Telomeric double-strand DNA-binding proteins DTN-1 and DTN-2 ensure germline immortality in Caenorhabditis elegans
Figures
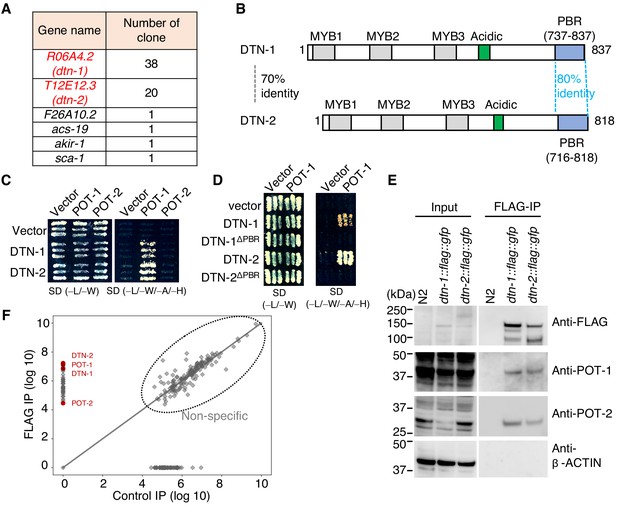
DTN-1 and DTN-2 form complexes with POT-1 and POT-2.
(A) Genes identified in the POT-1 Y2H screening with the number of identified clones. (B) Schematic of the DTN-1 and DTN-2 protein sequences highlighting the MYB domains, acidic domains, and C-terminus POT-1-binding regions (PBR). The amino acid identities between the full-length sequence and the PBR of DTN-1 and DTN-2 are shown. (C) Y2H interactions between POT-1 and POT-2 (prey) and DTN-1 and DTN-2 (bait). AH109 yeast cells containing plasmids encoding Gal4 BD, Gal4 BD-DTN-1, Gal4 BD-DTN-2, Gal4 AD, Gal4 AD-POT-1, and Gal4 AD-POT-2 were plated on non-selective (−L/−W) and selective (−L/−W/−A/−H) plates. (D) Y2H interactions between POT-1 (prey) and DTN-1, DTN-1ΔPBR, DTN-2, and DTN-2 ΔPBR (bait). AH109 yeast cells containing plasmids encoding Gal4 BD, Gal4 BD-DTN-1, Gal4 BD-DTN-1ΔPBR, Gal4 BD-DTN-2, Gal4 BD-DTN-2ΔPBR, Gal4 AD, and Gal4 AD-POT-1 were plated on non-selective (−L/−W) and selective (−L/−W/−A/−H) plates. (E) Immunoprecipitates with the FLAG antibody from wild type (N2) and knock-in worms (dtn-1::flag::gfp and dtn-2::flag::gfp). Input and immunoprecipitates (FLAG-IP) were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Note that the input blotted with anti-POT-1 was less intense compared to the FLAG-IP blotted with anti-POT-1 in order to avoid saturation of the input bands. (F) Quantitative mass spectrometry of immunoprecipitates with the FLAG antibody from a mixture of knock-in worms (dtn-1::flag::gfp and dtn-2::flag::gfp) (vertical axis) and control IP (horizontal axis). Combined peptide intensities are plotted for each protein. The whole protein list is provided in Supplementary file 1.
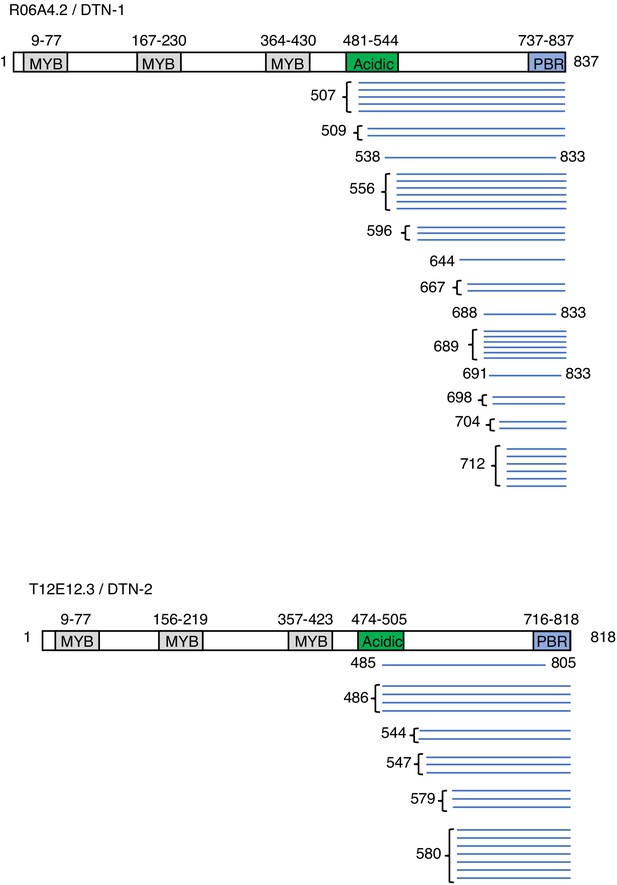
Results of the POT-1 Y2H screening blue bars indicate the individual peptides identified in the Y2H screening.
POT-1-binding region (PBR) is identified as the highly conserved region within the C-terminus regions of DTN-1 and DTN-2, which are commonly identified in the Y2H screening.
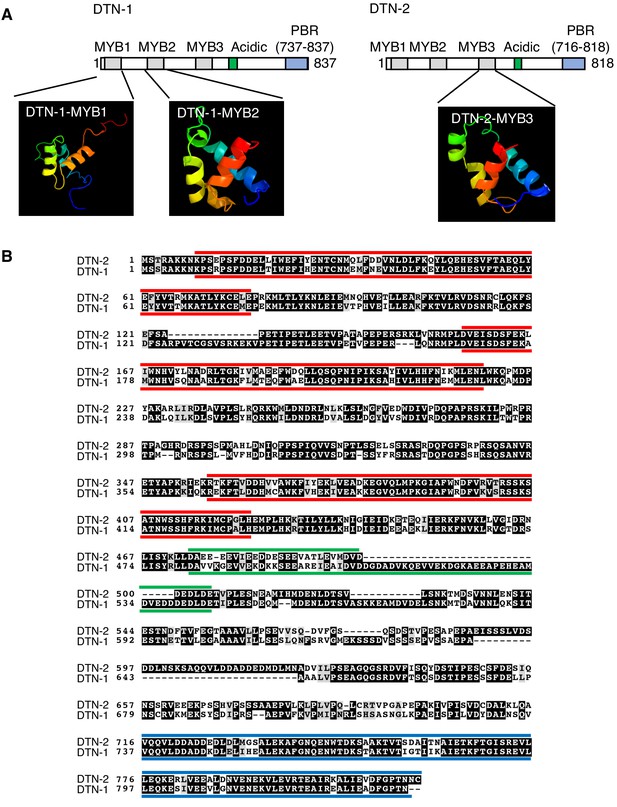
Structural modeling and domain conformation of DTN-1 and DTN-2.
(A) The Phyre two program (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index) identified two MYB domains (MYB1 and MYB2) in DTN-1 and one MYB domain (MYB3) in DTN-2 by the structural modeling. The rest of MYB domains were manually identified by the sequence alignment of DTN-1 and DTN-2 (MYB1 and MYB2 of DTN-2 are corresponding regions of MYB1 and MYB2 of DTN-1 identified by Phyre two and MYB3 of DTN-1 is corresponding regions of MYB3 of DTN-2 identified by Phyre 2). We have confirmed that all six MYB domains are indeed composed of three alpha helixes, characteristics of MYB domains, by the secondary structure prediction using Jpred 4 program (http://www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/jpred/). (B) Red bars indicate the three tandem MYB domains found at the N-terminus of each proteins. Green bars indicate the acidic domains at the middle of these proteins. Blue bars indicate the PBR.
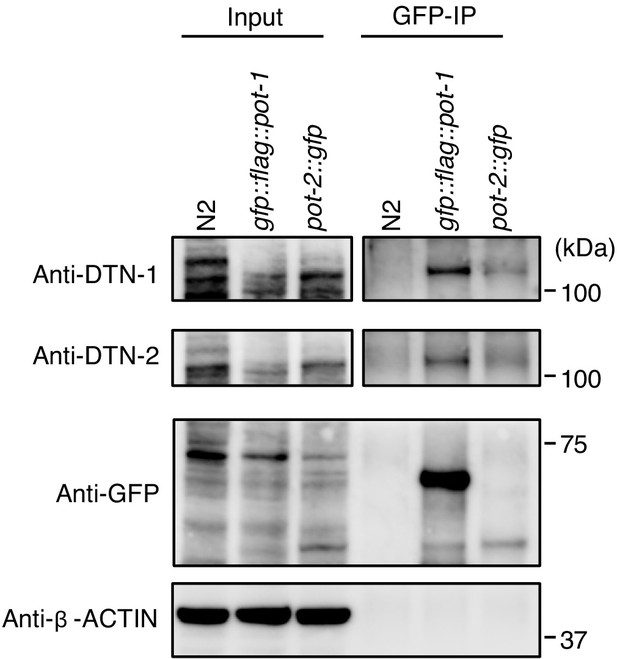
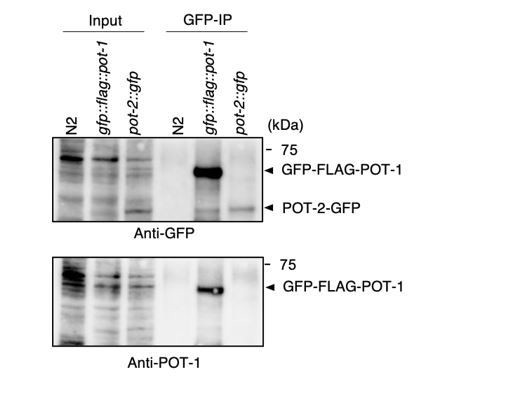
Validation of in vivo interactions between DTN-1/2, POT-1, and POT-2 immunoprecipitates with the GFP antibody from wild type (N2) and knock-in worms (gfp::flag::pot-1 and pot-2::gfp).
Input and immunoprecipitates (GFP-IP) were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Note that the inputs blotted with anti-DTN-1 and anti-DTN-2 were less intense compared to the GFP-IPs blotted with anti-DTN-1 and anti-DTN-2 in order to avoid saturation of the input bands.
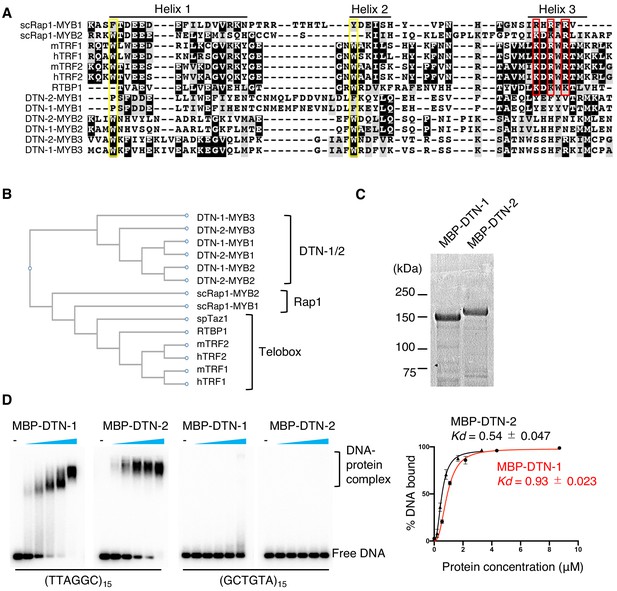
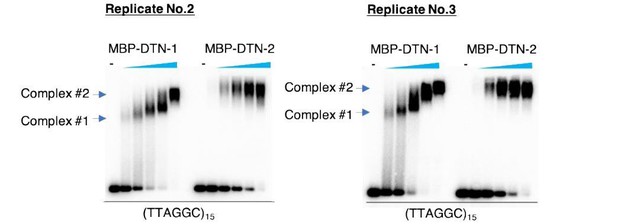
DTN-1 and DTN-2 bind to telomeric dsDNA.
(A) Sequence alignment of the MYB domains from budding yeast Rap1 (scRap1-MYB1 and MYB2), mouse and human TRF1 and TRF2 (mTRF1, mTRF2, hTRF1, and hTRF2), rice RTBP1, and C. elegans DTN-1 and DTN-2. The conserved tryptophan residues required for maintaining the helix-turn-helix structure are highlighted by the yellow rectangles. Amino acids that directly contact telomeric dsDNA identified in human TRF1 protein are highlighted by the red rectangles. (B) Phylogenetic tree of the MYB domains. (C) Coomassie-stained gel of MBP-DTN-1 and MBP-DTN-2. (D) EMSA with increasing amounts of MBP-DTN-1 (twofold steps up to 8.7 μM) and MBP-DTN-2 (twofold steps up to 3.3 μM). The labeled DNA probes were 0.2 nM of restriction fragment containing fifteen telomere repeats (TTAGGC)15 or scrambled repeats (GCTGTA)15. Quantifications of the EMSA are shown in the graph to the right. Error bars are ± SD from three independent experiments. Lines are Hill curves fit to the data. The apparent affinities of MBP-DTN-1 and MBP-DTN-2 for the DNA substrates were 0.93 ± 0.023 μM and 0.54 ± 0.047 μM, respectively.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Quantifications of the EMSA from three independent experiments.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64104/elife-64104-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
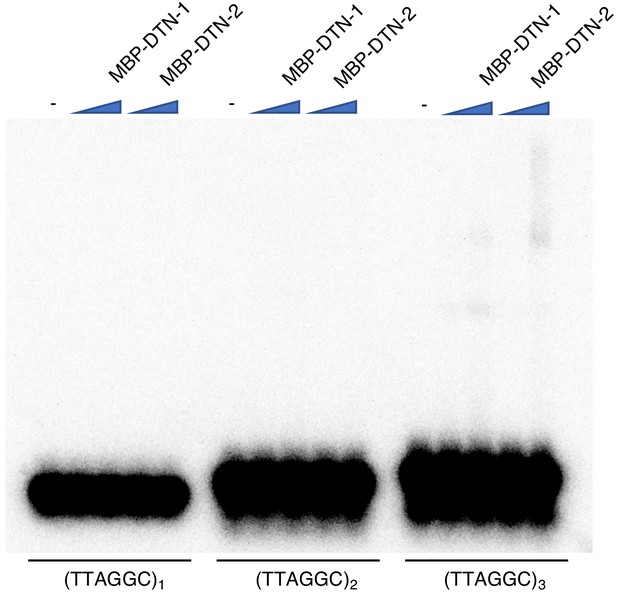
EMSA assay with short telomeric repeats EMSA assay with increasing amounts of MBP-DTN-1 (twofold steps up to 8.8 μM) and MBP-DTN-2 (twofold steps up to 3.2 μM).
The labeled DNA probes are 0.2 nM of ligated oligonucleotides containing one, two, and three telomere repeats.
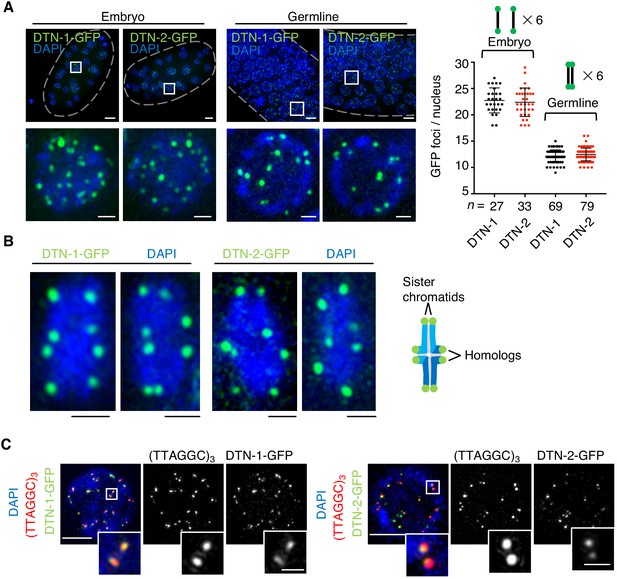
The constitutive telomeric localization of DTN-1 and DTN-2.
(A) Embryos or germlines from knock-in worms (dtn-1::flag::gfp and dtn-2::flag::gfp) fixed and stained with DAPI. The graph shows the number of GFP foci per nucleus. The mean value ± SD is shown. n shows the analyzed number of nuclei pooled from more than 10 embryos or worms. Scale bars, 5 μm or 1 μm (magnified panel). (B) Bivalent chromosomes from diakinesis-stage oocytes from knock-in worms (dtn-1::flag::gfp and dtn-2::flag::gfp) fixed and stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 1 μm. (C) Immuno-FISH of embryonic nuclei, stained with GFP antibody, hybridized with PNA probe (TTAGGC)3, and stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 5 μm and 1 μm (magnified panel).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Quantifications of the number of GFP foci per nucleus.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64104/elife-64104-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
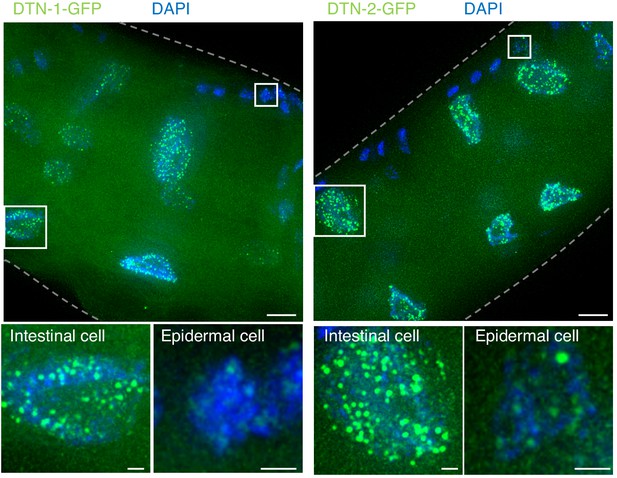
Constitutive telomeric localization of DTN-1-GFP and DTN-2-GFP.
Adult knock-in worms (dtn-1::flag::gfp and dtn-2::flag::gfp) were fixed and stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 5 μm and 1 μm (magnified panel).
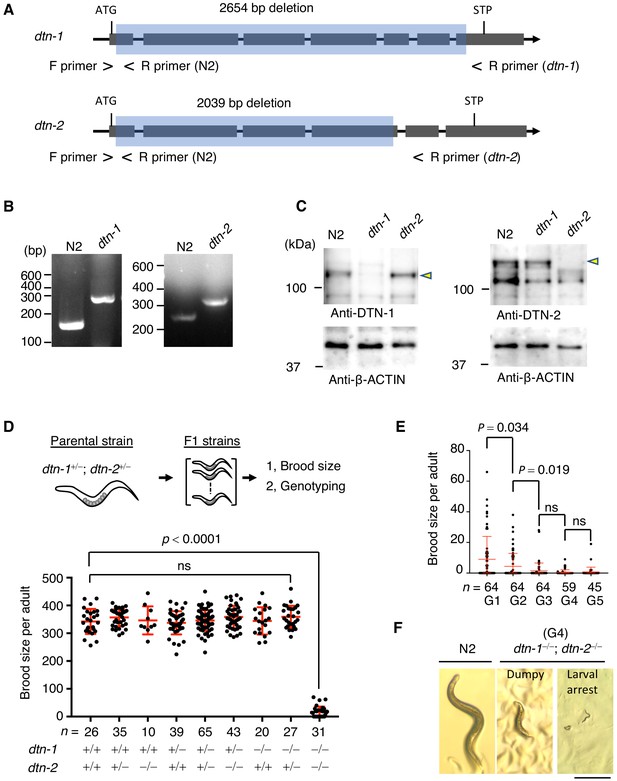
DTN-1 and DTN-2 are required for germline immorality.
(A) Schematic of the dtn-1 and dtn-2 KO alleles. Exons are shown as gray rectangles with the start codon (ATG) and stop codon (STP). The deleted regions are marked by blue rectangles. Primer positions used for the genotyping are shown. (B) Agarose gel showing the PCR results for the dtn-1+⁄+ (N2; 154 bp), dtn-1−⁄− (301 bp), dtn-2+⁄+ (N2; 267 bp), and dtn-2−⁄− (337 bp) alleles. (C) Western blot with the indicated antibody for the extracts from wild type (N2) and each KO worm (dtn-1 and dtn-2). Yellow arrowheads indicate the DTN-1 and DTN-2 proteins. (D) Schematic of the fertility assay. The brood size of each F1 adult worm is quantified in the graph with the genotyping results, and n shows the analyzed number of F1 worms for the indicated genotypes. The mean value ± SD is shown. (E) The brood size of dtn-1 and dtn-2 double KO worms self-fertilized for successive generations. n shows the analyzed number of worms for the indicated generations (G). The mean value ± SD is shown. (F) Representative morphological defects seen in dtn-1 and dtn-2 double KO worms at generation 4 (G4). Scale bar, 0.5 mm. Analyses were with one-way ANOVA (D) or two-tailed t-tests (E). ns., not significant.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
The brood size quantifications.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64104/elife-64104-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
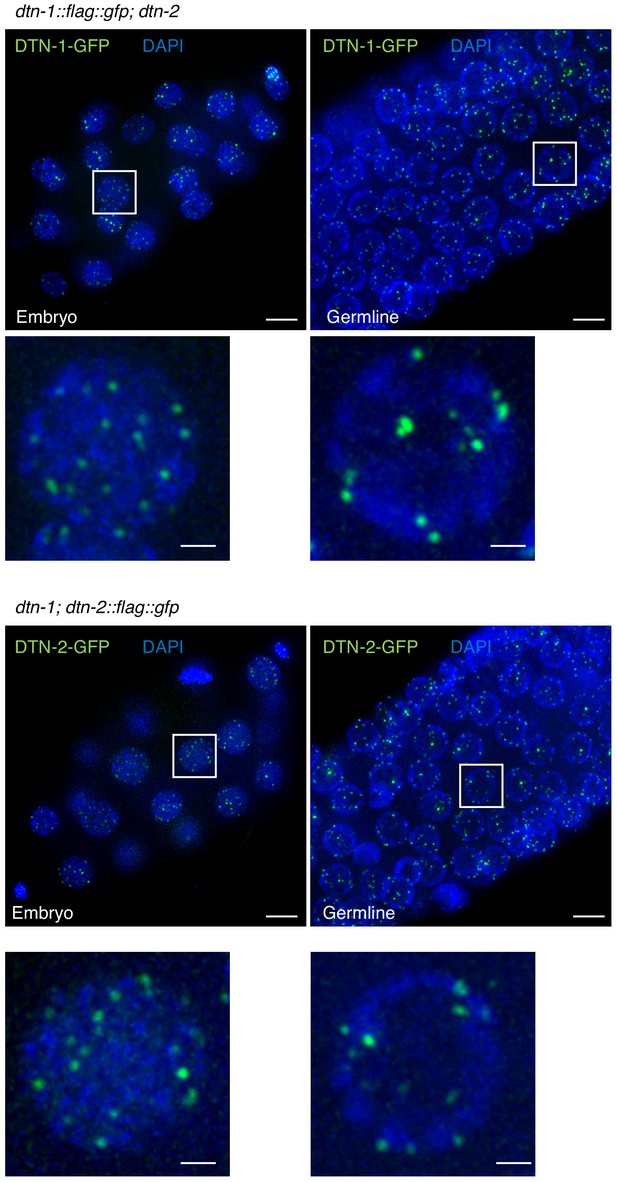
Mutually independent telomeric localization of DTN-1 and DTN-2.
Embryos or germlines from the indicated genotypes were fixed and stained with DAPI.
Note, DTN-1-GFP signals are visible even in the dtn-2 mutant worms and vice versa. Scale bars, 5 μm and 1 μm (magnified panel).
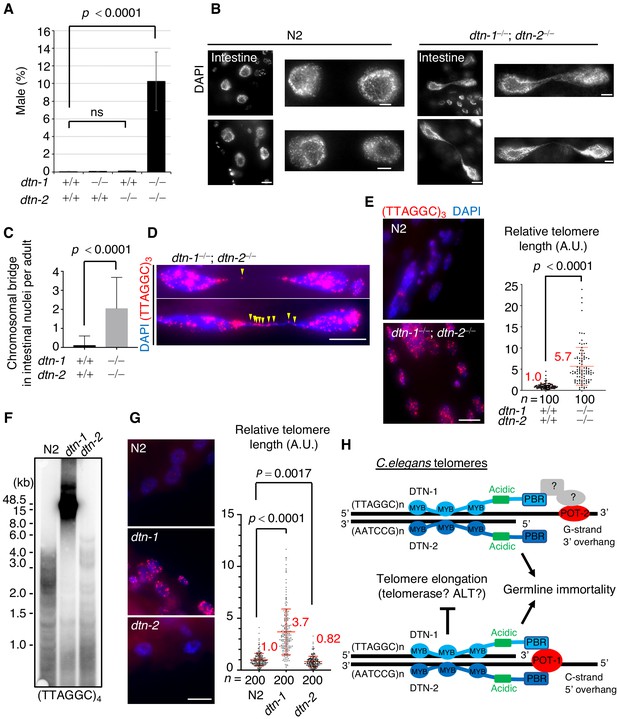
DTN-1 and DTN-2 are required for telomere length homeostasis.
(A) The frequency of male worms among the progeny from the indicated genotypes. In total, 6551, 13270, 12317, and 1113 worms were analyzed from each genotype (dtn-1+⁄+; dtn-2+⁄+, dtn-1−⁄−; dtn-2+⁄+, dtn-1+⁄+; dtn-2−⁄− and dtn-1−⁄−; dtn-2−⁄−). The mean value ± SD (from five biological replicates) is shown. (B) Intestinal nuclei from adult worms of the indicated genotypes stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 5 μm or 1 μm (magnified panel). (C) Quantification of the number of intestinal nuclei with chromosomal bridges per adult. A total of 17 and 18 adults were analyzed for dtn-1+⁄+; dtn-2+⁄+ and dtn-1−⁄−; dtn-2−⁄−, respectively. The mean value ± SD is shown. (D) Adult intestinal nuclei hybridized with PNA probe (TTAGGC)3 and stained with DAPI. Yellow arrowheads indicate telomeric FISH signals on the bridged DNAs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Adult somatic nuclei (epidermal and intestinal nuclei) hybridized with the PNA probe (TTAGGC)3 and stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 5 μm. The graph shows the quantification of individual telomeric FISH signals in epidermal nuclei. The average values are normalized to that of wild type (dtn-1+⁄+; dtn-2+⁄+). n shows the analyzed number of telomeres in 10 nuclei (10 telomeres from each nuclei) pooled from five different worms. The mean value ± SD is shown. (F) Southern blot analysis of telomere length for the wild type (N2) and each single KO worm (dtn-1 and dtn-2). The membrane was hybridized with DNA probes with four telomere repeats (TTAGGC)4. The ladder-like hybridization signals correspond to the internal telomere sequence. (G) Adult somatic nuclei (epidermal nuclei) hybridized with the PNA probe (TTAGGC)3 and stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 5 μm. The graph shows the quantification of individual telomeric FISH signals in epidermal nuclei. The average values are normalized to that of wild type (N2). n shows the analyzed number of telomeres in 20 nuclei (10 telomeres from each nuclei) pooled from 10 different worms. The mean value ± SD is shown. (H) Schematic summary of C. elegans telomere structures. Note that we did not detect any direct protein-protein interactions between DTN-1/2 and POT-2, thus they either form complexes only through DNA-mediated interactions or there are unidentified bridging proteins between them. All analyses were with two-tailed t-tests. ns, not significant.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Analyses of dtn-1, dtn-2, and the double KO worms.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64104/elife-64104-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
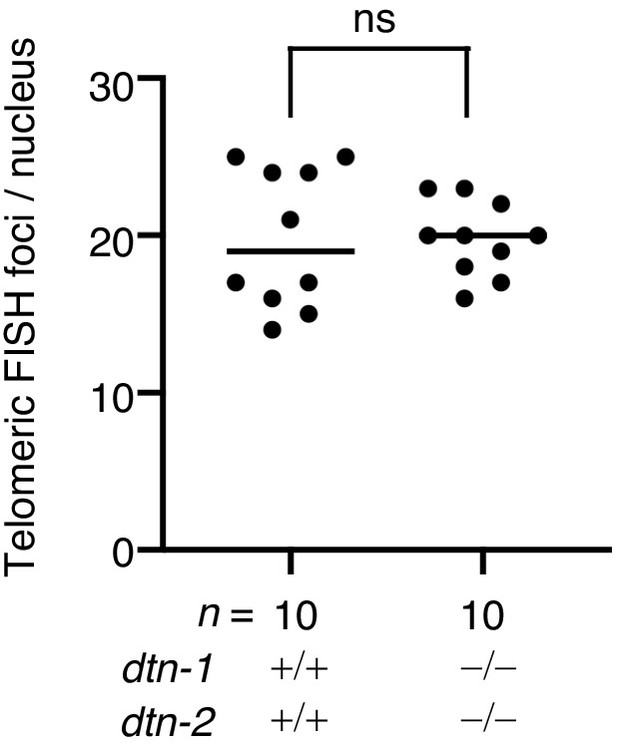
Quantification of telomeric FISH foci in epidermal cells.
The number of telomeric FISH foci per nucleus. The mean value is shown. n shows the analyzed number of nuclei pooled from five different worms. Analysis was with two-tailed t-tests. ns., not significant.
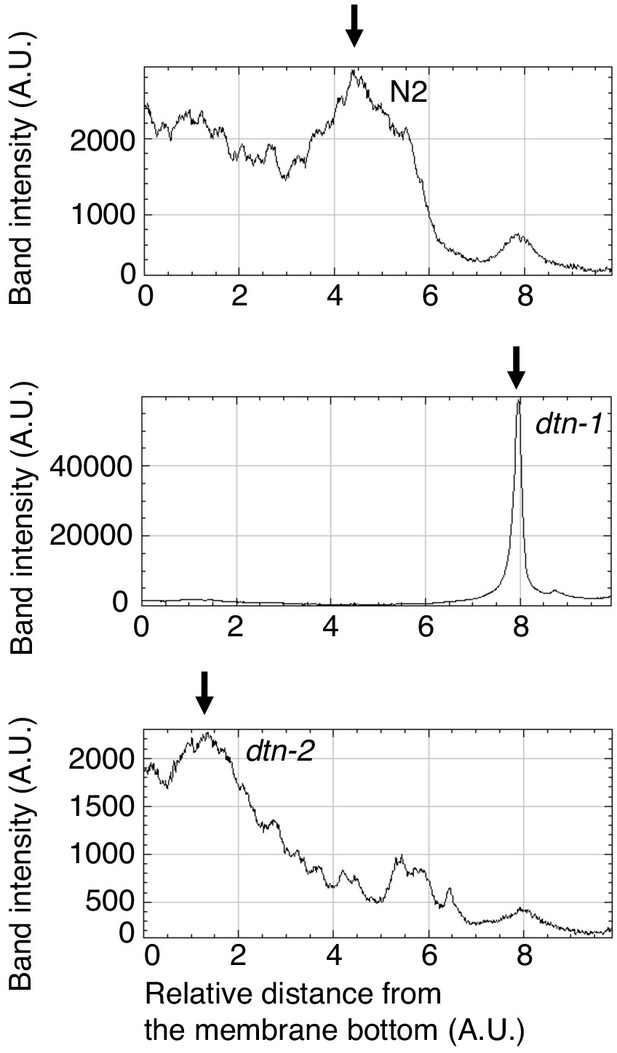
Quantification of Southern blot analysis.
The band intensities were quantified from the bottom to the top of the membrane. The allows show the peak positions, indicating that telomeric DNA from dtn-1 and dtn-2 show slower and faster migration, respectively, compared to N2.
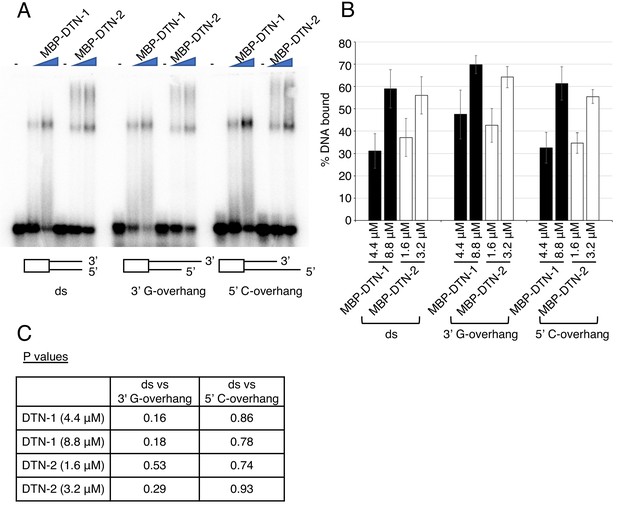
(A) EMSA with increasing amounts of MBP-DTN-1 (twofold steps up to 8.8 μM) and MBP-DTN-2 (twofold steps up to 3.2 μM). The labeled DNA probes are 0.2 nM of ligated oligonucleotides containing random dsDNA sequences (5’-GCTGTACTGGTA-3’) followed by four telomere repeat dsDNA (ds), four telomere repeat dsDNA with two telomere repeat 3’ ssDNA overhang (3’ G-overhang), and four telomere repeat dsDNA with two telomere repeat 5’ssDNA overhang (5’ C-overhang). (B) Quantifications of the EMSA. Error bars are ± SD from three independent experiments. (C) Statistical analyses of (B) with two-tailed t-tests.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | R06A4.2 / dtn-1 | This paper | N/A | (cloned from a mix stage cDNA library) |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | T12E12.3 / dtn-2 | This paper | N/A | (cloned from a mix stage cDNA library) |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | N2 (wild type) | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC); https://cbs.umn.edu/cgc/home | N2 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | dtn-1 | This paper | Aelle; syb1925 Strain: PHX1925 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | dtn-2 | This paper | Aelle; syb1886 Strain: PHX1886 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | dtn-1::flag::gfp | This paper | Aelle; syb2016 Strain: PHX2016 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | dtn-2::flag::gfp | This paper | Aelle; syb1995 Strain: PHX1995 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | dtn-1::flag::gfp; dtn-2 | This paper | Aelle; dtn-1::flag::gfp; dtn-2 Strain: HS001 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | dtn-1; dtn-2::flag::gfp | This paper | Aelle; dtn-1; dtn-2::flag::gfp Strain: HS002 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | nT1[qIs51]/dtn-2; dtn-1/dtn-1 | This paper | Aelle; nT1[qIs51]/syb1886; syb1925/syb1925 Strain: PHX2217 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | gfp::flag::pot-1 | This paper | Aelle; syb3002 Strain: PHX3002 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans, hermaphrodite) | pot-2::gfp | This paper | Aelle; syb889 Strain: PHX889 | |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (Rabbit polyclonal) | Invitrogen | Cat#A11122, LOT#2015993 | IF (1:1000), WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-DTN-1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | This paper | N/A | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-DTN-2 (Rabbit polyclonal) | This paper | N/A | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-POT-1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | This paper | N/A | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-POT-2 (Rabbit polyclonal) | This paper | N/A | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-β-ACTIN (Mouse monoclonal) | Sigma | Cat#A2228-200UL, LOT#067M4856V | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (Mouse monoclonal) | Roche | Cat#11814460001, LOT#42903200 | IP |
| Antibody | Donkey Anti-Rabbit Alexa 488 | Invitrogen | Cat#A21206, LOT#1834802 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Peroxidase Goat Anti-Mouse IgG | Bio Rad | Cat#170–6516 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Peroxidase Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG | Bio Rad | Cat#170–6515 | 1:1000 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMAL-c5X-dtn-1 (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMAL-c5X-dtn-2 (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET28c+-dtn-1 (a.a. 441–837) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET28c+-dtn-2 (a.a. 434–818) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET28c+-pot-2 | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGEX-6P-1-pot-1 (a.a. 100–300) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pB27-pot-1 | Hybrigenics Services | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pP6-mix-staged C. elegans cDNA | Hybrigenics Services | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGBKT-7-dtn-1 | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGBKT-7-dtn-2 | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGBKT-7-dtn-1ΔPBR(a.a. 1–736) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGBKT-7-dtn-2ΔPBR(a.a. 1–715) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGADT7-POT-1 | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGADT7-POT-2 | This paper | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-1 genotype Common-Forward | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- CGGCAATTTGGCACGATGTT −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-1 genotype WT-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- AATGACGGTCTTGACGGCTT −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-1 genotype KO-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- TGGCCCAAAATCAGCCTCAA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-2 genotype Common-Forward | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- TTGCGCTTTTGCTTCATCCG −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-2 genotype WT-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- CTCCGCCGTAAACACAGACT −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-2 genotype KO-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- GGGCACCAGAGGTAACTTCA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-1::flag::gfp genotype Common-Forward | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- GGCAACGTCGAGAACGAGAA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-1::flag::gfp genotype WT-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- ATGACTAGGGCGAGGGGTAA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-1::flag::gfp genotype mutant-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- CACCCTCTCCACTGACAGAAAA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-2::flag::gfp genotype Common-Forward | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- GCACAGAAGCCATCCGAAAA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-2::flag::gfp genotype WT-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- TAGGGCTGAGGCTAAAGAATGAA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | dtn-2::flag::gfp genotype mutant-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- TCACCCTCTCCACTGACAGA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | gfp::flag::pot-1 genotype Common-Forward | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- TATGCAACGAACGAGGCTCC −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | gfp::flag::pot-1 genotype WT-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- GACCCGGTACCAAATCCTGA −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | gfp::flag::pot-1 genotype mutant-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- ATGTTGCATCACCTTCACCCT −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | pot-2::gfp genotype Common-Forward | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- CGAAAACATTCGCTGAGGCT −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | pot-2::gfp genotype WT-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- GCTAGCGCCACAACCAAAC −3' |
| Sequence-based reagent | pot-2::gfp genotype mutant-Reverse | This paper | PCR primers | 5'- TGTTGCATCACCTTCACCCT −3' |
| Software, algorithm | SoftWoRx | GE healthcare life science | http://www.gelifesciences.com/webapp/wcs/stores/servlet/productById/en/GELifeSciences-se/29065728 | |
| Software, algorithm | CLUSTALW | https://www.genome.jp/tools-bin/clustalw | ||
| Software, algorithm | Phyre2 | http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/~phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index | ||
| Software, algorithm | Jpred 4 | http://www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/jpred/ |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Full list of peptides identified in control IP, DTN-1-FLAG-GFP IP, and DTN-2-FLAG-GFP IP.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64104/elife-64104-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64104/elife-64104-transrepform-v2.docx