Modular transcriptional programs separately define axon and dendrite connectivity
Figures
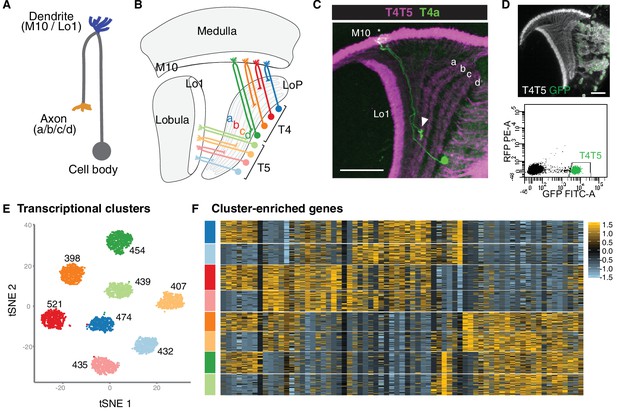
Single-cell sequencing reveals eight transcriptionally distinct populations of T4/T5 neurons.
(A) Common morphology of a T4/T5 neuron, with axon and dendrite wiring pattern variations in parentheses. (B) Arrangement of the eight T4/T5 subtypes in the optic lobe. Each subtype is defined by a combination of one dendrite (M10 or Lo1) and one axon (LoP a, b, c, or d) wiring pattern. (C) A single T4a neuron (green) with dendrites in M10 (asterisk) and axon terminal in LoP layer a (arrowhead). All T4/T5 neurons labeled in magenta. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D–F) Single-cell sequencing of T4/T5 neurons at 48 hr APF. Unsupervised analysis revealed eight distinct transcriptional clusters. (D) T4/T5 neurons were labeled with nuclear GFP, purified by FACS and used for single-cell RNA-Seq. (E) t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) plot of 3557 single-cell transcriptomes. Clusters are color-coded according to subtype identity based on following results. Cell numbers are displayed for each cluster. See also Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (F) Heatmap of expression patterns of cluster-enriched genes (‘one versus all’, see Materials and methods). Cells (rows) grouped by cluster identities as in (E). Genes (columns) are ordered by similarity of their expression patterns. Scaled expression levels are indicated, as in scale.
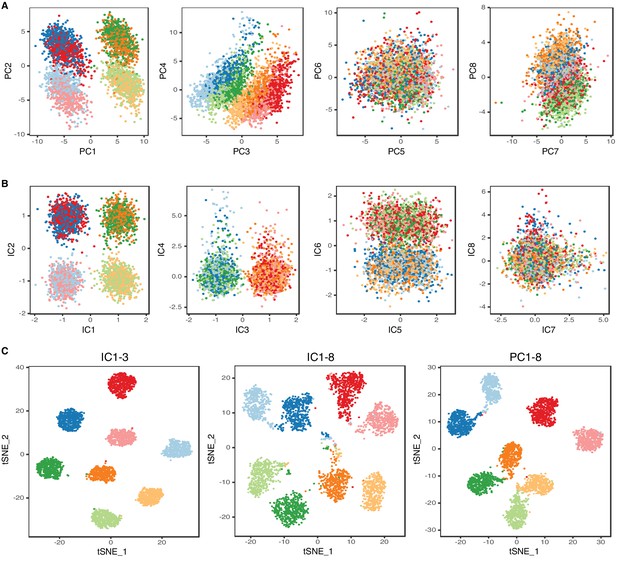
T4/T5 neurons robustly cluster into eight transcriptionally distinct populations (48 hr APF).
(A) Principal component analysis (PCA). (B) Independent component analysis (ICA). Distributions of cells along eight principal components (PCs) and eight independent components (ICs). (C) tSNE plots based on IC 1–3 (left), IC 1–8 (middle), PC 1–8 (right). Cells are color coded according to the final clustering results based on IC 1–3, as in Figure 1.
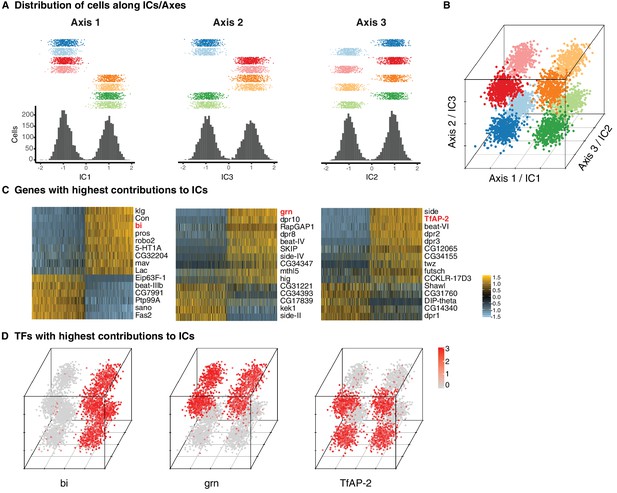
Three primary axes of transcriptional diversity define eight T4/T5 populations.
(A) Three independent components (ICs, henceforth Axis 1, 2, 3) separate cells into approximate halves. Histograms (bottom) and 1-D scatterplots (top) show the distributions of cells along each axis. Cells are grouped into rows based on cluster identities. ICs/Axes are ordered according to following results. Clusters are color-coded as in Figure 1E. See also Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (B) 3-D scatterplot of the distributions of cells along the three ICs/Axes. (C) Heatmaps of expression patterns of the top 15 genes with highest contribution (loading) to each IC/Axis. Cells (columns) are ordered according to a score for each IC/Axis. Genes (rows) are ordered according to the contribution to each IC/Axis. Scaled expression levels are indicated, as in scale. Axes ordered as in (A). (D) 3-D scatterplots with expression patterns of transcription factors (TFs) with highest contribution to each IC/Axis. Normalized expression levels are indicated by color, as in scale. Axes are arranged as in (B).
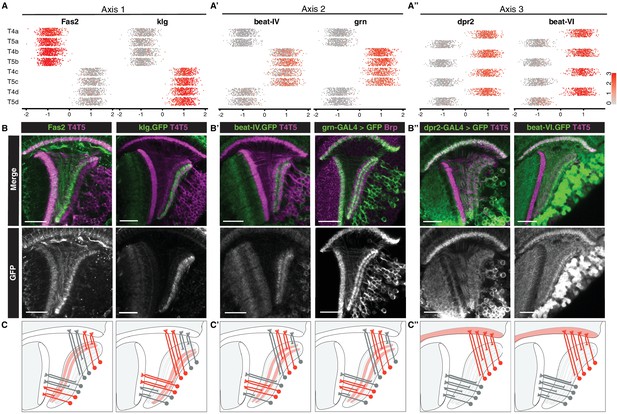
Primary axes of transcriptional diversity define groups of T4/T5 subtypes with shared wiring patterns.
(A–A”) 1-D scatterplots show distribution of cells along Axis 1, 2, and 3 for each cluster. Normalized expression levels are indicated by color, as in scale. (B–B”) In vivo expression of marker genes for each axis at 48 hr APF. Fas2 labels LoP layers a/b, klg labels LoP layers c/d, beat-IV and grn label LoP layers b/c, dpr2 and beat-VI label M10 but not Lo1. Scale bars, 20 μm. Sets of positive clusters in (A) are matched to specific sets of T4/T5 subtypes based on in vivo expression patterns in (B). Individual cluster identities are deduced based on combination of expression patterns. For example, T4a is Fas2+ (a/b), beat-IV- (not b/c), dpr2+ (M10). (C–C”) Schematic of wiring patterns of T4/T5 subtypes corresponding to the expression patterns of marker genes (red). See also Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
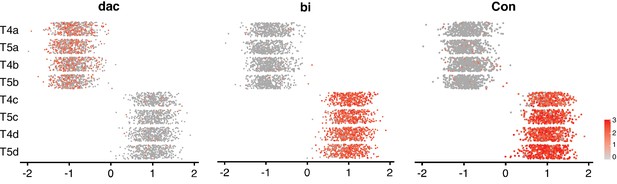
Expression patterns of known marker genes for a/b and c/d subtypes along Axis 1 at 48 hr APF.
See legend of Figure 3 for details.
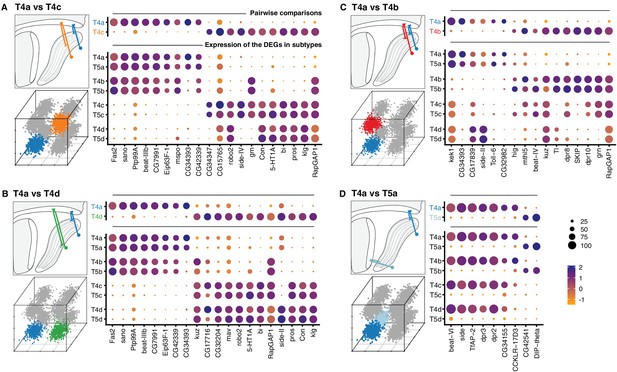
Transcriptional program of a single T4/T5 subtype.
Pairwise comparisons between T4a and other subtypes (‘one versus one’, see Materials and methods) that differ by either axonal outputs (A–C), or dendritic inputs (D). For each comparison, insets indicate morphologies (upper left) and cluster distributions along axes of transcriptional diversity (lower left). Expression patterns of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for each pairwise comparison are shown in upper right. Dot size indicates the percentage of cells in which the DEG was detected, color represents average scaled expression, as in scale. Genes are ordered by fold-change values. Top 20 DEGs are shown for (A) and (B). Expression patterns of DEGs among all eight subtypes are shown in lower right. See also Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
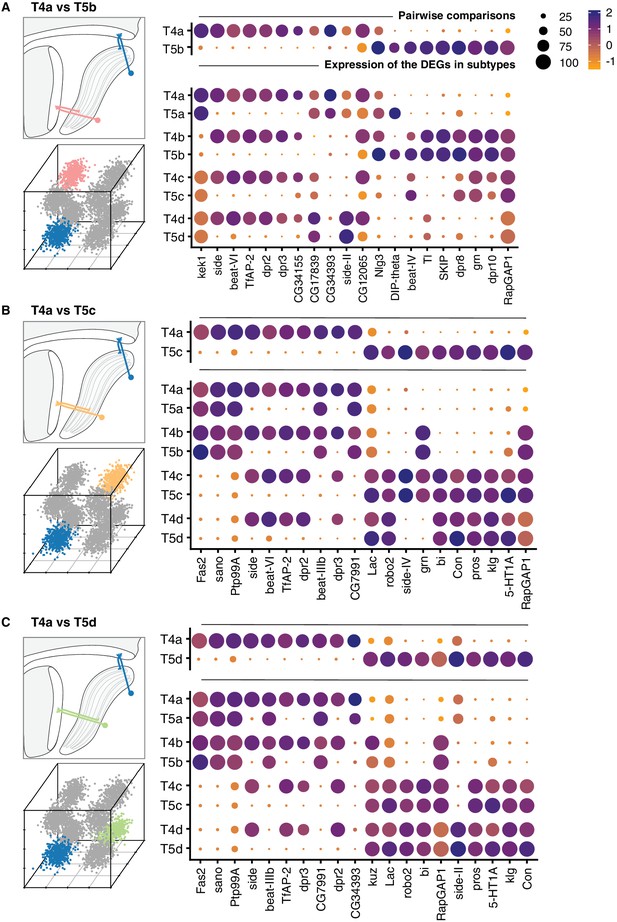
Pairwise comparisons between T4a and subtypes that differ by both axonal outputs and dendritic inputs.
Top 20 DEGs are shown for each comparison. See legend of Figure 4 for details.
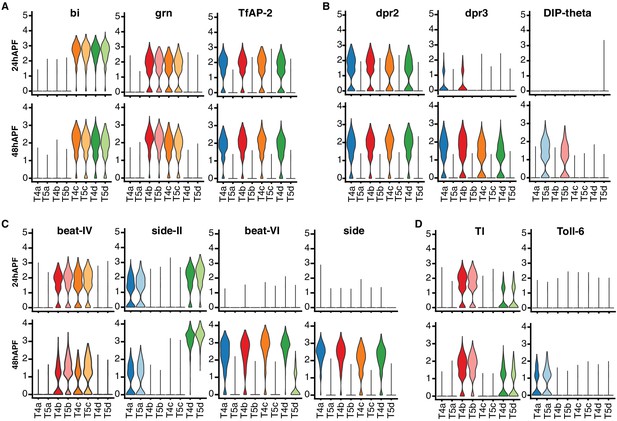
Dynamics of T4/T5 transcriptional programs during development.
Distributions of normalized expression levels of TFs (A) and selected families of CSPs (B-D) at 24 hr and 48 hr APF. Distributions for each subtype are color-coded as in Figure 1. See also Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
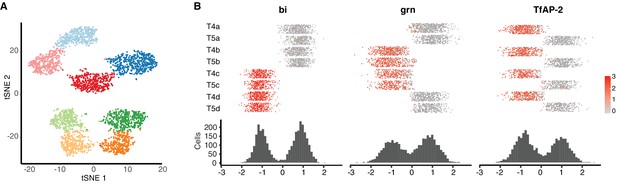
Single-cell profiling of T4/T5 neurons at 24 hr APF.
Unsupervised analysis revealed eight transcriptionally distinct populations. (A) tSNE plot of 3833 single-cell transcriptomes. (B). Distribution of cells along three primary axes of transcriptional diversity, and expression patterns of TF with highest contribution to each axis. See legends of Figures 1–3 for details.
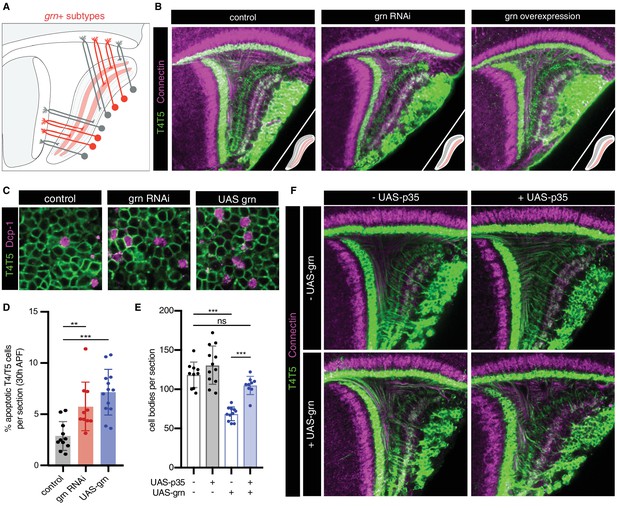
grn controls sublamination of T4/T5 axons into inner and outer LoP layers.
(A) Schematic of grn+ (red) T4/T5 subtypes in wild-type optic lobe. grn expression defines inner LoP layer subtypes. See also Figure 6—figure supplement 1. (B) grn RNAi and grn overexpression in all T4/T5 neurons specifically disrupts sublamination of a/b (Con-) and c/d (Con+) LoP subdomains into inner and outer layers. Insets depict LoP phenotypes. (C–D) Immunostaining for Death caspase-1 (Dcp-1) reveals increased apoptotic T4/T5 neurons under grn RNAi and overexpression (UAS-grn) conditions at 30 hr APF. See also Figure 6—figure supplement 2, and Figure 6—source data 1. (E) Ectopic expression of p35 in T4/T5 neurons (UAS-p35) rescues apoptotic cell death associated with overexpression of grn. (F) grn overexpression specifically disrupts axon sublamination when apoptosis is blocked. Statistical significance assessed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (**p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Bars and whiskers represent mean and standard deviation. Dots represent values for individual optic lobes.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Cell number quantification data for Figure 6D–E and Figure 6—figure supplement 2.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.50822.014
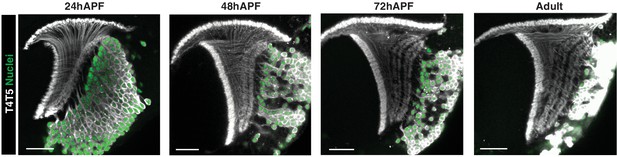
Sequential lamination of T4/T5 axons and four LoP layers.
23G12-Gal4 drives membrane localized RFP (grey) and nuclear localized GFP (green) in all T4/T5 neurons throughout pupal development.
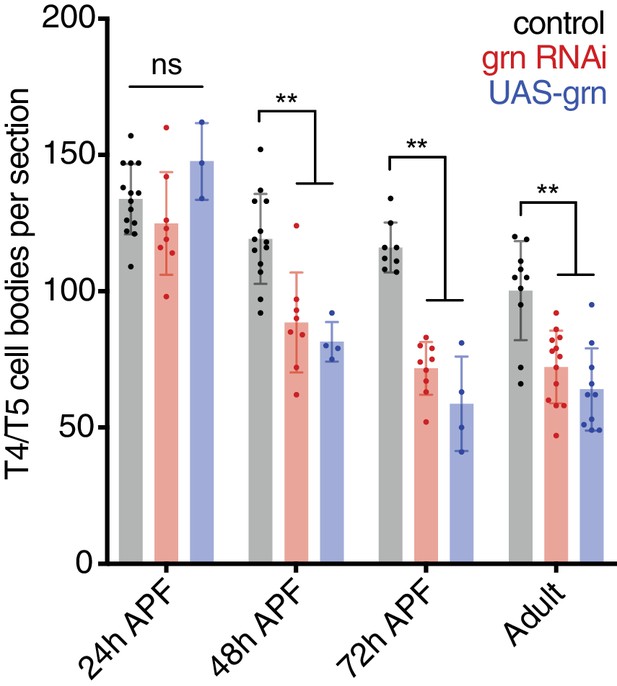
grn RNAi and grn overexpression cause significant loss of T4/T5 neurons between 24 and 48 hr APF.
Statistical significance assessed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (**p<0.01).
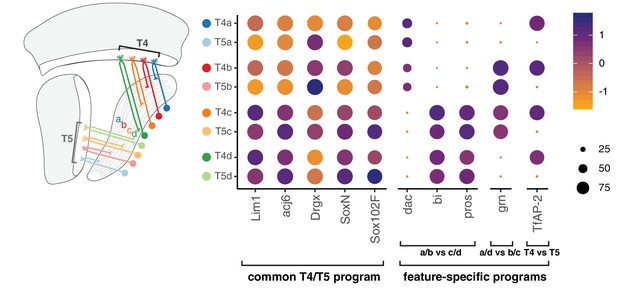
Modular transcription factor codes define eight T4/T5 subtypes.
A common T4/T5 regulatory program is defined by TFs expressed in all subtypes (Davie et al., 2018; Konstantinides et al., 2018; Contreras et al., 2018; Schilling et al., 2019). This program is diversified by modular combinations of feature-specific TFs defining unique wiring patterns of eight T4/T5 subtypes. Dot size indicates the percentage of cells in which the TF was detected, color represents average scaled expression, as in scale. Data shown for 48 hr APF. See also Figure 7—figure supplements 1 and 2.
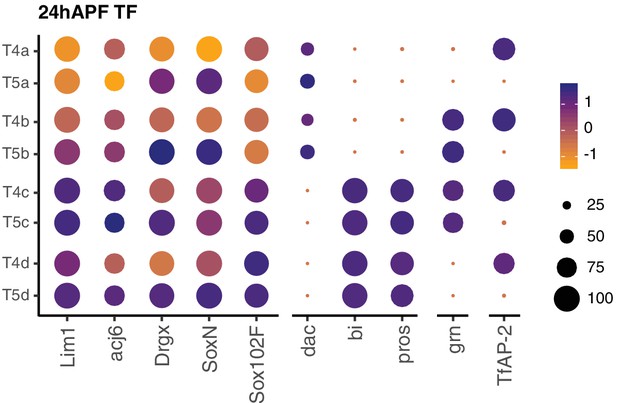
Expression patterns of TFs at 24 hr APF.
See Figure 7 legend for details.
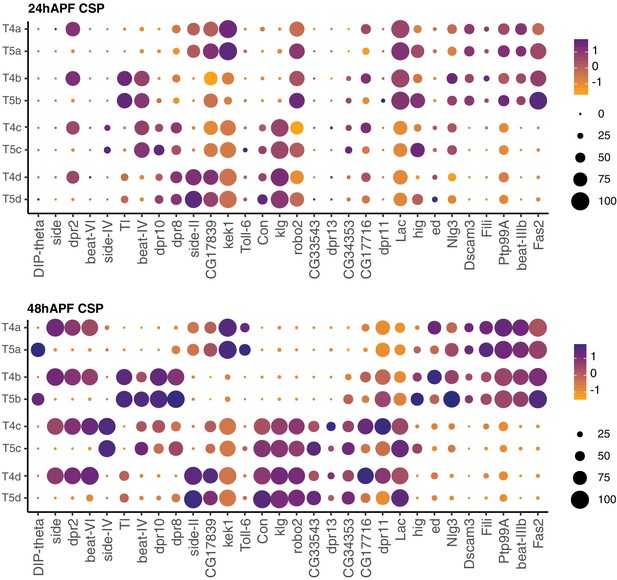
Expression patterns of subtype-enriched CSPs with cell adhesion domains.
Expression patterns of subtype-enriched CSPs with cell adhesion domains (e.g. Ig and LRR). Expression patterns are shown for 24 hr and 48 hr APF. CSPs are ordered by similarity of their expression patterns. See Figure 7 legend for details.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MCFO-1 (pBPhsFLP2::PEST;+; UAS-FSF-smGdP::HA_V5_FLAG) | PMID: 25964354 | RRID: BDSC_64085 | Gift from Aljoscha Nern and Gerald Rubin |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 10XUAS-IVS-myr::tdTomato | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_32222 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 23G12-GAL4 (T4/T5) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_49044 | T4/T5 driver |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 42F06-GAL4 (T4/T5) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_41253 | T4/T5 driver |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 23G12-LexA (T4/T5) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_65044 | T4/T5 driver |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | {R59E08-p65ADZp (attP40); R42F06-ZpGdbd (attP2)} (T4/T5 splitGAL4) | PMID: 28384470 | JRC_SS00324 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-CD4-tdGFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_35839 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-H2A::GFP | PMID: 26687360 | N/A | Gift from Barret Pfeiffer and Gerald Rubin |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | LexAop-myr::tdTomato | PMID: 24462095 | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 10XUAS-IVS-myr::GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_32197 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | 10XUAS-IVS-mCD8::RFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_32219 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Mi{PT-GFSTF.1}klg[MI02135-GFSTF.1] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_59787 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Mi{PT-GFSTF.1}beat-IV[MI05715-GFSTF.1] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_66506 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | dpr2-Gal4 | Hugo J. Bellen | N/A | Gift from Hugo J. Bellen |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{w[+mW.hs]=GawB}grn[05930-GAL4] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_42224 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Mi{y[+mDint2]=MIC}beat-VI[MI13252] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_58680 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{y[+t7.7] v[+t1.8]=TRiP.HMS01085}attP2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_33746 | UAS-grnRNAi |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P{UAS-p35.H}BH1 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | RRID: BDSC_5072 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-grn.ORF.3xHA | FlyORF | Stock #: F001916 | |
| Antibody | Chicken polyclonal anti-GFP | Abcam | Cat. #: ab13970 RRID: AB_300798 | IHC (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-dsRed | Clontech | Cat. #: 632496 RRID: AB_10013483 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Brp | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat. #: nc82 RRID: AB_2314866 | IHC (1:20) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-V5 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab27671 RRID: AB_471093 | IHC (1:300) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Dcp-1 | Cell Signalling | Cat. #: 9578 RRID: AB_2721060 | IHC (1:50) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-chicken IgY Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | Cat. #: A11039 RRID: AB_142924 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | Cat. #: A11029 RRID: AB_138404 | IHC (1:500) |
| Antibody | Goat monoclonal anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 568 | Invitrogen | Cat. #: A11011 RRID: AB_143157 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-rat IgG Alexa Fluor 568 | Invitrogen | Cat. #: A11077 RRID: AB_141874 | IHC (1:500) |
| Antibody | Goat oligoclonal anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 647 | Invitrogen | Cat. #: A27040 RRID: AB_2536101 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Donkey polyclonal anti-mouse IgG Cy5 | Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories | Cat. #: 715-175-150 RRID: AB_2340819 | IHC (1:200) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Papain | Worthington | Cat. #: LK003178 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Liberase protease | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. #: 5401119001 | |
| Software, algorithm | Cell Ranger 2.2.0 | https://10xgenomics.com | RRID:SCR_017344 | |
| Software, algorithm | Seurat 2.3.4 | https://satijalab.org/seurat/ | RRID: SCR_016341 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.50822.018





