Heterogeneity of proteome dynamics between connective tissue phases of adult tendon
Figures
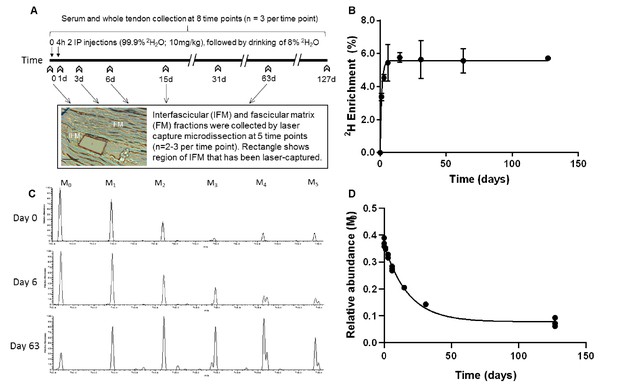
Metabolic labelling of rats using deuterium.
(A) Schematic showing 2H2O labelling of rats and details of sample collection, and interfascicular matrix isolation by laser capture microdissection (scale bar = 100 µm). (B) 2H enrichment in serum occurred rapidly, reaching a plateau of 5.6% by day 4 and remained constant throughout the study. Data are shown as mean ± SD and raw data provided in Figure 1—source data 1. (C) Example extracted ion chromatograms from tendon samples demonstrating increased abundance of higher mass isotopomer peaks over the course of the study (M1 – M5). (D) Example curve showing the relative abundance of the unlabelled monoisotopic peak (M0) for the cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) peptide QMEQTYWQANPFR, calculated by ProTurn software and plotted as a function of time.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Enrichment of serum water as measured by GC-MS.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
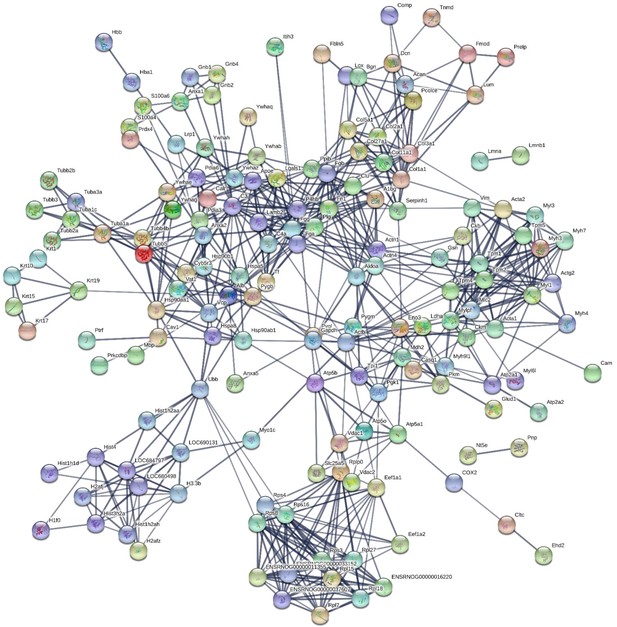
Protein-protein interaction map of proteins identified in whole tendon.
Unconnected nodes were removed to provide clarity of the interactome. The total cluster was built with STRING (Szklarczyk et al., 2019) allowing for experimentally verified and predicted protein-protein interactions at high confidence levels (0.700). Line thickness indicates the strength of supporting data. Source data are provided in Figure 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Proteins identified in whole tendon samples used to create protein-protein interaction maps.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
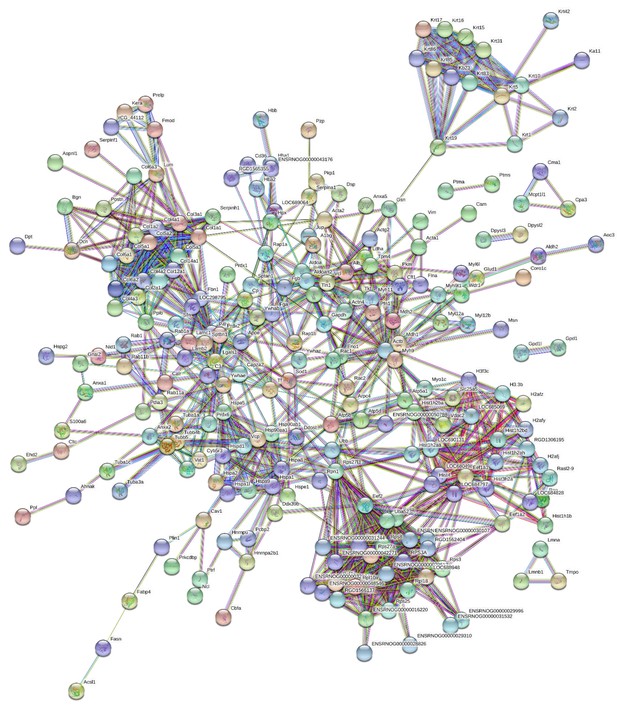
Protein-protein interaction map of proteins identified in the interfascicular matrix.
Unconnected nodes were removed to provide clarity of the interactome. The total cluster was built with STRING (Szklarczyk et al., 2019) allowing for experimentally verified and predicted protein-protein interactions at high confidence levels (0.700). Line thickness indicates the strength of supporting data. Source data are provided in Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Proteins identified in the interfascicular matrix used to create protein-protein interaction maps.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
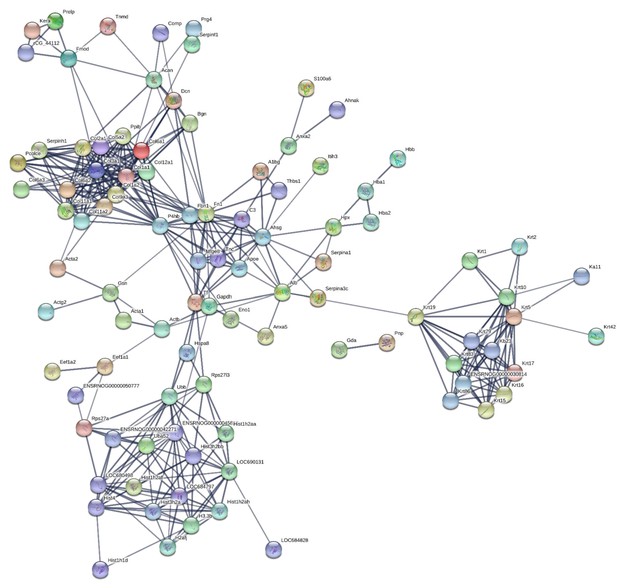
Protein-protein interaction map of proteins identified in the fascicular matrix.
Unconnected nodes were removed to provide clarity of the interactome. The total cluster was built with STRING (Szklarczyk et al., 2019) allowing for experimentally verified and predicted protein-protein interactions at high confidence levels (0.700). Line thickness indicates the strength of supporting data. Source data are provided in Figure 4—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Proteins identified in the fascicular matrix used to create protein-protein interaction maps.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
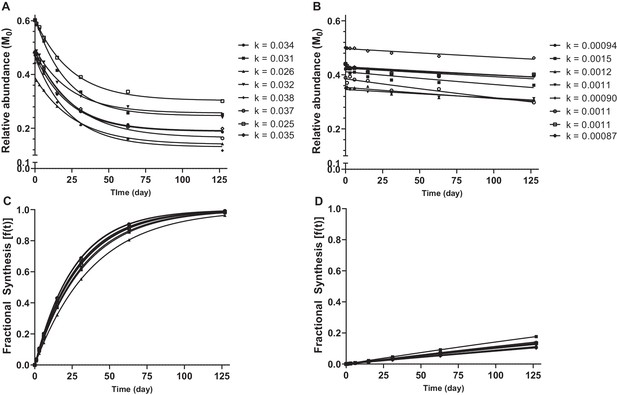
Calculation of protein turnover rate from mass isotopomer distribution over time.
Relative abundance of M0 in selected decorin (A) and collagen type 1, alpha one chain (B) peptides, and resulting k values calculated by non-steady state curve fitting using ProTurn software. Fractional synthesis rates (FSR), calculated from peptide k values, demonstrate more rapid turnover of decorin (C) compared to collagen type 1, alpha one chain (D). Source data, generated by ProTurn are available in Source data 1.
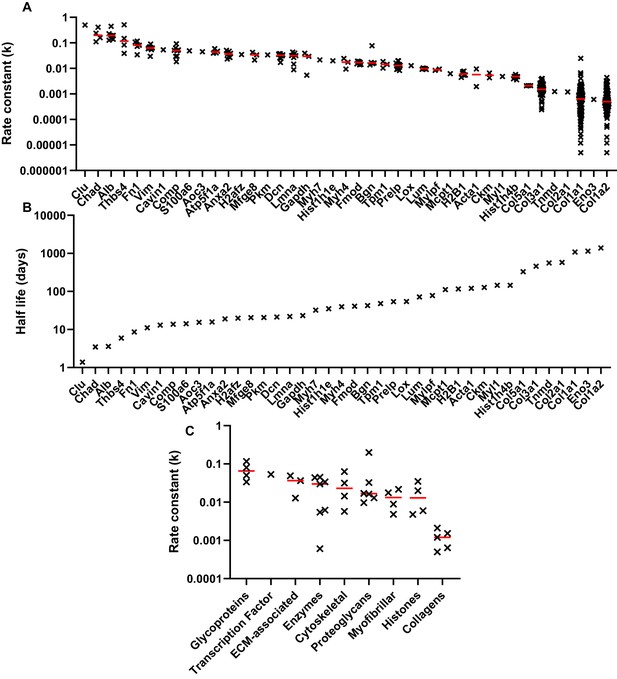
Peptide turnover rate constants and corresponding protein half-lives in whole tendon.
(A) The peptide rate constants (k) for individual proteins are plotted in descending order on a logarithmic scale, with the median value represented by a red line. (B) The median k values for each protein were used to calculate protein half-life, assuming a first order reaction. (C) Protein turnover rates plotted against MatrisomeDB and PANTHER categories, with the median value represented by a red line. Due to space constraints, gene, rather than protein, names are displayed in parts A and B. Source data, generated by ProTurn are available in Source data 1.
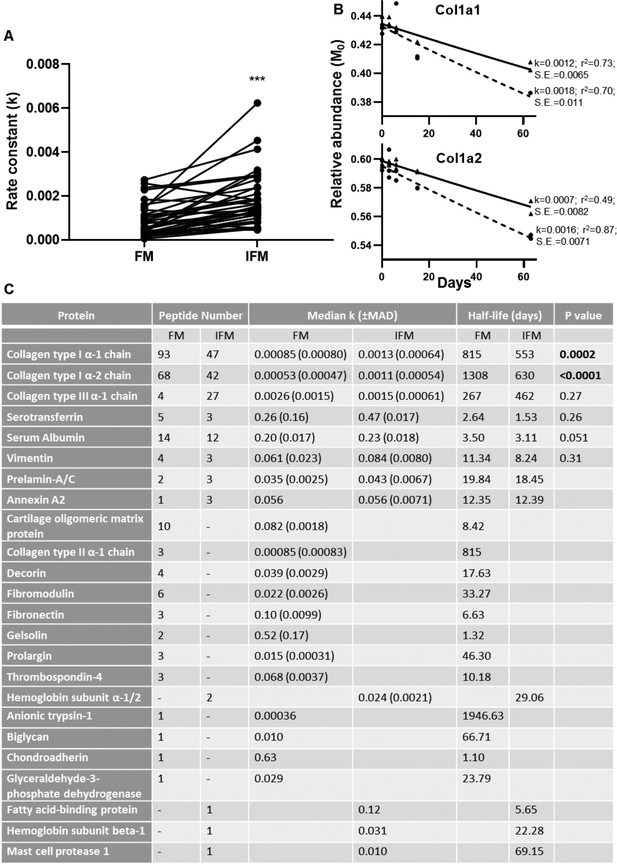
Peptide turnover rate constants and corresponding protein half-lives in tendon phases.
(A) Rate constants (k) for collagen type I peptides identified in both tendon phases were significantly greater in the IFM compared to the FM (n = 39). (B) Median peptide decay curves for Col1a1 and Col1a2 in the FM (▲; solid line) and IFM (●; dashed line), showing goodness of fit (r2) and standard error (S.E.). (C) Turnover rate constants (k) and corresponding half-lives for proteins identified in each phase. *** indicates p<0.0001. Source data, generated by ProTurn are available in Figure 7—source data 1 for the FM and Figure 7—source data 2 for the IFM.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
ProTurn output for FM.
hl tab contains protein half-life information organized by peptide sequence and hl-data tab contains isotopomer relative abundance at each time point.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-fig7-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 7—source data 2
ProTurn output for IFM.
hl tab contains protein half-life information organized by peptide sequence and hl-data tab contains isotopomer relative abundance at each time point.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-fig7-data2-v1.xlsx
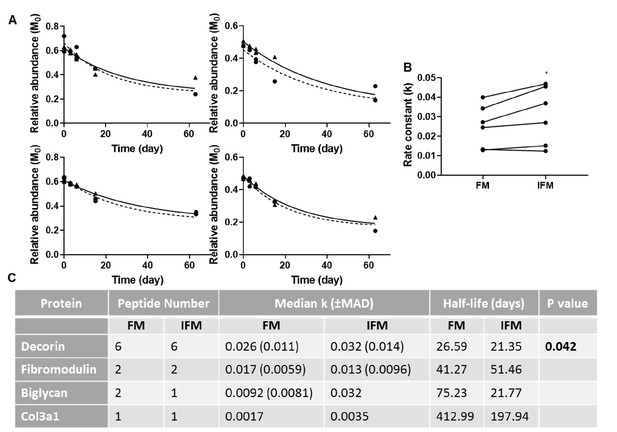
Manual calculation of turnover rate of selected proteins.
(A) Relative abundance of M0 as a function of time, and resultant non-linear curve fitting for peptides corresponding to decorin identified in the FM (▲; solid line) and IFM (●; dashed line). (B) Resultant k values for decorin peptides were significantly greater in the IFM than in the FM (p=0.042). (C) Manually calculated turnover rate constants (k) and corresponding half-lives for tendon proteins of interest. Source data are available in Figure 8—source data 1.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
GraphPad Prism output showing the manually calculated relative abundance of M0 at different time points for decorin, fibromodulin, biglycan and Col3a1 peptides, and resultant K values.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-fig8-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Rattus Norvegicus, Female) | Wistar | Charles River | RRID:RGD_13508588 | Female |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce protein assay | ThermoFisher | 22660 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | [2H]2O | CK isotopes LtD | DLM-2259 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid LCMS grade | Fisher Scientific | 10723857 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ammonium bicarbonate | Sigma | 09830 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Chondroitinase ABC | Sigma | C3667 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dithiothreitol | Melford laboratories | MB1015 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Formic acid (0.1% v/v) LCMS grade | Fisher Scientific | 10188164 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Guanidine hydrocholoride | Sigma | G3272 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Iodoacetamide | Sigma Aldrich | I1149 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | RapiGest SF | Waters | 186001861 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trifluoroacetic acid Optima | Fisher Scientific | 10723857 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trifluoroacetic acid (0.1% v/v) LCMS grade | Fisher Scientific | 10516625 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trypsin Gold MS grade | Promega | V5280 | |
| Software, algorithm | Peaks Studio v8.5 | Bioinformatics Solutions | www.bioinfor.com/peaks-studio | |
| Software, algorithm | STRING v11.0 | PMID:30476243 | string-db.org | |
| Software, algorithm | MatrisomeDB | PMID:21937732 | matrisomeproject.mit.edu | |
| Software, algorithm | PANTHER | PMID:23868073 | www.pantherdb.org | |
| Software, algorithm | ProLuCID | PMID:26171723 | fields.scripps.edu/yates/wp/?page_id = 821 | |
| Software, algorithm | ProteoWizard v3 | PMID:28188540 | proteowizard.sourceforge.net/index.html | |
| Software, algorithm | ProTurn | PMID:24614109 | proturn.heartproteome.org | |
| Software, algorithm | Prism v8.2 | GraphPad | www.graphpad.com | |
| Other | Filter units, Vivacon 500 10000 MWCO | Sartorius | VN01H02 |
Additional files
-
Source data 1
Source data for Figures 5 and 6.
ProTurn output for whole tendon. hl tab contains protein half-life information organized by peptide sequence and hl-data tab contains isotopomer relative abundance at each time point
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55262/elife-55262-transrepform-v1.docx





