Long non-coding RNAs in regulation of adipogenesis and adipose tissue function
Figures
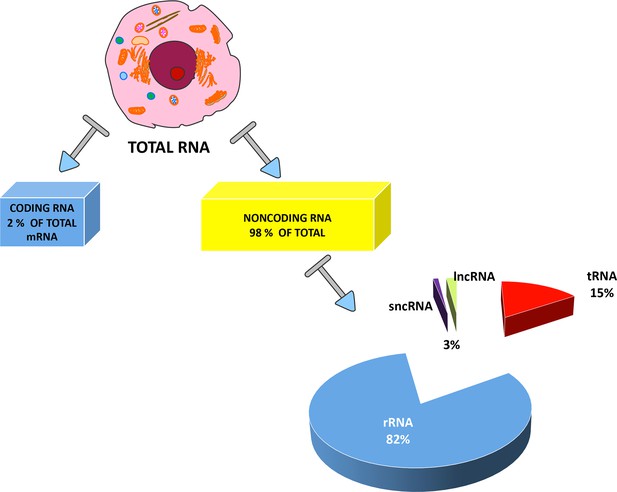
Types of RNAs present in eukaryotic cells.
RNAs are primarily divided between coding RNAs and noncoding RNAs. Coding RNAs contain one class of molecules: the messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that undergo the translation process. The other category contains noncoding RNAs, since they are not translated into proteins. Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are the two most abundant classes of noncoding RNAs, but several other RNA types have specific roles in eukaryotic cells. These other RNAs are usually divided into two groups: short noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs), consisting of RNAs with a length of less than 200 nucleotides; and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). The exact percentages of the various ncRNA classes are still under debate and the indicated values are reported in many studies.
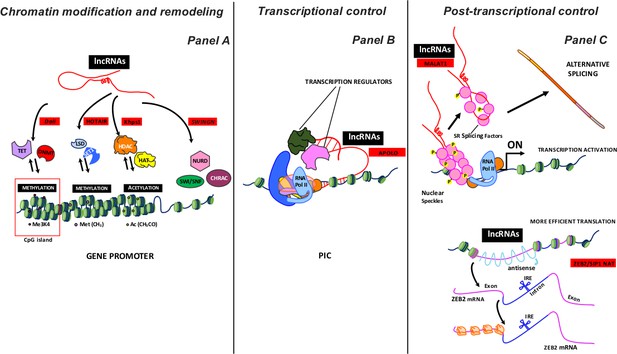
Some examples of lncRNA activity as a regulator of gene expression.
LncRNAs, working on proximal loci or at a great distance, can inhibit or activate the expression gene at various levels: i) chromatin modification and remodeling; ii) transcriptional control, and iii) post-transcriptional control. Panel A summarizes the different chromatin remodeling mechanisms. From left to right: nucleotide covalent modifiers (methylation) at CpG island (TET, DNMT enzymes); histone covalent modifiers, which regulate amino acid methylation (LSD, SET1 enzymes) and acetylation (HADC and HAT enzymes); ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes (SWI/SNF, NURD, CHRAC). The lncRNAs acting with different enzymatic complexes are depicted with red squares. Panel B shows lncRNAs involved in the early transcription stages. LncRNAs acquiring a specific R-loops structure interact with PIC (Preinitiation Complex) to modulate transcription by recruiting regulator factors. The lncRNA acting with different transcription regulators is depicted with a red square. Panel C shows some post-transcription activities of lncRNAs. Top: MALAT1 localizes to interchromatin granule clusters (nuclear speckles) and regulates alternative splicing by modulating the distribution and the levels of active SR splicing factors. Bottom: ZEB2/SIP1 NAT binds and masks specific splicing sites, causing intron retention. The retained intron contains an IRES site (internal ribosome entry site) that induces a more efficient ZEB2 protein translation. The lncRNAs acting with different enzymatic complexes are depicted with red squares.
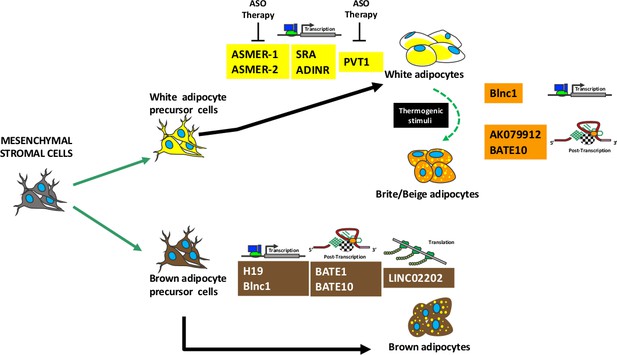
Summary of lncRNAs activity during adipogenesis.
Mesenchymal stromal cells contain stem cells that can be committed to white or brown precursor cells able to differentiate in white or brown adipocytes, respectively. A specific subpopulation of white adipocytes can transdifferentiate in brite/beige adipocytes following thermogenic stimuli. The picture shows several lncRNAs involved in adipocyte maturation and/or in brite/beige transdifferentiation. For each lncRNA is indicated the molecular mechanism of action: regulation of transcription or post-transcription or translation. The lncRNAs that can be target of antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) therapy are depicted.
Tables
Size and accession number of cited lncRNAs involved in adipogenesis.
| Homo sapiens | Mus musculus | |
|---|---|---|
| Blnc1 | 759 nt URS0000DBDC4C_9606 | 965 nt URS0000D77FA2_10090 |
| Lnc-BATE1 | 894 nt URS000075C5E3_10090 | |
| AK079912 | N.D. | N.D. |
| LncBATE10 | 1808 nt URS000075F077_10090 | |
| MIAT | 10,194 nt URS00007E4AF8_9606 | 9163 nt URS0000760956_10090 |
| LINC01119* | 1210 nt URS000075CEA4_9606 | |
| LINC02202 * | 2863 nt URS000075A437_9606 | |
| NONMMUG024827 | N.D | N.D. |
| H19* | 2.362 nt URS0000812128_960 | 2286 nt URS0000767B73_10090 |
| ASMER-1 | N.D. | N.D. |
| ASMER-2 | N.D. | N.D. |
| Plnc1 | N.D. | N.D. |
| SRA | 875 nt URS00001A8152_9606 | 829 nt URS00003EA2D2_10090 |
| ADINR | 2252 nt URS0000CCE086_9606 | |
| HOTAIR* | 2364 nt URS000075C808_9606 | 2222 nt URS000075BAE8_10090 |
| PVT1* | 1957 nt URS00008E3A67_9606 | 3319 nt URS000077AEFF_10090 |
-
*These lncRNAs have alternative transcripts.
N.D. Not Detected in RNA database (https://rnacentral.org).





