Inhibition of post-termination ribosome recycling at premature termination codons in UPF1 ATPase mutants
Figures
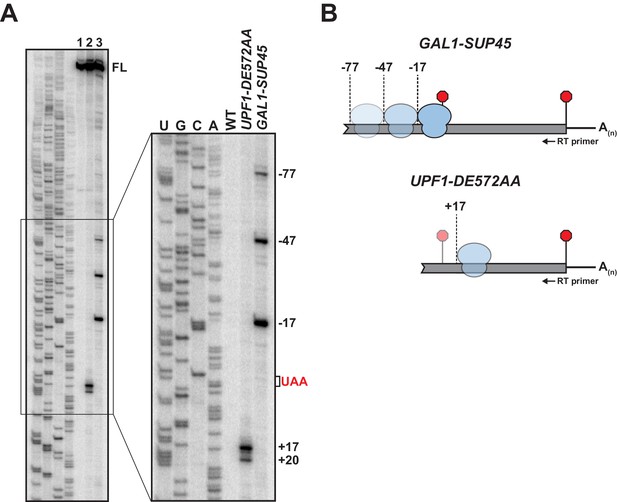
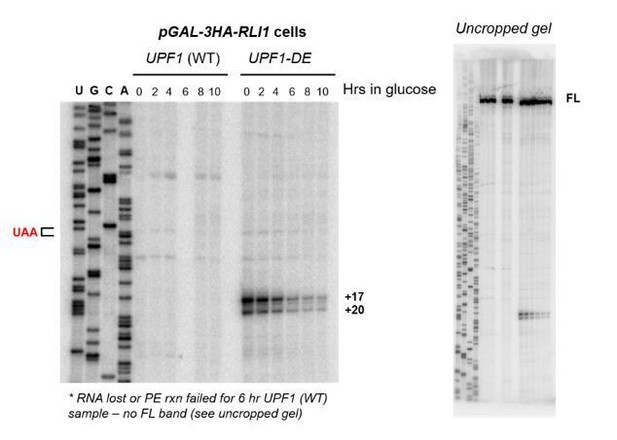
5’ termini of RNA decay fragments in UPF1 ATPase derive downstream of the PTC.
(A) Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC125 mRNA from cells expressing either wild type (WT) or ATPase-deficient UPF1 (UPF1-DE572AA), or depleted for translation termination factor eRF1 (GAL1-SUP45). Full-length cDNAs (FL) and products from RNA decay intermediates are indicated relative to the position of the premature stop codon (UAA, in red). (B) Schematic representation of the predicted sites of ribosome stalling in eRF1-depleted cells (top) and cells expressing ATPase-deficient UPF1 (bottom).
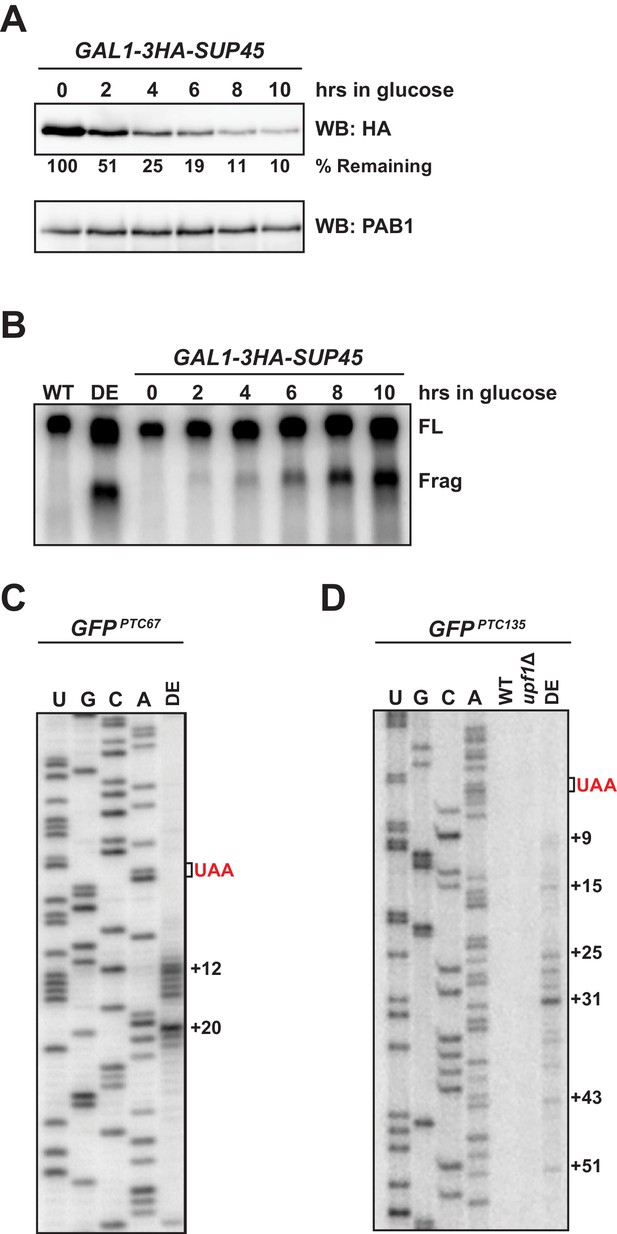
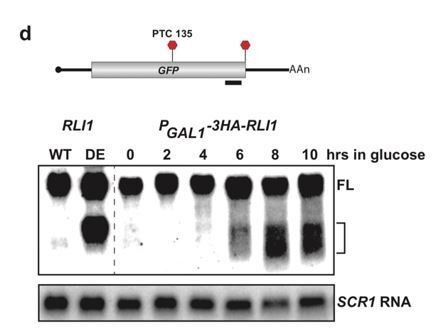
5’ termini of RNA decay fragments in UPF1 ATPase are downstream of the PTC.
(A) Western blot analysis of 3HA-SUP45 levels over time after inhibition of transcription (shift to growth in glucose). Protein levels relative to time zero and normalized to PAB1 shown. (B) Northern blot analysis of GFPPTC125 mRNA in wild type (WT), ATPase-deficient UPF1 mutants (DE), or eRF1-depleted cells (GAL-3HA-SUP45). Full-length mRNA (FL) and 3’ decay fragments (Frag) are indicated. Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC67 mRNA (C) and GFPPTC135 mRNA (D) from ATPase-deficient UPF1 (DE) mutants reveal 5’ ends of decay fragments downstream of the premature stop codon (UAA, in red).
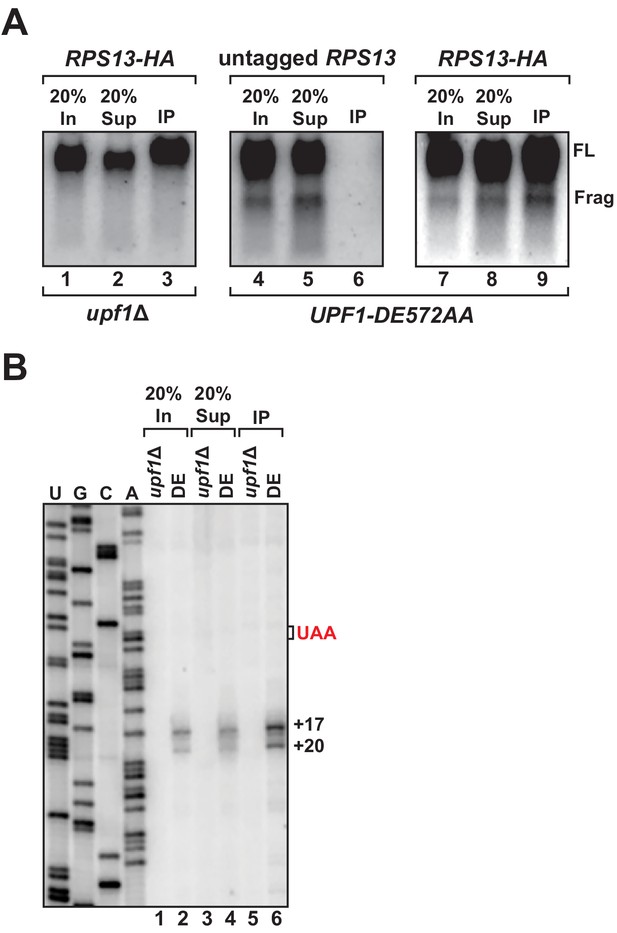
3’ RNA decay intermediates are ribosome bound.
(A) Northern blot analysis of GFPPTC125 mRNA co-immunopurified with untagged or epitope-tagged RPS13 (RPS13-HA) in cells deleted for UPF1 (upf1∆) or expressing the ATPase-deficient mutant, UPF1-DE572AA. Samples include input (In), supernatant (Sup) and immunopurified (IP) material; presence of 18S and 25S ribosomal RNA indicated. (B) Primer extension analysis of RNA samples from immunoprecipitation of RPS13-HA tagged ribosomes shown in (A). cDNA products from RNA decay intermediates are indicated relative to the position of the premature stop codon (UAA, in red).
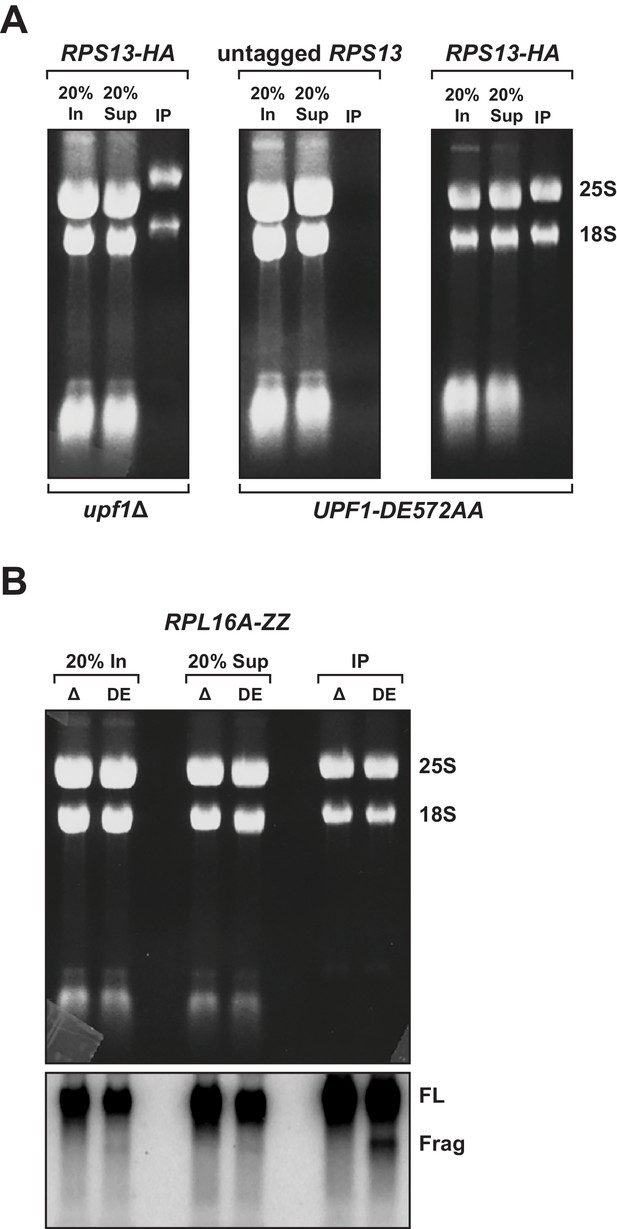
3’ RNA decay intermediates are ribosome bound.
(A) Agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining of material co-immunopurified with untagged or epitope-tagged RPS13 (RPS13-HA) in cells deleted for UPF1 (upf1∆) or expressing the ATPase-deficient mutant, UPF1-DE572AA. Samples include input (In), supernatant (Sup) and immunopurified (IP) material; presence of 18S and 25S ribosomal RNA indicated. (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining (top) and northern blot analysis of GFPPTC125 mRNA (bottom) on material co-immunopurified with epitope-tagged RPL16 (RPL16-ZZ) in cells deleted for UPF1 (∆) or expressing the ATPase-deficient mutant (DE). Full-length mRNA (FL) and 3’ decay fragments (Frag) indicated.
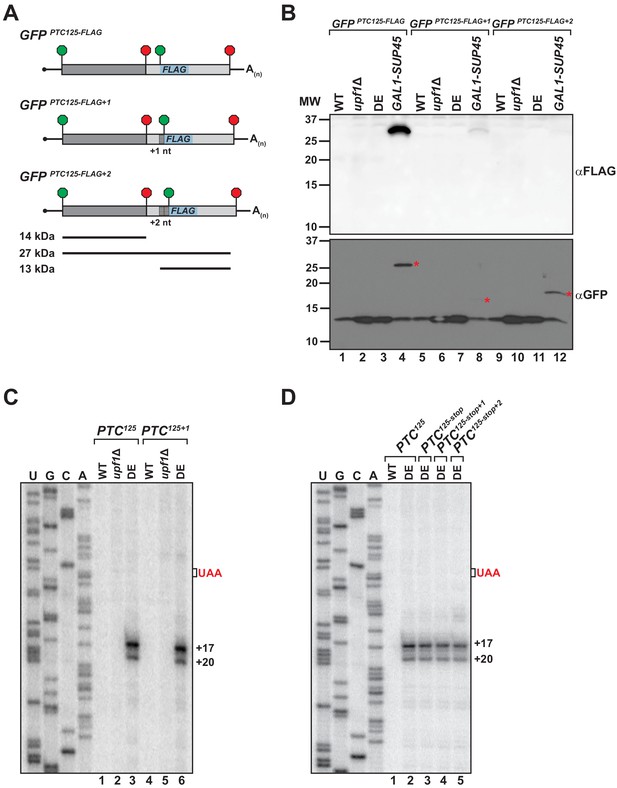
Translational read-through or reinitiation products are not detected in ATPase-deficient UPF1 mutants.
(A) GFPPTC125 reporters encoding an internal FLAG epitope downstream of the PTC in each translational reading frame. Predicted products for translation of GFP mRNA to the PTC (14 kDa), read-through to the natural stop codon (27 kDa), or from reinitiation upstream of the FLAG sequence (13 kDa) are shown. (B) Western blot analysis for FLAG-tagged protein products (top) or GFP protein (bottom) from wild type (WT), UPF1 deletion cells (upf1Δ), UPF1 ATPase mutants (DE) and eRF1-depleted cells (GAL1-SUP45) expressing the GFPPTC125-FLAG reporters. Red asterisks indicate GFP polypeptides expected for translational read-through at the PTC for the three GFPPTC125-FLAG reporters; size disparity reflect differences in translation termination of these products due to +1 and +2 shifts in the reading frames. (C) Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC125 and GFPPTC125+1 mRNA from WT, upf1Δ, and UPF1 ATPase mutants (DE). GFPPTC125+1 mRNA harbors a single-nucleotide insertion immediately downstream of the PTC. (D) Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC125 mRNA harboring a second stop codon in each translational reading frame beginning either 10, 11, or 12 nucleotides downstream of the PTC.
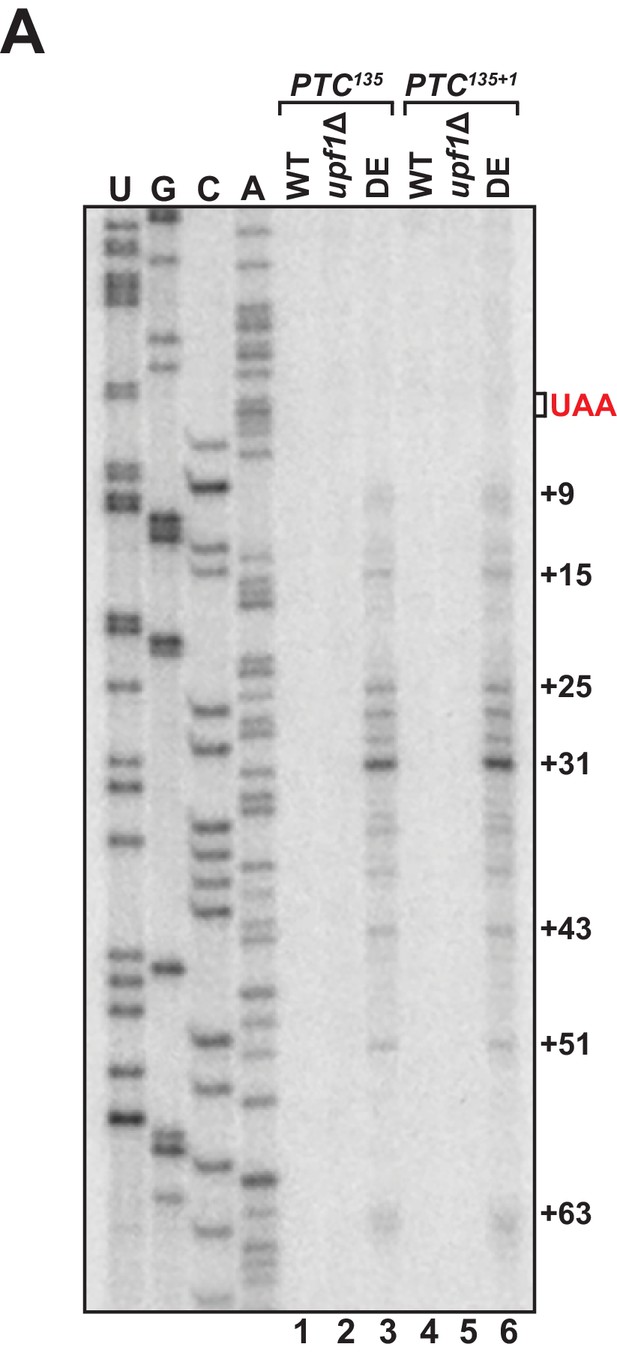
Alteration of translational reading frame downstream of the PTC does not alter primer extension products.
(A) Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC135 and GFPPTC135+1 mRNA from WT, upf1Δ, and UPF1 ATPase mutants (DE). GFPPTC125+1 mRNA harbors a single-nucleotide insertion immediately downstream of the PTC.
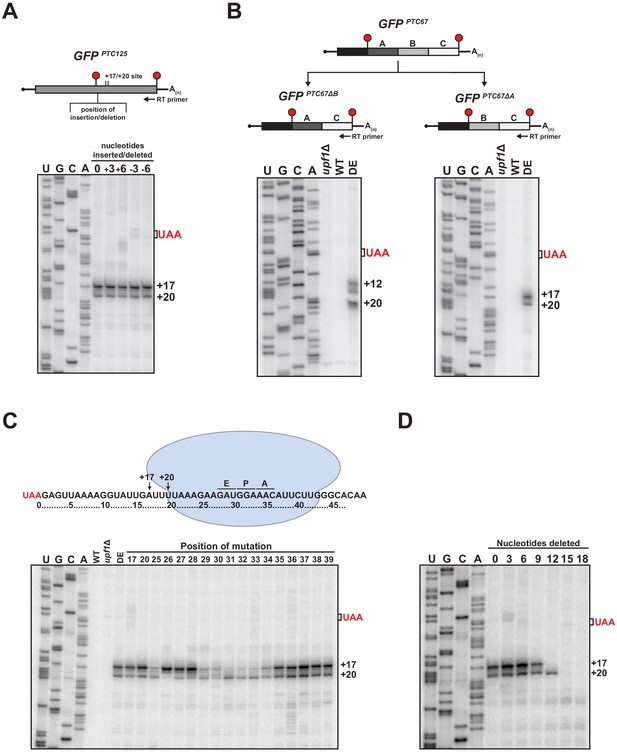
RNA sequence requirements for the accumulation of 3’ RNA decay fragments.
(A) Schematic of nucleotide insertions or deletions immediately downstream of the PTC in GFPPTC125 (top) and primer extension analysis of these reporter mRNAs from ATPase-deficient UPF1 mutants (bottom). (B) GFPPTC67 reporters lacking ~170 nt within an internal 3’ UTR region (GFPPTC67ΔB) or just downstream of the PTC (GFPPTC67ΔA) and primer extension analysis of these RNAs from UPF1 deletion cells (upf1Δ) or cells expressing wild type (WT) or ATPase-deficient UPF1 (DE). (C) Schematic representation of GFPPTC125 reporter mRNA and stalled ribosome whose 30 nt footprint would protect RNA from +17 to +46; predicted positions for the ribosome A, P, and E sites are indicated (top). Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC125 reporters in wild type, UPF1 deletion cells (upf1Δ), or UPF1 ATPase mutants (DE) and various GFPPTC125 mRNAs harboring single-nucleotide inversions (at positions indicated) from ATPase-deficient UPF1 cells. (D) Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC125 mRNAs deleted for nucleotides immediately downstream of PTC in UPF1 ATPase mutants.
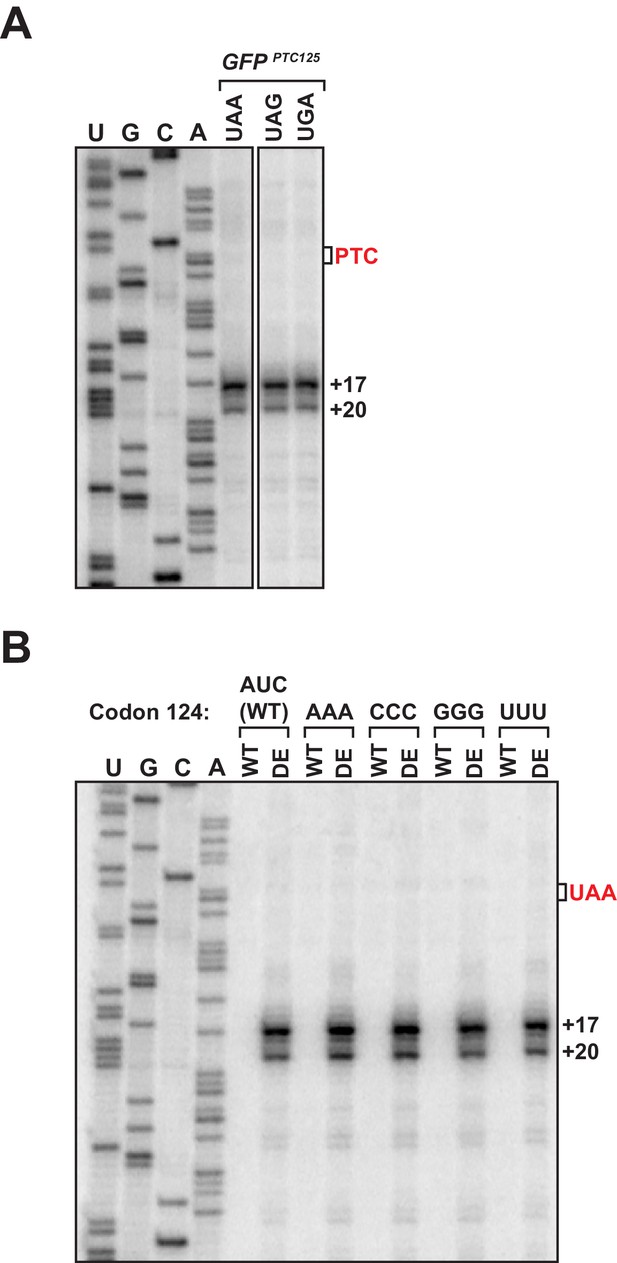
Accumulation of 3’ RNA decay intermediates in UPF1 ATPase mutants is unaffected by the nucleotide sequence of the PTC or penultimate sense codon.
(A) Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC125 mRNA harboring a UAA, UAG, or UGA nonsense codon from ATPase-deficient UPF1 mutants. (B) Primer extension analysis of GFPPTC125 mRNA with mutations within GFP codon 124 as indicated.
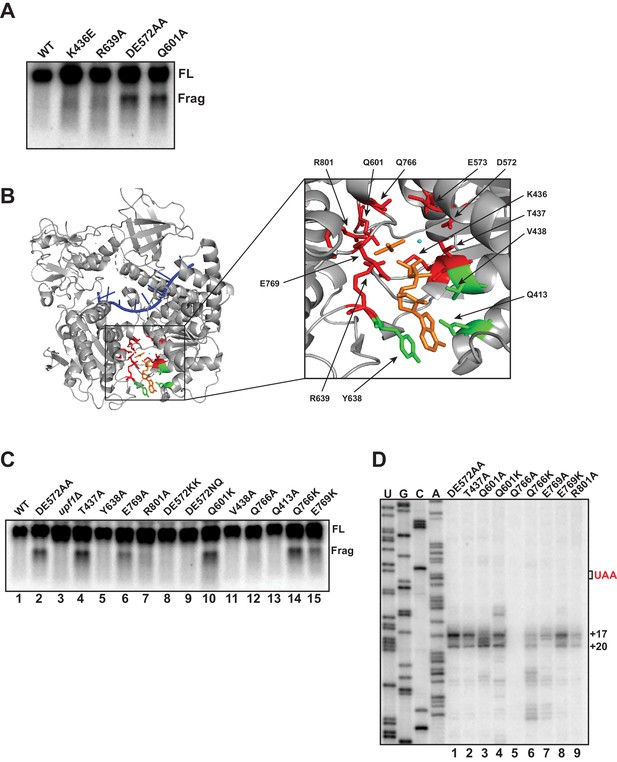
Mutational analysis of UPF1 active site correlates ATP hydrolysis with ribosome stalling.
Northern blot (A, C) and primer extension analysis (D) of GFPPTC125 mRNA from cells expressing either wild-type UPF1 or the indicated mutant allele with substitutions in the ATP binding pocket. Full-length mRNA (FL) and 3’ RNA decay fragments (Frag) are indicated. (B) Crystal structure of UPF1 in complex with RNA and ADP:AlF4- (PDB accession code 2XZL; Chakrabarti et al., 2011). RNA, ADP:AlF4- and Mg2+ are indicated in blue, orange, and cyan, respectively. Amino acid residues labeled green did not give rise to detectable 3’ RNA decay fragments from GFPPTC125 mRNA when mutated; residues in red accumulated 3’ RNA fragments when mutated.
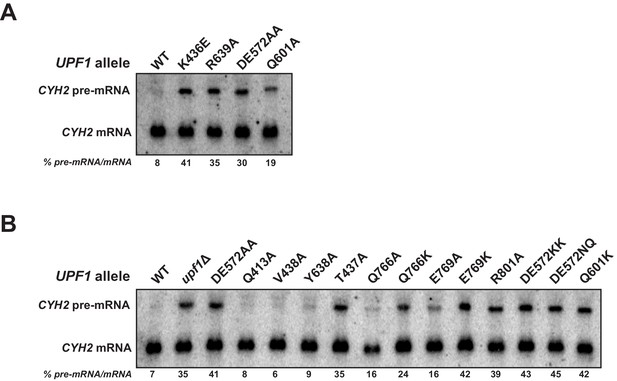
Impact of UPF1 active site mutations on NMD activity.
(A and B) Northern blot analysis of CYH2 RNA from cells expressing the indicated allele of UPF1. NMD-sensitive CYH2 pre-mRNA and NMD-insensitive CYH2 mRNA are indicated and NMD activity calculated as the ratio of CYH2 pre-mRNA to mRNA. Experiments were performed in duplicate and representative images and quantifications are shown.
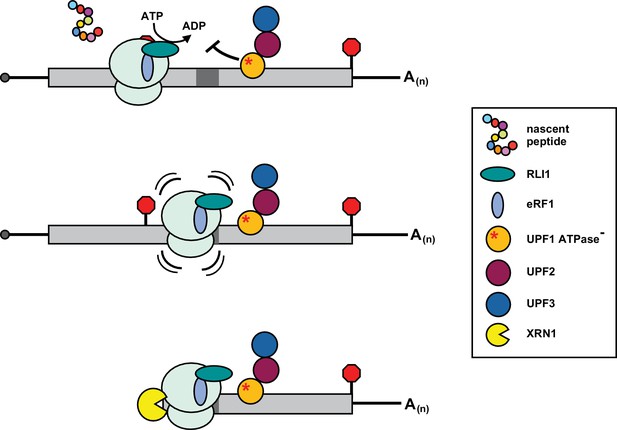
Inhibition of post-termination ribosome release during premature translation termination in UPF1-ATPase mutants.
RLI1 function in translation termination involves both stimulation of peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis by eRF1 and ATP hydrolysis-dependent ribosome subunit splitting. In UPF1 ATPase mutants, ribosomes efficiently recognize a PTC and release the C-terminally truncated polypeptide; however, ribosome subunits fail to be dissociated from the RNA. Post-termination ribosomes with an occupied A site migrate downstream of the PTC into the mRNA 3’ UTR where they stall in a manner dependent upon RNA sequence (dark gray box) and the nature of the inactivating mutation in the ATP binding pocket of UPF1, and block 5’ → 3’ degradation of the mRNA by XRN1.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | Wild type (WT) | Saccharomyces Genome Deletion Project | MATa, ura3, leu2, his3, met15 | |
| Genetic Reagent (S. cerevisiae) | upf1Δ | Saccharomyces Genome Deletion Project | MATa, ura3, leu2, his3, met15, upf1::KanMX | |
| Genetic Reagent (S. cerevisiae) | Rpl16-ZZ | This paper | MATa, ura3, leu2, his3, met15, upf1::KanMX, RPL16A-ZZ-HIS3 | |
| Genetic Reagent (S. cerevisiae) | Rps13-HA | This paper | MATa, ura3, leu2, his3, met15, upf1::KanMX, RPS13-HA-HIS3 | |
| Genetic Reagent (S. cerevisiae) | Sup45 depletion strain | This paper | MATa, ura3, leu2, his3, met15, upf1::KanMX, HIS3-PGAL-3HA-SUP45 | |
| Antibody | Anti-HA (Mouse monoclonal) | Covance | MMS-101P; RRID:AB_2314672 | WB: (1:5,000) IP: (4 µg) |
| Antibody | Anti-TAP (Rabbit polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher | CAB1001; RRID:AB_10709700 | IP: (4 µg) |
| Antibody | Anti-Pab1 (Mouse monoclonal) | Encore Biotechnology | MCA-1G1; RRID:AB_2572370 | WB: (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG-HRP (goat polyclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Sc-2005; RRID:AB_631736 | WB: (1:5,000) |
| Commercial Assay or Kit | Sequenase 2.0 DNA Sequencing Kit | Thermo Fisher | 70771KT | |
| Recombinant DNA Reagent | GFPPTC67 | This paper | pKB673 | CEN; URA3 |
| Recombinant DNA Reagent | GFPPTC125 | This paper | pKB674 | CEN; URA3 |
| Recombinant DNA Reagent | GFPPTC135 | This paper | pKB510 | CEN; URA3 |
| Recombinant DNA Reagent | UPF1-WT | PMID:28008922 | pKB556 | CEN; URA3 |
| Recombinant DNA Reagent | UPF1-DE572AA | PMID:28008922 | pKB576 | CEN; LEU2 |
| Sequence-based reagent | RT primer (GFPPTC125 primer extension analysis) | This paper | oKB132 | GGGCAGATTGTGTGGACAGGTAATGGTTGTCTGG |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Complete list of all yeast strains used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57834/elife-57834-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Complete list of all plasmids used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57834/elife-57834-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Complete list of all oligonucleotides used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57834/elife-57834-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57834/elife-57834-transrepform-v1.docx