Downregulation of glial genes involved in synaptic function mitigates Huntington's disease pathogenesis
Figures
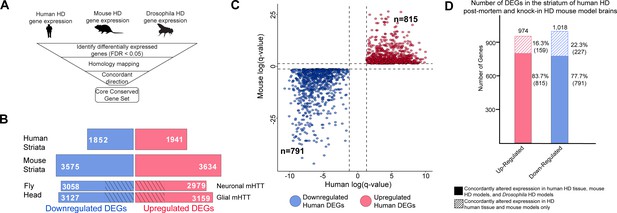
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Huntington's disease (HD) human striatal tissue are concordantly altered in mouse and Drosophila HD models.
(A) Our approach to identifying orthologous genes in tissues from humans, mice, and Drosophila with concordant expression changes (i.e., upregulated or downregulated in all three systems) following mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) expression. (B) The number of DEGs in each species-specific dataset that are downregulated (blue) or upregulated (red) (see Materials and methods). Drosophila DEGs were from flies expressing either the N-terminal (HTTNT231Q128) or full-length mHTT (HTTFLQ200) in neurons (elav-GAL4) or glia (repo-GAL4). The DEGs in flies are grouped according to the cell type expressing mHTT rather than the mHTT model. The cross-hatched regions of the Drosophila bars represent DEGs shared between the neuronal and glial sets: 1293 downregulated genes and 1181 upregulated genes. (C) Points in the scatterplot represent human DEGs identified by the strategy outlined in (A) that are concordantly dysregulated across all three species. Red nodes represent upregulated DEGs (n = 815), whereas blue nodes represent downregulated genes (n = 791). The overlap of these concordant DEGs represents approximately 40% of genes with altered expression in the human HD transcriptome that are upregulated (p=6.37×10−158) or downregulated (p=1.66×10−165). The p-value was calculated using a random background probability distribution over 2 × 105 random samplings. (D) The stacked bar graph highlights that a large majority of concordant DEGs in human HD striata and knock-in HD mouse models are also concordantly altered in Drosophila models of HD.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
List of up- and down-regulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in humans, mice, and Drosophila affected by mutant Huntingtin (mHTT).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Lists of up- and down-regulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in humans, mice, and Drosophila affected by mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) grouped by homology for each Drosophila Huntington's disease (HD) model.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig1-data2-v2.zip
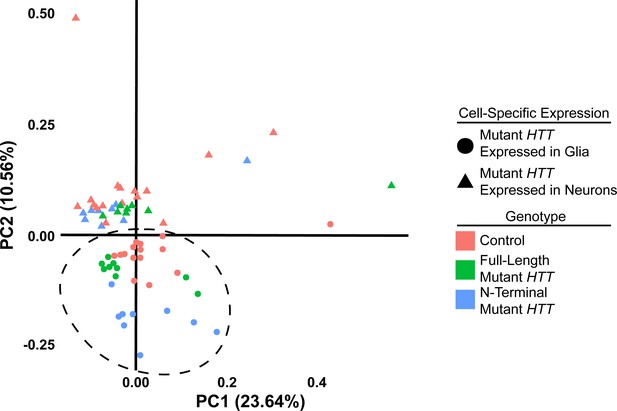
Expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) in Drosophila glia or neurons leads to distinct gene expression profiles.
In contrast, the full-length and N-terminal models show relatively similar gene expression profiles. Principal component analysis (PCA) plot of RNA-sequencing samples. Circles represent samples with transgenic expression in glia (repo-GAL4), while triangles represent samples with transgenic expression in neurons (elav-GAL4). Red points represent control w1118 controls, green points represent animals expressing the full-length protein mHTT transgene (HTTFLQ200), and blue points represent animals expressing the N-terminal mHTT fragment transgene (HTTNT231Q128). Outliers skew the first component on the x-axis (23.64% of the variability). Samples expressing mHTT in glia separate from those expressing it in neurons along the second component on the y-axis (10.56% of the variability; dashed circle).
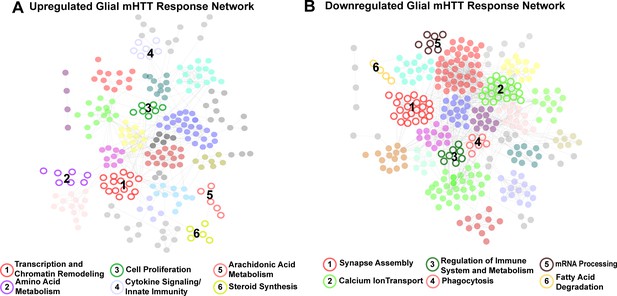
Clusters of concordant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between human and mouse Huntington's disease (HD) striata and Drosophila expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) in glia.
Clustered protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks of DEGs (STRING-db) that have higher (A) or lower (B) concordant expression in HD human tissue, an allelic series of knock-in HD mouse models, and Drosophila expressing mHTT (HTTNT231Q128 or HTTFLQ200) in glia. Clusters of DEGs (nodes) that were dysregulated in response to mHTT expression in glia are numbered and represented by open circles. Annotations listed below each network correspond to each numbered cluster and represent a synthesis of the top five most significantly enriched GO Panther Biological processes and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) terms with a false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 (Supplementary file 2). Nodes represented by solid circles were dysregulated in response to mHTT expression in glia but are also significantly similar in gene membership to clusters of DEGs in response to mHTT expression in neurons (Figure 2—figure supplement 1, hypergeometric test, p<1×10−5).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Lists of human Huntington's disease (HD) differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (Entrez IDs) concordantly dysregulated in mouse and Drosophila HD models.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
List of proteins expressed in the human striata.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig2-data2-v2.zip
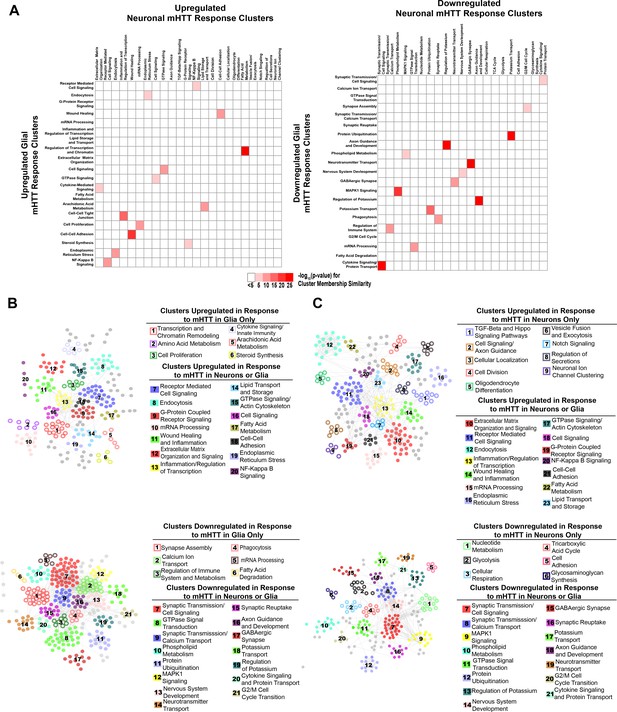
Network of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) responding concordantly to mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) expression in glia or neurons.
(A) Heatmap representing all pairwise comparisons between clusters of upregulated (left) and downregulated (right) DEGs in response to glial (x-axis) or neuronal (y-axis) mHTT expression. Clusters are labeled using annotations for biological processes represented by DEGs within each cluster (refer to Supplementary file 3). Color is scaled to represent the significance of membership similarity calculated using a hypergeometric distribution. Colors represent the -log10(p-value) and range from white (<5) to dark red (>25). (B) Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network (STRING-db) of upregulated (top) and downregulated (bottom) DEGs in human Huntington's disease (HD) tissue, HD mouse models, and Drosophila expressing mHTT in glia. (C) PPI network (STRING-db) of upregulated (top) and downregulated (bottom) DEGs in human HD tissue, HD mouse models, and Drosophila expressing mHTT in neurons. Refer to Supplementary file 3 for gene membership, as well as GO Panther and KEGG terms enriched genes within each cluster. Numbers in (B) and (C) correspond to annotations. Hollow circles correspond to clusters of DEGs that are dysregulated in response to mHTT (HTTFLQ200 or HTTNT231Q128) expression in only glia (repo-GAL4) or neurons (elav-GAL4). Solid circles correspond to clusters of DEGs that are dysregulated in response to mHTT expression in neurons or glia.
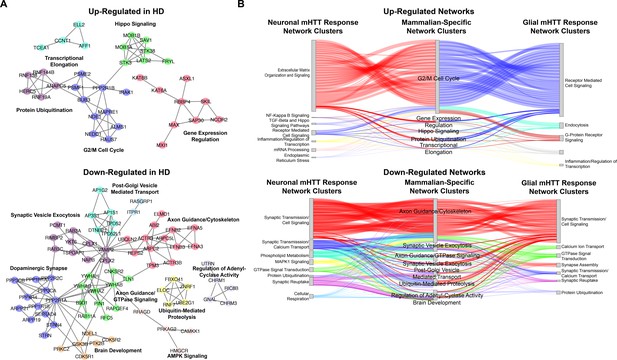
Network of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) concordantly altered in human Huntington's disease (HD) tissue and HD mouse models, but not in Drosophila HD models.
(A) Clustered, annotated protein-protein interaction (PPI) network (STRING-db) of DEGs concordantly upregulated (top) and downregulated (down) in human HD striatal tissue collected post-mortem (Hodges et al., 2006) and the allelic series of knock-in HD mouse models (Langfelder et al., 2016), but not in the Drosophila models (this study). Clusters are annotated for the synthesis of the top five most significantly enriched GO Panther Biological Process and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) terms (false discovery rate [FDR] < 0.05). (B) Sankey plot for genes concordantly upregulated (top) and upregulated (bottom) in HD patients and mouse model only (middle) connecting to cluster of DEGs that are concordantly upregulated in patients, mice, and Drosophila as a consequence of expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) (HTTFLQ200 or HTTNT231Q128) in neurons (elav) (left) or in glia (repo) (right). Edges represent PPIs between connected DEGs (STRING-db).
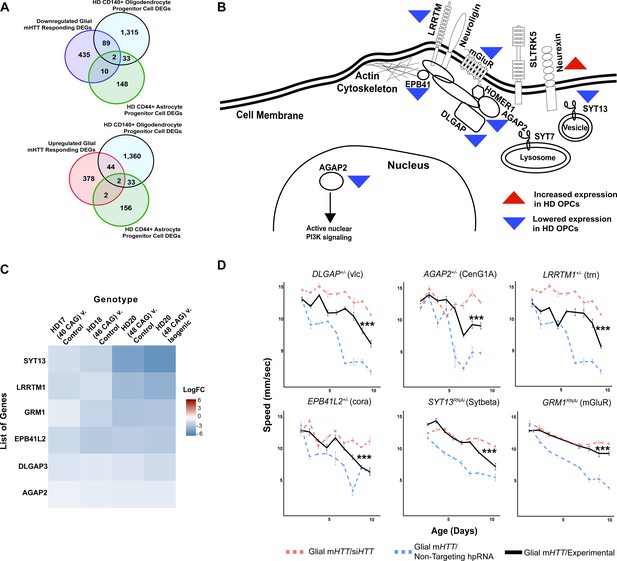
Reducing the expression of Synapse Assembly cluster genes in glia mitigates mutant Huntingtin (mHTT)-induced behavioral impairments.
(A) Overlaps between concordant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the cross-species analysis defined as responding to mHTT expression in glia and DEGs identified in Huntington's disease (HD) human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) that have been differentiated into either CD140+ oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) or CD44+ astrocyte progenitor cells (APCs) (Osipovitch et al., 2019). (B) Model placing Synapse Assembly cluster proteins into cellular context. The Synapse Assembly cluster was significantly enriched for DEGs in HD OPCs (Fisher’s exact test, p<0.001). Only one gene, NRXN3, was upregulated in HD OPCs compared to controls (upward red triangle); the rest (AGAP2, GRM1, LRRTM1, EPB41L2, DLGAP3, and SYT13) were downregulated (downward blue triangles). (C) Heatmap representing genes with lower expression in HD OPCs compared to controls (presented as LogFC) that belong to the Synapse Assembly cluster. Each row is one downregulated gene; each column is a different HD human embryonic stem cell line, with CAG repeat length ranging from 40 to 48, compared to respective controls (Osipovitch et al., 2019). (D) Behavioral assessment of fruit flies that express mHTT only in glia, after reducing the expression of the overlapping DEGs in HD OPCs and the Synapse Assembly cluster. Plots show climbing speed as a function of age. ***p<0.001 between positive control and experimental (by linear mixed effects model and post-hoc pairwise comparison; see Materials and methods). Points and error bars on the plot represent the mean ± SEM of the speed for three technical replicates. Each genotype was tested with 4–6 replicates of 10 animals. Modifying alleles in (D) are listed in the Key resources table. Additional climbing data for these genes can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 1A, and a summary of statistical analysis for this data can be found in Supplementary file 4. Control climbing data for these alleles can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 1B. Drosophila genotypes: positive control (w1118;UAS- non-targeting hpRNA/+; repo-GAL4,UAS-HTTNT231Q128/+), treatment control (w1118; repo-GAL4,UAS- HTTNT231Q128/UAS-siHTT), and experimental (w1118; repo-GAL4,UAS- HTTNT231Q128/modifier).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw behavioral data for Drosophila expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) in glia following reduced expression of synaptic genes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx

Suppressors of glial mutant Huntingtin (mHTT)-induced behavioral impairments among differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the Synapse Assembly cluster.
(A) Representative graphs of behavioral assays (climbing speed as a function of time) of Drosophila expressing mHTT in glia (repo >HTTNTNT231Q128) and alleles knocking down genes in the Synapse Assembly cluster. ***p<0.001 between the positive control (dashed blue line) and experimental allele (solid black line) by linear mixed effects model and post-hoc, pairwise analysis (see Materials and methods). Refer to Supplementary file 4 for a summary of the full statistical analysis. (B) Representative graphs of the climbing speed of wildtype Drosophila as a function of time with the glial driver (repo-GAL4) expressing alleles that suppress glial mHTT-induced behavioral impairments. Points and error bars on the plot represent the mean speed ± SEM of three technical replicates. Each experimental genotype was tested with 4–6 replicates of 10 animals. The gray line represents climbing speed of animals expressing the modifier allele in the repo-GAL4 background. Drosophila genotypes: positive control (w1118/+;UAS- non-targeting hpRNA/+; repo-GAL4,UAS- HTTNT231Q128/+), treatment control (w1118; repo-GAL4,UAS- HTTNT231Q128/UAS-siHTT), experimental (w1118; repo-GAL4,UAS- HTTNT231Q128/modifier), negative control (w1118; UAS- non-targeting hpRNA/+; repo-GAL4/+), and experimental control (w1118; repo-GAL4/modifier).
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw behavioral data for Drosophila expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) in glia following reduced expression of synaptic genes, expanded number of genes, and alleles.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
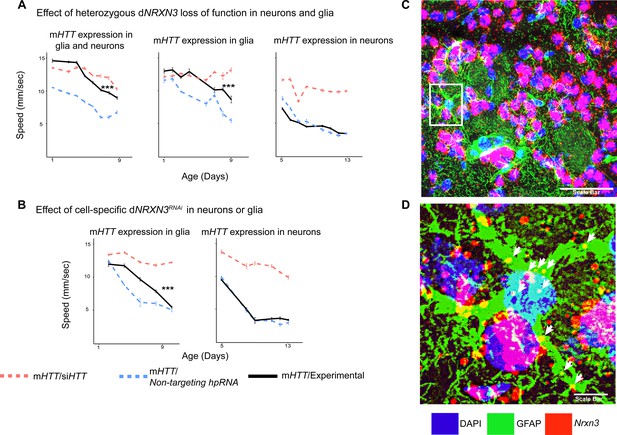
Glia-specific dNRXN3 knockdown mitigates impairments caused by mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) expression.
(A) Behavioral assays (climbing speed as a function of age) showing that dNRXN3 heterozygous loss of function (LOF) ameliorates behavioral impairments caused by expression of mHTT in both neurons and glia and in glia alone, but not in neurons alone. (B) Glia-specific dNRXN3 knockdown mitigates behavioral impairments caused by mHTT expressed solely in glia; however, neuron-specific knockdown of dNRXN3 does not affect impairments induced by mHTT expressed solely in neurons. ***p<0.001 between positive control and experimental by linear mixed effects model and post-hoc pairwise comparison (see Materials and methods). Points and error bars on the plot represent the mean ± SEM of the speed for three technical replicates. Each genotype was tested with 4–6 replicates of 10 animals. A full summary of the statistical analysis for this data can be found in Supplementary file 4. Control climbing data for these alleles can be found in Figure 3—figure supplement 1B. (C) Astrocytes in the striatum of 6-month-old knock-in HD mice (HdhzQ175/+) expressing Nrxn3. In situ probe for Nrxn3 mRNA is in red (appears magenta when overlapping with the DAPI channel), astrocytes are immunostained using an antibody specific for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in green, and DAPI in blue. Image was taken at ×63 magnification using a Leica SP8 confocal microscope. Scale bar (in white on the bottom right) represents 50 µm. 3/5 (60%) of astrocytes in this field appear Nrxn3 positive. (D) Magnified image of the astrocyte highlighted in the white box in (C). White arrows indicate yellow puncta where Nrxn3 mRNA localizes to astrocytes. Scale bar (in white on the bottom right) represents 5 µm. See Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for additional images and quantification of Nrxn3 in situ signal in striatal astrocytes in HdhzQ175/+ mice. Drosophila genotypes: dNRXN3 LOF allele (y1 w*; Mi{y+mDint2=MIC}nrx-1MI02579or nrx-1LOF, BDSC: 61696), dNRXN3 RNAi allele (UAS-nrx-1hpRNA, VDRC: 36326), neuronal and glial Huntington's disease (HD) model with dNRXN3 mutant (elavc155-GAL4/y1 w*; repo-GAL4,UAS-HTTNT231Q128/Experimental allele), glial HD model with dNRXN3 mutant (w1118/y1 w*; repo-GAL4,UAS-HTTNT231Q128/Experimental allele), and neuronal model with dNRXN3 mutant (elavc155-GAL4/y1 w*; UAS-HTTNT231Q128/Experimental allele).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Raw behavioral data for Drosophila expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) following reduced expression of dNRXN.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
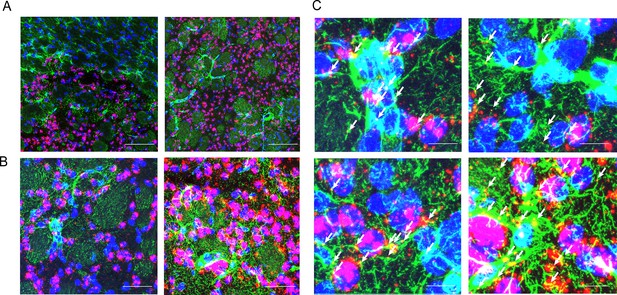
Additional images of astrocytes expressing Nrxn3 in the striatum of HdhzQ175/+ mice and quantification.
Astrocytes in the striatum of 6-month-old knock-in Huntington's disease (HD) mice (HdhzQ175/+) expressing Nrxn3. In situ probe for Nrxn3 mRNA is in red (appears magenta when overlapping with the DAPI channel), astrocytes are immunostained using an antibody specific for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in green, and DAPI in blue. Images were taken at ×20 (A) and ×63 (B) magnification using a Leica SP8 confocal microscope. 10/22 (45.5%) astrocytes were clearly Nrxn3 positive. In digitally magnified images in (C), white arrows highlight localization of anti-GFAP and Nrxn3 mRNA staining.
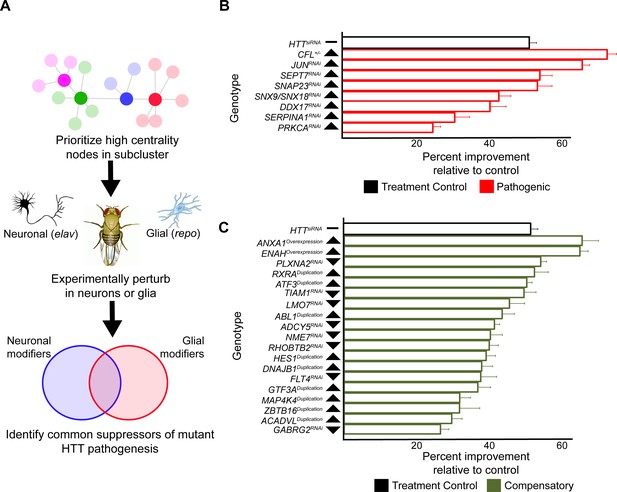
Compensatory and pathogenic gene expression changes shared by neurons and glia in response to mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) expression.
(A) Our approach for identifying modifiers of mHTT-induced behavioral impairments common to both neurons and glia. Genes that were central to their respective clusters were prioritized and manipulated in Drosophila expressing mHTT (HTTNT231Q128) in either neurons (elav-GAL4) or glia (repo-GAL4). (B) Red bars represent the percent improvement in behavior over a 9-day trial compared to positive control (non-targeting hpRNA) in Drosophila expressing mHTT in neurons and glia, after we antagonized pathogenic gene expression changes. (C) Green bars represent the percent improvement in behavior over a 9-day trial compared to control (see B), after we mimicked compensatory gene expression alterations. In (B) and (C), the top black bars represent the effect of directly targeting the mHTT transgene using a small interfering RNA (siRNA). Arrowheads indicate the direction of the conserved, concordant altered expression for each gene as a result of mHTT expression in humans, mice, and Drosophila. Behavioral assay graphs corresponding to the data presented in (B) and (C) can be found in Figure 5—figure supplement 1A. Corresponding statistical analysis for (B) and (C) can be found in Supplementary file 6. Corresponding controls for behavioral data can be found in Figure 5—figure supplement 1B, C. Drosophila genotypes: positive control (elavc155-GAL4/w1118;UAS- non-targeting hpRNA/+; repo-GAL4,UAS-HTTNT231Q128/+), treatment control (elavc155-GAL4/w1118; repo-GAL4, UAS- HTTNT231Q128/UAS-siHTT), and experimental (elavc155-GAL4/w1118; repo-GAL4, UAS- HTTNT231Q128/modifier).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Numerical data for bar charts summarizing the improvement in behavior in Drosophila expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) in neurons and glia by manipulating common pathogenic and compensatory alterations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx

Genetic modifiers suppress behavioral impairments caused by mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) expression in neurons and glia.
(A) Representative graphs of the climbing speed of animals expressing mutant HTT in neurons and glia in combination with common modifiers as a function of time. ***p<0.001 between the positive control (dashed blue line) and experimental allele (solid black line) by linear mixed effects model and post-hoc, pairwise analysis. Refer to Supplementary file 6 for full statistical analysis of each genotype in neurons, glia, and both. (B) Representative graphs of the speed of wildtype Drosophila with the glial driver (repo-GAL4) and alleles that suppressed mutant HTT-induced behavioral impairments in both neurons and glia. The dashed red line represents the longitudinal climbing speed of animals expressing a non-targeting hpRNA in glia, while the gray line represents climbing speed of animals expressing the common modifier allele in the repo-GAL4 background. (C) Representative graphs of the speed of wildtype Drosophila with the neuronal driver (elav-GAL4) expressing the alleles that suppressed mutant HTT-induced behavioral impairments in both neurons and glia as a function of time. The dashed green line represents the climbing speed of animals expressing a non-targeting hpRNA in neurons, while the black line represents climbing speed of animals expressing the common modifier allele in the elav-GAL4 background. Points and error bars on the plot represent the mean speed ± SEM of three replicates. Each genotype was tested with 4–6 replicates of 10 animals. Drosophila genotypes: neuronal and glial mHTT positive control (elavc155-GAL4/w1118;UAS-non-targeting hpRNA/+; repo-GAL4, UAS- HTTNT231Q128/+), neuronal and glial mHTT treatment control (elavc155-GAL4/w1118; repo-GAL4, UAS-HTTNT231Q128/UAS-siHTT), neuronal and glial experimental (elavc155-GAL4/w1118; repo-GAL4, UAS- HTTNT231Q128/modifier), glial control (elavc155-GAL4/w1118; UAS-non-targeting hpRNA/+), glial experimental control (elavc155-GAL4/w1118; modifier/+), neuronal control (w1118; UAS-non-targeting hpRNA/+; repo-GAL4/+), and neuronal experimental control (w1118; repo-GAL4/modifier).
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw behavioral data for Drosophila expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) in neurons and glia by manipulating common pathogenic and compensatory alterations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
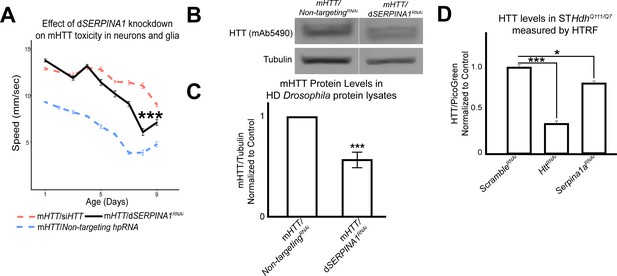
Antagonizing the pathogenic overexpression of SERPINA1 in neurons and glia mitigates mutant Huntingtin (mHTT)-induced behavioral impairments and lowers mHTT protein levels in Drosophila and Huntington's disease (HD) mouse striatal cells.
(A) Behavioral assays following knockdown of dSERPINA1 in Drosophila expressing mHTT in neurons and glia. *** indicates p<0.001 by linear mixed effects model and post-hoc pairwise comparison between positive control and experimental animals. Points and error bars on the plot represent the mean ± SEM of three technical replicates. Each genotype was tested with 4–6 replicates of 10 animals. (B) Representative western blot showing lower levels of mHTT following knockdown of dSERPINA1 in Drosophila expressing mHTT in neurons and glia. (C) Quantification of five independent immunoblots showing the effect of dSERPINA1 knockdown on mHTT levels in Drosophila head protein lysates. ***p<0.001 between positive control and dSERPINA1 knockdown by one-way t-test. (D) Quantification of HTT protein levels in HD mouse striatal-derived cells (STHdhQ111/Q7) measured by homogenous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) following treatment with a pool of scramble small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) (negative control), a pool of siRNAs against Htt, and a pool of siRNAs against Serpina1a. Quantification is presented as a ratio of the emission signal from the fluorescent D2 dye (HTT)/PicoGreen (number of cells per well). n = 9 for each treatment group. *p<0.05 and ***p<0.001 between genotypes by Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test. Drosophila genotypes: dSERPINA1 RNAi allele (UAS-Spn42DehpRNA, VDRC: 102622), positive control (elavc155-GAL4/w1118;UAS- non-targeting hpRNA/+; repo-GAL4,UAS-HTTNT231Q128/+), treatment control (elavc155-GAL4/w1118; repo-GAL4, UAS- HTTNT231Q128/UAS-siHTT), and dSERPINA1 experimental (elavc155-GAL4/w1118;UAS-Spn42DehpRNA/+; repo-GAL4, UAS-HTTNT231Q128/+).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Raw behavioral data for Drosophila expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) in neurons and glia following knockdown of Spn42De.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Summary of numerical and raw data for western blots of protein lysates from Drosophila heads expressing mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) in neurons and glia with knockdown of Spn42De.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig6-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Summary of numerical and raw data for homogenous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) for protein lysates of STHdhQ111/Q7 treated with pooled small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) against Serpina1a.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig6-data3-v2.xlsx
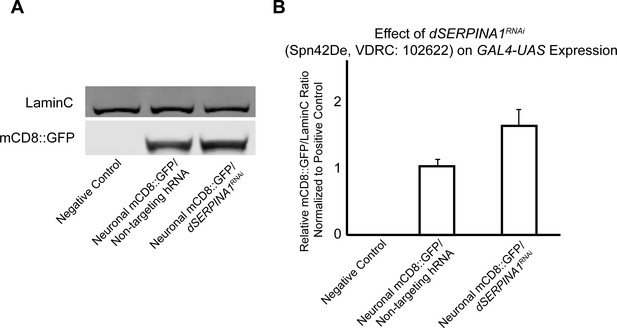
dSERPINA1 knockdown does not reduce the expression of the GAL4-UAS system.
(A) Representative immunoblot performed on Drosophila protein lysates assessing mCD8::GFP protein levels as a proxy for GAL4-UAS expression. mCD8::GFP was expressed in neurons using the elav-GAL4 driver. The negative control in this experiment was elav >GAL4 driving the expression of a non-targeting hpRNA (left lane). The positive control was elav >GAL4 expressing the mCD8::GFP construct and a non-targeting hpRNA (middle lane). The experimental was elav >GAL4 driving the expression of the mCD8::GFP construct and the dSERPINA1RNAi (Spn42De, VDRC: 102622) allele that reduced mutant protein levels in Figure 6 (right lane). LaminC was used as a loading control in this immunoblot. (B) Quantification of the three replicates from the immunoblot in (A) represented as the ratio of mCD8::GFP to LaminC, normalized to the average of the positive control (presented as mean ± SEM).
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Summary of numerical and raw data for western blots of protein lysates from Drosophila heads expressing mCD8::GFP in neurons with knockdown of Spn42De.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
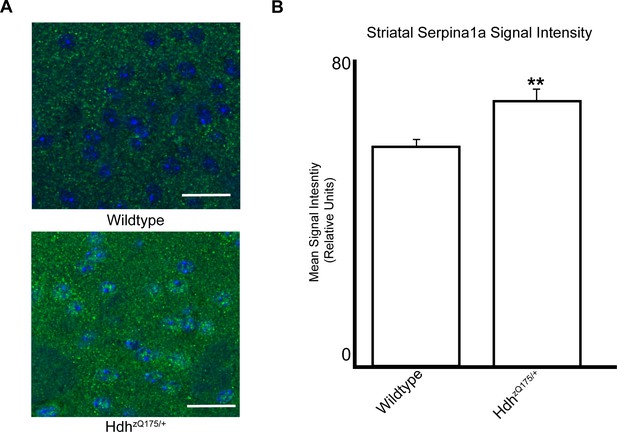
Serpina1a protein accumulates in the striata of HdhzQ175/+ mice compared to wildtype littermates.
(A) Representative images of fixed, paraffin-embedded coronal brain slices at the striatum of HdhzQ175/+ and wildtype mice, stained with an antibody against Serpina1a (green). Images were taken on a Leica SP8 confocal microscope using a magnification of ×20 along with ×6.93 digital zoom. DAPI staining is in blue. (B) Quantification of measured mean signal intensity (presented as mean ± SEM) for Serpina1a, comparing HdhzQ175/+ and wildtype mice. ** indicates significant difference between the HdhzQ175/+ and wildtype mice by a two-way t-test assuming unequal variances (p=0.003). Statistical analysis and raw data are available in Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Summary of numerical and raw data for immunohistochemistry analysis of Serpina1 staining in 8.5-month-old mouse striata from wildtype and zQ175 mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Anti-HTT (mouse monoclonal) | EMD Millipore | mAb5490, RRID:AB_2233522 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | ThermoFisher | A-11122, RRID:AB_221569 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-HTT (mouse monoclonal) | Novartis | 2B7 | HTRF (0.023 μg/mL) |
| Antibody | Anti-laminC (mouse monoclonal) | Hybridoma Bank | LC28.26, RRID:AB_528339 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-GFAP (rabbit polyclonal) | DAKO | Z0334, RRID:AB_10013382 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Alpha-tubulin (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | EP1332Y, RRID:AB_922700 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-HTT (mouse monoclonal) | SigmaAldrich | mAb2166, RRID:AB_11213141 | HTRF (1.4 μg/mL) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit IgG Alexa 488 (goat polyclonal) | Invitrogen | A-11008, RRID:AB_143165 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-Serpina1a (rabbit polyclonal) | Invitrogen | PA5-16661, RRID:AB_10985745 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | RDye 680RD anti-Rabbit IgG (goat polyclonal) | LI-COR Biosciences | 925-68071, RRID:AB_2721181 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | IRDye 800CW anti-Mouse IgG (goat polyclonal) | LI-COR Biosciences | 925-32210, RRID:AB_2687825 | WB (1:5000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamine 2000 | Life Technologies | 11668 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EDTA-free protease inhibitor | Calbiochem | 539134 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | miRNeasy Mini Kit | Qiagen | 217004 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Illumina TruSeq Stranded mRNA | Illumina | 20020595 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Tyramide-Cy3 Plus kit | Perkin Elmer | NEL744001KT | |
| Commercial assay, kit | PicoGreen | Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit | P7589 | |
| Cell line (Mus musculus) | STHdhQ111/Q7 Cells | Coriell Cell Repositories | CH00096 | |
| Strain, strain background (Drosophila) | White mutant, background genotype | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | 3605 | w1118 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Non-targeting hpRNA | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | 13974 | |
| Strain, strain background (Drosophila) | repo-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | 7415 | w1118; P{w+m*=GAL4}repo/TM3, Sb1 |
| Strain, strain background (Drosophila) | elav-Gal4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | 458 | P{GawB}elavC155 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | N-terminal HD model | Botas Laboratory | Branco et al., 2008 | UAS-HTTNT231Q128/TM6B, tubulin-GAL80 (N-terminal) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Full-length HD model | Botas Laboratory | This paper | UAS-HTTFL200Q/CyO (full-length) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | siRNA against human mutant HTT | Botas Laboratory Kaltenbach et al., 2007 | UAS-siHTT | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Classic CenG1A loss-of-function allele | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | 44301 | CenG1ALOF or y1w*;Mi{MIC}CenG1AMI06024 (Figure 3D) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Classic vlc loss-of-function allele | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | 10366 | vlcLOF or y1w67c23;P{w+mc = lacW}vlck01109/CyO (Figure 3D) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Classic trn loss-of-function allele | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | 4550 | trnLOF or y1w67c23;P{w+mc = lacW}trnS064117/TM3, Sb1 Ser1 (Figure 3D) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Classic cora loss-of-function allele | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | 9099 | coraLOF or P{ryt7.2=neoFRT}43D cora14/CyO (Figure 3D) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | RNAi against Sytbeta | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | 106559 | UAS-SytbetahpRNA (Figure 3D) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | RNAi against mGluR | National Institute of Genetics, Japan | 11144 R-3 | UAS-mGluRRNAi (Figure 3D) |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Neuronal mCD8::GFP reporter line | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | 5146 | P{w+mW.hs=GawB}elavC155, P{w+mC = UAS-mCD8::GFP.L}Ptp4E[LL4], P{ry[+t7.2]=hsFLP}1, w* |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Classical loss of function and overexpression alleles in Drosophila | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | Provided in Supplementary files 4 and 5 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | RNAi alleles in Drosophila | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | Provided in Supplementary files 4 and 5 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila) | Cytological duplication alleles in Drosophila | GenetiVision | Provided in Supplementary files 4 and 5 | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | HdhzQ175 Mice | Jackson Laboratories | 027410 | B6J.129S1-Htttm1Mfc/190ChdiJ |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMF3 Vector | Drosophila Genome Resource Center | 1237 | |
| Software, algorithm | Adept Desktop | Omron | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | Video Savant | IO Industries | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | MatLab with Image Processing Toolkit and Statistics Toolkit | MathWorks | https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html | |
| Software, algorithm | RSLogix | Rockewell Automation | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | Ultraware | Rockewell Automation | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | Assay Control | SRI International | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | FastPhenoTrack Vision Processing | SRI International | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | TrackingServer Data Management | SRI International | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | ScoringServer Behavioral Scoring | SRI International | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | Trackviewer Visual Tracking and Viewing | SRI International | N/A | |
| Software, algorithm | Illustrator CC | Adobe | https://www.adobe.com | |
| Software, algorithm | R | R Project for Statistical Computing | https://www.r-project.org/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | The Fiji Team | https://fiji.sc/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Image Studio Lite | LI-COR Biosciences | https://www.licor.com/bio/image-studio-lite/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Bowtie | Langmead and Salzberg, 2012 | http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/index.shtml | |
| Software, algorithm | RSEM | Li and Dewey, 2011 | https://github.com/deweylab/RSEM | |
| Software, algorithm | DESeq2 | Love et al., 2014 | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/DESeq2.html | |
| Software, algorithm | DIOPT | Hu et al., 2011 | https://www.flyrnai.org/cgi-bin/DRSC_orthologs.pl | |
| Software, algorithm | MGI | The Mouse Genome Database | http://www.informatics.jax.org/genes.shtml | |
| Software, algorithm | STRING | Szklarczyk et al., 2015 | https://string-db.org/ | |
| Software, algorithm | InfoMap | Rosvall and Bergstrom, 2008 | https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/igraph/index.html | |
| Software, algorithm | Cytoscape | The Cytoscape Consortium | https://cytoscape.org | |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | AllStars Negative Control siRNA (Scramble) | Qiagen | 1027280 | |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | Htt SMARTPool siRNAs | Horizon Discovery Limited | L-040632-01-0005 | 5′- GAAAUUAAGGUUCUGUUGA-3′ 5′- CCACUCACGCCAACUAUAA-3′ 5′- GAUGAAGGCUUUCGAGUCG-3′ 5′- UAACAUGGCUCAUUGUGAA-3′ |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | Serpina1a SMARTPool siRNAs | Horizon Discovery Limited | L-043380-01-0005 | 5′- GAAUAUAACUUGAAGACAC-3′ 5′-GGGCUGACCUCUCCGGAAU-3′ 5′- UGGUAGAUCCCACACAUAA-3′ 5′- GAAAGAUAGCUGAGGCGGU-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers for cloning human HTT | This paper | See experimental model detail | Forward 5′-gaattcGCACCGACCAAAGAAAGAAC-3′ Reverse 5′-tctagaGGCAGAAGGTTCACCAGGTA-3′ |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers for generating in situ probes for mouse Nrxn3 including RNA polymerase promoter sequences for T3 (forward) and T7 (reverse) | Allen Brain Atlas | https://portal.brain-map.org/ | Forward: 5′- GCGAATTAACCCTCACTAAAGGGTCCTTCCCCTTTCCTCCTAA-3′ Reverse: 5′-GCGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAGGCATGCTCTGTACTCCA-3′ |
Additional files
-
Source code 1
R script for prefiltering differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Drosophila Huntington's disease (HD) models.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code1-v2.zip
-
Source code 2
R script for identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Drosophila Huntington's disease (HD) models.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code2-v2.zip
-
Source code 3
Python code for identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in postmortem human Huntington's disease (HD) striata.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code3-v2.zip
-
Source code 4
Python code for identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from Huntington's disease (HD) mouse models.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code4-v2.zip
-
Source code 5
Python code for homology mappings across humans, mice, and Drosophila.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code5-v2.zip
-
Source code 6
Python code for comparing Huntington's disease (HD) differentially expressed genes (DEGs) across species.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code6-v2.zip
-
Source code 7
Python code for clustering networks.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code7-v2.zip
-
Source code 8
R script for network analysis in a striatal background summarized in Supplementary file 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code8-v2.zip
-
Source code 9
R script for analyzing Drosophila behavioral assays.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-code9-v2.zip
-
Supplementary file 1
Mappings of orthologous Huntington's disease (HD) human, mouse, and Drosophila differentially expressed genes (DEGs).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Network connectivity of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) responding to glial or neuronal mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Cluster membership and summary of cluster annotations for differentially expressed genes (DEGs) responding to glial or neuronal mutant Huntingtin (mHTT) expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Summary of statistical analysis for alleles in the Synapse Assembly cluster that modify glial mutant Huntingtin (mHTT)-induced behavioral impairments.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Summary of alleles screened and results for common modifiers of mutant Huntingtin (mHTT)-induced behavioral impairments in neurons and glia.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-supp5-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
Summary of statistics for alleles that are common suppressors of neuronal and glial mutant Huntingtin (mHTT)-induced behavioral impairments.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-supp6-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64564/elife-64564-transrepform-v2.docx





