An ultralong CDRH2 in HCV neutralizing antibody demonstrates structural plasticity of antibodies against E2 glycoprotein
Figures
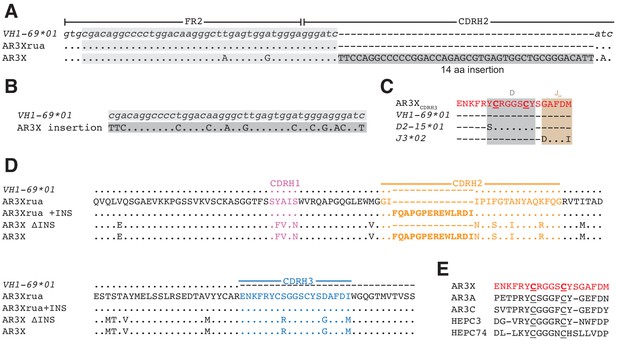
AR3X includes a 14-residue insertion in CDRH2.
(a) Sequence alignment of a portion of the heavy chain variable region gene sequences of AR3X and the AR3X germline precursor (AR3Xrua) (uppercase letters) and the VH1-69 gene segment (lowercase letters). The CDRH2 insertion is indicated by a dark gray box with the position of the potential duplication site indicated by a light gray box. CDR loops were defined based on Kabat nomenclature Kabat and National Institutes of Health (U.S.). Office of the Director, 1991). Dots indicate identical nucleotides and dashes indicate gaps. (b) Sequence alignment of the CDRH2 insertion and the potential duplication origin site in VH1-69. (c) Amino acid sequence alignment of the AR3X CDRH3 and the AR3X germline precursor genes determined by IMGT/V-QUEST. Dots indicate identical amino acids and dashes indicate regions encoded by other gene segments or N-nucleotide additions. Two cysteines encoded by the D gene segment are highlighted in bold and underscored. (d) Amino acid sequence alignment of the heavy chain variable region sequences of AR3X, AR3X ΔINS (AR3X without insertion), AR3Xrua (germline precursor of AR3X), and AR3Xrua + INS (germline precursor of AR3X with insertion). CDR loops were defined based on Kabat nomenclature and colored purple (CDRH1), orange (CDRH2), and blue (CDRH3), with the CDRH2 insertion highlighted in bold. Dots indicate identical amino acids and dashes indicate gaps. (e) Alignment of AR3X, AR3A, AR3C, HEPC3, and HEPC74 CDRH3 sequences. The AR3X sequence is highlighted in red and the two cysteines in each CDRH3 are underscored.
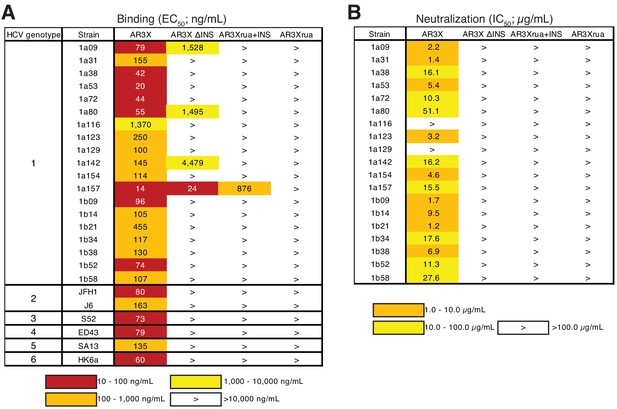
The CDRH2 insertion in AR3X is required for maximal binding and broad neutralization.
(a) Heat map showing the binding of AR3X and its variants to a panel of HCV E2ecto proteins. The EC50 value for each E2ecto-mAb combination is shown, with dark red, orange, yellow, or white shading indicating high, intermediate, low, or no detectable binding, respectively. The > symbol indicates EC50s greater than 10 µg/mL or EC50s in which the OD450 values at the highest antibody concentration tested were lower than 0.5. One experiment representative of two independent experiments is shown. (b) Heat map showing neutralization activities of AR3X and AR3X variants measured using a panel of genotype 1 HCVpp. IC50 values for each virus-mAb combination are shown. The > symbol indicates IC50s greater than 100 µg/mL or IC50s in which the percent neutralization at the highest antibody concentration tested was lower than 50%.
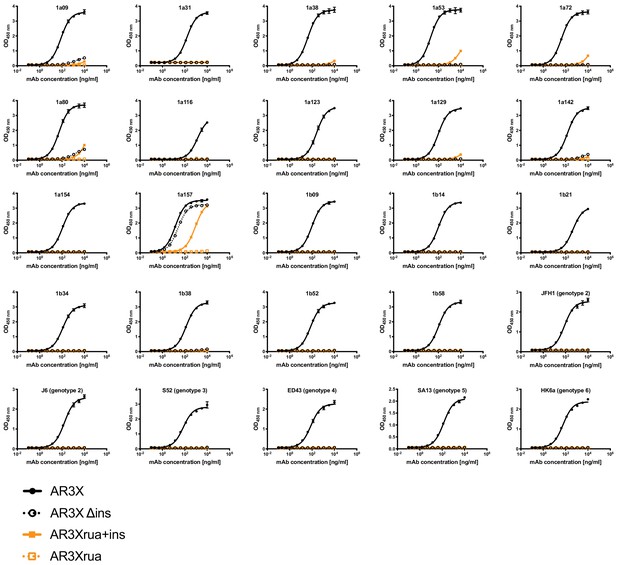
Binding of AR3X and its variants to a panel E2ecto proteins.
Values shown are means ± s.d. of duplicates. One experiment representative of two independent experiments is shown.
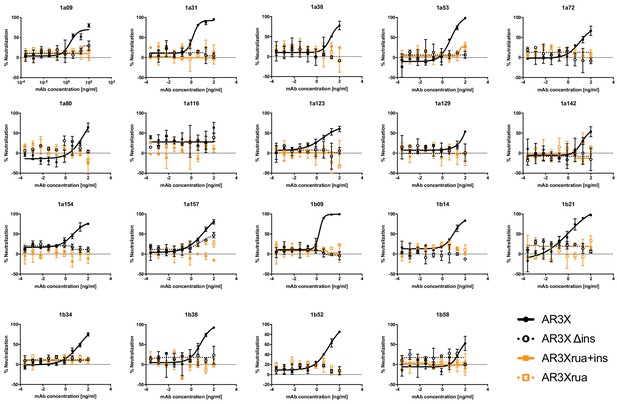
Neutralization activities of AR3X and its variants against a panel of genotype 1 HCVpp.
Values shown are means ± s.d. of duplicates.
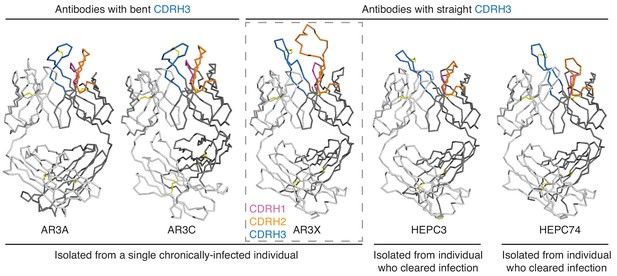
The shared CDRH3 motif in E2 front layer-specific HCV bNAbs adopts different orientations.
Fab structures in liganded state of AR3A (PDB 6BKB), AR3C (PDB 4MWF), AR3X (this paper), HEPC3 (PDB 6MEI), and HEPC74 (PDB 6MEH). The structures were superimposed on their VH domains. Protein backbones are shown as ribbons and CDR loops are purple (CDRH1), orange (CDRH2), and blue (CDRH3).
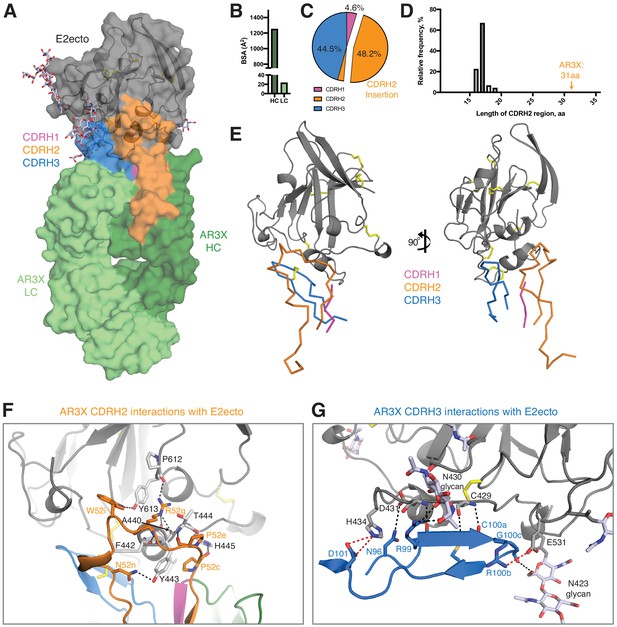
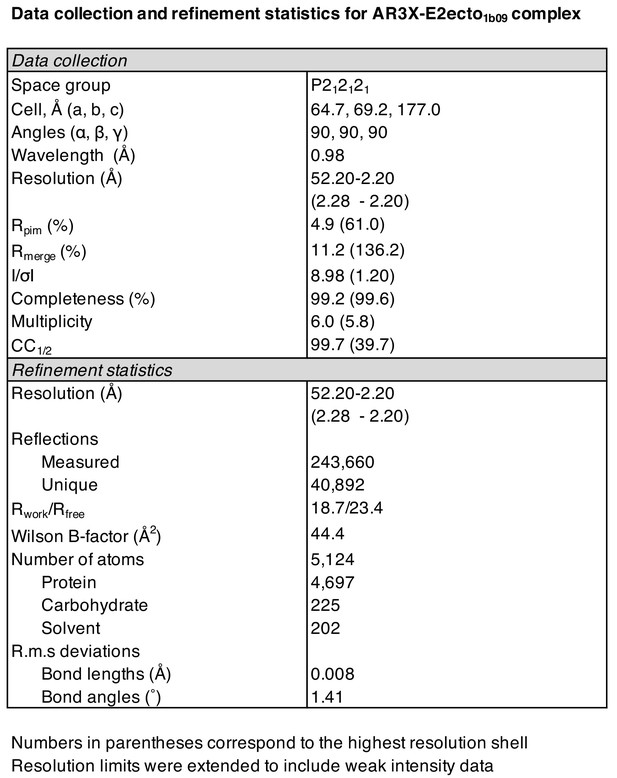
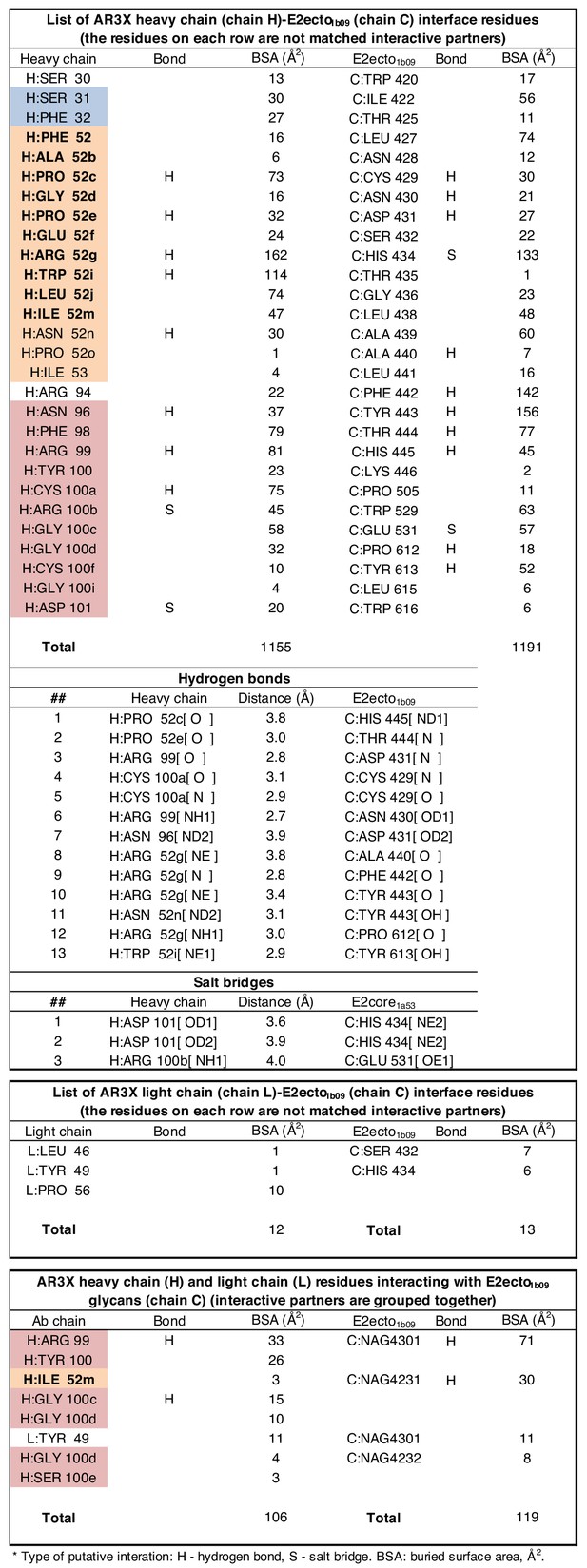
Details of the AR3X interactions with E2ecto.
(a) Crystal structure of the AR3X-E2ecto complex. E2ecto is shown as a cartoon representation within a transparent surface with N-glycans highlighted as sticks and disulfide bonds shown as yellow sticks. The AR3X Fab is shown in a surface representation with highlighted CDRs. (b) Comparison of buried surface areas (BSAs) of E2ecto on the HC and LC of AR3X. (c) Percentage of BSA contributed from CDRH loops of the total BSA on the AR3X HC. The portion of CDRH2 within the CDRH2 insertion is separated from the main pie chart. (d) Length distribution of human CDRH2s. Human CDRH2 lengths were extracted from the online abYsis system (http://www.bioinf.org.uk/abysis/) using the Kabat numbering scheme Kabat and National Institutes of Health (U.S.). Office of the Director, 1991). (e) Interactions of AR3X heavy chain CDRs with E2ecto. CDRs are purple (CDRH1), orange (CDRH2), and blue (CDRH3) tubes. Disulfide bonds are shown as yellow sticks. (f) CDRH2 interactions with E2ecto. Interacting residues are shown as sticks. AR3X CDRH1 – purple, AR3X CDRH2 – orange, and AR3X CDRH3 – blue. Disulfide bonds are shown as yellow sticks. Potential H-bonds are shown as black dashed lines, and residues at the interface are indicated. (g) CDRH3 interactions with E2ecto. Interacting residues shown as sticks. For clarity, only the CDRH3 of AR3X is shown. Disulfide bonds are shown as yellow sticks and E2 glycans are shown as sticks with light blue, red, and dark blue colors for carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms, respectively. Potential H-bonds and salt bridges are shown as black or red dashed lines, respectively. Residues at the interface are indicated.
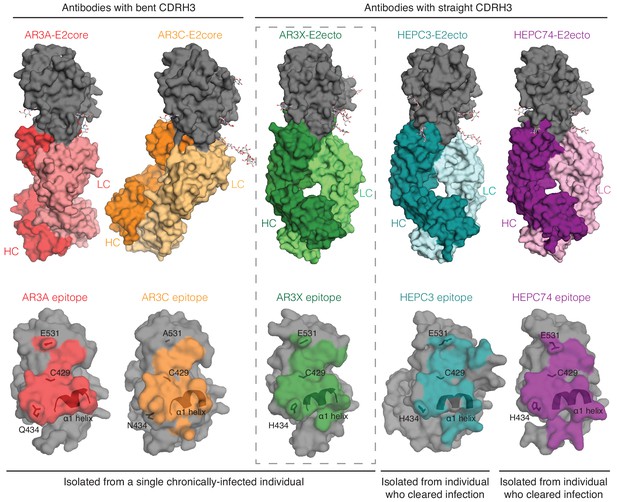
A structural plasticity of VH1-69-derived bNAbs with the CDRH3 disulfide motif.
(Top) Surface representations of AR3X-E2 and other bNAb-E2 structures. E2, gray; AR3A-HC, red; AR3A-LC, light red; AR3C-HC, orange; AR3C-LC, yellow; AR3X-HC, green; AR3X-LC, light green; HEPC3-HC, blue; HEPC3-LC, light blue; HEPC74-HC, purple; HEPC74-LC, pink. (Bottom) Comparison of AR3A (red), AR3C (orange), AR3X (green), HEPC3 (blue), and HEPC74 (purple) epitopes. Epitopes on the E2 front layer (surface representation) were defined as residues in E2 containing an atom within 4 Å of the bound Fab.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HEK293-6E | National Research Council of Canada | 11565 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | Expi293F | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A14527 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | Hep3B2.1–7 | ATCC | HB-8064 | |
| Antibody | Anti-Human IgG-HRP (Goat polyclonal) | SouthernBiotech | 2040–05 | 1:4000 dilution |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pTT5 mammalian expression vector (used to express IgGs and Fabs) | National Research Council of Canada | N/A | |
| Commercial assay or kit | 1-Step Ultra TMB-ELISA Substrate Solution | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 34028 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PEGRx HT | Hampton Research | HR2-086 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PEG/Ion HT | Hampton Research | HR2-139 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | JCSG-plus HT-96 | Molecular Dimensions | MD1-40 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Kifunensine | Sigma | K1140 | |
| Software, algorithm | Pymol | Schrödinger, LLC | RRID:SCR_000305 | |
| Software, algorithm | Phenix | (Adams et al., 2010) | https://www.phenix-online.org | |
| Software, algorithm | Coot | (Emsley and Cowtan, 2004) | http://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/personal/pemsley/coot/ | |
| Software, algorithm | PDBePISA | (Krissinel and Henrick, 2007) | http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/pisa/ | |
| Software, algorithm | abYsis system | http://www.bioinf.org.uk/abysis/ | ||
| Other | Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 GL | GE Healthcare | 17517501 | |
| Other | HisTrap FF column | GE Healthcare | 17531901 | |
| Other | HiTrap Protein A HP column | GE Healthcare | 17040301 | |
| Other | HCV 1b09 strain E1E2 sequence | GenBank | KJ187984.1 |