The vascular niche controls Drosophila hematopoiesis via fibroblast growth factor signaling
Figures
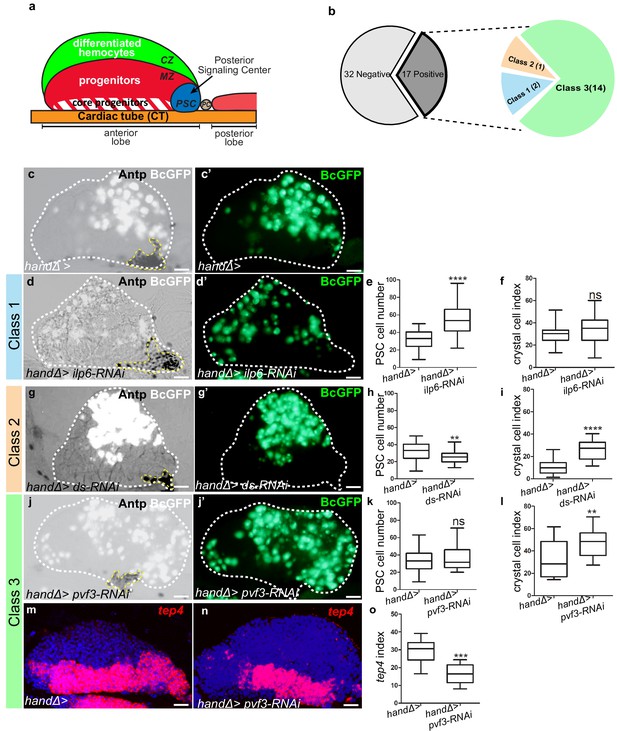
Lymph gland organization and RNAi screen results.
(a) Representation of lymph gland anterior and posterior lobes from third instar larvae. The anterior lobe is composed of progenitors (red) and core progenitors (hatched red), and the cortical zone (CZ, green). The PSC is blue and the cardiac tube (CT)/vascular system, is orange. PC corresponds to pericardial cell. (b) Summary of the screen performed by expressing RNAi in cardiac cells using the handΔ-gal4 driver. The number of genes corresponding to the different classes of phenotype is given. Subsequent panels illustrate the control and observed lymph gland defects (c, d, g, j). Anterior lobe and PSC are delimited by white and yellow dashed lines, respectively. Black-cell-GFP (BcGFP, white) labels crystal cells and Antp (black) the PSC. (c’, d’, g’, j’) BcGFP is in green; (e, h, k) PSC cell numbers; (f, i, l) Crystal cell index. (c–f) Reducing ilp6 in cardiac cells (d, d’) augments PSC cell number (e) without affecting crystal cell differentiation (f); this defines class 1. (g–i) Knocking down dachsous (ds) in cardiac cells (g, g’) decreases PSC cell number (h) and increases crystal cell index (i); this defines class 2. (j–l) Reducing pvf3 in cardiac cells (j, j’) does not modify PSC cell number (k) but increases crystal cell differentiation (l); this defines class 3. (m, n) tep4 (red) labels core progenitors. Decrease in tep4 expression is observed when pvf3 is knocked down in cardiac cells. (o) tep4 index. For all quantifications and figures, statistical analysis t-test (Mann-Whitney nonparametric test) was performed using GraphPad Prism five software. Error bars represent SEM and *p<0,1;**p<0,01; ***p<0,001; ****p<0,0001 and ns (not significant). In all confocal pictures nuclei are labeled with Topro (blue) and scale bars = 20 µm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Results of the RNAi ligand screen RNAi was expressed in cardiac cells by using the handΔ-gal4 and/or NP1029-gal4 driver.
Crystal cells were labeled by BcGFP, PSC cells were immune-stained with Antp antibody, and to visualize the core progenitors tep4 in situ hybridization was performed. In most cases, 2 RNAi lines were tested per ligand, and at least 15 lymph glands per RNAi were analyzed. Crystal cell index and PSC cell number were established. The green and red colored boxes indicate an increase and a decrease, respectively, compared to the control. Black dashes indicate that no difference was observed compared to the control. A white box indicates that this condition was not tested. Most RNAi lines that gave a modification in crystal cell index with the handΔ-gal4 driver were also analyzed with another cardiac cell driver NP1029-gal4, and proPO antibody immunostainings were performed to visualize crystal cells. Finally, for all RNAi lines that led to a defect in crystal cell differentiation with the handΔ-gal4 driver, tep4 in situ hybridizations were performed and the tep4 index was established.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Results of the RNAi ligand screen.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig1-data2-v1.xlsx
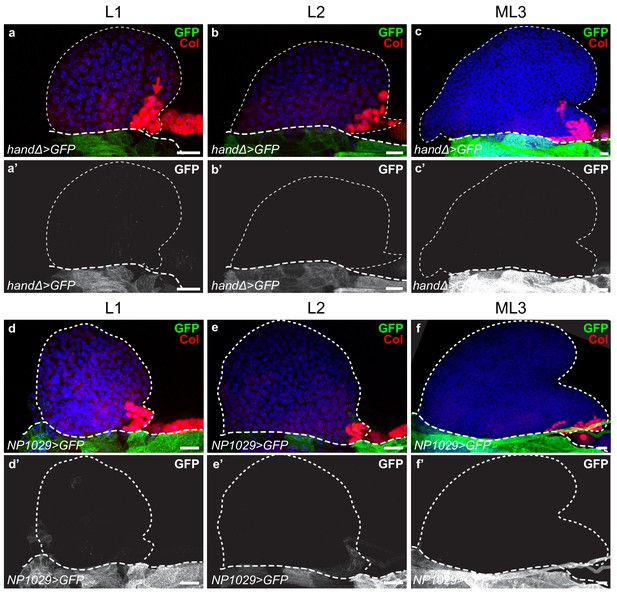
Expression pattern of handΔ-gal4 and NP1029-gal4 driver in lymph glands during larval development.
(a–c’) HandΔ-gal4 > mcd8 GFP is green in (a–c) and white in (a’–c’). (d–f’) NP1029-gal4 > mcd8 GFP is green in (d–f) and white in (d’–f’). The PSC is labeled by Col (red and arrow in a); thin and thick dashed lines indicate the contours of the lymph gland and the cardiac tube, respectively.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
RNAi screen quantification data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
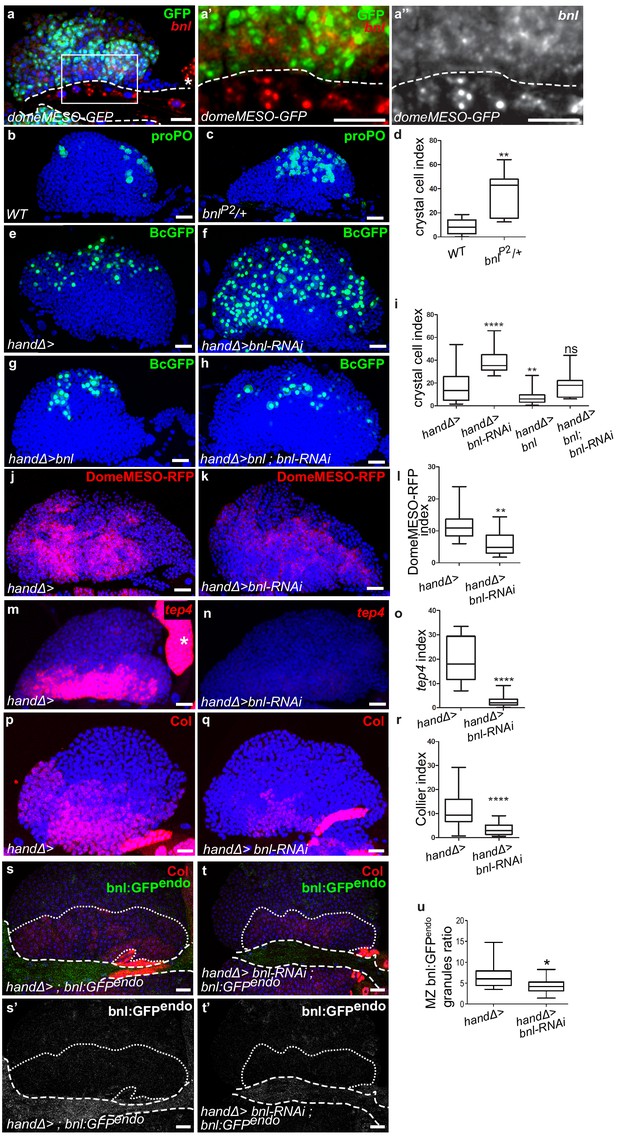
Ligand Bnl is expressed in cardiac cells and controls lymph gland homeostasis.
(a) A maximum projection of 5 confocal lymph gland sections, bnl (red) is expressed in cardiac cells and MZ progenitors that express domeMESO-GFP (green). (a’, a’’) An enlarged view, bnl is red (a’) or white (a”). A white dashed line indicates the cardiac tube. * indicates a pericardiac cell. (b, c) proPO (green) labels crystal cells. bnlP2/+ heterozygous mutant lymph glands have an increased number of crystal cells (c) compared to the control (b). (e–f, g–h) Black-cell GFP (BcGFP, green) labels crystal cells. (d, i) Crystal cell index. Co-expression of bnl and bnl-RNAi in cardiac cells restores the wildtype number of crystal cells (i). (j, k) DomeMESO-RFP (red) labels MZ progenitors. Compared to the control (j) barely detectable DomeMESO-RFP levels are observed when bnl is knocked down in cardiac cells (k). (l) DomeMESO-RFP index. (m, n) tep4 labels core progenitors. Compared to the control (m) lower levels of tep4 (red) are observed when bnl is knocked down in cardiac cells (n). (o) tep4 index. (p–q) Col labels core progenitors. Compared to the control (p) lower levels of Col are observed in the core progenitors when bnl is knocked down in cardiac cells (q). (r) Col index. (s–t’) Maximum projection of 5 confocal sections of the lymph gland expressing bnl:GFP endo (green) and Col immunostaining that labels MZ progenitors (red). Compared to the control (s, s’) a decrease in bnl:GFP endo in green (t) and white (t’) is observed when bnl is knocked down in cardiac cells. Fine and thick dashed lines indicate the MZ and CT contours, respectively. (u) Bnl:GFPendo granules ratio in the MZ.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
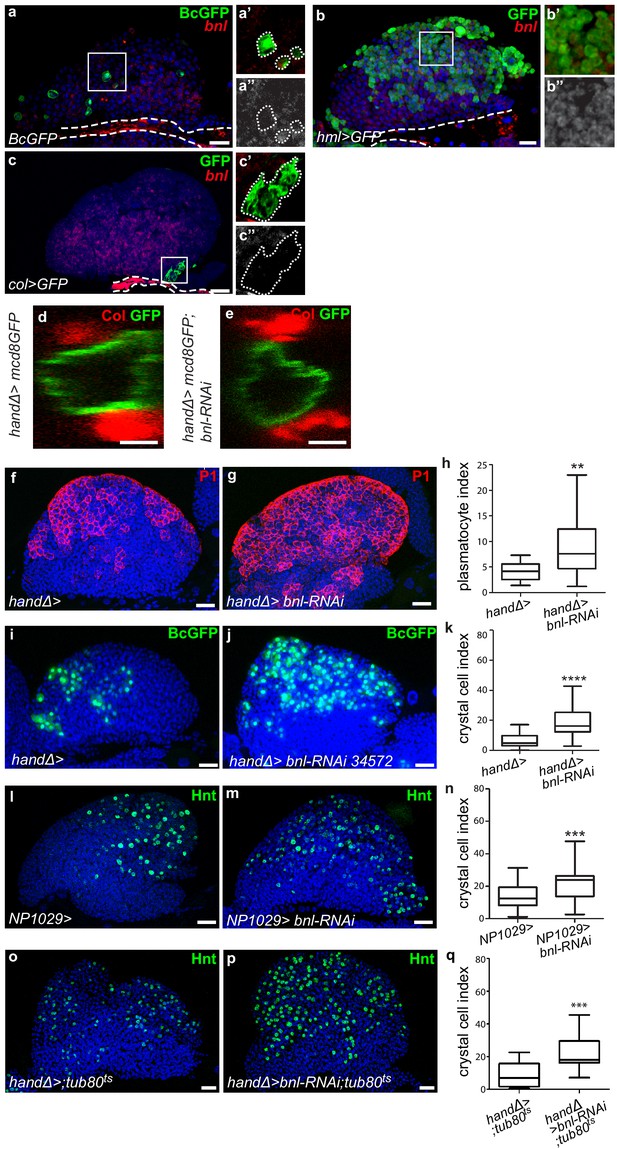
The ligand Bnl in cardiac cells controls lymph gland hemocyte differentiation homeostasis.
(a–c”) A maximum projection of 5 confocal lymph gland sections, bnl is in red. (a,b,c) and white in (a”,b”,c”). BcGFP (green) labels crystal cells. (a’–a”) An enlarged view, crystal cells are green (a’) and bnl is white (a”). (b–b”) hml >GFP (green) labels differentiating hemocytes in the CZ. (b’–b”) An enlarged view, differentiating hemocytes are green (b’) and bnl is white (b”). (c–c”) col >GFP (green) labels PSC cells. (c’–c”) An enlarged view, the PSC is green (c’) and bnl is white (c”). White large dashed line indicates the cardiac tube contour. (d, e) Cardiac cells express mcd8-GFP (handΔ>mcd8 GFP, green). A transversal section is shown. PSC cells are labeled by Col (red). No difference in cardiac tube morphology is observed when bnl is knocked down in cardiac cells at the larval stage (e) compared to the control (d). (f, g) Plasmatocytes (red) are labeled by P1 antibody. An increase in plasmatocyte number is observed when bnl expression is decreased in cardiac cells (g) compared to the control (f). (h) Plasmatocyte index. (i–j) Crystal cells (GFP, green) express the Black-cell GFP (BcGFP) marker. An increase in crystal cell number (j) is observed when bnl expression is decreased in cardiac cells compared to the control (i), when another bnl-RNAi is used (j) or when another cardiac cell driver NP1029 is used (l, m). (k, n) Crystal cell index. (o, p) Hnt labels crystal cells. Compared to the control (o) crystal cell number is increased when bnl is knocked down in cardiac cells from the L2 stage by using the conditional Gal4/Gal80ts system (p). (q) Crystal cell index.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
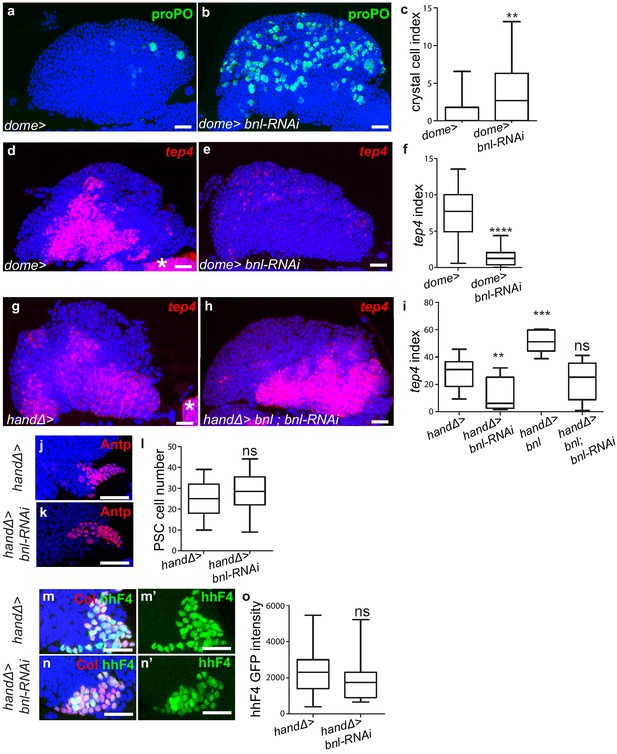
Whereas the ligand Bnl in cardiac cells does not control PSC cells, it is required in MZ progenitors to regulate lymph gland homeostasis.
(a, b) Crystal cells are labeled by proPO antibody (green). An increase in crystal cell number is observed when bnl expression is decreased in MZ progenitors (b) compared to the control (a). (c) Crystal cell index. (d–e, g–h) tep4 (red) is expressed in MZ progenitors. Compared to the control (d) barely detectable levels of tep4 are observed when bnl is knocked down in MZ progenitors (e). Co-expression of bnl and bnl-RNAi in cardiac cells restores WT levels of tep4 expression (h and i) compared to the control (g). (f, i) tep4 index. (j, k) PSC cells are labeled by Antp (red) antibody. No difference in PSC cell numbers is observed when bnl is knocked down in cardiac cells (k) compared to the control (j). (l) Quantification of PSC cell number. (m– n’) hhF4-GFP labels PSC cells (GFP, green). No difference in hhF4-GFP expression is observed when bnl is knocked down in cardiac cells (n) compared to the control (m). (o) Quantification of hhF4-GFP intensity.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 2—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
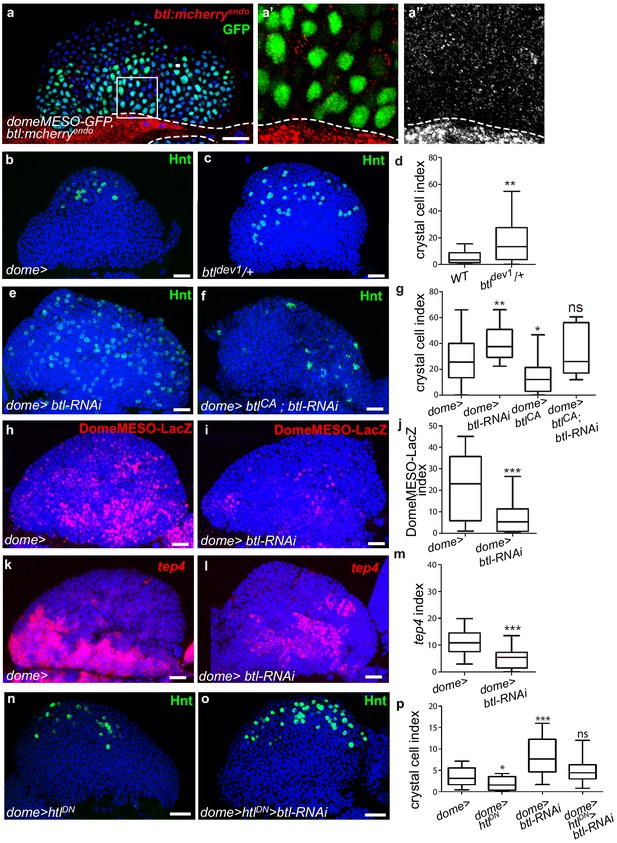
Receptor Btl is expressed in hematopoietic progenitors and required to control lymph gland homeostasis.
(a) A maximum projection of 5 confocal lymph gland sections of larvae expressing btl:cherryendo (red) and domeMESO-GFP that labels MZ progenitors (green). (a’, a’’) An enlarged view, btl:cherryendo red (a’) or white (a”). Dashed lines indicate the cardiac tube contour. btl:cherryendo is expressed in cardiac cells and MZ progenitors. (b–c, e–f) Hindsight (Hnt, green) labels crystal cells. Crystal cell differentiation is increased in btldev1/+ heterozygous mutant larvae (c) compared to the control (b). (e, f) Crystal cell numbers increase when btl is knocked down in progenitors (e) and crystal cell differentiation is rescued when a constitutive activated btl receptor (btlCA) is expressed in the btl-RNAi context (f). (d, g) Crystal cell index. (h, i) DomeMESO-LacZ (red) labels MZ progenitors. Compared to the control (h) barely detectable domeMESO-LacZ levels are observed when btl is knocked down in progenitors (i). (k, l) Lower levels of tep4 (red) are observed when btl is knocked down in progenitors (l) compared to the control (k). (j, m) DomeMESO-LacZ and tep4 index, respectively. (n, p) Crystal cell numbers decrease when a dominant negative htl receptor (htlDN) is knocked down in progenitors (n) and crystal cell differentiation is increased when htlDN is co-expressed with btl-RNAi (o). (p) Crystal cell index.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
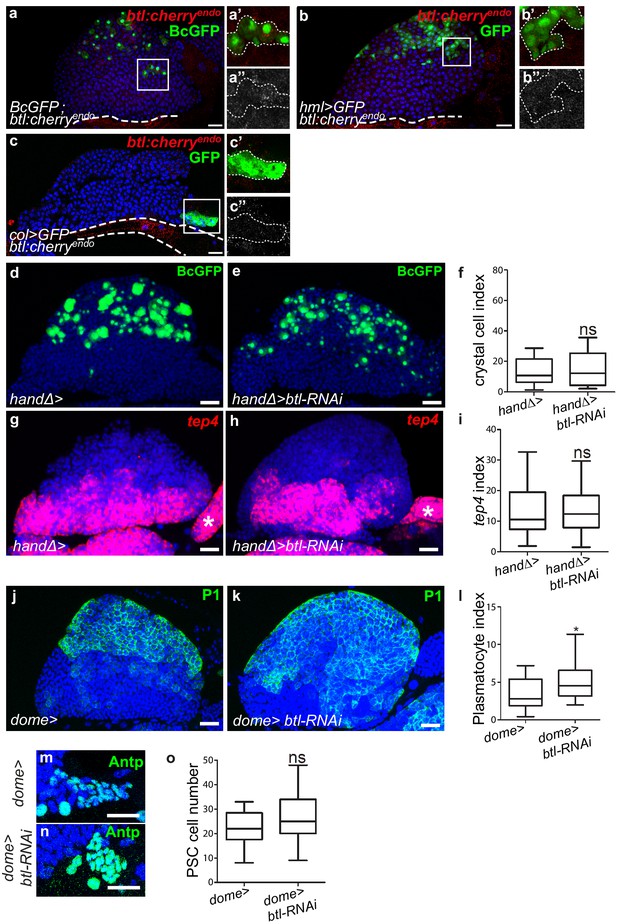
The Btl receptor in progenitors controls lymph gland hemocyte differentiation without affecting PSC size.
(a–c”) A maximum projection of 5 confocal lymph gland sections of larvae expressing btl:cherryendo (red). (a–a’) BcGFP (green) labels crystal cells. (a’–a”) An enlarged view, crystal cells are green (a’) and btl:cherryendo is white (a”). (b–b”) hml >GFP (green) labels differentiating hemocytes in the CZ. (b’–b”) An enlarged view, differentiating hemocytes are green (b’) and btl:cherryendo is white (b”). (c–c”) Col >GFP (green) labels PSC cells. (c’–c”) An enlarged view, the PSC is green (c’) and btl:cherryendo is white (c”). (a, b, c) White large dashed line indicates the cardiac tube contour. (d, e) BcGFP (green) labeled crystal cells. No significant difference in crystal cell number is observed when btl expression is decreased in cardiac cells (e) compared to the control (d). (f) Crystal cell index. (g, h) Decreasing btl expression in cardiac cells (h) does not change tep4 expression (red) compared to the control (g). (i) tep4 index. (j, k) An increase in plasmatocyte number (labeled by P1 antibodies, green) is observed when btl expression is decreased in progenitors (k) compared to the control (j). (l) Plasmatocyte index. (m, n) PSC cells are labeled by Antp (green) antibody. No difference in PSC cell number is observed when btl is knocked down in progenitors (n) compared to control (m). (o) Quantification of PSC cell number.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
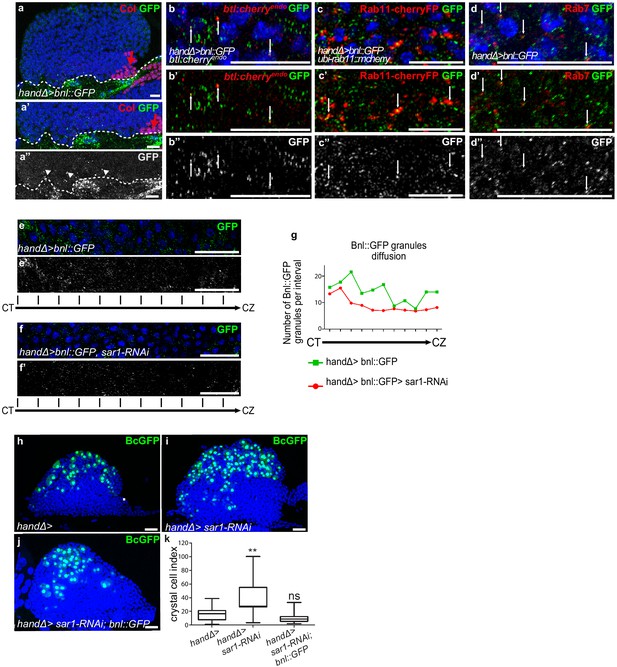
Ligand Bnl secreted by cardiac cells controls lymph gland crystal cell differentiation.
(a) Active bnl::GFP fusion protein is expressed in cardiac cells using handΔ-gal4 driver. Dashed lines indicate cardiac tube and the PSC is labeled by Collier (Col, red and red arrow). (a’, a’’) An enlarged view; Bnl::GFP is green (a’) or white (a”). Bnl::GFP positive granules are detected in cardiac and lymph gland cells (arrowheads). (b–b”) Enlargement of MZ area close to the cardiac tube in larvae expressing Bnl::GFP fusion protein (green) in cardiac cells (handΔ-gal4 > Bnl::GFP) and Btl:mcherryendo (red). Bnl::GFP cytoplasmic punctate dots (green in b-b’ and white in b’) co-localize with Btl:mcherryendo (yellow and arrows in b’). (c,c”) Enlargement of MZ area close to the cardiac tube in larvae expressing ubi-Rab11cherryFP (red), a marker for recycling endocytic vesicles; Bnl::GFP fusion protein (green) is expressed in cardiac cells (handΔ-gal4 > Bnl::GFP). Bnl::GFP cytoplasmic punctate dots (green in c-c’ and white in c’) co-localize with ubi-Rab11cherryFP (yellow and arrows in c’). (d–d”) Enlargement of MZ area close to the cardiac tube in larvae expressing Bnl::GFP fusion protein (green) in cardiac cells (handΔ-gal4 > Bnl::GFP) and Rab7 immunostainings (red in d, d’ and white in d’). (d–d’) Bnl::GFP cytoplasmic punctuate dots co-localize with Rab7 positive dots (yellow and arrows in d’). (e–f’) Enlargement of lymph gland cross sections extending from the cardiac tube (CT) to the cortical zone (CZ). Bnl::GFP fusion protein, expressed in cardiac cells (handΔ-gal4 > Bnl::GFP) is green (e, f) and white (e’, f’). Knocking down sar1 in cardiac cells (f, f’) leads to a decrease in Bnl::GFP cytoplasmic punctate dots compared to the control (e, e’). (g) Quantification of Bnl::GFP cytoplasmic punctate dots/granules. (h, j) BcGFP (green) labels crystal cells. Knocking down sar1 in cardiac cells (i) increases crystal cell numbers compared to the control (h). Crystal cell differentiation rescue is observed when bnl::GFP is co-expressed with sar1-RNAi (j, k). (k) Crystal cell index.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
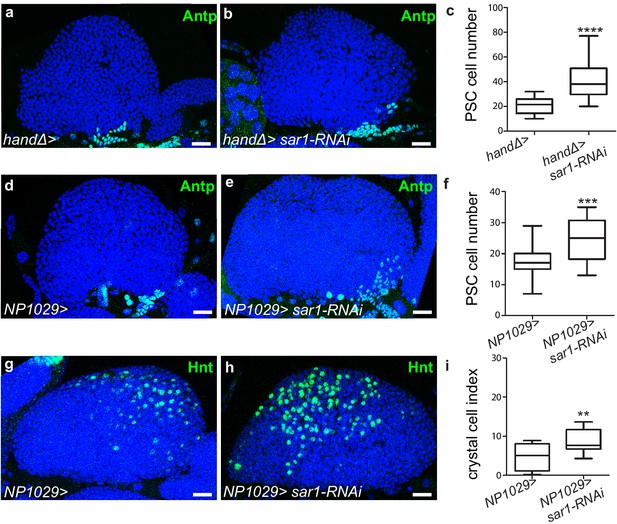
Knocking down sar1 in cardiac cells impairs crystal cell differentiation and increases PSC size.
(a–b, d–e) PSC cells are labeled with Antp (green) antibody. An increase in PSC cell numbers is observed when sar1 is knocked down in cardiac cells using the handΔ driver (b) compared to the control (a). (c) Quantification of PSC cell numbers. (d–f) An increase in PSC cell number is observed when sar1 is decreased in cardiac cells using the NP1029 driver (e) compared to the control (d). (f) PSC cell numbers. (g, h) Crystal cells are labeled with Hnt (green) antibody. An increase in crystal cell number is observed when sar1 is knocked down in cardiac cells using NP1029, another cardiac cell driver (h) compared to the control (g). (i) Crystal cell index.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
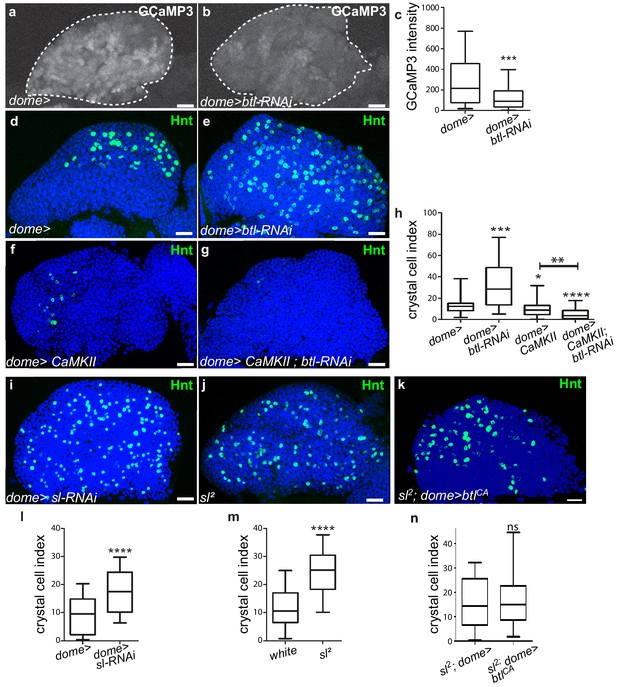
Btl receptor interacts genetically with CamKII to control blood cell differentiation by preventing high Ca2+ levels in progenitors.
(a, b) GCaMP3 Ca2+ sensor (dome >UAS-GCaMP3) is white. GCaMP3 intensity decreases when btl is knocked down in MZ progenitors (b) compared to the control (a). (c) Quantification of GCaMP3 intensity. (d–g, i–k) Hnt (green) labels crystal cells. Crystal cell differentiation decrease is observed when Ca2+ levels increased due to CaMKII expression in progenitors (dome >CaMKII, f) compared to the control (d). Co-expression of CaMKII and btl-RNAi in progenitors (dome >CaMKII; btl-RNAi, g) leads to a decrease in crystal cell number compared to the btl knock-down alone (e). (h, l–n) Crystal cell index. Crystal cell differentiation increase is observed in sl2 homozygous mutant larvae (j, m) and when sl is knocked down in progenitors (i, l) compared to the control (d). (k, n) No difference in crystal cell index is observed in sl2 homozygous mutant larvae and in a sl2 homozygous mutant where btlCA is expressed in MZ progenitors (sl2; dome >btlCA).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
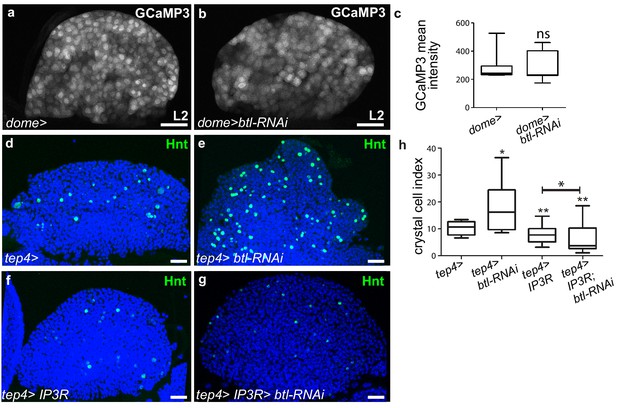
Ca2+ levels in progenitors regulate crystal cell differentiation.
(a, b) L2 larval lymph glands and the GCaMP3 Ca2+ sensor (dome >UAS-GCaMP3) is white. No difference observed in GCaMP3 intensity between the control (a) and when btl is knocked down in MZ progenitors (b). (c) GCaMP3 intensity. (d–e, f–g) Crystal cells are labeled with Hnt (green) antibody. A decrease in crystal cell numbers is observed when IP3R is knocked down in progenitors using the tep4 driver (f) compared to the control (d). Co-expression of IP3R and btl-RNAi in progenitors prevents crystal cell differentiation (g) compared to the control (f). (h) Crystal cell index.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/64672/elife-64672-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
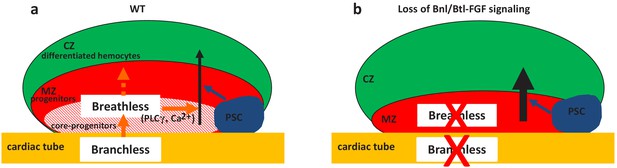
Two niches control lymph gland homeostasis.
(a–b) Schematic representation of third instar larvae lymph gland anterior lobes. Progenitors and core progenitors are in red and hatched red, respectively. The cortical zone (CZ) is in green, the PSC and the cardiac tube (CT)/vascular system are in blue and orange, respectively. (a) In a wildtype (WT) lymph gland, under normal conditions the PSC, the first niche identified, regulates the maintenance of the progenitor pool except for core progenitors (blue arrow). Here, we show that by directly acting on core progenitors (orange arrow) the cardiac tube corresponds to a second niche present in the lymph gland. Bnl produced by cardiac cells activates its receptor Btl in progenitors. Btl-FGF activation regulates intracellular Ca2+ levels via PLCγ, and controls the maintenance of core progenitors and in turn the whole progenitor pool. (b) When bnl or btl are knocked down in cardiac cells and progenitors, respectively, an increase in blood cell differentiation in the CZ is observed at the expense of the progenitor pool.





