Peripheral natural killer cells in chronic hepatitis B patients display multiple molecular features of T cell exhaustion
Figures

NK cell functionality is impaired in CHB patients.
(A) PBMCs from HD (n = 30) or CHB patients (n = 32) were co-cultured with K562 during 4 hr, and the proportion of NK cells expressing CD107a was determined by immunostaining. Representative flow-cytometry plots as well as proportion of CD107a+ NK cells are shown for each individual. (B) PBMCs from HD (n = 17) or CHB patients (n = 15) were co-cultured with K562 NanoLuc at the indicated effectors:targets ratios during 4 hr. Supernatants were then collected to measure bioluminescence. Shown in the figure is the average bioluminescence ± SD in an experiment with five HD and five CHB representative of four independent experiments. PBMCs from HD or CHB patients were co-cultured with K562 (C), Rituximab-coated Granta (D), or with IL-12 and IL-18 (10 ng/mL each) during 4 hr. Intracellular stainings for the indicated cytokines were performed. Representative flow-cytometry plots as well as proportion of NK cells expressing the indicated molecule is shown for each individual (C, n = 30 HD and n = 32 CHB, D and E, n = 17 HD and n = 15 CHB). Statistical analysis was performed by logistic regression as described in the Materials and methods section, and adjusted p-values are indicated on the graph. NS: non-stimulated.
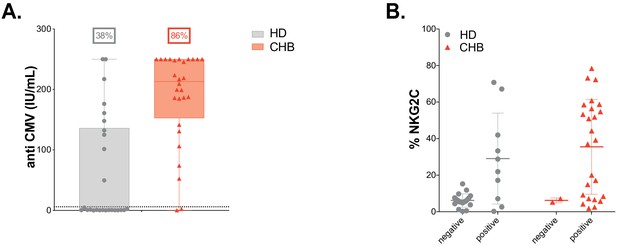
HCMV status.
(A) The concentrations of anti-CMV IgG antibodies were measured in serum from patients and HD to determine HCMV seropositivity. (B) The percentage of NKG2C+-adaptive NK cells in patients and HD was determined by flow cytometry and represented according to HCMV seropositivity.
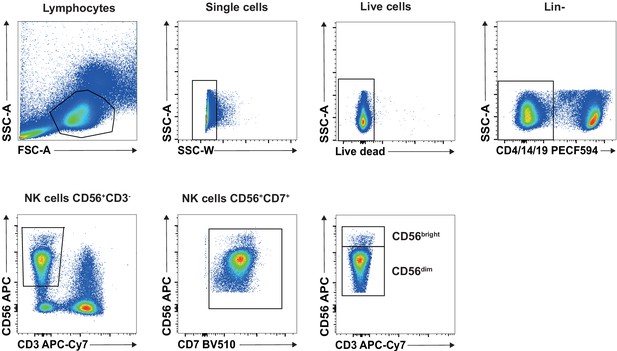
Gating strategy.
Gating strategy used for flow cytometry analysis. First, lymphocytes through SSC and FSC analyses were selected. Then doublets were eliminated as well as dead cells. We then removed CD4+, CD14+, and CD19+ cells prior to gate on NK cells by CD56+ and CD3− cells. CD7 marker was used to confirm the gating, and NK bright and dim were then separated.
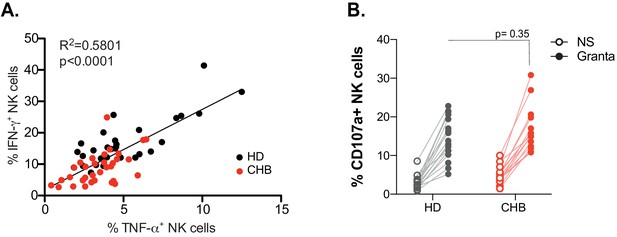
Functional properties.
(A) Dot plot showing the correlation between the percentage of IFN-γ and TNF-α-positive NK cells following K562 stimulation of HD and CHB patients PBMCs. Each dot represents an individual. Regression curves, R (Plummer et al., 2016) and p-value are indicated. (B) PBMCs from HD (n = 17) or CHB patients (n = 17) were co-cultured with Rituximab-coated Granta cells during 4 hr. CD107a staining was performed. The proportion of CD107a+ NK cells is shown for each individual.
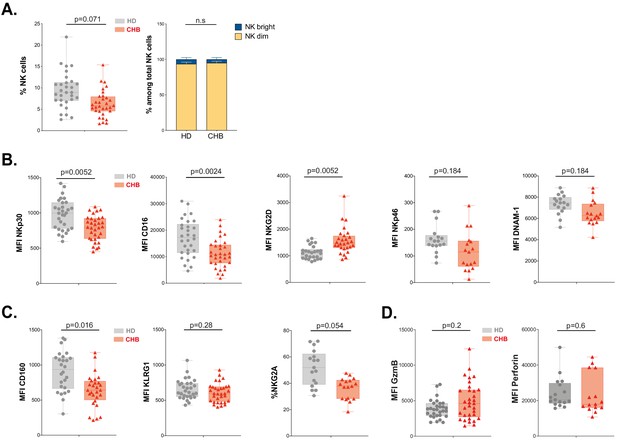
NK cell from CHB patients display an altered phenotype.
(A) PBMCs from 30 HD and 32 CHB samples were stained with live/dead, CD4, CD14, CD19, CD3, CD7, and CD56 antibodies. The percentage of NK cells in each sample (± SD), and the proportion of CD56bright versus CD56dim NK cells ± SD), determined by flow cytometry, are shown. (B,C) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of indicated NK activating (B) and inhibitory (C) receptors was determined by flow cytometry on total NK cells among PBMCs from HD or CHB patients. The median expression (± SD) as well as values for each individual are represented, n = 30 HD and 32 CHB samples for NKp30, CD16, NKG2D, KLRG1, and CD160, n = 17 HD and 15 CHB samples for NKp46, DNAM-1, and NKG2A. (D) MFI of Granzyme B and Perforin were determined by flow cytometry on total NK cells among PBMCs from HD or CHB patients. The median expression (± SD) as well as values for each individual are represented, n = 30 HD and 32 CHB samples for Granzyme B, n = 17 HD and 15 CHB samples for Perforin. Adjusted p-values are indicated on the graph. n.s: non-significant.
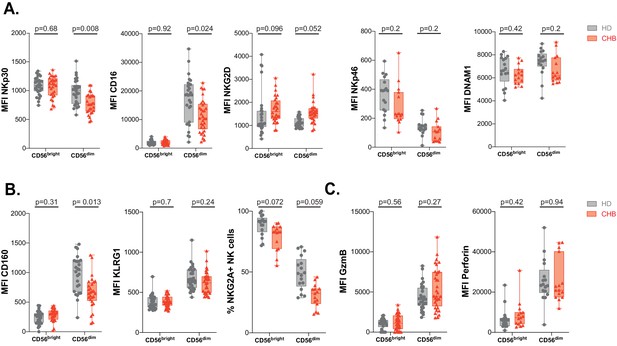
Phenotype of CHB patients NK cells along differentiation.
Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of indicated NK activating (A) and inhibitory (B) receptors was determined by flow cytometry on CD56Bright and CD56Dim NK cells among PBMCs from HD or CHB patients. The median expression (± SD) as well as values for each individual are represented, n = 30 HD and 32 CHB samples for NKp30, CD16, NKG2D, KLRG1, and CD160, n = 17 HD and 15 CHB samples for NKp46, DNAM-1, and NKG2A. (C) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Granzyme B and Perforin were determined by flow cytometry on CD56Bright and CD56Dim NK cells among PBMCs from HD or CHB patients. The median expression (± SD) as well as values for each individual are represented, n = 30 HD and 32 CHB samples for Granzyme B, n = 17 HD and 15 CHB samples for Perforin.
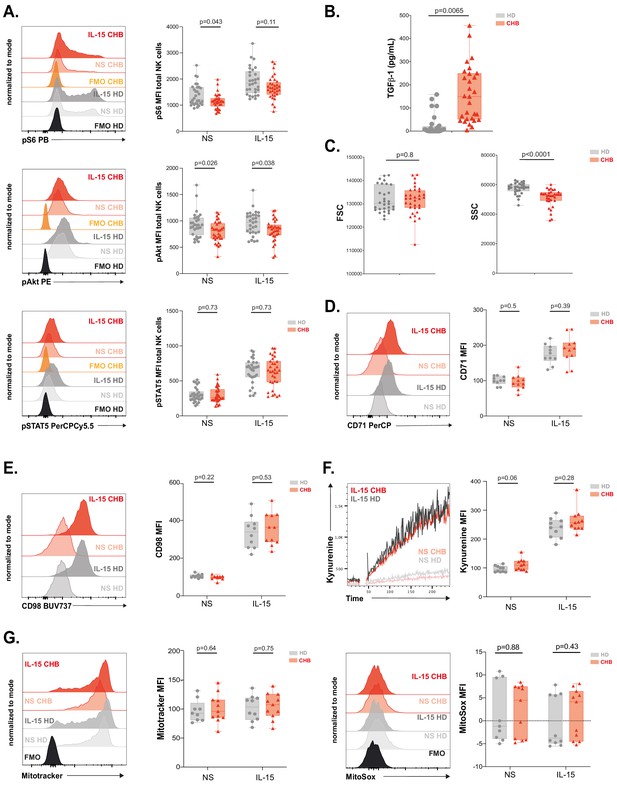
mTOR activation is impaired in NK cells from patients.
(A) PBMCs from HD or CHB patients were stimulated or not with IL-15 at 100 ng/mL for 30 min prior to phospho-epitope staining (pS6 Ser235/236, pAKT S473, and pSTAT5 Y694). Overlays of representative histograms are shown (left panels). The median expression (± SD) as well as MFI values for each individual are represented, n = 30 HD and 32 CHB (right panels). (B) Active TGF-β1 levels were measured in serum samples from 30 HD and 32 CHB patients, and the median (± SD) as well as values for each individual are represented. (C) FSC-A and SSC-A parameters on NK cells were measured by flow cytometry in 30 HD and 32 CHB samples. The median of the MFI (± SD) as well as MFI values for each individual are represented. MFI of (D) CD71 and (E) CD98 was determined by flow cytometry on total NK cells from HD or CHB patients with or without prior stimulation with 100 ng/mL IL-15 O/N. Overlays of representative histograms are shown (left panels). The median expression (± SD) as well as values for each individual are represented, n = 10 HD and 11 CHB samples (right panels). (F) PBMCs from 10 HD and 11 CHB patients were stimulated or not O/N with 100 ng/mL IL-15 and their kynurenine uptake capacity was evaluated. A representative kinetic analysis is shown (left panel). MFI was determined in a 30 s time slice centred on 2 min after the beginning of the kynurenine treatment. The mean of the MFI (± SD) as well as MFI values for each individual are represented (right panel). (G) PBMCs from 10 HD and 11 CHB patients were stained with Mitotracker Green and MitoSOX Red with or without prior stimulation with 100 ng/mL IL-15 O/N. Overlays of representative histograms are shown (left panels). Median (± SD) as well as MFI values for each individual for the analysed marker are represented (right panels). p-values are indicated on each graph.
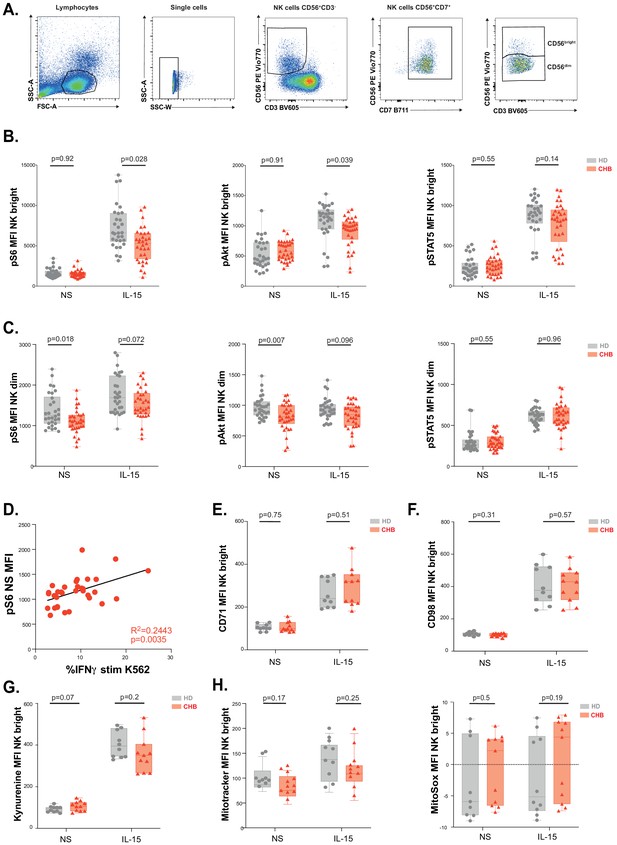
Gating strategy, phospho-epitopes, and metabolic analysis.
(A) Gating strategy used for phospho-flow cytometry analysis: First, lymphocytes through SSC and FSC analysis were selected. Then doublets were eliminated. We then selected CD56+, CD3− cells. CD7 marker was used to confirm the gating and NK bright and dim were then separated. (B,C) PBMCs from HD or CHB patients were stimulated or not with IL-15 at 100 ng/mL for 30 min prior to phospho-epitope staining (pS6 Ser235/236, pAKT S473, and pSTAT5 Y694). The median expression (± SD) as well as MFI values for each individual are represented for CD56Bright (B) and CD56Dim (C) subsets, n = 30 HD and 32 CHB. (D) Dot plot showing the correlation between the percentage of IFN-γ-positive NK cells following K562 stimulation of CHB patients PBMCs and the basal pS6 MFI. Each dot represents an individual. Regression curves, R (Plummer et al., 2016), and p-value are indicated. MFI of (E) CD71 and (F) CD98 was determined by flow cytometry on CD56Bright and CD56Dim NK cells from HD or CHB patients with or without prior stimulation with 100 ng/mL IL-15 O/N. The median expression (± SD) as well as values for each individual are represented, n = 10 HD and 11 CHB samples. (G) PBMCs from 10 HD and 11 CHB patients were stimulated or not O/N with 100 ng/mL IL-15 and their kynurenine uptake capacity was evaluated. MFI was determined in a 30 s time slice centred on 2 min after the beginning of the kynurenine treatment. The median of the MFI (± SD) as well as MFI values for each individual are represented. (H) PBMCs from 10 HD and 11 CHB patients were stained with MitoSOX Red and Mitotracker Green with or without prior stimulation with 100 ng/mL IL-15 O/N. Median (± SD) as well as MFI values for each individual for the analysed marker are represented (right panels). Adjusted p-values are indicated on each graph.
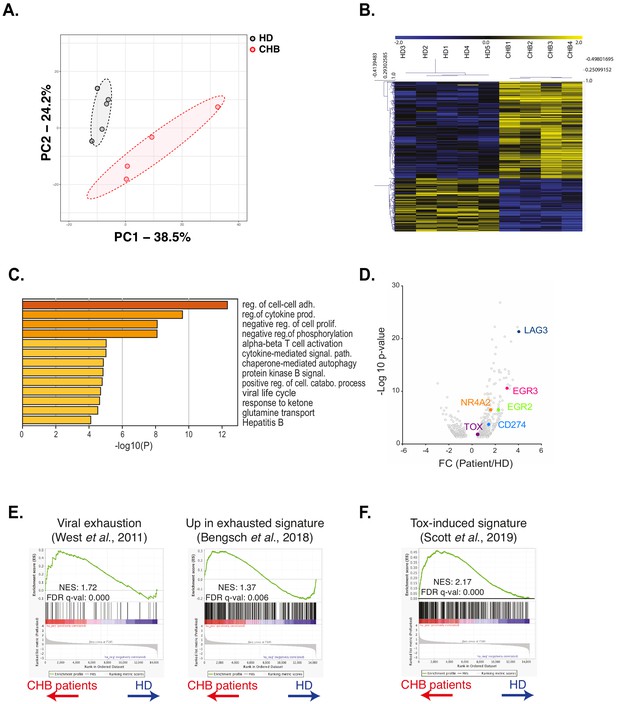
RNAseq analysis identifies an exhaustion-like signature in patient NK cells.
(A) Principal component analysis of the RNAseq data is shown. (B) Heatmap of the DEG genes between HD and CHB. (C) Gene Ontology analysis of DEG up-regulated in CHB patients using Metascape. Selected terms are shown among the most significant ones. (D) Volcano plots of the DEG highlighting genes belonging to the T cell exhaustion pathway. (E,F) GSEA plots comparing HD and CHB patients are shown for the indicated gene sets. The normalised enrichment scores (NES) and FDR q-values are indicated.
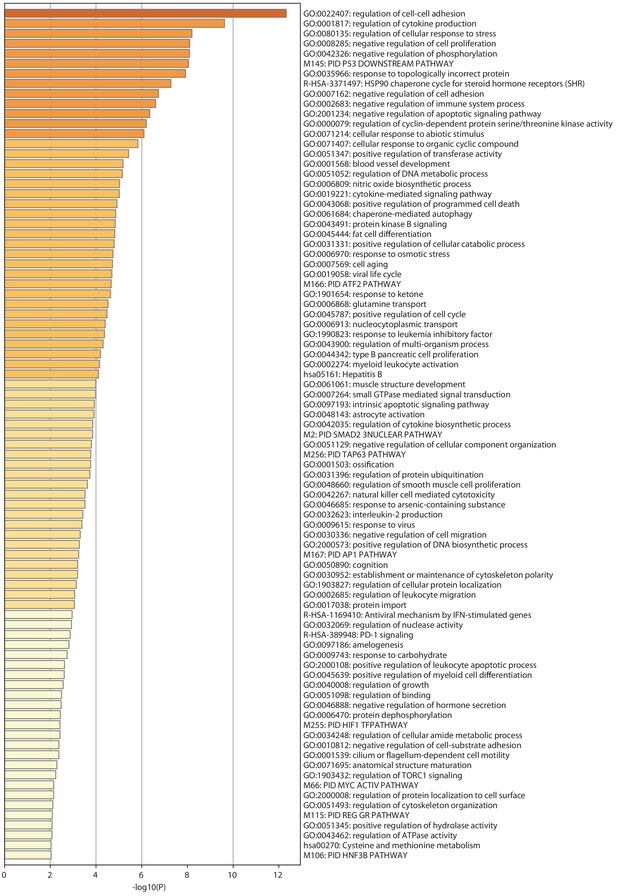
Metascape analysis of CHB patients up-regulated genes.
Full results for the Gene Ontology analysis of DEG up-regulated in CHB patients performed with Metascape and presented in Figure 4C.
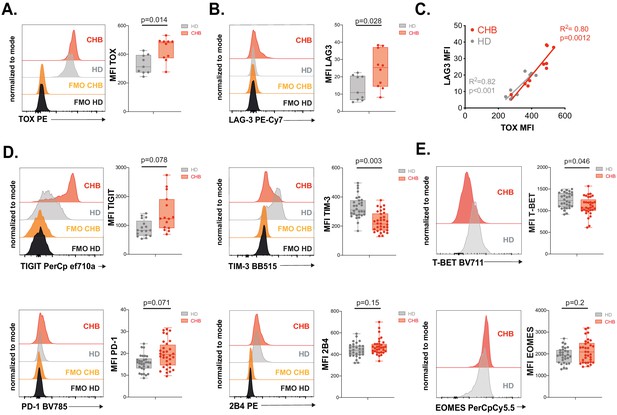
Validation of the exhausted phenotype at the protein level.
(A) Intracellular staining for TOX was performed on PBMCs from 9 HD and 10 CHB samples and the MFI measured. A representative FACS histogram overlay (left panel) as well as the median MFI and individual values for each sample (right panel) are represented. (B) LAG3 expression was measured by flow cytometry on PBMCs from 9 HD and 10 CHB samples. A representative FACS histogram overlay (left panel) as well as the median MFI and individual values for each sample (right panel) are represented. (C) Linear regression plots showing the correlation between TOX MFI and LAG3 MFI using 9 HD and 10 CHB samples. The R (Plummer et al., 2016) and p-value calculated by linear regression are indicated. (D) ICP expression was measured by flow cytometry on NK cells from PBMCs of 17 HD and 15 CHB samples (TIGIT) or 30 HD and 32 CHB patients (TIM-3, PD-1, and 2B4). A representative FACS histogram overlay for each molecule (left panels) as well as the median MFI and individual values for each sample (right panels) are represented. (E) T-BET and EOMES expression were measured by intracellular staining on total NK cells of 30 HD and 32 CHB samples. A representative FACS histogram overlay (left panel) as well as the median MFI and individual values for each sample (right panel) are represented. Adjusted p-values are indicated on the graphs.

TOX expression in CD56Bright and CD56Dim NK cells.
(A) Intracellular staining for TOX was performed on PBMCs from 10 HD and 10 CHB samples and the MFI measured in CD56Bright and CD56Dim NK cells. The median MFI (± SD) and individual values for each sample are represented.
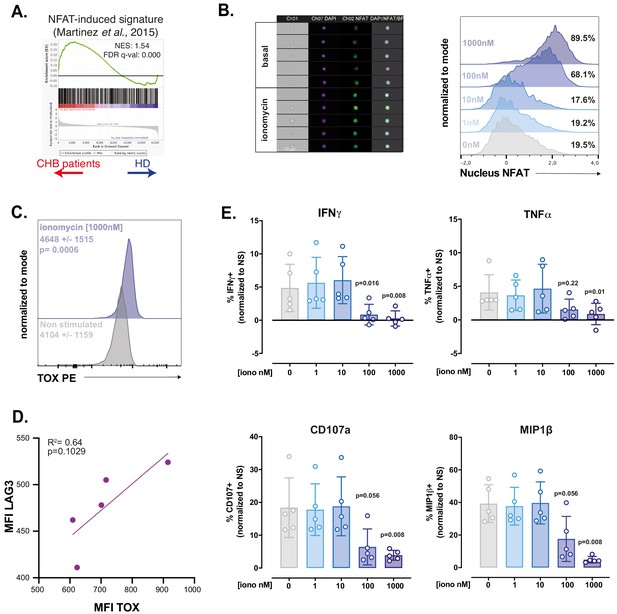
RNAseq and in vitro modelling suggest that NK cell dysfunction is due to unbalanced Ca2+ signalling.
(A) A GSEA plot comparing HD and CHB patients is shown for the gene set regulated by partnerless NFAT. The normalised enrichment score (NES) and FDR q-values are indicated. (B) PBMCs from HD were exposed to ionomycin at the indicated concentration for 1 hr. NFAT1 localisation was then analysed by image cytometry. Representative images of the transmission, nuclear (DAPI), and NFAT1 staining in NK cells at basal state or after 1 hr ionomycin treatment are shown (left panel). Histogram overlays of the parameter quantifying NFAT1 translocation are shown on the right. The experiment was performed twice. (C) PBMCs from HD were exposed to ionomycin for 4 hr and stained for TOX expression. A representative histogram overlay as well as the average expression ± SD is shown (n = 10). (D) Linear regression plots showing the correlation between TOX MFI and LAG3 MFI after O/N ionomycin treatment (1 µM) is shown. The R (Plummer et al., 2016) and p-value calculated by linear regression are indicated. (E) PBMCs from five HD were incubated with ionomycin at the indicated concentration for 16 hr. NK cell capacity to degranulate or produce the indicated cytokines upon K562 stimulation was then measured by flow cytometry. The average (± SD) and individual values of the proportion of positive NK cells normalised to the non-stimulated condition is shown. The experiment has been performed twice. Exact p-values are indicated on the graphs.
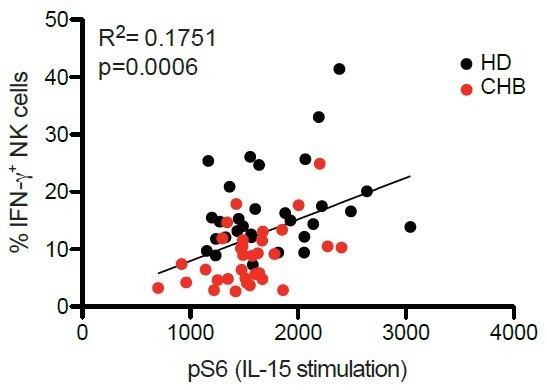
Correlation between percentages of IFN-γ+ following K562 stimulation and pS6 level following IL-15 stimulation.
PBMCs from HD (n=30) or CHB patients (n=32) were co-cultured with K562 during 4 hours and the proportion of NK cells expressing IFN-γ was determined by immunostaining. The same samples were stimulated with IL-15 100ng/ml for 30 minutes and pS6 level was measured after phospho-epitope staining. The result of both readouts were correlated on a patient by patient basis.
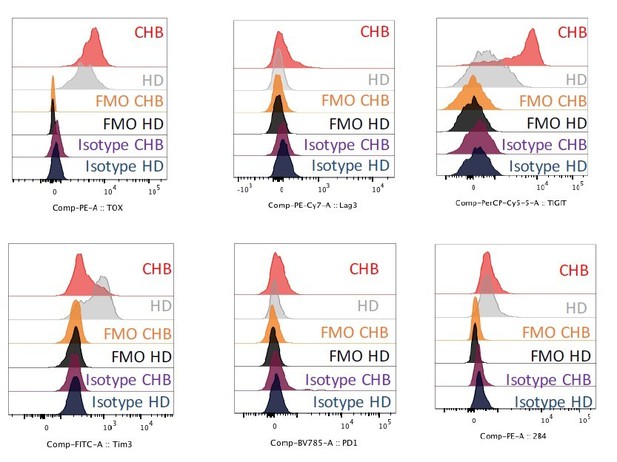
Representative histogram plots showing the expression level of the indicated markers as well as FMO and isotype control stainings on NK cells of HD or CHB patients.

Correlation between pS6 level in CD56Dim and CD56Bright NK cells following IL-15 stimulation.
PBMCs from HD (n=30) or CHB patients (n=32) were stimulated with IL-15 at 100 ng/mL for 30 min, prior to phospho-epitope staining (pS6 Ser235/236). MFI values for each individual are represented.

Representative FACS-plot showing TOX and T-BET coexpression in total NK cells of a CHB patient.
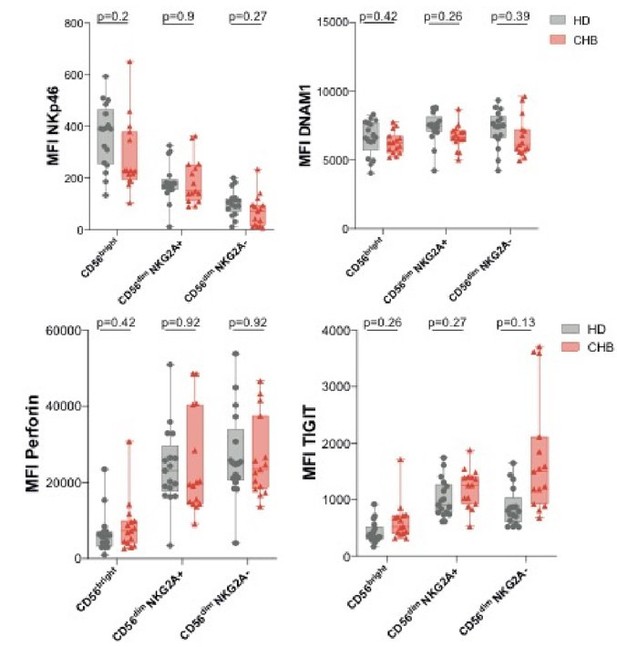
Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the indicated markers was determined by flow cytometry on CD56Bright, CD56Dim NKG2A+ and CD56Dim NKG2A- NK cells among PBMCs from HD or CHB patients.
Box-plots as well as values for each individual are represented.
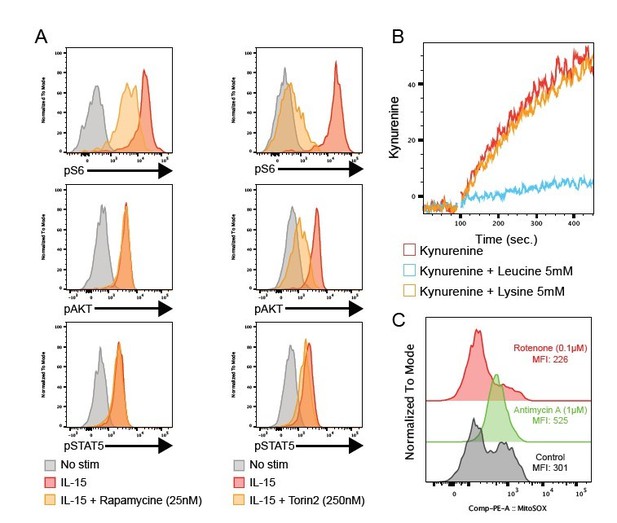
(A) Histogram overlays showing the level of the indicated phosphoepitope following 1h IL-15 stimulation in the presence or absence of the mTOR inhibitors Rapamycine (left) or Torin2 (right).
(B) Kinetic of Kynurenine uptake with or without excess Leucine or Lysine, inhibitors of Slc7a6 or Slc7a5 respectively. (C) Histogram overlays showing the level of mitochondrial ROS with or without Antimycine A (complex III inhibitor) or Rotenone (complex I inhibitor).
Tables
Characteristics of patients and HD enrolled in the study.
| Parameter | CHB Patients 1st cohort | Healthy Donors 1st cohort | CHB Patients 2nd cohort | Healthy Donors 2nd cohort |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 32 | 30 | 12 | 10 |
| Age (y) Mean Median (range) | 39 ± 13 38 (19–77) | 38 ± 13 36.5 (20–65) | 33 ± 13 30.5 (20–57) | 37 ± 8 38 (26–50) |
| Sex, n (%) Male Female | 20 (62.5) 12 (37.5) | 22 (73) 8 (27) | 8 (66.6) 4 (33.3) | 5 (50) 5 (50) |
| HBV load (IU/mL) Median | 2844 (10–62,225) | / | 1919 (18–32,785) | / |
| HBsAg (IU/mL) Median | 5770 (0.05–34,971) | / | 17,306(4,189–29,890) | / |
| ALT (IU/mL) Median | 20 (6–56) | NA | 21 (12–35) | NA |
| AST (IU/mL) Median | 21 (11–34) | NA | NA | NA |
| HCMV seropositive, % | 86 | 38 | NA | NA |
-
ALT, serum alanine aminotransferase levels; AST, aspartate transaminase levels; NA, not available.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Antibodies used.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/60095/elife-60095-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/60095/elife-60095-transrepform-v2.docx





