Neural network of social interaction observation in marmosets
Figures
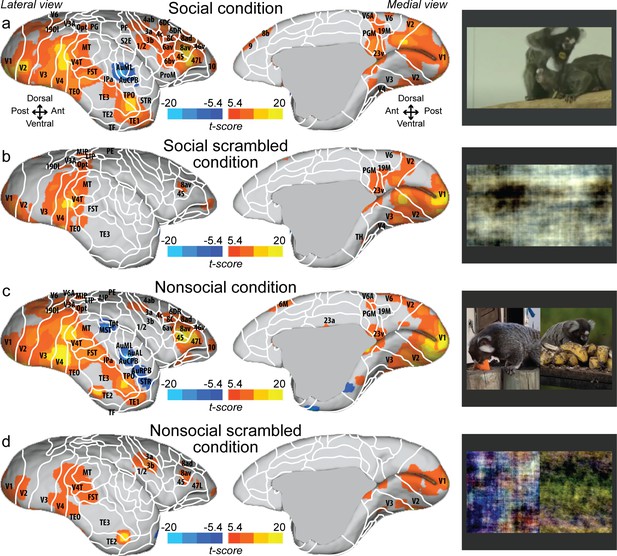
Group functional topology maps for social (a), social scrambled (b), nonsocial (c), and nonsocial scrambled conditions (d).
Maps are displayed on the right fiducial brain surface (lateral and medial views). The white line delineates the regions based on the atlas from Paxinos et al., 2011. The regions associated with yellow/orange scale correspond to t-scores ≥ 5.4 (p<0.001, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). The regions associated with blue scale correspond to t-scores ≤ –5.4 (p<0.001, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). Group maps for the left hemisphere and individual maps for both hemispheres are shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 1 and Figure 1—figure supplement 2, respectively.
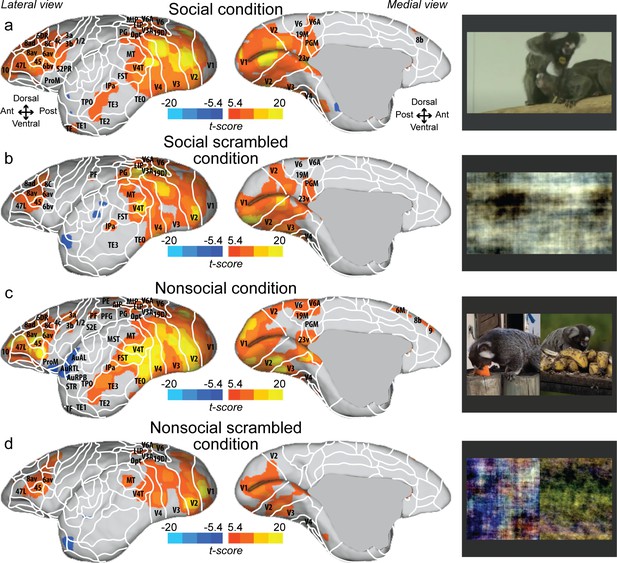
Group functional topology maps for social (a), social scrambled (b), nonsocial (c), and nonsocial scrambled conditions (d).
Maps are displayed on the left fiducial brain surface (lateral and medial views). The white line delineates the regions based on the atlas from Paxinos et al., 2011. The regions associated with yellow/orange scale correspond to t-scores ≥ 5.4 (p<0.001, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). The regions associated with blue scale correspond to t-scores ≤ –5.4 (p<0.001, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05).
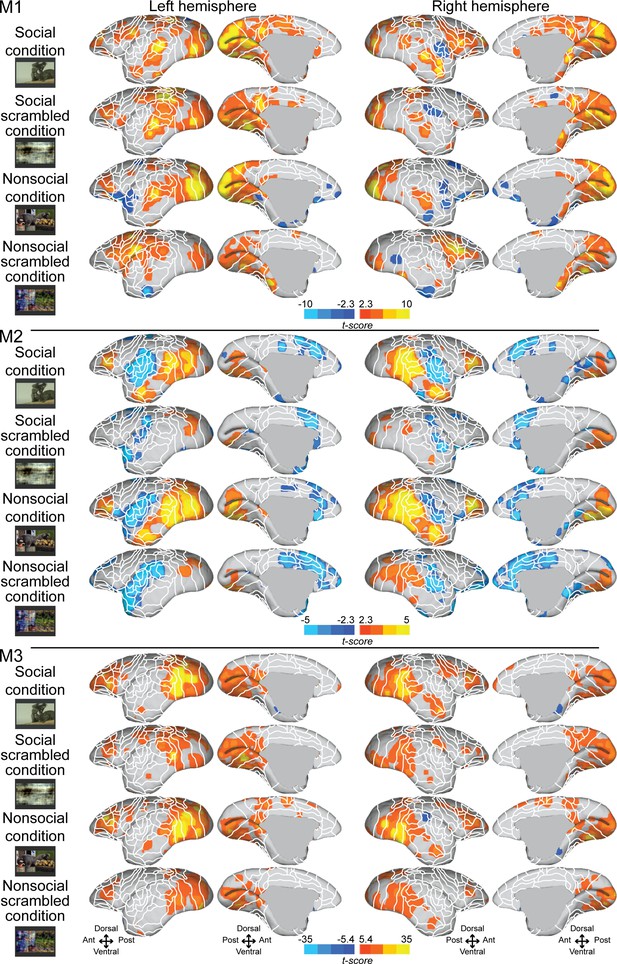
Individual functional topology maps for social (a), social scrambled (b), nonsocial (c), and nonsocial scrambled conditions (d) in monkeys 1–3.
Maps are displayed on both fiducial brain surface (lateral and medial views). The white line delineates the regions based on the atlas from Paxinos et al., 2011. The regions associated with yellow/orange scale correspond to t-scores ≥ 2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05) for monkeys 1 and 2; and t-scores ≥ 5.4 (p<0.001, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05) for monkey 3. The regions associated with blue scale correspond to t-scores ≤ –2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05) for monkeys 1 and 2; and t-scores ≥ −5.4 (p<0.001, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05) for monkey 3.
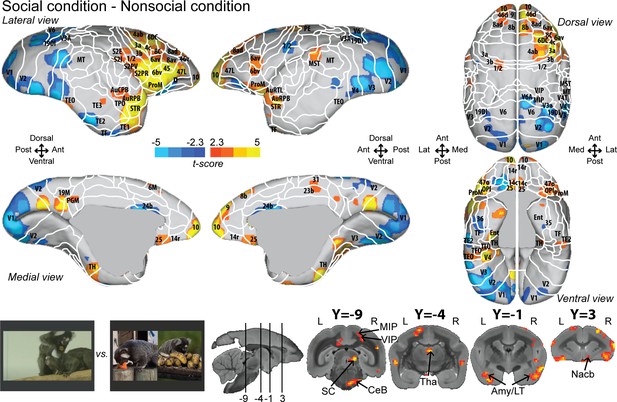
Group functional topology comparisons between social and nonsocial conditions.
Groups maps are displayed on the right and left fiducial marmoset brain surface (lateral, medial, ventral, and dorsal views) and coronal slices. The white line delineates the regions based on the atlas from Paxinos et al., 2011. Y-coordinates are calculated with respect to the anterior commissure (in millimeters). The regions associated with yellow/orange scale correspond to t-scores ≥ 2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). The regions associated with blue scale correspond to t-scores ≤ –2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). Nomenclature for coronal slices is as follows: Amy/LT: amygdala/lateral temporal; CeB: cerebellum; MIP: medial intraparietal area; Nacb: nucleus accumbens; SC: superior colliculus; Tha: thalamus; VIP: ventral intraparietal area. Individual maps for both hemispheres are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
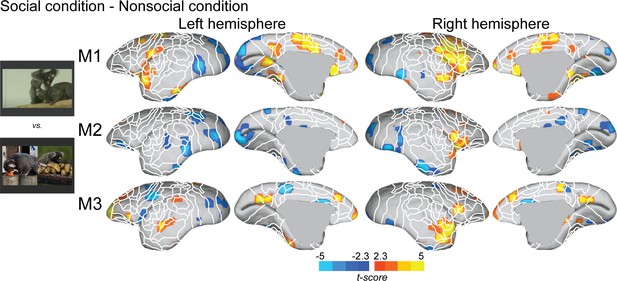
Individual functional topology comparisons between social and nonsocial conditions.
Individual maps are displayed on the right and left fiducial marmoset brain surface (lateral, medial, ventral, and dorsal views) for monkeys 1–3. The white line delineates the regions based on the atlas from Paxinos et al., 2011. Y-coordinates are calculated with respect to the anterior commissure (in millimeters). The regions associated with yellow/orange scale correspond to t-scores ≥ 2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). The regions associated with blue scale correspond to t-scores ≤ –2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05).
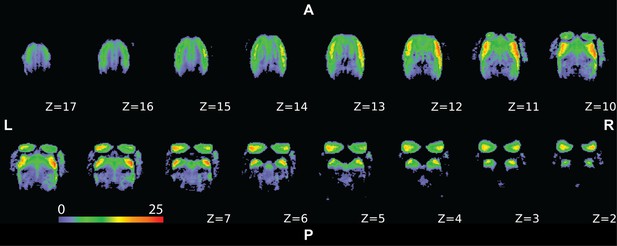
Temporal signal-to-noise ratio (tSNR) map for the group data.
The group map is represented on the axial slices of the marmoset brain surface. The left hemisphere shows slightly lower tSNR than the right hemisphere. A, P, L, and R indicate anterior, posterior, left, and right orientation, respectively.
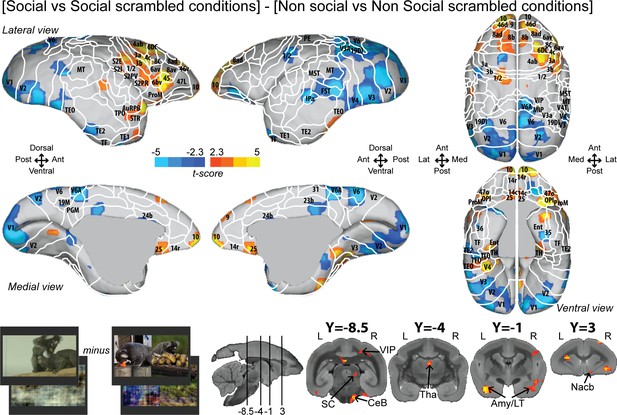
Group functional topology of the interaction effect [social vs. social scrambled] minus [nonsocial vs. nonsocial scrambled].
Groups maps are displayed on the right and left fiducial marmoset brain surface (lateral, medial, ventral, and dorsal views) and coronal slices. The white line delineates the regions based on the atlas from Paxinos et al., 2011. Y-coordinates are calculated with respect to the anterior commissure (in millimeters). The regions associated with yellow/orange scale correspond to t-scores ≥ 2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). The regions associated with blue scale correspond to t-scores ≤ –2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). Nomenclature for coronal slices is as follows: Amy/LT: amygdala/lateral temporal; CeB: cerebellum; Nacb: nucleus accumbens; SC: superior colliculus; Tha: thalamus; VIP: ventral intraparietal area. Individual maps for both hemispheres are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
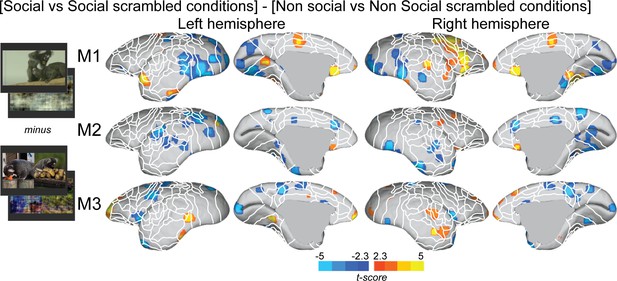
Individual functional topology of the interaction effect [social vs. social scrambled] minus [nonsocial vs. nonsocial scrambled].
Individual maps are displayed on the right and left fiducial marmoset brain surface (lateral, medial, ventral, and dorsal views) for monkeys 1–3. The white line delineates the regions based on the atlas from Paxinos et al., 2011. Y-coordinates are calculated with respect to the anterior commissure (in millimeters). The regions associated with yellow/orange scale correspond to t-scores ≥ 2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05). The regions associated with blue scale correspond to t-scores ≤ –2.3 (p<0.05, AFNI’s 3dttest++, cluster-size correction from Monte Carlo simulation, α = 0.05).
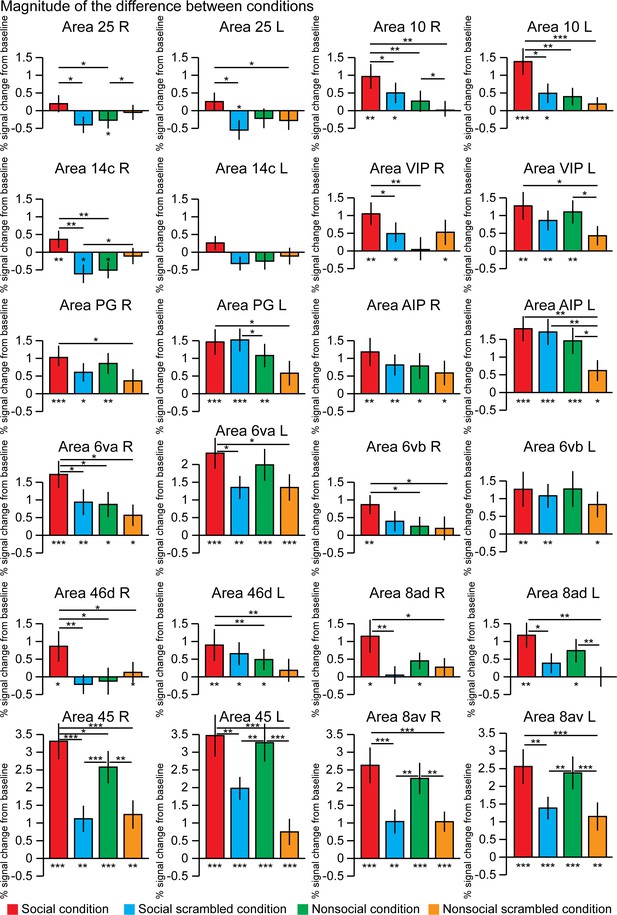
The magnitude of the difference between conditions within 12 regions of interests.
These differences were calculated after extraction of the time series from these regions defined in the left and right hemisphere using the Paxinos et al., 2011 atlas and based on the group activation maps. The differences from the baseline (below each bar graph) and conditions (horizontal bars) were assessed using paired t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. The error bars correspond to the standard error.
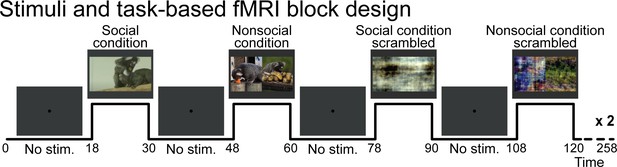
Stimuli and task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging block design.
Social condition videos, nonsocial condition videos, and their scrambled versions were displayed in a screen during task conditions blocks (12 s each) and separated by baseline blocks where a central dot was displayed in the center of the screen (18 s each). A gray background was displayed behind the dot and videos through the sequence.
Tables
Detailed description of the actions in each of the 'social interaction’ condition for each order displayed, each clip within a block (two clips of 6 s) and each repetition (two repetitions) within the run.
| Social interaction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Order 1 | Playing (roll over the other and touching the head) | Grooming (one is lying down, the other one is sitting and grooming the other one's body) |
| Grooming (one is lying down, the other is sitting and grooming the other's head) | Eating a biscuit (sharing food between a mother and her baby) | |
| Order 2 | Playing in the forest (roll over the other and touching all body parts) | Playing in the forest (roll over the other and touching all body parts including playful biting) |
| Grooming on a branch tree (one is lying down, the other one is sitting and grooming the other one's head) | Fighting and catching each other | |
| Order 3 | Grooming on a branch tree (one is lying down, the other one is sitting and grooming the other one's head) | Fighting and catching each other |
| Playing (roll over the other and touching the head) | Grooming (one is lying down, the other one is sitting and grooming the other one's body) | |
Detailed description of the actions in each of the 'nonsocial interaction’ condition for each order displayed, each clip within a block (two clips of 6 s) and each repetition (two repetitions) within the run.
| Nonsocial interaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Order 1 | Exploring a camera tripod | Eating (mostly chewing) | Eating banana peel | Scratching and exploring its environment |
| Eating lettuce while lying on a nest bed | Eating on a tree branch | Eating on a tree branch | Eating while sitting on a table and looking at the camera | |
| Order 2 | Eating banana and other fruits, frontal face view | Eating while sitting on a table and looking at the camera | Exploring and looking at its hand | Eating fruits profile view |
| Frontal face view before eating sweet potatoes | Eating bananas and visually exploring | Looking backward, chasing insects | Looking backward before eating sweet potatoes | |
| Order 3 | Eating lettuce while lying on in a nest bed | Eating on a tree branch | Eating on a tree branch | Eating while sitting on a table and looking at the camera |
| Frontal face view before eating sweet potatoes | Eating bananas and visually exploring | Looking backward, chasing insects | Looking backward before eating sweet potatoes | |





