) 10 µm. (B) Boxplot showing the numbers of Trh+ cells in each placode (tr4, 5 and 6) at stage 10 before invagination and stage 14 after invagination.
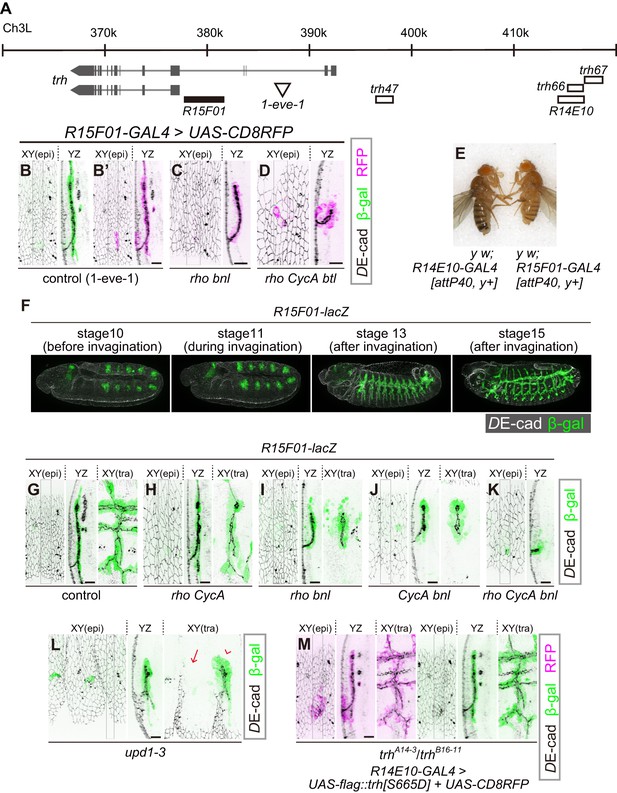
R15F10 reproduces the tubule-restricted Trh pattern.
(A) Genomic positions of R15F01, other enhancers, and the insertion site of 1-eve-1 at the trh locus (B–D) Enhancer activity of R15F01 monitored using R15F01-GAL4 with UAS-mCD8RFP in a control (B’), rhodel1 bnlP1 mutant (C), and rhodel1 CycAC8LR1 btldeltaOh10 mutant (D) embryo. β-gal indicates the expression from a lacZ enhancer trap line for trh, 1-eve-1 (B). (E) Phenotype in adult cuticle pigmentation. The R15F01-GAL4 fly had a lighter body color than the R14E10-GAL4 fly, indicating that R15F01 represses an adjacent mini-yellow gene. (F–M) Enhancer activity of R15F01 monitored using the direct lacZ reporter in control embryos and in several invagination mutants: rhodel1 CycAC8LR1 (H), rhodel1 bnlP1 (I), CycAC8LR1 bnlP1 (J), rhodel1 CycAC8LR1 bnlP1 (K), Df(1)BSC352 (deficient in all upd1, 2 and 3), arrowhead: a segment with invaginated trachea, arrow: a segment without trachea (L), and trhA14-3/B16-11 R14E10-GAL4 > UAS-flag::trh[S665D] (M). Scale bars, 10 μm.
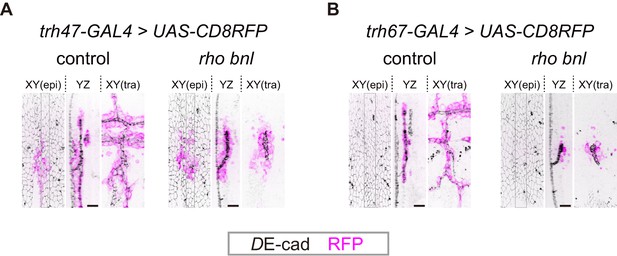
Activity of trh enhancers in tracheal cells and surrounding epidermal cells.
(A) The trh47 activity in control and rhodel1 bnlP1 mutant embryos. In both cases, cells activating the trh47 element were observed in both the trachea and epidermis at stage 14 after invagination. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) The trh67 activity in control and rhodel1 bnlP1 mutant embryos. In both cases, the trh67 element was activated in tracheal cells in a sporadic manner. Scale bars, 10 μm.
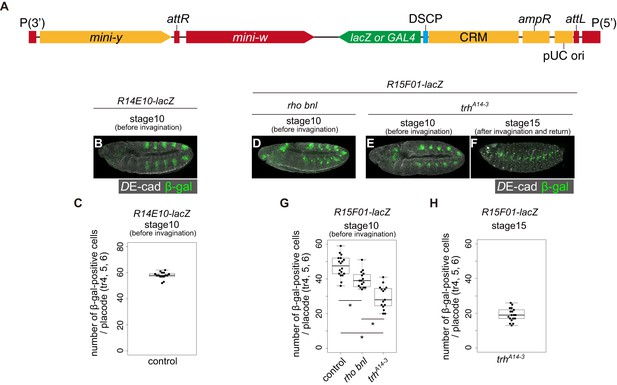
Activity of R14E10 and R15F01 in rho bnl and trh mutants.
(A) Schematic of the GAL4- or lacZ transgene structure after integration into the attP2 or attP40 site. (B) β-gal reporter expression in a R14E10-lacZ strain at stage 10 (before invagination). (C) Boxplot of the number of β-gal positive cells in each placode (tr4, 5 and 6). n = 15. (D–E) Enhancer activity of R15F01 monitored using the direct lacZ reporter at stage 10 (before invagination): in a rhodel1 bnlP1 mutant (d) and a trhA14-3 mutant (e). (F) Enhancer activity of R15F01 monitored using the direct lacZ reporter at stage 15 in a trhA14-3 mutant. (G) Boxplot of the number of β-gal positive cells in each placode (tr4, 5 and 6) at stage 10 (before invagination). n = 18 (control), n = 15 (rho bnl), n = 15 (trh). *: Steel-Dwass test, p<0.01 (control vs rho bnl: p=0.0027, control vs trh: p=5.8 × 10−6, rho bnl vs trh: p=5.0 × 10−4. (H) Boxplot of the number of β-gal positive cells in each placode (tr4, 5 and 6) at stage 15 in trh mutants. n = 15.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3—figure supplement 2C,G,H.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45145.013
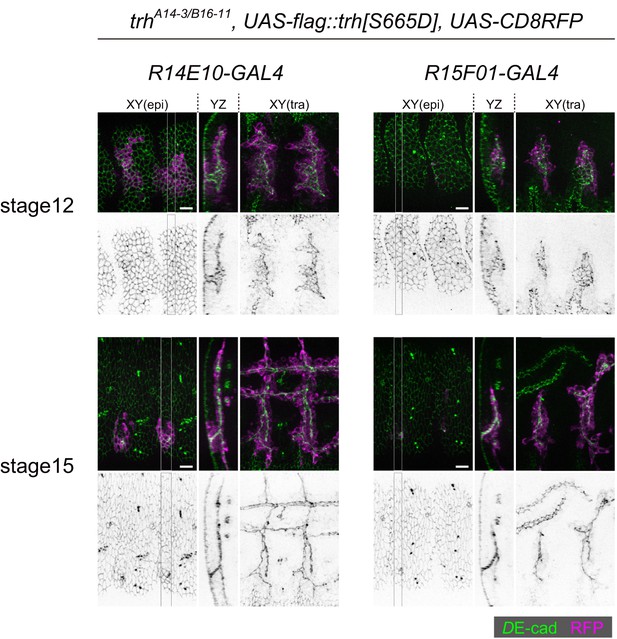
trh-overexpression by using R15F01-GAL4 rescued the trh mutant phenotype in maintaining invaginated structures.
trh-OE using R14E10-GAL4 rescued both tracheal invagination and the maintenance of invaginated structures of trh mutants. On the other hand, trh-OE using R15F01-GAL4 did not rescue the invagination phenotype at stage 12, which may be due to the delayed onset of R15F01 and/or a smaller number of R15F01-positive cells, but allowed cells to keep invaginated structures later.
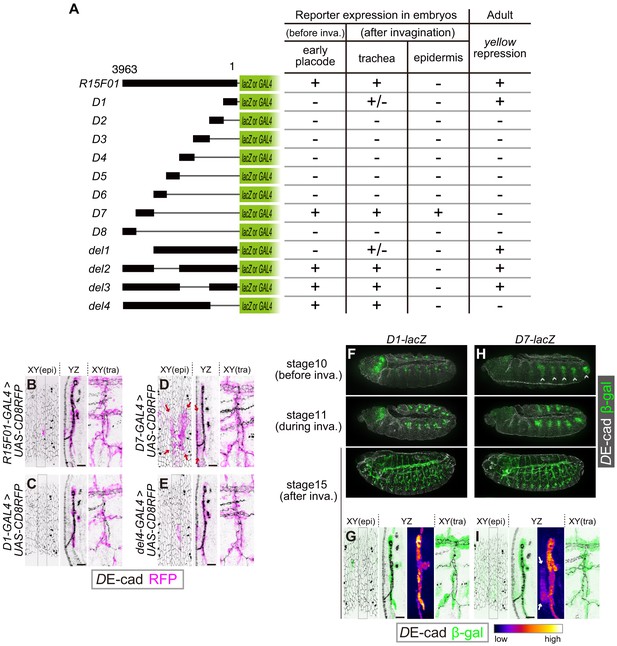
The R15F10 CRM contains multiple tracheal enhancers and epidermal silencers.
(A) Summary of the domain mapping of R15F01. ± indicates sporadic expression. (B–E) Activities of R15F01 (full length), D1, D7, and del4 monitored using GAL4 and UAS-mCD8RFP. D7 activated RFP expression in both tracheal and surrounding epidermal cells (arrows in E). D1 induced RFP expression in a sporadic manner. (F–I) Activities of D1 and D7 monitored using the direct lacZ reporter at stage 10 (before invagination), stage 11 (during invagination), and stage 15 (after invagination). D7 showed enhancer activity in the tracheal placodes before invagination, but D1 activated the reporter in tracheal cells after invagination. Arrows in I indicate epidermal expression of β-gal. Scale bars, 10 μm.
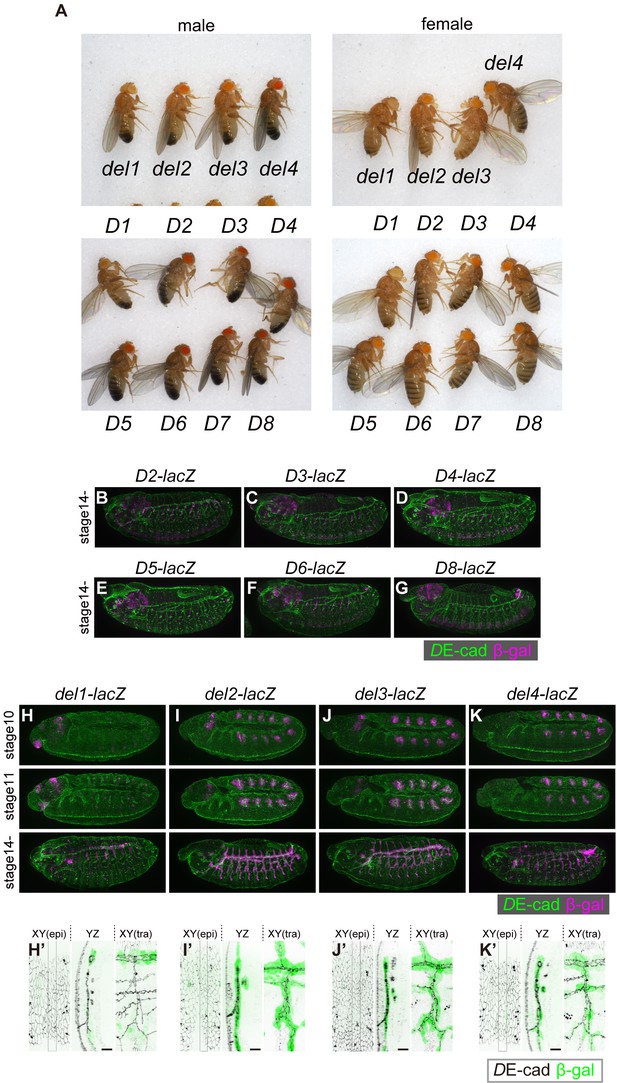
Enhancer and silencer activities of truncated R15F01 elements.
(A) Adult body colors of each transgenic strain. (B–G) β-gal reporter expression in D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, and D8-lacZ strains at stage 14 or 15 after invagination. (H–K) β-gal reporter expression in del1, del2, del3, and del4-lacZ strains at stage 10 (before invagination), stage 11 (during invagination), and stage 14 (after invagination). del1-lacZ did not show β-gal expression before invagination and showed sporadic tracheal expression after invagination. Scale bars, 10 μm.
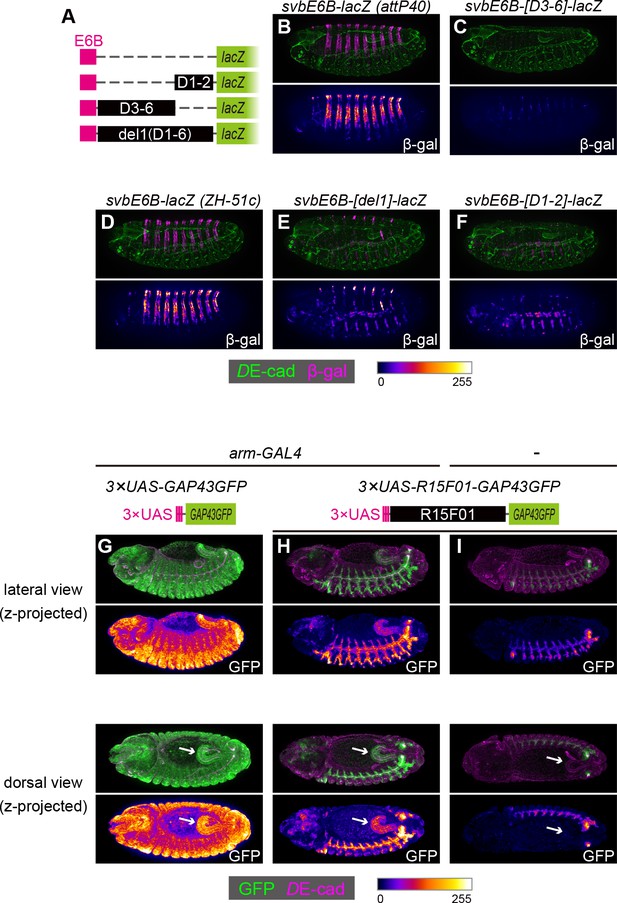
The R15F01 epidermal silencers counteract a heterologous epidermal enhancer.
(A) Schematic of chimeric reporters with svb-E6B and R15F01 fragments (B, C) Reporter β-gal expression (magenta or fire) from E6B-lacZ and E6B-[D3-6]-lacZ integrated at the attP40 site. The epidermal β-gal expression in E6B-[D3-6]-lacZ was significantly weaker than that in E6B-lacZ. (D–F) Reporter β-gal expression (magenta or fire) from E6B-lacZ, E6B-[D1-2]-lacZ, and E6B-[del1]-lacZ integrated at the ZH-51c site. The epidermal β-gal expression in E6B-[D1-2]-lacZ and E6B-[del1]-lacZ was significantly weaker than that in E6B-lacZ, while both showed tracheal reporter expression. (G–I) Reporter GFP expression (green or fire) in (G) arm-GAL4 >3×UAS-GAP43GFP, (H) arm-GAL4 >3 × UAS-R15F01-GAP43GFP, and (I) 3×UAS-GAP43GFP only. Both 3×UAS-GAP43GFP and 3×UAS-R15F01-GAP43GFP transgenes were integrated at the attP2 site. The epidermal GFP expression (the surface of embryos) in arm-GAL4 >3×UAS-R15F01-GAP43GFP was significantly weaker than that of 3×UAS-GAP43GFP, while hindgut GFP expression was detectable. Embryos possessing only 3×UAS-GAP43GFP showed tracheal GFP expression but not hindgut expression. Arrows indicate the hindgut.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | trh[1] | Kyoto stock center | DGRC:106845; FLYB: FBal0017036 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | trh[A14-3] | Kondo et al., 2014 | FLYB: FBal0344676 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | trh[B16-11] | Kondo et al., 2014 | FLYB: FBal0344695 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | 1-eve-1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 8744; FLYB: FBti0002897 | FlyBase symbol: P{ET-L}trh-1-eve-1 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R14E10-GAL4(attP2) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 48641 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-GAL4(attP2) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 45071; FLYB: FBti0133347 | FlyBase symbol: P{GMR15F01-GAL4}attP2 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-mCD8.ChRFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 27392; FLYB: FBti0115769 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-mCD8.ChRFP}3 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-nls-lacZ | Kyoto stock center | DGRC:108782; FLYB: FBti0002781 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-GFP::lacZ.nls}30.1 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-flag::trh | PMID: 11740943 | FLYB: FBal0150204 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-flag::trh[S665D] | PMID: 11740943 | FLYB: FBal0150205 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-btl::GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 41802; FLYB: FBti0148917 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-btl::GFP-S65T}3 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-p35 | Kyoto stock center | DGRC: 108018; FLYB:FBti0012594 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-p35.H}BH1 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | rho[del1] | PMID: 2110920 | FLYB: FBal0017860 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | bnl[P1] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 6384; FLYB: FBal0057745 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | CycA[C8LR1] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 6627; FLYB: FBal0065308 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | btl[deltaOh10] | Ohshiro and Saigo, 1997 | FLYB: FBal0083056 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Df(1)BSC352 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 24376; FLYB: FBab0045128 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Par6::GFP | PMID: 18854163 | FLYB: FBal0243990 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | His2Av::mRFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 23651; FLYB: FBti0077845 | FlyBase symbol: P{His2Av-mRFP1}II.2 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | His2Av::mRFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC: 23650; FLYB: FBti0077846 | FlyBase symbol: P{His2Av-mRFP1}III.1 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | arm-GAL4[11] | Kyoto stock center | DGRC:106387; FLYB: FBti0002793 | FlyBase symbol: P{GAL4-arm.S}11 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | trh66-lacZ | Sotillos et al., 2010 | FLYB: FBal0265118 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R14E10-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R14E10 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D1-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-D1 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D2-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-D2 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D3-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-D3 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D4-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-D4 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D5-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-D5 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D6-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-D6 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D7-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-D7 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D8-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-D8 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-del1-lacZ(ZH-51C) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-del1 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-del1-lacZ[FS](attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-del1 fragment, but lacZ CDS contains a frameshift mutation |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-del2-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-del2 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-del3-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-del3 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-del4-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with R15F01-del4 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | trh47-GAL4(attP2) | this paper | N/A | GAL4 transgene with trh47 regulatory region |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | trh67-GAL4(attP2) | this paper | N/A | GAL4 transgene with trh67 regulatory region |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-GAL4(attP40) | this paper | N/A | GAL4 transgene with R15F01 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R14E10-GAL4(attP40) | this paper | N/A | GAL4 transgene with R14E10 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D1-GAL4(attP2) | this paper | N/A | GAL4 transgene with R15F01-D1 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-D7-GAL4 (attP2) | this paper | N/A | GAL4 transgene with R15F01-D7 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | R15F01-del4-GAL4 (attP2) | this paper | N/A | GAL4 transgene with R15F01-del4 fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | svbE6B-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with svbE6B regulatory region, integrated into attP40 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | svbE6B-D3-6-lacZ(attP40) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with svbE6B-R15F01-D3-6 fusion fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | svbE6B-lacZ(ZH-51C) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with svbE6B regulatory region, integrated into ZH-51C |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | svbE6B-D1-2-lacZ(ZH-51C) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with svbE6B-R15F01-D1-2 fusion fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | svbE6B-del1-lacZ(ZH-51C) | this paper | N/A | lacZ reporter with svbE6B-R15F01-del1 fusion fragment |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | 3×UAS-GAP43GFP (attP2) | this paper | N/A | GFP reporter with3 × UAS sequences |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | 3×UAS-R15F01-GAP43GFP (attP2) | this paper | N/A | GFP reporter with 3 × UAS-R15F01 fusion |
| Antibody | anti-β-galactosidase | MP Biomedicals | 55976, RRID:AB_2334934 | rabbit polyclonal, 1:5000 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-β-galactosidase | Abcam | ab9361, RRID:AB_307210 | chick polyclonal, 1:1000 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-DE-cad | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | DSHB: DCAD2, RRID:AB_528120 | rat monoclonal, 1:20 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-RFP | MBL | M155-3, RRID:AB_1278880 | mouse monoclonal, 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-DsRed | BD Biosciences | 632397 | rabbit polyclonal, 1:5000 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-GFP | Molecular Probes | A-11122, RRID:AB_221569 | rabbit polyclonal, 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-Trh | other | rabbit polyclonal, 1:100 for IHC, Dr Jordi Casanova (IRB Barcelona) | |
| Antibody | Anti-MAP Kinase, Activated | Signa-Aldrich | M8159, RRID:AB_477245 | mouse monoclonal, 1:1000 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor Plus 488 | Molecular Probes | A-32731, RRID:AB_2633280 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor Plus 555 | Molecular Probes | A-32732, RRID:AB_2633281 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor Plus 488 | Molecular Probes | A-32723, RRID:AB_2633275 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor Plus 555 | Molecular Probes | A-32727, RRID:AB_2633276 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 488 | Molecular Probes | A-11034, RRID:AB_2576217 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 555 | Molecular Probes | A-21429, RRID:AB_141761 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 488 | Molecular Probes | A-11029, RRID:AB_138404 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 555 | Molecular Probes | A-21424, RRID:AB_141780 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-Rat IgG DyLignt 649 | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 112-495-167 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-Rat IgG DyLignt 650 | Abcam | ab102263, RRID:AB_10711247 | 1:50 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-chick IgY Alexa Fluor 488 | Abcam | ab150173 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-chick IgY Alexa Fluor 555 | Abcam | ab150174 | 1:300 for IHC |
| Antibody | anti-mouse IgG-biotin | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 715-065-151, RRID:AB_2340785 | 1:500 for TSA amplification |
| Commercial assay or kit | VECTASTAIN Universal Elite ABC Kit | Vector Laboratories | PK-6100 | Use Reagent A and Reagent B for TSA amplification |
| Commercial assay or kit | TSA Cyanine 3 System | PerkinElmer | NEL704A001KT | 1:50 for TSA amplification |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of PCR primers.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45145.018
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45145.019





