Ageing compromises mouse thymus function and remodels epithelial cell differentiation
Figures
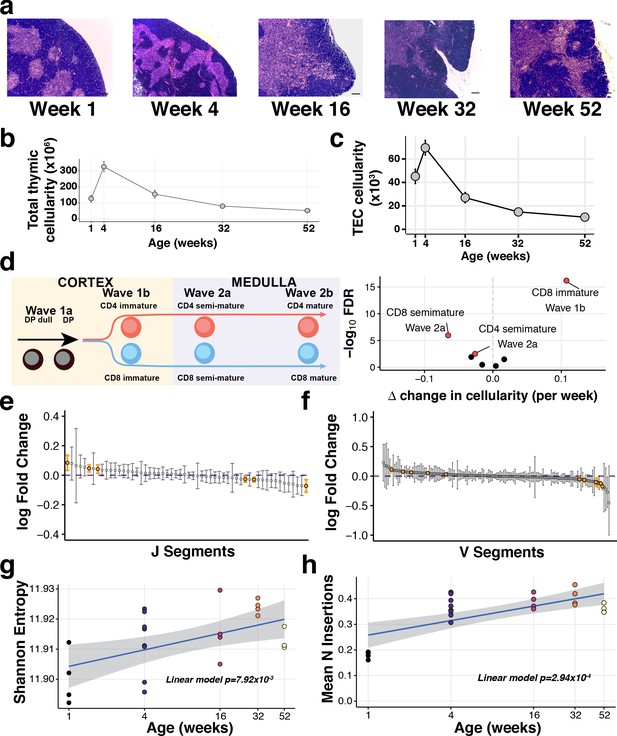
The decline of thymic cellularity and immune function with age.
(a) Age-dependent changes in thymic architecture, as shown by representative H and E staining of thymic sections. Scale bars represent 150 µm. Medullary islands stain as light purple while cortical regions stain as dark purple. (b) Total and (c) TEC cellularity changes in the involuting mouse thymus. Error bars represent mean +/- standard error (five mice per age). (d) Thymocyte-negative selection declines with age: (Left) Schematic showing the progression of T cell development and Wave selection stages in the thymus that were investigated; (Right) Volcano plot showing the differential abundance of each of these thymocyte negative selection populations over age. Populations that are statistically significantly altered with age (FDR 1%) are labelled and highlighted in red. (e–f) The distribution of log-fold changes showing the alterations in individual TCR J segment (e) and V segment (f) usage with age. Log fold changes +/- 99% confidence intervals are plotted, with differentially abundant segments coloured in orange. (g) Mature thymocyte TCR repertoire diversity changes with age. The y-axis indicates the Shannon entropy of M2 thymocyte TCR CDR3 clonotypes at each age (n = 4–7 mice per time point), derived from TCR-sequencing of ~15,000 cells per sample. p-Value has been calculated from a linear model that regresses Shannon entropy on age. (h) The number of non-templated nucleotide insertions detected by TCR sequencing increases with age. The displayed p-value is from a linear model that regresses the mean number of inserted nucleotides on age.

Alterations in TEC composition throughout ageing.
(a) Thymocyte cellularity fluctuations over age. (b) Ratio of %TEC:%thymocytes over age. (c) TEC cellularity over age for mTEC and cTEC FAC-sorted populations. Error bars represent mean +/- standard error (five mice per age) in all panels.
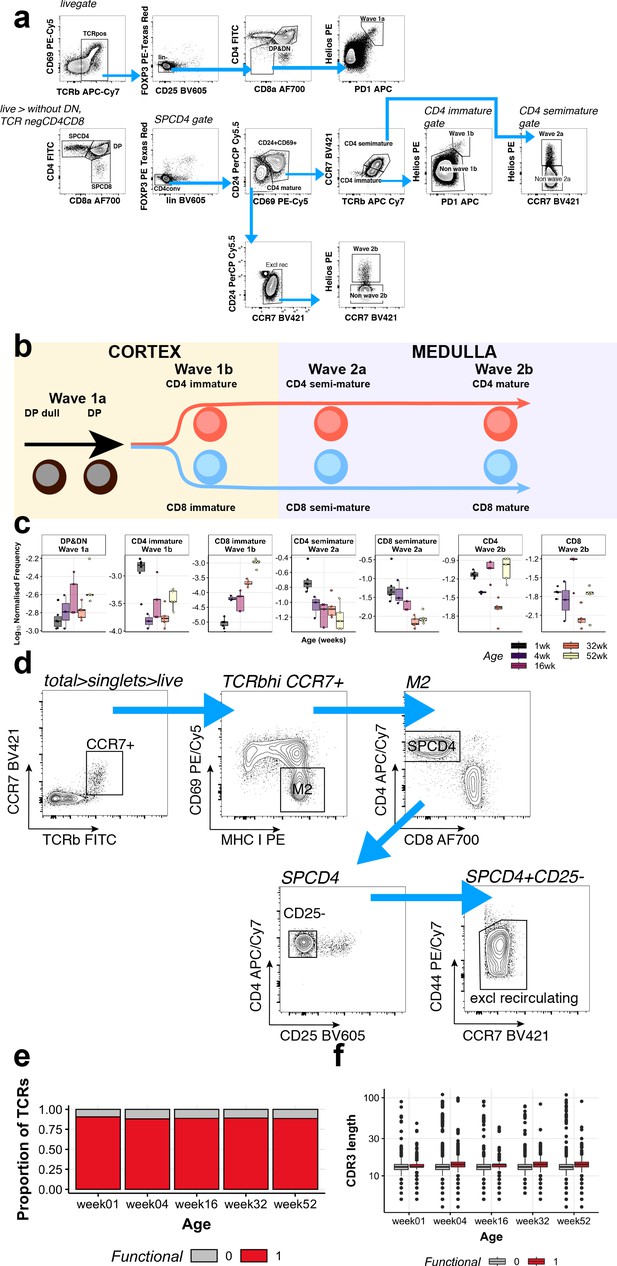
Changes in T-cell populations throughout ageing.
(a) FACS gating strategy to separate different T-cell subtypes. (b) Maturation trajectory and negative selection checkpoints for TCR-positive thymocytes. (c) Frequency of different thymocyte subpopulations by age. (d) Flow cytometry gating scheme showing the selection of M2 thymocytes, and the exclusion of regulatory and re-circulating T cells. (e) Proportions of viable TCRs amongst all constructed CDR3 sequences. Functional sequences are coloured in red and non-productive sequences, defined by an incomplete sequence, premature stop codon or missing start codon, are coloured in grey. (f) CDR3 amino acid length distributions per age (X-axis). Boxplots are coloured by either productive (red) or non-productive (grey) TCR sequences.
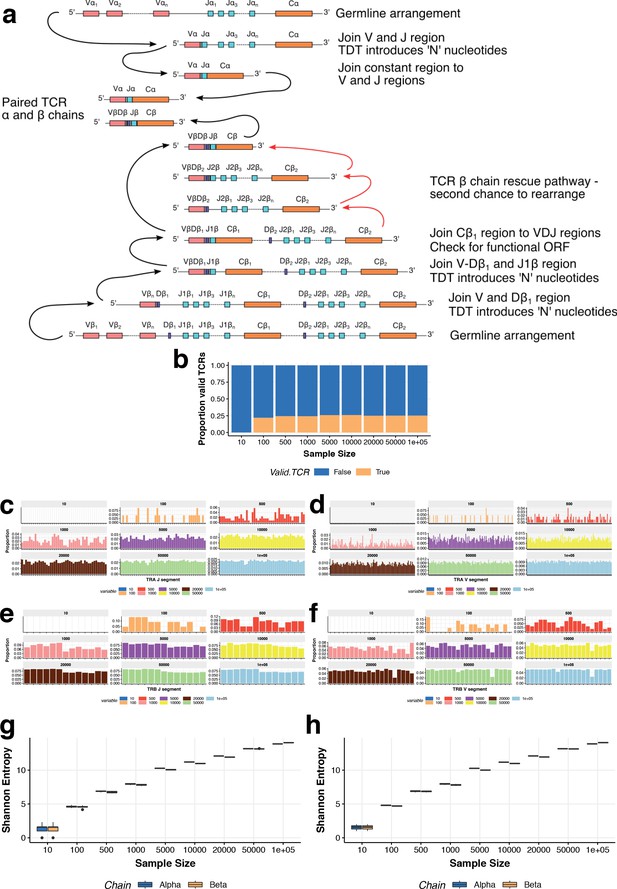
T cell receptor repertoire simulations.
(a) A schematic of T cell receptor rearrangements used to design simulations. (b) Proportions of productive TCRs (y-axis) simulated at different sample sizes (x-axis). (c–f) Proportions of TCR alpha (c and d) and beta (e and f) chain segments from simulated TCRs at different sample sizes. (g–h) TCR repertoire diversity defined as the Shannon entropy across clonotypes in each of 10 (g) and 3 (h) independent TCR simulations. Entropy was calculated in each run using only the productive TCRs.
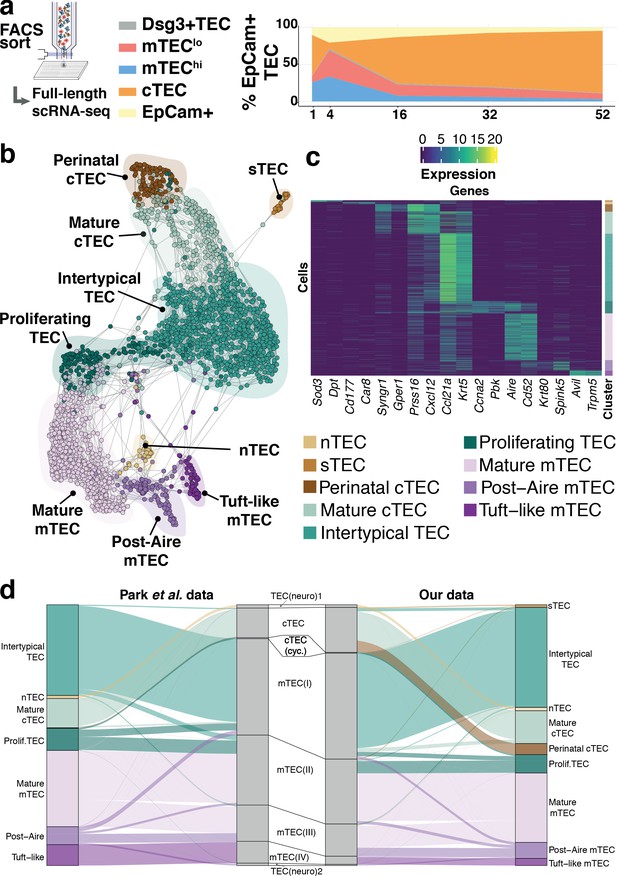
Thymic stromal composition remodelling during ageing.
(a) A schematic showing the experimental design and FACS phenotypes of sorted cells for single-cell RNA-sequencing. Right panel shows cell composition fluctuations as a relative fraction of all EpCAM+ TEC with respect to the TEC subsets investigated. Remaining EpCAM+ cells not FACS-sorted are represented in the EpCAM+ population. (b) A SPRING-layout of the shared nearest-neighbour graph of single TEC, derived from scRNA-seq transcriptional profiles. Graph nodes represent single cells and edges represent shared k-nearest neighbours (k = 5). Cells are coloured by a clustering that joins highly connected networks of cells based on a random walk (Walktrap Pons and Latapy, 2005). Clusters are annotated based on comparisons to known TEC subsets and stereotypical expression profiles. (c) A heatmap of marker genes for TEC subtypes identified from single-cell transcriptome profiling annotated as in (b). (d) River plots illustrating the mapping between our TEC subtype labels and those from Park et al., using k-NN classifiers. Each line represents a single cell from the respective data set (postnatal and adult mice from Park et al.), where the central pillar shows the TEC labels from Park et al., and the outer pillars show the labels for our TEC subtypes; lines are coloured according to the TEC subtype labels in (b).

Experimental investigation of the ageing thymus.
(a) FACS gating strategy for TEC isolation. Identical gating strategies were used for all time points. (b) Filtering strategy to identify high-quality TEC libraries. (c–f) Fractions of libraries filtered out based on sparsity threshold (c), the fraction of reads from mitochondrial genes expressed (d), library size thresholds (e), or ERCC-spike in RNA % expression threshold (f). (g) Sparsity in each single-cell cluster by age. (h) Reassignment of libraries to clusters based on downsampling fraction. Excessive downsampling leads to an accumulation of the low-diversity library.

Comparison of Bornstein et al., 2018, Park et al., 2020 single-cell transcriptomes to the TEC subtypes defined in this study.
This figure depicts the assignment of single TEC from the Bornstein, the Park or our Ageing dataset to our nine TEC subtypes (left side) or the Bornstein/Park mTECI-IV nomenclature.

Relationship between classical FAC sorted subpopulations and transcriptionally defined single-cell subtypes.
(a) Observed percentages (%) of TEC based on pre-scoring into FAC sorted subpopulations. (b) Estimated contributions of each FACS sort type to each single cell subtype through age. Each coloured dot represents data from an independent experiment.

Expression of selected marker genes overlaid on SPRING plot.
Each subplot is a SPRING-layout of the shared nearest-neighbour graph of single TEC, derived from scRNA-seq transcriptional profiles as in Figure 2. Graph nodes are coloured according to the expression of a particular marker gene as listed in the legend. Nodes with no detected expression of the specified marker gene are coloured in grey.

MSigDB pathways enriched for expression of marker genes for each single-cell subtype.
The X-axis shows the fraction of marker genes that overlap the specified pathway, the size of the dot represents the number of marker genes in the enriched pathway, and the colour of the dot represents the p-value adjusted for multiple tests.
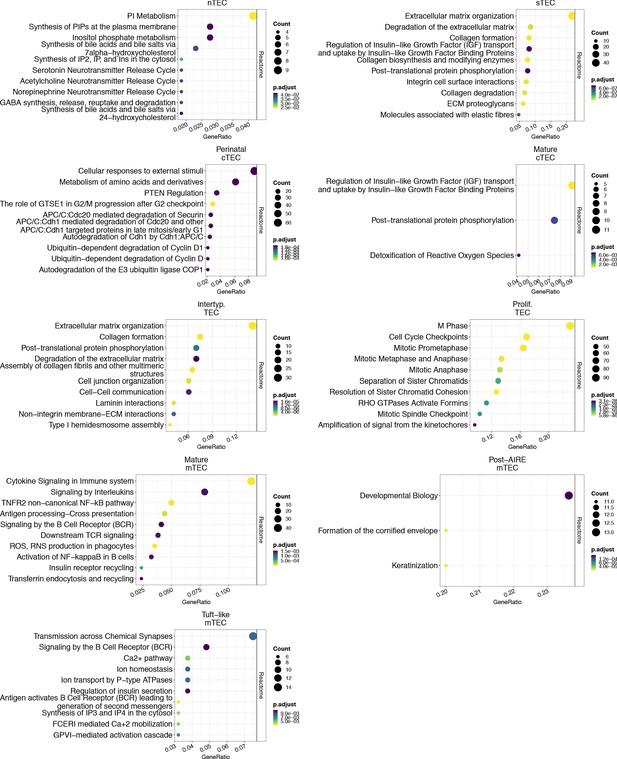
Reactome pathways enriched for expression of marker genes for each single cell subtype.
The X-axis shows the fraction of marker genes that overlap the specified pathway, the size of the dot represents the number of marker genes in the enriched pathway, and the colour of the dot represents the p-value adjusted for multiple tests.
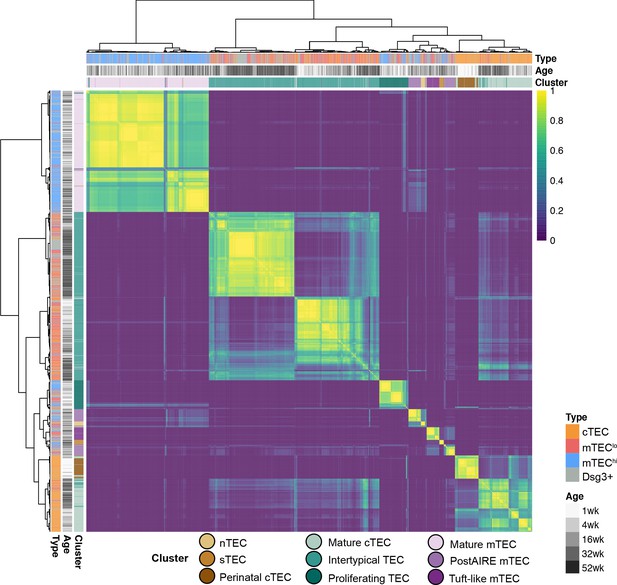
Consensus clustering of ageing single-cell TEC libraries.
The heatmap shows the fraction of times that the libraries are co-clustered based on a variety of transformations, clustering methods and the number of features (Materials and methods). The heatmap shows that the achieved clustering is robust to these different clustering methods.
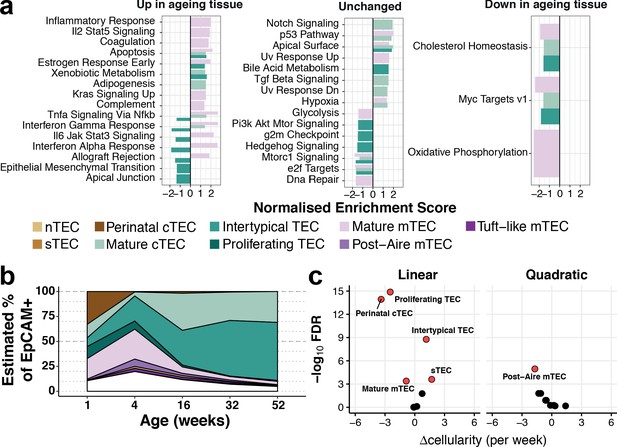
Thymic stromal remodelling during ageing.
(a) Enrichment of MSigDB biological pathways with age in mature cTEC, intertypical TEC and mature mTEC, annotated as in (Figure 2b). Bars denote normalised enrichment score (NES) for significant pathways (FDR 5%), with enrichments coloured by cell type. Age-related alterations are shown in the context of pathways that are up-regulated (left), down-regulated (right) or do not change (middle) across multiple tissues and species (Benayoun et al., 2019). (b) A ribbon-plot demonstrating the compositional changes in TEC subtypes across ages, as an estimated fraction of all TEC (EpCAM+). Colours indicating each subtype are shown as in Figure 2 above the plot with unsorted TEC indicated in white. (c) A volcano-plot of a negative binomial generalised linear model (GLM) showing linear (left) and quadratic (right) changes in cell cluster abundance as a function of age. X-axis denotes the change (Δ) in cellularity per week, and the Y-axis shows the -log10false discovery rate (FDR). Subtypes with statistical evidence of abundance changes (FDR 1%) are labelled and shown as red points.

Differential expression of genes throughout ageing.
Each panel shows a heatmap and a MA-plot depicting the expression of the differentially expressed genes within the (a) mature cTEC, (b) intertypical TEC, or (c) mature mTEC subtypes. The heatmaps show the scaled (by row/gene) expression of the differentially expressed genes at each collected timepoint (x-axis; weeks). The MA-plots show the average expression (log2) and the log2 fold-change with age for each single cell subtype. Significantly altered genes are shown in green and the total number of up- or down-regulated genes per subtype are shown in the green font along the y-axis. The top five up- or down-regulated genes are labelled, where present.
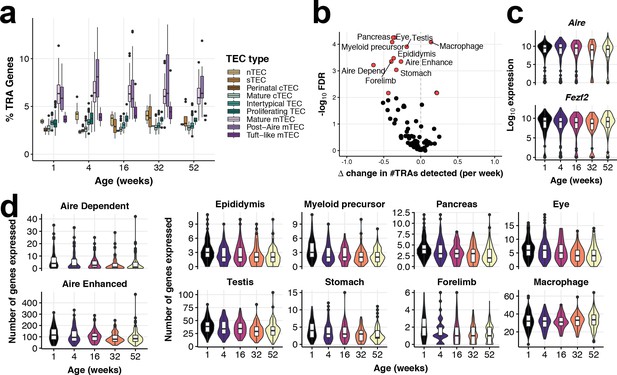
Tissue-restricted gene expression in mTEC.
(a) TRA expression enriched in Mature mTEC and Post-Aire mTEC. Shown is the percentage of expressed genes that are classed as TRAs (see Materials and methods), for each TEC subtype across mouse ageing. (b) A volcano plot of differential TRA abundance testing, showing the consistent down-regulation of TRAs in mature mTEC. The X-axis denotes the change (Δ) in TRAs detected per week, and the Y-axis shows the -log10 false discovery rate (FDR). Tissue types or categories of promiscuously gene expression (PGE) with statistical evidence of abundance changes (FDR 1%) are labelled and shown as red points. (c) Violin plots of mTEC single-cell gene expression distributions across mouse ages of known promiscuous gene expression (PGE) regulators, Aire and Fezf2. (d) Violin plots of the number of mTEC-expressed tissue antigen genes in TRA groups that are differentially abundant over age, as in (b).
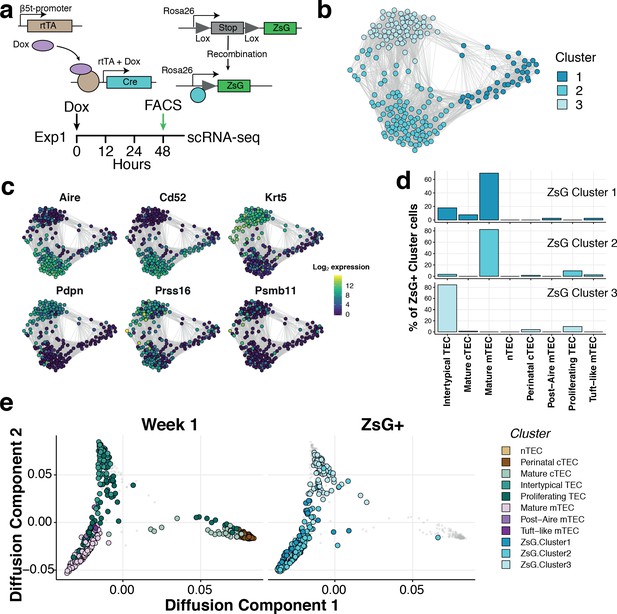
Intertypical TEC and medullary TEC are derived from a β−5t+ progenitor.
(a) A schematic representing the transgenic Dox-inducible ZsGreen (ZsG) lineage tracing of β−5t-expressing mTEC precursors (top), and lineage tracing experiment in 1-week-old thymi (bottom). The green arrow denotes the interval post-Dox treatment. (b) A Fruchterman-Reingold layout of the shared nearest neighbor (SNN) graph of FACS-sorted ZsG+ mTEC from 1-week-old mice, 48 hr-post Dox treatment. Graph nodes represent cells coloured by a clustering of closely connected cells. (c) Expression levels of key medullary (Aire, Cd52), cortical (Psmb11, Prss16) and Intertypical TEC (Krt5, Pdpn) marker genes. (d) A β−5t-expressing precursor is the common origin of intertypical TEC and mature mTEC as shown by random forest classification of ZsG+ TEC. (e) A joint diffusion map between single TEC at week 1 (left panel), and ZsG+ TEC (right panel). Points represent single cells and are coloured by their assigned cluster as in Figure 2 (week 1 TEC) or (c) (ZsG+ TEC).

Details of the ZsGreen labelling and sorting strategy.
(a) Representative FACS plots depicting the labelling efficiency of cTEC and mTEC of 1-week-old mice, 48 hr after treatment with 0.3 mg of doxycycline per mouse. (b) FACS gating strategy employed for the isolation of newly generated ZsGreen+ mTEC (defined as EpCAM+ CD45- MHCII+ UEA1+ CD86-) 48 hr after treatment of 1 week old mice with 0.3 mg of doxycycline per mouse.
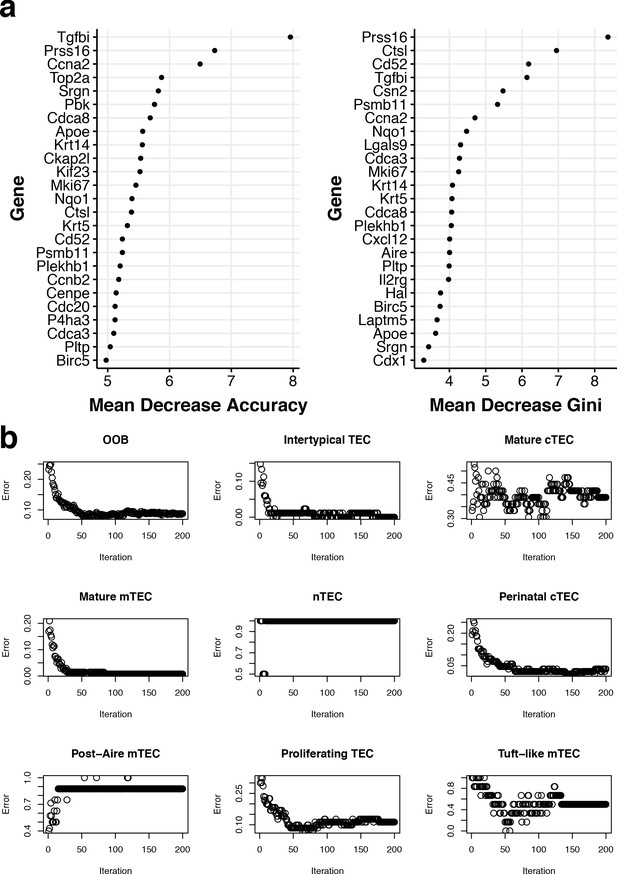
Random Forest training using 1-week-old single TEC.
(a) The top genes that discriminate between TEC subtypes trained using single TEC from 1-week-old mice. Shown is the mean decrease in accuracy when dropping each gene in the random forest (left) and the mean decrease in the Gini index. (b) The out-of-bag and class-specific errors at each iteration of the random forest during training.
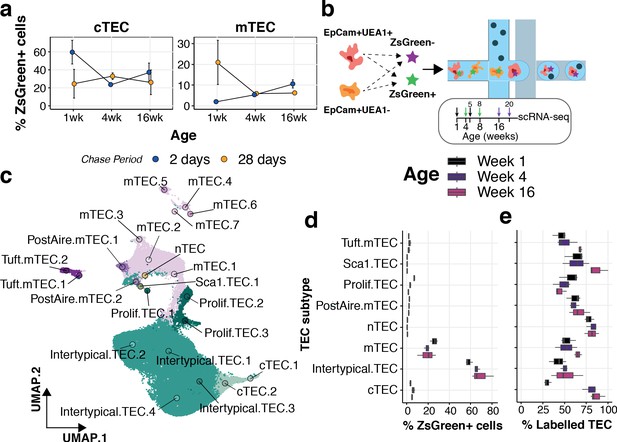
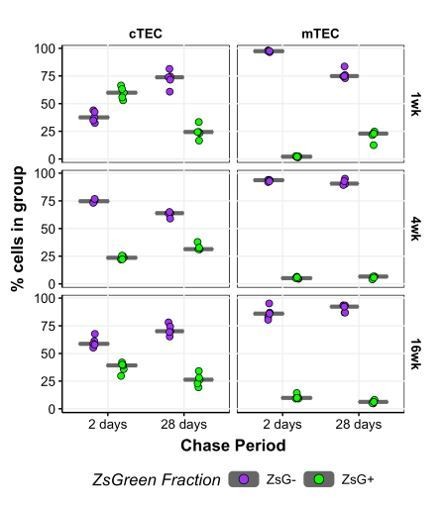
Lineage tracing and scRNA-seq reveal the dynamics of TEC precursor - progeny relationship across ages.
(a) The mean percentage of cTEC (left) and mTEC (right) labelled either 2 days (blue points) or 28 days (orange points) after doxycycline treatment of 3xtgβ5t mice. Error bars are the mean +/- the standard error across five mice. (b) A schematic of the droplet single-cell RNA-sequencing of lineage traced cTEC and mTEC. Inset panel: schematic representation of ZsG lineage tracing of TEC across mouse ages. Paired colour arrows denote the time and age of doxycycline treatment and the subsequent collection of TEC (black: 1wk; green: 4wk; purple: 16wk). Numbers above the arrows represent the age of mice at the time of single-cell measurements. (c) A UMAP of all single TEC following quality control, coloured by an annotation into TEC subtypes according to the expression of TEC subtype marker genes. Filled circles are the average UMAP position of each TEC sub-cluster. (d) Box plots showing the distribution of ZsGreen+ sorted cells across TEC subtypes, coloured by mouse age at time of doxycycline treatment. (e) Box plots showing the percentage of cells in each TEC subtype that came from the ZsGreen+ fraction, coloured by mouse age at the time of doxycycline treatment.

Representative FACS plots depicting the gating strategy employed to determine the labelling efficiency of cTEC and mTEC of 1-week-old, 4-week-old and 16-week-old mice, 2 or 28 days after treatment with 0.004 mg (newborns) or 2 mg (adult mice) of doxycycline per mouse.
(a) cTEC/mTEC distribution as traditionally defined by flow cytometry using the surface markers Ly51 and reactivity to UEA1. (b) Proportion of ZsGreen-labelled total TEC detected at each time-point, for each of the analysed mouse ages. Proportion of cTEC and mTEC found within the (c) ZsGreen- or (d) ZsGreen+ TEC fraction.
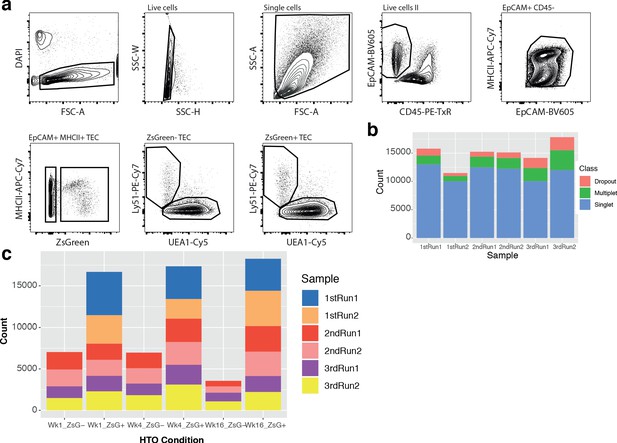
Summary of multiplexed single-cell droplet RNA sequencing.
(a) FAC-Sorting gating strategy for the isolation of ZsGreen +/- TEC subpopulations. (b) Multiplet detection using multiplexed hashtag oligos (HTO). Coloured bars denote the number of cells in each sample (Chromium chip well), where either no (Dropout), multiple (Multiplet) or a single HTO was detected in a droplet. (c) The distribution of singlet cells across samples and experimental conditions (age and ZsGreen fraction).
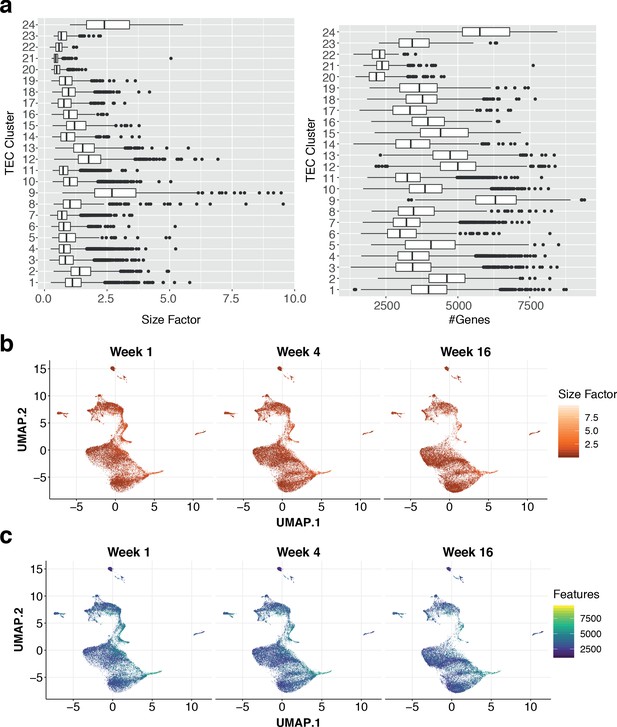
Quality control of multiplexed single-cell droplet RNA sequencing.
(a) Boxplots showing the distributions of the estimated deconvolution size factors (left) and number of detected genes for each single-cell cluster (right). (b) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP). Points are single cells coloured by the estimated deconvolution size factors. Cells are split into panels based on the age of the mouse at the time of doxycycline treatment. (c) The number of detected genes (log expression >0) in single cells overlaid on a UMAP and split by age.
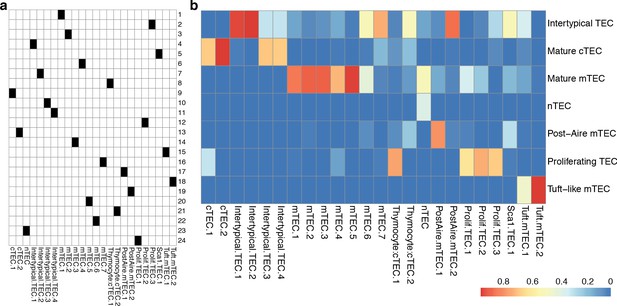
Droplet single-cell RNA-sequencing cluster annotation and comparison with TEC subtypes.
(a) A mapping of single-cell clusters onto TEC subtype phenotypes. (b) A confusion matrix showing the proportions of single-cells in each TEC cluster (columns) and their classification into Ageing TEC subtypes (rows) using a random forest classifier trained on all single-cells in Figure 2b, as in Figure 5—figure supplement 2.

Marker gene expression profiles across TEC clusters from β−5t lineage-traced single cells.
Boxplots showing the distribution of marker gene expression (y-axis) for TEC subtypes across TEC clusters (x-axis). Boxes are coloured by the inferred TEC subtype to which they belong.
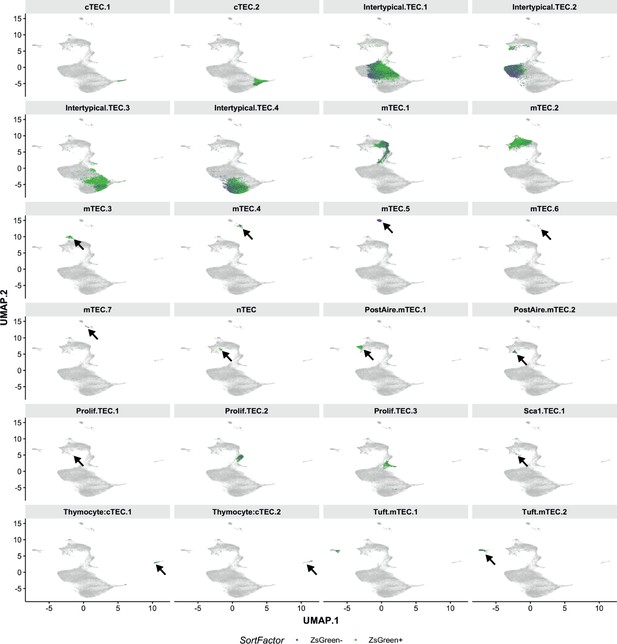
UMAP visualisation of TEC sub-clusters across all single-cells from lineage-traced thymi.
Each panel is coloured according to the TEC subtype annotation and corresponds to Figure 6c. Arrows point to the positions of the relevant clusters in the UMAP.
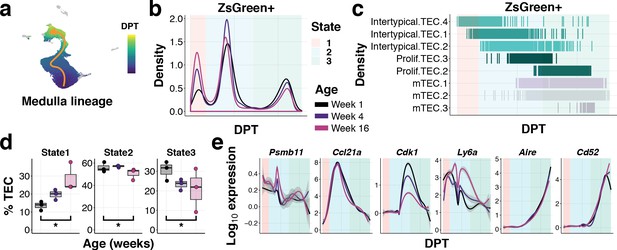
Ageing restricts the differentiation of intertypical TEC into mature mTEC.
(a) UMAP as in (Figure 6c) coloured by diffusion pseudotime (DPT) distance in the medullary lineage (see Figure 7—figure supplement 1 for details). (b) Changes in ZsGreen+ labelled TEC differentiation from the Intertypical TEC compartment as a function of age are shown as the density of cells ordered along pseudotime (DPT) in the medulla lineage, coloured by mouse age at time of doxycycline treatment. Three meta-stable TEC states defined by a Gaussian mixture model are highlighted in coloured rectangles. (c) A rug plot showing the TEC sub-clusters (y-axis) ordered along pseudotime (x-axis), coloured as in (Figure 6c). Shaded rectangles represent the span of the meta-stable states along DPT as in (b). (d) Boxplots showing the percentage of TEC coloured by age in mTEC differentiation states, as in (b). *denotes Poisson GLM p-values≤0.01 (see Methods). (e) Expression of TEC progenitor, Intertypical TEC and proliferating TEC markers across pseudotime. Each line shows the loess smooth expression coloured by age. Shaded rectangles represent the TEC meta-stable states shown in (b).

Pseudotime trajectory inference across medullary lineages.
(a–b) Diffusion maps of single mTEC and Intertypical TEC, showing two medulla branches on DC1 vs DC2 (a) and DC2 vs DC3 (b). (c) A UMAP subset to mTEC and Intertypical TEC coloured by DPT on both branches 1 and 2, split by ZsGreen-labelling fraction. (d) Rug plot showing the ordering of TEC sub-clusters across DPT in medulla branch 1. Shaded rectangles denote meta-stable state boundaries as in Figure 7. (e) Kernel density plots of TEC in medulla branch one ordered by DPT, calculated from the apex cell in (a) with the smallest value on DC1, split by ZsGreen-labelling. (f) Rug plot showing the ordering of TEC sub-clusters across DPT in medulla branch 2. Shaded rectangles denote meta-stable state boundaries as in Figure 7. (g) Kernel density plots of TEC in medulla branch one ordered by DPT, calculated from the apex cell in (a) with the smallest value on DC1, split by ZsGreen-labelling. (h) Boxplots of single TEC from medulla branch one partitioned into meta-stable states across ages and split by ZsGreen-labelling fraction. (i) Boxplots of single TEC from medulla branch two partitioned into meta-stable states across ages and split by ZsGreen-labelling fraction.
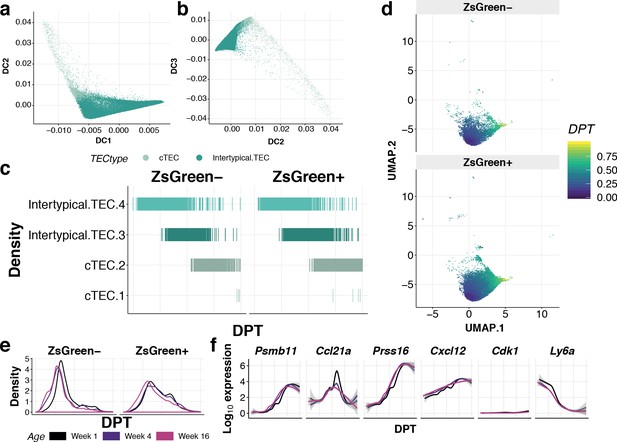
Pseudotime trajectory inference in the cortical lineage.
(a–b) Diffusion maps of single cTEC and Intertypical TEC showing diffusion components (DC) (a) 1 vs. 2 and (b) 2 vs. 3. (c) A rug plot showing the positions of TEC sub-clusters (y-axis) along the cortical lineage ordered by diffusion pseudotime distance (DPT; x-axis) and split by ZsGreen-label fraction. Each line represents a single-cell coloured by filled points in Figure 6c. DPT was calculated from the apex cell in (a) identified as the lowest value on DC1. (d) A UMAP subset to cTEC and Intertypical TEC populations overlaid with DPT as in (c), split by ZsGreen-label fraction. (e) Kernel density of ZsG- and ZsG+ cortical lineage across pseudotime, coloured by ages. (f) Log10 expression of Intertypical, cortical and progenitor TEC marker genes across diffusion pseudotime in ZsGreen+ single TEC.
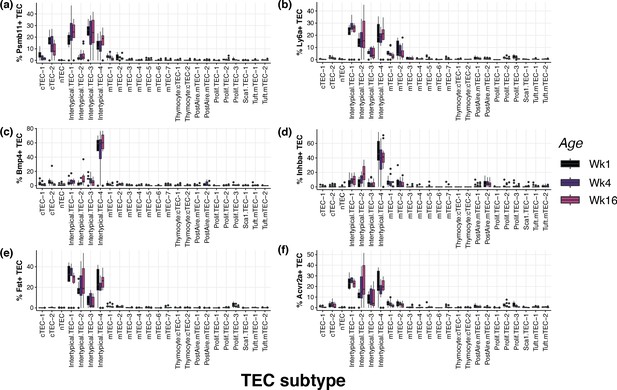
Percentage of cells in each subtype with expression of key TEC genes.
Boxplot showing the proportion of TEC in each subtype cluster which express key genes linked to thymic involution and TEC identity: (a) Psmb11 (β5-t), (b) Ly6a (Sca1), (c) Bmp4, (d) Inhba (Activin A), (e) Fst (follistatin) and (f) Acvr2a (Activin A receptor 2a). Boxplots are coloured by age of dox-treatment administered to 3xtgβ5t mice.
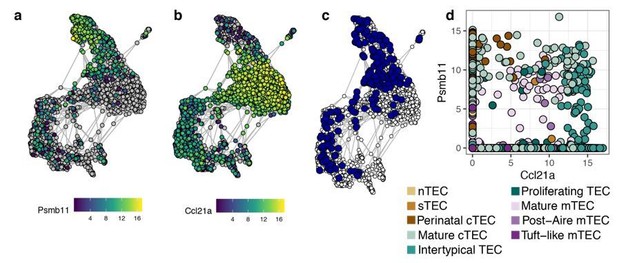
Co-expression of Psmb11 and Ccl21a in single TEC.
Expression in single TEC of (a) Psmb11 , (b) Ccl21a , (c) both (Psmb11+/Ccl21a+; blue), and (d) expression levels of Psmb11 vs. Ccl21a, with TEC subtype indicated by colour. TEC with no detected expression of the relevant gene are coloured in grey (a-b).
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Tables listing relevant experiment related information.
(Table 1) Numbers of TEC isolated in the single-cell experiment. (Table 2) Marker genes for each subtype of TEC. (Table 3) Tests conducted for marker proteins in TEC. (Table 4) Single-cell defined TEC subtypes and known concordant phenotypes. (Table 5) Details of antibodies used in flow cytometry staining panels to identify TEC and thymocytes undergoing negative selection. (Table 6) ADT primers for Droplet sequencing. (Table 7) HTO primers for Droplet sequencing. (Table 8) Tissue-specific gene classification via FANTOM5 Cage-Seq:Tissue samples were grouped into 27 broad groups based on the annotation data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56221/elife-56221-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56221/elife-56221-transrepform-v2.docx