A broadly neutralizing macaque monoclonal antibody against the HIV-1 V3-Glycan patch
Figures
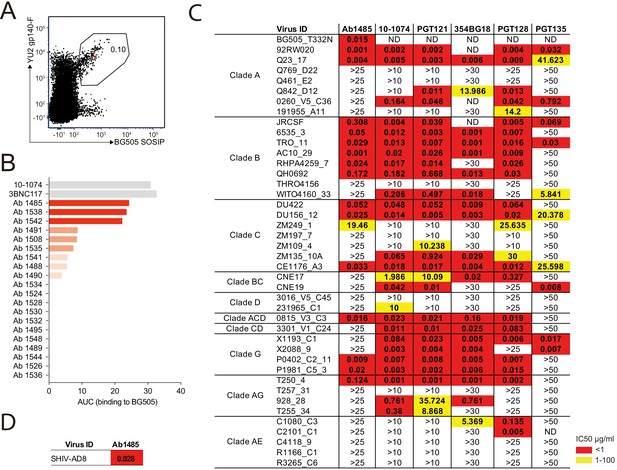
Broadly neutralizing antibody isolated from a SHIVAD8-infected rhesus macaque.
(A) FACS plot showing germinal center B cells that bind to YU2 gp140-F and BG505 SOSIP from a lymph node collected from macaque CE8J at week 115 after SHIVAD8 infection. The gate shows the sorting window. The B cell carrying the isolated bNAb (Ab1485) is highlighted in red. (B) Graph shows the binding of several monoclonal antibodies isolated from macaque CE8J to BG505 SOSIP (Antibodies were tested for binding to BG505 two or three times. Graph shows data from a representative ELISA). Data is shown as area under the ELISA curve (AUC). (C and D) Table shows the neutralization activity of Ab1485 and other human V3-glycan bNAbs determined in TZM-bl assays against a panel of 42 multi clade tier 1B and tier two pseudoviruses (C) and replication-competent SHIVAD8 (D).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Macaque antibody sequences.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61991/elife-61991-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
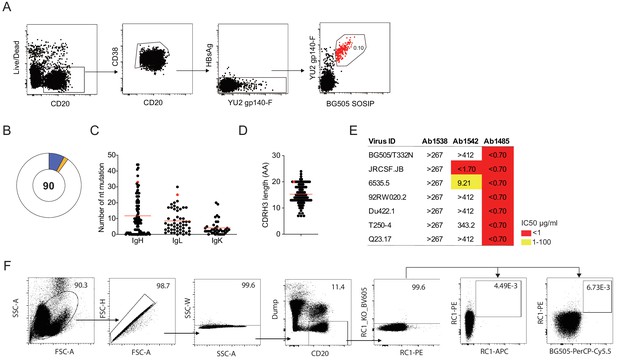
Antibodies isolated from a SHIVAD8-infected rhesus macaque.
(A) FACS plots show the gating strategy used to isolate single germinal center B cells that bind to YU2 gp140-F and BG505 SOSIP from a lymph node sample collected from the elite neutralizer macaque CE8J. The sorted population of B cells is highlighted in red. (B) Pie chart shows the clonal analysis of antibodies cloned from macaque CE8J. Expanded clones are represented in colored slices while singles are shown in white. The number of analyzed sequences is shown in the middle of the pie chart. (C) Graph shows the number of nucleotide mutations in the VH, VL, and VK genes of the antibodies shown in B. (D) Length of CDRH3 for antibodies shown in B and C. The red dot corresponds to Ab 1485. (E) Neutralization activity of Ab1538, Ab1542, and Ab1485 determined in TZM-bl assays against a panel of 7 tier 1B and tier two pseudoviruses. (F) Sorting strategy used in an attempt to isolate Env-specific B cells from a PBMC sample collected from macaque CE8J at week 38 post-SHIVAD8 infection.
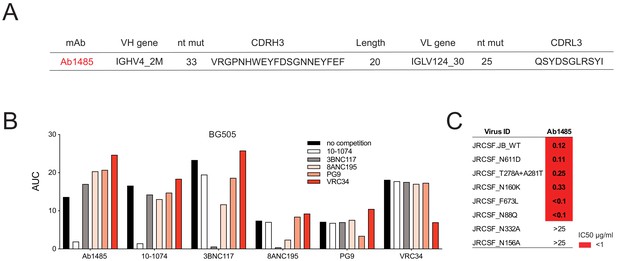
Mapping of Ab1485 binding to Env.
(A) Description of Ab1485. (B) Representative ELISA graph showing binding of Ab1485 to BG505 in competition with antibodies that target the V3-glycan epitope (10–1074), the CD4- binding site (3BNC117), the gp120-gp41 interface (8ANC195), the apex (PG9) or the fusion peptide (VRC34) and in the absence of a competing antibody (n = 3). (C) Table shows the neutralization activity of Ab1485 determined in TZM-bl assays against a JRCSF pseudovirus and a series of JRCSF mutants that affect the binding of human bNAbs to the interface (N611D), the CD4-binding site (T278A+ A281T), the apex (N160K), the MPER (F673L), and the fusion peptide (N88Q).
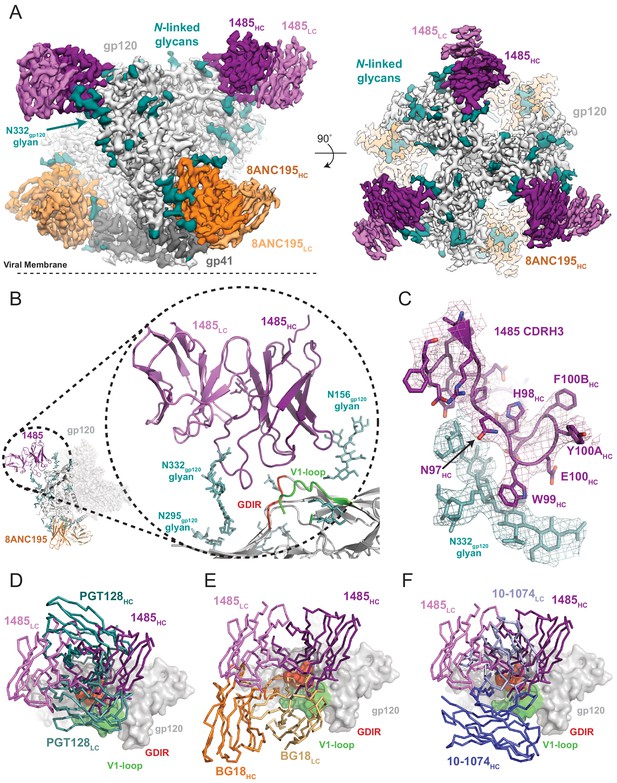
Cryo-EM reconstruction of the Ab1485-BG505 complex reveals a distinct Env-binding orientation relative to human bNAbs.
(A) Cryo-EM map of the BG505 SOSIP.664 trimer bound to three Ab1485 (purple shades) and three 8ANC195 (orange shades) Fabs. Densities for glycans are colored in dark teal. (B) Cartoon depiction of the modeled complex with a close-up view of the Ab1485 Fab – gp120 interface. Conserved regions of the V3-epitope are highlighted. (C) Cartoon and stick representation of the Ab1485 CDRH3 recognition of the N332gp120-glycan. Reconstructed cryo-EM map shown as a mesh, contoured at three sigma. (D–F) Comparison of Ab1485’s (purple) Env-binding orientation to (D) PGT128 (teal, PDB 5ACO), (E) BG18 (orange, PDB 6CH7), and (F) 10–1074 (blue, PDB 5T3Z).
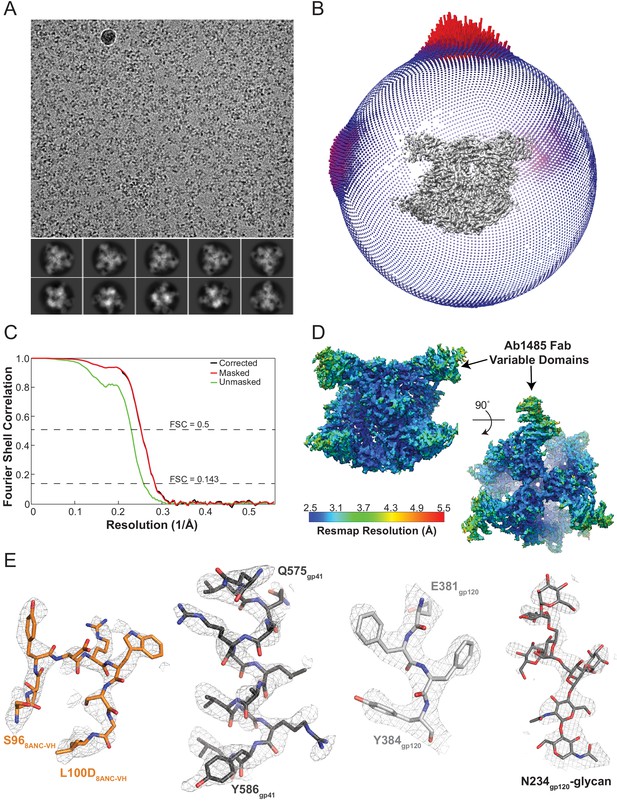
Cryo-EM data processing and validation.
(A) Representative micrograph and 2D class averages shown for Ab1485-BG505-8ANC195 complex data. (B) Angular distribution, (C) Gold-standard Fourier shell correlation plot, with dashed lines showing resolutions at 0.5 and 0.143. (D) Local resolution as determined by ResMap depicted on side and top views of reconstructed volume. (E) Representative density contoured at three sigma for different regions of the complex.
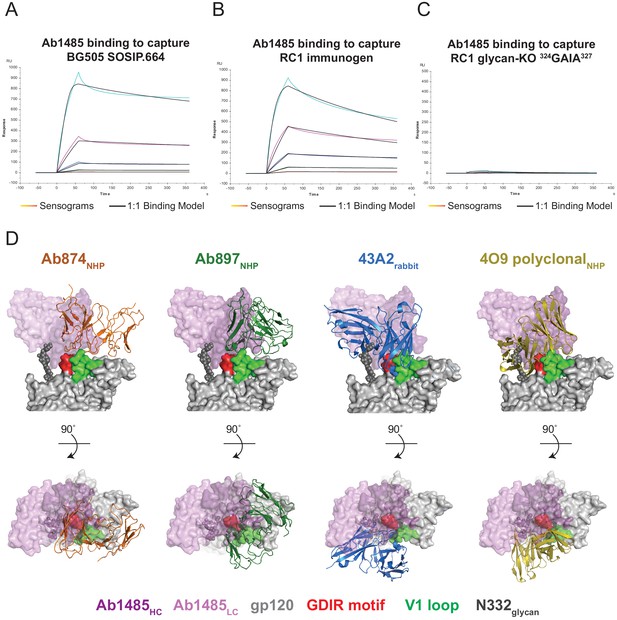
Binding assays and structural comparison to V1//V3 antibodies raised in animals.
(A–C). SPR sensorgrams for binding of Ab1485 Fab to immobilized BG505 (A), RC1 (B), or RC1-glycan KO 324GAIA327 (C). Sensorgrams traces are shown in colors; the fits to a 1:1 binding model are shown in black. (D) Comparison of Ab1485 (purple shades) Env-binding orientation to antibodies 874NHP (PDB: 6ORN; orange), 897NHP (PDB: 6ORO; green), and 43A2rabbit (PDB:6VO0; blue). Comparison with the predominant V1/V3 binding orientation observed after repeated challenge with SHIVBG505 is also shown (modeled Fab (olive)) based on cryo-EM density (EMD-20396).
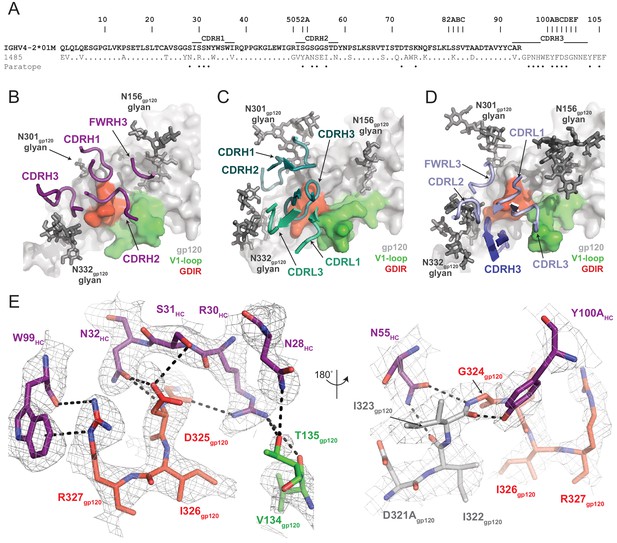
Molecular details of Ab1485-gp120 interactions.
(A) Sequence alignment of mature Ab1485 heavy chain with germline VH4-2*01M. Paratope residues are highlighted. (B–D) Comparison of the paratope CDR loops and FWRs involved in epitope recognition for (B) Ab1485, (C) PGT128, and (D) 10–1074. (E) Stick representation of interactions between Ab1485 (purple) and either the GDIR peptide motif (red) or V1 loop (green). Potential H-bonds defined are shown as black dashes.
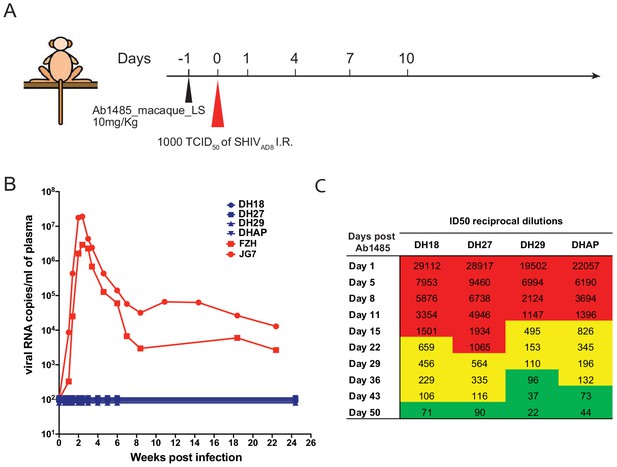
Ab1485 protects macaques against a high dose intrarectal challenge with SHIVAD8.
(A) Diagrammatic representation of the regimen used to assess the protective efficacy of Ab1485. Macaques were administered with Ab1485 at a dose of 10 mg kg−1 and challenged one day later with 1000 TCID50 of SHIVAD8 intrarectally (I.R.) (B) Longitudinal analysis of plasma viral loads in two control macaques (FZH and JG7) receiving no Ab and four macaques (DH18, DH27, DH29, and DHAP) infused with Ab1485 24 hr prior to SHIVAD8 challenge. (C) Serum neutralizing antibody titers in macaques receiving Ab1485. The IC50 titers are color coded: 1:21–99 in green; 1:100–999 in yellow and ≥1:1000 in red.
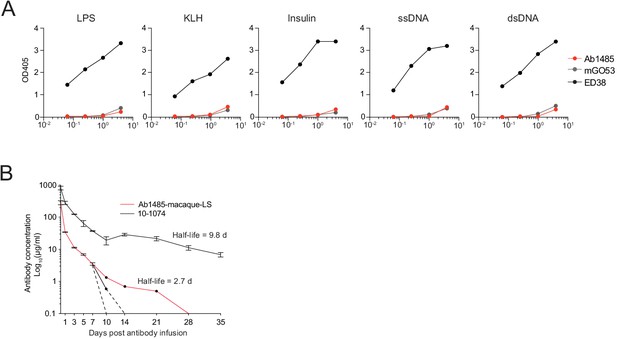
Characterization of Ab1485.
(A) ELISA graphs showing binding of Ab1485 to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), Keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH), Insulin, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). Antibody ED38 (Barouch et al., 2013; Nishimura et al., 2017) and antibody mGO53 (Barouch et al., 2013) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively (n = 1). (B) Graph shows the antibody concentrations of Ab1485-macaque-LS and the control 10–1074 in the serum of mice that carry a null mutation for the mouse neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) and a transgene for the human FcRn at different time points after intravenous infusion of the antibodies (Representative experiment. n = 2).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| strain, strain background (Mus musculus Female) | B6. Cg-Fcgrttm1Dcr Tg(CAG-FCGRT)276Dcr/DcrJ mice (FcRn -/- hFcRn) | The Jackson Laboratory | 004919 | 7–8 weeks of age |
| cell line (human) | HEK293-6E | National Research Council of Canada | RRID:CVCL_HF20 | |
| Cell line (human) | Expi293F cells | Invitrogen | A14527 | |
| cell line (CHO) | CHO Flp-InTM cells | Invitrogen | R75807 | Chung et al., 2014 PMID:24767177 |
| Recombinant protein | Avi-tagged BG505 SOSIP | Kindly provided by Dr. Rogier W. Sanders and Dr. Marit van Gils. | Sok et al., 2013 PMID:25422458 | |
| Recombinant protein | Avi-tagged YU2-gp140 fold-on | Kindly provided by Dr. R. Wyatt | ||
| Recombinant protein | Avi-tagged Hepatitis B surface antigen | Protein Specialists | hbs-875 | |
| Recombinant protein | Avi-tagged RC1 | Escolano et al., 2019 PMID:31142836 | ||
| Recombinant protein | Avi-tagged RC1_KO | Escolano et al., 2019 PMID:31142836 | ||
| Recombinant protein | BG505 SOSIP.664 trimer | Schoofs et al., 2019 PMID:31126879 | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | Zombie NIR Fixable Viability Kit | Biolegend | 77184 | (1:400) |
| Commercial assay or kit | TCL lysis buffer | Qiagen | 1031576 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNAClean XP | Beckman Counter | A63987 | |
| antibody | anti CD3-APC-eFluor 780 (mouse monoclonal) | Invitrogen | 47-0037-41 | (1:200) |
| antibody | anti CD14-APC-eFluor 780 (mouse monoclonal) | Invitrogen | 47-0149-42 | (1:200) |
| antibody | anti CD38 FITC | Stem Cell | 60131FI | (1:200) |
| antibody | anti CD16-APC-eFluor 780 (mouse monoclonal) | Invitrogen | 47-0168-41 | (1:200) |
| antibody | anti CD8-APC-eFluor 780 (mouse monoclonal) | Invitrogen | 47-0086-42 | (1:200) |
| antibody | anti CD20-PE-Cy7 (mouse monoclonal) | BD Biosciences | 335793 | (1:200) |
| antibody | HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG (Fc) CH2 Domain antibody (mouse monoclonal) | Bio-Rad | MCA647P | (1:5000) |
| software, algorithm | WinNonlin 6.3 | Certara Software | ||
| software, algorithm | MacVector v.17.0.2 | MacVector | ||
| software, algorithm | FlowJo v.10.6.1 | Becton Dickinson | ||
| software, algorithm | FCS EXPRESS | De Novo | ||
| software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 7 | GraphPad | ||
| software, algorithm | SeqIO | Biopython | ||
| software, algorithm | cutadapt v.2.3 | cutadapt | ||
| Software, algorithm | Change-O toolkit v.0.4.5 | PMID:26069265 | ||
| software, algorithm | SerialEM v3.7 | RRID:SCR_017293 | Mastronarde, 2005 PMID:16182563 | |
| software, algorithm | cryoSPARCv2.14 | RRID:SCR_016501 | Punjani et al., 2017 PMID:28165473 | |
| software, algorithm | Relion v3.0 | RRID:SCR_016274 | Zivanov et al., 2018 PMID:30412051 | |
| software, algorithm | UCSF Chimera v1.13 | RRID:SCR_004097 | Goddard et al., 2007, PMID:16963278 | |
| software, algorithm | Phenix v1.17 | RRID:SCR_014224 | Afonine, et al, ACTA D, 2018, PMID:29872004 | |
| software, algorithm | Coot v0.8.9 | RRID:SCR_014222 | Emsley et al., 2010, PMID:20383002 | |
| software, algorithm | PyMOL v1.8.2.1 | Schrodinger, Inc | RRID:SCR_000305 | https://pymol.org/2/ |
| software, algorithm | Biacore T200 Evaluation Software v3.2 | Cytiva |





