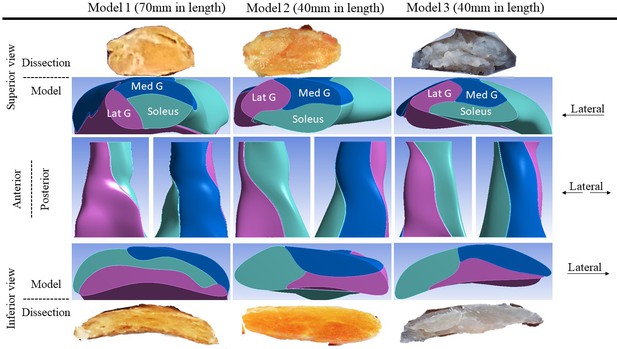
Individual variation in Achilles tendon morphology and geometry changes susceptibility to injury
Figures
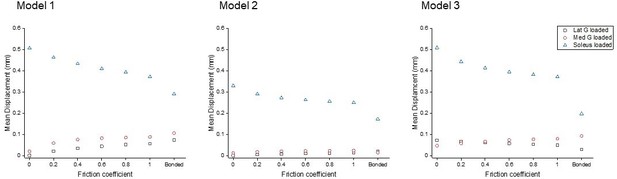
Mean displacement of the proximal soleus face of three models with different friction contacts when each sub-tendon was loaded in isolation.
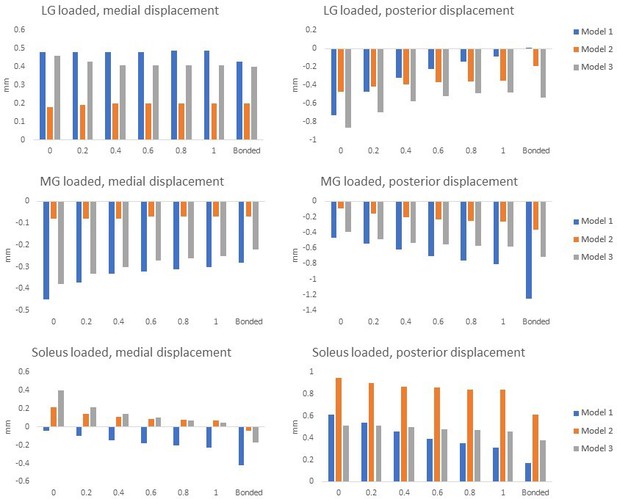
Mean transverse plane displacements (in mm) of the proximal soleus face of the three models with different friction contacts (x-axes) when each sub-tendon was loaded in isolation.
Large variations in displacements and directions were noted between different models under different loading conditions. The scale of the y-axes differs to allow better visualisation of differences in the data.
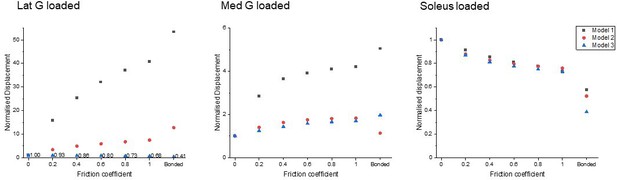
Normalised (to frictionless, coefficient = 0) proximal soleus face displacement of different friction contacts when each sub-tendon was loaded in isolation.
Note the scale of the y-axes differs to allow better visualisation of differences in the data.
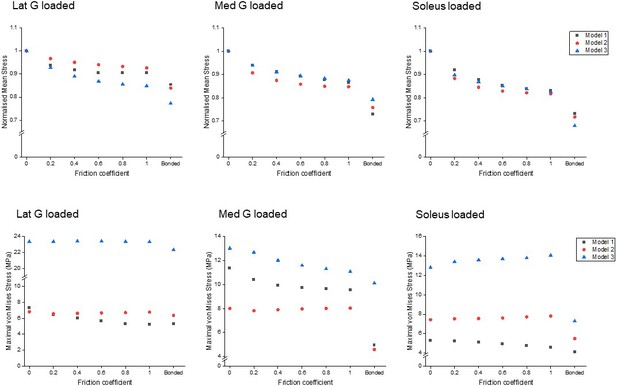
Mean normalised (upper row) and peak (lower row) von Mises stress of the whole Achilles tendon for different friction coefficients when each sub-tendon was loaded in isolation.
Note the scale of the y-axes differs to allow better visualisation of differences in the data.
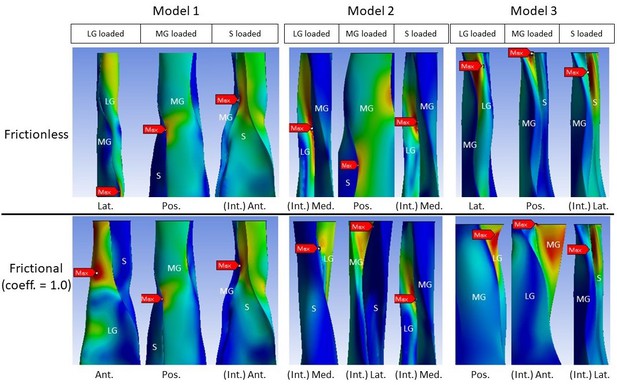
Change in peak stress location when shifting from frictionless (upper row) to frictional (lower row) contact is structure dependent.
LG: lateral gastrocnemius, MG: medial gastrocnemius, S: soleus sub-tendon. View planes: Ant.: anterior, Pos.: posterior, Lat.: lateral, Med.: medial, Int.: internal view with the covering sub-tendon removed.
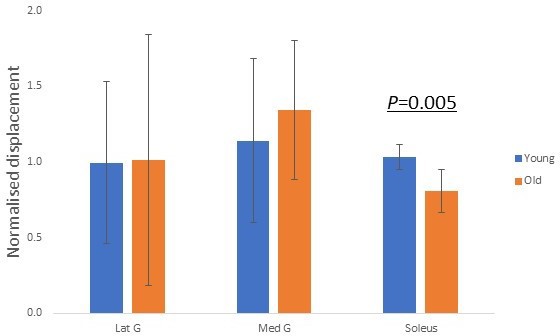
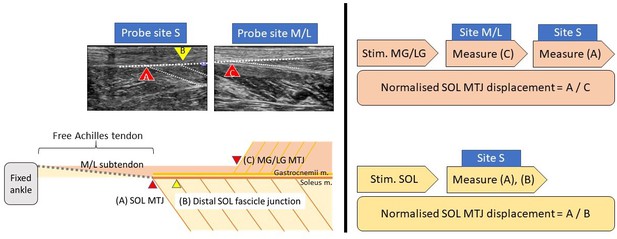
Group differences in normalised soleus junction displacement during different stimulation trials.
Tables
Mechanical testing results of three Achilles sub-tendons.
| Specimen | CSA (mm2) | Failure force (N) | Ultimate stress (MPa) | Ultimate strain (%) | Young’s modulus (MPa) | Stiffness (N/mm) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (age–sex) | LG | MG | S | LG | MG | S | LG | MG | S | LG | MG | S | LG | MG | S | LG | MG | S |
| 69 M | 13.6 | 14.5 | 39.2 | 325.0 | 402.2 | 1701.2 | 24.0 | 27.7 | 45.3 | 9.7 | 10.0 | 19.1 | 353.9 | 375.8 | 399.4 | 79.9 | 97.6 | 260.6 |
| 78 F | 12.4 | 10.8 | 20.6 | 154.7 | 571.1 | 1155.6 | 12.5 | 52.6 | 56.2 | 11.6 | 8.9 | 17.5 | 175.0 | 771.1 | 421.1 | 36.7 | 145.6 | 167.8 |
| 84 F | 5.7 | 10.7 | 30.9 | 503.6 | 621.8 | 1577.0 | 89.0 | 58.3 | 51.0 | 8.9 | 12.2 | 10.4 | 1231.5 | 636.9 | 734.9 | 118.2 | 121.4 | 385.1 |
| 85 F | 10.4 | 14.0 | 38.2 | 787.5 | 688.3 | 1090.9 | 75.8 | 49.0 | 28.6 | 11.9 | 10.6 | 15.8 | 853.6 | 617.2 | 239.9 | 151.7 | 144.7 | 156.6 |
| 87 M | 4.6 | 17.0 | 35.2 | 301.6 | 647.7 | 1578.5 | 65.9 | 38.1 | 44.9 | 8.2 | 10.2 | 10.8 | 1033.4 | 496.2 | 606.2 | 80.9 | 143.0 | 349.6 |
| Mean | 9.3* | 13.4* | 32.8 | 414.5* | 586.2* | 1420.6 | 53.4 | 45.1 | 45.2 | 10.1 | 10.4 | 14.7 | 729.5 | 579.4 | 480.3 | 93.5* | 130.5* | 263.9 |
| SD | 4.0 | 2.7 | 7.6 | 242.5 | 111.3 | 277.1 | 33.4 | 12.2 | 10.4 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 3.9 | 449.5 | 149.9 | 192.7 | 43.5 | 20.9 | 103.4 |
-
CSA: cross-sectional area, LG: lateral gastrocnemius, MG: medial gastrocnemius, S: soleus sub-tendon. *Significantly different from soleus sub-tendon after post hoc analysis (p<0.017).
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Statistical analysis outcome of three sub-tendon mechanical properties.
(File separated uploaded).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63204/elife-63204-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63204/elife-63204-transrepform-v1.docx