Mutational resilience of antiviral restriction favors primate TRIM5α in host-virus evolutionary arms races
Figures
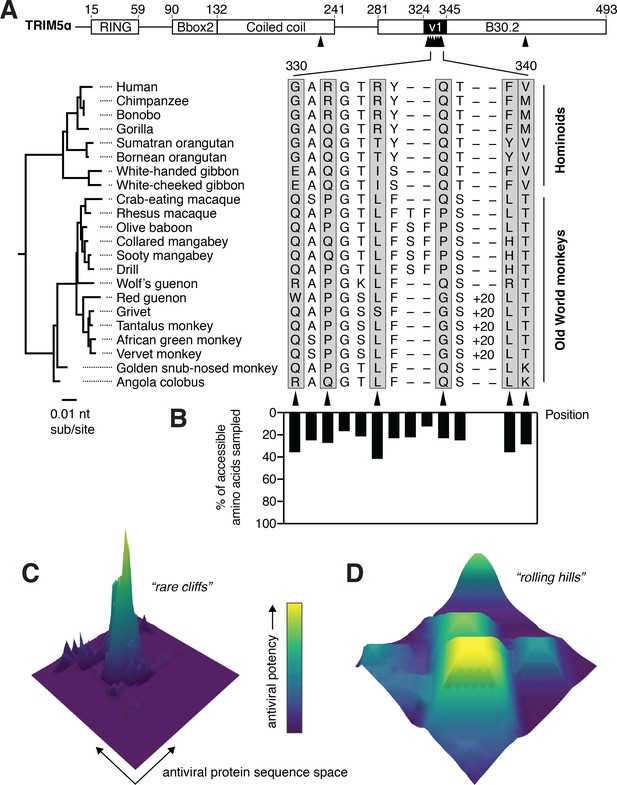
TRIM5α has sampled limited amino acid diversity, even at rapidly evolving positions.
(A) Alignment of TRIM5α from simian primates. A 20-amino acid duplication in the v1 loop of the African green monkey clade is abbreviated as ‘+20’. Amino acid numbering follows human TRIM5α. Rapidly evolving residues are indicated with black arrows and gray boxes. (B) Evolutionarily accessible amino acids were defined as within 1 nucleotide of any codon in this alignment, and the fraction of accessible variants sampled among aligned sequences was determined for each position. (C-D) Theoretical possibilities for antiviral protein evolutionary landscapes, with antiviral potency represented in z and color axes as it varies with single point mutations. Fitness landscapes might be highly constrained (C) or permissive (D).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Codons that are evolutionarily accessible to primate TRIM5α.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
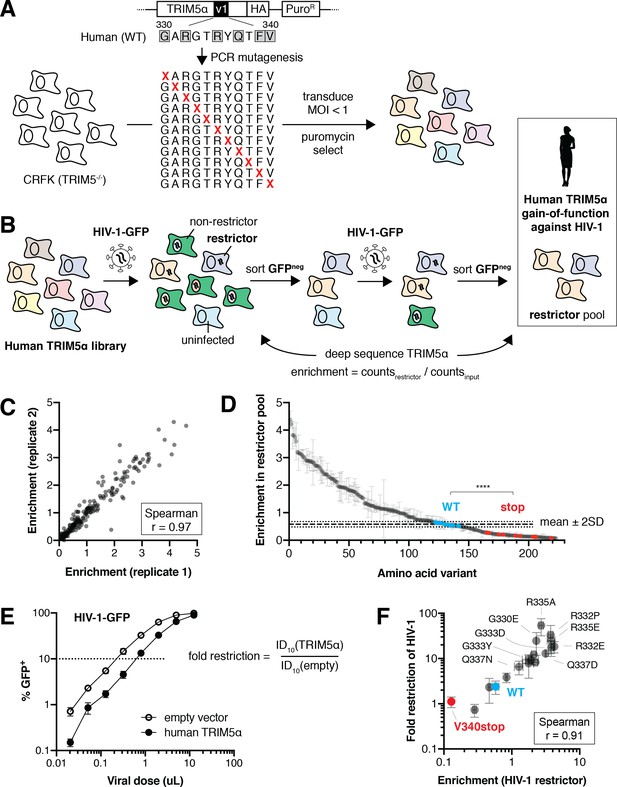
Selection scheme to identify human TRIM5α variants that gain HIV-1 restriction.
(A) A DMS library, encoding all single amino acid variants within the v1 loop (rapidly evolving sites are boxed), was generated by PCR with degenerate NNS codons. The library was transduced into naturally TRIM5α-deficient CRFK cells at low MOI (multiplicity of infection) and selected using puromycin. Colors represent different TRIM5α variants. (B) Pooled TRIM5α-expressing cells were infected with HIV-1-GFP virus-like particles (VLPs) at a high dose. GFP-negative cells were FACS sorted, re-infected, and re-sorted. Restrictive TRIM5α variants were then sequenced, and variant frequencies were normalized to input representation. (C) Amino acid enrichment scores are highly correlated across two biological replicates. Each dot represents a unique amino acid sequence, averaged across synonymous codons. (D) Nonsense variants (red, n = 11) are depleted relative to WT (blue, n = 10) and most missense (gray) variants; ****p<0.0001, student’s unpaired t-test. Enrichment is averaged across synonymous codons and replicates, except for WT variants, which are averaged only across replicates to better visualize variance (WT mean ±2 standard deviations is indicated). (E) HIV-1 fold-restriction by TRIM5α was measured by the increase in ID10 (viral dose at which 10% of cells are infected) relative to an empty vector control. (F) Enrichment scores are highly correlated with HIV-1 restriction (n ≥ 3 biological replicates) for re-tested variants. (D-F) Error bars, SD.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Quality control of DMS libraries.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Enrichment scores for human TRIM5α gain-of-function against HIV-1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig2-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Validation of human TRIM5α gain-of-function screen against HIV-1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig2-data3-v1.xlsx
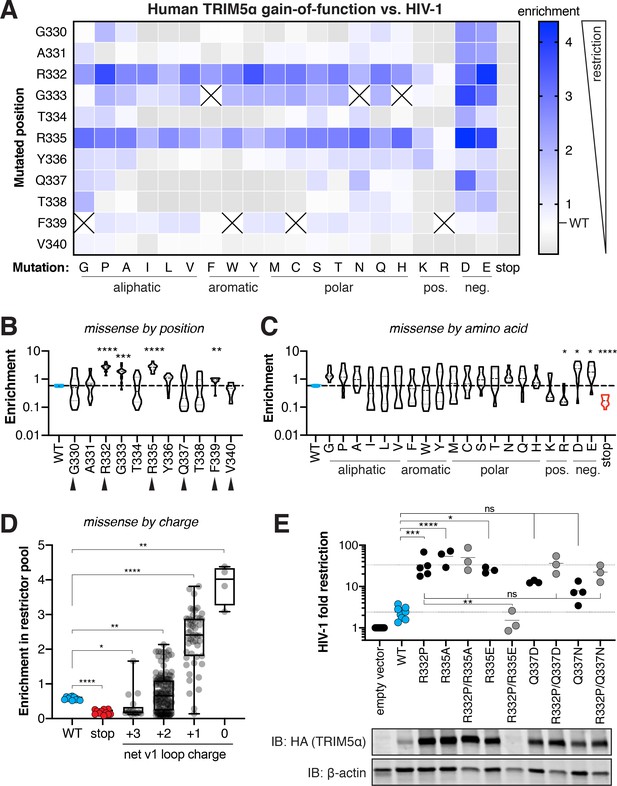
Many single mutations improve human TRIM5α restriction of HIV-1, primarily by removal of positive charge.
(A) Enrichment in the HIV-1 restrictor pool relative to WT (white) for each TRIM5α variant, arrayed by position mutated and amino acid mutation, is indicated by color intensity. Variants marked with X were excluded due to low input representation. (B-C) Enrichment scores for each position across all amino acid variants (B) or each amino acid across all positions (C); statistics reported in comparison to WT. Rapidly evolving sites are indicated by black arrows. (D) Box plot of missense mutations grouped by their effect on the net v1 loop charge; WT has a net v1 charge of +2. (E) Gain-of-function mutations were tested against HIV-1 individually or in combination with R332P, and fold-restriction was determined as in Figure 2E. TRIM5α expression levels in CRFK cells were analyzed by immunoblot (IB) against the C-terminal HA tag (blot representative of three independent experiments). (B-E) *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s correction for multiple comparisons and (B-D) correction for unequal variances.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Enrichment scores and p-values for human TRIM5α gain-of-function against HIV-1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Raw western blots of human TRIM5α variants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig3-data2-v1.png.pdf
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Quantification of human TRIM5α western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig3-data3-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 4
HIV-1 fold restriction by human TRIM5α double mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig3-data4-v1.xlsx
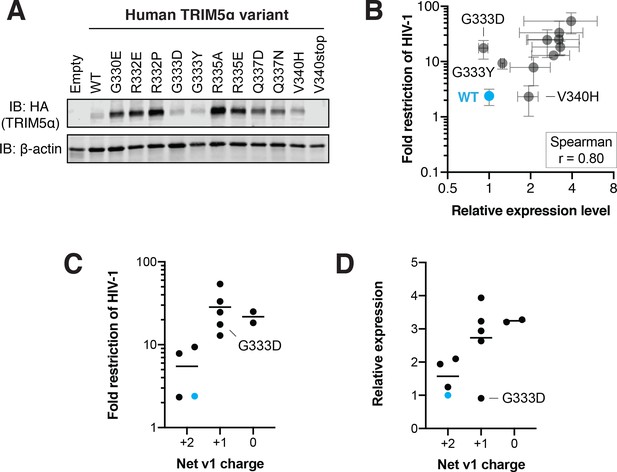
Some, but not all, human TRIM5α gain-of-function mutations against HIV-1 increase TRIM5α expression level.
(A) Representative immunoblot (IB) for TRIM5α expression in CRFK cells. (B) TRIM5α-HA band intensity was normalized to β-actin, and then further normalized to WT TRIM5α to determine relative expression. Results from three independent experiments. HIV-1 restriction was calculated in Figure 2F. Error bars, SD. (C-D) TRIM5α variants from (B) were grouped according to net v1 charge to assess the effect of charge on HIV-1 restriction (C) or TRIM5α expression level (D).
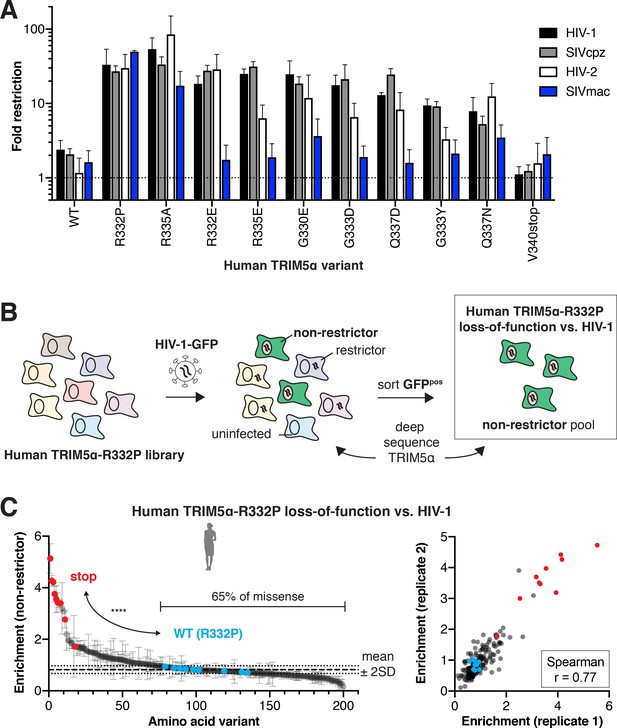
Evolutionary landscapes are generally permissive for evolving novel lentiviral restriction, which is resilient to most mutations once achieved.
(A) CRFK cells expressing the indicated human TRIM5α variant were challenged with GFP-marked lentiviral VLPs to determine fold-restriction as in Figure 2E. Results from at least three independent experiments. (B) To determine whether newly acquired viral restriction tolerates mutations, a second human TRIM5α v1 DMS library was generated with R332P fixed in all variants. This library of cells was infected with HIV-1-GFP VLPs, and GFP-positive (non-restrictor) cells were sorted and sequenced. (C) Stop codon variants (red, n = 10) are highly enriched in the non-restrictor pool compared to WT (R332P, blue, n = 9) variants (****p<0.0001, student’s unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction), while 65% of all missense variants fall less than 2 SD above WT (R332P) mean. Enrichment scores between two biological replicates are well correlated. (A, C) Error bars, SD.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
TRIM5α v1-dependence of lentivirus restriction.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Lentiviral restriction by human TRIM5α single mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig4-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Enrichment scores and p-values for human TRIM5α-R332P loss-of-function against HIV-1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig4-data3-v1.xlsx
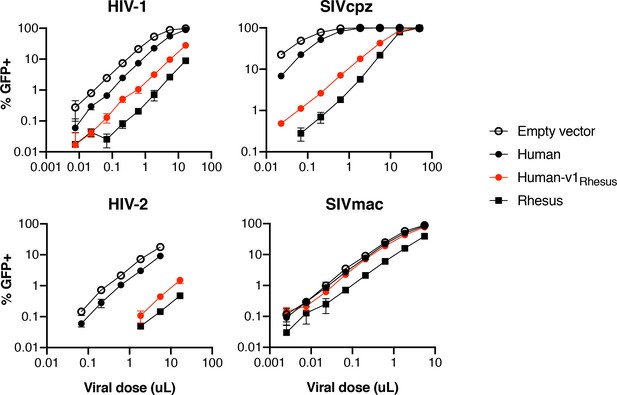
Lentiviral restriction by TRIM5α is v1-dependent.
CRFK cells expressing human, rhesus, or human TRIM5α with the v1 loop exchanged for that of rhesus were challenged with GFP-marked lentiviral VLPs. Results representative of at least three independent experiments.
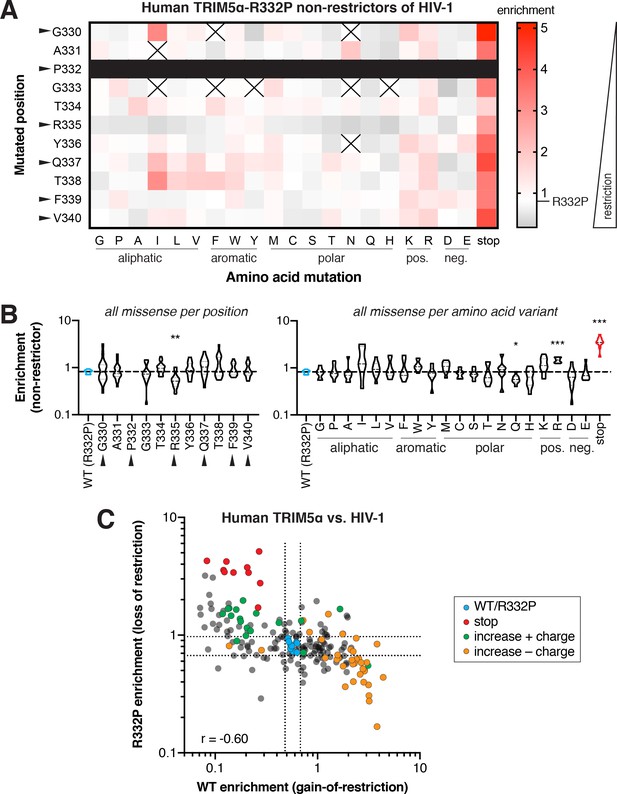
Biochemical preferences for human TRIM5α-R332P restriction of HIV-1.
(A) Enrichment in the HIV-1 non-restrictor pool relative to R332P (white) for each human TRIM5α-R332P variant, arrayed by position and amino acid variant, is indicated by color intensity. Variants marked with X were excluded due to low input representation; no variation was present at position 332 (black box). Arrows indicate rapidly evolving sites. (B) Missense variants at each position (across all variants) or each amino acid (across all positions); one-way ANOVA compared to R332P with corrections for multiple comparisons (Holm-Sidak) and unequal variances (Geisser-Greenhouse); *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. (C) Positive charge is detrimental to human TRIM5α restriction of HIV-1, both for WT and R332P variants (Spearman r = −0.60). Missense mutations that increase positive charge (green) weaken R332P restriction, while those that negate positive charge (orange) improve WT restriction of HIV-1. Dashed lines indicate 2 SD above or below the mean enrichment for WT variants (blue) in each screen.
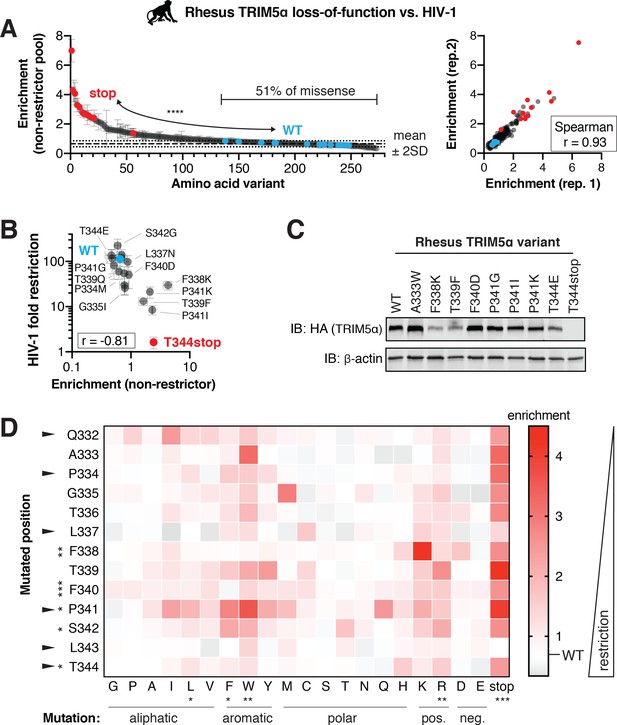
Rhesus macaque TRIM5α restriction of HIV-1 tolerates many mutations.
A rhesus TRIM5α v1 DMS library was infected with HIV-1-GFP VLPs, and GFP-positive (non-restrictor) cells were sorted and sequenced. (A) Nonsense variants are highly enriched in the non-restrictor pool compared to WT (n = 13; ****p<0.0001, student’s unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction), while half of all missense variants fall less than 2 SD above WT. Enrichment scores between two biological replicates are highly correlated. (B) Re-testing individual variants confirms that enriched variants have partially lost HIV-1 restriction, while depleted variants do not differ from WT. Spearman r; error bars, SD; n ≥ 3 biological replicates. (C) Steady-state levels of TRIM5α variants stably expressed in CRFK cells; results representative of two independent immunoblots (IB). (D) Enrichment in the HIV-1 non-restrictor pool relative to WT (white) for each variant, arrayed by position and amino acid mutation, is indicated by color intensity. The color scale was slightly compressed to avoid exaggerating a single mutant (L343stop) with enrichment >4.5. Rapidly evolving sites are indicated with arrows. Statistical tests compare each position (across all variants) or each amino acid (across all positions) to WT, one-way ANOVA with Geisser-Greenhouse non-sphericity and Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons corrections; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Enrichment scores and p-values for rhesus TRIM5α loss-of-function against HIV-1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Validation of rhesus TRIM5α loss-of-function screen against HIV-1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig5-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Raw western blots of rhesus TRIM5α.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig5-data3-v1.png.pdf
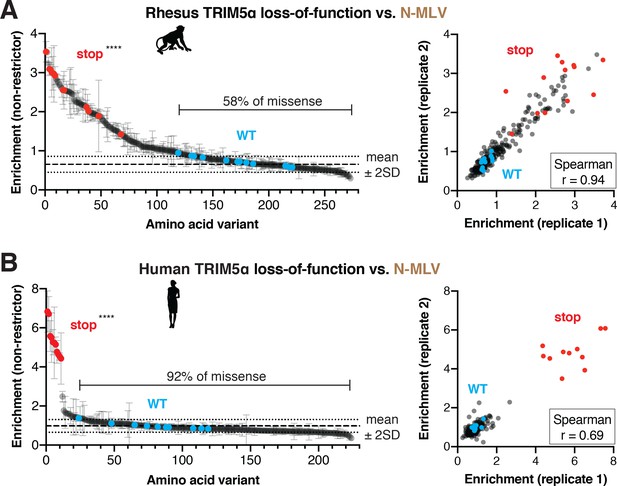
N-MLV restriction by primate TRIM5α is robust to single point mutations.
The rhesus (A) or WT human (B) v1 DMS libraries were infected with N-MLV-GFP VLPs, and GFP-positive (non-restrictor) cells were sorted and sequenced. Nonsense variants are highly enriched in the non-restrictor pool compared to WT in both screens; ****p<0.0001, student’s unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. Error bars, SD. The fraction of all missense variants less than 2SD above WT mean is indicated. Enrichment scores between two biological replicates are highly correlated.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Enrichment scores and p-values for human and rhesus TRIM5α loss-of-function against N-MLV.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Validation of human and rhesus TRIM5α loss-of-function screen against N-MLV.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59988/elife-59988-fig6-data2-v1.xlsx
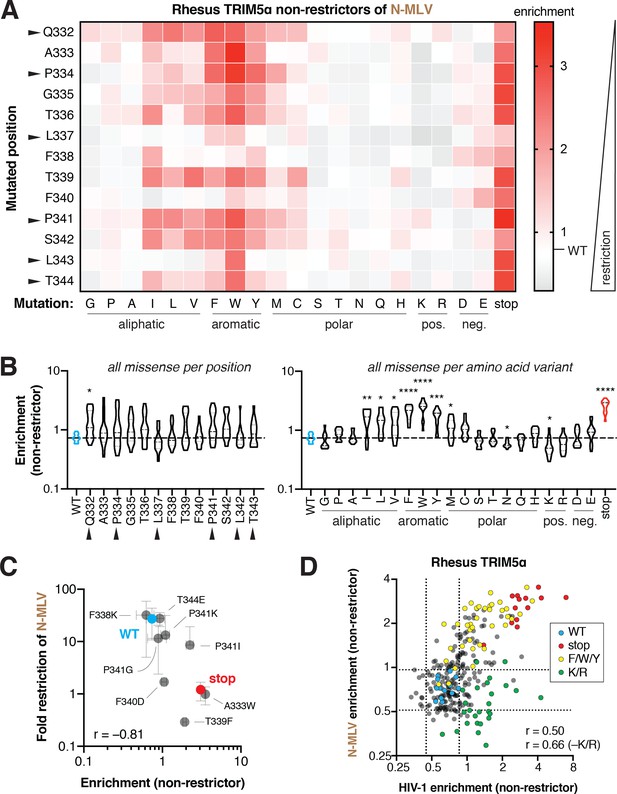
Biochemical preferences for rhesus TRIM5α restriction of N-MLV are distinct from HIV-1.
(A) Enrichment scores in the N-MLV non-restrictor pool for each variant are arrayed by position and amino acid mutation. Enrichment (decreased restriction, red) relative to WT (white) is indicated by color intensity. (B) Missense variants at each position (across all variants) or each amino acid (across all positions); one-way ANOVA compared to WT with Geisser-Greenhouse non-sphericity and Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons corrections; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. (C) Re-testing individual mutations confirms that enriched mutants have lost restriction (Spearman r = −0.81). Error bars, SD; n = 2 biological replicates. (D) Rhesus TRIM5α restriction of HIV-1 and N-MLV has partially overlapping biochemical requirements. Positive charge (K/R, green) breaks only HIV-1 restriction, whereas stop codons (red) and aromatic residues (F/W/Y, yellow) weaken restriction of both viruses. Excluding K and R improves the correlation compared to all variants (Spearman r = 0.66 or 0.50, respectively). Dashed lines indicate 2 SD above and below the mean enrichment for WT variants (blue) in each screen.
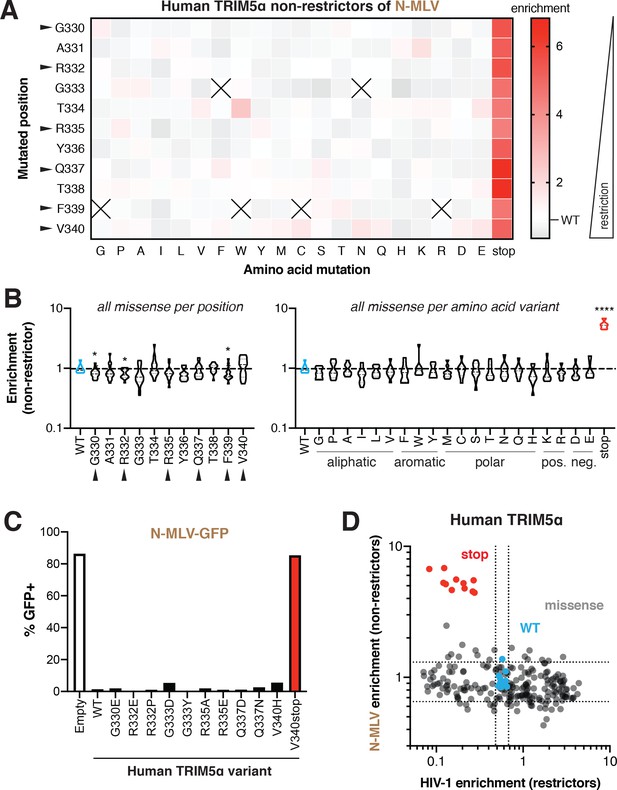
Missense mutations do not disrupt human TRIM5α restriction of N-MLV.
(A) Enrichment scores in the N-MLV non-restrictor pool for each variant are arrayed by position and amino acid mutant. Enrichment (decreased restriction, red) relative to WT (white) is indicated by color intensity. Variants marked with X were excluded due to low input representation. Rapidly evolving residues are indicated with black arrows. (B) Missense variants at each position (across all variants) or each amino acid (across all positions); one-way ANOVA compared to WT with Geisser-Greenhouse non-sphericity and Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons corrections; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. (C) Re-testing individual mutations confirms that mutations have little effect on N-MLV restriction. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments. (D) HIV-1 gain-of-restriction compared to N-MLV loss-of-restriction. No anti-correlation is evident, with the exception of stop codons (red). Dashed lines indicate 2 SD above and below the mean enrichment for WT variants (blue) in each screen.
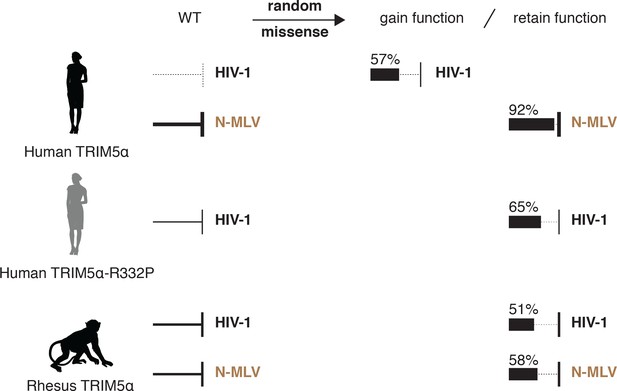
Summary of deep mutational scanning results.
Random missense mutations in human TRIM5α frequently improve HIV-1 restriction. Multiple TRIM5α orthologs, including a de novo HIV-1 restrictor (human TRIM5α-R332P), display high mutational resilience against two distantly related retroviruses. Arrow thickness represents antiviral potency; the fraction of missense mutants that gain or retain function are indicated.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Homo sapiens) | TRIM5α | NCBI | NM_033034.2 | |
| Gene (Macaca mulatta) | TRIM5α | NCBI | NM_001032910.1 | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | DH5α | NEB | C2987H | Chemically competent cells |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK-293T/17 | ATCC | CRL-11268; RRID:CVCL_1926 | Purchased fresh stock from ATCC |
| Cell line (Felis catus) | CRFK | ATCC | CCL-94; RRID:CVCL_2426 | Purchased fresh stock from ATCC |
| Cell line (Felis catus) | CRFK + Human TRIM5α | This study | Cell line stably expressing human TRIM5α (from ~ single random integration event per cell); see Materials and methods | |
| Cell line (Felis catus) | CRFK + Human-v1DMS TRIM5α | This study | Cell line stably expressing library of human TRIM5α single amino acid variants; see Materials and methods | |
| Cell line (Felis catus) | CRFK + Human-R332P TRIM5α | This study | Cell line stably expressing human TRIM5α-R332P; see Materials and methods | |
| Cell line (Felis catus) | CRFK + Human-R332P-v1DMS TRIM5α | This study | Cell line stably expressing library of human TRIM5α-R332P single amino acid variants; see Materials and methods | |
| Cell line (Felis catus) | CRFK + Rhesus TRIM5α | This study | Cell line stably expressing rhesus TRIM5α; see Materials and methods | |
| Cell line (Felis catus) | CRFK + Rhesus-v1DMS TRIM5α | This study | Cell line stably expressing library of rhesus TRIM5α single amino acid variants; see Materials and methods | |
| Antibody | anti-HA.11 (mouse monoclonal) | Biolegend | 901516; RRID:AB_2565335 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-β-actin (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab8227; RRID:AB_2305186 | (1:5000) |
| Antibody | IRDye 680RD anti-mouse (donkey polyclonal) | LI-COR | 926–68072; RRID:AB_10953628 | (1:10,000) (secondary) |
| Antibody | IRDye 800CW anti-rabbit (donkey polyclonal) | LI-COR | 926–32213; RRID:AB_621848 | (1:10,000) (secondary) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | MD2.G | Addgene | 12259 | VSV-G expression, CMV promoter |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | L-VSV-G | PMID:9245614 | VSV-G expression, Tat-driven | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CMV-Tat | PMID:9245614 | Tat expression, CMV promoter | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pHIV-ZsGreen | PMID:18371425 | HIV-1 transfer vector | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pALPS-eGFP | PMID:30546110 | HIV-1 transfer vector | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p8.9NdSB bGH Blp1 BstEII | PMID:15479815 | NL4.3 HIV-1 gag/pol | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p8.9NdSB bGH Blp1 BstEII HIV-2 CA | PMID:26181333 | NL4.3 HIV-1 gag/pol with HIV-2ROD CA residues 1–202 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pHIV-MAC | PMID:18417575 | HIV-1 gag/pol with SIVmac239 CA residues 1–146 (A77V) | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pHIV-Gb2 | PMID:18417575 | HIV-1 gag/pol with SIVcpzGab2 CA residues 1–146 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCIG3N | PMID:10906195 | N-MLV gag/pol | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQCXIP | Takara Bio | 631516 | Puromycin-selectable retroviral expression cassette |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQCXIP-eGFP | This study | N-MLV transfer vector; see Materials and methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQCXIP-Human TRIM5α-HA | This study | Stable expression of human TRIM5α; see Materials and methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQCXIP-Human-R332P TRIM5α-HA | This study | Stable expression of human TRIM5α-R332P; see Materials and methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQCXIP-Human-v1rhesus TRIM5α-HA | This study | Stable expression of human TRIM5α containing rhesus v1 loop; see Materials and methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQCXIP-Rhesus TRIM5α-HA | This study | Stable expression of rhesus TRIM5α; see Materials and methods | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Q5 high-fidelity DNA polymerase | NEB | M4091L | Used for Quikchange and DMS library construction |
| Commercial assay or kit | NEBuilder HiFi DNA assembly cloning kit | NEB | E5520S | Gibson assembly kit |
| Commercial assay or kit | PureYield plasmid miniprep kit | Promega | A2495 | Transfection-quality plasmid miniprep (low LPS) |
| Commercial assay or kit | NuceloBond Xtra midiprep kit | Takara Bio | 740410.50 | Transfection-quality plasmid midiprep (low LPS) |
| Commercial assay or kit | DNeasy Blood and Tissue kit | Qiagen | 69504 | Genomic DNA purification |
| Commercial assay or kit | QIAquick PCR purification kit | Qiagen | 28106 | PCR cleanup kit |
| Commercial assay or kit | Agencourt Ampure XP beads | Beckman Coulter | A63880 | Double-sided size selection of PCR products |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trans-IT 293T transfection reagent | Mirus Bio | MIR 2700 | Transfect plasmids into HEK-293T |
| Chemical compound, drug | polybrene | Sigma | TR-1003-G | Transduction reagent |
| Cchemical compound, drug | puromycin | Fisher | 50488918 | Antibiotic selection for stably transduced cells |
| Software, algorithm | DMS data analysis | This study | https://github.com/jtenthor/T5DMS_data_analysis | R scripts for DMS data analysis; see Materials and methods |
| Software, algorithm | PAML | PMID:967129 | For analysis of rapid evolution |
Primers used in this study.
| Primer | Use | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Subcloning TRIM5α constructs (human, human-v1rhesus, rhesus) into pQCXIP | ||
| oJT029 | Amplify human or rhesus TRIM5α-HA (Fwd), add NotI site, for cloning into pQCXIP | caagcggccgcgccaccATGGCTTCTGGAATC |
| oJT030 | Amplify human or rhesus TRIM5α-HA (Rev), add EcoRI site, for cloning into pQCXIP | gcggaattcTCAagcgtagtctgggacgtc |
| DMS library construction | ||
| oJT037 | Flanking primer for all DMS library construction (Fwd), amplifies pQCXIP backbone 5' of NotI site for Gibson cloning with pQCXIP-TRIM5α digested with NotI and BamHI | acctgcaggaattgatccgcggcc |
| oJT038 | Flanking primer for rhesus DMS library construction (Rev), amplifies rhesus TRIM5α 3' of BamHI site for Gibson cloning with pQCXIP-TRIM5α digested with NotI and BamHI | GGATTGGAAGCCAGCACATACCCCCAG |
| oJT003 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon Q332 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | CGGAACCCACAGATAATGTATNNSGCACCAGGGACATTATTTAC |
| oJT004 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon Q332 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | GTAAATAATGTCCCTGGTGCSNNATACATTATCTGTGGGTTCCG |
| oJT005 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon A333 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | GAACCCACAGATAATGTATCAGNNSCCAGGGACATTATTTACGTTTC |
| oJT006 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon A333 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | GAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGSNNCTGATACATTATCTGTGGGTTC |
| oJT007 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon P334 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | CCACAGATAATGTATCAGGCANNSGGGACATTATTTACGTTTCCG |
| oJT008 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon P334 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | CGGAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCSNNTGCCTGATACATTATCTGTGG |
| oJT009 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon G335 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | CAGATAATGTATCAGGCACCANNSACATTATTTACGTTTCCGTCAC |
| oJT010 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon G335 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | GTGACGGAAACGTAAATAATGTSNNTGGTGCCTGATACATTATCTG |
| oJT011 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon T336 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | ATGTATCAGGCACCAGGGNNSTTATTTACGTTTCCGTCACTCAC |
| oJT012 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon T336 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | GTGAGTGACGGAAACGTAAATAASNNCCCTGGTGCCTGATACAT |
| oJT013 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon L337 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | TATCAGGCACCAGGGACANNSTTTACGTTTCCGTCACTCAC |
| oJT014 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon L337 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | GTGAGTGACGGAAACGTAAASNNTGTCCCTGGTGCCTGATA |
| oJT015 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon F338 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | CAGGCACCAGGGACATTANNSACGTTTCCGTCACTCACG |
| oJT016 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon F338 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | CGTGAGTGACGGAAACGTSNNTAATGTCCCTGGTGCCTG |
| oJT017 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon T339 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | AGGCACCAGGGACATTATTTNNSTTTCCGTCACTCACGAATTTC |
| oJT018 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon T339 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | GAAATTCGTGAGTGACGGAAASNNAAATAATGTCCCTGGTGCCT |
| oJT019 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon F340 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | CACCAGGGACATTATTTACGNNSCCGTCACTCACGAATTTCAAT |
| oJT020 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon F340 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | ATTGAAATTCGTGAGTGACGGSNNCGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGTG |
| oJT021 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon P341 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | ACCAGGGACATTATTTACGTTTNNSTCACTCACGAATTTCAATTATTGTA |
| oJT022 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon P341 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | TACAATAATTGAAATTCGTGAGTGASNNAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGT |
| oJT023 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon S342 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | GGGACATTATTTACGTTTCCGNNSCTCACGAATTTCAATTATTGTACT |
| oJT024 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon S342 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | AGTACAATAATTGAAATTCGTGAGSNNCGGAAACGTAAATAATGTCCC |
| oJT025 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon L343 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | GACATTATTTACGTTTCCGTCANNSACGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGC |
| oJT026 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon L343 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | GCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCGTSNNTGACGGAAACGTAAATAATGTC |
| oJT027 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon T344 (Fwd primer, use w/oJT038 for C-term half) | CATTATTTACGTTTCCGTCACTCNNSAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCGTC |
| oJT028 | Randomize rhesus TRIM5α at codon T344 (Rev primer, use w/oJT037 for N-term half) | GACGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTSNNGAGTGACGGAAACGTAAATAATG |
| oAS024 | Flanking primer for human DMS libraries (Rev), amplifies human TRIM5α 3' of BamHI site for Gibson cloning with pQCXIP-TRIM5α digested with NotI and BamHI | AGCACATACCCCCAGGATCCAAGCAG |
| oAS002 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT or R332P) before codon G330, to hybridize w/randomized G330 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | ATATATTATCTGTGGTTTCGGAGAGC |
| oAS001 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon G330 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | GCTCTCCGAAACCACAGATAATATATNNSGCACGAGGGACAAGATACC |
| oJT142 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon G330 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | GCTCTCCGAAACCACAGATAATATATnnsGCACcAGGGACAAGATACCA |
| oAS004 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT or R332P) before codon A331, to hybridize w/randomized A331 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | CCCATATATTATCTGTGGTTTCGG |
| oAS003 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon A331 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | CCGAAACCACAGATAATATATGGGNNSCGAGGGACAAGATACCAGA |
| oJT143 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon A331 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | CCGAAACCACAGATAATATATGGGnnsCcAGGGACAAGATACCAGAC |
| oAS006 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon R332 to hybridizew/randomized R332 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TGCCCCATATATTATCTGTGGTTTC |
| oAS005 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon R332 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | GAAACCACAGATAATATATGGGGCANNSGGGACAAGATACCAGACATTTG |
| oAS008 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon G333 to hybridizew/randomized G333 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TCGTGCCCCATATATTATCTGTG |
| oAS007 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon G333 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | CACAGATAATATATGGGGCACGANNSACAAGATACCAGACATTTGTGAATT |
| oJT144 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (R332P) before codon G333 to hybridize w/randomized G333 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TgGTGCCCCATATATTATCTGTG |
| oJT145 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon G333 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | CACAGATAATATATGGGGCACcAnnsACAAGATACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTC |
| oAS010 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon T334 to hybridizew/randomized T334 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | CCCTCGTGCCCCATATATTA |
| oAS009 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon T334 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | TAATATATGGGGCACGAGGGNNSAGATACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCA |
| oJT146 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (R332P) before codon T334 to hybridizew/randomized T334 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | CCCTgGTGCCCCATATATTATCTG |
| oJT147 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon T334 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | CAGATAATATATGGGGCACcAGGGnnsAGATACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTA |
| oAS012 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon R335 to hybridizew/randomized R335 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TGTCCCTCGTGCCCCAT |
| oAS011 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon R335 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | ATggggcacgagggacaNNStaccagacatttgtgAATTTCAATTATTG |
| oJT148 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (R332P) before codon R335 to hybridizew/randomized R335 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TGTCCCTgGTGCCCCATATA |
| oJT149 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon R335 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | TATATGGGGCACcAGGGACAnnsTACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTG |
| oAS014 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon Y336 to hybridizew/randomized Y336 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TCTTGTCCCTCGTGCCC |
| oAS013 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon Y336 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | GGGCACGAGGGACAAGANNSCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTG |
| oJT150 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (R332P) before codon Y336 to hybridize w/randomized Y336 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TCTTGTCCCTgGTGCCCC |
| oJT151 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon Y336 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | GGGGCACcAGGGACAAGAnnsCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTAC |
| oAS016 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon Q337 to hybridize w/randomized Q337 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | GTATCTTGTCCCTCGTGCC |
| oAS015 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon Q337 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | GCACGAGGGACAAGATACNNSACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTG |
| oJT152 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (R332P) before codon Q337 to hybridize w/randomized Q337 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | GTATCTTGTCCCTgGTGCC |
| oJT153 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon Q337 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | GGCACcAGGGACAAGATACnnsACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGG |
| oAS018 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon T338 to hybridize w/randomized T338 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | CTGGTATCTTGTCCCTCGTG |
| oAS017 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon T338 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | CACGAGGGACAAGATACCAGNNSTTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGG |
| oJT154 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (R332P) before codon T338 to hybridize w/randomized T338 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | CTGGTATCTTGTCCCTgGTG |
| oJT155 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon T338 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | CACcAGGGACAAGATACCAGnnsTTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCAT |
| oAS020 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon F339 to hybridizew/randomized F339 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTC |
| oAS019 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon F339 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | GAGGGACAAGATACCAGACANNSGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGC |
| oJT156 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (R332P) before codon F339 to hybridizew/randomized F339 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | TGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTgG |
| oJT157 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon F339 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | CcAGGGACAAGATACCAGACAnnsGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCATC |
| oAS022 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (WT) before codon V340 to hybridizew/randomized V340 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | AAATGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTC |
| oAS021 | Randomize human TRIM5α (WT) at codon V340 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | AGGGACAAGATACCAGACATTTNNSAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCATCC |
| oJT158 | Amplify N-term half of human TRIM5α (R332P) before codon V340 to hybridizew/randomized V340 C-term half (Rev primer, use w/oJT037) | AAATGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTg |
| oJT159 | Randomize human TRIM5α (R332P) at codon V340 (Fwd primer, use w/oAS024 for C-term half) | cAGGGACAAGATACCAGACATTTnnsAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCATCCTG |
| Illumina library construction | ||
| oJT055 | Illumina library construction, PCR1 Fwd primer (rhesus TRIM5α only), amplifies v1 loop and adds adaptor | tcgtcggcagcgtcagatgtgtataagagacagTGAGCTCTCGGAACCCACAGATAATGTAT |
| oJT056 | Illumina library construction, PCR1 Rev primer (rhesus TRIM5α only), amplifies v1 loop and adds adaptor | gtctcgtgggctcggagatgtgtataagagacagGCCCAGGACGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATT |
| oJT113 | Illumina library construction, PCR1 Fwd primer (human TRIM5α libraries) amplifies v1 loop and adds adaptor | tcgtcggcagcgtcagatgtgtataagagacagCAAGTGAGCTCTCCGAAACCACAGATAATATAT |
| oJT114 | Illumina library construction, PCR1 Rev primer (human TRIM5α libraries), amplifies v1 loop and adds adaptor | gtctcgtgggctcggagatgtgtataagagacagGAGCCCAGGATGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATT |
| oJT057 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Fwd primer (all libraries), adds P5 adaptor | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACtagatcgcTCGTCGGCAGCGTC |
| oJT058 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N701 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATtcgccttaGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT059 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N702 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATctagtacgGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT060 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N703 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATttctgcctGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT115 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N704 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATgctcaggaGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT116 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N705 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATaggagtccGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT117 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N706 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATcatgcctaGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT118 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N707 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATgtagagagGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT119 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N708 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATcctctctgGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT138 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N709 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATagcgtagcGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT139 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N710 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATcagcctcgGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT140 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N711 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATtgcctcttGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT141 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N712 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATtcctctacGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT166 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N714 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTCATGAGCGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT167 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N715 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCCTGAGATGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT168 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N716 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTAGCGAGTGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT169 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N718 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGTAGCTCCGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT170 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N719 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTACTACGCGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT171 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N720 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATAGGCTCCGGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT172 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N721 barcoode | AAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGCAGCGTAGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT173 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N722 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCTGCGCATGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT174 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N723 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGAGCGCTAGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT175 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N724 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCGCTCAGTGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT176 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N726 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGTCTTAGGGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT177 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N727 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATACTGATCGGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT178 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N728 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATTAGCTGCAGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| oJT179 | Illumina library construction, PCR2 Rev primer (all libraries), adds P7 adaptor and N729 barcoode | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATGACGTCGAGTCTCGTGGGCTCGG |
| RhT5-IlluminaF | Custom sequencing primer for rhesus TRIM5α Illumina libraries, sequences rhesus TRIM5α v1 loop (39 nt) | TGAGCTCTCGGAACCCACAGATAATGTAT |
| HsT5-IlluminaF | Custom sequencing primer for human TRIM5α Illumina libraries, sequences human TRIM5α v1 loop (33 nt) | CAAGTGAGCTCTCCGAAACCACAGATAATATAT |
| Quikchange PCR for targeted mutagenesis | ||
| oCY001 | Generate G330E mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY002) | CTCCGAAACCACAGATAATATATGaGGCACGAGGGACAAGATAC |
| oCY002 | Generate G330E mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY001) | GTATCTTGTCCCTCGTGCCtCATATATTATCTGTGGTTTCGGAG |
| oCY003 | Generate A331E mutation in human TRIM5α F(wd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY004) | GAAACCACAGATAATATATGGGGaACGAGGGACAAGATACCAG |
| oCY004 | Generate A331E mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY003) | CTGGTATCTTGTCCCTCGTtCCCCATATATTATCTGTGGTTTC |
| oCY005 | Generate R332E mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY006) | ACCACAGATAATATATGGGGCAgaAGGGACAAGATACCAGACATT |
| oCY006 | Generate R332E mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY005) | AATGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTtcTGCCCCATATATTATCTGTGGT |
| oJT040 | Generate R332P mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT041) | CCACAGATAATATATGGGGCACcAGGGACAAGATACCAGACATTTG |
| oJT041 | Generate R332P mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT040) | CAAATGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTgGTGCCCCATATATTATCTGTGG |
| oCY007 | Generate G333Y mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY008) | CACAGATAATATATGGGGCACGAtacACAAGATACCAGACATTTGTGAATT |
| oCY008 | Generate G333Y mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY007) | AATTCACAAATGTCTGGTATCTTGTgtaTCGTGCCCCATATATTATCTGTG |
| oCY009 | Generate G333D mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY010) | CAGATAATATATGGGGCACGAGatACAAGATACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTC |
| oCY010 | Generate G333D mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY009) | GAAATTCACAAATGTCTGGTATCTTGTatCTCGTGCCCCATATATTATCTG |
| oCY011 | Generate T334D mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY012) | GATAATATATGGGGCACGAGGGgacAGATACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTC |
| oCY012 | Generate T334D mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY011) | GAAATTCACAAATGTCTGGTATCTgtcCCCTCGTGCCCCATATATTATC |
| oJT246 | Generate R335A mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT247) | TATGGGGCACGAGGGACAgcATACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTG |
| oJT247 | Generate R335A mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT246) | CAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTCTGGTATgcTGTCCCTCGTGCCCCATA |
| oCY013 | Generate R335E mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY014) | TGGGGCACGAGGGACAgaATACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTG |
| oCY014 | Generate R335E mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY013) | CAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTCTGGTATtcTGTCCCTCGTGCCCCA |
| oCY015 | Generate Y336E mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY016) | GGGCACGAGGGACAAGAgAaCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTAC |
| oCY016 | Generate Y336E mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY015) | GTACAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTCTGtTcTCTTGTCCCTCGTGCCC |
| oCY017 | Generate Q337D mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY018) | GGCACGAGGGACAAGATACgAtACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTG |
| oCY018 | Generate Q337D mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY017) | CAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTaTcGTATCTTGTCCCTCGTGCC |
| oAS2019-05 | Generate Q337N mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-06) | GGCACGAGGGACAAGATACaacACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGG |
| oAS2019-06 | Generate Q337N mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-05) | CCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTgttGTATCTTGTCCCTCGTGCC |
| oCY019 | Generate T338E mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY020) | ACGAGGGACAAGATACCAGgaATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGC |
| oCY020 | Generate T338E mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY019) | GCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATtcCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTCGT |
| oCY021 | Generate F339E mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY022) | GAGGGACAAGATACCAGACAgaaGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCA |
| oCY022 | Generate F339E mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY021) | TGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCACttcTGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTC |
| oCY023 | Generate V340E mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY024) | GGGACAAGATACCAGACATTTGaGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCATCC |
| oCY024 | Generate V340E mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY023) | GGATGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCtCAAATGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCC |
| oAS2019-07 | Generate V340H mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-08) | GAGGGACAAGATACCAGACATTTcacAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCATCCT |
| oAS2019-08 | Generate V340H mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-07) | AGGATGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTgtgAAATGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTC |
| oJT162 | Generate V340stop mutation in human TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT163) | GAGGGACAAGATACCAGACATTTtaGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCATCC |
| oJT163 | Generate V340stop mutation in human TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT162) | GGATGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCtaAAATGTCTGGTATCTTGTCCCTC |
| oJT248 | Generate R335A double mutation in human TRIM5α-R332P (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT249) | TATGGGGCACcAGGGACAgcATACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTG |
| oJT249 | Generate R335A double mutation in human TRIM5α-R332P (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT248) | CAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTCTGGTATgcTGTCCCTgGTGCCCCATA |
| oAS2019-03 | Generate R335E double mutation in human TRIM5α-R332P (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-04) | TGGGGCACcAGGGACAgaaTACCAGACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTG |
| oAS2019-04 | Generate R335E double mutation in human TRIM5α-R332P (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-03) | CAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTCTGGTAttcTGTCCCTgGTGCCCCA |
| oAS2019-01 | Generate Q337D double mutation in human TRIM5α-R332P (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-02) | GGCACcAGGGACAAGATACgacACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGG |
| oAS2019-02 | Generate Q337D double mutation in human TRIM5α-R332P (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-01) | CCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTgtcGTATCTTGTCCCTgGTGCC |
| oAS2019-09 | Generate Q337N double mutation in human TRIM5α-R332P (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-10) | GGCACcAGGGACAAGATACaacACATTTGTGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGG |
| oAS2019-10 | Generate Q337N double mutation in human TRIM5α-R332P (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oAS2019-09) | CCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCACAAATGTgttGTATCTTGTCCCTgGTGCC |
| oJT122 | Generate Q332E mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT123) | CTCGGAACCCACAGATAATGTATgAGGCACCAGGGACATTATTTAC |
| oJT123 | Generate Q332E mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT122) | GTAAATAATGTCCCTGGTGCCTcATACATTATCTGTGGGTTCCGAG |
| oJT120 | Generate A333E mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT121) | GAACCCACAGATAATGTATCAGGaACCAGGGACATTATTTACGTTTCC |
| oJT121 | Generate A333E mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT120) | GGAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGTtCCTGATACATTATCTGTGGGTTC |
| oCY063 | Generate A333W mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY064) | GAACCCACAGATAATGTATCAGtggCCAGGGACATTATTTACGTTTC |
| oCY064 | Generate A333W mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oCY063) | GAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGCCACTGATACATTATCTGTGGGTTC |
| oJT124 | Generate P334M mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT125) | CCCACAGATAATGTATCAGGCAatgGGGACATTATTTACGTTTCCGTC |
| oJT125 | Generate P334M mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT124) | GACGGAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCcatTGCCTGATACATTATCTGTGGG |
| oJT095 | Generate G335I mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT096) | ACAGATAATGTATCAGGCACCAatcACATTATTTACGTTTCCGTCACTC |
| oJT096 | Generate G335I mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT095) | GAGTGACGGAAACGTAAATAATGTgatTGGTGCCTGATACATTATCTGT |
| oJT097 | Generate T336Q mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT098) | GATAATGTATCAGGCACCAGGGcaaTTATTTACGTTTCCGTCACTCAC |
| oJT098 | Generate T336Q mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT097) | GTGAGTGACGGAAACGTAAATAAttgCCCTGGTGCCTGATACATTATC |
| oJT099 | Generate L337N mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT100) | GTATCAGGCACCAGGGACAaacTTTACGTTTCCGTCACTCACG |
| oJT100 | Generate L337N mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT99) | CGTGAGTGACGGAAACGTAAAgttTGTCCCTGGTGCCTGATAC |
| oJT103 | Generate F338K mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT104) | TCAGGCACCAGGGACATTAaagACGTTTCCGTCACTCACG |
| oJT104 | Generate F338K mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT103) | CGTGAGTGACGGAAACGTcttTAATGTCCCTGGTGCCTGA |
| oJT126 | Generate F338Q mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT127) | TCAGGCACCAGGGACATTAcagACGTTTCCGTCACTCACGA |
| oJT127 | Generate F338Q mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT126) | TCGTGAGTGACGGAAACGTctgTAATGTCCCTGGTGCCTGA |
| oJT105 | Generate T339F mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT106) | CAGGCACCAGGGACATTATTTttcTTTCCGTCACTCACGAATTTCA |
| oJT106 | Generate T339F mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT105) | TGAAATTCGTGAGTGACGGAAAgaaAAATAATGTCCCTGGTGCCTG |
| oJT128 | Generate T339Q mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT129) | CAGGCACCAGGGACATTATTTcaGTTTCCGTCACTCACGAATTTC |
| oJT129 | Generate T339Q mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT128) | GAAATTCGTGAGTGACGGAAACtgAAATAATGTCCCTGGTGCCTG |
| oJT130 | Generate F340D mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT131) | GCACCAGGGACATTATTTACGgaTCCGTCACTCACGAATTTCAATTA |
| oJT131 | Generate F340D mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT130) | TAATTGAAATTCGTGAGTGACGGAtcCGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGTGC |
| oJT132 | Generate P341G mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT133) | CACCAGGGACATTATTTACGTTTggGTCACTCACGAATTTCAATTATTGT |
| oJT133 | Generate P341G mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT132) | ACAATAATTGAAATTCGTGAGTGACccAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGTG |
| oJT107 | Generate P341I mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT108) | CACCAGGGACATTATTTACGTTTataTCACTCACGAATTTCAATTATTGTAC |
| oJT108 | Generate P341I mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT107) | GTACAATAATTGAAATTCGTGAGTGAtatAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGTG |
| oJT109 | Generate P341IK mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT110) | CACCAGGGACATTATTTACGTTTaaaTCACTCACGAATTTCAATTATTGTAC |
| oJT110 | Generate P341IK mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT109) | GTACAATAATTGAAATTCGTGAGTGAtttAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCTGGTG |
| oJT134 | Generate S342G mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT135) | AGGGACATTATTTACGTTTCCGggACTCACGAATTTCAATTATTGTACTG |
| oJT135 | Generate S342G mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT134) | CAGTACAATAATTGAAATTCGTGAGTccCGGAAACGTAAATAATGTCCCT |
| oJT101 | Generate T344E mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT102) | CATTATTTACGTTTCCGTCACTCgagAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCGTC |
| oJT102 | Generate T344E mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT101) | GACGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTctcGAGTGACGGAAACGTAAATAATG |
| oJT111 | Generate T344stop mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT112) | CATTATTTACGTTTCCGTCACTCtagAATTTCAATTATTGTACTGGCGTC |
| oJT112 | Generate T344stop mutation in rhesus TRIM5α (Rev primer, amplify full plasmid with oJT111) | GACGCCAGTACAATAATTGAAATTctaGAGTGACGGAAACGTAAATAATG |
| Sequencing primers | ||
| pQCXIP-F | Sequencing primer from pQCXIP backbone 5' of multiple cloning site (Fwd) | acaccgggaccgatccag |
| HsT5-midF | Sequencing primer from midpoint of human TRIM5α (Fwd) | GATCTGGAGCATCGGCTG |
| HsT5-midR | Sequencing primer from midpoint of human TRIM5α (Rev) | CAAGGTCACGTTCTCCGTC |
| RhT5-midF | Sequencing primer from midpoint of rhesus TRIM5α (Fwd) | CTCATCTCAGAACTGGAGCATC |
| RhT5-midR | Sequencing primer from midpoint of rhesus TRIM5α (Rev) | CTTCAAGGTCATGTTCTCAATCC |





