Differentiation of mouse fetal lung alveolar progenitors in serum-free organotypic cultures
Figures
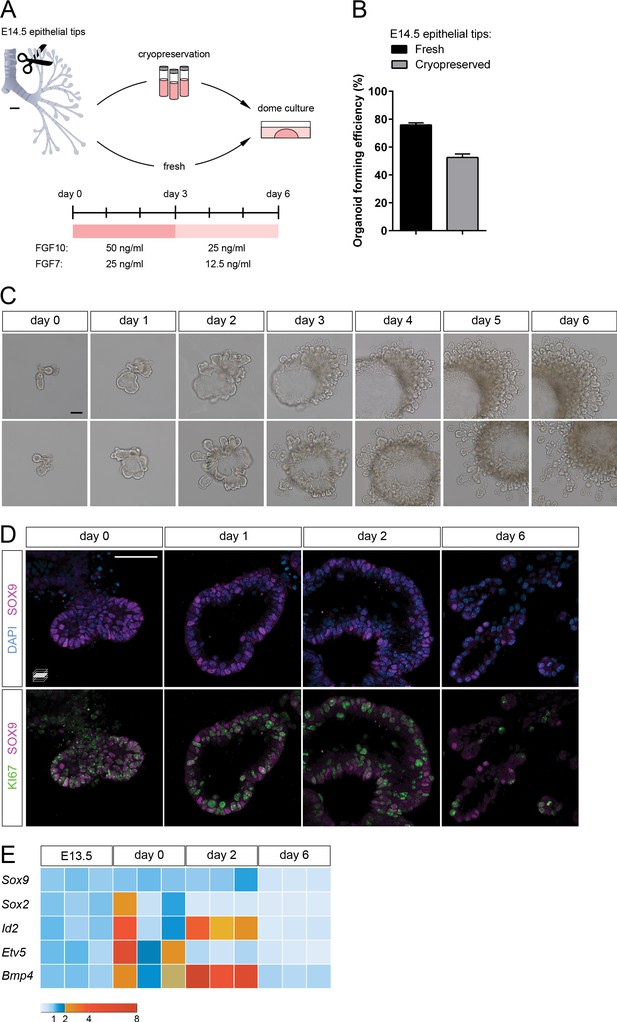
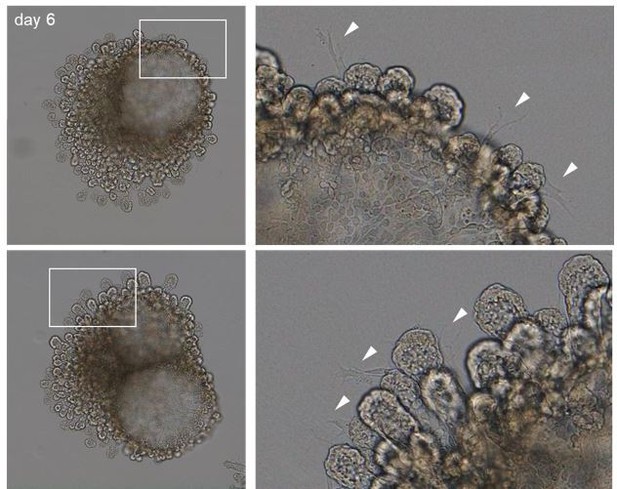
Lung distal progenitor marker expression is progressively lost in 3D explant cultures.
(A) Schematic of the organoid establishment procedure. (B) Organoid forming efficiency from fresh (black bar) and cryopreserved (gray bar) epithelial tips. (C) Representative organoids over time (brightfield imaging). Isolated tips lumenize by day 2 and subsequently form digit-like branches. (D) Distal epithelial progenitor marker SOX9 expression becomes progressively restricted by day 6 of culture, correlating with a reduced number of proliferating KI67+ cells. (E) Distal epithelial progenitor markers are upregulated by day 2 and downregulated by day 6. Expression values are normalized to transcript levels in isolated E13.5 distal epithelial tips. Each box depicts one biological replicate, showing the mean value among two technical replicates; 27 tip cultures were used for each time point. Scale bars: 100 µm (A, C), 50 µm (D). (B) Mean values are displayed; error bars represent S.D.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Organoid forming efficiency counts, fresh vs. frozen tissue. Normalized expression values of progenitor markers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65811/elife-65811-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
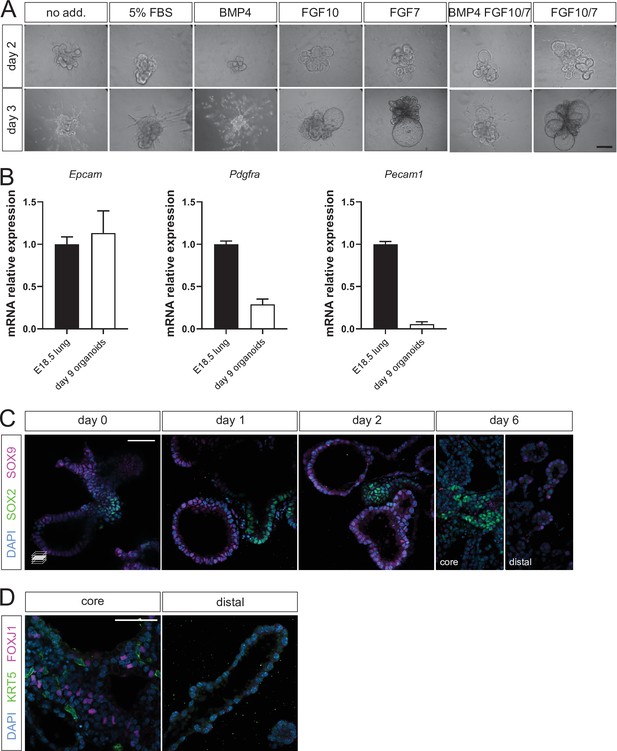
Growth factors, cellular composition and patterning of the organoids.
(A) Combined FGF treatment supports epithelial cell expansion. Organoid morphology in absence (no add.) or presence of growth factor additives (brightfield imaging). (B) Alveolar organoids mainly contain epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Transcript expression of epithelial (Epcam), mesenchymal (Pdgfra), and endothelial (Pecam1) markers in day 9 organoids (white columns). Displayed values represent mRNA levels relative to expression in E18.5 distal lung tissue (black columns). (C) SOX9 expression is localized to the distal region of organoids, while SOX2 is expressed in the organoid core. (D) Distal regions in day 6 organoids do not display expression of proximal airway differentiation markers. KRT5 (basal cells) and FOXJ1 (ciliated cells) can be variably expressed in the central (proximal) region of organoids. Scale bars: 50 µm. (B) Mean values are displayed; error bars represent S.D.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Normalized expression values of epithelial, mesenchymal, and endothelial markers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65811/elife-65811-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
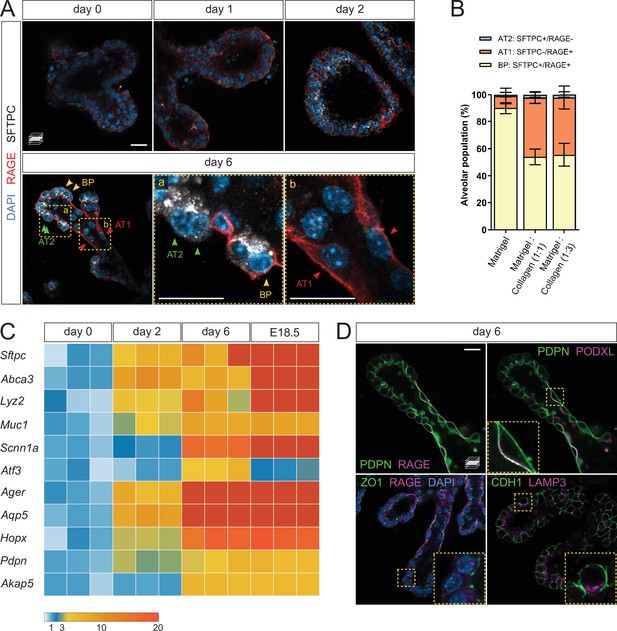
Lung distal progenitor cells differentiate in 3D explant cultures.
(A) Whole-mount immunostaining for the alveolar cell markers SFTPC and RAGE at consecutive culture days. By day 2, SFTPC and RAGE are expressed by most cells. Day 6 epithelial branches comprise both bipotent progenitor (BP) cells (SFTPC+/RAGE+) and differentiated alveolar cells (AT1, SFTPC-/RAGE+ and AT2, SFTPC+/RAGE-) in an organotypic pattern. (B) Collagen I promotes AT1 cell differentiation, compared with Matrigel alone. Cell identities were scored on day 6. (C) Markers of differentiated AT1 and AT2 cells are transcriptionally upregulated by day 6 of culture, at levels comparable with E18.5 distal lung tissue. Expression values are normalized to culture day 0. Each box depicts one biological replicate, showing the mean value among two technical replicates; 27 tip cultures were used for each time point. (D) AT1 and AT2 cells in organoids are morphologically distinct and display apico-basal polarity. AT1 cells are elongated and often populate stalk regions. Upper row: AT1 cells display basolateral localization of the AT1 cell marker RAGE and apical localization of PODXL. Lower row: epithelial branches in organoids display adhesions typical of intact epithelia, such as tight junctions (ZO-1). The AT2 cell marker LAMP3 is localized to the apical secretory compartment of surfactant-producing cells. Scale bars: 20 µm. (B) Mean values are displayed; error bars represent S.D.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Counts of alveolar cell types in organoid culture, Matrigel vs. Collagen. Normalized expression values of alveolar markers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65811/elife-65811-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
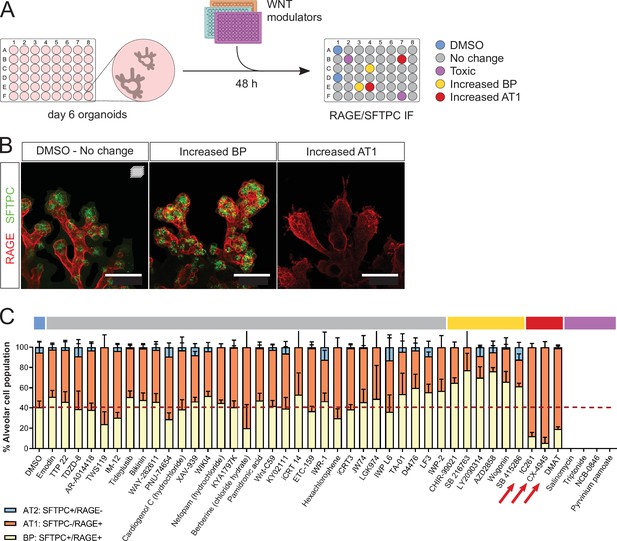
A WNT pathway chemical screen identifies modulators of alveolar cell differentiation.
(A) Screening workflow schematic. Organoids at day 6 were treated for 48 h with WNT-modulating compounds. (10 µM). Phenotypes were scored by cell counting after immunostaining for SFTPC and RAGE and F-actin co-staining (Phalloidin). (B) Phenotypic classes observed in the chemical screen comprise an increased proportion of SFTPC+/RAGE+ cells (BP, middle panel) and increased proportion of SFTPC-/RAGE+ cells (AT1, right panel). (C) Casein Kinase inhibitors IC261, CX-4945, and DMAT (arrows) led to a higher proportion of AT1 cells at the expense of progenitors, while a majority of the compounds tested did not alter the proportion of differentiated alveolar cells in culture. Four biological replicates were analyzed, 12 tip cultures per compound. Scale bars: 50 µm. (C) Mean values are displayed; error bars represent S.D.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Counts of alveolar cell types in the WNT modulators screen. Percentages of alveolar cell types in the WNT modulators screen.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65811/elife-65811-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
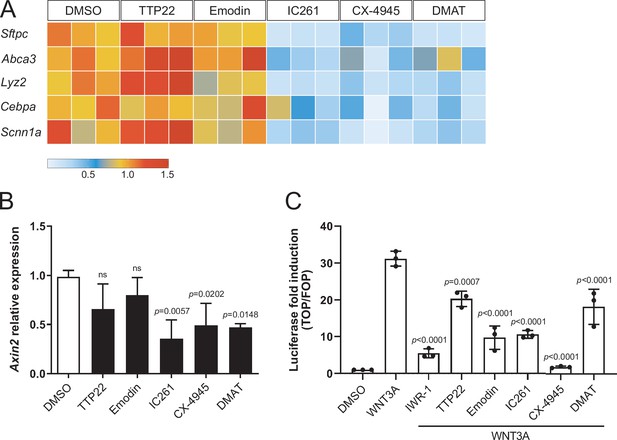
Compounds promoting AT1 cell differentiation lead to concomitant loss of AT2 marker gene expression and WNT-dependent transcription.
(A) IC261, CX-4945, and DMAT treatments (48 h) lead to downregulation of AT2 cell markers. TTP22 and Emodin (also CK2 inhibitors) do not lead to the same phenotype, possibly due to differences in potency/target affinity. Expression levels relative to DMSO control. Three biological replicates (consisting of 2 technical replicates each) were analyzed per compound. (B) Casein Kinase inhibition by IC261, CX-4945, and DMAT (6 h) leads to reduced Axin2 relative expression. Treatment with TTP22 or Emodin does not significantly affect Axin2 levels. More than three biological replicates were analyzed. (C) CK inhibition reduced WNT/β-catenin-dependent transcription in HEK293T epithelial cells (SuperTOPFlash-based luciferase assay). (B) Mean values are displayed; error bars represent S.D.; p-values from one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Mean values displayed; error bars represent S.D.; p-values from one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; displayed p-values refer to comparisons with WNT3A-treated condition.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Normalized expression values of AT2 cell markers, CK inhibitors vs. DMSO control. Normalized Axin2 expression values, CK inhibitors vs. DMSO control and related statistics. Raw luciferase data. Normalized luciferase values and related statistics.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65811/elife-65811-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | C57BL/6J mice | https://www.jax.org/strain/000664 | RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK-293T | ATCC | ATCC:CRL-3216; RRID:CVCL_0063 | |
| Other | Rat-tail Collagen I | Corning | Corning:354236 | |
| Other | Growth factor reduced Matrigel | Corning | Corning:356231 | |
| Other | DMEM/F12 | Sigma | Sigma:D6434 | |
| Other | L-Glutamine | Sigma | Sigma:G7513 | |
| Other | Penicillin/Streptomycin | Sigma | Sigma:P4333 | |
| Other | DNAse I | Roche | Roche:10104159001 | |
| Other | 10% BSA | Sigma | Sigma:A1595 | |
| Other | MEM Non-Essential Amino Acids solution | Gibco | Thermo Fisher Scientific:11140050 | |
| Other | Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium-Ethanolamine (ITS-X) | Gibco | Thermo Fisher Scientific:51500056 | |
| Other | Primocin | Invivogen | Invivogen:ant-pm-1 | |
| Other | 10x DMEM | Sigma | Sigma:D2429 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 1 N NaOH | Sigma | Sigma:S2770 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Human recombinant FGF10 | R&D Systems | R&D Systems:345-FG | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Human recombinant FGF7 | Peprotech | Peprotech:100–19 | |
| Other | CryoStor CS10 | Stem Cell Technologies | Stem Cell Technologies:07959 | |
| Other | Normal donkey serum | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Jackson Immuno Research:017-000-121; RRID:AB_2337258 | |
| Antibody | Anti-SOX9 (rabbit polyclonal) | Millipore | Millipore:AB5535; RRID:AB_2239761 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-KI67 (rat monoclonal) | Invitrogen | Thermo Fisher Scientific:14-5698-82; RRID:AB_10854564 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-SOX2 (goat polyclonal) | R&D Systems | R&D Systems:AF2018; RRID:AB_355110 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-KRT5 (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Abcam:ab53121; RRID:AB_869889 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-FOXJ1 (mouse monoclonal) | Invitrogen | Thermo Fisher Scientific:14-9965-82; RRID:AB_1548835 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-ProSP-C (rabbit polyclonal) | Millipore | Millipore:AB3786; RRID:AB_91588 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-RAGE (rat monoclonal) | R&D Systems | R&D Systems:MAB1179; RRID:AB_2289349 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-PDPN (sheep polyclonal) | R&D Systems | R&D Systems:AF3670; RRID:AB_2162070 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-PDPN (syrian hamster monoclonal) | DSHB | DSHB:8.1.1; RRID:AB_531893 | (1:20) |
| Antibody | Anti-PODXL (goat polyclonal) | R&D System | R&D Systems:AF1556; RRID:AB_354858 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-ZO1/TJP1 (mouse monoclonal) | Invitrogen | Thermo Fisher Scientific:33–9100; RRID:AB_2533147 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-CDH1 (goat polyclonal) | R&D Systems | R&D Systems:AF748; RRID:AB_355568 | (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-LAMP3 (rat monoclonal) | Dendritics | IMGENEX:DDX0192; RRID:AB_1148779 | (1:250) |
| other | Phalloidin, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate | InvitrogenThermo Fisher Scientific:A12379 | Thermo Fisher Scientific:A12379 | (1:500) |
| other | DAPI | Sigma | Sigma:D9542 | (1 µg/ml) |
| Antibody | Alexa 488-, 568-, 647- or Cy3-conjugated secondaries | Invitrogen | (1:500) | |
| Antibody | Alexa 488-, 568-, 647- or Cy3-conjugated secondaries | Jackson ImmunoResearch | (1:500) | |
| Other | DMEM + Glutamax | Gibco | Thermo Fisher Scientific:31966021 | |
| Other | FBS superior | Sigma | Sigma:S0615 | |
| Other | Lipofectamine 3000 Transfection Reagent | Invitrogen | Thermo Fisher Scientific:L3000001 | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | M50 Super 8x TOPFlash (plasmid) | Addgene | Addgene:12456; http://n2t.net/addgene:12456; RRID:Addgene_12456 | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | M51 Super 8x FOPFlash (TOPFlash mutant) (plasmid) | Addgene | Addgene:12457; http://n2t.net/addgene:12457; RRID:Addgene_12457 | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | pRL-TK (plasmid) | Promega | Promega:E2241 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant human WNT3A | Proteintech | Proteintech:HZ-1296 | (500 ng/ml) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | Sigma | Sigma:D2650 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Emodin | Tocris | Tocris:3811 | (10 µM) |
| Chemical compound, drug | TTP22 | Tocris | Tocris:4432 | (10 µM) |
| Chemical compound, drug | IC261 | Sigma | Sigma:I0658 | (10 µM) |
| Chemical compound, drug | CX-4945 | Enzo Life Sciences | Enzo Life Sciences: ENZ-CHM151 | (10 µM) |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMAT | Sigma | Sigma:SML2044 | (10 µM) |
| Chemical compound, drug | IWR-1 | Sigma | Sigma:I0161 | (10 µM) |
| Commercial assay or kit | Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System | Promega | Promega:E1910 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NucleoSpin RNA kit | Macherey-Nagel | Macherey- Nagel:740955.50 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Superscript III Reverse Transcriptase system | Invitrogen | Thermo Fisher Scientific:18080093 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | DyNAmo ColorFlash SYBR green qPCR kit | Thermo Scientific | Thermo Fisher Scientific:F416XL | |
| Sequence- based reagent | qPCR | This paper | Supplementary file 1 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji/ImageJ 1.53 c | Schindelin et al., 2012; doi:10.1038/nmeth.2019 | RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 8 | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table of qPCR primers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65811/elife-65811-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/65811/elife-65811-transrepform1-v1.pdf