An N-terminal motif in NLR immune receptors is functionally conserved across distantly related plant species
Figures
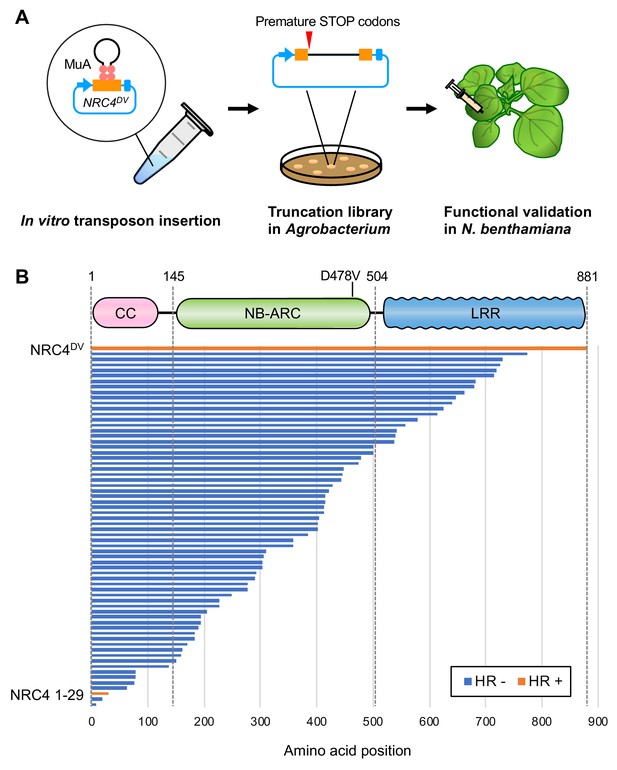
Transposon-based truncation mutagenesis reveals a short 29 amino-acid region sufficient for NRC4-mediated cell death.
(A) Overview of the strategy for transposon-based C-terminal random truncation of NRC4 proteins. Hairpin Mu-STOP transposon and MuA proteins forming Mu transpososome were used for in vitro transposition into target plasmid. The truncation libraries (NRC4DV::Mu-STOP) were transformed into Agrobacterium for transient expression in N. benthamiana leaves. The tube, petri dish and syringe are not drawn to scale. (B) NRC41-29::Mu-STOP triggers cell death in N. benthamiana leaves. In total, 65 truncated variants of NRC4DV were expressed in N. benthamiana leaves, and the cell death activities are described as cell death induction (orange, HR+) and no visible response (blue, HR-).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Sequences of NRC4 truncation library.
The Mu-STOP transposon insertion sites were confirmed by PCR amplicon sequencing with Mu-STOP seq Rv primer. The 65 truncate sequences of NRC4 are listed in this file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig1-data1-v2.txt
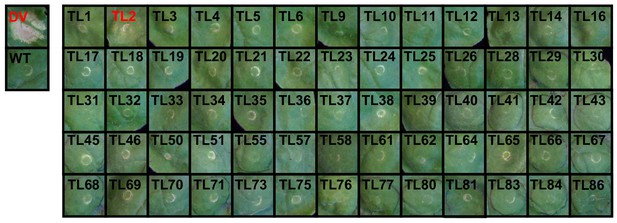
Images of N. benthamiana leaves expressing truncated NRC4DV::Mu-STOP variants.
The images were taken 7 days after agroinfiltration. ‘DV’, ‘WT’ and ‘TL’ describe autoactive NRC4DV mutant, wild-type NRC4 and the truncation library, respectively. Red characters indicate clones triggering HR in N. benthamiana leaves.
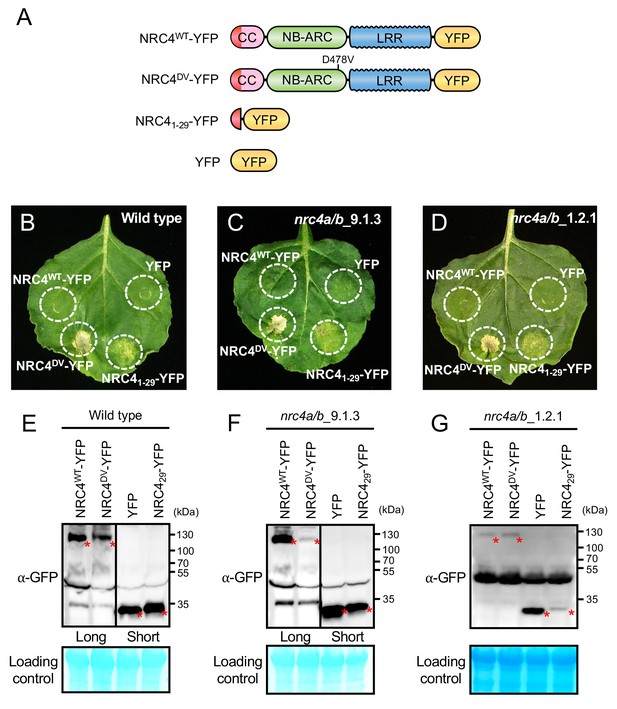
NRC41-29-YFP induces cell death in Nicotiana benthamiana independently of endogenous NRC4.
(A) Schematic representation of wild-type NRC4-YFP (NRC4WT-YFP) and the variants used for the in planta expression assays. The colour code is: red represents NRC4 1 to 29 amino acid region. (B) NRC41-29-YFP triggers cell death in wild-type N. benthamiana leaves. NRC4WT-YFP, NRC4DV-YFP, NRC41-29-YFP and YFP were co-expressed with the gene silencing suppressor p19 and photographed at 7 days after agroinfiltration. (C, D) NRC41-29-YFP triggers cell death in N. benthamiana independently of endogenous NRC4. Leaves of two independent N. benthamiana nrc4a/b lines were used for agroinfiltration assays as described in B. (E, F, G) Anti-GFP immunoblots of NRC4WT-YFP, NRC4DV-YFP, NRC41-29-YFP and YFP expressed in N. benthamiana wild-type and nrc4a/b mutants. Total proteins were prepared from wild-type and nrc4a/b N. benthamiana leaves at 1 day after agroinfiltration. Given that the full-length NLRs accumulate at much lower levels than the shorter peptide, we showed different exposures as indicated by the black line. Red asterisks indicate expected band sizes.
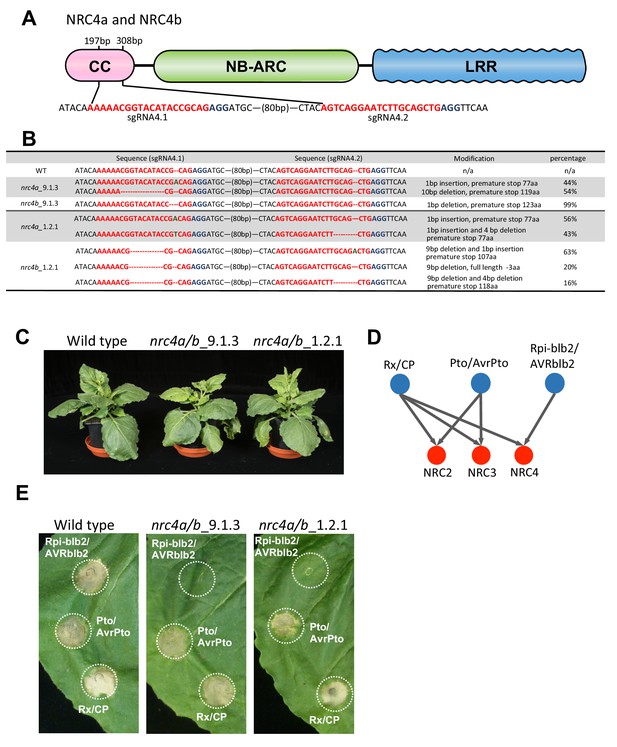
Knocking out of NRC4a and NRC4b in Nicotiana benthamiana impairs Rpi-blb2-mediated HR cell death.
(A) Schematic representation of sgRNA positions targeting NRC4a and NRC4b. The PAM motifs are marked in blue, and the sequences of sgRNAs are marked in red. (B) Genotyping results of selected T2 nrc4a/b plants. Sequences of the two sgRNA positions in NRC4a and NRC4b were confirmed by amplicon sequencing. ‘Percentage’ represents the proportion of Illumina reads belonging to each sequence category. (C) NRC4 knockout lines did not exhibit any growth defects when compared to wild type plants. Photographs of five weeks old wild type and nrc4a/b knock out N. benthamiana plants. (D) Schematic representation showing the genetic dependency of Rpi-blb2, Pto, and Rx on different NRCs according to previous finding with virus-induced gene silencing analysis (Wu et al., 2017). (E) Rpi-blb2-mediated HR cell death was compromised in the NRC4 knockout lines. Rpi-blb2/AVRblb2, Pto/AvrPto and Rx/CP were transiently expressed in leaves of wild type and nrc4a/b N. benthamiana according to the method described previously in Wu et al. (2017). The pictures were taken at 7 days after agroinfiltration.
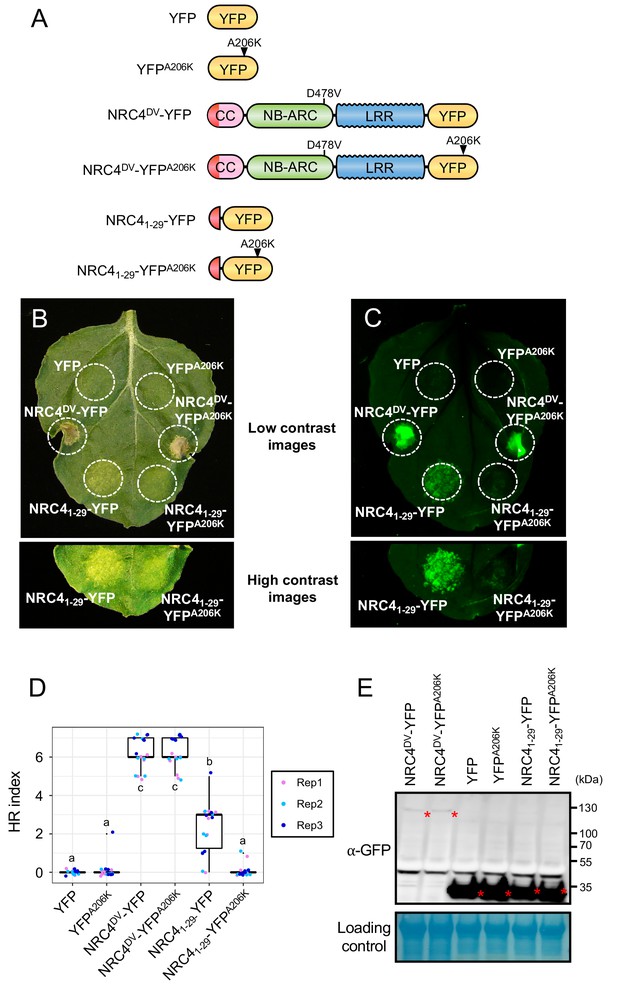
NRC41-29-YFP cell death is compromised by YFP A206K mutation.
(A) Schematic representation of NRC4DV-YFP, NRC41-29-YFP and the variants used for the in planta expression assays. Arrowheads show A206K mutation site in YFP. The red colour represents NRC4 1 to 29 amino acid region. (B, C) YFP A206K mutation reduces NRC41-29-YFP cell death in wild-type N. benthamiana leaves. NRC4DV-YFP, NRC41-29-YFP, YFP and the A206K variants were co-expressed with p19 and photographed at 7 days after agroinfiltration. Cell death-related autofluorescence was detected with Odyssey Infrared Imager (800 nm channel, LI-COR) (D) Box plots showing cell death intensity scored as an HR index based on three independent experiments. Statistical differences among the samples were analysed with Tukey’s HSD test (p<0.01). (E) In planta accumulation of NRC proteins. For anti-GFP immunoblots of NRC4DV-YFP, NRC41-29-YFP, YFP and the mutant proteins, total proteins were prepared from wild-type N. benthamiana leaves at 36 hr after agroinfiltration. Red asterisks indicate expected band sizes.
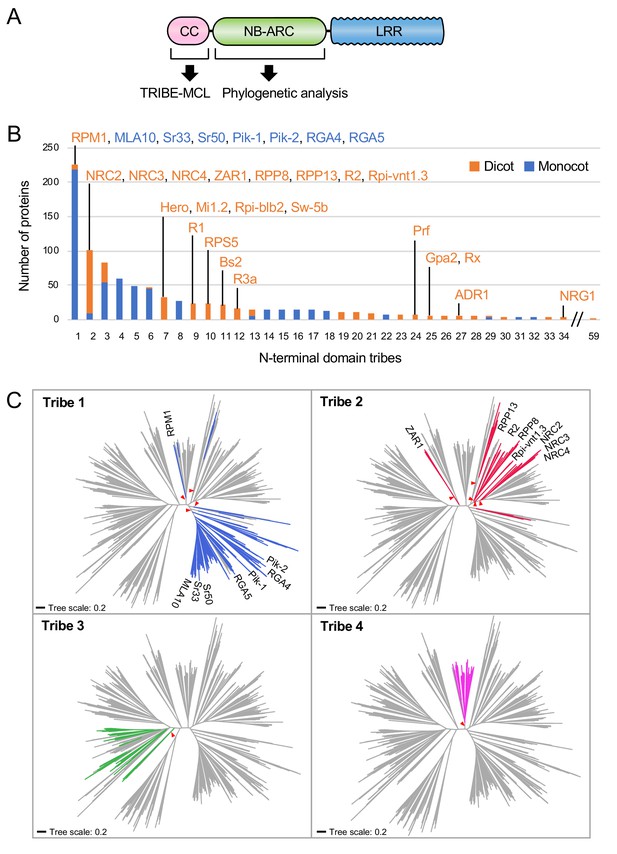
NRC4 carries N-terminal sequences that are conserved across distantly related CC-NLRs.
(A) Schematic representation of the different NLR domains used in TRIBE-MCL and phylogenetic analyses. (B) Distribution of plant NLRs across N-terminal domain tribes. The colour codes are: orange for dicot NLRs and blue for monocot NLRs. (C) NLRs from the same N-terminal tribe are dispersed across NLR phylogeny. The phylogenetic tree was generated in MEGA7 by the neighbour-joining method using the NB-ARC domain sequences of 988 CC-NLRs identified from N. benthamiana, tomato, sugar beet, Arabidopsis, rice and barley. Tribe 1 to Tribe 4 members are marked with different colours as indicated in each panel. Red arrow heads indicate bootstrap support >0.7 and is shown for the relevant nodes. The scale bars indicate the evolutionary distance in amino acid substitution per site. The full phylogenetic tree can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Amino acid sequences of full-length NLRs in the CC-NLR database.
988 NLR sequences used for HMMER analysis are listed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig3-data1-v2.txt
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Amino acid sequences of N-terminal domains in the CC-NLR database.
N-terminal domain sequences of 988 proteins used for Tribe-MCL analysis are listed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig3-data2-v2.txt
-
Figure 3—source data 3
N-terminal domain tribes of CC-NLRs.
Results of the Tribe-MCL analysis are included in this file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig3-data3-v2.xlsx
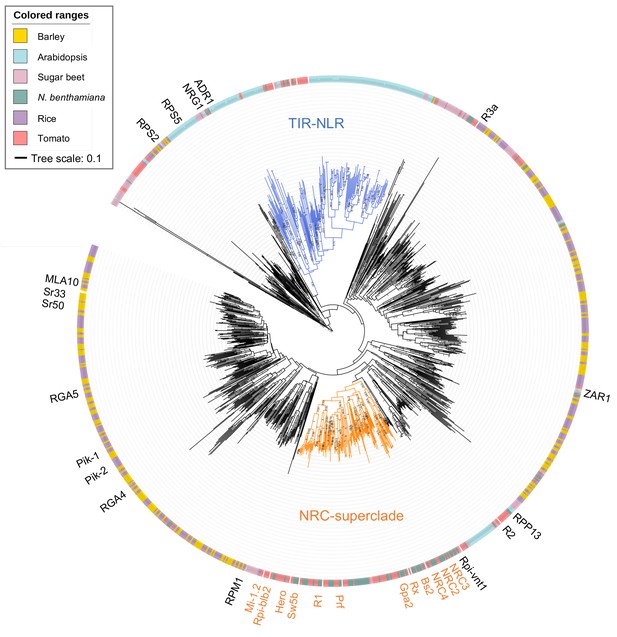
Phylogenetic analysis of NLR proteins from dicot and monocot plant species.
NLR proteins were predicted by NLR-parser from N. benthamiana (NbS-), tomato (Solyc-), Arabidopsis (AT-), sugar beet (Bv-), rice (Os-) and barley (HORVU-) proteomes, and were used for the MAFFT multiple alignment and phylogenetic analyses. The phylogenetic tree was constructed with the NB-ARC domain sequences in MEGA7 by the neighbour-joining method. Each leaf is labelled with different colour ranges indicating plant species. Well-supported TIR-NLR clade and NRC-superclade members are marked in blue and orange, respectively. The bootstrap supports (>0.7) are indicated as texts. The scale bar indicates the evolutionary distance in amino acid substitution per site.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Amino acid sequences for CC/TIR-NLR phylogenetic tree.
NB-ARC domain sequences used for phylogenetic analysis are shown with the IDs, N. benthamiana (NbS-), tomato (Solyc-), Arabidopsis (AT-), sugar beet (Bv-), rice (Os-) and barley (HORVU-).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.txt
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 2
CC/TIR-NLR phylogenetic tree file.
The phylogenetic tree was saved in newick file format.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig3-figsupp1-data2-v2.txt
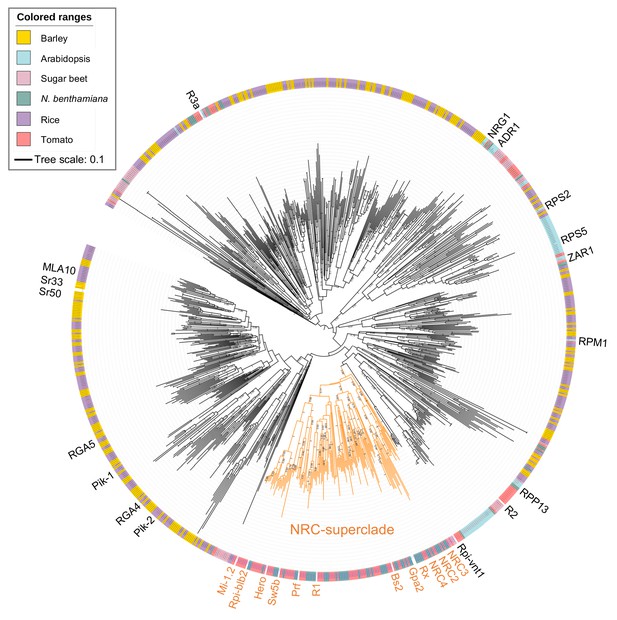
Phylogenetic analysis of CC-NLR proteins from dicot and monocot plant species.
The phylogenetic tree was constructed with the NB-ARC domain sequences of CC-NLRs as described in Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 2. Each leaf is labelled with different colour ranges indicating plant species. Well-supported NRC-superclade members are marked in orange. The bootstrap supports (>0.7) are indicated as texts. The scale bar indicates the evolutionary distance in amino acid substitution per site.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Amino acid sequences for CC-NLR phylogenetic tree.
NB-ARC domain sequences used for phylogenetic analysis are shown with the IDs, N. benthamiana (NbS-), tomato (Solyc-), Arabidopsis (AT-), sugar beet (Bv-), rice (Os-) and barley (HORVU-).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig3-figsupp2-data1-v2.txt
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 2
CC-NLR phylogenetic tree file.
The phylogenetic tree was saved in newick file format.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig3-figsupp2-data2-v2.txt
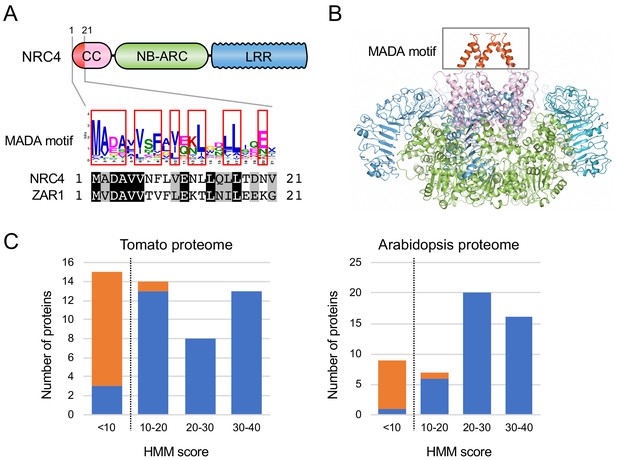
The MADA motif is a conserved unit at the very N-terminus of NRC4 and ZAR1.
(A) Schematic representation of a classical CC-NLR protein highlighting the position of the MADA motif. Consensus sequence pattern of the MADA motif identified by MEME along with an alignment of NRC4 and ZAR1. Red boxes refer to residues conserved over 45% in Tribe 2 NLRs. (B) A structure homology model of NRC4 based on ZAR1 resistosome illustrating the position of the MADA motif. Each of the modelled five monomers is illustrated in cartoon representation. The colour code is: red for the MADA motif. The grey box highlights the N-terminal α helices, which contain the MADA motif. (C) Distribution of the MADA motif in tomato (left) and Arabidopsis (right) proteomes following HMMER searches with the MADA motif HMM. The number of proteins in each HMM score bin is shown. NLR and non-NLR proteins are shown in blue and orange, respectively. The dashed line indicates the cut-off used to define the most robust MADA-CC-NLR. NLRs with scores < 10.0 were classified as MADA-like NLRs (MADAL-NLRs).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Output of the HMMER search using the MADA motif HMM against tomato and Arabidopsis proteomes.
HMM scores are listed with the IDs, tomato (Solyc-) and Arabidopsis (AT-), and annotation information.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Amino acid sequences of the MADA motif.
The sequences were extracted from MEME output against N-terminal domain Tribe 2 and were used to build the MADA motif HMM.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig4-data2-v2.xls
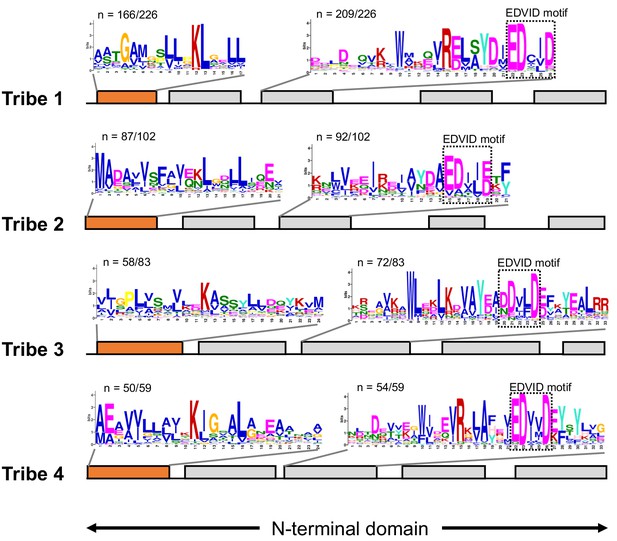
CC-NLRs have conserved protein sequence patterns in the beginning of the N-terminal domains.
Consensus sequence patterns in N-terminal domains were identified by MEME from 226 Tribe 1, 102 Tribe 2, 83 Tribe 3 and 59 Tribe 4 members. Motif logos describe the N-terminal consensus patterns from proteins in each tribe, as highlighted in orange, and EDVID motif patterns, as shown in black boxes.
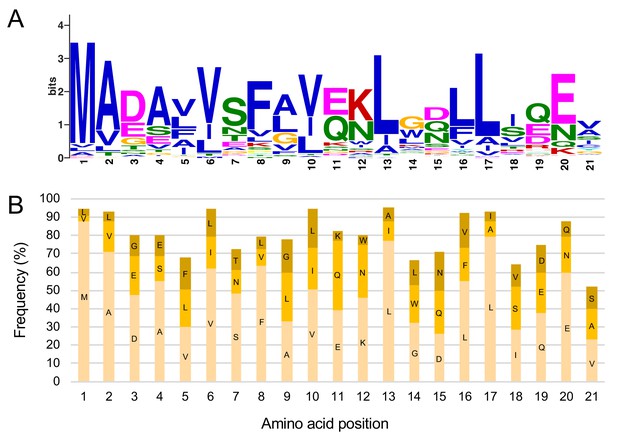
N terminus of NRC4 possesses a consensus pattern coined MADA motif.
(A) Consensus sequence of the MADA motif. The MADA motif logo was generated by MEME from 87 N-terminal domains of Tribe 2 members. (B) Graphical representation of the MADA HMM used to screen MADA-CC-NLR. The three most abundant amino acids at each position in the motif are shown by frequency and labelled with their one-letter code.
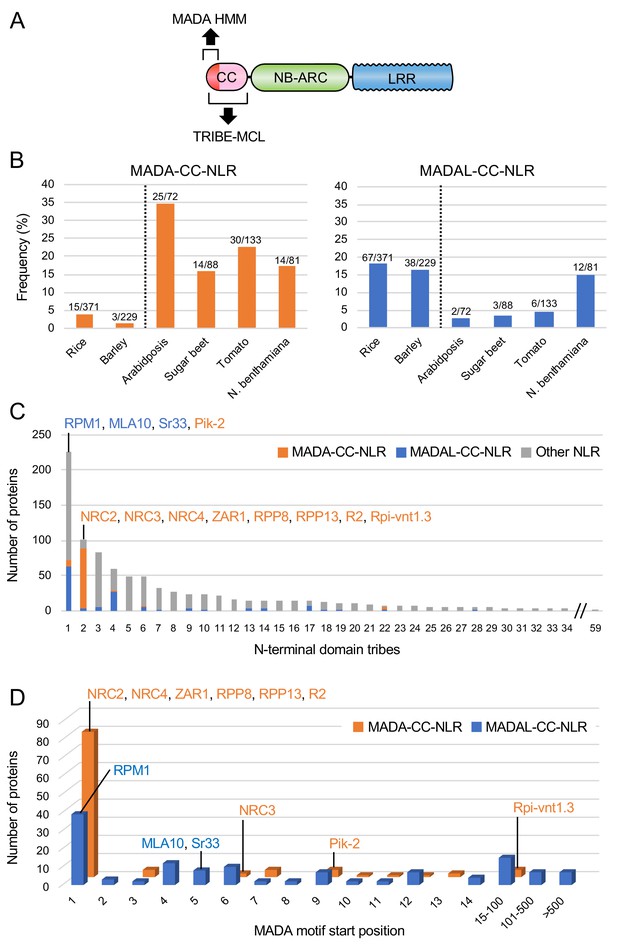
The MADA motif is conserved in ~20% of CC-NLRs.
(A) Schematic representation of a classical CC-NLR protein highlighting the regions used for HMMER searches (MADA-HMM) and for TRIBE-MCL. (B) Occurrence of MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs in representative species of monocots and dicots. The frequency of MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs for each plant species was calculated as a percentage of all predicted CC-NLR proteins. (C) Occurrence of MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs in N-terminal domain tribes of CC-NLRs. (D) Position distribution of MADA/MADAL motif relative to the start codon position among the identified 103 MADA-CC-NLRs and 129 MADAL-CC-NLRs. The colour codes are: orange for MADA-CC-NLRs, blue for MADAL-CC-NLRs and grey for other NLRs.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Output of the HMMER search using the MADA motif HMM against the CC-NLR database.
HMM scores of the predicted MADA motifs are listed by IDs, N. benthamiana (NbS-), tomato (Solyc-), Arabidopsis (AT-), sugar beet (Bv-), rice (Os-) and barley (HORVU-), with Tribe-MCL result, the start (‘MADA_strat’) and end (‘MADA_end’) positions of the MADA motifs in the CC-NLRs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
List of the predicted Arabidopsis MADA-CC-NLRs.
The IDs are listed with the HMM score.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig5-data2-v2.xlsx
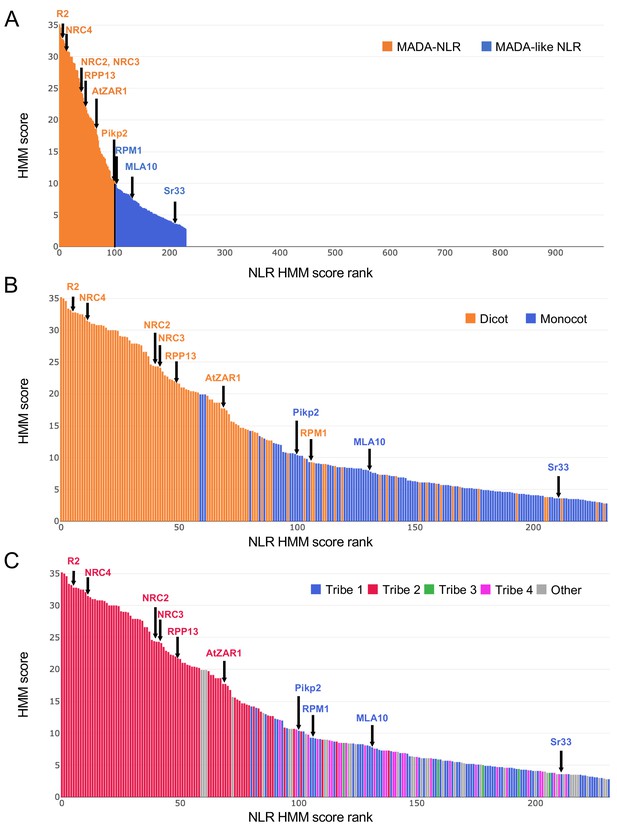
Bar graph of MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs according to HMM score.
(A) HMM score bar graph for CC-NLR database (988 proteins). MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs from HMMER analysis are shown in orange and blue, respectively. (B) HMM score bar graph with plant species information. MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs from dicot and monocot plant species are shown in orange and blue, respectively. (C) HMM score bar graph with N-terminal domain tribe information. MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs in tribe 1–4 from Tribe-MCL analysis are shown in blue, red, green and pink, respectively. MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs from the other N-terminal domain tribes are shown in grey.
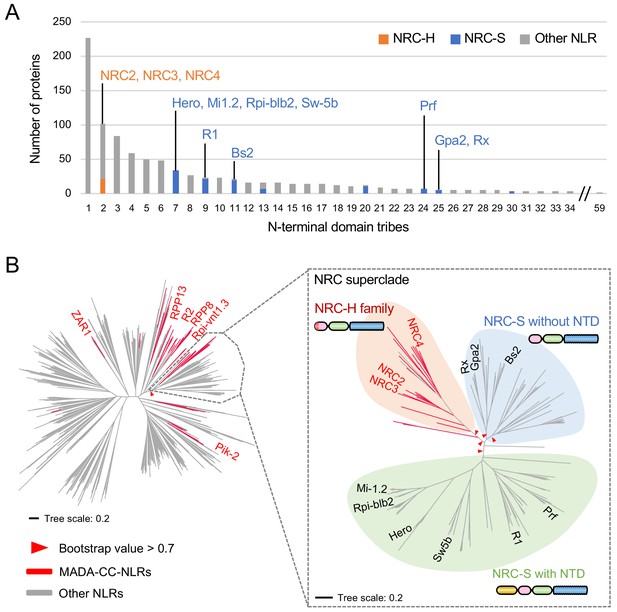
NRC-dependent sensors (NRC-S) do not have the MADA motif.
(A) Distribution of NRCs (NRC-H) and NRC-dependent sensors (NRC-S) across N-terminal domain tribes of CC-NLRs. Individual NLR members of the NRC superclade were classified based on phylogenetic analysis as described in Figure 3—figure supplement 2. The colour codes are: orange for the NRCs (NRC-H), blue for the NRC-sensors (NRC-S) and grey for other NLRs. (B) NRC-dependent sensors (NRC-S) do not contain the MADA motif. The phylogenetic tree of the 988 CC-NLRs described in Figure 3C is shown in the left panel with the NRC superclade marked by the grey lines. The NRC superclade phylogenetic tree is shown on the right panel and highlights the well-supported subclades NRC-H and the expanded NRC-S. The NRC-S clade is divided into NLRs that lack an N-terminal extension domain (NTD) prior to their CC domain and those that carry an NTD. MADA-CC-NLRs are highlighted in red in both trees. Red arrowheads mark bootstrap supports >0.7 in relevant nodes. The scale bars indicate the evolutionary distance in amino acid substitution per site. The full phylogenetic tree can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Schematic representation of domain architecture of the depicted classes of NLR protein is also shown similar to the other figures but with the ~600 amino acid NTD shown in yellow.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
HMM scores of NRC-superclade proteins.
HMM scores are listed by IDs, N. benthamiana (NbS-), tomato (Solyc-) and sugar beet (Bv-) with Tribe-MCL result, the start (‘MADA_strat’) position of the MADA motifs and NRC clade information (‘NRC-H’ and ‘NRC-S’).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
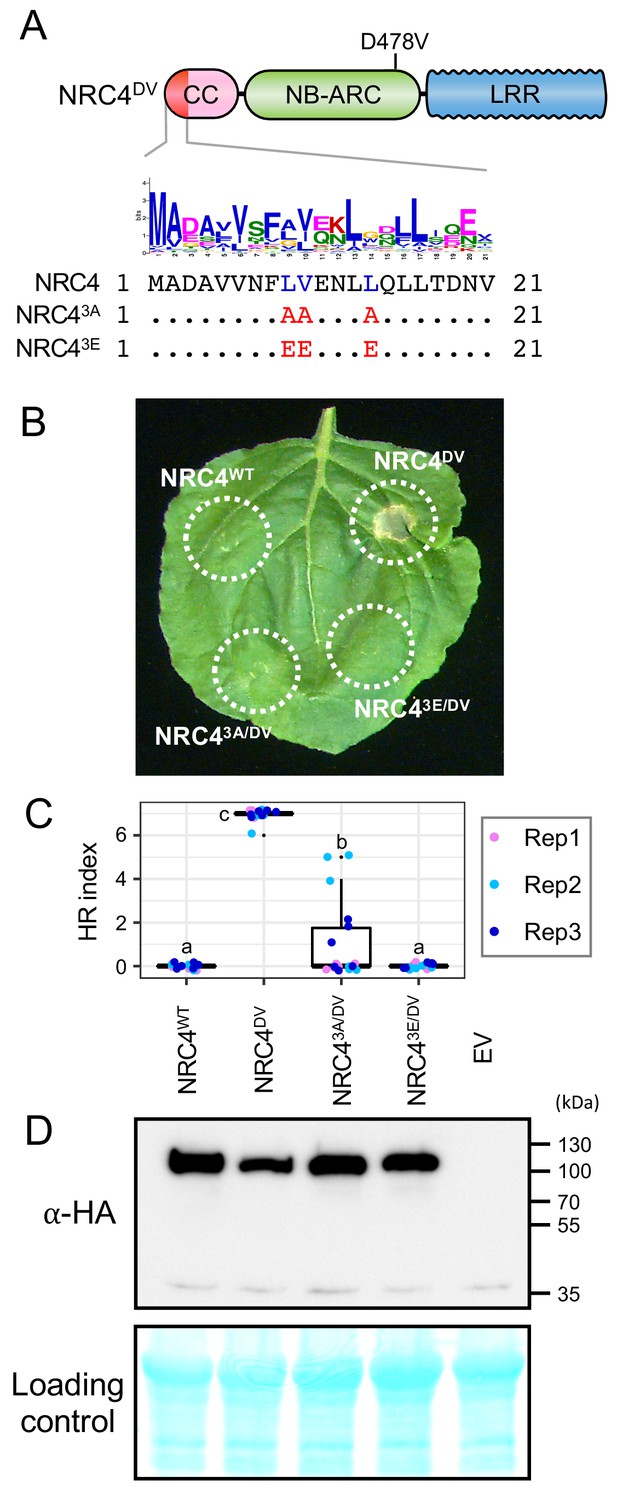
L9, V10 and L14 triple mutation impairs cell death activity of autoimmune NRC4DV.
(A) Schematic representation of NRC4 and the mutated sites in the MADA motif. Mutated sites and substituted residues are shown as red characters in the NRC4 sequence alignment. (B) Cell death observed in N. benthamiana after expression of NRC4 mutants. N. benthamiana leaf panels expressing NRC4WT-6xHA, NRC4DV-6xHA, NRC43A/DV-6xHA and NRC43E/DV-6xHA were photographed at 5 days after agroinfiltration. (C) Box plots showing cell death intensity scored as an HR index based on three independent experiments. Statistical differences among the samples were analysed with Tukey’s honest significance difference (HSD) test (p<0.01). (D) In planta accumulation of the NRC4 variants. For anti-HA immunoblots of NRC4 and the mutant proteins, total proteins were prepared from N. benthamiana leaves at 1 day after agroinfiltration. Empty vector control is described as EV. Equal loading was checked with Reversible Protein Stain Kit (Thermo Fisher).
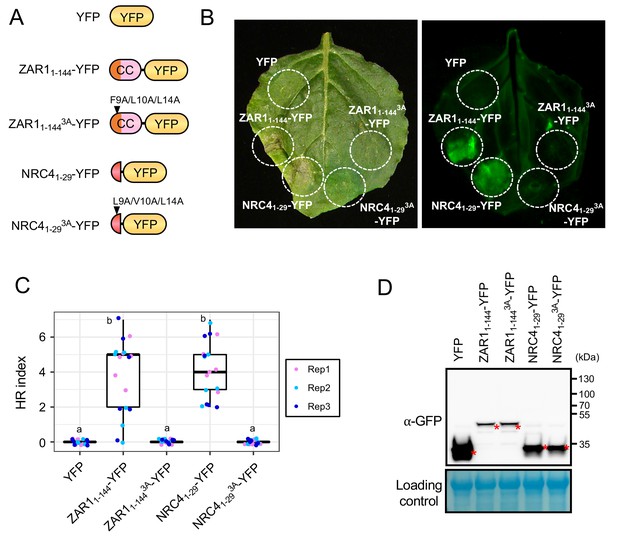
NRC41-29-YFP cell death is compromised by L9, V10 and L14 triple mutation.
(A) Schematic representation of NRC41-29-YFP, ZAR11-144-YFP and the variants used for the in planta expression assays. Arrowheads show triple alanine mutation sites in NRC41-29 and ZAR11-144. The colour code is: red represents NRC4 1 to 29 amino acid region. (B) L9, V10 and L14 triple mutation impairs NRC41-29-YFP cell death. Wild-type N. benthamiana leaves were inoculated with Agrobacterium strain including pTRBO::YFP, pTRBO::ZAR11-144-YFP, pTRBO::ZAR11-144F9A/L10A/L14A-YFP, pTRBO::NRC41-29-YFP or pTRBO::NRC41-29L9A/V10A/L14A-YFP and photographed at 7 days after agroinfiltration. Cell death-related autofluorescence was detected with Odyssey Infrared Imager (800 nm channel, LI-COR) (C) Box plots showing cell death intensity scored as an HR index based on three independent experiments. Statistical differences among the samples were analysed with Tukey’s HSD test (p<0.01). (D) In planta accumulation of NRC proteins. For anti-GFP immunoblots of NRC41-29-YFP, ZAR11-144-YFP and the mutant proteins, total proteins were prepared from wild-type N. benthamiana leaves at 3 days after agroinfiltration. Red asterisks indicate expected band sizes.
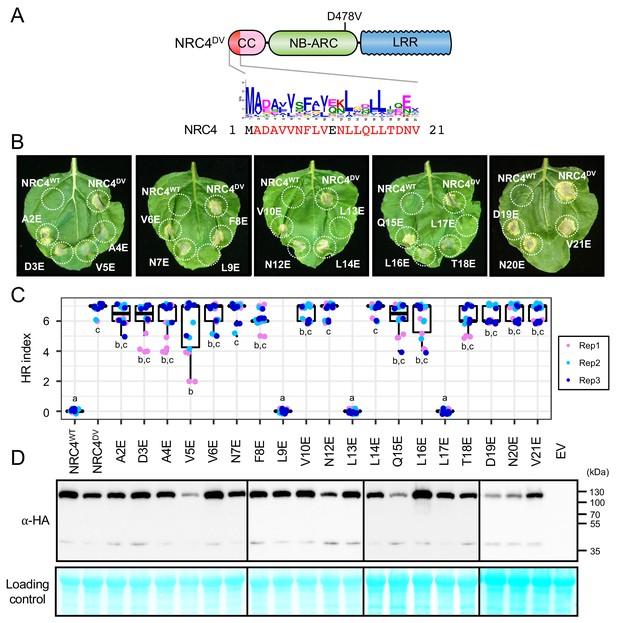
L9E, L13E and L17E single mutations impair cell death activity of autoimmune NRC4DV.
(A) Schematic representation of NRC4 and the glutamic acid (E) mutant scan of the MADA motif. Mutated sites are shown as red characters in the NRC4 sequence. (B) Cell death observed in N. benthamiana after expression of NRC4 mutants. N. benthamiana leaf panels expressing NRC4WT-6xHA, NRC4DV-6xHA and the corresponding E mutants were photographed at 5 days after agroinfiltration. (C) Box plots showing cell death intensity scored as an HR index based on three independent experiments. Statistical differences among the samples were analysed with Tukey’s HSD test (p<0.01). (D) In planta accumulation of the NRC4 variants. Immunoblot analysis was done as described in Figure 7D.
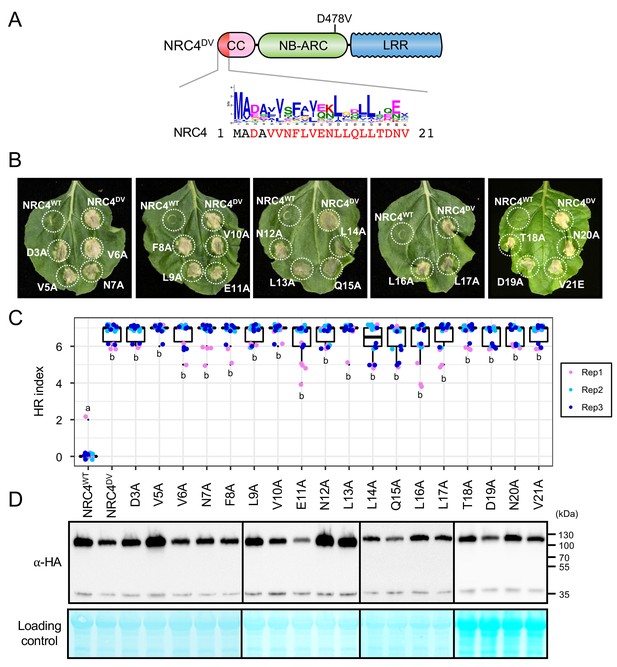
Alanine mutants do not compromise HR cell death triggered by autoactive NRC4.
(A) Schematic representation of NRC4 and the alanine (A) mutant scan of the MADA motif. Mutated sites are shown as red characters in the NRC4 sequence. (B) Cell death observed in N. benthamiana after expression of NRC4 mutants. N. benthamiana leaf panels expressing NRC4WT-6xHA, NRC4DV-6xHA and the corresponding A mutants were photographed at 5 days after agroinfiltration. (C) Box plots showing cell death intensity scored as an HR index based on three independent experiments. Statistical differences among the samples were analysed with Tukey’s HSD test (p<0.01). (D) In planta accumulation of the NRC4 variants. Immunoblot analysis was done as described in Figure 7D.
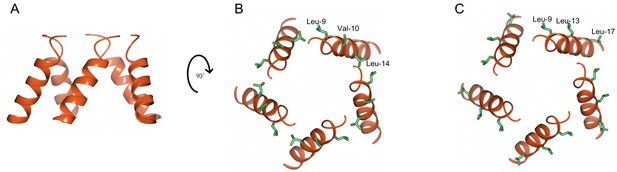
Mapping loss of function mutations on N-terminal α helices of NRC4.
(A) Cartoon representation of N-terminal α helices of NRC4 resistosome (zoom in grey box of Figure 4B). (B, C) N-terminal α helices are rotated 90 degrees and mutated amino acids are shown as stick representation and labelled.
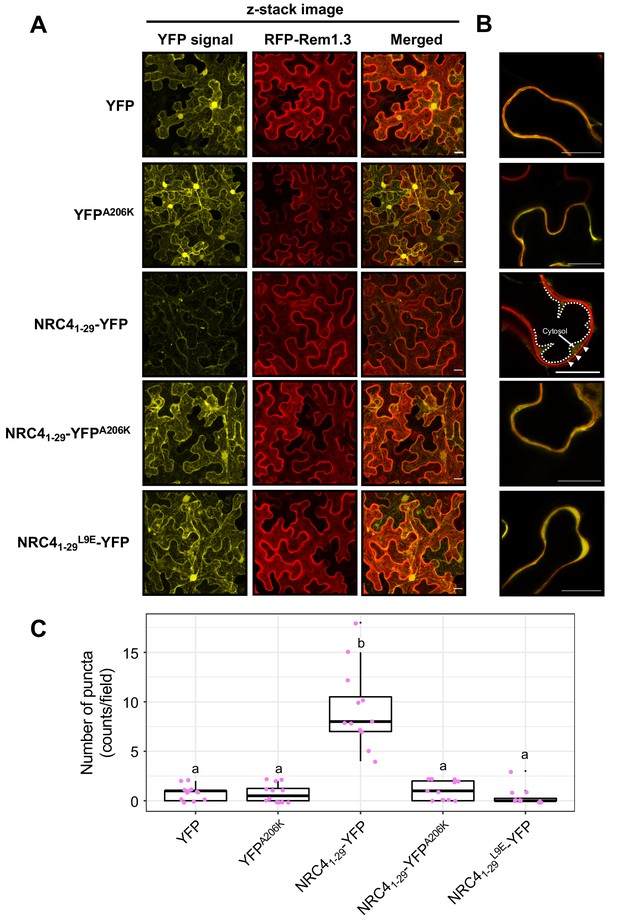
NRC41-29-YFP forms MADA- and YFP-dependent puncta.
(A) Subcellular localization of NRC41-29-YFP and the mutant proteins in N. benthamiana epidermal cells. N. benthamiana leaves expressing YFP, YFPA206K, NRC41-29-YFP, NRC41-29-YFPA206K and NRC41-29L9E-YFP were imaged 2 days after agroinfiltration. (B) Single plain image of NRC41-29-YFP puncta. White dotted line indicates the tonoplast in N. benthamiana epidermal cell. White arrowheads point to NRC41-29-YFP puncta. Scale bars are 20 µm. (C) Quantification of puncta formation. The number of high intensity puncta was counted using maximum intensity Z-projection images from 12 independent observations. Statistical differences among the samples were analysed with Tukey’s HSD test (p<0.01).
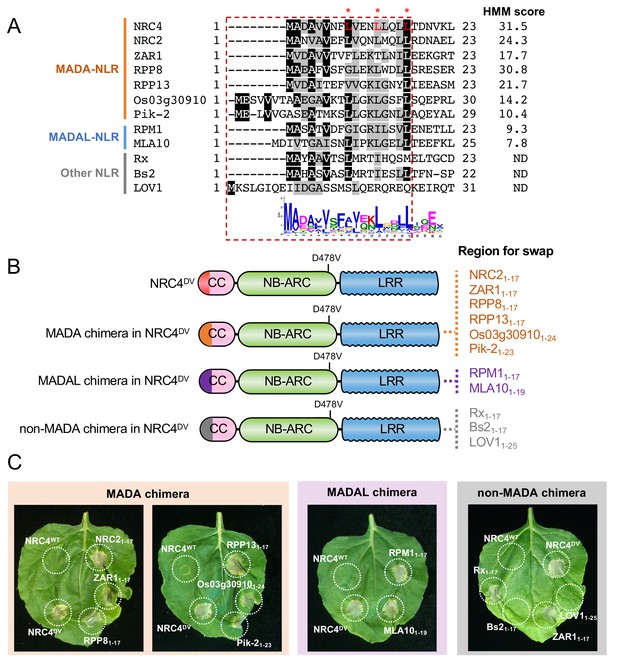
First 17 amino acids of NRC4 can be functionally replaced by the N-terminus of other MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs.
(A) Alignment of the N-terminal region of the MADA/MADAL-CC-NLRs. Key residues for cell death activity identified in Figure 8 are marked as red characters with asterisks in the sequence alignment. Each HMM score is indicated. (B) Schematic representation of NRC4 MADA motif chimeras with MADA, MADAL and non-MADA sequences from other CC-NLRs. The first 17 amino acid region of other MADA-CC-NLR (orange), MADAL-CC-NLR (purple) or non-MADA-CC-NLR (grey) was swapped into NRC4DV, resulting in the NRC4 chimeras with MADA/MADAL/non-MADA sequences originated from other NLRs. (C) Cell death phenotypes induced by the NRC4 chimeras. NRC4WT-6xHA, NRC4DV-6xHA and the chimeras were expressed in N. benthamiana leaves. Photographs were taken at 5 days after agroinfiltration.
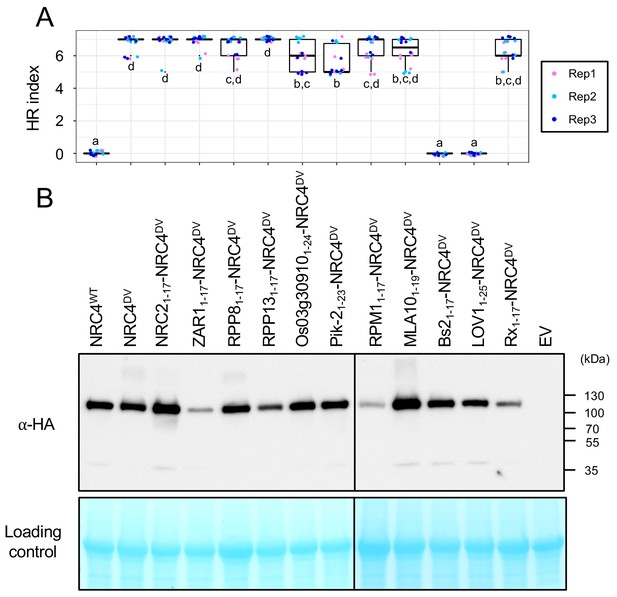
Quantification of cell death triggered by NRC4 MADA motif chimeras.
(A) Box plots showing cell death intensity scored as an HR index based on three independent experiments. Statistical differences among the samples were analysed with Tukey’s HSD test (p<0.01). (B) In planta accumulation of the NRC4 variants. Immunoblot analysis was done as described in Figure 7D.
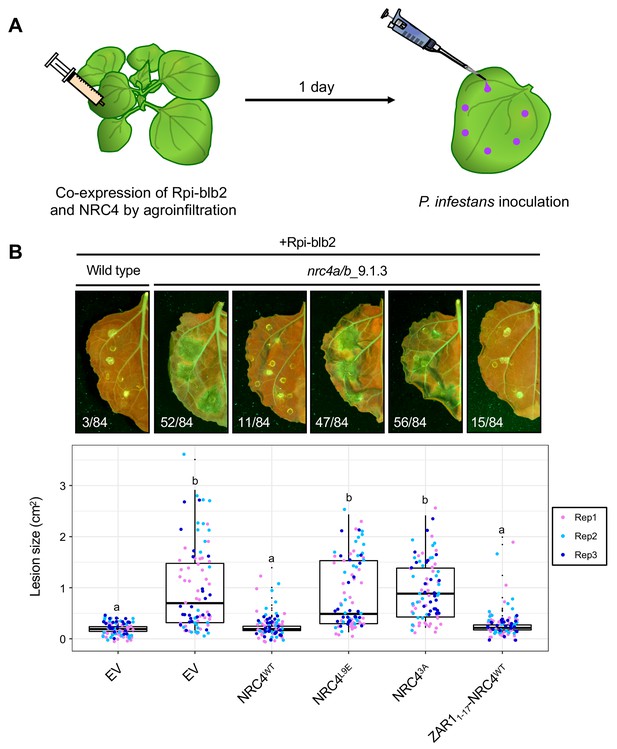
The chimeric protein ZAR11-17-NRC4 complements NRC4 function in Rpi-blb2-mediated resistance.
(A) Schematic representation of NRC4 complementation assay for Rpi-blb2-mediated resistance. Wild-type and the variants of NRC4 were co-expressed with RFP-Rpiblb2 in wild-type or nrc4a/b_9.1.3 N. benthamiana leaves by agroinfiltration. The leaves were inoculated with droplets of zoospore suspension from P. infestans strain 88069 at 1 day after the agroinfiltration. The syringe and pipet are not drawn to scale. (B) Disease and resistance phenotypes on NRC4/Rpi-blb2-expressed leaves. Images were taken under UV light at 7 days post inoculation. The lesion size (bottom panel) was measured in Fiji (Fiji Is Just ImageJ). Experiments were repeated three times with totally 84 inoculation site each. The numbers on the photographs indicate the sum of spreading lesions/total inoculation sites from the three replicates. Statistical differences among the samples were analysed with Tukey’s HSD test (p<0.01).
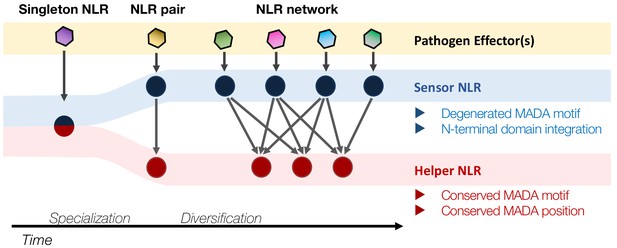
Evolution of NLRs from singletons to networks.
We propose that the N-terminal MADA motif/α1 helix has emerged early in the evolution of CC-NLRs and has remained constrained throughout time as singletons evolved from multifunctional proteins into specialized paired and networked NLR helpers. In contrast, the MADA motif/α1 helix has degenerated in sensor CC-NLRs as they rely on their NLR helper mates for executing the immune response (‘use-it-or-lose-it’ model of evolution). In addition, some sensor NLRs, such as a large subset of NRC-S proteins, have acquired N-terminal domains (NTDs)—prior to their CC domains—that function in pathogen detection. Such NTDs would preclude a free N-terminal α1 helix, which would be incompatible with the current model of ZAR1 resistosome activation.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Nicotiana benthamiana) | NRC4-KO N. benthamiana (nrc4a/b_9.1.3 and nrc4a/b_1.2.1) | This paper | Materials and methods: Generation of N. benthamiana nrc4a/b CRISPR/Cas9 mutants | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGEM::Mu-STOP | This paper | Materials and methods: Mu-STOP in vitro transposition | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Mutation Generation System Kit | Thermo Fisher | Cat #: F-701 | Materials and methods: Mu-STOP in vitro transposition |
| Gene (Solanum lycopersicum) | Tomato genome sequence (Tomato ITAG release 2.40) | Sol Genomics Network (https://solgenomics.net/) | Materials and methods: Bioinformatic and phylogenetic analyses | |
| Gene (N. benthamiana) | N. benthamiana genome sequence (N. benthamiana Genome v0.4.4) | Sol Genomics Network (https://solgenomics.net/) | Materials and methods: Bioinformatic and phylogenetic analyses | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | Arabidopsis genome sequence (Araport11) | https://www.araport.org/ | Materials and methods: Bioinformatic and phylogenetic analyses | |
| Gene (Beta vulgaris) | Sugar beet genome sequence (RefBeet-1.2) | http://bvseq.molgen.mpg.de/index.shtml | Materials and methods: Bioinformatic and phylogenetic analyses | |
| Gene (Oryza sativa) | Rice genome sequence (Rice Gene Models in Release 7) | http://rice.plantbiology.msu.edu/ | Materials and methods: Bioinformatic and phylogenetic analyses | |
| Gene (Hordeum vulgare) | Barley genome sequence (IBSC_v2) | https://www.barleygenome.org.uk/ | Materials and methods: Bioinformatic and phylogenetic analyses | |
| Other | 3D structure of ZAR1 | Protein Data Bank | 6J5T | Materials and methods: Structure homology modelling |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Primers used for generating NRC4 variants by Golden Gate cloning.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-supp1-v2.pptx
-
Supplementary file 2
The MADA-HMM for HMMER analysis.
This MADA-HMM was used for searching MADA-CC-NLRs from CC-NLR database (Figure 3—source data 1).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-supp2-v2.hmm
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/49956/elife-49956-transrepform-v2.pdf





