Deficient spermiogenesis in mice lacking Rlim
Figures
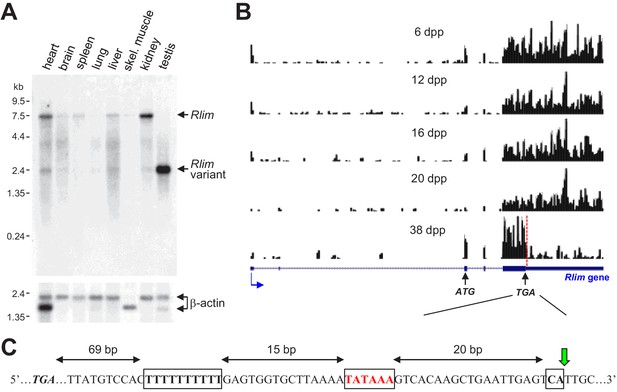
A short Rlim mRNA variant highly expressed in testis is generated via alternative polyadenylation in mature male mice.
(A) A Northern blot containing RNA extracts from various adult mouse tissues (WT for Rlim) was hybridized with an Rlim probe (upper panel) and a probe recognizing β-actin as loading control (lower panel). (B) Modified from the UCSC Genome Browser: Cumulative raw reads from RNA-seq datasets of testes RNA isolated from post-natal mice at 6, 12, 16, 20, and 38 days post-partum (dpp) (Margolin et al., 2014) were mapped on the Rlim locus (variable scales). Structure of the Rlim gene is shown below in blue with boxed exon regions. Protein coding regions are indicated in thicker stroke. Blue arrow indicates direction of transcription. ATG start codon, TGA stop codon and site of alternative polyadenylation sequence (red dotted line) is indicated. Note low relative read density 3’ of the alternative polyadenylation site specifically in 38 dpp animals. (C) Nucleotide sequence containing an alternative polyadenylation site downstream of the TGA stop codon. Conserved motifs including a T-rich sequence, A/TATAAA, and CA motifs are boxed. The cleavage position is indicated (green arrow).
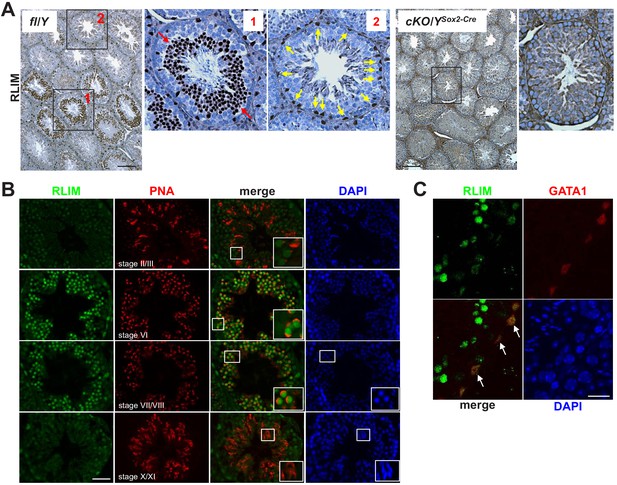
High RLIM protein expression specifically in round spermatids and in Sertoli cells.
Tissue sections of mouse testes were stained using IHC with indicated antibodies. Boxed areas are shown in higher magnification. (A) DAB staining of testes sections generated from fl/Y and, as negative control, Rlim cKO/YSox2-Cre males littermates using antibodies against RLIM. Left panel: fl/Y male. Red arrows (box 1) and yellow arrows (box 2) point at spermatogenic cells and cells located in the periphery of seminiferous tubules that exhibit high RLIM staining, respectively. Right panels: cKO/Y male. Scale bars = 150 μm. (B) IHC on fl/Y testis co-staining with antibodies against RLIM (green) and PNA (red) to determine differentiation stages of spermatogenic cells within seminiferous tubules (indicated). Scale bar = 60 μm. (C) IHC on fl/Y testis co-staining with antibodies against RLIM (green) and GATA1 (red), a Sertoli cell marker. Scale bar = 25 μm.
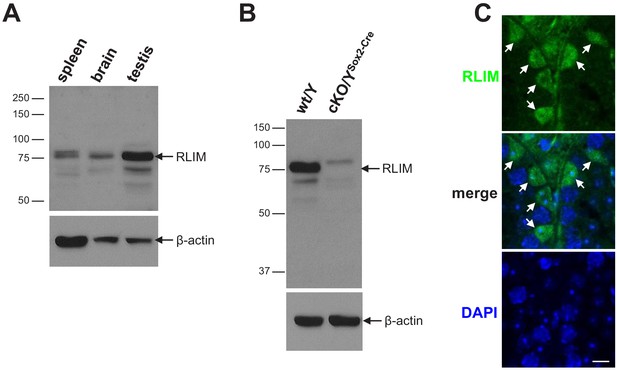
RLIM protein in testis.
(A) Comparison of RLIM protein expression in mouse spleen, brain, and testis using western blot analysis. Note high levels of full-length RLIM (arrow) in testis. As loading control, the same blot was stripped and hybridized with antibodies against β-actin (lower panel). (B) RLIM (arrow) is undetectable in testis of cKO/YSox2-Cre males. A slightly higher migrating band is unspecific. (C) IHC staining of sections from WT/Y testis using RLIM antibodies. Note RLIM-positive cells in the periphery of seminiferous tubules (arrows) containing triangular-shaped nuclei. Scale bar = 10 μm.
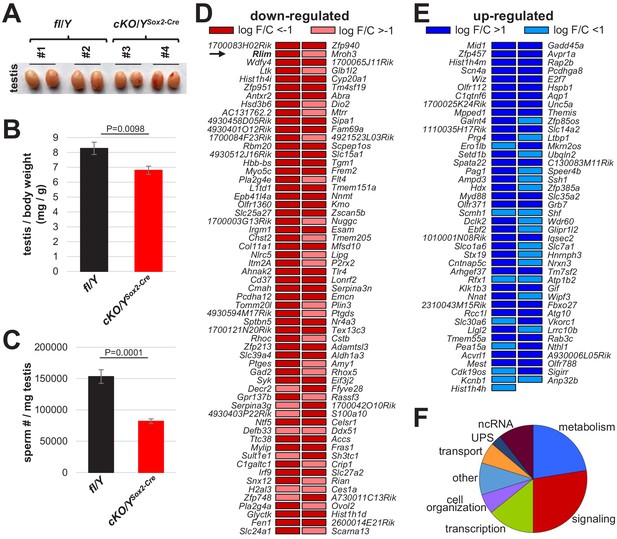
Lack of Rlim affects sperm production.
Males systemically lacking Rlim were generated via Sox2-Cre mediated Rlim deletion (cKO/YSox2-Cre) and directly compared to fl/Y male littermates at 8 weeks of age. (A) Deletion of Rlim results in smaller testes. Representative testes isolated from adult male fl/Y control animals (#1,2) and cKO/YSox2-Cre littermates (#3,4) are shown. (B) Significantly decreased weight of testes isolated from cKO/YSox2-Cre animals (n = 9) when compared to fl/Y littermates (n = 7). Values were normalized against total body weight and represent the mean ± s.e.m. p Values are shown (students t-test). (C) Significantly decreased numbers of sperm in animals lacking Rlim. Cauda epididymal sperm were collected via swim-out in HTF medium. After 10 min of swim-out, total sperm numbers were determined (n = 7 fl/Y; n = 9 cKO/YSox2-Cre). s.e.m. and p Values are indicated. (D, E) Differentially expressed genes in testes of fl/Y and cKO/YSox2-Cre mice as determined by RNA-seq experiments on biological replicates. Genes significantly (p<0.05) down-regulated and up-regulated upon the Rlim deletion in each experiment are shown in (C) and (D), respectively. Arrow indicates Rlim. (F) Differentially expressed genes distribute in eight functional categories that include metabolism, signaling, transcription, cell organization, transport, UPS, ncRNA and other.
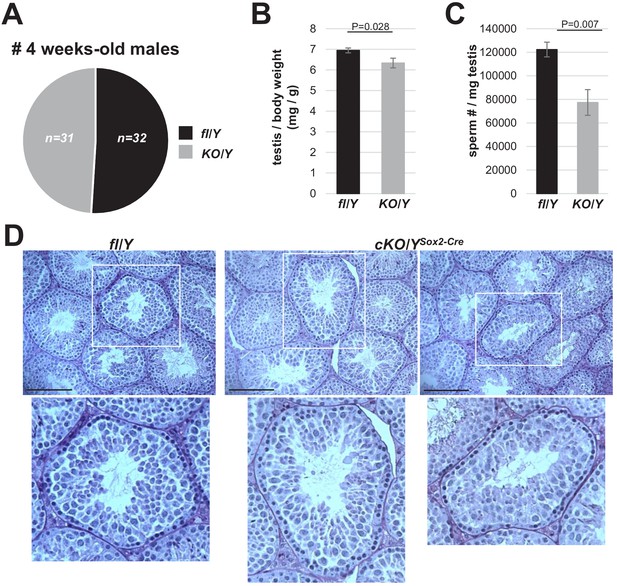
Decreased sperm production in males lacking Rlim.
(A) Rlim has no essential functions during male embryogenesis and post-natal development. Using Rlimfl/KO as dames, a similar number of males out of 9 litters receiving a germline KO or the fl Rlim allele were born and appeared healthy beyond 4 weeks of age. (B) Significantly decreased weight of testes isolated from 8 weeks old cKO/Y animals (n = 8) when compared to fl/Y littermates (n = 6). Values were normalized against total body weight and represent the mean ± s.e.m. p Values are shown (students t-test). (C) Significantly decreased numbers of sperm in animals lacking Rlim. Cauda epididymal sperm were collected via swim-out in HTF medium. After 10 min of swim-out, total sperm numbers were determined (n = 6 fl/Y; n = 9 cKO/Y). s.e.m. and p Values are indicated. (D) No major difference in seminiferous tubules at step nine between fl/Y and cKO/YSox2-Cre in PAS-stained testes sections. Scale bars = 150 μm.
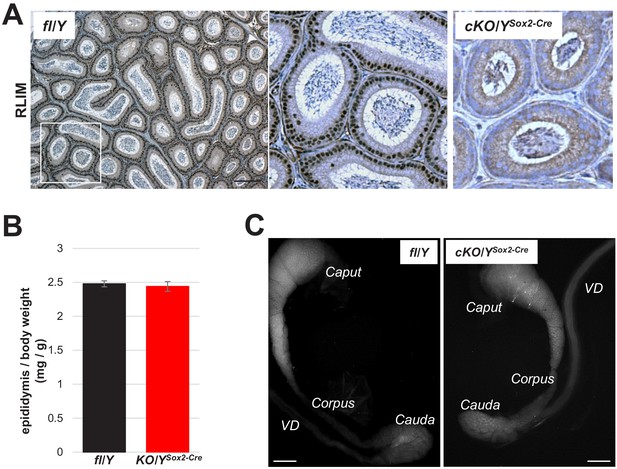
Normal epididymal appearance in males lacking Rlim.
(A) Robust staining of most/all nuclei of epithelial cells lining epididymal tubules in IHC on a cross-section through the Cauda region of fl/Y males using Rlim antibodies. cKO/YSox2-Cre sections served as control. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Similar weights of fl/Y and cKO/YSox2-Cre epididymides (n = 9 animals, each). (C) Visualization of epididymal structure via de-lipidation. Caput, Corpus, Cauda regions as well as Vas Deferens (VD) are indicated.
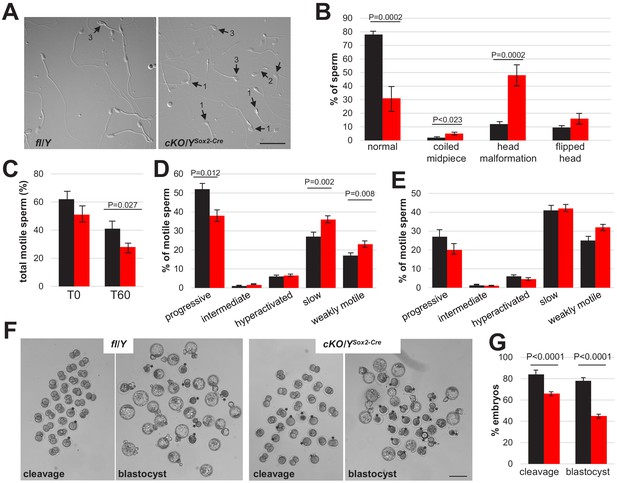
Increased abnormalities and decreased functionality in sperm lacking Rlim.
Cauda epididymal sperm were collected via swim-out from 8-week-old males (n = 7 fl/Y ▪; n = 9 cKO/YSox2-Cre). (A) Sperm morphology was assessed by light microscopy. Representative images of difference interference contrast (DIC) display the morphological patterns found indicated by arrows: 1, Head malformation; 2, Coiled midpiece; 3, Flipped head. Scale bar = 25 µm. (B) Quantification of the morphology patterns. Percentages of normal sperm, coiled midpiece, head malformation, and flipped head out of the sperm population. At least 100 sperm per sample were counted, total sperm counted 1146 for fl/Y and 1077 for cKO/YSox2-Cre. Values represent the mean ± s.e.m. (C) Sperm motility was evaluated in the swim-out (T0) and after 60 min of incubation in conditions that support capacitation (T60). Sperm motility was examined using the CEROS computer-assisted semen analysis (CASA) system. Percentage of total motile sperm in the population. n = 12, values represent the mean ± s.e.m. (D) Classification of type of motility (progressive, intermediate, hyperactivated, slow, and weakly motile; in percentage) out of the total motile population at T0. n = 12, values represent the mean ± s.e.m. (E) Classification of type of motility (in percentage) out of the total motile population after 60 min of incubation in capacitation conditions (T60). n = 12, values represent the mean ± s.e.m. (F) Representative images for cleavage and blastocyst stages at 24 hr and 96 hr, respectively. Asterisks indicate embryos not reaching anticipated embryonic stage. Scale bar = 100 μm. (G) Summary of IVF results. n = 142 and 313 presumed oocytes for fl/Y and cKO/Y sperm, 7 and 8 animals, respectively. Values represent the mean ± s.e.m.
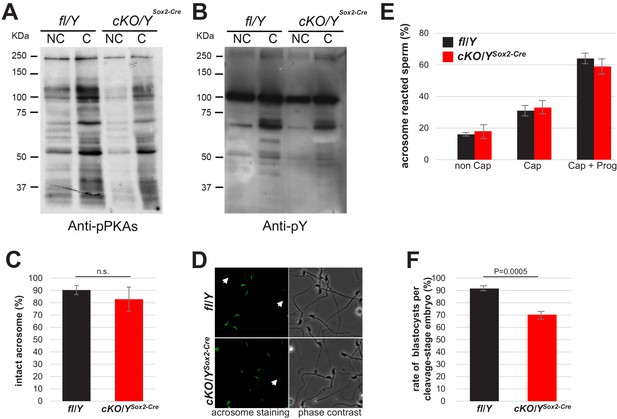
Evaluation of molecular and physiological events related to sperm capacitation.
Sperm were incubated at 37°C for 60 min in m-TYH (non-capacitating conditions, NC) or in m-TYH supplemented with 15 mM NaHCO3 and 5 mg/ml BSA (capacitating conditions, (C)). (A) After 60 min of incubation proteins were extracted, subjected to SDS–PAGE, and electro-transferred to PVDF membranes. Then, phosphorylation of PKA substrates was detected by immunoblotting with Anti-pPKAs antibody. Representative image of four independent experiments. (B) Membranes were stripped and then phosphorylation of proteins in tyrosine residues (pY) was detected by immunoblotting with Anti-pY antibody. Representative image of four independent experiments. (C) Evaluation of capacitation through the ability to acrosome react. After 60 min of capacitation in m-TYH Cap medium, sperm samples were incubated with progesterone (Prog, 10 µM) or with DMSO (vehicle) in m-TYH Cap at 37°C for additional 30 min, and then acrosomal status was assessed by Alexa Fluor 488-PNA staining. Acrosome reaction after 90 min in non-capacitating (Non Cap) conditions was also evaluated. Results are indicated in percentage of acrosome reacted sperm. n = 4, at least 200 sperm per sample were counted. Values represent the mean ± s.e.m. (D) Evaluation of acrosomal status by Alexa Fluor 488-PNA staining. Representative fluorescence images of the acrosomal staining (left panel), and their corresponding phase contrast images (right panel). (E) Sperm displaying uniform fluorescence along their acrosomes were counted as intact. n = 9, at least 200 sperm per sample were counted. Values represent the mean ± s.e.m. (F) Rates of blastocysts per cleavage staged embryos sired by fl/Y or cKO/YSox2-Cre sperm in IVF.
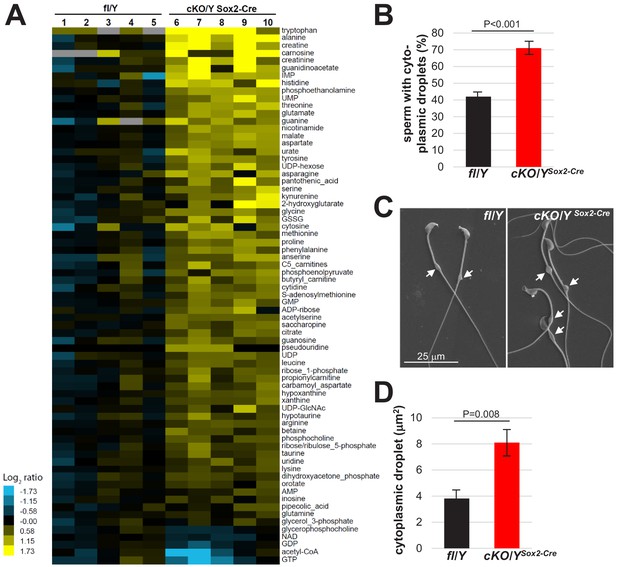
Increased size of cytoplasmic droplet in caudal sperm of males lacking Rlim.
(A) Cauda epididymal sperm were collected from 8-week-old fl/Y or cKO/YSox2-Cre mice and polar metabolites were determined via LC-MS. Samples were run and data analyzed by the Metabolite Profiling Core Facility at the Whitehead Institute. Note general increased content of metabolites in cKO/YSox2-Cre sperm. (B) Cauda sperm was collected from 8-week-old fl/Y or cKO/YSox2-Cre mice and after 10 min separation, immediately fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde followed by SEM analysis. Sperm with or without cytoplasmic droplets were counted. n = 250, each. (C) Increased size of cytoplasmic droplets in cKO/YSox2-Cre sperm. Representative images are shown. Droplets are indicated by arrows. (D) Increased size of cytoplasmic droplets in cKO/YSox2-Cre sperm. Droplet surface size was determined via ImageJ. n = 100, each.
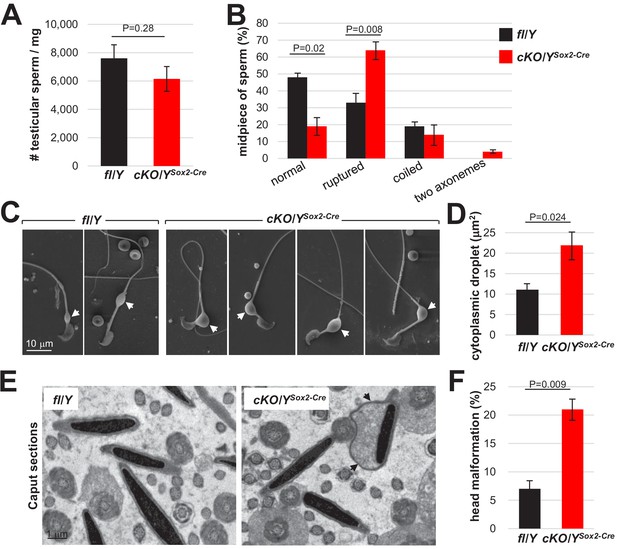
Rlim plays important roles for cytoplasmic reduction.
Analyses of testicular sperm isolated from 8 weeks-old fl/Y or cKO/YSox2-Cre mice. (A) Quantification of sperm yield normalized against testis weight. n = 30, each genotype. (B) Quantification of sperm morphology scoring ruptured, coiled sperm and sperm with two axonemes. n = 250. (C) Larger cytoplasmic droplets in cKO/YSox2-Cre sperm. Representative images are shown. Droplets are indicated by arrows. (D) Increased size of cytoplasmic droplets in cKO/YSox2-Cre sperm. Droplet surface size was determined via ImageJ. n = 100, each. (E) Sperm head malformations within the epididymal Caput region as determined via TEM. Representative images are shown. Arrows point at cytoplasmic pocket. (F) Quantification of sperm exhibiting excessive head cytoplasmic pocket.

Evaluation of sperm structure within testes of cKO/YSox2-Cre animals.
(A) Examples of cKO/YSox2-Cre sperm exhibiting two axonemes (SEM). Left panel: Sperm with two axonemes. Boxed area is shown in higher magnification. Middle panel: Sperm with two axonemes and ruptured midpiece. Right panel: TEM showing sperm with two axonemes, as indicated by the same orientation of dynein arms. (B) Head malformations as detected in TEM on testes sections are indicated by arrows. Arrows point at cytoplasmic pockets. (C, D) No major structural deficiencies were detected via TEM on testes sections in the midpiece (C) and the tail (D). 1=inner microtubule doublet of the axoneme (2); 2=outer microtubule doublet of the axoneme (9); 3=fibrous sheath; 4=plasma membrane.
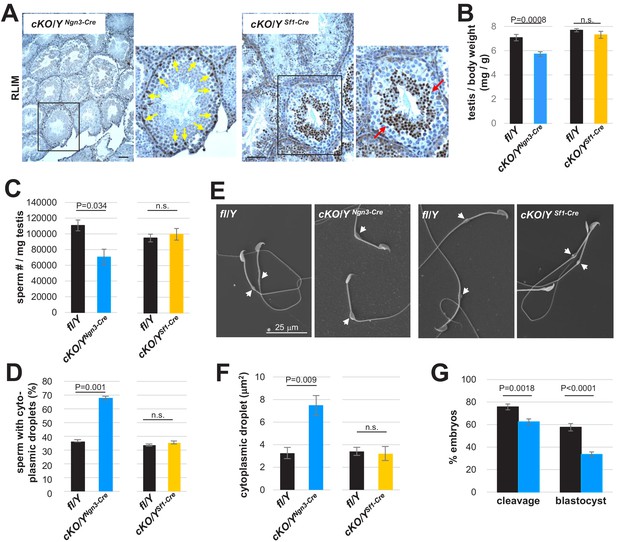
Functions of Rlim predominantly in the spermatogenic cell lineage.
Animals with an Rlim cKO in the spermatogenic cell lineage or in Sertoli cells were generated via Ngn3-Cre and SF1-Cre (cKO/YNgn3-Cre and cKO/YSF1-Cre), respectively. (A) IHC on testis sections of cKO/YNgn3-Cre and cKO/YSF1-Cre animals using RLIM antibodies. Correct targeting is indicated by lack of RLIM specifically in spermatogenic cells but not Sertoli cells (yellow arrows) in cKO/YNgn3-Cre animals, and in Sertoli cells but not round spermatids (red arrows) in cKO/YSF1-Cre males. Scale bars = 75 μm. (B) Significantly decreased weight of testes isolated from cKO/YNgn3-Cre males but not from cKO/YSf1-Cre animals (n = 18 fl/Y; 14 cKO/YNgn3-Cre) (n = 16 fl/Y; 10 cKO/YSf1-Cre). cKO animals were directly compared to their respective fl/Y male littermates at 8 weeks of age. Values were normalized against total body weight and represent the mean ± s.e.m. p Values are shown (students t-test). (C) Significantly decreased numbers of sperm isolated from cKO/YNgn3-Cre males but not from cKO/YSf1-Cre animals. Cauda epididymal sperm were collected via swim-out in HTF medium. After 10 min of swim-out, total sperm numbers were determined (n = 7 fl/Y; n = 9 cKO/YNgn3-Cre; n = 9 fl/Y; n = 11 cKO/YSf1-Cre). s.e.m. and p values are indicated. (D) Cauda sperm was collected from 8 weeks-old mice and visualized via SEM (n = 3 per genotype). Sperm with or without cytoplasmic droplets were counted. n = 250, per animal. (E) Increased size of cytoplasmic droplets in cKO/YNgn3-Cre sperm. Representative SEM images are shown. Upper panels: cKO/YNgn3-Cre and fl/Y control. Lower panel: cKO/YSf1-Cre and fl/Y control. Droplets are indicated by arrows. (F) Summary of cytoplasmic droplets in cKO/YNgn3-Cre sperm. Droplet surface size of SEM images was determined via ImageJ. n = 100, each. (G) Summary of IVF using sperm isolated from cKO/YNgn3-Cre and littermate control males. n = 262 and 324 presumed oocytes for fl/Y and cKO/Y sperm, respectively, seven animals, each. Values represent the mean ± s.e.m.
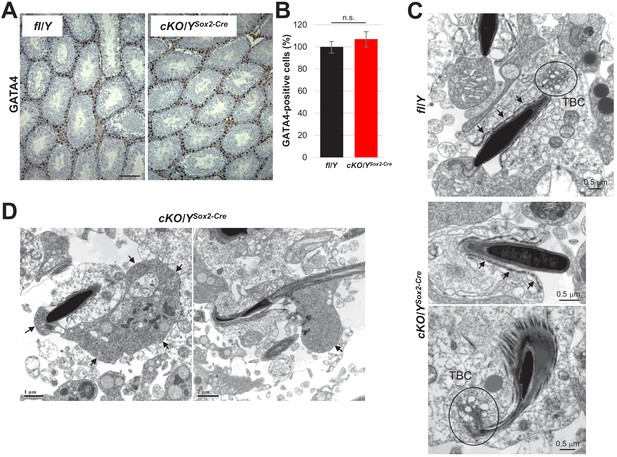
Normal numbers of Sertoli cells in testes lacking Rlim.
(A) DAB staining of paraffin-embedded testes sections of cKO/YSox2-Cre and fl/Y animals using antibodies against Sertoli cell marker GATA4. Scale bars = 150 μm. (B) Quantification of GATA4-positive cells within seminiferous tubules. (C) Normal development of Sertoli cell structures during spermiation in animals lacking Rlim as shown via TEM on testes sections including the apical ectoplasmic specialization (ES; arrows) and the apical tubulobulbar complex (TBC circled). (D) Cytoplasmic reduction during spermiation in mice lacking Rlim (TEM). Arrows point at spermatid cytoplasmic lobes being shed during spermiation.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Rlimflox | PMID:20962847 | MGI:1342291 | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Sox2-Cre | Jackson Laboratory | JAX #008454 | PMID:14516668 |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Neurog3-Cre (Ngn3-Cre) | PMID:15183725 | JAX #005667 | Dr. Andrew Leiter (UMMS) |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Sf1-Cre | Jackson Laboratory | JAX #012462 | PMID:16423694 |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-Rlim (rabbit polyclonal) | PMID:11882901 | IHC (1:250) WB (1:1000) | |
| Antibody | Rat anti-GATA1 (rat monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc265 | IHC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-GATA4 (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab84593 | IHC (1:500) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-phosphoPKA (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling clone 100G7E | 9624 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti-PY (mouse monoclonal) | Millipore clone 4G10 | 05–321 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | Mouse anti- β-actin (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc47778 | WB (1:250) |
| Antibody | Rabbit anti-cleaved caspase3 (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling | ab9664 | IHC (1:300) |





