Pleiotropic mutations can rapidly evolve to directly benefit self and cooperative partner despite unfavorable conditions
Figures
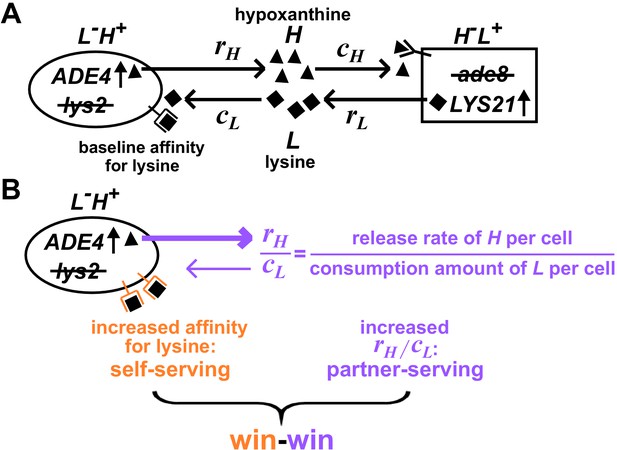
Win-win mutation in a nascent cooperative community.
(A) CoSMO (Cooperation that is Synthetic and Mutually Obligatory) consists of two non-mating cross-feeding yeast strains, each engineered to overproduce a metabolite required by the partner strain. Metabolite overproduction is due to a mutation that renders the first enzyme of the biosynthetic pathway resistant to end-product inhibition (Armitt and Woods, 1970; Feller et al., 1999). Hypoxanthine and lysine are released by live L-H+ and live H-L+ cells at a per cell rate of rH and rL, respectively (Hart et al., 2019a), and are consumed by the partner at a per cell amount of cH and cL, respectively. The two strains can be distinguished by different fluorescent markers. (B) Win-win mutation. A pleiotropic win-win mutation confers a self-serving phenotype (orange) and a partner-serving phenotype (lavender).

Self-serving mutations stabilize the high affinity lysine permease Lyp1 on cell membrane and improve cell growth rates at low lysine.
(A) Recurrent mutations are self-serving. We measured growth rates of mutant and ancestral strains in minimal SD medium with various lysine concentrations, using a calibrated fluorescence microscopy assay (Hart et al., 2019c). Briefly, for each sample, total fluorescence intensity of image frames was tracked over time, and the maximal positive slope of ln(fluorescence intensity) against time was used as the growth rate. Evolved strains grew faster than the ancestor in community environment (the gray dotted line corresponds to the lysine level supporting a growth rate of 0.1/hr as observed in ancestral Cooperation that is Synthetic and Mutually Obligatory [CoSMO] Hart et al., 2019a). Measurements performed on independent days (≥3 trials) were pooled and the average growth rate is plotted. Fit lines are based on Moser’s equation , where b(L) is the cell birth rate at metabolite concentration L, bmax is the maximum birth rate in excess lysine, KL is the lysine concentration at which half maximum birth rate is achieved, and n is the cooperitivity cooefficient describing the sigmoidal shape of the curve (Hart et al., 2019c). Evolved strains are marked with evo; engineered or backcrossed mutants are marked with the genotype. Data for DISOMY14 are reproduced from Hart et al., 2019b as a comparison. Data can be found in Figure 2—source data 1. (B) Self-serving mutations stabilize Lyp1 localization on cell membrane. We fluorescently tagged Lyp1 with GFP (green fluorescent protein) in ancestor (WY1620), ecm21Δ (WY2355), and rsp5(P772L) (WY2356) to observe Lyp1 localization. We imaged each strain in a high lysine concentration (164 µM) as well as after 4 and 10 hr incubation in low lysine (1 µM). Note that low lysine was not consumed during incubation (Hart et al., 2019c). During prolonged lysine limitation, Lyp1 was stabilized to cell membrane in both mutants compared to the ancestor. Images contain samples from several fields of view so that more cells can be visualized.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Growth parameters of ancestral and mutant strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57838/elife-57838-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
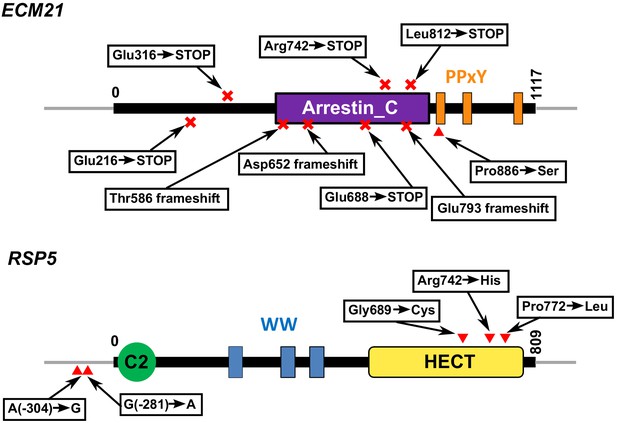
Functional domains and positions of mutations in Ecm21 and Rsp5 proteins.
Mutations and their locations are marked with respect to the functional domains of the proteins. Numbers indicate amino acid positions, except in non-coding regions. Domain structures are obtained from the ‘protein’ tab of SGD (https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000000927/protein; https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000000197/protein). HECT domain is found in ubiquitin-protein ligases. WW domain can bind proteins with particular proline-motifs such as the PPxY motif. Arrestin C-terminal-like domain is involved in signaling and endocytosis of receptors. For ECM21, mutating the three poly-proline-tyrosine (PY) motifs after amino acid 884 inhibited the stress-induced endocytosis of the manganese transporter Smf1 (Nikko et al., 2008). Most ecm21 mutations we recovered introduced premature stop codons before the PY motifs. In RSP5, the region including and upstream of -470 is required for RSP5 function (Hein et al., 1995). Mutations from coculture and monoculture isolates are marked above and below the gene, respectively.
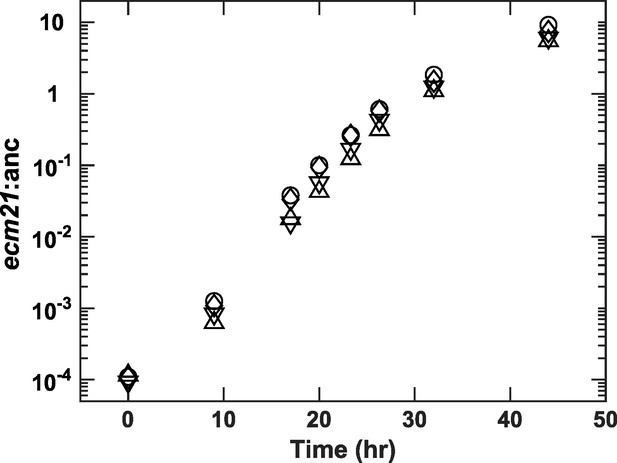
ecm21Δ rapidly outcompetes ancestor in lysine-limited chemostats.
We competed ancestor (expressing the mCherry fluorescent protein) and ecm21Δ (expressing the blue fluorescent protein) in four independent lysine-limited chemostats (represented by different symbols). Minimal medium containing 20 µM lysine is pumped in to achieve an 8-hr doubling time (similar to Cooperation that is Synthetic and Mutually Obligatory [CoSMO] doubling time). Periodically, we measured strain ratio using flow cytometry (Methods, 'Quantification methods'). The fitness advantage of ecm21Δ over ancestor is 0.315±0.014/hr (calculated from the slope using all data except the last time point when ecm21Δ had risen to be the majority). Since ancestor’s growth rate is ln(2)/8=0.0866/hr, ecm21Δ grows 4.7 times as fast as the ancestor. This is consistent with Figure 2A: The ancestor achieves a doubling time of 8 hr at 1.38 μM lysine, and at this concentration, ecm21Δ grows at 0.38/hr, 4.4 times as fast as the ancestor. Data can be found in Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Population dynamics of strain competition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57838/elife-57838-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
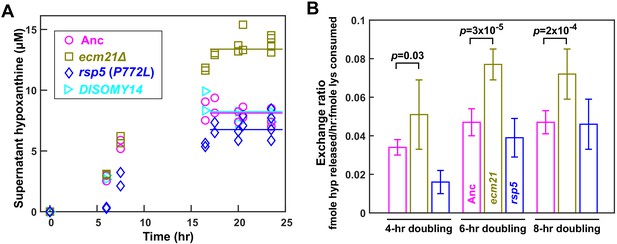
ecm21Δ improves hypoxanthine release rate per lysine consumption.
(A) Hypoxanthine accumulates to a higher level in ecm21Δ chemostats than in ancestor chemostats. We cultured individual strains in lysine-limited chemostats (20 µM input lysine) at 6 hr doubling time (similar to Cooperation that is Synthetic and Mutually Obligatory [CoSMO] doubling time). Periodically, we quantified live and dead cell densities using flow cytometry (Figure 3—figure supplement 1), and hypoxanthine concentration in filtered supernatant using a yield-based bioassay (Hart et al., 2019a). The steady state hypoxanthine concentration created by the ancestor (WY1335) was lower than ecm21Δ (WY2226), and slightly higher than rsp5(P772L) (WY2475). DISOMY14 (WY2349) was indistinguishable from the ancestor, similar to our previous report (Hart et al., 2019b). (B) ecm21Δ has a higher hypoxanthine-lysine exchange ratio than the ancestor. Cells were cultured in lysine-limited chemostats that spanned the range of CoSMO environments. In all tested doubling times, the exchange ratios of ecm21Δ were significantly higher than those of the ancestor. The exchange ratios of rsp5(P772L) were similar to or lower than those of the ancestor. Mean and two standard deviations from four to five experiments are plotted. p-values are from two-tailed t-test assuming either unequal variance (4 hr doubling) or equal variance (6 and 8 hr doublings; verified by F-test). Data and p-value calculations can be found in Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Dynamics and exchange ratios measured in chemostats.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57838/elife-57838-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
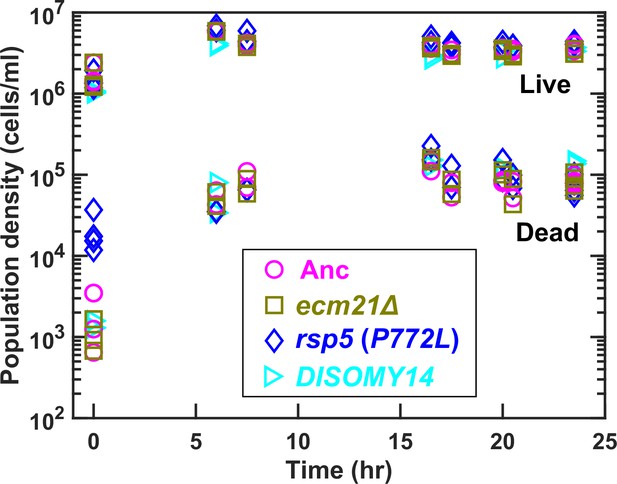
Population dynamics in chemostats.
We cultured ancestor and mutant strains in lysine-limited chemostats (20 µM input lysine) at 6 hr doubling time (similar to Cooperation that is Synthetic and Mutually Obligatory [CoSMO] doubling time). Periodically, we measured live and dead cell densities using flow cytometry (Hart et al., 2019a). After a lag, live and dead cell densities reached a steady state. Data can be found in Figure 3—source data 1.

ecm21Δ increases the growth rate of community and of partner.
To prevent rapid evolution, we grew CoSMO containing ancestral H-L+ and ancestral or ecm21Δ L-H+ in a spatially structured environment on agarose pads, and periodically measured the absolute abundance of the two strains using flow cytometry (Hart et al., 2019a). (A) Growth dynamics. After an initial lag, CoSMO achieved a steady state growth rate (slope of dotted line). (B) ecm21Δ increases the growth rate of CoSMO and of partner. Steady state growth rates of the entire community (left) and of partner H-L+ (right) were measured (n ≥ 6), and the average and two standard deviations are plotted. p-values are from two-tailed t-test with equal variance (verified by F-test). The full data set and outcomes of statistical tests can be found in Figure 4—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Community growth dynamics.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57838/elife-57838-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
Tables
Mutations that repeatedly arose in independent lines.
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and chromosomal duplications from Illumina re-sequencing of L-H+ from Cooperation that is Synthetic and Mutually Obligatory (CoSMO) communities (top) and lysine-limited chemostats (bottom). All clones except for two (WY1592 and WY1593 of line B3 at Generation 14) had either an ecm21 or an rsp5 mutation, often in conjunction with chromosome 14 duplication. Note that the RM11 strain background in this study differed from the S288C strain background used in our earlier study (Waite and Shou, 2012). This could explain, for example, why mutations in DOA4 were repeatedly observed in the earlier study (Waite and Shou, 2012) but not here. For a schematic diagram of the locations of mutations with respect to protein functional domains in ecm21 and rsp5, see Figure 2—figure supplement 1. For other mutations, see Table 1—source data 1.
| L-H+ | Line | Generation | ecm21 | rsp5 | Chromosome duplicated | Strain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoSMO comm. | A1 | 24 | Glu316 -> Stop | – | 11, 14 | WY1588 |
| – | Pro772 -> Leu | 11 | WY1589 | |||
| 151 | – | Pro772 -> Leu | – | WY1590 | ||
| – | Pro772 -> Leu | 11, 14, 16 | WY1591 | |||
| B1 | 25 | Leu812->Stop | – | 14 | WY1584 | |
| 49 | – | Gly689 -> Cys | 14 | WY1585 | ||
| 76 | – | Gly689 -> Cys | – | WY1586 | ||
| Gly689 -> Cys | 14 | WY2467 | ||||
| – | Gly689 -> Cys | 14 | WY1587 | |||
| B3 | 14 | – | – | – | WY1592 | |
| – | – | 14 | WY1593 | |||
| 34 | Arg742 -> Stop | – | 14, 16 | WY1594 | ||
| Arg742 -> Stop | – | 14, 16 | WY1595 | |||
| 63 | Arg742 -> Stop | Arg742 -> His | 12, 14 | WY1596 | ||
| Lysine-limited chemostat mono-culture | 7.Line1 | 30 | Asp652 frameshift | 14 | WY1601 | |
| Glu216 -> Stop | 14 | WY1602 | ||||
| 7.Line2 | 30 | Pro886 -> Ser | 11, 14, 16 | WY1603 | ||
| 7.Line3 | 30 | Thr586 frameshift | 14 | WY1604 | ||
| Thr586 frameshift | 14 | WY1605 | ||||
| 11.Line1 | 19 | Glu688 -> Stop | 14, 16 | WY1606 | ||
| G(−281) ->A | – | WY1608 | ||||
| 11.Line2 | 19 | A(−304) -> G | – | WY1607 | ||
| 50 | Glu793 frameshift | 14 | WY1609 |
-
Table 1—source data 1
Summary of mutations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57838/elife-57838-table1-data1-v2.xlsx
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57838/elife-57838-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57838/elife-57838-transrepform-v2.docx





