Discovery of surrogate agonists for visceral fat Treg cells that modulate metabolic indices in vivo
Figures
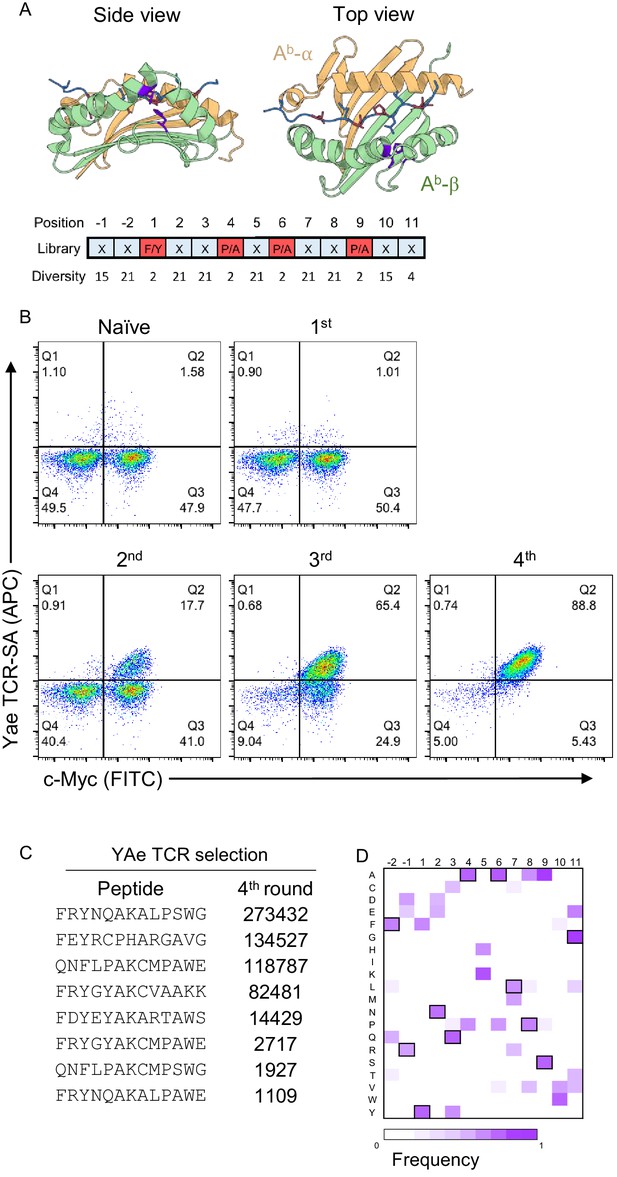
Development of a peptide-Ab yeast library.
(A) A degenerate codon with maximum diversity at TCR-facing positions (blue) and optimal residues at anchor positions (red) was used to generate a peptide-MHC yeast library containing up to 1 × 109 peptides. (B) To validate the library a proxy TCR of known specificity, YAe, was used to perform four consecutive rounds of selection. (C) Enriched yeast clones were isolated at all steps and deep-sequenced following appropriate plasmid purification and PCR amplification in order to quantify the peptide frequency. The top eight enriched peptides found in the fourth round of YAe selection are shown. (D) Positional frequency matrix based on the deep sequence of the fourth round of selection.
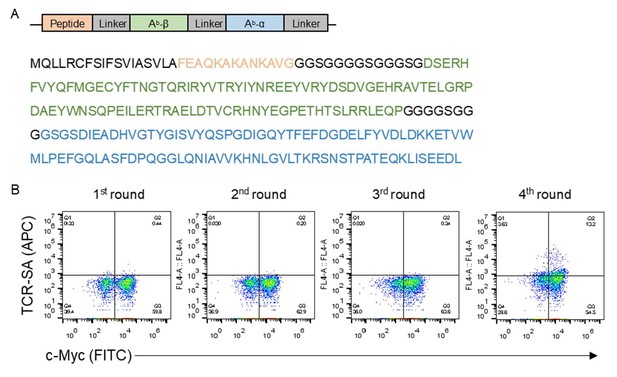
Evolution of peptide-Ab yeast display.
(A) Cartoon representation and protein sequence used for the peptide-Ab yeast display. (B) TCR tetramer staining of the naïve library and the four consecutive rounds of yeast selection using the YAe TCR. The peptide-Ab library was generated following the random mutagenesis by error-prone PCR of the construct shown in (A). (C) Size exclusion chromatography of the vTreg53 TCR following purification by Ni-NTA column and overnight biotinylation using BirA enzyme. (D) Reducing and non-reducing SDS-PAGE of the vTreg53 TCR fractions collected in (C).
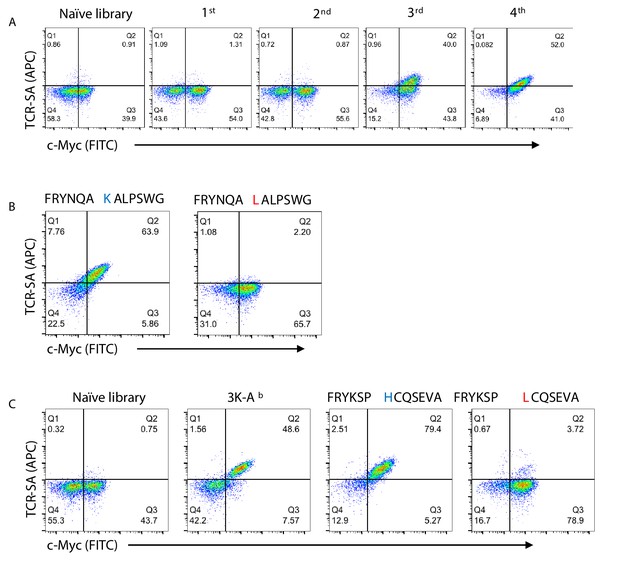
Validation of the peptide-Ab yeast display platform.
(A) 2W TCR tetramer staining together with c-myc staining is shown for the naïve library and four consecutive rounds of selection of the peptide-Ab yeast library. TCR tetramer and c-myc staining of enriched peptide sequences (single clones) isolated from the YAe (B) or 2W (C) TCR selections. Naïve library, 3 k peptide and single point mutations (red) in central positions of the enriched peptides were used as controls to confirm the specificity of the peptide-Ab/TCR SA interaction.
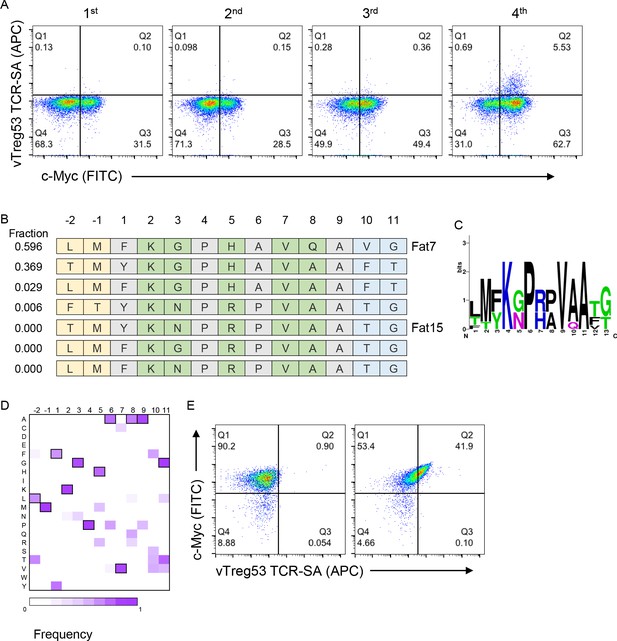
Identification of surrogate peptides recognized by the vTreg53 TCR.
(A) The vTreg53 TCR was used to screen and isolate the peptide-MHC yeast display. vTreg53 TCR tetramer staining (500 nM of TCR-SA) together with c-Myc staining is shown for the naïve library and four consecutive rounds of selection. (B) Deep sequencing of the fourth round of selection reveals a small subset of peptides which share key residues at TCR facing positions (shown in green). (C) Positional frequency representation from the deep sequencing of the third round of selection with vTreg53. (D) Positional frequency matrix based on the deep sequencing of the fourth round of the peptide-MHC yeast selection. (E) A single peptide-MHC yeast clone, displaying the top enriched peptide, LMFKGPHAVQAVG (Fat 7; right panel; left panel shows staining for Eα control peptide), shows a positive Fat-TCR tetramer staining (500 nM final tetramer concentration). Data shown are representative of at least two independent experiments.
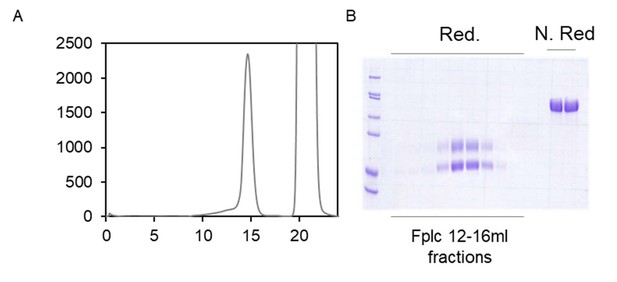
Evolution of peptide-Ab yeast display.
(A) Size exclusion chromatography of the vTreg53 TCR following purification by Ni-NTA column and overnight biotinylation using BirA enzyme. (B) Reducing and non-reducing SDS-PAGE of the vTreg53 TCR fractions collected in (A).
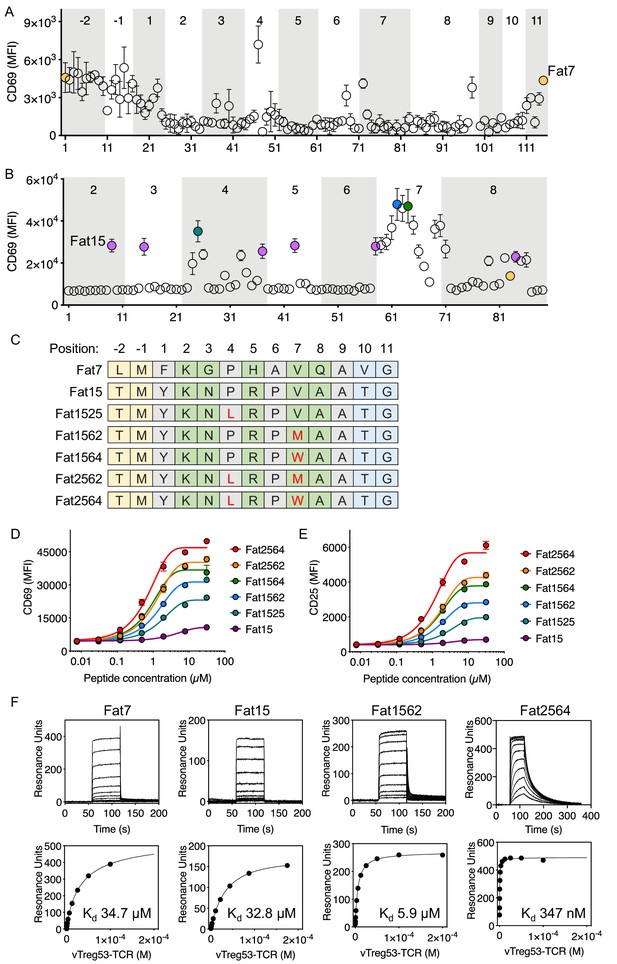
Identification of robust vTreg53 TCR agonists.
Single-point mutants based on the Fat7 (A) or Fat15 (B) peptides were used to stimulate Fat-TCR transduced Jurkat T cells. Data shown are mean fluorescence intensity for CD69 up-regulation following overnight stimulation with the indicated peptides at 100 µM. (C) Potent SPs based on Fat15. Single-residue mutations from the Fat15 are shown in red. Anchor positions are shown in grey and potential TCR-facing positions are shown in green. A peptide titration of single- and double-point mutants from the Fat15 SP show up to ~4- (D; CD69) or ~8 fold (E; CD25) increase in Emax. (F) Surface plasmon resonance for Fat7, Fat15, Fat1562 and Fat2564 was used to determine the pMHC/Fat TCR affinity. All biotinylated pMHC were purified by SEC and immobilized in a streptavidin-coated SPR sensor chip from 200 up to 600 RU. Data are mean ± SD from n = 2 (A, D, E) or 3 (B) biological replicates from 1 representative of 3 independent experiments. Data shown in (F) is representative of 2 independent experiments.
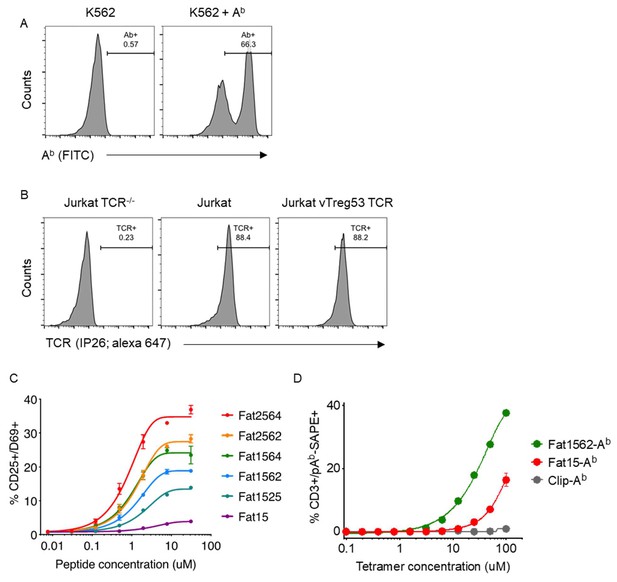
In vitro peptide stimulation of the vTreg53 TCR cells.
(A) Expression of wild-type Ab MHC in stably transduced K562 cells. (B) Expression of vTreg53 TCR in stably transduced Jurkat T cells (TCRαβ-/-). (C) Fraction of CD25+/CD69+ cells following overnight stimulation with Fat mimotopes at the indicated concentrations. (D) Peptide-Ab - streptavidin PE (pAb -SAPE) titration of vTreg53 transduced Jurkat T cells. Cells were stained with 250 nM of pAb-SAPE tetramer for 1 hr. (C, D) Data are mean ± SD from n = 2 biological replicates from 1 representative of 3 independent experiments.
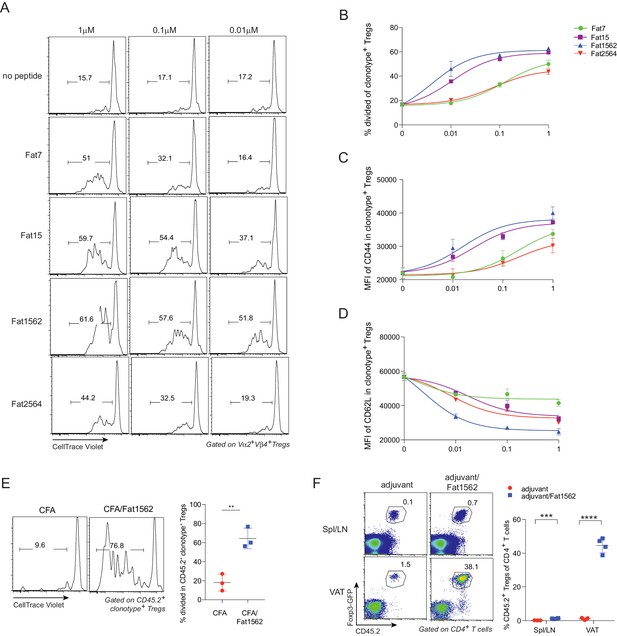
SPs induce proliferation and activation of vTreg53 Treg cells in vitro and in vivo.
(A–D) Proliferation and activation of vTreg53 Treg cells by different concentrations of SPs for 3 days in vitro (n = 3). (A) Representative flow cytometric plot of cell division. (B) Summary of cell proliferation. (C) Mean flourescence intensity (MFI) of CD44 staining in clonotype+ Treg cells. (D) MFI of CD62L staining in clonotype+ Treg cells. (E) Proliferation of transferred CD45.2+ vTreg53 Treg cells in the spleen of CD45.1+ B6 recipient mice immunized s.c. with CFA or CFA/Fat1562 at day 3 (n = 3). (F) Expansion of transferred CD45.2+ vTreg53 Treg cells in the Spl/LNs or VAT of CD45.1+ B6 recipient mice that were primed with CFA/fat1562 s.c. and boosted with IFA/Fat1562 i.p. (n ≥ 3). Data are mean ± SD. Data shown are representative of at least two independent experiments.
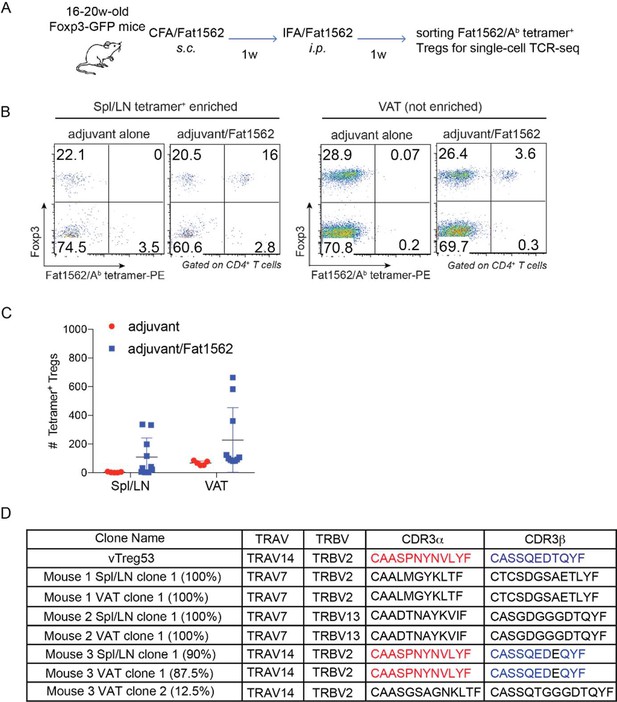
Single cell TCR sequencing (scTCR-seq) analyses of fat1562-reactive endogenous Treg cells following immunization.
(A) Scheme of the experiment. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of fat1562/Ab -PE tetramer+ Treg cells in Spl/LNs (enriched by anti-PE beads) or VAT (not enriched) of mice immunized with adjuvant alone or adjuvant/fat1562. Plot is a representative of mice that did show detectable expansion of tetramer+ Tregs. (C) Numbers of fat1562/Ab -PE tetramer+ Treg cells in Spl/LNs or VAT of mice immunized with adjuvant alone or adjuvant/fat1562 (D) Summary of the frequency and CDR3 sequences of expanded fat1562/Ab -PE tetramer+ Treg clones.
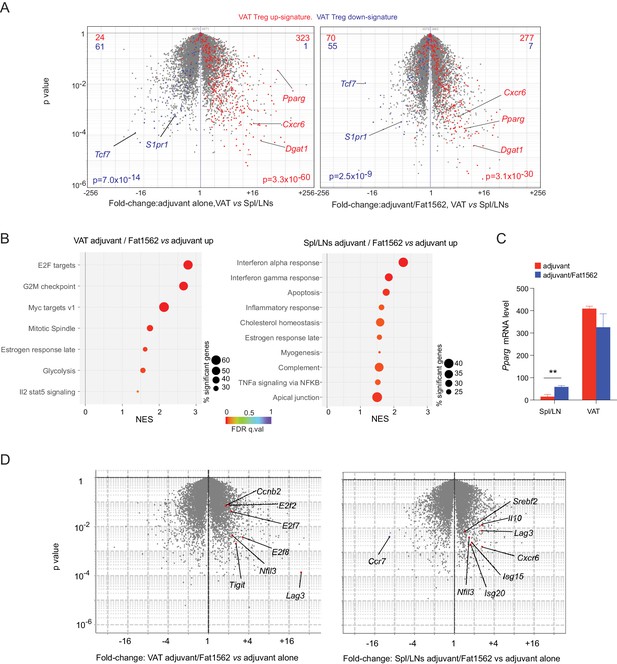
Transcriptional analyses of vTreg53 Treg cells stimulated by Fat1562 in vivo.
(A–C) CD45.2+ vTreg53 Treg cells were transferred i.v. into CD45.1+ B6 mice. 6 weeks later, the recipient mice were immunized with CFA alone or CFA/Fat1562 s.c., and one week later, boosted with IFA alone or IFA/Fat1562 i.p. CD45.2+ clonotype+ Treg cells were sorted from Spl/LNs or VAT of the recipient mice one week later for RNA-Seq. (A) Volcano plot comparing gene expression of transferred clonotype+ Treg cells in the VAT and Spl/LNs of recipient mice immunized with adjuvant alone (left) or with adjuvant/Fat1562 (right). VAT-Treg signature genes are highlighted in red (induced) or blue (repressed). The number of genes from each signature preferentially expressed by one or the other population are shown at the top. (B) GSEA analysis of top KEGG pathways (p<0.05) that are enriched in cells activated by adjuvant/Fat1562 compared with adjuvant alone in VAT (left) or Spl/LN (right). NES, normalized enrichment score. FDR, false discovery rate. (C) Normalized reads of Pparg transcript in CD45.2+ clonotype+ Treg cells sorted from mice immunized with adjuvant alone or adjuvant/Fat1562. Data are mean ± SD. (D) Volcano plot comparing gene expression of transferred clonotype+ Treg cells in mice immunized with adjuvant/Fat1562 and adjuvant alone in the VAT (left) and spleen (right). Representative transcripts are highlighted.
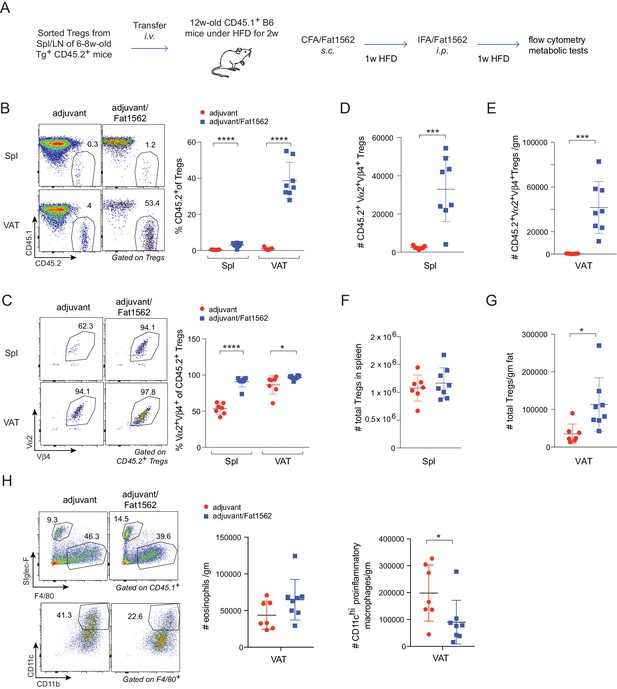
Immunization with Fat1562 expands transferred vTreg53 Treg cells and suppresses HFD-induced VAT inflammation.
(A) Scheme of the transfer and immunization protocol. (B) Frequencies of CD45.2+ cells in Treg cells (n ≥ 7). (C) Frequencies of clonotype+ cells in transferred CD45.2+ Treg cells (n ≥ 7). (D) Number of clonotype+ CD45.2+ Treg cells in the spleen (n ≥ 7). (E) Number of clonotype+ CD45.2+ Treg cells in the VAT (n ≥ 7). (F) Number of total Treg cells in the spleen (n ≥ 7). (G) Number of total Treg cells in VAT (n ≥ 7). (H) Numbers of eosinophils and CD11chi inflammatory macrophages in VAT (n ≥ 7). Data are mean ± SD. Data shown are representative of at least two independent experiments.
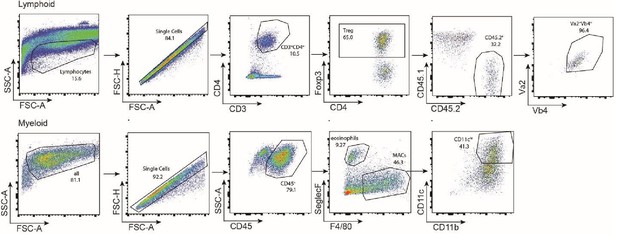
Gating strategy.
Gating strategy used for detection of VAT Treg cells (top) and, eosinophils or macrophage cells (bottom) by flow cytometry.
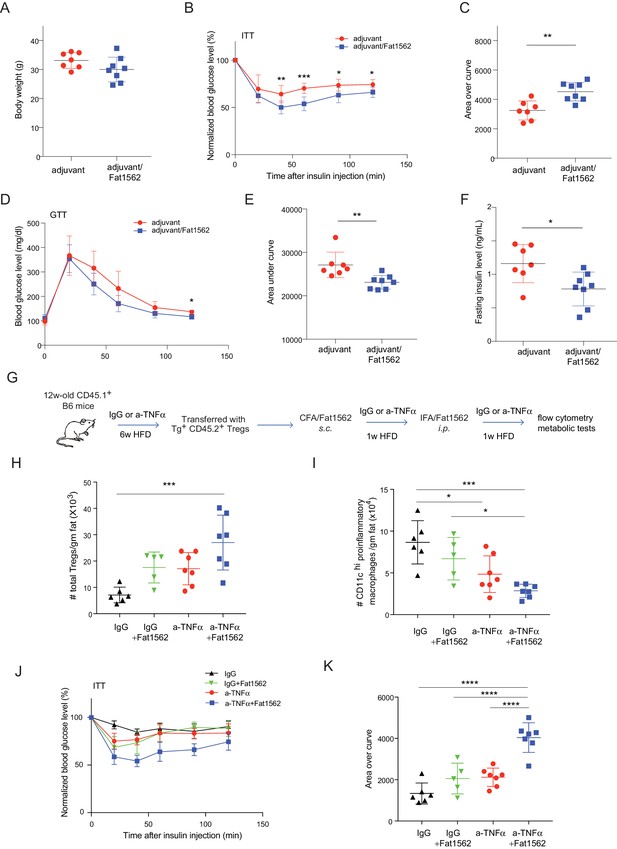
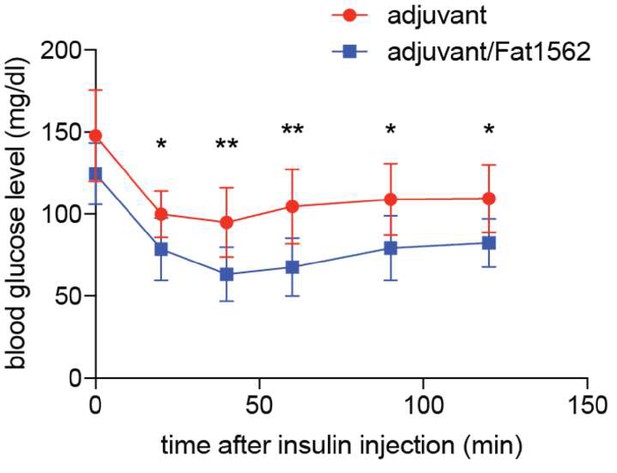
Immunization with Fat1562 following vTreg53 Treg transfer ameliorates HFD-induced insulin resistance.
(A–F) Metabolic indices of mice treated as in Figure 6A (n ≥ 7). (A) Body weight. (B) Insulin tolerance test (ITT). (C) Area over curve for ITT analysis. (D) Glucose tolerance test (GTT). (E) Area under curve for GTT analysis. (F) Plasma insulin levels after 6 hr of fasting. Data shown are representative of at least two independent experiments. (G) Scheme of the anti-TNFα experiment. (H) Number of total Treg cells in VAT (n ≥ 5). (I) Number of CD11chi inflammatory macrophages in VAT (n ≥ 5). (J) ITT (n ≥ 5). (K) Area over curve for ITT analysis (n ≥ 5). Data are mean ± SD.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus. musculus) | C57BL/6(J) | Jackson lab | Stock No: 000664 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus. musculus) | CD45.1. C57BL/6 | Jackson lab | Stock No: 002014 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus. musculus) | vTreg53 TCR-tg | Li et al., 2018 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Mus. musculus) | Foxp3-GFP | Gift of Vijay. Kuchroo, (Brigham and Women’s Hospital) | ||
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | Jurkat E6.1 | ATCC | Cat# TIB-152 RRID:CVCL_0367 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | Lenti-X 293T | Takara Bio | Cat# 632180 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | K-562 | ATCC | Cat# CCL-243, RRID:CVCL_0004 | |
| Antibody | anti-CD45.1 (clone A20) | Biolegend | Cat# 110724 RRID:AB_493733 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD45.2 (clone 104) | Biolegend | Cat# 109824 RRID:AB_830789 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD3 (clone 17A2) | Biolegend | Cat#: 100214 RRID:AB_493645 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD4 (clone GK1.5) | Biolegend | Cat#: 100422 RRID:AB_312707 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-TCR Vα2 (clone B20.1) | Biolegend | Cat#: 127806 RRID:AB_1134188 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD44 (clone IM7) | Biolegend | Cat#: 103032 AB_2076204 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD62L (clone MEL-14) | Biolegend | Cat#: 104418 RRID:AB_313103 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD45 (clone 30-F11) | Biolegend | Cat#: 103126 RRID:AB_493535 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD11b (clone M1/70) | Biolegend | Cat#: 101228 RRID:AB_893232 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD11c (clone N418) | Biolegend | Cat#: 117318 RRID:AB_493568 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-F4/80 (clone BM8) | Biolegend | Cat#: 123116 RRID:AB_893481 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-c-Myc Alexa Fluor 488 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9402 RRID:AB_2151827 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD69 (clone FN40) | Biolegend | Cat# 104508, RRID:AB_313111 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-CD25 (clone M-A25) | Biolegend | Cat# 356110, RRID:AB_2561977 | FACS (1:100) |
| Recombinant protein | Streptavidin APC | Biolegend | Cat#: 405243 | FACS (40–400 nM) |
| Antibody | anti-TCR Vβ4 (KT4) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 553366 RRID:AB_394812 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-Siglec-F (E50-2440) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 552126 RRID:AB_394341 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-Foxp3 (clone FJK-16s) | ThermoFisher | Cat#: 17-5773-82 RRID:AB_469457 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | anti-TNFα (clone XT3.11) | BioXCell | Cat#: BE0058 RRID:AB_1107764 | In vivo 10 μg/g |
| antibody | isotype control IgG (clone HRPN) | BioXCell | Cat#: BE0088 RRID:AB_1107775 | In vivo 10 μg/g |
| Commercial assay or kit | Streptavidin microbeads | Miltenyi | Cat#: 130-048-101 | 50 μl/sample |
| Commercial assay or kit | Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | ThermoFisher | Cat#: 00-5523-00 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | CellTrace Violet dye | ThermoFisher | Cat#: C34557 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Ultra Sensitive Mouse Insulin ELISA Kit | Crystal Chem | Cat#: 90080 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | D-(+)-Glucose | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#: G8270-1KG | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Humulin R | Lilly | Cat#: U-100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Freund’s Adjuvant, Complete | Sigma | Cat#: F5881 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Freund’s Adjuvant, Incomplete | Sigma | Cat#: F5506 | |
| Software, algorithm | Multiplot Studio | Genepattern | https://www.genepattern.org/modules/docs/Multiplot/2 | |
| Software, algorithm | GSEA | Broad Institute | https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/index.jsp | |
| Software, algorithm | V-QUEST | IMGT | http://www.imgt.org/IMGT_vquest/user_guide |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Deep-sequencing of peptide-Ab yeast library after selection with vTreg53 TCR.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58463/elife-58463-supp1-v3.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58463/elife-58463-transrepform-v3.docx