Inhibiting IRE1α-endonuclease activity decreases tumor burden in a mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma
Figures
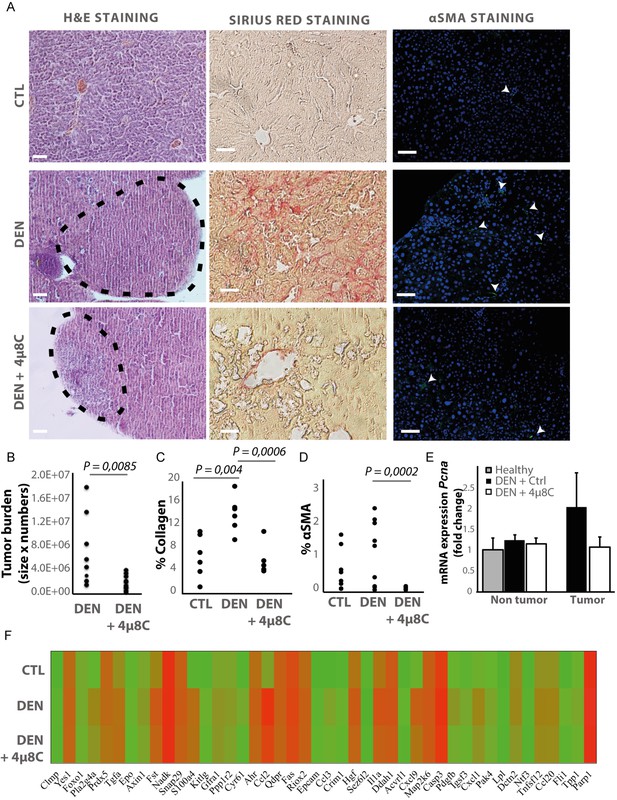
Inhibiting IRE1α reduces tumor burden in vivo.
(A) Representative images of liver slides stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H and E), Sirius red and αSMA-antibodies. (B) tumor burden of mice with DEN-induced HCC treated with 4μ8C or vehicle-treated controls. (C) Quantification of percentage of collagen and (D) αSMA on liver slides. (E) mRNA expression of Pcna in liver tissue from mice with HCC treated with 4μ8C (F). Heatmap showing protein expression levels in healthy liver, DEN-induced HCC and DEN-induced HCC treated with 4μ8C from three biological replicates per group. p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test, scale bars = 120 μm.
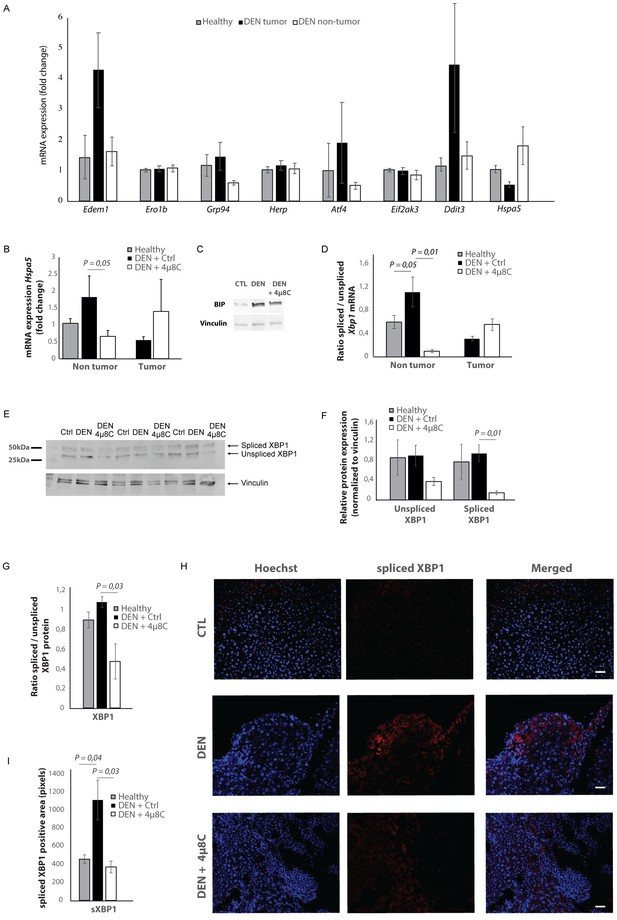
Increased expression of ER-stress markers in mice with HCC.
(A) mRNA expression of ER-stress markers Edem1, Ero1b, Grp94, Herp, Atf4, Eif2ak3, Ddit3, and Hspa5 in liver tissue from healthy mice; and tumor tissue and surrounding non-tumoral tissue from mice with DEN-induced HCC. (B) Hspa5-mRNA and (C) protein expression of BIP in murine liver tissue. (D) Ratio of spliced to unspliced XBP1 in liver tissue from healthy mice; and tumor tissue and surrounding non-tumoral tissue from mice with DEN-induced HCC, treated with 4μ8C. (E) Representative western blot image of spliced and unspliced XBP1 protein and vinculin in healthy liver, DEN-induced HCC and DEN-induced HCC treated with 4μ8C. (F) quantification of spliced and unspliced XBP1, normalized to total vinculin levels. (G) Ratio of spliced to unspliced XBP1 protein levels. (H) Representative images and (I) quantification of liver tissue sections stained with antibodies against spliced XBP1. p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test with five biological replicates per group. Scale bars = 120 μm.
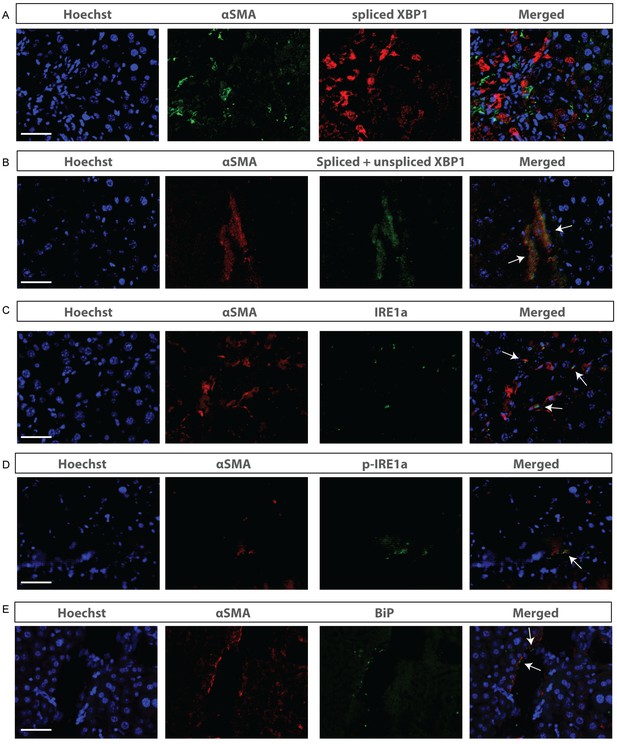
Activation of the unfolded protein response is mainly located in the stroma of mice with HCC.
Liver tissue from mice with DEN-induced HCC, stained with αSMA-antibodies and co-stained with antibodies against (A) spliced XBP1, (B) total XBP1, (C) IRE1α (D) phopho-IRE1α, and (E) BIP. Scale bars = 50 μm.
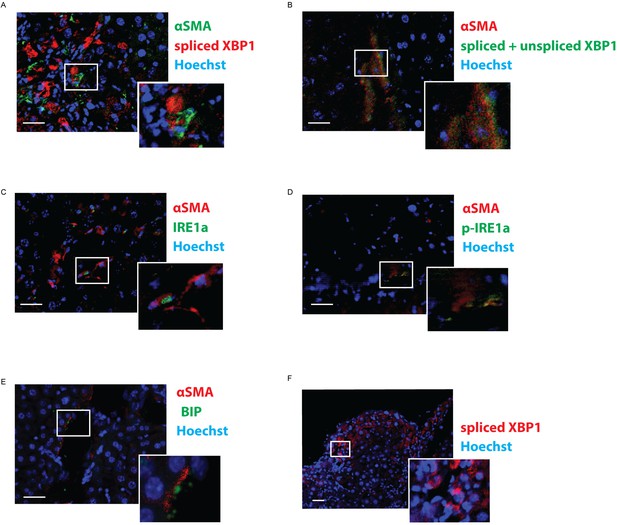
Expression of ER-stress markers is localized in close vicinity to αSMA.
Immunofluorescent images from tissue from mice with DEN-induced HCC, stained with αSMA-antibodies and co-stained with antibodies against (A) spliced XBP1, (B) total XBP1, (C) IRE1α, (D) phopho-IRE1α, and (E) BIP. (F) Immunofluorescent image from DEN-induced HCC stained with antibodies against spliced XBP1.
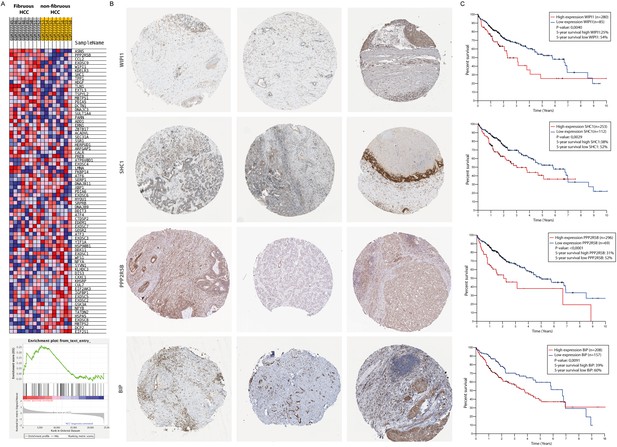
Activation of the unfolded protein response pathway is increased in patients with fibrotic HCC.
(A) Heat map showing gene-set enrichment analysis results from samples from fibrous HCC versus non-fibrous HCC. (C) Immunohistochemically stained liver biopsies from HCC-patients obtained from the human protein atlas, using antibodies against IRE1α-mediated actors of the unfolded protein response: WIPI1, SHC1, PPP2R5B, and BIP. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of HCC-patients with high or low expression of WIPI1, SHC1, PPP2R5B, and BIP. p-Values were calculated via a Log-Rank test.
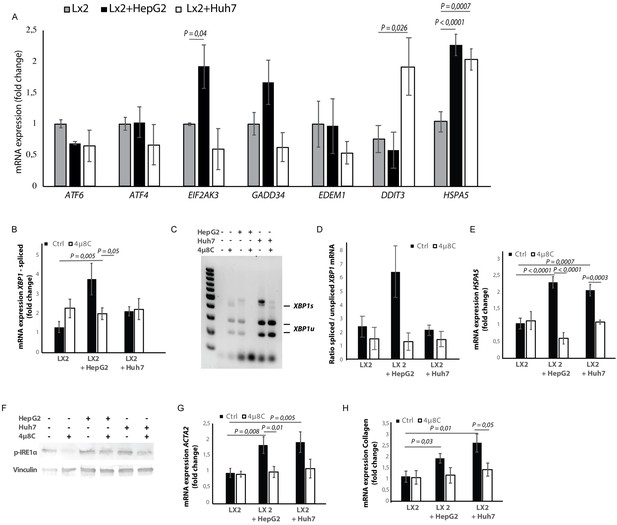
Tumor cells secrete factors that induce ER-stress in stellate cells, which contributes to their activation.
(A) mRNA-expression of ER-stress markers ATF6, ATF4, EIF2AK3, GADD34, EDEM1, DDIT3 and HSPA5, in stellate cells (LX2) co-cultured with cancer cells (HepG2 or Huh7) and treated with 4μ8C or control. (B) Detection of spliced (XBP1s) and unspliced XBP1 (XBP1u) via qPCR and (C) via digestion of the XBP1u-RT-qPCR product by Pst-I and subsequent visualization by separation of on agarose gel. (D) Quantified ratio of spliced and unspliced measured on agarose gel after digestion by Pst-I (E) mRNA expression of HSPA5 in stellate cells (LX2) co-cultured with cancer cells (HepG2 or Huh7) and treated with 4μ8C or control. (F) protein expression of p-IRE1α and vinculin in stellate cells (LX2) co-cultured with cancer cells (HepG2 or Huh7) in transwell assays and treated with 4μ8C or control. (G) mRNA-expression of stellate cell activation markers ACTA2 and (H) collagen in LX2-cells co-cultured with HepG2 or Huh7-cells and treated with or without 4μ8C. p-Values were calculated via ANOVA with 10 biological replicates per group.
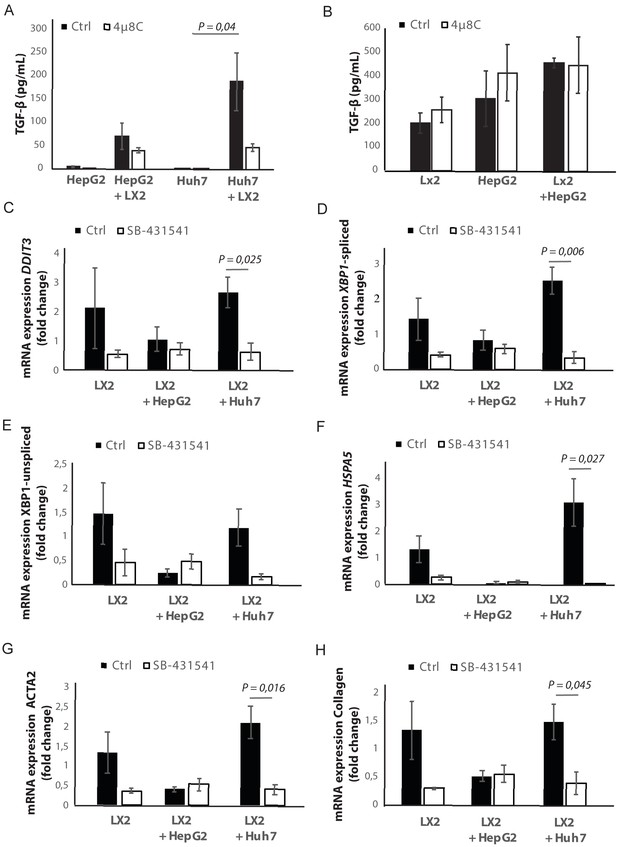
Secretion of TGFβ by tumor cells activates stellate cells and induces ER-stress.
(A) Concentration of TGFβ in medium from tumor cells (HepG2 or Huh7) grown in mono-culture or co-cultured with LX2-stellate cells, treated with 4μ8C or control. (B) Concentration of TGFβ in medium from liver scaffolds engrafted with stellate cells (C) (LX2) and tumor cells (HepG2) treated with 4μ8C or control. mRNA-expression of the ER-stress markers DDIT3, (D) spliced XBP1, (E) unspliced XBP1 and (F) HSPA5 in hepatic stellate cells (LX2) grown as mono-culture or in co-cultures with the cancer cell lines HepG2 and Huh7 treated with the TGFβ receptor inhibitor SB-431541 or control. (G) mRNA-expression of stellate cell activation markers ACTA2 and (H) collagen in LX2-cells grown with HepG2 or Huh7-cells and treated with SB-431541 or control. p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test from seven biological replicates per group.
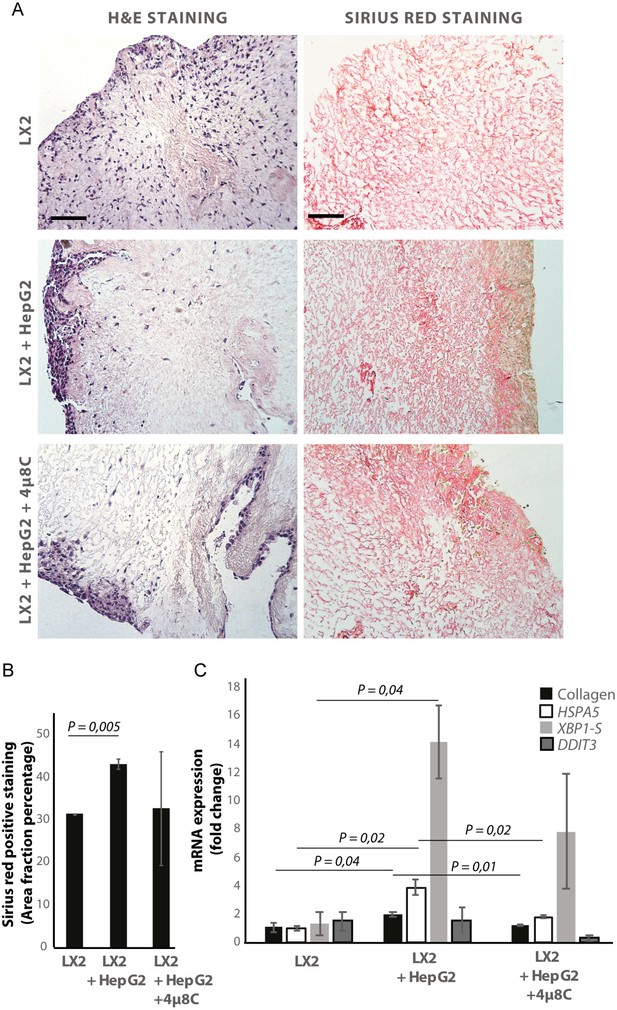
Inhibiting IRE1α decreases stellate cell activation in human liver 3D scaffolds engrafted with stellate cells and tumor cells.
(A) Representative images of H and E and Sirius red stained slides of decellularized human liver scaffolds engrafted with LX2 stellate cells and HepG2-tumor cells treated with 4μ8C or control. (B) Quantification of collagen-stained area fraction of liver scaffolds engrafted with LX2 stellate cells and HepG2-tumor cells treated with 4μ8C or control. (C) mRNA-expression of the stellate cells activation marker collagen and ER-stress markers HSPA5, spliced XBP-1 (XBP1-S), and DDIT3 in liver scaffolds engrafted with stellate cells (LX2) and cancer cells (HepG2), treated with 4μ8C or control. p-Values were calculated via ANOVA from three biological replicates per group, scale bars = 100 μm.
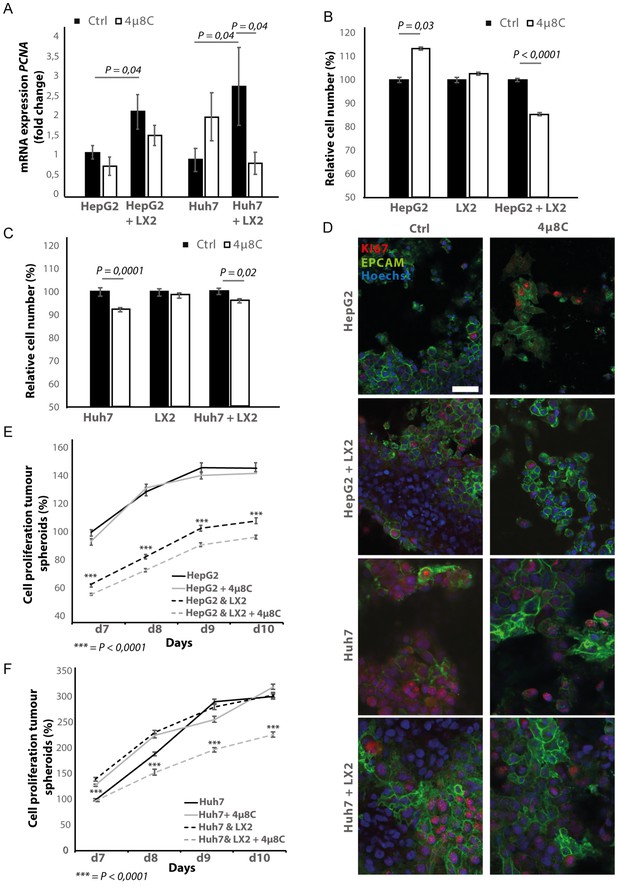
Inhibition of IRE1α decreases tumor cell proliferation.
(A) PCNA mRNA-expression of HepG2 or Huh7-cells grown with LX2-cells in transwell inserts and treated with the IRE1α-inhibitor 4μ8C or control. (B) Relative cell number of LX2 and HepG2 or (C) LX2 and Huh7-cells treated with 4μ8C or control. (D) Representative images of tumor cells (HepG2 or Huh7) and LX2-stellate cells stained with antibodies against the HCC-marker EPCAM and the proliferation marker KI67. (E) Cell proliferation of HepG2 or HepG2+LX2 spheroids and (F) Huh7 or Huh7+LX2 spheroids treated with 4μ8C or control. p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test from nine biological replicates per group, scale bars = 50 μm.
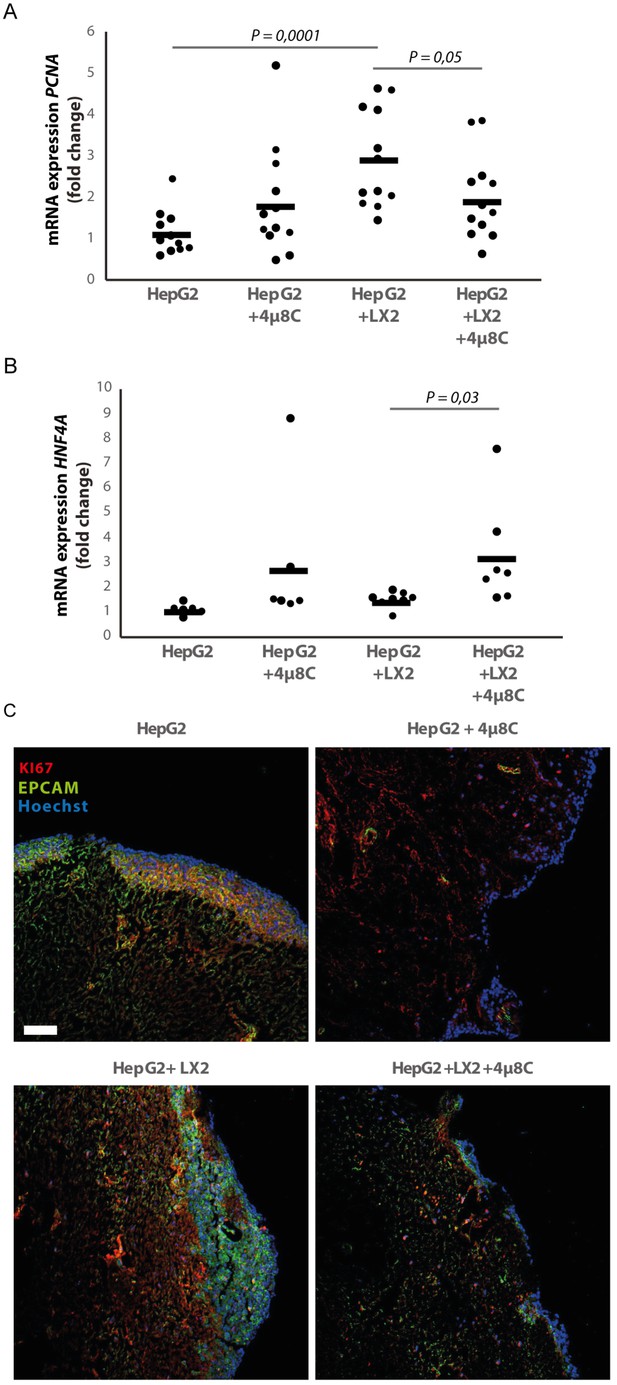
Inhibition of IRE1α decreases cell proliferation and improves liver function in human liver scaffolds engrafted with stellate cells and tumor cells.
(A) PCNA and (B) HNF4A expression of human liver scaffolds engrafted with HepG2-tumor cells and LX2-stellate cells, treated with 4μ8C or control. (C) Representative images of tumor cells (HepG2) and LX2-stellate cells stained with antibodies against the HCC-marker EPCAM and the proliferation marker KI67. p-Values were calculated via ANOVA on three biological replicates per group, scale bars = 100 μm.
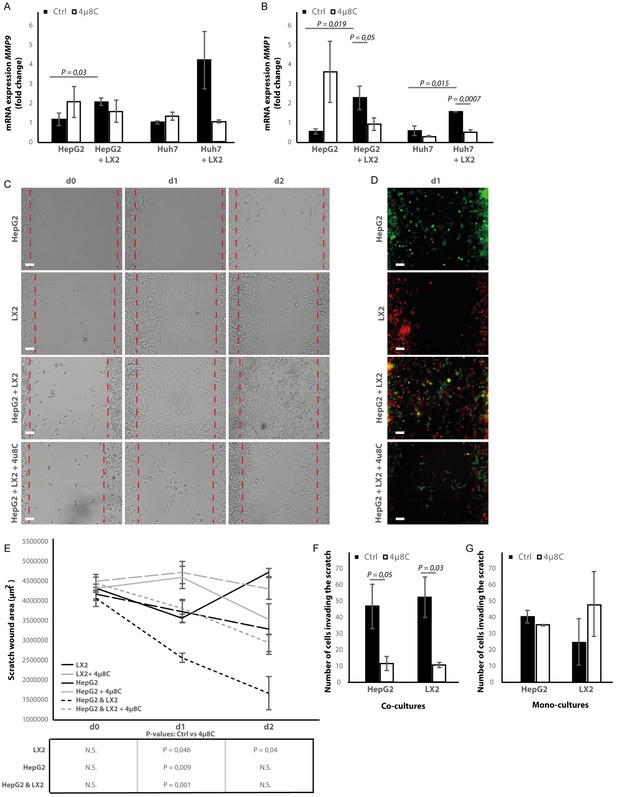
Inhibition of IRE1α decreases cell migration.
(A) mRNA-expression of pro-metastatic markers MMP9 and (B) MMP1 in HepG2 and Huh7-cells co-cultured with LX2-cells and treated with 4μ8C or control. (C) Scratch wound on HepG2-cells and LX2-cells treated with 4μ8C or control. (D) Images of Cell Tracker stained HepG2-cells (Green) and LX2-cells (Red) invading the scratch area. (E) Quantification of wound size in HepG2-cells and LX2-cells treated with 4μ8C or control. (F) Number of HepG2-cells and LX2-cells invading the scratch wound after 24 hr in co-cultures and (G) mono-cultures. p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test from 10 biological replicates per group (panel A and B) or six biological replicates per group (panel E-G), scale bars = 120 μm.
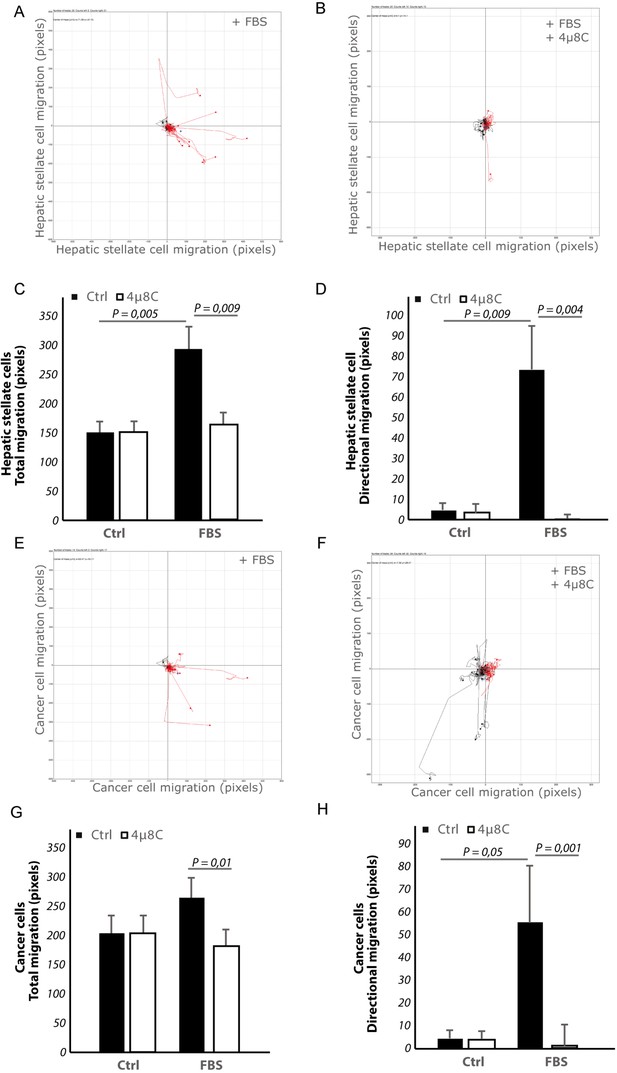
Inhibiting IRE1α decreases chemotaxis.
(A) Migration plots of LX2-cells co-cultured with HepG2-cells exposed to an FBS-gradient (increasing towards the right) and treated with control or (B) 4μ8C (C) Quantification of total migration and (D) directional migration of LX2-cells (co-cultured with HepG2-cells) toward an FBS-gradient with or without 4μ8C. (E) Migration plots of HepG2-cells co-cultured with LX2-stellate cells and exposed to an FBS-gradient and treated with control or (F) 4μ8C. (G) Quantification of total migration and (H) directional migration of HepG2-cells (co-cultured with LX2-cells) towards an FBS-gradient with or without 4μ8C. p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test from three biological replicates per group. Red lines indicate migration toward the gradient, while black lines indicate migration away from the gradient.
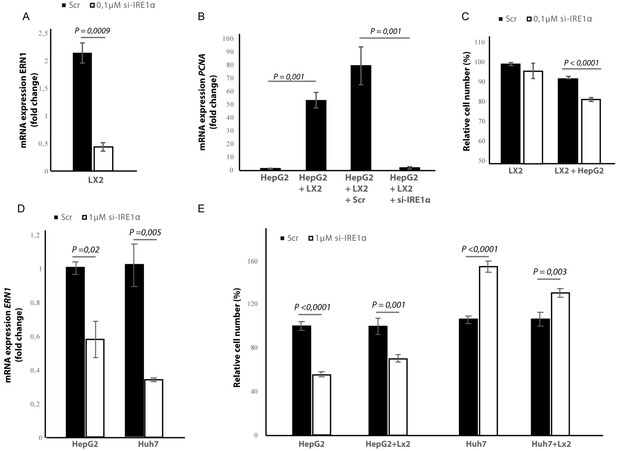
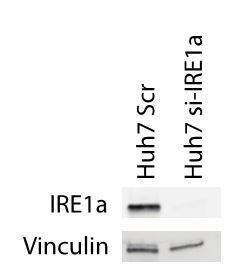
Silencing IRE1α in LX2-cells mimics 4μ8C.
(A) ERN1-mRNA-expression of LX2-cells transfected with IRE1α-siRNA (si-IRE1α) or mock-transfected (Scr) (B) PCNA-mRNA-expression of HepG2-cells co-cultured with IRE1α-silenced LX2-cells or controls (C). Relative cell numbers in co-cultures of HepG2-cells and IRE1α-silenced LX2-cells or controls. (D) ERN1-mRNA-expression of HepG2- and Huh7-cells transfected with IRE1α-siRNA (si-IRE1α) or mock-transfected (Scr). (E) Relative cell numbers in co-cultures LX2-cells or and si-RNE. Transfected HepG2 or Huh7 cells or mock-transfected controls (Scr). p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test from three biological replicates per group (panel A, B and D) or six biological replicates (panel C and E).
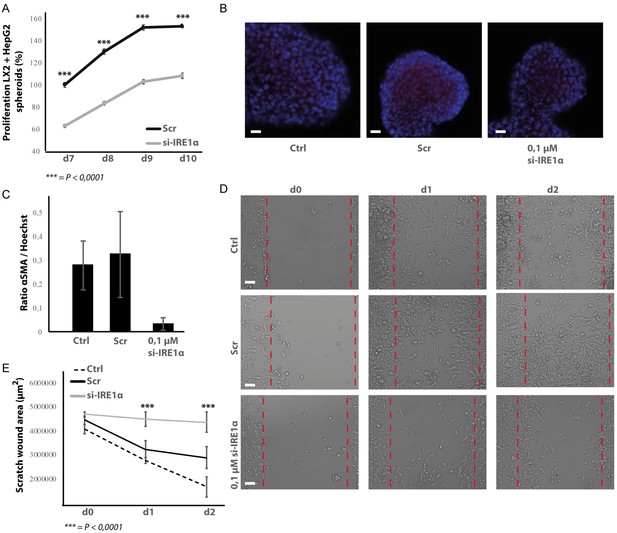
Proliferation and migration after silencing IRE1α in LX2-cells.
(A) Proliferation of spheroids of HepG2-cells and IRE1α-silenced LX2-cells or controls (B) Images and (C) quantification of αSMA-stained spheroids with HepG2-cells and IRE1α-silenced LX2-cells or controls. (D) Images and (E) quantification of scratch wound of HepG2-cells co-cultured with IRE1α-silenced LX2-cells or controls. p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test from three biological replicates per group, scale bars = 50 μm (E) or 120 μm (G).
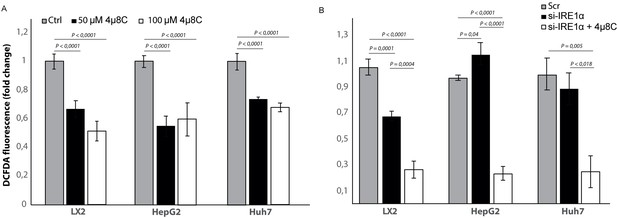
Inhibiting IRE1α alters generation of ROS.
(A) intracellular ROS-levels in LX2, HepG2, and Huh7 cells treated with 50 μM 4μ8C, 100 μM 4μ8C or controls. (B) intracellular ROS-levels in LX2, HepG2 and Huh7 cells transfected with IRE1α-siRNA (si-IRE1α) or mock-transfected (Scr). p-Values were calculated via the Student's T-test from three biological replicates per group.
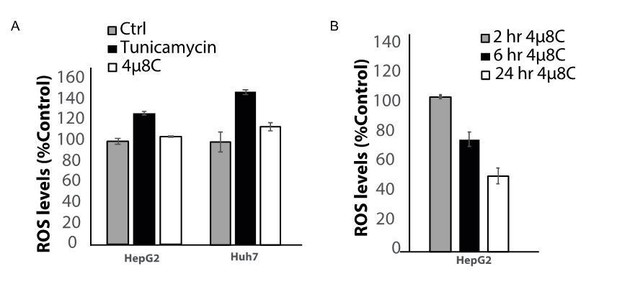
Effect of ER-stress on ROS production.
(A) the ER-stress inducer increases ROS levels in HepG2 and Huh7 cells. (B) The ROS-scavenging effect of 4u8C increases over time.
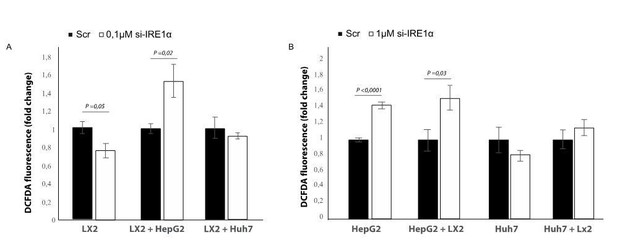
Effect of silencing IRE1a in different co-culture conditions.
(A) LX2-cells transfected with si-RNA targeting IRE1a or mock-transfected (Scr) in mono-culture or co-culture with tumor cells (HepG2 and Huh7). (B) HepG2 or Huh7-cells transfected with si-RNA targeting IRE1a or mock-transfected (Scr) in mono-culture or co-culture with LX2-stellate cells.

Visible bands in lane 2 and 4, which corresponds to LX2-monocultures and LX2+Hep2 co-cultures treated with 4u8C.
Tables
A proteomics array using the Olink Mouse Exploratory assay – source data Figure 1F.
| CTL | Den | DEN+4 u8c | Statistical significance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein name | Biological process | Mean | St. Dev | Average | St. Dev | Average | St. Dev | DEN vs Ctrl | DEN vs 4 u8C | Ctrl vs 4 u8c |
| Clmp | Not prognostic in HCC | 1.68 | 0.14 | 2.97 | 1.00 | 2.48 | 0.64 | * | ||
| Yes1 | HCC promotor | 7.11 | 0.29 | 7.51 | 0.20 | 7.44 | 0.19 | * | ||
| Foxo1 | Tumor suppressor | 4.15 | 0.06 | 4.12 | 0.73 | 3.87 | 0.49 | |||
| Pla2g4a | HCC promotor | 3.42 | 0.38 | 5.70 | 1.36 | 5.04 | 0.80 | * | * | |
| Prdx5 | HCC promotor | 7.37 | 0.49 | 7.23 | 0.26 | 6.67 | 0.34 | * | ||
| Tgfa | Tumor growth factor | 5.36 | 0.52 | 6.81 | 0.64 | 6.93 | 0.88 | * | * | |
| Epo | Unfavorable prognotic marker | 3.20 | 0.34 | 3.71 | 0.35 | 3.37 | 0.33 | |||
| Axin1 | HCC promotor | 4.24 | 0.38 | 4.80 | 0.37 | 4.39 | 0.35 | |||
| Fst | HCC promotor | 5.87 | 0.31 | 8.04 | 0.73 | 7.50 | 0.71 | * | * | |
| Nadk | Not prognostic in HCC | 10.10 | 0.13 | 10.14 | 0.18 | 10.30 | 0.27 | |||
| Snap29 | Not prognostic in HCC | 7.70 | 0.32 | 7.87 | 0.32 | 7.62 | 0.30 | |||
| S100a4 | HCC promotor | 2.73 | 0.74 | 7.01 | 0.62 | 6.85 | 0.97 | * | * | |
| Kitlg | Metastasis | 2.48 | 0.42 | 3.74 | 0.62 | 3.31 | 0.98 | * | ||
| Gfra1 | HCC promotor | 4.40 | 0.35 | 5.07 | 0.40 | 4.92 | 0.39 | * | ||
| Ppp1r2 | Not prognostic in HCC | 4.37 | 0.16 | 4.86 | 0.46 | 4.47 | 0.43 | |||
| Cyr61 | HCC promotor | 2.40 | 0.53 | 4.14 | 1.64 | 3.13 | 1.22 | * | ||
| Ahr | Not prognostic in HCC | 6.95 | 0.46 | 7.68 | 0.74 | 7.38 | 0.64 | |||
| Ccl2 | HCC promotor | 4.59 | 0.58 | 9.69 | 2.04 | 8.93 | . | * | * | |
| Qdpr | Not prognostic in HCC | 7.71 | 0.11 | 7.72 | 0.14 | 7.54 | 0.15 | |||
| Fas | HCC promotor | 8.66 | 0.18 | 8.83 | 0.18 | 8.70 | 0.18 | |||
| Riox2 | HCC promotor | 7.10 | 0.15 | 7.71 | 0.38 | 7.59 | 0.14 | * | * | |
| Epcam | HCC promotor | 1.56 | 0.33 | 3.16 | 1.14 | 3.27 | 0.89 | * | ||
| Ccl3 | Prognostic marker | 1.49 | 0.39 | 4.42 | 1.86 | 3.73 | 1.07 | * | * | |
| Crim1 | HCC promotor | 2.46 | 0.28 | 3.71 | 1.09 | 3.21 | 0.56 | * | * | |
| Hgf | Tumor growth factor | 6.69 | 0.35 | 7.94 | 1.01 | 7.41 | 0.71 | * | ||
| Sez6l2 | HCC promotor | −0.29 | 0.15 | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.19 | 0.29 | * | ||
| Il1a | Inflammation and fibrosis | 6.65 | 0.51 | 8.35 | 0.65 | 7.62 | 0.54 | * | * | |
| Ddah1 | HCC promotor | 8.04 | 0.22 | 8.18 | 0.05 | 7.84 | 0.18 | * | ||
| Acvrl1 | Not prognostic in HCC | 2.09 | 0.18 | 3.44 | 1.31 | 2.81 | 0.47 | |||
| Cxcl9 | Inflammation and fibrosis | 3.68 | 0.86 | 7.71 | 1.68 | 6.65 | 1.58 | * | * | |
| Map2k6 | Not prognostic in HCC | 7.75 | 0.15 | 7.98 | 0.41 | 7.88 | 0.28 | |||
| Casp3 | Tumor surrpressor | 9.22 | 0.19 | 9.74 | 0.35 | 9.43 | 0.26 | |||
| Pdgfb | Tumor growth factor | 3.52 | 0.31 | 4.96 | 1.27 | 3.97 | 0.40 | * | ||
| Igsf3 | Unfavorable prognotic marker | 3.12 | 0.28 | 4.19 | 0.82 | 3.64 | 0.72 | |||
| Cxcl1 | HCC promotor | 3.77 | 0.40 | 5.74 | 0.78 | 5.06 | 0.51 | * | * | |
| Pak4 | HCC promotor | 3.47 | 0.42 | 4.39 | 0.68 | 3.93 | 0.54 | |||
| Lpl | Not prognostic in HCC | 1.66 | 0.40 | 2.44 | 0.45 | 2.02 | 0.60 | |||
| Dctn2 | Unfavorable prognotic marker | 5.48 | 1.31 | 5.67 | 0.70 | 4.98 | 0.55 | |||
| Ntf3 | Not prognostic in HCC | 2.16 | 0.27 | 2.80 | 0.71 | 2.27 | 0.40 | |||
| Tnfsf12 | HCC promotor | 5.28 | 0.35 | 6.00 | 0.76 | 5.59 | 0.62 | |||
| Ccl20 | Unfavorable prognotic marker | 5.20 | 0.34 | 5.92 | 0.81 | 5.53 | 0.66 | |||
| Fli1 | HCC promotor | 1.91 | 0.22 | 3.73 | 1.38 | 2.98 | 0.83 | |||
| Tpp1 | Unfavorable prognotic marker | 3.67 | 0.38 | 4.24 | 0.64 | 3.73 | 0.50 | |||
| Parp1 | Unfavorable prognotic marker | 10.30 | 0.72 | 10.93 | 0.49 | 10.51 | 0.62 | |||
Genes the contributed to the core-enrichment of the GSEA.
| Probe | Description | Rank Gene list | Rank Metric score | Core enrichment | UPR branch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASNS | Asparagine synthetase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:753] | 207 | 0.940 | Yes | Perk |
| PPP2R5B | Protein phosphatase two regulatory subunit B'beta [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:9310] | 423 | 0.821 | Yes | Ire1a |
| CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:10618] | 847 | 0.689 | Yes | Ire1a and Perk |
| EXOSC9 | Exosome component 9 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:9137] | 1004 | 0.654 | Yes | Ire1a and Perk |
| WIPI1 | WD repeat domain, phosphoinositide interacting 1 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:25471] | 1022 | 0.649 | Yes | Ire1a |
| KDELR3 | KDEL endoplasmic reticulum protein retention receptor 3 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:6306] | 1106 | 0.635 | Yes | Ire1a |
| SHC1 | SHC adaptor protein 1 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:10840] | 2691 | 0.432 | Yes | Ire1a |
| TPP1 | Tripeptidyl peptidase 1 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:2073] | 2884 | 0.414 | Yes | Ire1a |
| HDGF | Heparin binding growth factor [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:4856] | 3235 | 0.386 | Yes | Ire1a |
| TLN1 | Talin 1 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:11845] | 3264 | 0.384 | Yes | Ire1a |
| EXTL3 | Exostosin like glycosyltransferase 3 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:3518] | 3488 | 0.365 | Yes | Ire1a |
| TSPYL2 | TSPY like 2 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:24358] | 3680 | 0.350 | Yes | Ire1a |
| MBTPS1 | Membrane-bound transcription factor peptidase, site 1 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:15456] | 3996 | 0.327 | Yes | Atf6 |
| PDIA5 | Protein disulfide isomerase family A member 5 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:24811] | 4530 | 0.294 | Yes | Ire1a |
| DCTN1 | Dynactin subunit 1 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:2711] | 4638 | 0.287 | Yes | Ire1a |
| DNAJC3 | DnaJ heat-shock protein family (Hsp40) member C3 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:9439] | 4761 | 0.281 | Yes | Ire1a |
| SULT1A4 | Sulfotransferase family 1A member 4 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:30004] | 4938 | 0.272 | Yes | Ire1a |
| PARN | Poly(A)-specific ribonuclease [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:8609] | 5037 | 0.266 | Yes | Perk |
| ADD1 | Adducin 1 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:243] | 5375 | 0.250 | Yes | Ire1a |
| ERN1 | Endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 1 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:3449] | 5411 | 0.248 | Yes | Ire1a |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | Sv129 mice | Taconic | 129S6 | HCC mouse model, Heindryckx et al., 2010; Heindryckx et al., 2012 |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HepG2 | ATCC | HB-8065 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | Huh7 | Gifted, Karolinska institute | ||
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | LX2 | Sigma-Aldrich | SCC064 | |
| Transfected construct (human) | si-IRE1α | ThermoFisher | s200432 | 0,1–1 µM |
| Transfected construct (human) | Si-Ctrl; Scr | ThermoFisher | 4390843 | 0,1–1 µM |
| Antibody | KI67 (rat monoclonal) | eBioscience | SolA15 | 1:100 |
| Antibody | EPCAM (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab71916 | 1:100 |
| Antibody | Spliced XBP1 (goat monoclonal) | Abcam | Ab85546 | 1:50 |
| Antibody | Total XBP1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Ab37152 | 5 µg/ml |
| Antibody | IRE1a (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Ab37073 | 1 µg/ml |
| Antibody | p-IRE1 (rabbit polyclonal) | AbNova | PAB12435 | 1:100 |
| Antibody | αSMA (Rabbit Polyclonal) | ThermoFisher | 710487 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | αSMA (Goat monocolonal) | Abcam | Ab21027 | 1–2 µg/ml |
| Antibody | BIP (goat polyclonal) | Abcam | Ab21027 | 1 µg/ml |
| Antibody | Vinculin (Mouse monoclonal) | ThermoFisher | 14-9777-82 | 1–5 µg/ml |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Pst-I | ThermoFisher | ER0615 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce BCA-protein assay kit | ThermoFisher | 233225 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | EZNA RNA isolation Kit II | VWR | R6934-02 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNeasy Universal Mini Kit | Qiagen | 73404 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Diva Decloacker solution | Biocare | DV2004 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | DCFDA - Cellular ROS Detection Assay Kit | Abcam | ab113851 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | N-Nitrosodiethylamine, DEN | Sigma-Aldrich | 1002877809 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4μ8C | Sigma-Aldrich | SML0949-25MG | Heindryckx et al., 2016 |
| Chemical compound, drug | SB-431541, TGF-ß receptor inhibitor | Tocris | 1614 | 10 μM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Resazurin | Sigma-Aldrich | R7017-1G | 1:80 dilution |
| Commercial assay or kit | Ingenio electroporation solution | Mirus Bio LLC | MIR50114 | Ice-cold |
| Commercial assay or kit | CellTracker Red CMTPX | ThermoFisher | C34552 | 1 μM |
| Commercial assay or kit | CellTracker Green CMFDA | ThermoFisher | C2925 | 1 μM |
| Other | 12-well CorningCostar Transwellplates | Sigma-Aldrich | 3460 | Calitz et al., 2020 |
| Other | Corning CostarUltra-Low attachment 96-well plates | Sigma-Aldrich | CLS3471 | Calitz et al., 2019 |
| Other | CellDirector | GradienTech | 11-001-10 | Fuchs et al., 2020 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table with primer sequences.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55865/elife-55865-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Table with antibodies used for staining.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55865/elife-55865-supp2-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/55865/elife-55865-transrepform-v2.docx