Dose-dependent action of the RNA binding protein FOX-1 to relay X-chromosome number and determine C. elegans sex
Figures
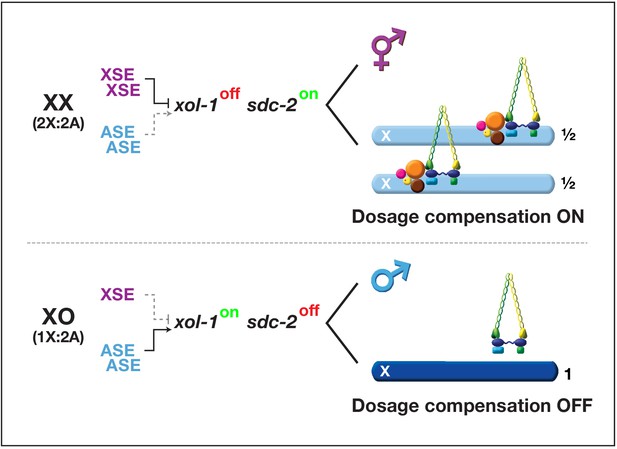
Overview of the X:A signal and regulatory hierarchy that control sex determination and X-chromosome dosage compensation.
The X:A signal includes a set of genes on X called X-signal elements (XSEs) that repress their direct target gene xol-1 (XO lethal) in a cumulative dose-dependent manner via transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms and set of genes on autosomes called autosomal signal elements (ASEs) that stimulate xol-1 transcription in a cumulative dose-dependent manner. xol-1 is the master sex-determination switch gene that must be activated in XO animals to set the male fate and must be repressed in XX animals to permit the hermaphrodite fate. xol-1 triggers male sexual development by repressing the feminizing switch gene sdc-2 (sex determination and dosage compensation). sdc-2 induces hermaphrodite sexual development and triggers binding of a dosage compensation complex (DCC) to hermaphrodite X chromosomes to repress gene expression by half. xol-1 mutations enable the DCC to bind to the single male X chromosome and thereby kill all XO animals by causing reduced X-chromosome expression. The dying xol-1 XO mutant animals are also feminized. Hence, mutations that disrupt elements of the X:A signal transform sexual fate and also alter X-chromosome gene expression.
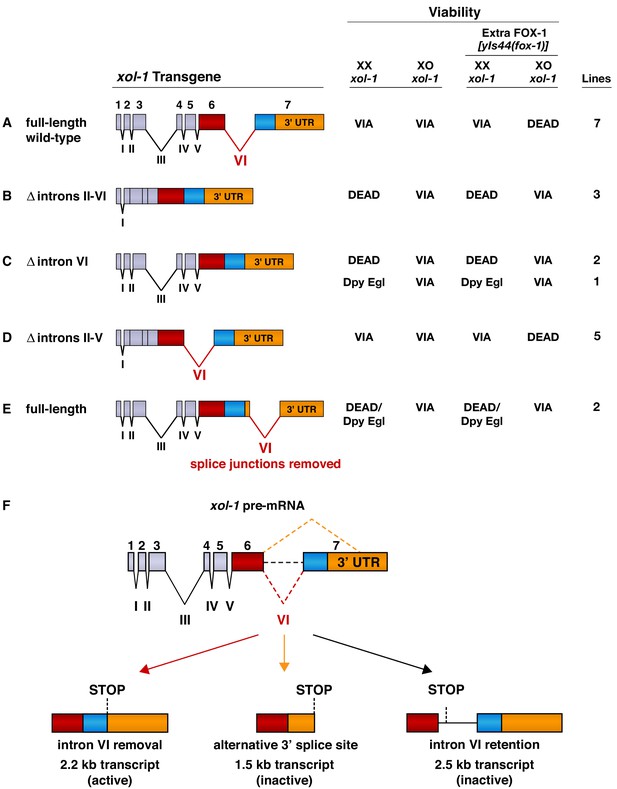
Intron VI is essential for repression of xol-1 by FOX-1.
(A–E) Assays of wild-type xol-1 transgenes and deletion derivatives with different combinations of introns show that removal of intron VI prevents FOX-1 from repressing xol-1. Diagrams on the left show the intron–exon structure of xol-1 sequences in the transgene derivatives. Exon 7 includes both coding sequences (blue) and the 3' UTR (orange). The wild-type parent transgene rescues the XO-specific lethality caused by xol-1 null mutations but permits XX animals to be viable. Intron deletion derivatives have genomic regions of xol-1 replaced by corresponding xol-1 cDNA to remove introns without altering protein coding sequence. Shown on the right is the viability of XX and XO xol-1(y9) deletion mutant animals carrying extra-chromosomal arrays of the different transgene derivatives. The arrays were made and assayed in him-5(e1490); xol-1(y9) mutants that produce 33% XO and 67% XX embryos and then crossed into him-5; xol-1 strains producing high levels of FOX-1 from an integrated array [yIs44 (fox-1)] carrying multiple copies of fox-1. The far right shows the number of independent extra-chromosomal arrays assayed. The term ‘dead’ means that all animals of the genotype were inviable, and no extra-chromosomal arrays could be established in XX animals. The arrays could only be established and maintained through XO males. The term ‘via’ means the animals were viable and appeared wild type. The term ‘Dpy Egl’ refers to the phenotype of dosage-compensation-defective XX animals that escape lethality. XX animals are typically dumpy (Dpy) in body size and egg-laying defective (Egl). The term ‘dead/Dpy Egl’ means that most animals (greater than 90%) were dead, and rare escapers were Dpy Egl. High levels of FOX-1 kill all XO animals only if a spliceable form of intron VI is present. FOX-1 does not repress xol-1 in XO animals if intron VI is absent or is relocated to the 3' UTR without splice junctions. Transgenes lacking intron VI kill XX animals, as do wild-type xol-1 transgenes in strains with a fox-1 null mutation, because all transgenes are expressed at a somewhat higher level than the endogenous xol-1 gene in XX animals. (F) Structures of the three most abundant splice variants of xol-1 transcripts are shown. Only the 2.2 kb variant, which lacks intron VI (red dashed line) and includes essential exon 7 coding sequences (blue) and 3' UTR, is necessary and sufficient for survival of XO animals. This isoform corresponds to Wormbase.org transcript C18A11.5b.1. Transcripts that retain intron VI (2.5 kb isoform corresponding to Wormbase.org transcript C18A11.5c.1) (black dashed line) or lack exon 7 coding sequences (1.5 kb isoform corresponding to Wormbase.org transcript C18A11.5a) (orange dashed line) due to use of an alternative 3' splice acceptor site cannot produce essential XOL-1 male-determining proteins.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
xol-1 transcription is not repressed by high levels of FOX-1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62963/elife-62963-fig2-data1-v3.docx
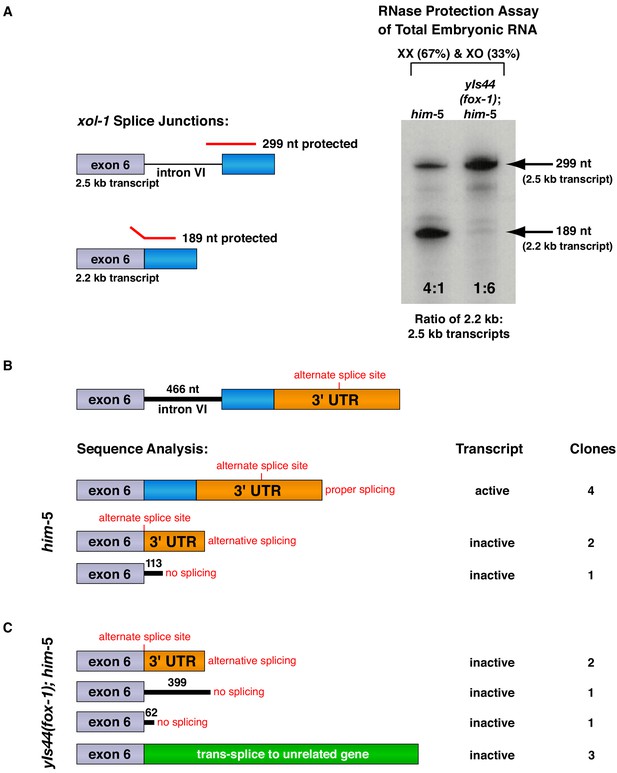
FOX-1 inhibits formation of the active 2.2 kb xol-1 transcript by promoting intron retention and alternative 3' splice acceptor selection.
(A) RNase protection assays show that FOX-1 causes intron VI retention. Shown on the left are diagrams of relevant splice junctions for exon 6 (grey) and coding sequences of exon 7 (blue) that pertain to the inactive 2.5 kb and active 2.2 kb xol-1 transcripts. Also shown are portions of the probe protected against RNase by each transcript: 299 nt for the 2.5 kb transcript and 189 nt for the 2.2 kb transcript. On the right is an image of the RNase protection assay of xol-1 transcripts in him-5 and in yIs44(fox-1); him-5 strains quantified by a phosphorimager. The probe is labeled with 32P-UTP: 43 U residues in the intron VI portion and 44 U residues in the exon 7 portion. Prior to quantifying the ratio of 2.2 kb to 2.5 kb transcripts, the 299 nt signal was divided in half to compensate for its higher number of U residues. The assay demonstrates that FOX-1 inhibits production of the male-determining 2.2 kb transcript by preventing the removal of intron VI. Levels of the act-1 control transcript were also assayed in these two RNA samples (Figure 3—figure supplement 1D). Quantification of a separate RNase protection experiment using this pMN86 probe is shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1B. (B, C) Sequence analysis of cDNA clones from xol-1 transcripts shows that FOX-1 causes intron VI retention and also alternative 3' splice acceptor selection in xol-1. FOX-1 also causes trans-splicing of xol-1 pre-mRNA to pre-mRNA of unrelated genes. Below the diagram of xol-1's relevant intron–exon structure (exon 6 in grey and exon 7 coding sequences in blue) are diagrams representing the splicing pattern revealed by DNA sequence analysis of xol-1 cDNAs from him-5 (B) and from yIs44(fox-1); him-5 strains (C). Also shown are the predicted xol-1 activity states of transcripts with the different splicing patterns and the number of cDNA clones with each pattern. In instances of intron VI retention, the number of intron VI nucleotides in each clone is shown with blue numbers. During trans-splicing (C), the proper 5' donor at the exon 6–intron VI junction was used together with a naturally occurring 3' acceptor at an intron–exon junction of an unrelated gene identified in the text. Resulting trans-splicing events had the junction expected from proper use of the 5' and 3' sites.
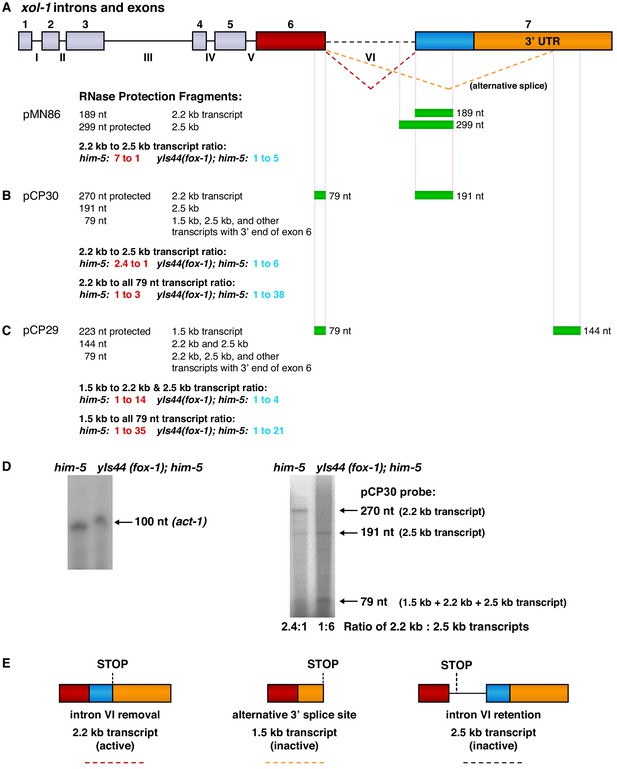
RNase protection experiments show that FOX-1 promotes intron VI retention and partial exon 7 deletion to inhibit formation of the functional 2.2 kb xol-1 transcript.
(A) Diagram (top) shows the intron and exon structure of xol-1 and the alternative splicing patterns that produce the active 2.2 kb transcript (red dashed line indicating intron VI removal), the inactive 2.5 kb transcript (dashed black line indicating intron VI retention), and the inactive 1.5 kb transcript dashed orange line indicating deletion of exon 7 coding sequences (blue) and part of the 3' UTR (orange). Diagrams of the mature transcripts are shown in part (E). Below the intron and exon diagram are maps showing xol-1 locations (green) that are protected by xol-1 transcripts in the different 32P-labeled RNA probes (A) pMN86, (B) pCP30, and (C) pCP29. Sizes of protected fragments expected for each probe for the different xol-1 transcripts are listed on the left. Probe sizes are the following: pMN86, 299 nt; pCP30, 270 nt; pCP29, 223 nt. Quantification is shown for the relative abundance of different transcripts in the him-5 strain versus the yIs44(fox-1); him-5 strain. The high level of FOX-1 in yIs44 increases the abundance of the inactive 2.5 kb and 1.5 kb xol-1 transcripts relative to the active 2.2 kb xol-1 transcript. The abundance of the universal 79 nt protected fragment in the yIs44; him-5 strain indicates that other xol-1 splice variants must exist beyond the 1.5 kb, 2.2 kb, and 2.5 kb transcripts when high FOX-1 levels are provided. (D) (Left) Image of RNase protection assays for a 100 nucleotide probe within the 3' UTR of the control gene act-1 in RNAs of him-5 vs. yIs44(fox-1); him-5 strains quantified by a phosphorimager. The him-5 RNA sample has 1.5 times the amount of protected act-1 probe as that in the yIs44(fox-1); him-5 strain. (Right) Image of RNase protection assays for different xol-1 transcripts using the probe described for pCP30 in (A). The same amount of RNA was used for each strain to assay xol-1 transcripts as used to assay act-1 shown to the left. (E) Diagrams of the three prevalent mature xol-1 transcripts that arise from the different RNA processing events indicated in (A). The colored dashed lines below the diagrams correspond to the splicing events shown in (A).
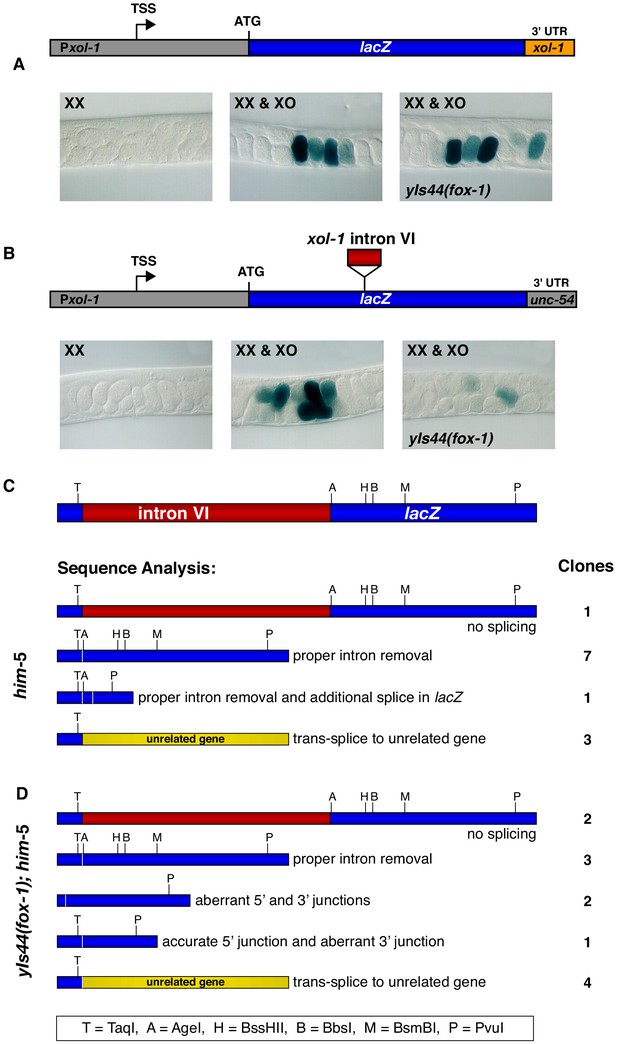
Intron VI of xol-1 is sufficient to confer FOX-1 repression.
(A) The promoter and 3' UTR of xol-1 are not sufficient for FOX-1 to repress xol-1. Below the diagram of the Pxol-1::lacZ::xol-1 3' UTR reporter transgene (pMN27) are sections of adult gonads from different genotypes stained with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-D-galactopyranoside. Genotypes of embryos in the gonads include: (left) XX, unc-76; yEx231 [pMN27 and unc-76 (+)]; (middle) XX and XO, him-5 unc-76; yEx231 [pMN27 and unc-76 (+)]; (right) XX and XO, yIs44(fox-1); him-5 unc-76; yEx231 [pMN27 and unc-76 (+)]. The lacZ reporter is sex-specifically regulated: high levels of β-galactosidase in XO embryos but low levels in XX embryos. High levels of FOX-1 do not diminish β-galactosidase activity in the absence of intron VI, indicating that the xol-1 promoter and xol-1 3' UTR cannot confer FOX-1 repression. Five independent extra-chromosomal array strains of each genotype carrying pMN27 showed the results represented. At least 1000 embryos were examined for each genotype derived from each of the five independent arrays. (B) Intron VI of xol-1 is sufficient for FOX-1 to repress a lacZ reporter gene. Shown is a diagram of the Pxol-1::lacZ::intronVI::unc-54 3' UTR reporter transgene (pMN110) in which the 3' UTR is from the body-wall myosin gene unc-54. Genotypes of adult gonads stained for β-galactosidase activity are the same as listed in (A), except the array is yEx280 [(pMN110) and unc-76 (+)]. This intron VI-containing lacZ reporter is also sex-specifically regulated: active in XO embryos and repressed in XX embryos. High levels of FOX-1 (from yIs44) greatly diminish the level of β-galactosidase activity in XO embryos, indicating that intron VI alone is sufficient for FOX-1 repression. Four independent extra-chromosomal array strains of each genotype carrying pMN110 showed the results represented. At least 1000 embryos were examined for each genotype derived from each of the four independent arrays. (C, D) Sequence analysis of cDNA clones from lacZ transcripts shows that excess FOX-1 increases intron VI retention and also causes alternative pre-mRNA splicing using 3' splice acceptor sites in lacZ via cis-splicing and also 3' splice acceptor sites in unrelated genes via trans-splicing. Below the diagram of lacZ's relevant intron–exon structure and restriction sites is the sequence analysis of lacZ cDNAs from him-5 (C) and from yIs44(fox-1); him-5 (D) strains. Shown are the splicing patterns revealed by DNA sequence analysis and also the number of lacZ clones with each indicated structure. During trans-splicing, the proper 5' donor at the lacZ exon–intron VI junction was used in combination with a naturally occurring 3' acceptor at an intron–exon junction of an unrelated gene (see text).
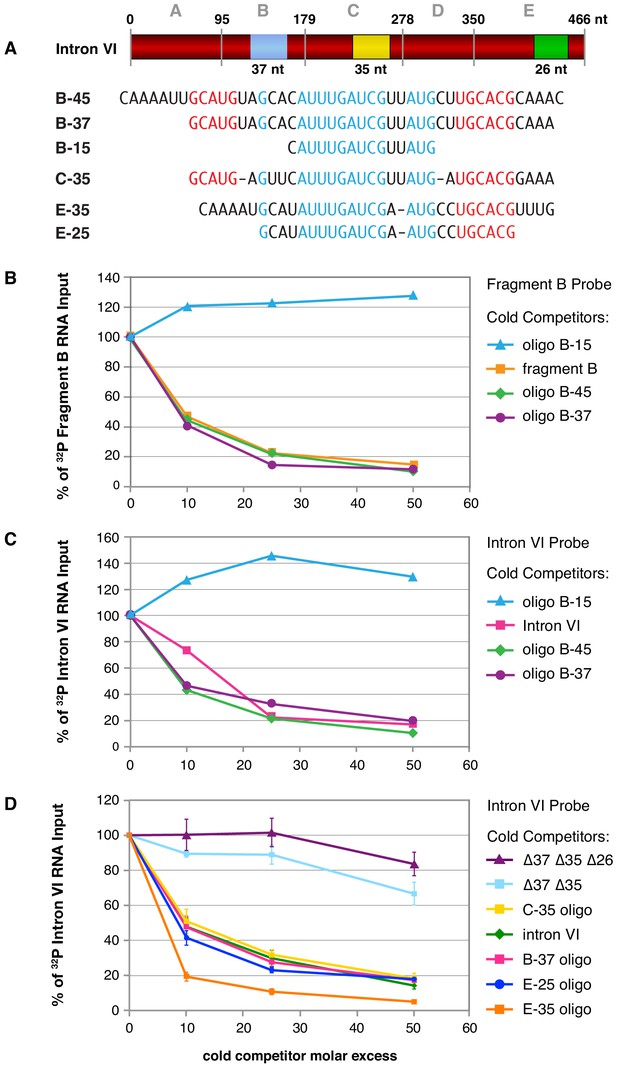
Purified FOX-1 protein binds in vitro to multiple sites in intron VI using motifs GCAUG and GCACG.
(A) The diagram of intron VI shows the intron VI fragments (A–E) and smaller regions (RNA oligonucleotides B-45 to E-25) tested for direct FOX-1 binding in vitro. Only RNAs from fragments B, C, and E bind to purified FOX-1 (Figure 5—figure supplement 1C). Motifs GCAUG and GCACG (red) and sequences common to all three fragments (light blue) are shown below the diagram. Blue, yellow, and green rectangles indicate the locations of sequences B-37, C-35, and E-25, respectively, within FOX-1 binding fragments of intron VI. The RNA oligonucleotides listed were used in competition experiments with 32P-labeled fragment B (panel B) and 32P-labeled intron VI (panels C and D). (B) Small RNA oligonucleotides corresponding to sequences within fragment B compete for FOX-1 binding in vitro. Graphs show cross-linking competition experiments in which binding of FOX-1 (32 ng) to 32P-labeled fragment B RNA was challenged with an increasing molar excess of either cold fragment B RNA or small RNA oligonucleotides to sequences in fragment B that are also found in the other FOX-1 binding regions in fragments C and E. Binding is expressed as the percent of 32P fragment B bound by FOX-1 without any competitor RNA. (C) RNA oligonucleotides compete for FOX-1 binding to intron VI. The cross-linking competition experiments are similar to those in panel (A), except the probe is 32P-labeled full-length intron VI RNA. Binding is expressed as the percent of 32P intron VI bound by FOX-1 without any competitor RNA. The finding that the B-15 oligonucleotide fails to compete with either fragment B probe or intron VI probe, while the B-45 and B-37 oligonucleotides compete well, indicates that GCAUG, GCACG, or both are utilized for FOX-1 binding. (D) FOX-1 binds to multiple sites within intron VI using both GCAUG and GCACG. Graphs show results of cross-linking competition experiments in which binding of FOX-1 (32 ng) to 32P-labeled intron VI RNA was challenged with an increasing molar excess of several cold RNAs, as indicated. Binding is expressed as the percent of 32P intron VI RNA bound by FOX-1 without any competitor RNA. Cold intron VI RNA carrying deletions of the common sequences in B (Δ37) and C (Δ35) competed very poorly with intron VI probe for FOX-1 binding, and cold intron VI with deletions in all three common regions [B (Δ37), C (Δ35), and E (Δ26)] competed even less efficiently, demonstrating the critical role of these sequences in FOX-1 binding. In contrast, RNA oligonucleotides (C-35, B-37, E-35, and E-25) of sequences in fragments B, C, and E competed very effectively with intron VI for binding to FOX-1, further supporting the conclusion that FOX-1 binds to multiple sites in intron VI. The 25 nt RNA oligonucleotide in fragment E contains only the motif GCACG, but not GCAUG, indicating that GCACG promotes robust FOX-1 binding. The deletion in E (Δ26) is one nucleotide longer than the E-25 oligonucleotide, including deletion of a 3' U. Error bars, SEM.
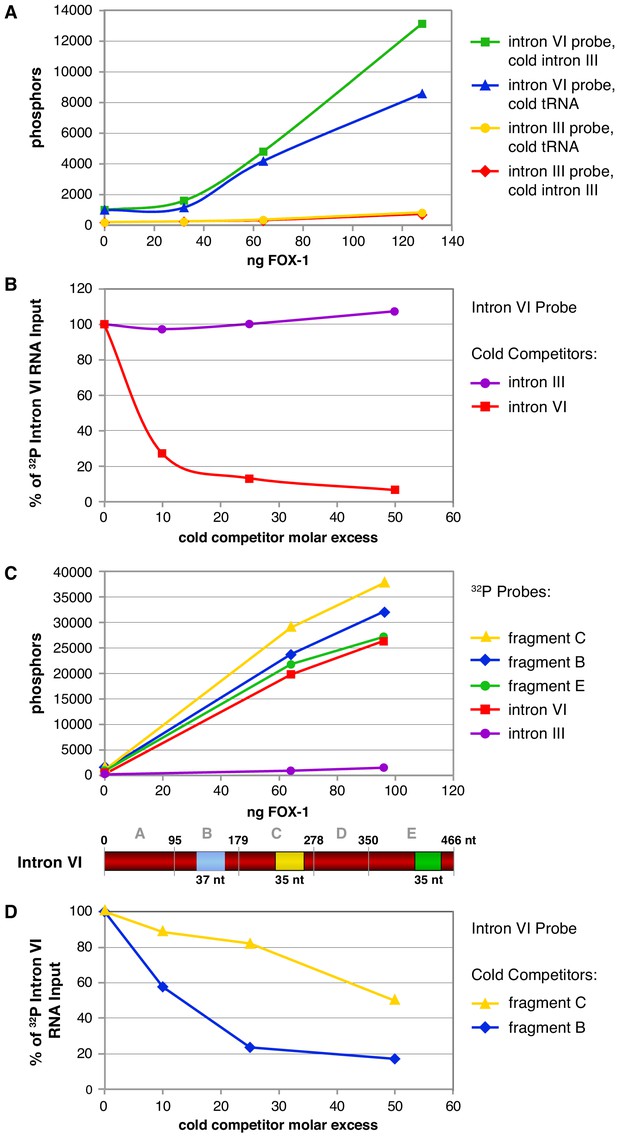
Cross-linking experiments show that FOX-1 binds directly to multiple sites in intron VI.
(A) Graphs show cross-linking experiments comparing binding to 32P-labeled RNA probes of intact intron VI or intron III with different concentrations of purified FOX-1 protein and different cold RNA carriers to inhibit nonspecific FOX-1 binding. Compared are cold intron III RNA (100-fold molar excess) and cold tRNA (100-fold molar excess). FOX-1 binds directly to intron VI but not intron III. tRNA can partially reduce FOX-1 binding to intron VI. (B) Graphs show cross-linking competition experiments in which FOX-1 binding (32 ng) to 32P-labeled intron VI RNA was challenged with an increasing molar excess of either cold intron VI or cold intron III RNA. Intron III RNA does not compete with 32P-labeled intron VI RNA for binding to FOX-1, consistent with it not binding FOX-1 in (A). Binding is expressed as the percent of 32P intron VI RNA bound by FOX-1 without any competitor RNA. Based on experiments in (A) and (B), cold intron III was chosen as the cold carrier for subsequent cross-linking experiments (C) Multiple subregions within intron VI bind directly to FOX-1. Graphs show the results of cross-linking experiments between different concentrations of purified FOX-1 protein and 32P-labeled probes of intact intron III, intron VI, and subregions within intron VI. The diagram of intron VI below the graphs shows the subregions tested for direct binding in vitro. These graphs show that only B, C, and E can bind FOX-1, but they do not reveal the relative binding affinities of the different fragments. (D) Graphs show cross-linking competition experiments in which FOX-1 binding (32 ng) to 32P intron VI RNA was challenged with an increasing molar excess of cold fragment B or cold fragment C RNAs. These graphs confirm that FOX-1 binds to the B and C subregions of intron VI.
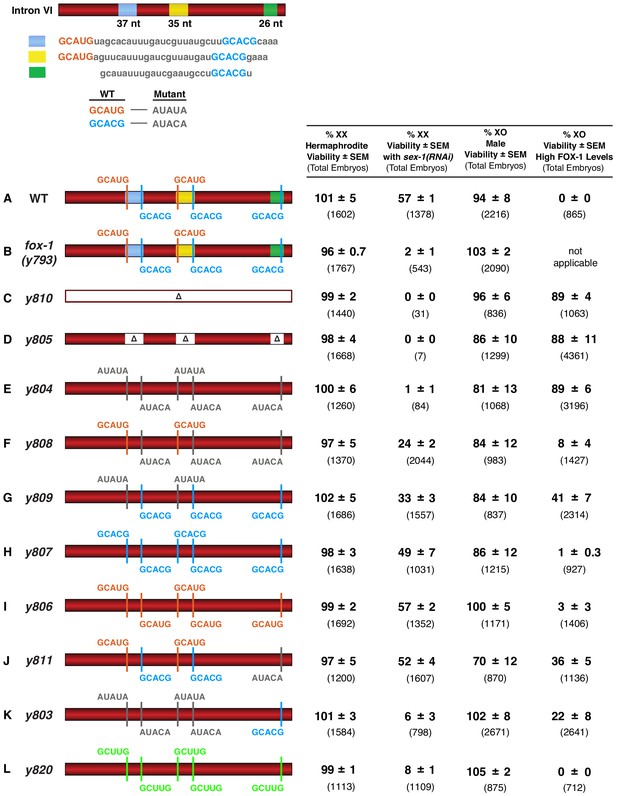
FOX-1 binds in vivo to multiple binding sites in xol-1 intron VI using both GCAUG and GCACG motifs to regulate alternative splicing.
The diagram of intron VI (top left) shows locations of the three regions (blue, yellow, and green) shown to exhibit FOX-1 binding in vitro. RNA sequences corresponding to each color-coded region are shown below the diagram. CRISPR/Cas9 editing was used to modify endogenous DNA encoding these regions and thereby identify cis-acting sites that control xol-1 splicing in vivo. The motif GCAUG was changed to AUAUA, and the motif GCACU was changed to AUACA. (A–L) Diagrams of introns with the different CRISPR/Cas9 edits used for testing xol-1 splicing regulation in vivo are shown on the left side. Multiple assays (right side) evaluate the effects on X:A signal activity of these intron mutations as well as a Cas9-induced deletion of endogenous fox-1(y793). The effects on X:A signal activity are judged by the viability of XX and XO animals with different combinations of X-signal element (XSE) levels. Viability of XX hermaphrodites with mutations only in FOX-1 regulatory regions of xol-1 measures the full contribution of splicing regulation toward X:A signal activity in the context of wild-type XSE levels and hence normal transcriptional repression by XSEs. Viability of XX xol-1 mutants treated with RNAi against the XSE gene sex-1, which encodes a nuclear hormone receptor transcriptional repressor of xol-1, monitors the synergy between transcriptional and splicing regulation when transcriptional regulation is compromised such that xol-1 expression is elevated. XX mutants were treated with sex-1(RNAi) for one generation to cause only partial sex-1 inhibition and enable 57% survival. Viability of XO xol-1 mutant animals in the context of high FOX-1 levels tests the efficacy of single and multiple FOX-1 binding sites on splicing regulation under conditions in which FOX-1 levels are not limiting for splicing regulation. The viability of xol-1 XO mutant animals with wild-type FOX-1 levels serves as a control for any adverse effects of intron VI mutations unrelated to repression by excess FOX-1. All formulae for calculating viabilities of XX and XO animals with different XSE levels are provided in Materials and methods. For all assays, the average viability of multiple broods, each from a single hermaphrodite, is shown with the standard error of the mean (SEM). The total number of embryos scored for viability from all broods is indicated in parenthesis. The experiments show that splicing regulation becomes essential when transcriptional repression is compromised. Multiple FOX-1 binding sites utilizing GCACG and GCAUG motifs are required for full splicing regulation. The number of binding sites is more critical than whether the motif sequence is GCAUG or GCACG. However, replacing all high-affinity motifs with the low-affinity secondary motif GCUUG promotes only minimal non-productive alternative splicing. High-affinity motifs are essential for FOX-1 mediated repression. Eliminating intron VI revealed no greater benefits for male viability than deleting the entire fox-1 gene.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Overexpression of ASD-1 kills both XO males and XX hermaphrodites.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62963/elife-62963-fig6-data1-v3.docx
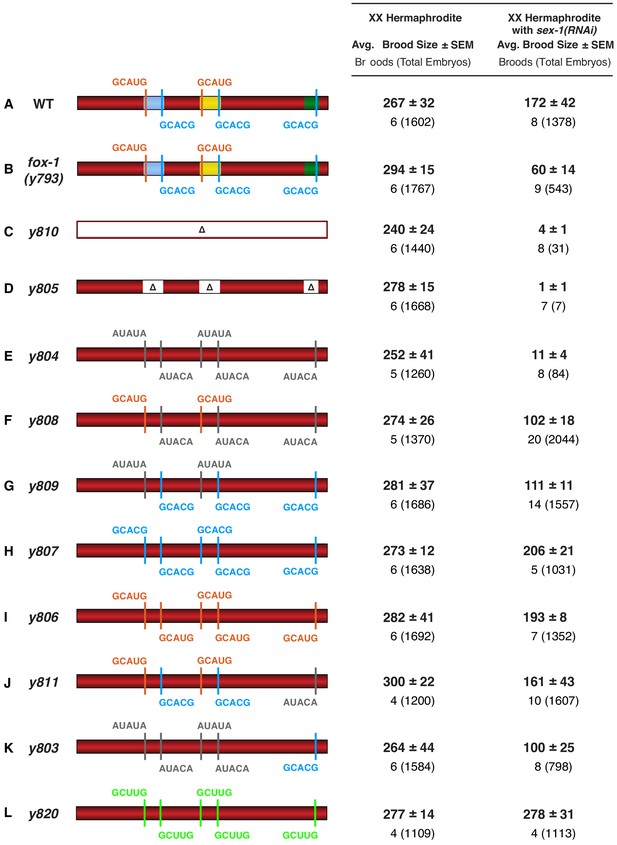
Brood sizes of XX animals with cis-acting xol-1 mutations in intron VI are consistent with the strain viability.
(A–L) The values in this supplemental figure expand upon the viability information for the same XX genotypes provided in Figure 6. Shown are the average brood sizes and SEM (right side) of xol-1 XX mutants with different CRISPR/Cas9 induced mutations in endogenous DNA encoding intron VI (left side). Below the average brood sizes are the numbers of broods counted, each from a single hermaphrodite, with the total number of embryos from all broods in parenthesis. Animals with genotypes in which the viability is reduced also have a corresponding reduction in brood size.
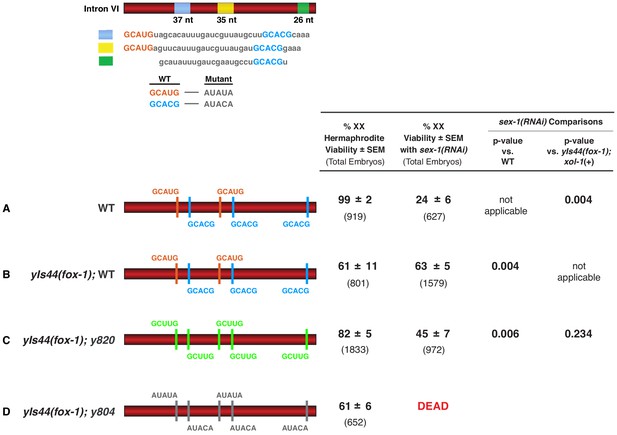
High FOX-1 levels in XX animals repress xol-1 with multiple low-affinity GCUUG motifs in intron VI.
Diagrams on the left show the configurations of wild-type and mutant motifs in intron VI of XX animals with either two doses of fox-1 (A) or high doses of fox-1 supplied by an integrated array (yIs44) carrying multiple copies of fox-1 (B–D). Comparison is shown for viability of these different XX strains with sex-1(RNAi) or without. p-values compare the significance of viability differences among sex-1(RNAi) XX animals. High levels of FOX-1 are not fully tolerated by XX animals, because only 63% of these animals are viable. Nonetheless, it is evident that high levels of FOX-1 suppress the XX-specific lethality caused by sex-1(RNAi) when intron VI has five wild-type high-affinity GCAUG and GCACG motifs (B) or five low-affinity GCUUG motifs (C) but not five mutant motifs (D).
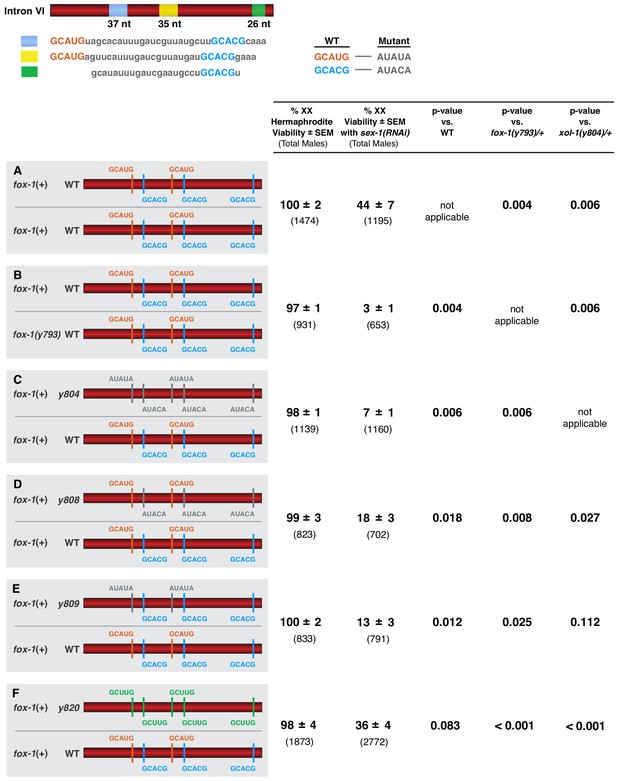
FOX-1 acts in a dose-dependent manner to regulate xol-1 splicing in XX animals and thereby determine sex.
(A–F) Diagrams on the left show sequences for the two different xol-1 intron VI combinations assayed in each cohort of sex-1(RNAi) XX animals to assess the dose-dependence of FOX-1 action in regulating xol-1 splicing. Viability of both sex-1(+) and sex-1(RNAi) animals is shown on the right along with statistical comparisons of viability across different genotypes. Except for (A, B) in which both copies of intron VI have unaltered FOX-1 binding sites, one xol-1 intron VI has mutated FOX-1 binding sites as indicated and one intron has unaltered FOX-1 binding sequences (C–F). (B) Low viability of sex-1(RNAi) XX animals with only one dose of fox-1 [fox-1(y793) / +] shows strong dose-dependence of FOX-1 action in xol-1 splicing regulation. (C–F) The impact of heterozygous combinations of intron VI mutations on viability of sex-1(RNAi) XX animals also indicates that FOX-1 functions as a dose-dependent X signal element to regulate xol-1 splicing and thereby communicate X-chromosome dose. Viability assays were conducted using the protocols that follow. Separate matings were performed between Prps-0::mNeonGreen::4xNLS::unc-54 green males and hermaphrodites of genotypes: wild-type XX for (A), fox-1(y793) XX for (B), xol-1(y804) XX for (C), xol-1(y808) for (D), xol-1(y809) for (E), and xol-1(y820) for (F). For the sex-1(RNAi) experiments, matings were performed on plates with bacteria containing plasmids that produce double-stranded sex-1 RNA when XX animals were young adults. For the control set of matings, males and hermaphrodites were grown on bacteria that do not produce double-stranded sex-1 RNA (pL4440 empty vector control). For both sets of crosses, all green hermaphrodites and green males were counted. Since viability of XO animals is not affected by sex-1(RNAi), the number of green XX hermaphrodites expected if all were viable would be the same as the number of green XO males. Percent XX viability was calculated by (Number of green hermaphrodites/Number of green males) × 100.
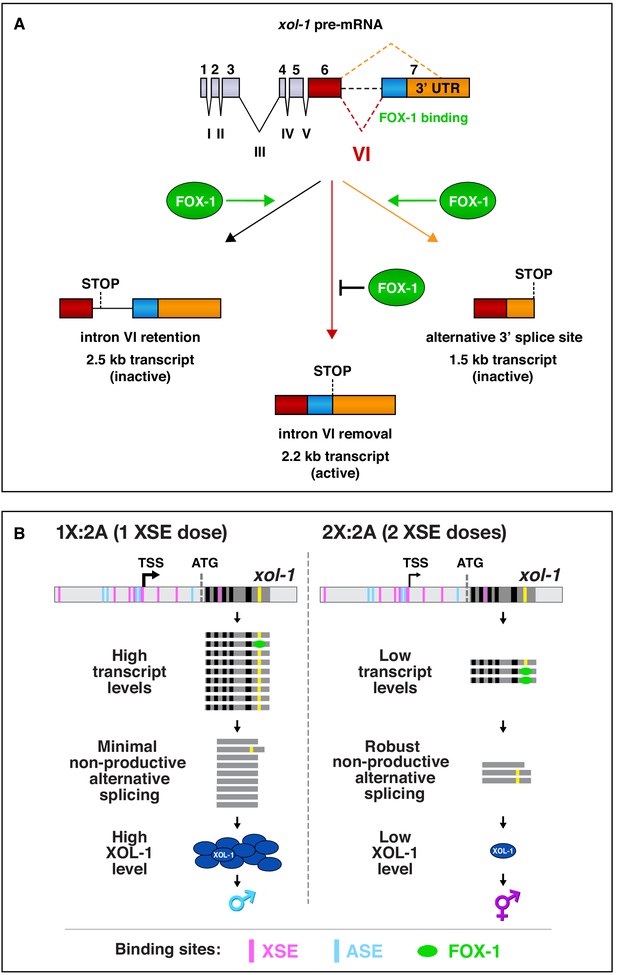
Summary of xol-1 splicing regulation by FOX-1 and model for X:A signal assessment.
(A) Summary of xol-1 splicing regulation by FOX-1. Through binding to multiple GCAUG and GCACG motifs in intron VI of xol-1, FOX-1 reduces formation of the male-determining 2.2 kb transcript by causing intron VI retention (2.5 kb transcript) or by directing use of an alternative 3' splice acceptor site, causing deletion of essential exon 7 coding sequences (blue) and part of the 3' UTR (orange) (1.5 kb transcript). (B) Model for X:A signal assessment: two tiers of xol-1 repression. X-signal elements (XSEs) and autosomal signal elements (ASEs) bind directly to numerous non-overlapping sites in the 5' regulatory region of xol-1 to antagonize each other's opposing transcriptional activities and thereby control xol-1 transcription (Farboud et al., 2013). Molecular rivalry at the xol-1 promoter between the XSE transcriptional repressors and ASE transcriptional activators causes high xol-1 transcript levels in 1X:2A embryos with one dose of XSEs and low levels in 2X:2A embryos with two doses of XSE. All binding sites for the XSEs (nuclear receptor SEX-1 and homeodomain protein CEH-39) are shown in magenta and binding sites for the T-box transcription factor ASE called SEA-1 are shown in blue. Binding sites for the zinc finger ASE called SEA-2 have not been mapped precisely enough in this xol-1 regulatory region to represent. In a second tier of xol-1 repression shown by our studies, the XSE RNA binding protein FOX-1 (green) then enhances the fidelity of X-chromosome counting by binding to numerous GCAUG and GCAUG motifs in intron VI (yellow) of the residual xol-1 pre-mRNA, thereby causing non-productive alternative splicing and hence xol-1 mRNA variants that have in-frame stop codons or lack essential exons. High XOL-1 protein induces the male fate and low XOL-1 permits the hermaphrodite fate. Black rectangles represent xol-1 exons, dark gray rectangles represent xol-1 introns, and light gray rectangles represent 5' and 3' xol-1 regulatory regions.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of primers.
This table includes a complete list of primers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62963/elife-62963-supp1-v3.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
List of target-specific sequences for guide RNAs used in CriSPR/Cas9 genome editing experiments.
This table lists the gene targets, the target-specific sequence for each Cas9 guide RNA, the figure in which the results are presented, the genomic coordinates corresponding to each guide RNA, and the reference name of each guide. Two guides were used together to delete the fox-1 gene, and two guides were used together to replace sequences within intron VI of xol-1. Coordinates are based on Wbcel235/c11 version of the C. elegans genome.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62963/elife-62963-supp2-v3.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
DNA sequences of repair templates used for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing experiments.
This table presents information for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing experiments involving HDR using single-stranded repair templates. The table lists the gene targets that were edited, the figure in which the results are presented, the DNA sequences of the repair template, with SNPs highlighted in red letters and deletion junctions highlighted in blue letters, the reference names of related guides, and the reference names of the oligonucleotide repair template. Two guide RNAs were used together in combination with the repair template to delete the endogenous fox-1 gene, resulting in the allele fox-1(y793). The double-stranded repair templates used for inducing mutations in the DNA encoding intron VI of endogenous xol-1 are available upon request but are too long to include in this table.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62963/elife-62963-supp3-v3.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
List of oligonucleotides used to screen for CRISPR/Cas9 induced mutations and to determine sequences of resulting mutations.
The table lists the gene targets, the figure or table in which the results are presented, the sequences of oligonucleotides used to screen for CRISPR/Cas9 induced mutations or to determine sequences of resulting mutations, the reference name of each oligonucleotide, and the function of each oligonucleotide. For asd-1, the oligos were used to verify the construction of strains built with a pre-existing asd-1 mutation, not for identifying new mutations made using Cas9. The oligonucleotides BF-2507 and BF-2508 were used to synthesize xol-1 repair templates rather than to identify Cas9-induced mutations in intron VI.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62963/elife-62963-supp4-v3.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/62963/elife-62963-transrepform-v3.docx





