Monoubiquitination by the human Fanconi anemia core complex clamps FANCI:FANCD2 on DNA in filamentous arrays
Figures
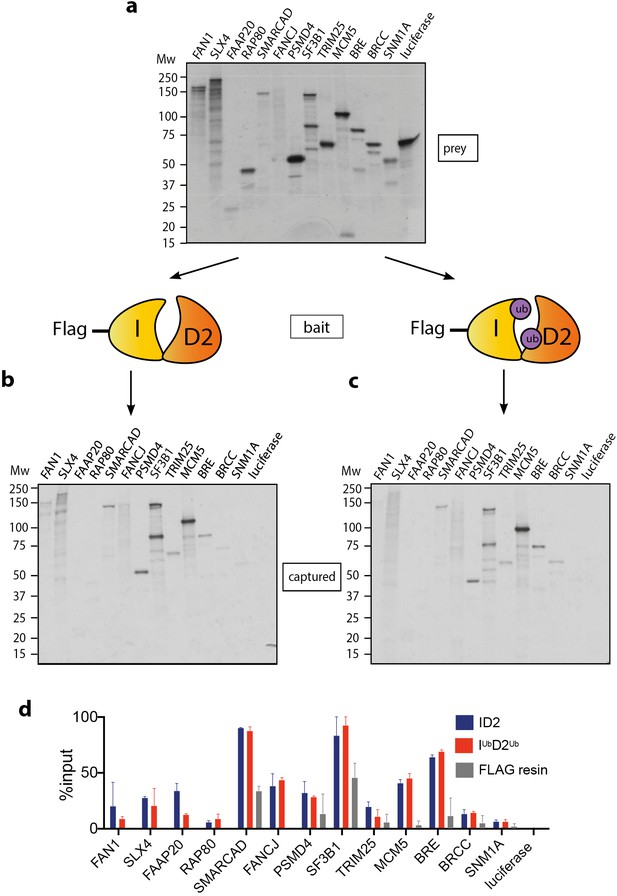
Mono-ubiquitination does not alter interaction of FANCI:FANCD2 with DNA repair proteins.
(a) 35S-labelled FAN1, SLX4, FAAP20, RAP80, SMARCAD, FANCJ, PSMD4, SF3B1, TRIM25, MCM5, BRE, BRCC, SNM1A or luciferase (control) inputs were expressed using reticulocyte extracts. (b–c) The inputs prepared from (a) were incubated with the indicated FLAG-ID2 (b) or FLAG-IubD2ub (c) followed by FLAG pull-down and elution. The complexes were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and radiolabelled proteins were detected by autoradiography (representative experiment of n = 2). (d) Quantification showing percentage of ID2, IubD2ub or FLAG resin binding to inputs.
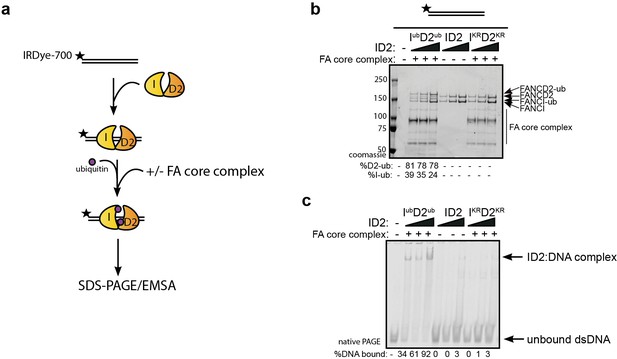
Monoubiquitination locks FANCI:FANCD2 on DNA.
(a) Schematic of the electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) using IRDye-700 labeled dsDNA. (b) Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel showing monoubiquitination of FANCI:FANCD2 using recombinant FA core complex and IR-dye700 labeled dsDNA. 25, 50 and 100 nM of ID2 or IKRD2KR were incubated with 25 nM of the IR-dye700 dsDNA for 90 min. The respective percentage of FANCI or FANCD2 monoubiquitination were calculated and shown under SDS-PAGE gel. (c) Monoubiquitination reactions from (b) were resolved on 6% native PAGE gel for EMSA analysis. The percentage of ID2 binding to DNA was calculated and shown under native PAGE gel.
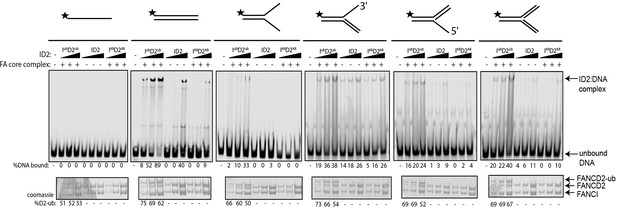
Monoubiquitinated FANCI:FANCD2 binds to any type of dsDNA.
EMSA gels showing binding of monoubiquitinated or unmodified ID2 complex to different oligo-based DNA substrates. Above each panel, a schematic representing the tested DNA substrate is shown. 25, 50 and 100 nM of ID2 or IKRD2KR were incubated with 25 nM of the indicated DNA substrate and the protein:DNA complexes were resolved on 6% PAGE gels (top). The percentage of DNA binding was calculated and shown under each EMSA gel. Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel (bottom) showing the ubiquitination reactions used in the EMSA. The percentage of FANCD2 monoubiquitination was calculated and shown under each SDS-PAGE gel.
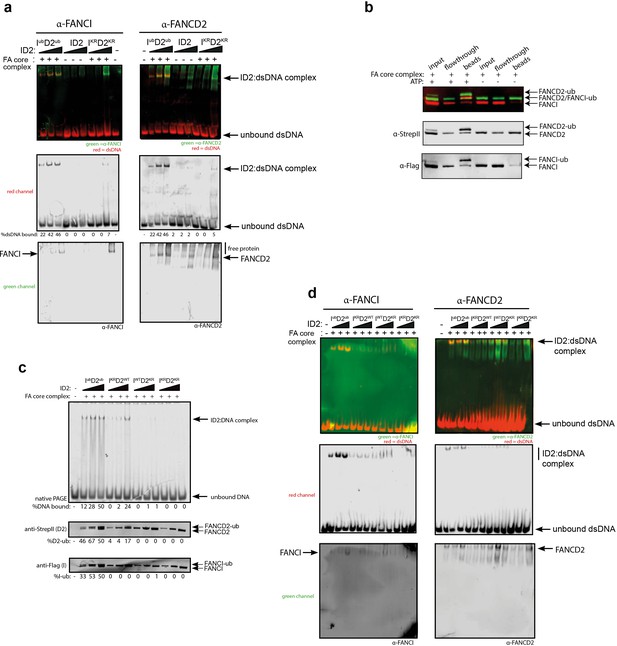
FANCD2 monoubiquitination is sufficient for FANCI:FANCD2 locking to DNA, but stimulated by FANCI monoubiquitination.
(a) Western blots of the EMSA gels containing 50, 100 and 200 nM of IubD2ub, ID2 or IKRD2KR in the presence of 25 nM IRDye-700 labeled dsDNA (red). Left panels correspond to anti-FANCI antibody (green) and right panels correspond to anti-FANCD2 antibody (green) (b) StrepII affinity purification of mono-ubiquitinated (+ATP) and non-ubiquitinated ID2 (-ATP). (c) EMSA gels (top) and western blots (bottom) showing the monoubiquitination of 25, 50 and 100 nM IWTD2WT, IKRD2WT, IWTD2KR or IKRD2KR in the presence of 25 nM IRDye-700 labeled dsDNA. (d) Western blots of the EMSA gels showing monoubiquitination of 50, 100 and 200 nM IWTD2WT, IKRD2WT, IWTD2KR or IKRD2KR in the presence of 25 nM IRDye-700 labeled dsDNA. FANCI (left, green) and FANCD2 (right, green) remained bound to IRDye-700 labeled DNA (red) after mono-ubiquitination.
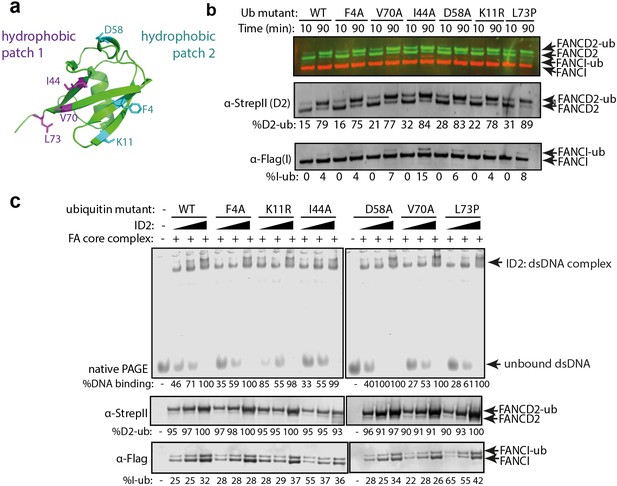
Mutations in different ubiquitin patches do not affect ID2 mono-ubiquitination or DNA binding.
(a) Crystal structure of ubiquitin with ubiquitin mutant sites depicted (PDB: 1UBQ). Hydrophobic binding pockets are indicated in blue and pink. (b) Western blots showing the time course ubiquitination assays of ID2 using wild-type ubiquitin or ubiquitin F4A, V70A, I44A, D58A, K11R and L73P mutants. (c) EMSA gels showing 25, 50 and 100 nM monoubiquitinated ID2 binding to 25 nM IRDye-700 dsDNA using various ubiquitin mutants (top). Western blots of ID2 ubiquitination products were shown at the bottom and the percentage of FANCI and FANCD2 ubiquitination were shown at the bottom of each western blot panel.
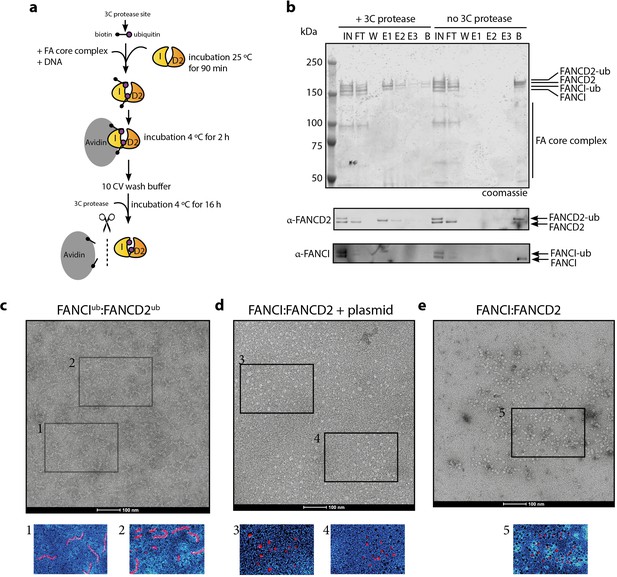
Mono-ubiquitinated FANCI:FANCD2 complex assemble into filament-like arrays.
(a) Schematic of purification of monoubiquitinated FANCI:FANCD2 using Avi-ubiquitin. (b) Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel (top) and western blots (bottom) showing the purification of monoubiquitinated FANCI:FANCD2 complex eluted using PreScission protease (lanes 1–7) compared to without PreScission protease (lanes 8–14). (c–e) Representative negative-stained EM image of purified FANCIub:FANCD2ub complex bound to 2.7 kb plasmid, unmodified FANCI:FANCD2 incubated with 2.7 kb plasmid and unmodified FANCI:FANCD2 complex. Pseudo-colored regions are shown to highlight particular filament-like arrays in FANCIub:FANCD2ub but not other samples.
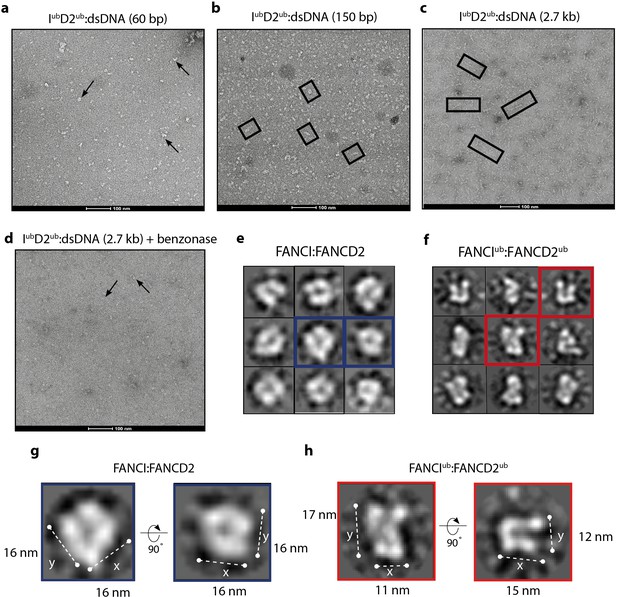
Monoubiquitinated FANCI:FANCD2 assembles into filamentous arrays along the length of dsDNA.
(a–d) Representative EM image of monoubiquitinated FANCI:FANCD2 bound to (a) 60 bp dsDNA, (b) 150 bp dsDNA, (c) 2.7 kb dsDNA, and (d) 2.7 kb dsDNA and Benzonase-treated. Scale bar, 100 nm. Arrows indicate formation of 1–2 ID2 array; boxes indicate multiple ID2 arrays. (e) Representative 2D class average of ID2. Views of the side and top of ID2 are shown, framed in blue for comparison. (f) Representative 2D class average of IubD2ub bound to 60 bp DNA. Views of the side and top of IubD2ub are shown, framed in red for comparison. (g–h) Example comparison of the length (y) and width (x) of class average images ID2 and IubD2ub (likely an overestimate, because uranyl formate staining increases apparent particle size).
Tables
List of proteins containing ubiquitin binding domain that are described or predicted to bind to ubiquitinated FANCD2.
| Protein | Function | Domain | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAN1 | Nuclease | UBZ4 | (Kratz et al., 2010) |
| SLX4 | Nuclease | UBZ1 | (Lachaud et al., 2014) |
| FAAP20 | FANCA partner | UBZ | (Hein et al., 2015) |
| RAP80 | BRCA1 partner | UIM | (Castillo et al., 2014) |
| SMARCAD1 | Chromatin remodeler | CUE | (Densham et al., 2016) |
| FANCJ | Helicase | - | (Raghunandan et al., 2015) |
| PSMD4 | Protease | UIM | (Jacquemont and Taniguchi, 2007) |
| SF3B1 | RNA binding protein | UBZ | (Moriel-Carretero et al., 2017) |
| TRIM25 | E3 ligase | RING finger | (Lossaint et al., 2013) |
| MCM5 | CMG component | - | (Lossaint et al., 2013) |
| BRE | BRCA1 partner | - | (Wang, 2007) |
| BRCC | BRCA1 partner | - | (Wang, 2007) |
| SNM1A | Nuclease | UBZ | (Yang et al., 2010) |
| CtIP* | Nuclease activator | C2H2 zinc finger | (Murina et al., 2014) |
| Rev1* | Translesion polymerase | UBZ3 | (Moldovan et al., 2010) |
-
*Indicates not tested in our experiments, because protein not produced in TnT system.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant DNA reagent (X. laevis) | pFastbac1-FLAG-xFANCI | (Klein Douwel et al., 2014) | Gift from Puck Knipscheer | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (X. laevis) | pFastbac1-StrepII-xFANCD2 | (Klein Douwel et al., 2014) | Gift from Puck Knipscheer | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (H. sapiens) | pFL-EGFP-His-hFANCI | (Tan et al., 2020a) | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent (H. sapiens) | pFastbac1-FLAG-hFANCD2opt | (Tan et al., 2020a) | RRID:Addgene_ 134904 | Gift from Angelos Constantinou |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (H. sapiens) | pFL/pSPL-EGFP-FLAG-B-L-100 | (van Twest et al., 2017) | Codon optimized FANCB | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (H. sapiens) | pFL-MBP-C-E-F | (van Twest et al., 2017) | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent (H. sapiens) | pGEX-KG-GST-UBE2T | (van Twest et al., 2017) | Codon optimized | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (E. coli) | pet16b-Avi-ubiquitin_rbs_BirA | (Tan et al., 2020a) | RRID:Addgene_134897 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (E. coli) | pSRK2706-GST-HRV-3Cprotease | (Raran-Kurussi and Waugh, 2016) | RRID:Addgene_78571 | A gift from David Waugh |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (E. coli) | pUC19 plasmid | New England BioLabs | N3041S | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | BL21 (DE3) | Agilent Technologies | 200131 | |
| Cell line (Spodoptera frugiperda) | Sf9 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | RRID:CVCL_0549 | Maintained in Sf-900 II SFM |
| Cell line (Trichoplusia ni) | High Five | Thermo Fisher Scientific | RRID:CVCL_C190 | Maintained in Sf-900 II SFM |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal antibodies against StrepII | Abcam | RRID:AB_76949 | one in 3000 dilution |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal antibodies against FANCI | Abcam | RRID:AB_74332 | one in 3000 dilution |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal antibodies against FANCD2 | Abcam | RRID:AB_10862535 | one in 3000 dilution |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal antibodies against FLAG | Aviva Biosciences | RRID:AB_10884242 | one in 3000 dilution |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | FLAG peptide | Sigma-Aldrich | F3290 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant Human His6-Ubiquitin E1 Enzyme carrier free | Boston Biochem | E-304–050 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Ubiquitin and associated mutant variants | Boston Biochem | U-110H, UM-I44A, UM-D58A, UM-F4A, UM-L73P, UM-K11R | |
| Commercial assay or kit | TNT T7 Quick Coupled Transcription/Translation System | Promega Corporation | L1170 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Anti-FLAG-M2 affinity gel | Sigma Aldrich | RRID:AB_10063035 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EasyTagL-[35S]-Methionine | PerkinElmer Life Sciences | NEG709A500UC | |
| Software, algorithm | XMIPP | (de la Rosa-Trevín et al., 2013) |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
(A) DNA oligonucleotides used in this study. The following oligonucleotides were ordered from IDTDNA. (B) Combination of oligonucleotides annealed to generate DNA substrates used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54128/elife-54128-supp1-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54128/elife-54128-transrepform-v2.docx





