Learning precise spatiotemporal sequences via biophysically realistic learning rules in a modular, spiking network
Figures
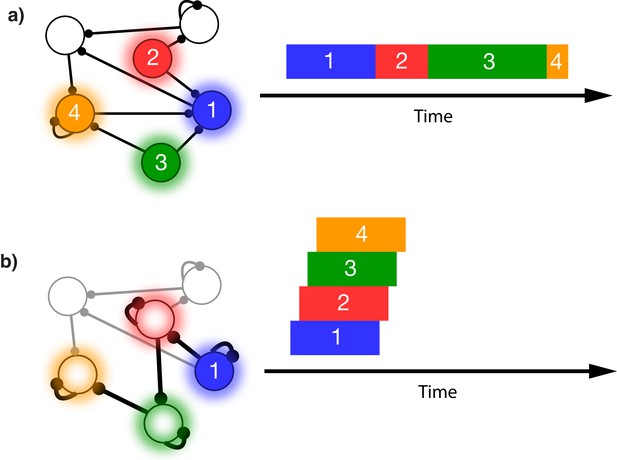
Sequence representation in networks.
(a) A network composed of different populations of cells, each population is activated by a specific stimulus, and there are plastic connections between and within these populations. Initially these connections are random and weak. Upon presentation of a sequence of stimuli (filled circles, left), the populations will become activated for the duration and in the order in which they are stimulated (right). (b) After many presentations of a particular sequence, successful asymmetric Hebbian learning encodes the order of the stimuli into the synaptic weights of the network. After training, upon presentation of the first element of the sequence (filled circle, left), the network can recall (right) the order of presentation, but the timing and duration of each element is lost. In a generic network such as this, the timing of recall is determined by intrinsic time constants of the system and not the duration in the sequence that was presented.
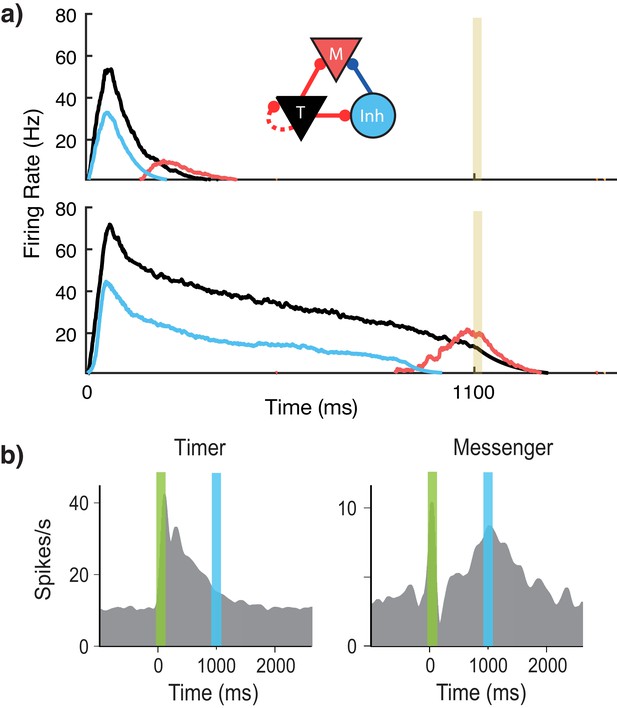
Microcircuit learns time intervals.
(a) Mean firing rates of Timer (black), Messenger (red), and inhibitory populations (light blue) in a microcircuit before learning (top) and after learning (bottom) to represent an 1100 ms interval. Inset: Core neural architecture (CNA) microcircuit. Solid lines indicate fixed connections, while dotted lines indicate learned connections. (b) Timer and Messenger cell type responses to delayed reward task in V1. Green bar represents stimulus and blue bar represents reward. Schematic representation of data from Liu et al. (2015).
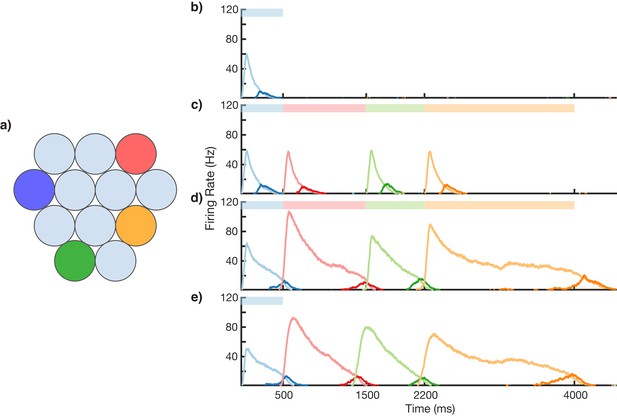
Sequence learning and recall.
(a) Network of 12 columns, each containing a core neural architecture (CNA) microcircuit selective for a different stimulus. Columns containing microcircuits responding to blue, red, green, and orange stimuli are indicated. (b–e) Mean firing rates for Timer cells (light colors) and Messenger cells (dark colors) of four different columns during different stages of learning. Stimuli presented are shown as color bars in the top of plots. During learning, columns are stimulated in the sequence indicated by the color bars (500, 1000, 700, and 1800 ms for blue, red, green, and orange, respectively). (b) Before learning, the stimulation of a particular column only causes that column to be transiently active. (c) During the first trial of learning, all columns in the sequence become activated by the stimuli but have not yet learned to represent duration (through recurrent learning of Timer cells) or order (through feed-forward learning of the Messenger cells). (d) After many trials, the network learns to match the duration and order of presented stimuli. (e) After learning, presenting the first element in the sequence is sufficient for recall of the entire sequence. Figure 3—figure supplements 1–6 provide additional information on the network’s construction, accuracy, robustness, spiking statistics, dynamics, and limits.
Input layer dynamics.
(a) Simulations showing response of input layer units to 400 ms stimulus (fixed spot size, seven degrees). The input is approximated as a 50 ms pulse of Poisson spikes. This is the approximation used in the main figures of the paper. (b) Same as (a), but with input approximated by a 50 ms pulse of Poisson spikes followed by a decaying exponential tail of Poisson spikes for the remainder of the stimulus time. (c) Recall of a learned sequence, in a network with the ‘pulse+decaying tail’ input structure, as in (b).
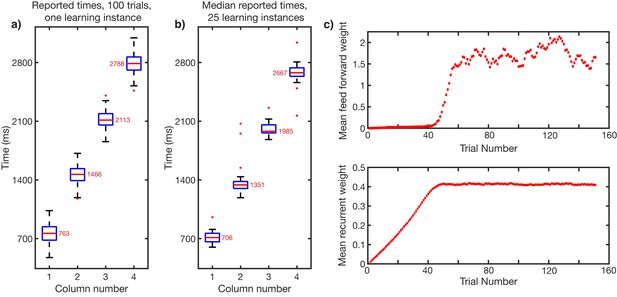
Accuracy of learning and recall.
A network is trained to a sequence of four elements, each 700 ms in duration. Owing to stochastic nature of spiking network, reported times can fluctuate from presentation to presentation, and from learning instance to learning instance. ‘Reported time’ is the time at which the sequence, up to and including that column, drops below 10 Hz. (a) Recall fluctuations. Reported times for 100 trials of recall, after one learning instance. Median reported time indicated by red bar. Top and bottom of box indicate 25th and 75th percentiles of reported times. The whiskers indicate the maximum and minimum reported times not considered outliers. Red dots indicate outliers. (b) Learning fluctuations. Reported times over 25 learning instances. Each data point in the box and whisker in (b) is the median reported time for 100 recall trials (red bars in a) for one particular learning instance. (c) Evolution of weights in during training for network shown in (a). Top, evolution of mean feed-forward weights from column one to column two. Bottom, evolution of mean recurrent weights in column one.
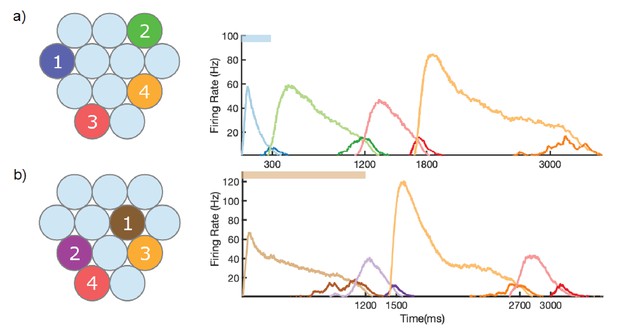
Learning of different sequences.
Left, identity and order of stimuli shown during training. Right, mean firing rate of network after training, upon stimulation of first column in sequence. (a) Blue, green, red, and orange columns (numbers 4, 3, 11, 10) stimulated at times of 0, 300, 1200, and 1800 ms, respectively. (b) Brown, purple, orange, and red columns (numbers 6, 8, 10, 11) stimulated at times of 0, 1200, 1500, and 2700, respectively.
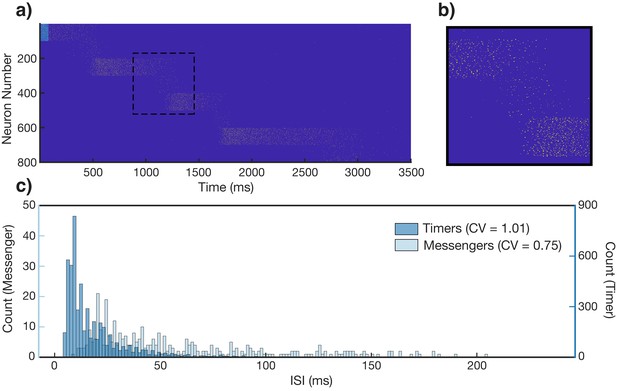
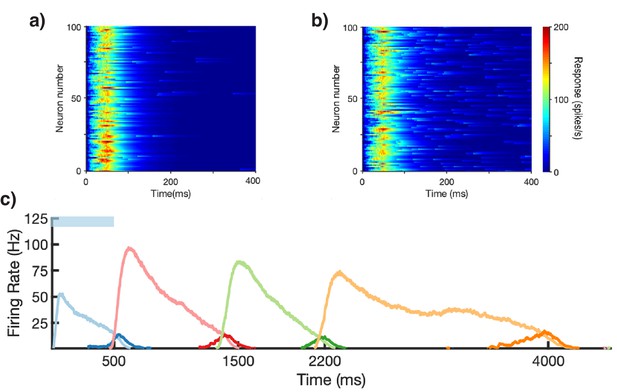
Spiking statistics in learned network.
(a) Spike raster of network response to stimulation of first column (light blue bar), after learning a sequence of stimuli (500, 750, 500, and 1250 ms for columns 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively). Neurons are sorted by population and sequentially by column. Neurons 1–100 are the Timer cells of the first column, neurons 101–200 are the Messenger cells of the first column, neurons 201–300 are the Timer cells of the second column, etc. (b) Zoomed in inset of dashed box in (a). (c) Histograms of interspike intervals (ISIs), segregated into Timers (dark blue) and Messengers (light blue). Coefficients of variation of the ISIs are 1.01 and 0.75 for the two populations, respectively.
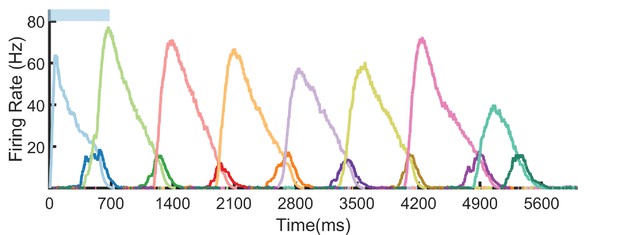
Eight element sequence recall.
Recall after learning a sequence of eight elements, each with duration 700 ms. Only the first element is stimulated. Notice that because of stochasticity, some elements (1 and 8) underreport their duration, while others (element 7) overreport their duration. In general, these errors can propagate in recall. For example, even though element 2 reports the correct duration (~700 ms), the sequence still underreports 1400 ms because of the errors in element 1.
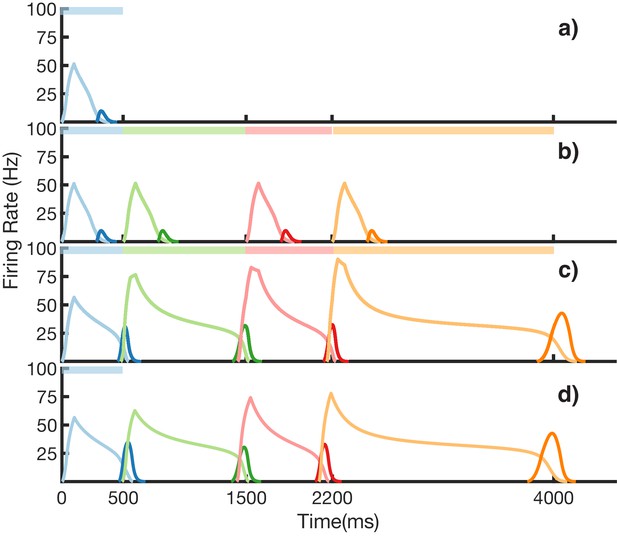
Rate-based learning and recall.
Recreation of Figure 3 from the main text, but using the rate-based formulation described in 'Materials and methods'. Each population of previously spiking neurons (e.g. red Timers) is now represented by one rate neuron. (a–d) Firing rates for Timer cells (light colors) and Messenger cells (dark colors) of four different columns during different stages of learning. Stimuli presented are shown as color bars in the top of plots. During learning, columns are stimulated in the sequence indicated by the color bars (500, 1000, 700, and 1800 ms for blue, red, green, and orange, respectively). (a) Before learning, the stimulation of a particular column only causes that column to be transiently active. (b) During the first trial of learning, all columns in the sequence become activated by the stimuli but have not yet learned to represent duration (through recurrent learning of Timer cells) or order (through feed-forward learning of the Messenger cells). (c) After many trials, the network learns to match the duration and order of presented stimuli. (d) After learning, presenting the first element in the sequence is sufficient for recall of the entire sequence.
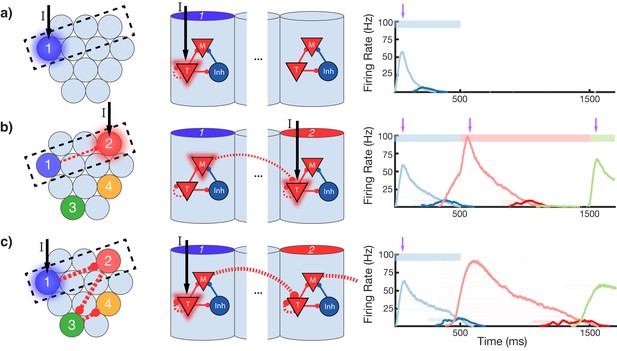
Change in connectivity patterns resulting from learning.
(a) Before, (b) during, and (c) after learning a sequence. Left, view of columnar structure and learned intercolumnar connections. Dotted box indicates region shown in side view, middle. Middle, the detailed view of two columns and their core neural architectures (CNAs) and learned intracolumnar connectivity. Dotted lines indicate learned connections, continuous lines indicate fixed connections. Right, illustration of mean firing rates for color coded columns. Light colors indicate Timer cells, dark colors indicate Messenger cells. Color bars indicate stimulated columns. Purple arrows indicate global neuromodulator release. (a) Before learning, stimulus of a column's Timer (T) cells only causes that column to be transiently active. (b) If another column is stimulated shortly after the first, the Messenger (M) cells of the previous column will be coactive with the Timer cells of the stimulated column, thereby increasing the feed-forward synaptic weights between these two populations. (c) After learning, a physical synaptic pathway has been traced out which links columns in the temporal order in which they were stimulated during training. Figure 4—figure supplements 1 and 2 demonstrate the dynamics of trace learning in the recurrent and feed-forward cases, respectively.
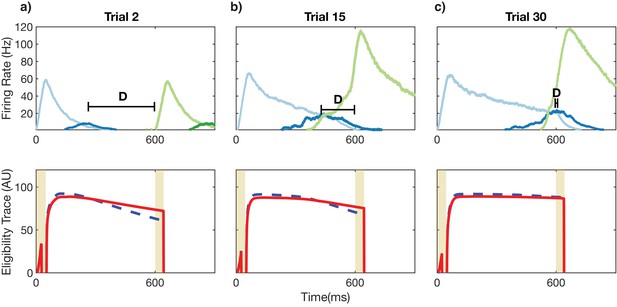
Recurrent learning evolution.
Top row: firing rates of Timer (light colors) and Messenger (dark colors) populations for the first two columns over the course of learning. Bottom row: eligibility traces corresponding to the recurrent weights for the Timer cells in the first column (light blue in top row). (a) For initial trials, the long-term potentiation (LTP) eligibility trace (solid red line) dominates the long-term depression (LTD) eligibility trace (dashed blue line) in the reward windows (vertical yellow lines). This leads in a net increase in synaptic efficacy. Learning aims to minimize D, the time between the end of firing in one column and the beginning of firing in the next. (b) For intermediate trials, the net difference (LTP-LTD) in the reward windows is still positive but smaller than before. Synaptic efficacy continues to increase but at a slower rate. (c) As the Timer population ‘extends’ to represent the appropriate time interval (top), the net difference between the traces during the reward windows goes to zero. The synaptic weights reach a fixed point and learning is complete.
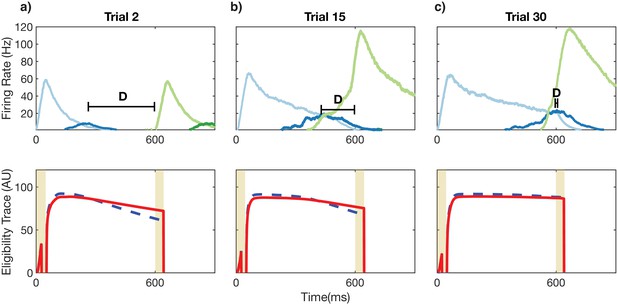
Feed-forward learning evolution.
Top row: firing rates of Timer (light colors) and Messenger (dark colors) populations for the first two columns. Bottom row: eligibility traces corresponding to the feed-forward weights between the Messenger cells of the first column (dark blue in top row) and the Timer cells of the second column (light green in top row). (a) For initial trials, there is no overlap between the Messenger cells of the first column and the Timer cells of the second column, so there is no activation of the eligibility traces. (b) For intermediate trials, as the Timers learn their duration, there starts to be an overlap term which activates the traces. The net difference between the traces (long-term potentiation-long-term depression [LTP-LTD]) in the two reward windows is positive, which causes the amplitude of the feed-forward weights to increase. (c) As the Messenger cells of the first column excite the Timer cells of the second column to have an elevated firing rate (top), the traces begin to saturate in the rising phase, and the net difference between the traces during the two reward windows goes to zero. The synaptic weights reach a fixed point and learning is complete.
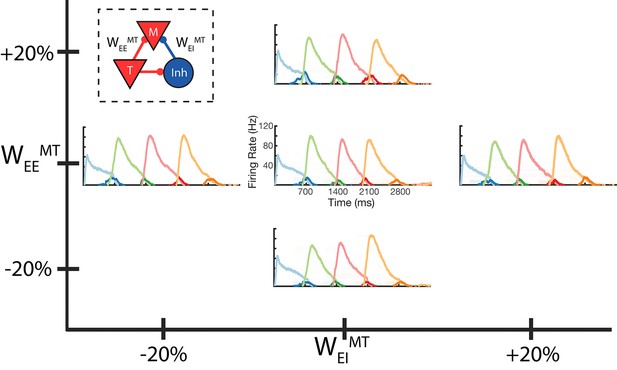
Robustness to core neural architecture (CNA) weight changes.
Firing rates of four columns, after learning a four element sequence, each of 700 ms duration. Only the first element is stimulated for recall. Before learning, static CNA weights WEEMT and WEIMT are either set as in Supplementary file 1 (center plot), or independently adjusted +/– 20% from their values in Supplementary file 1. In each of the four ‘modified’ cases, sequence learning is still successful and retains the correct timing. The most noticeable difference is along the WEEMT axis, where the amplitude of the Messenger cells can be seen to increase as WEEMT increases. Inset: CNA microcircuit with labeled connections. Figure 5—figure supplement 1 demonstrates a two-column network’s robustness to random variations in the learning parameters. Figure 5—figure supplement 2 shows the success and failure cases for a network with a 20 ms excitatory time constant.
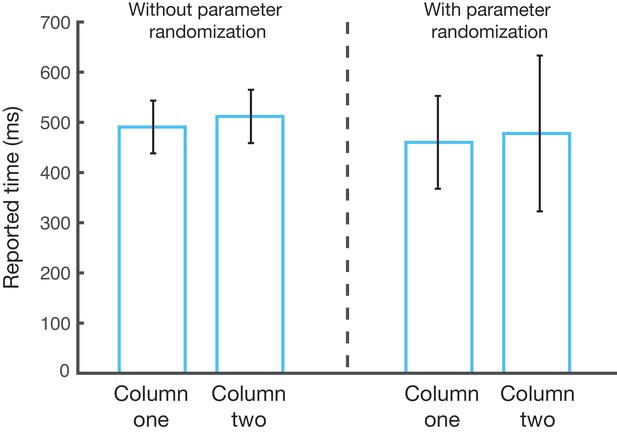
Robustness of parameter randomization.
Left, a two-column network learns a two-element sequence (500 ms, 500 ms) over 100 different learning epochs. The mean recalled time (bar) and standard deviation of the recalled times (whiskers) are shown. Right, the same process is performed, but this time for each learning epoch, we draw eight of the learning parameters (τp, τd, ηp, ηd, τpFF, τdFF, ηpFF, ηdFF) independently and randomly from a uniform distribution with bounds of 80–120% around the original value of the given parameter. For each epoch, this randomization is different, so the 100 performed epochs represent 100 different random parameter sets. The resulting mean reported times for the randomized parameter trials closely match the mean reported times for unrandomized trials. The standard deviation of the reported times for the randomized trials increases for both columns when compared to the standard parameters, but the increase is moderate and of the same order of magnitude.
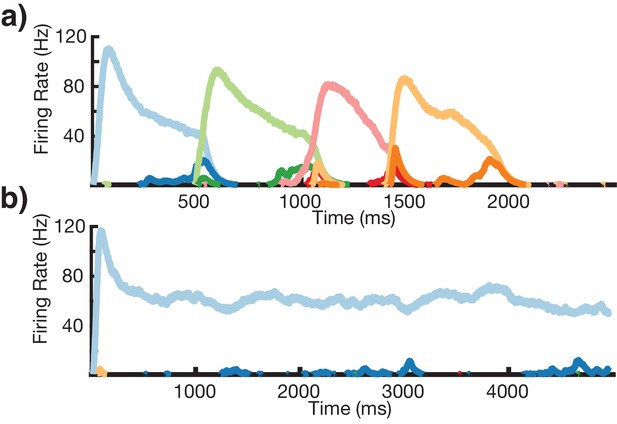
Sequence learning with 20 ms excitatory time constant.
(a) A network with 20 ms excitatory time constants recalls (only first element stimulated) a learned four element sequence of 500 ms each. Sequence learning is successful and network timing is preserved. (b) A network with 20 ms excitatory time constants recalls (only first element stimulated) a learned four element sequence of 1000 ms each. The Timers in the first column reach bistability and are unable to represent 1000 ms, causing failure in sequence learning.
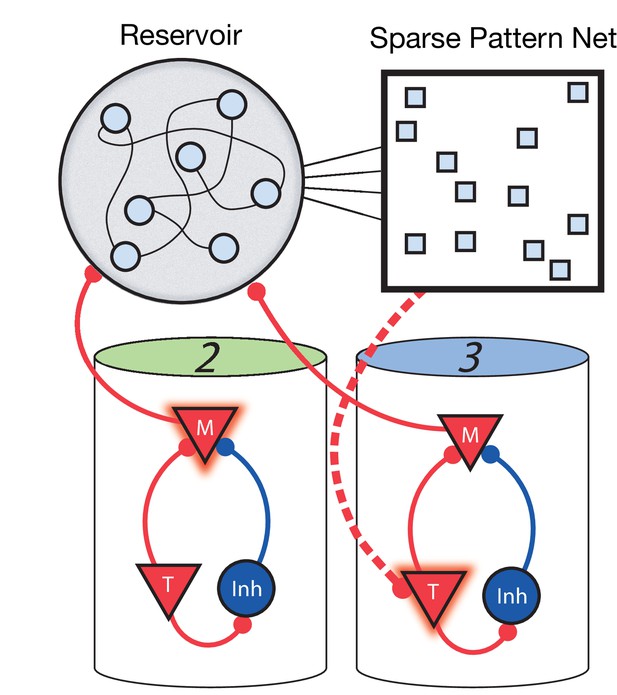
Non-Markovian sequence learning and recall.
Three-stage network. Two sequentially activated columns (2–3) learn to connect to each other through a reservoir and sparse pattern net. At time t, Messenger cells from column 2 are active and act as inputs into the reservoir (earlier, Messenger cells from column 1 also fed into the reservoir). The sparse pattern net receives input from the reservoir, so as to be a unique representation of the history of the network up to and including time t. Timer cells active at t + Δt (column 3) connect to the sparse pattern via Hebbian learning.
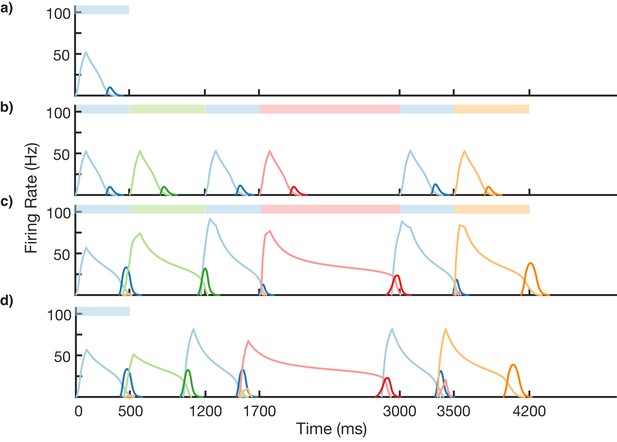
Non-Markovian sequence learning and recall.
Mean firing rates for Timer cells (light colors) and Messenger cells (dark colors) of four different columns during different stages of learning (before, first trial of learning, last trial of learning, after learning). Stimuli presented are shown in color bars inset in top of plots (500, 700, 500, 1300, 500, and 700 ms for blue, green, blue, red, blue, and orange, respectively).
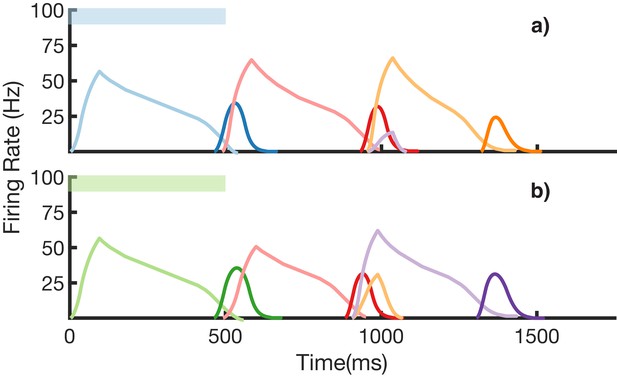
Recall of two overlapping sequences.
Mean firing rates for Timer cells (light colors) and Messenger cells (dark colors) during recall of two sequences. Both blue-red-orange (BRO) and green-red-purple (GRP) have been stored in the network via learning. (a) Recall of BRO, following presentation of a blue stimulus. (b) Recall of GRP, following presentation of a green stimulus. Note that R transitions to a different element in the two sequences. Figure 8—figure supplement 1 demonstrates the network’s robustness to perturbations of the reservoir’s initial state.
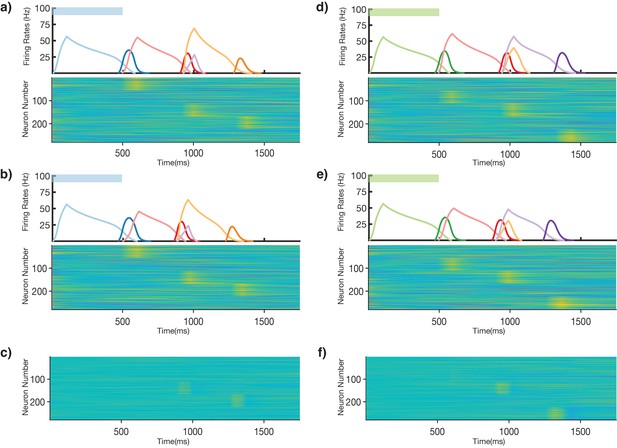
Robustness in non-Markovian recall.
A three-stage network trained on two non-Markovian sequences (BRO and GRP) recalls the two sequences with and without a perturbation to the initial state of the reservoir. (a) The trained network is excited with a 500 ms blue stimulus without an initial perturbation to the reservoir. Top, mean firing rates of Timer cells (light colors) and Messenger cells (dark colors) in the columnar network. Bottom, firing rates in the reservoir. The initial state of each unit in the reservoir is drawn from a normal distribution N(0,1.2), and the dynamics follow the equations in 'Materials and methods'. (b) Same as in (a) but a perturbation (normal distribution N(0,0.25)) is applied to the initial state of the reservoir. In this example a slight sequence compression is observed, but the integrity of the transitions is maintained. (c) The difference in reservoir firing rates between the perturbed trial and the unperturbed trial (same scale as (a) and (b)). (d–f) Same as (a–c), but this time stimulating with a 500 ms green stimulus, as to recall sequence GRP.
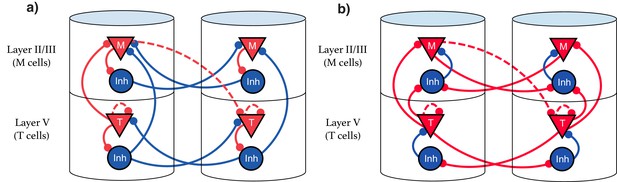
Explicit microcircuit structure.
(a,b) Two examples of complete microcircuit structure displayed in laminar architecture of cortical columns. Dashed lines represented learned connections, while continuous lines represent fixed connections. (a) Intercolumn inhibition produces soft winner-take-all dynamics between columns, interlaminar inhibition generates core neural architecture (CNA). (b) Same functionality as (a) but rearranged so as to only have local inhibition.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table of main model parameters.
For full code, see http://modeldb.yale.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63751/elife-63751-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Table of reservoir, sparse net, and rate-based model parameters.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63751/elife-63751-supp2-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/63751/elife-63751-transrepform-v2.pdf





