NMDA receptors control development of somatosensory callosal axonal projections
Figures
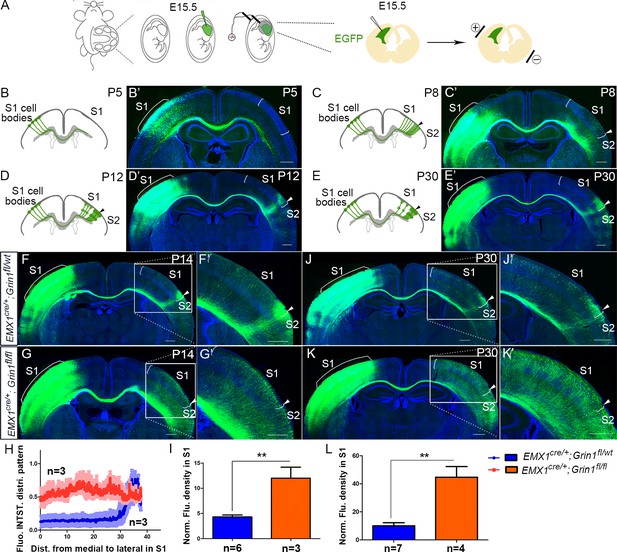
The callosal somatosensory innervation pattern was disrupted in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice.
(A–E) Postnatal development of callosal projection in S1. (A) EGFP plasmid injected into lateral ventricle of embryo at embryonic day 15.5 (E15.5) and electrical pulse given to enable the plasmid to enter cortical progenitor cells of layer II/III in the ventricular zone. (B, B’) At postnatal day 5 (P5), the callosal axons from S1 had reached the white matter underneath contralateral S1. (C, C’) At P8, the callosal axons were diffusely distributed in contralateral S1. (D, D’) By P12, pruning of excess projections led to a refined innervation pattern with a narrow band limited to the S1/S2 border. (E, E’) After P12, the pattern was stable as observed at P30. (F) In P14 control mice (Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/wt), the callosal innervation pattern of S1 of the contralateral cortex is well differentiated with a dense innervation at S1/S2 border. The pattern persists to P30 (J). (G) In GluN1 KO mice (Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl), the innervation pattern was disrupted and projections were extremely diffused which also persisted to P30 (K). (H) Quantification of fluorescent intensity across the medial to lateral extent of the S1. (I, L) Quantification of fluorescence density of S1 region of control vs. GluN1 KO mice at P14 (I, p=0.002) and P30 (L, p=0.0003). Scale bar: 500 μm for all images. S1: primary somatosensory cortex; S2: secondary somatosensory cortex.
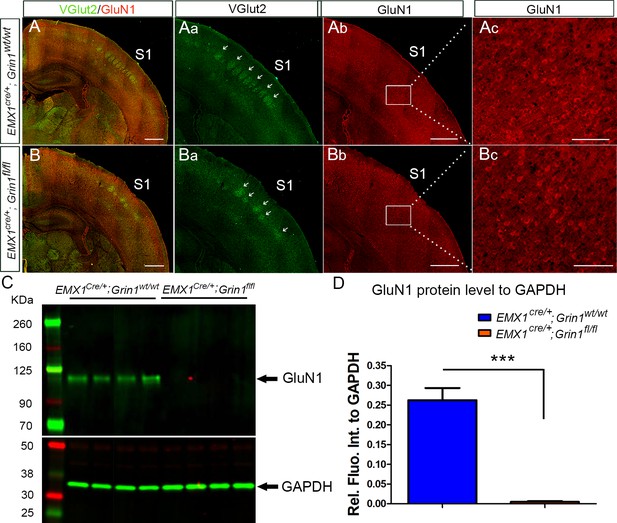
The expression of NMDAR in cortex was reduced in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice.
Examples of 12 µm coronal brain sections from P8 Emx1cre/+; Grin1wt/wt (A) and Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl (B) of the same litter. Immunostaining of vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGult2) showed thalamocortical barrels in Layer IV of S1 which are pointed out by arrows. The VGlut2 staining in Emx1cre/+; Grin1wt/wt mice revealed a clear barrel pattern (Aa). However, the barrel pattern in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice was disrupted and less distinct (Ba). The GluN1 staining in Emx1cre/+; Grin1wt/wt mice were dense and strong in cortex (Ab, Ac). However, the staining in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice was less bright and apparently reduced in Layer V and VI (Bb, Bc). (C) Western blot of cortical protein extracts from P8 S1. Relative to the loading control GAPDH, the protein levels of GluN1 were greatly reduced in the four samples of Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice compared to the four samples of controls. (D) Quantification of protein levels of GluN1 relative to GAPDH. p=0.0002. Scale bar: 100 μm for Ac and Bc; 500 μm for rest of images.
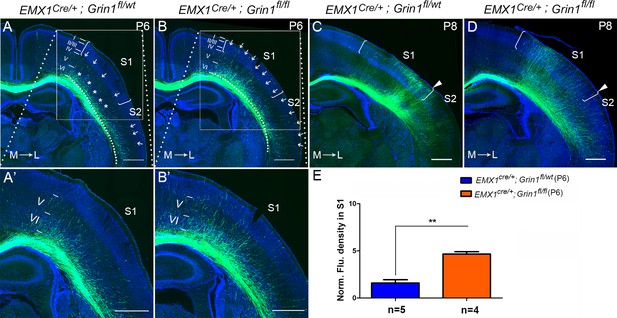
The callosal innervation defect was first detected at P6 in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice.
(A, A’) At P6, most axons in control grew into deeper layer VI of S1 (see ‘*’); a few axons grew to layer V from medial to lateral S1 (see arrows). However, axons projecting to lateral S2 had grown to layer IV which was apparently faster than the axons in S1 (see arrows). (B, B’) In GluN1 KO mice, most axons had grown to layer V and some even grew to layer I (see arrows) at P6. (C, D) At P8, axons in control and mutant mice had grown to the superficial layer of cortex. However, the innervation patterns were different. Controls showed more axon innervation in the lateral S1 with dense callosal innervation at S1/S2 border (C). Mutants showed slightly more axon innervation in the medial S1 (D). (E) The fluorescence density of mutant mice in S1 was significantly higher than in control mice at P6 which suggested that the mutants had increased axon innervation in contralateral S1 at P6. p=0.003. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images. The square brackets in all images outline the S1. The arrow heads in all images outline the S1/S2 border. White lines outline different layers in the cortex of A–D. M: medial; L: lateral.
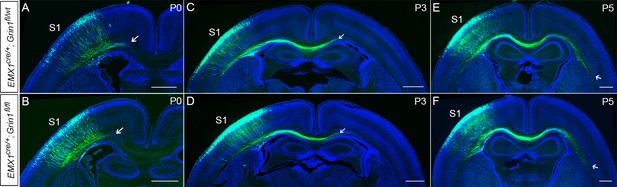
There was no difference between Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/wt and Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice during axonal extension into the ipsilateral CC (P0) and to the contralateral CC (P5).
(A, B) The callosal axons in S1 formed a bundle and grew into the ipsilateral CC at P0 in control and GluN1 KO littermates (Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/wt and Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice). The arrows show the extent of axon growth into the CC. By P3, the callosal axons crossed the midline (C, D) and by P5, the callosal axons have grown to underneath the contralateral S1 (E, F). Scale bar: 500 μm for all images.
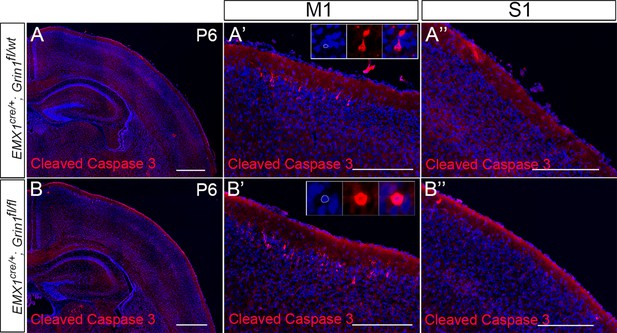
No increased cell death in S1 of Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice at P6.
(A) In control mice (Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/wt), cleaved caspase-3+ cells were mostly detected in layer II/III of M1 (A’), only rare cell death was observed in other cortical regions, such as S1 (A’’). (B) Compared with controls, there was increased cell death in layer II/III of motor cortex in mutant mice (Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl) (B’). However, compared with controls, there was no increased cell death in other cortical regions in mutant mice, such as S1 (B’’). Scale bar: 500 μm for A and B; 200 μm for A’, A’’, B’, and B’’.
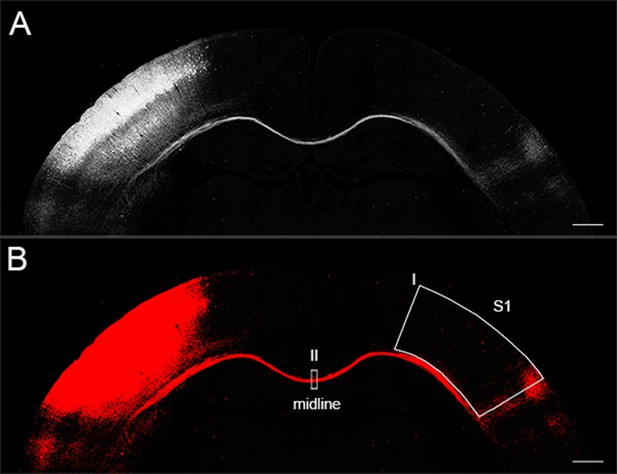
Callosal axon density analysis by Image J.
(A) This picture was an 8-bit image. (B) Fluorescence signals within threshold in image A turned to red after setting up threshold range. Box I was drawn to encompass only the S1. Box II was used to measure axon density in the midline.
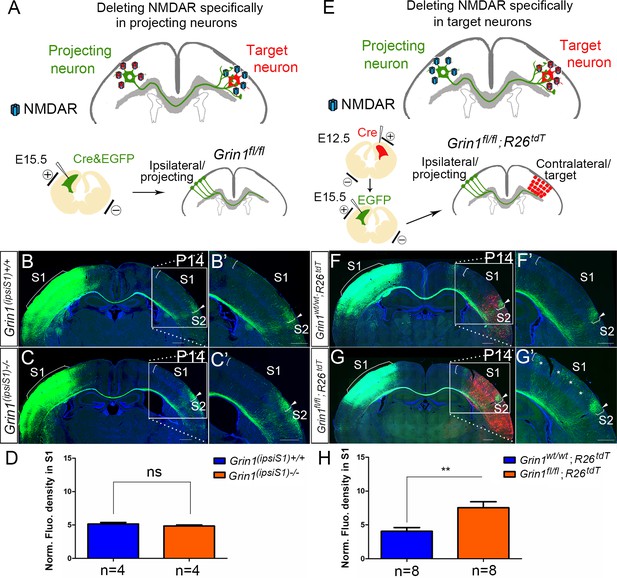
NMDAR is required in target neurons for normal callosal innervation.
(A–D) Deleting NMDAR specifically in projecting neurons. Vectors expressing Cre-recombinase (Cre) and EGFP were delivered into S1 of floxed GluN1 mice (Grin1fl/wt x Grin1fl/wt) by in utero electroporation at E15.5 (A). Callosal innervation patterns at P14 in control Grin1+/+ mice (B) and mice after ipsilateral deletion (C). (D) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.317. (E–H) Deleting NMDAR specifically in target neurons. GluN1 was deleted in target contralateral S1 by in utero electroporation of Cre at E12.5 in Grin1fl/fl; Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice, the ipsilateral projecting neurons were labeled by EGFP at E15.5 (E). Compared with control Grin1wt/wt; Rosa26fs-tdTomato (F), Grin1fl/fl; Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice which specifically deleted GluN1 in target S1 showed increased callosal innervation in S1 as ‘*’ shows (G). (H) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.002. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images. R26tdT: Rosa26fs-tdTomato.
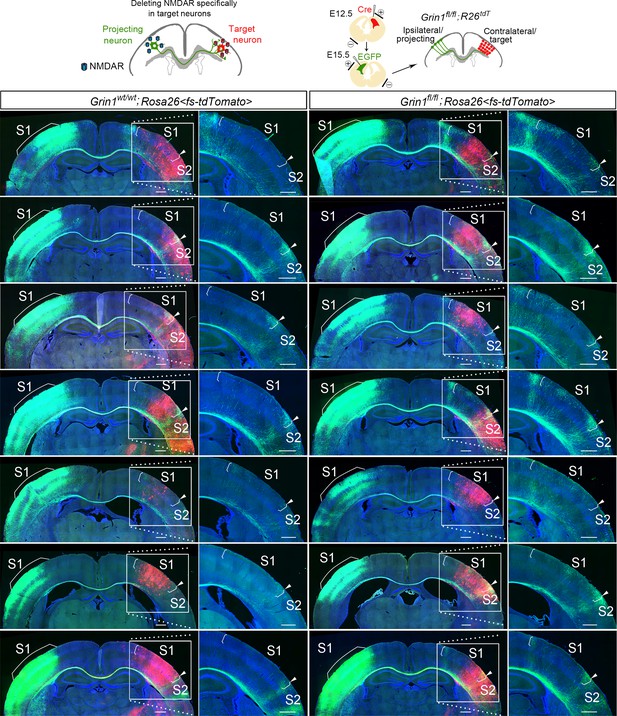
Deleting NMDAR specifically in target neurons.
GluN1 was deleted in target contralateral S1 by in utero electroporation of Cre at E12.5 in Grin1fl/fl; Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice, the ipsilateral projecting neurons were labeled by EGFP at E15.5. This figure shows images from all of the animals that were analyzed for the statistical analysis. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images. R26tdT: Rosa26fs-tdTomato.
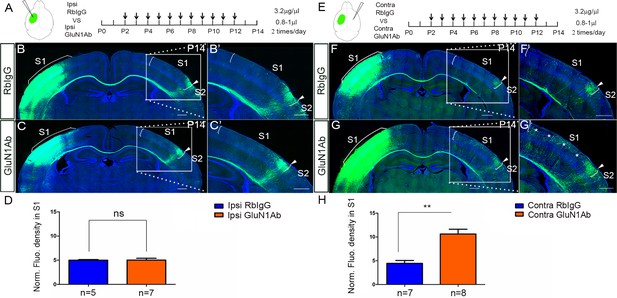
Increased callosal innervation in S1 after contralateral but not ipsilateral injection of anti-NMDAR antibodies from P2 to P12.
(A–D) Anti-GluN1 antibodies were injected into the lateral ventricle from P2 to P12 in ipsilateral cortex. RbIgG served as control. Compared with control (B), antibody injection in mice did not show increased callosal innervation in S1 at P14 (C). (D) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.94. (E–H) Anti-GluN1 antibodies were injected into the lateral ventricle from P2 to P12 in contralateral cortex. Compared with control (F), antibody injection in mice showed increased callosal innervation in S1 at P14 (see ‘*', G). (H) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.0002. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images.
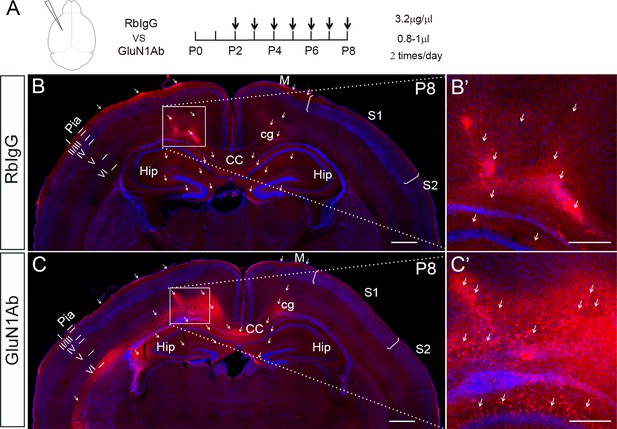
The efficiency of intraventricular antibody injection and the distribution territory in the cortex after 3 hr of last injection.
(A) Anti-GluN1 antibodies were injected into the lateral ventricle from P2 to P8 and mice were perfused 3 hr later after last injection. Rabbit IgG served as control. Mouse brains then were stained with anti-Rabbit secondary coupled with Alexa594. The red fluorophore of Alexa594 indicated where the antibodies had distributed to. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images. (B, B’) In control, the fluorescence signals were mostly detected in the cortex of the ipsilateral injection side, and few in the contralateral cortex. In the ipsilateral injection side, the signals were detected in all the cortical layers, but most strongly in the pia, layer I, layer V, layer VI, cingulum, and corpus callosum (see arrows). The signals were also detected in the hippocampus and contralateral motor cortex (see arrows). (C, C’) The general antibody distribution pattern was similar as seen in control. Moreover, the anti-GluN1 antibody can bind to NMDAR on the cell membranes, which thus showing beautiful cell membrane staining (see arrows in C’). Scale bar: 500 μm for B, C; 200 μm for B’, C’. CC: corpus callosum; cg: cingulum; Hip: hippocampus; M: motor cortex; S1: primary somatosensory cortex; S2: secondary somatosensory cortex.
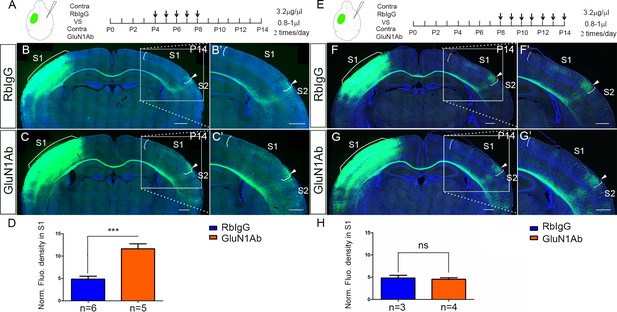
Contralateral injection of anti-NMDAR antibodies from P4 to P8 but not P8 to P14 had increased callosal innervation in S1.
(A–D) Anti-GluN1 antibodies were injected into the lateral ventricle from P4 to P8 in contralateral cortex. RbIgG served as control. Compared with control (B), antibody injection in mice show increased callosal innervation in S1 at P14 (C). (D) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.004. (E–H) Anti-GluN1 antibodies were injected into the lateral ventricle from P8 to P14 in contralateral cortex. Compared with control (F), antibody injection in mice did not show increased callosal innervation in S1 at P14 (G). (H) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.69. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images.
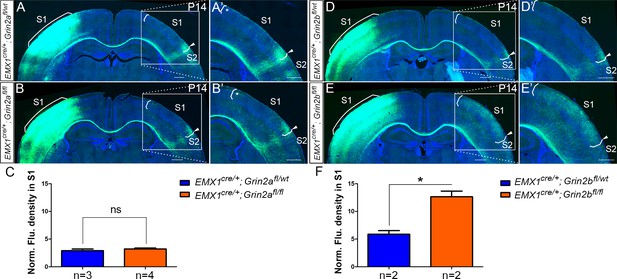
Emx1cre/+; Grin2bfl/fl but not Emx1cre/+; Grin2afl/fl mice had the same disrupted callosal innervation patterns as Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl at P14.
Callosal innervation patterns in control Emx1cre/+; Grin2afl/wt (A) and Emx1cre/+; Grin2afl/fl mice (B) at P14. ‘*’ points out M1/S1 border. (C) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.392. Callosal innervation patterns in control Emx1cre/+; Grin2bfl/wt (D) and Emx1cre/+; Grin2bfl/fl mice (E) at P14. (F) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.03. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images.
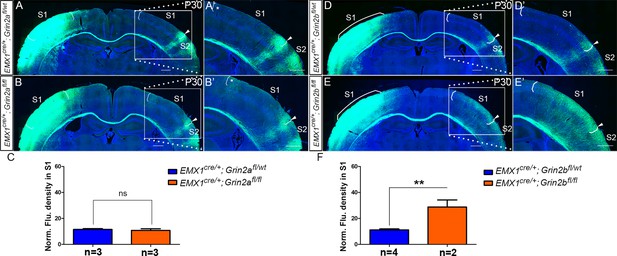
NR2B (Emx1cre/+; Grin2bfl/fl) but not NR2A (Emx1cre/+; Grin2afl/fl) mice had same disrupted callosal innervation patterns as Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl at P30.
(A) The callosal innervation pattern in S1 at P30 in control mice (Emx1cre/+; Grin2afl/wt) is similar as the pattern in P14 WT control mice, with few axons in S1 but a dense innervation at S1/S2 border. (B) In the mutant mice (Emx1cre/+; Grin2afl/fl), the general innervation pattern was as same as control. However, the increased callosal innervation at the border of M1 and S1 was persistent at P30 (see ‘*’ in B’). (C) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.63. (D) In control Emx1cre/+; Grin2bfl/wt mice, the callosal innervation pattern at P30 was as normal as WT control. (E) However, the increased callosal innervation in Emx1cre/+; Grin2bfl/fl mice lasted at least to P30 as we observed in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice at P30. (F) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.007. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images.
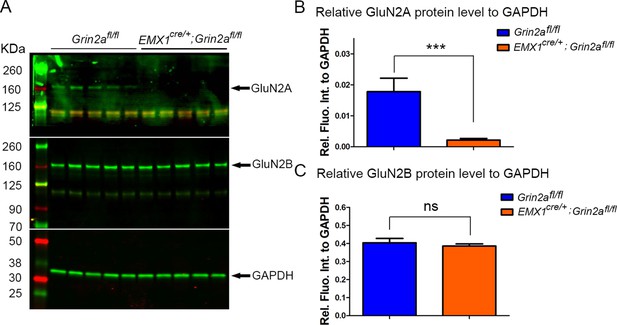
The protein expression level of GluN2A and GluN2B in S1 at P8.
(A) Western blot analysis of cortical protein extracts from P8 S1 showed that GluN2A protein has been expressed in S1 at P8. Relative to the loading control GAPDH, the protein levels of GluN2A were greatly reduced in the five samples of Emx1cre/+; Grin2afl/fl mice compared to the five samples of controls. However, the protein levels of GluN2B were same between the five samples of Emx1cre/+; Grin2afl/fl mice and the five samples of controls. (B) Quantification of protein levels of GluN2A relative to GAPDH. p=0.007. (C) Quantification of protein levels of GluN2B relative to GAPDH. p=0.5.
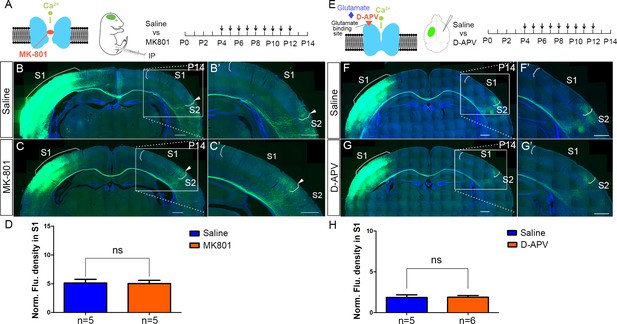
NMDAR regulates callosal circuit development independent of NMDAR channel activity.
(A–D) Blocking Ca2+ influx through NMDAR by MK-801. MK-801 enters the open NMDAR channel and binds to the ‘blocking site’ located deep in the pore (A). Callosal innervation patterns in Saline (B) and MK-801 (C) injected mice at P14. (D) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.91. (E–H) Blocking NMDAR channel opening by D-APV. D-APV competitively inhibits glutamate binding site to NMDAR (E). Callosal innervation patterns in saline (F) and D-APV (G) injected mice at P14. (H) Quantification of fluorescence density. p=0.93. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images.
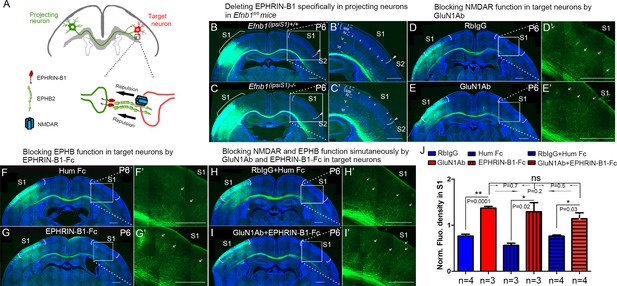
NMDARs cooperate with EPHRIN-B/EPHB in controlling axon targeting in S1.
(A) EPHRIN-B1, expressed by the projecting neuronal axons, signals through EPHB2 and NMDAR, located on the target neurons, regulates axon extension in contralateral cortex. (B, C) Deleting EPHRIN-B1 in projecting neurons in Efnb1fl/fl mice. Vectors expressing Cre and EGFP were delivered into S1 of all pups from Efnb1fl/wt × Efnb1fl/wt crosses by in utero electroporation at E15.5. Compared with control mice (B), ipsilaterally deleted mice showed earlier callosal innervation at P6 (C). (D, E) Blocking NMDAR function in target neurons by intraventricular injection of GluN1Ab in contralateral cortex, from P3 to P6. Compared with control RbIgG injected mice (D), GluN1Ab injected mice showed earlier callosal innervation at P6 (E). (F, G) Blocking EPHB function in target neurons by intraventricular injection of EPHRIN-B1-Fc in contralateral cortex, from P3 to P6. Compared with control Hum Fc injected mice, EPHRIN-B1-Fc injected mice showed earlier callosal innervation at P6 (G). (H, I) Blocking NMDAR and EPHB function simultaneously by GluN1Ab and EPHRIN-B1-Fc in contralateral cortex, from P3 to P6. Compared with control RbIgG + Hum IgG injected mice (H), GluN1Ab + EPHRIN-B1-Fc injected mice showed earlier callosal innervation at P6 (I). (J) Quantification of fluorescence density. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images. Arrows pointed out axon terminals in the target cortex.
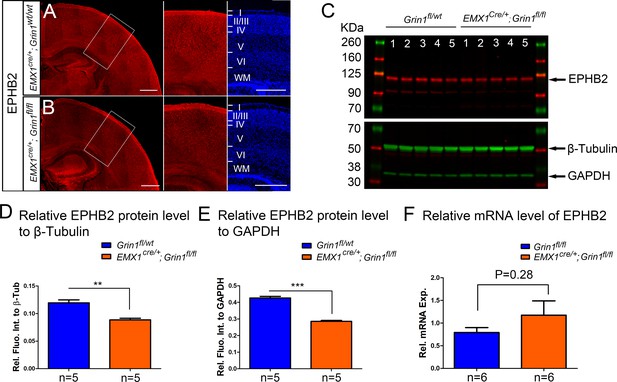
The protein but not RNA level of EPHB2 was reduced in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice at P8.
(A, B) EPHB2 protein expression is decreased in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice at P5. In control Emx1cre/+; Grin1wt/wt mice, EPHB2 was expressed both in CC and cortex (A). EPHB2 in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice was decreased in cortex (B). (C) Western blot analysis of cortical protein extracts from P8 S1 showed that, relative to the loading control beta-tubulin (β-Tub) and GAPDH, lower levels of EPHB2 were observed in the five samples of Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice compared to the five samples of controls. (D) Quantification of protein levels relative to β-Tub. p=0.001. (E) Quantification of protein levels relative to GAPDH. p<0.0001. (F) The quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis showed no expression difference of EPHB2 between Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice and controls. Scale bar: 500 μm for A, B.
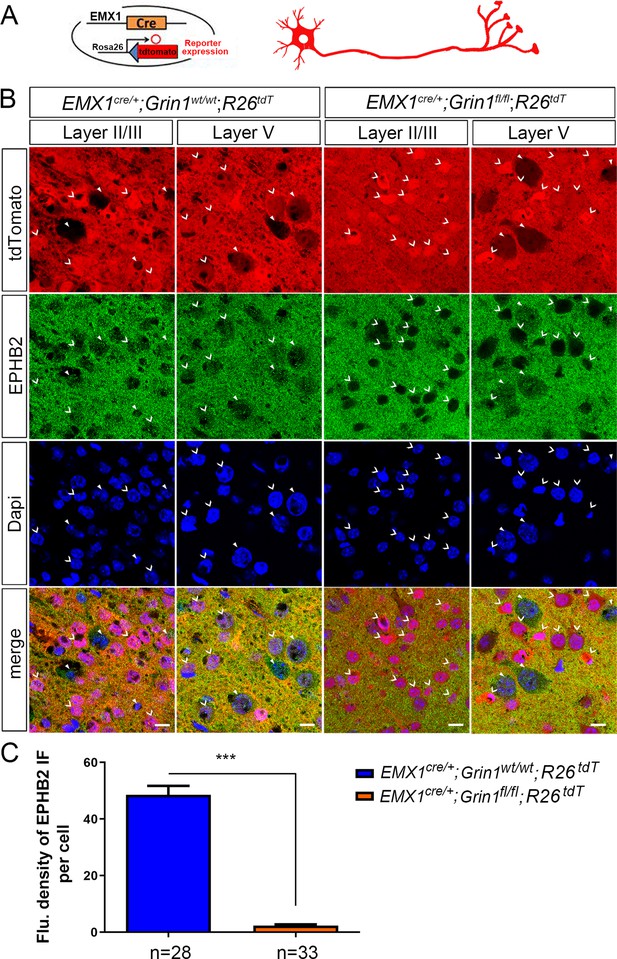
The cell membrane expression of EPHB2 was absent in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl; Rosa26fs-tdTomato positive cells.
(A) We crossed Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl mice with Cre-reporter Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice to produce GluN1 knockout cells labeled with red fluorescence. (B) 12 µm coronal brain sections from P8 Emx1cre/+; Grin1wt/wt; Rosa26fs-tdTomato and Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl; Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice of the same litter. Immunostaining of EPHB2 was done in all brain sections. Broad arrowheads pointed the cells with Cre recombination. Triangle arrowheads pointed to cells with Cre recombination. V shaped arrowheads pointed to cells without Cre recombination. In control Emx1cre/+; Grin1wt/wt; Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice, EPHB2 signals were detected on both Cre recombination and non-Cre recombination cells. However, in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl; Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice, EPHB2 signals were only detected on non-Cre recombination cells, but absent on Cre recombination cells with deletion of GluN1. (C) Quantification of fluorescence density of EPHB2 immunostaining for each cell. Compared to control (Emx1cre/+; Grin1wt/wt; Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice), the protein expression of EPHB2 in Cre recombination cells in Emx1cre/+; Grin1fl/fl; Rosa26fs-tdTomato mice was dramatically decreased. p<0.0001. Scale bar: 10 μm for all images in B. R26tdT: Rosa26fs-tdTomato.





