Keratin 14-dependent disulfides regulate epidermal homeostasis and barrier function via 14-3-3σ and YAP1
Figures
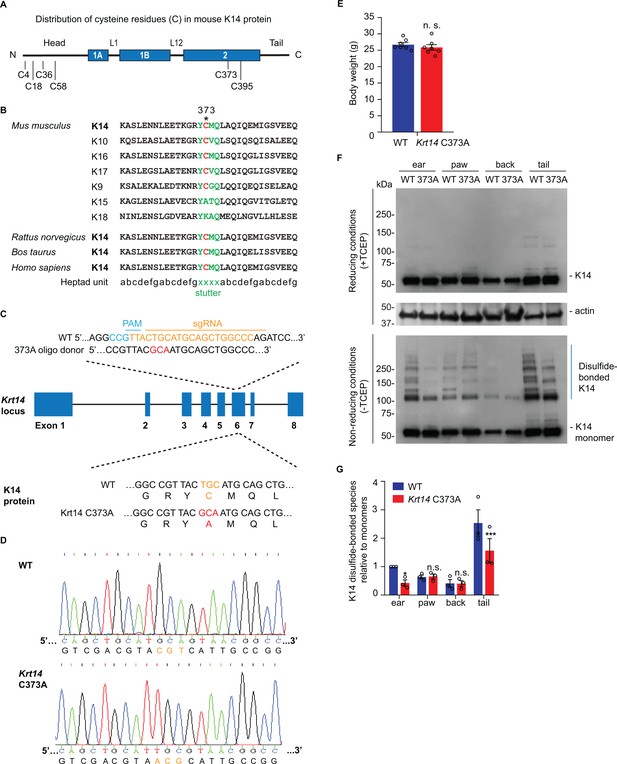
Decreased K14-dependent disulfide-bonded species and thickened epidermis in Krt14 C373A mouse skin.
(A) Location of cysteine (C) residues in mouse K14 protein (C4, C18, C36, C58, C373, C395), in which N-terminal head and C-terminal tail domains are flanking the central α-helical rod domain (coils 1A, 1B and 2 (blue boxes) separated by linkers L1 and L12). (B) Alignment of the sequence context flanking residue C373 in mouse K14 and other mouse type I keratins (top) as well as for K14 in other species (bottom). The heptad repeat is shown at the bottom. ‘xxxx’ marks the location of the stutter sequence (green letters). (C) Schematic diagram of the strategy used to generate Krt14 C373A mice using the Crispr/Cas9 system. sgRNA, single guide RNA; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif. (D) Sanger sequencing showing the TGC to GCA transversion at codon 373 (cysteine to alanine) in the Krt14 gene. (E) Young adult Krt14 C373A WT littermate male mice show a similar body mass. N = 7 for each genotype. (F) Immunoblotting analysis of total protein lysates from ear, paw, back skin, and tail skin from WT and Krt14 C373A young adult mice subjected to SDS-PAGE electrophoresis under reducing (+TCEP) and non-reducing (-TCEP) conditions. (G) Quantification of relative amounts of K14-dependent disulfides over monomers (see c). N = 3 replicates. Data represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: n.s., no statistical difference; *p<0.05; ***p<0.005.
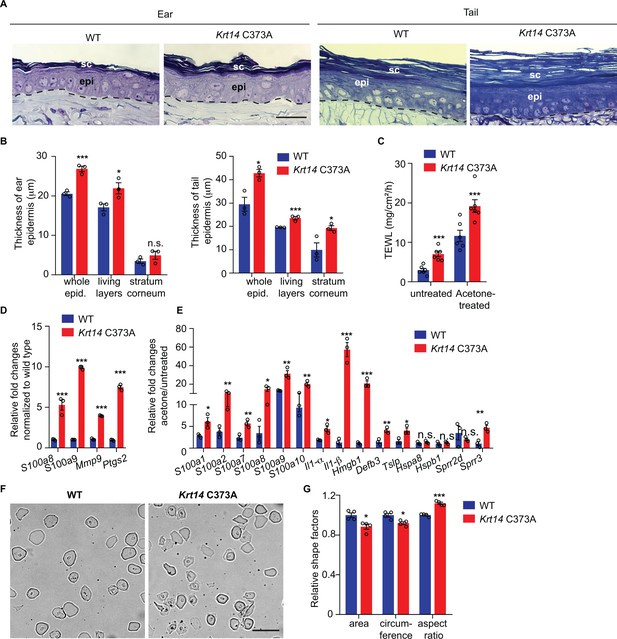
Alternations in morphology and barrier status in Krt14 C373A skin.
(A) Toluidine blue-stained sections (1 mm thick from epoxy-embedded skin of young adult WT and Krt14 C373A mice. (B) Quantification of whole epidermal thickness (living epidermal layers and stratum corneum layers) in ear (left) and tail (right) skin of WT and Krt14 C373A mice. Five random fields were sampled for each of 3 mice per genotype. Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) Trans-epidermal water loss measurements of WT and Krt14 C373A ear skin at baseline (untreated) and after acetone-induced barrier disruption. N = 6 per sample. D. Relative fold change in mRNA levels (qRT-PCR) for Danger-Associated Molecular Patters (DAMPs) in WT and Krt14 C373A skin at baseline. N = 3 biological replicates. (E) Relative fold change in mRNA levels (qRT-PCR) for DAMPs after acetone treatment. N = 3 biological replicates. (F) Representative phase contrast microscopy images of cornified envelopes isolated from WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin. (G) Quantitation of surface area, circumference, and aspect ratio of cornified envelopes in d. Approximately 100 CEs were counted for each of four mice. Data represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.005; n.s., no statistical difference. Scale bar, 100 µm.
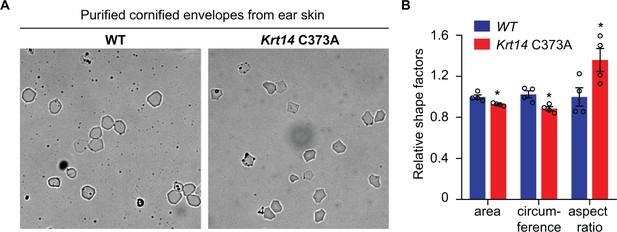
Analysis of purified cornified envelopes from ear skin.
(A) Representative microscopic images of cornified envelopes isolated (CE) from WT and Krt14 C373A ear skin. Bar, 100 µm. (B) Quantitation of surface area, circumference, and aspect ratio of CEs. N = 4. Approximately 100 CE pieces were measured per mouse. Data represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: *p<0.05, n.s., no statistical difference.
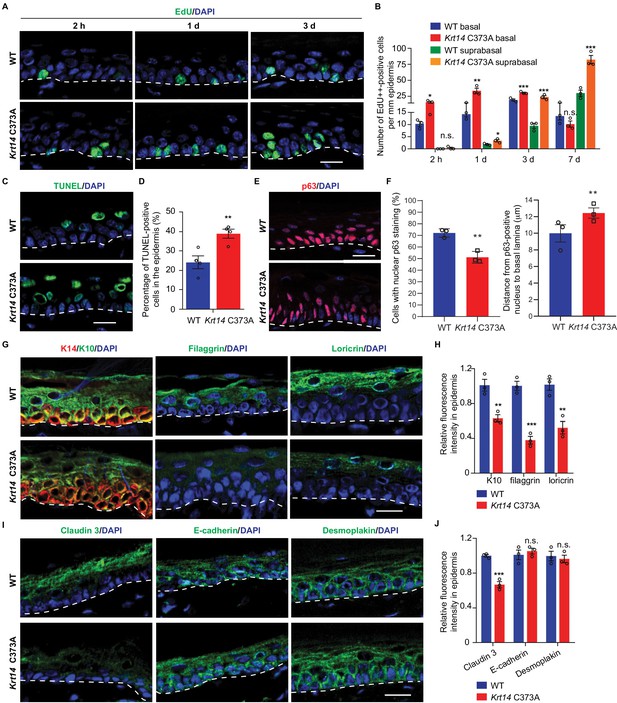
Altered tissue homeostasis and dysregulated keratinocyte differentiation in Krt14 C373A skin.
(A) Indirect immunofluorescence for Edu in tail skin section from WT and Krt14 C373A at 2 hr, 1 d, and 3 d after treatment with thymidine analog EdU. Nuclei as stained with DAPI (blue). (B) Quantification of number of EdU-positive nuclei in basal and suprabasal layers per mm of epidermis. N = 3 replicates for each sample. (C) TUNEL staining in tail epidermis of young adult WT and Krt14 C373A mice. D. Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells shown in frame c. N = 4 mice per sample. E. Indirect immunofluorescence for p63 in tail skin section from WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin. Dashed lines depict the dermo-epidermal interface. (F) Quantification of the number of p63-positive nuclei per mm of epidermis (left) and their distance from the basal lamina (right). N = 3 replicates for each sample. (G) Indirect immunofluorescence for K14 (green), K10 (red), filaggrin, and loricrin from tail skin sections of WT and Krt14 C373A mice. (H) Quantification of relative fluorescence intensity of data shown in frame g, normalized to WT. N = 3 mice per sample. (I) Indirect immunofluorescence for claudin 3, E-cadherin and desmoplakin in tail skin sections from WT and Krt14 C373A mice. (J) Quantitation of relative fluorescence intensity in g. N = 3 mice per sample. In a, c, e, g, and I, nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue), and dashed lines depict the dermo-epidermal interface. Scale bars, 20 µm. Data in b, d, f, h and g represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.005; n.s., no difference.
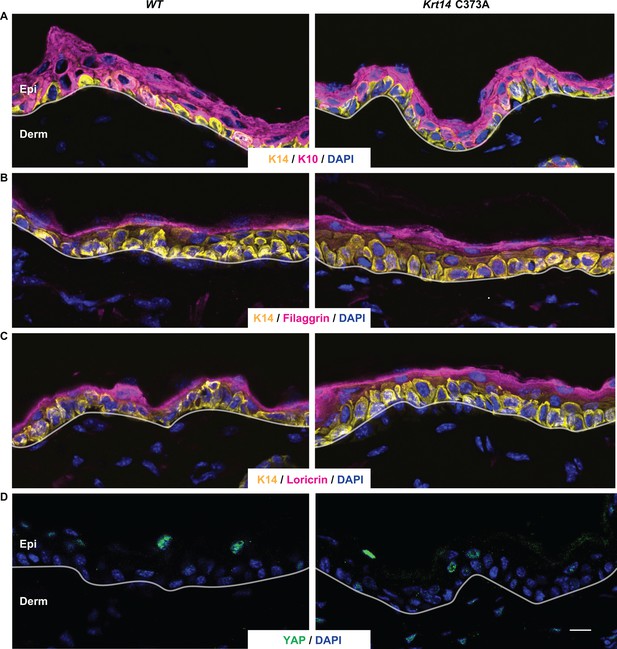
Analysis of terminal differentiation in mouse back skin tissue.
(A-C) Cryosections of back skin tissue from young adult WT and Krt14 C373A were subjected to dual indirect immuno-fluorescence using antibodies to (A) K14 and K10; (B) K14 and filaggrin; and (C) K14 and loricrin. (D) Same as A, except that an antibody to Yap1 was used. Unlike the case for tail and ear skin tissue (see Figures 2 and 3), Krt14 C373A epidermis exhibits a normal thickness, a normal distribution of differentiation markers. Consistent with the literature (Beverdam et al., 2013), YAP1 staining is much reduced and not confined to the basal layer in back skin epidermis. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue), and dashed lines depict the dermo-epidermal interface. Epi, epidermis; Derm, dermis. Scale bar, 20 µm.
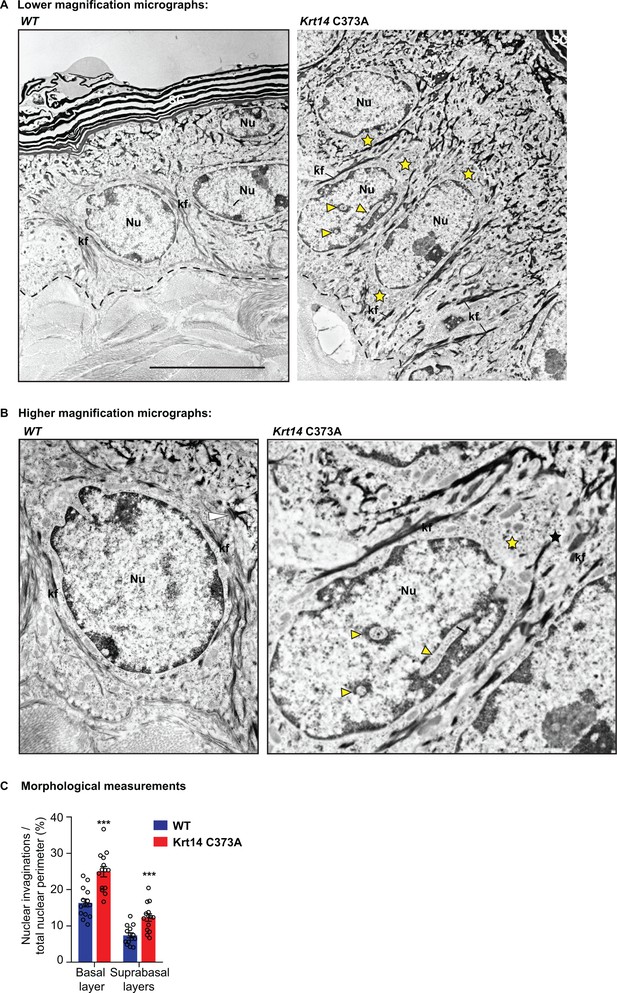
Ultrastructural changes and abnormal nuclei in Krt14 C373A keratinocytes.
(A) Transmission electron micrograph of ear skin epidermis from WT and Krt14C373A mice. (B) High magnification images of representative cells in frame a. Dotted lines mark the dermo-epidermal interface. Asterisks depict areas showing abnormal gaps between keratin filaments (kf) and the nucleus (Nu) in mutant Krt14 C373A keratinocytes. Arrowheads depict cytoplasmic invaginations into the nucleus in Krt14 C373A keratinocytes. Scale bar, 5 µm. (C) Quantification of frequency of nuclear invaginations (n = 14 nuclei from two biological replicates for each genotype). Data represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: ***p<0.005.
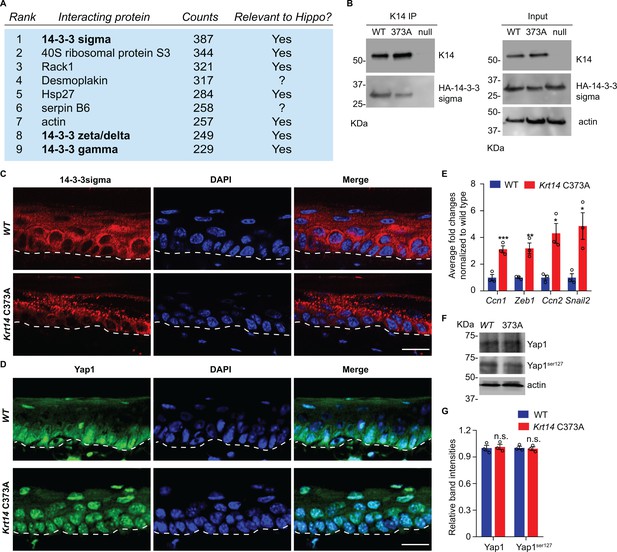
14-3-3σ interacts with K14, and abnormal localization 14-3-3σ and YAP in Krt14 C373A epidermis.
(A) Top nine most abundant non-keratin entries from a mass spectrometry screen for proteins interacting with K14 in WT newborn skin keratinocytes (primary culture,1 mM calcium, 4 days). Spectral counts and known relevance to Hippo signaling are indicated. See Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for full listing. (B) Immunoprecipitation of K14 from WT or Krt14 C373A skin keratinocytes in primary culture. Both K14 WT and, albeit to a lesser extent, the 373A mutant interact with HA-tagged 14-3-3σ. KDa, kilodalton. (C) Indirect immunofluorescence for 14-3-3σ in WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin sections. Dashed lines depict the dermo-epidermal interface. (D) Indirect immunofluorescence for YAP in WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin sections. (E) Relative mRNA levels (qRT-PCR) for YAP target genes Ccn1, Zeb1, Ccn2, and Snail2 in adult WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin. N = 3 biological replicates per genotype. (F) Immunoblotting analysis for total YAP and YAPSer127 in WT and Krt14 C373A tail skin protein lysates. (G) Quantification of relative protein levels shown in frame d. Data are mean ± SEM from three biological replicates. Student’s t test: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.005; n.s., no statistical difference. Scale bars, 20 µm.
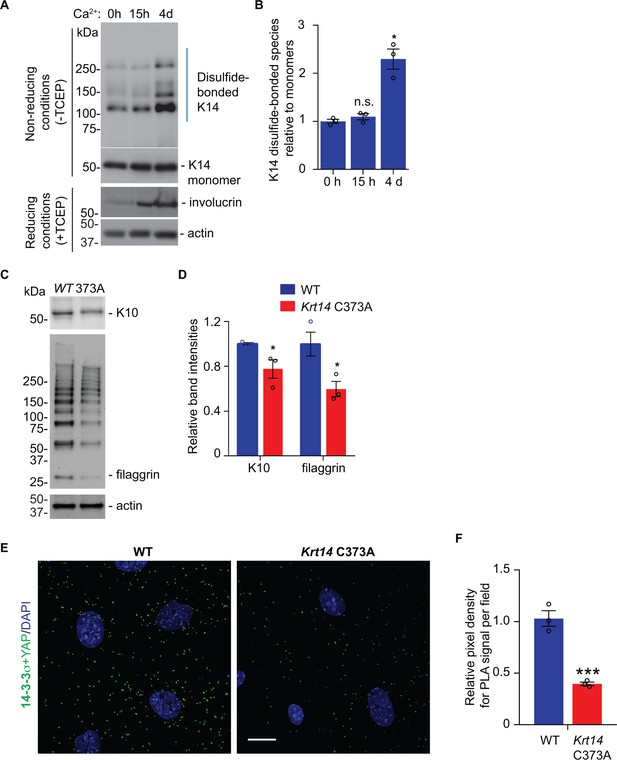
Additional analyses of newborn skin keratinocytes in primary culture.
(A) Western blot analysis of total protein extracts from WT newborn keratinocytes in primary culture, in the absence (0 hr) and presence of calcium for 15 hr and 4 days (4d) after addition of calcium. Gels were run is the absence or presence of TCEP reduction as indicated at left. This analysis shows the kinetics of formation of K14-dependent disulfide species after adding calcium. Involucrin is shown as a marker of terminal keratinocyte differentiation; actin is used as a loading control. (B) Quantification (gel scanning densitometry) of the gel data shown in frame A. Data represent mean ± SEM from N = 3 biological replicates. (C) Western blot analysis comparing the steady state levels of K10 and filaggrin at 4 days after adding calcium to primary cultures of WT and Krt14 C373A newborn keratinocytes in primary culture. Filaggrin presents as a gallery of discrete size products consistent with its modular repeat substructure. (D) Quantification (gel scanning densitometry) of the gel data shown in frame C. Data represent mean ± SEM from N = 3 biological replicates. (E) Proximity ligation assays (PLA) for 14-3-3σ and YAP1 in WT and Krt14 C373A newborn keratinocytes in primary cultures subjected to 1 mM calcium-induced differentiation for 4 days. Bar = 20 µm. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (F) Quantitation of the data shown in frame E. N = 42 cell we counted for each genotype. Data represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: ***p<0.005; n.s., no difference.
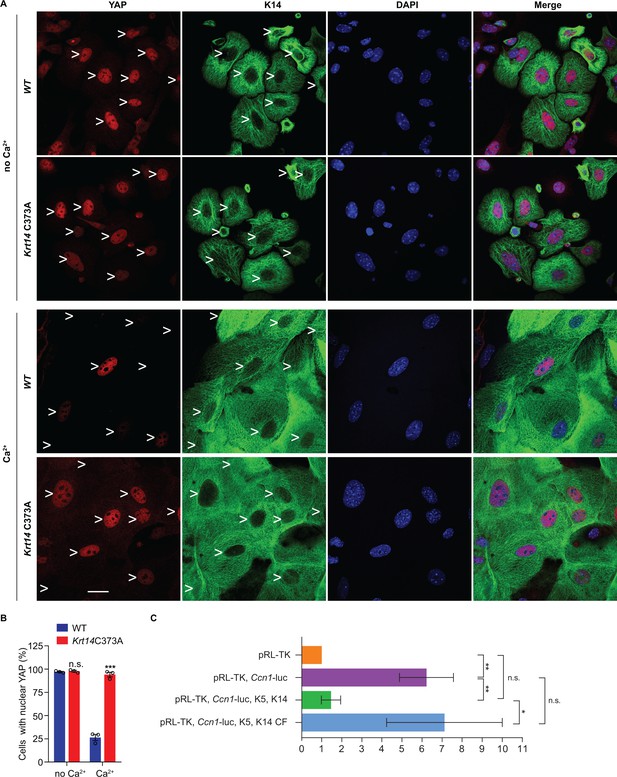
Localization and interaction of 14-3-3σ and YAP activity in Krt14 C373A keratinocytes.
(A) Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy for YAP (red) and K14 (green) in WT and Krt14 C373A newborn skin keratinocytes in primary culture in the absence and presence of 1 mM calcium (for 4 d). Arrowheads depict location of nuclei. (B) Quantification of cells with nuclear YAP in frame a. N = 3 biological replicates. Approx. 100 cells were counted for each genotype for each condition. N = 3 biological replicates. Data represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: n.s., no statistical difference; ***p<0.005. Scale bars, 20 µm. (C) Luciferase assays in HeLa cells transfected with a Ccn1-Luciferase reporter construct (see Materials and methods). Data were normalized with regard to transfection efficiency and signal obtained with pRL-TK vector control. Data represent mean ± SEM three biological replicates consisting of 6 technical replicates each. Mann-Whitney tests were performed to compare each parameter using GraphPad Prism 8. **p<0.01, *p<0.05, n.s., non-significant.
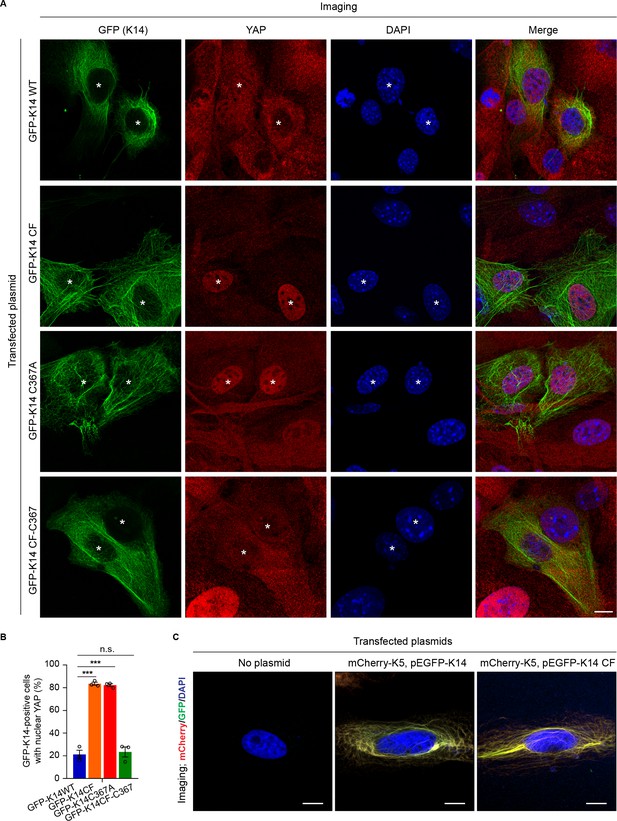
Localization of YAP is specifically regulated by cysteine residue 367 in human K14.
Newborn skin keratinocytes from Krt14 null mice were seeded in primary culture, transiently transfected with either GFP-K14 WT, GFP-K14CF, GFP-K14C367A or GFP-K14CF-C367 constructs, and cultured in 1 mM calcium for 36 hr prior to analysis. (A) Indirect immuno-fluorescence showing successfully transfected and viable cells (see asterisks). Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) Quantitation of the percentage of GFP-K14 transfected cells with nuclear YAP staining. N = 3 biological replicates. N = 100 cells were counted for each genotype and each construct. Data represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: ***p<0.005; n.s., no difference. (C) Organization of keratin filaments in HeLa cells transiently co-tranfected with no plasmid (left), mCherry-K5 (WT) and pEGFP-K14 (WT) (center), and mCherry-K5 (WT) and pEGFP-K14 CF (right). Nuclei are stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 µm.
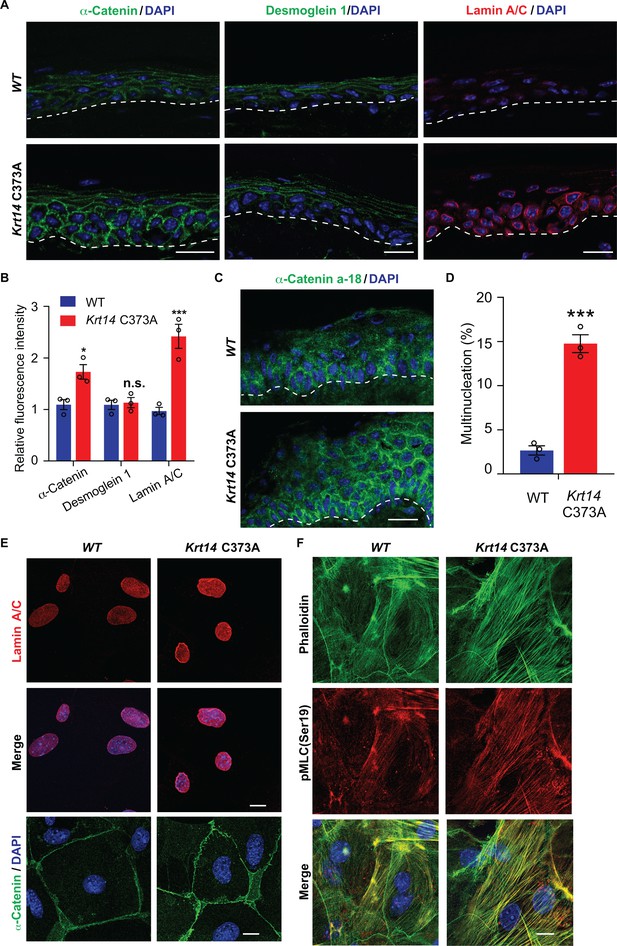
Altered mechanics in Krt14 C373A epidermis and keratinocytes in culture.
(A-C) Studies involving tail skin sections from young adult WT and Krt14 C373A mice. A. Indirect immuno-fluorescence microscopy for α-catenin, desmoglein one and lamin A/C. Dashed lines depict the dermo-epidermal interface. B. Quantification of relative fluorescence intensity, as shown in frame a, for WT and Krt14 C373A. N = 3 biological replicates. (C) Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy for the a-18 mechanosensitive epitope in α-catenin in tail skin sections from WT and Krt14 C373A mice (see A). D-F: Studies involving newborn skin keratinocytes in primary culture. (D) Percentage of cells with multinucleation in WT and Krt14 C373A keratinocytes cultured as described for frames a,c. N = 3 biological replicates (total of 100 cells counted each time per genotype). (E) Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy for lamin A/C (top and middle rows) and α-catenin (bottom row) in primary cultures of WT and Krt14 C373A newborn keratinocytes. (F) same as E, except that F-actin (via phalloidin) and Ser19-phosphorylated myosin light chain pMLC (Ser19) are stained. Nuclei are stained with DAPI in frames A, C, E and F. Scale bars, 20 µm. Data in B and F represent mean ± SEM. Student’s t test: *p<0.05; ***p<0.005; n.s., no statistical difference.
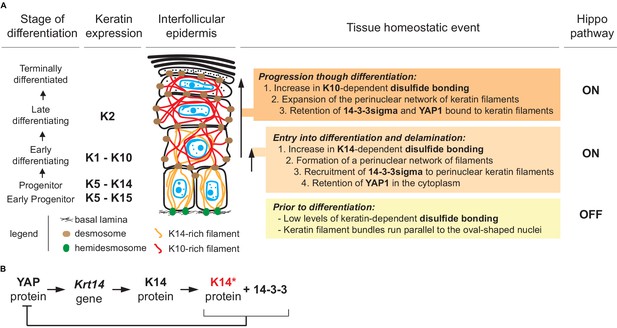
Model depicting the role of keratin-dependent disulfide bonding in integrating signaling and mechanical cues as keratinocytes initiate terminal differentiation in epidermis.
(A) Left to right: the stage of epidermal differentiation, keratin expression, epidermal morphology, and state of keratin filament organization are related to 14-3-3 binding, YAP1 subcellular partitioning, and Hippo activity status. The model proposes that initiation of terminal differentiation in late stage progenitor keratinocytes in the basal layer entails: (1) the formation of K14-dependent disulfides via the conserved stutter cysteine in coil two domain; (2) a reorganization of keratin filaments around the nucleus; (3) recruitment of 14-3-3 onto keratin filaments; and (4) effective sequestration of YAP1 in the cytoplasm, resulting in activation of Hippo signaling. The model proposes an identical role for the conserved cysteine in coil 2 of keratin 10, which is expressed early during terminal differentiation, thereby maintaining YAP1’s sequestration to the cytoplasm and active Hippo signaling. These changes are coupled to a redistribution of tension-related forces and cell-cell adhesion complexes as basal keratinocytes delaminate and move from the basal to the suprabasal compartment of epidermis (Miroshnikova et al., 2018; Nekrasova et al., 2018; Wickström and Niessen, 2018). (B) Illustration of a negative feedback loop whereby, once modified in a specific manner (phosphorylation and disulfide bonding), K14 protein sequesters YAP1 and interrupts its activity towards promoting keratinocyte proliferation, thereby initiating terminal differentiation (see Figure 7—figure supplement 1 and 2 for related data).
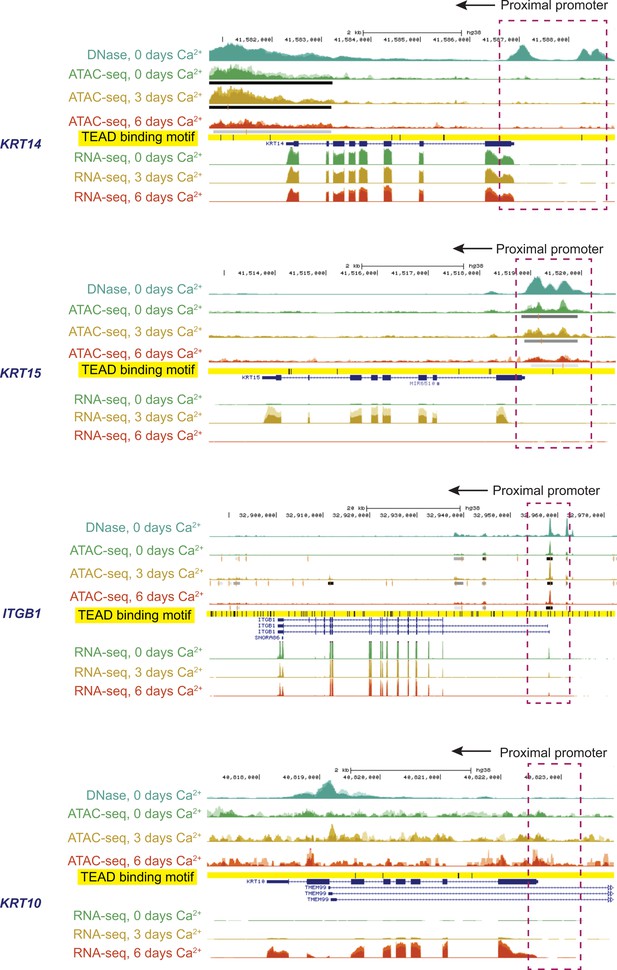
Genomic context, gene expression, chromatin organization, and presence of TEAD binding sites in gene loci of interest.
This information was obtained from the ENCODE project (www.encodeproject.org) and applies to human fore-skin keratinocytes cultured in the presence or absence of calcium (see Materials and methods for details). Representative data from four genes (KRT14, KRT15, ITGB1 and KRT10) are shown. Cells were subjected to calcium treatment for 0, 3 and 6 days. Chromatin structure (e.g., open, closed) was assessed by DNAse treatment at baseline (0 days calcium) or by ATAC-SEQ at 0, 3, and 6 days after calcium treatment. Transcript levels were measured by RNA-seq at 0, 3, and 6 days after calcium treatment. Peak scaling is identical between days 0, 3, and six but optimized between genes. Gene diagrams are shown in blue. The location of TEAD consensus binding sites depicted by short vertical bars and highlighted in yellow. Proximal promoter regions are boxed (dashed lines), and direction of transcription is shown by arrows.
Additional files
-
Source data 1
Raw data used for quantitation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53165/elife-53165-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 1
Mass spectrometric screen for proteins interacting with wildtype K14 in WT newborn skin keratinocyte in primary culture.
List of all proteins with at least 35 spectral counts (cumulative over three biological replicates). Gene symbols are provided at left. WT1, WT2, WT3, WT4 and WT5 represent different regions of silver stained protein electrophoretic gels subjected to MS analysis (data not shown). Keratin protein entries dominate this screen, as expected, and are listed using blue lettering. 14-3-3 protein isoforms are listed using red lettering. The top non-keratin protein from this screen is 14-3-3sigma.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53165/elife-53165-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Summary of data relating genomic context, gene expression, chromatin organization, and presence of TEAD binding sites in gene loci of interest.
This summary account applies to human foreskin keratinocytes cultured in the absence (day 0) or presence of calcium for 6 days (see Figure 7—figure supplement 1) and is derived from the ENCODE project. Ratings for gene expression levels (low, moderate (med), high or very high) and promoter accessibility (low, moderate (med) or high are reported for keratin genes known to be expressed in progenitor (KRT14, KRT15, KRT5) and differentiating keratinocytes (KRT10, KRT1, KRT2) in epidermis, and for additional genes that are relevant to our study (SFN, ITGB1, CCN1, TP63, YAP1, and TEAD1). The presence of consensus TEAD binding sites in the proximal promoter of these genes (either 1–2 sites, shown as ‘+”, or >3 sites, shown as ‘+++””) is also reported. See Discussion for further information.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53165/elife-53165-supp2-v2.ai
-
Supplementary file 3
List of oligonucleotide primers used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53165/elife-53165-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Key Resources Table.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53165/elife-53165-supp4-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53165/elife-53165-transrepform-v2.docx





