Allosteric communication in DNA polymerase clamp loaders relies on a critical hydrogen-bonded junction
Figures
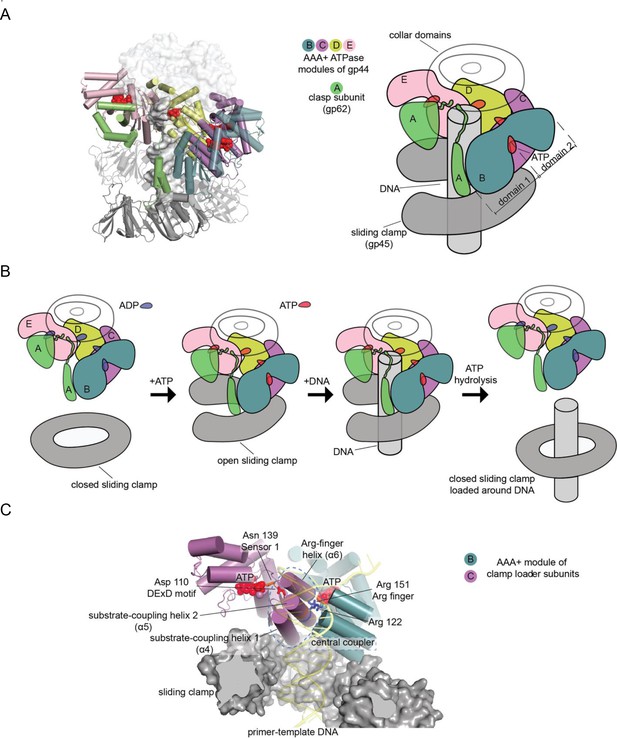
Clamp-loader complex of T4 bacteriophage.
(A) Crystal structure (left) and schematic diagram (right) of the clamp loader. (B) The clamp loading cycle, from left to right, showing the key stages of loading the sliding clamp around primer-templated DNA. (C) Key elements of AAA+ modules, shown here at the interface between neighboring ATPase subunits at positions B and C with DNA and the sliding clamp.
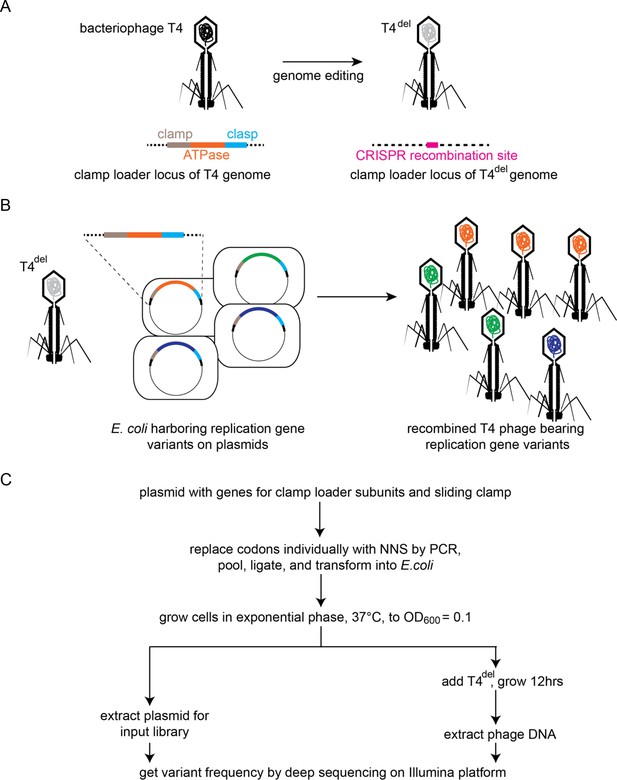
Clamp-loader activity assay through phage propagation.
(A) Schematic depicts the generation of T4del. The clamp-loader locus in wild-type T4 bacteriophage, containing genes for the sliding clamp and the ATPase and clasp subunits of the clamp loader, is replaced with a CRISPR-cas12 target site. See methods for details. (B) In the high-throughput phage-propagation assay, T4del infects bacteria carrying (i) a plasmid-encoded CRISPR-cas12 (not shown) programmed to target the recombination site inserted in A and (ii) a plasmid containing variant genes of the clamp-loader locus. Upon infection, the clamp-loader locus recombines into the T4del genome, and this genome is replicated by the variant of the clamp and clamp-loader genes present in each cell. Variants with reduction in function in the clamp-loader activity will produce fewer phage particles relative to the variants with wildtype-like activity. (C) Workflow for comprehensive assessment of fitness effects of all possible single amino-acid mutants of the sliding clamp and the clamp-loader subunits. Codons corresponding to each amino acid are individually mutagenized to NNS (N is a mixture of all four nucleotide bases, S is a mixture of G and C) by PCR, combined in equimolar ratios and transformed into E. coli for cloning.
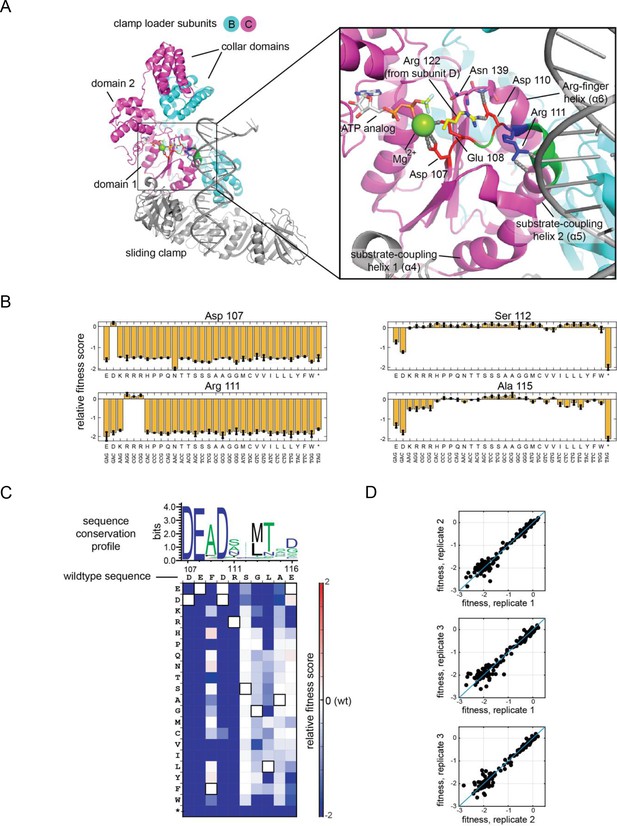
Validation of the high-throughput phage-propagation assay with a library targeting the 10-residue region including the Walker B motif of the ATPase subunit.
(A) The location of the 10-residue region in the structure of the clamp loader. (B) Relative fitness values of all 32 codons from the NNS substitutions at mutationally sensitive positions (107 and 111) and mutationally tolerant positions (112 and 115). (C) Relative fitness values for each amino acid substitution in the 10-residue region depicted as a heatmap, with wildtype-like fitness as white (score of 0), loss of function as shades of blue and gain of function as shades of red. Pixels corresponding to the amino acid present in the wild-type sequence at each position are outlined in black. Sequence logo generated from 1000 related phage ATPase sequences, with the sequence of T4 bacteriophage shown above the heatmap for reference. (D) Agreement between fitness measurements from three replicate experiments, where each point in the scatter plot represents the fitness measurements made from two trials.

Biochemical measurements for selected mutants of the ATPase subunit.
(A) ATP hydrolysis rates of clamp loader variants with point mutations in the ATPase subunit, measured by a coupled-kinase assay (Goedken et al., 2005) (see Materials and methods for details). (B) DNA replication assay (Seville et al., 1996) performed with M13 phage genomic ssDNA as template. -DNA Pol. refers to the reaction setup with all the necessary proteins from wild-type bacteriophage T4 except the T4 DNA polymerase. DNA replication with the Phusion DNA polymerase system (ThermoFisher), with and without the DNA primer, sets the expected dynamic range of the assay.
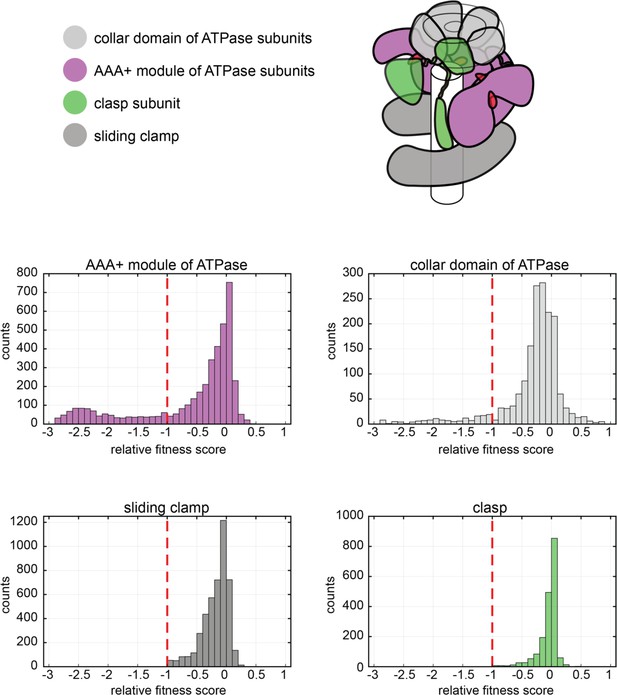
Distribution of relative fitness values from deep mutagenesis of the clamp loader system.
The histograms show the spread of relative fitness values for AAA+ module and collar domain of the ATPase subunit, the clasp subunit and the sliding clamp.

Mutational sensitivity of the T4 sliding clamp (gp45).
The fitness scores for all point mutations to the sliding clamp (residue 2–228) are depicted as a heatmap. Gray pixels denote mutations with insufficient counts (fewer than 20 counts) when sequencing the plasmid library. Amino acid substitutions that result in the wild-type sequence are denoted by pixels with a black border. The secondary structure of the wild-type sequence is indicated below the wild-type sequence, with α helices as rectangles and β strands as arrows.

Mutational sensitivity of the clasp subunit (gp62) of the T4 clamp loader.
The data are shown as in Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
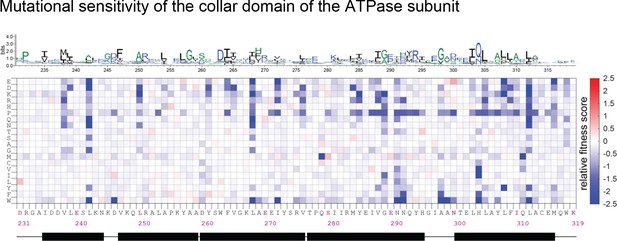
Mutational sensitivity of the collar domain (residue 231–319 of gp44) of the ATPase subunit.
The data are shown as in Figure 4—figure supplement 1.

Mutational sensitivity of the AAA+ module of the ATPase subunit.
The fitness scores for all point mutations to the AAA+ module are shown as a heatmap, as in Figure 3C. The secondary structure of the wildtype sequence is indicated above the heatmap, with annotations identifying key elements of the AAA+ module (Cullmann et al., 1995; Guenther et al., 1997). The sequence-conservation profile derived from 1000 phage clamp-loader sequences is depicted above the secondary-structural elements as a sequence logo (Crooks et al., 2004).

Comparison of mutational sensitivity in the AAA+ module of the ATPase subunit to evolutionary sequence conservation.
(A) Receiver-operator characteristic curve illustrating the ability of binarized-sequence-conservation scores (show here for three different threshold values) to predict the mean mutational sensitivity of the positions in the AAA+ module (see Methods for details). (B) The mean effect of making the evolutionarily most-likely substitution at each position (see Methods for details).
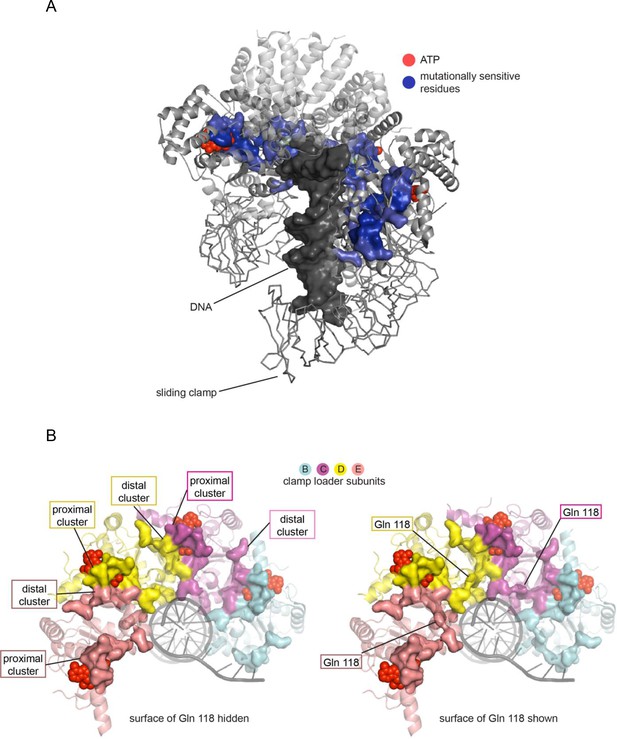
Mutationally-sensitive residues form a contiguous network in the structure of the clamp-loader complex, connecting sites interacting with ATP, DNA and the sliding clamp.
(A) Positions with mean mutational effect <= −1.6 are rendered in surface representation and colored blue. (B) Mutationally sensitive residues, viewed from the top (collar domain not shown) without (left) and with (right) Gln 118 shown.
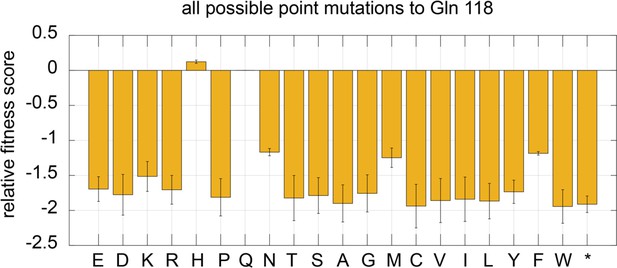
Mutational sensitivity of residue 118 in the ATPase subunit of the T4 clamp loader, tested with a small library of 20 amino acid substitutions.

Expression levels of mCherry tagged wildtype and Q118N variant of the clamp loader, observed by flow cytometry.
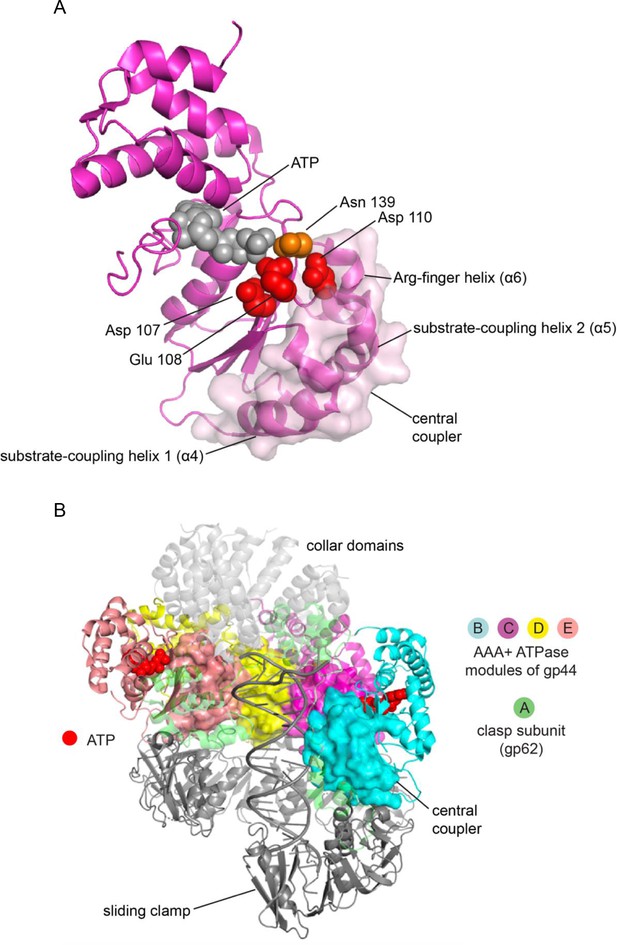
The central coupler in the bacteriophage T4 clamp loader.
(A) The subunit at C position of the T4 clamp loader is shown, with the surface of the central coupler displayed. (B) The structure of the complete clamp-loader complex is shown, with the surfaces of the four central-coupler units depicted. (PDB ID: 3u60 Kelch et al., 2011).
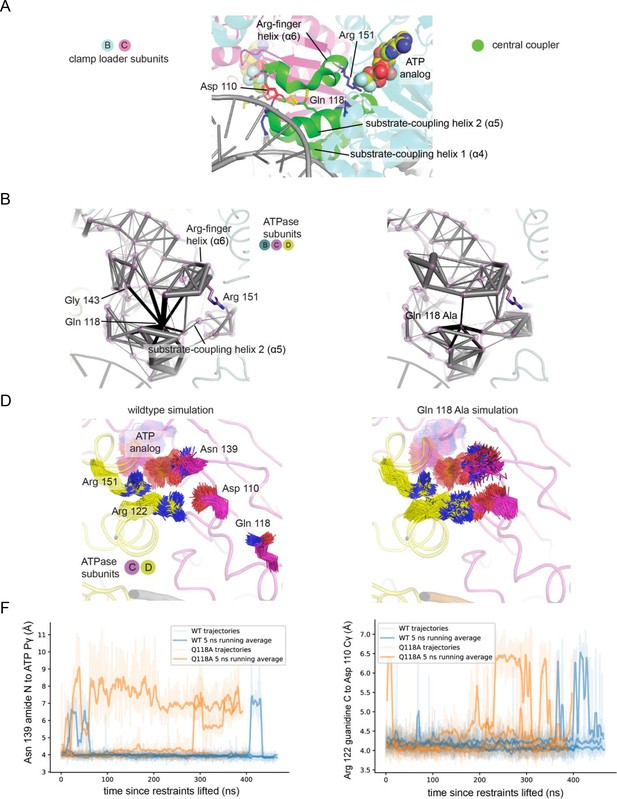
Molecular dynamics simulations of the of the wildtype T4 clamp loader and Q118A mutant.
(A) The central-coupler unit of the clamp loader is shown in green. Pairs of residues in subunit C that show correlated motions in simulations of the wildtype structure (B) and Q118A structure (C) are connected by gray cylinders (black cylinders connect residues to position 118), with the diameter of the cylinder proportional to the magnitude of correlated motions. Values are averaged from four trajectories. The sidechain positions of important residues in subunit C, from the wildtype (D) and Q118A (E) simulations. (F) The distance between the amide of sensor-I residue Asn 139 and the γ-phosphate of ATP bound by subunit C from four trajectories of the wild-type clamp loader and the Q118A mutant. (G) The distance between the γ-carbon of Asp 110 in the walker B motif of subunit C and guanidine carbon of Arg 122 of subunit D from four trajectories of the wild-type clamp loader and the Q118A mutant.
Subunit C heavy-atom root-mean-square fluctuations from AAA+ module aligned trajectories, for wildtype and Q118A trajectories.
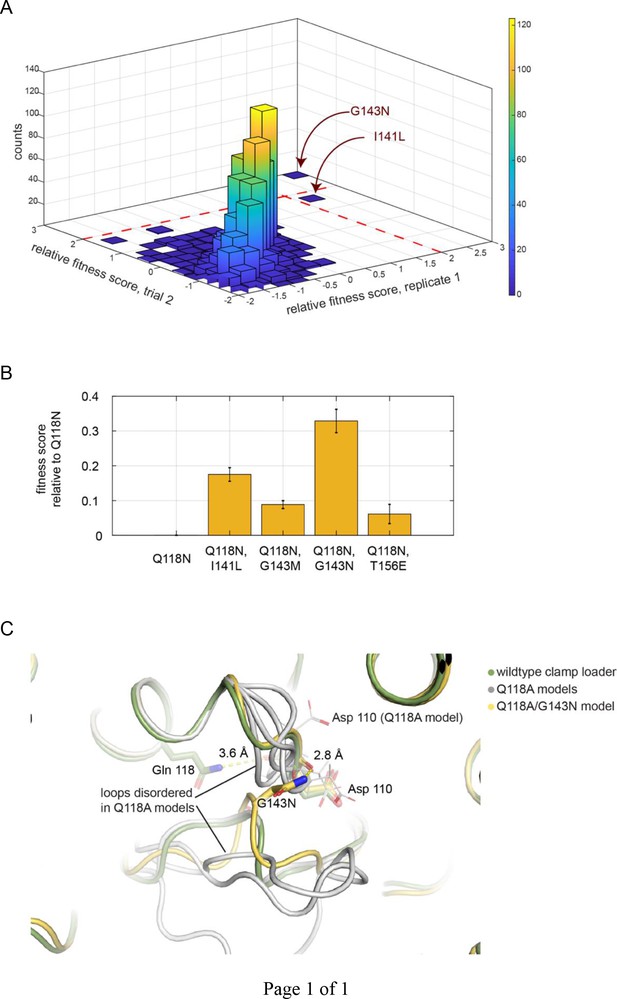
Screen for second-site suppressor mutations, in the Q118N background.
(A) The distribution of fitness scores (relative to that for the Q118N mutant) from two independent trials. G143N is the best performing mutant in both trials. (B) The top four best performing mutants were tested in competition with Q118N using the phage-propagation assay. (C) The spatial orientation of Asp 110 is destabilized in four independent trials modeling the effect of Q118A (gray). The Q118A/G143N double mutant stabilizes and restores the orientation of Asp 110 (yellow).
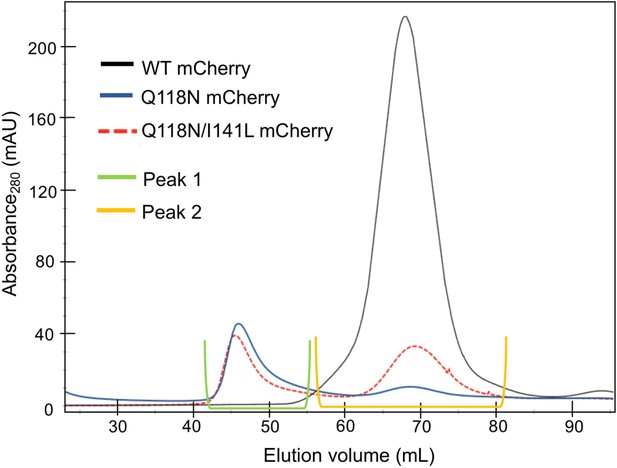
Elution profile of mCherry-tagged clamp loader variants in size-exclusion chromatography.
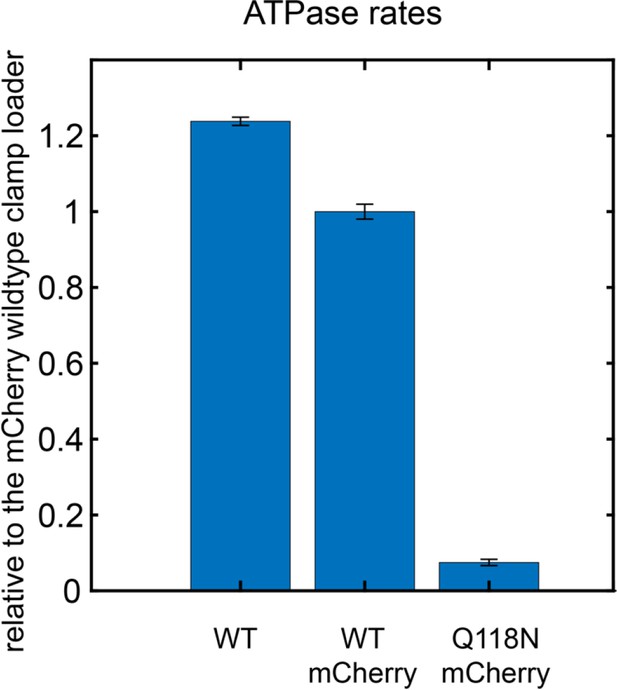
ATPase activity of mCherry-tagged clamp loader variants, in the presence of clamp and DNA.
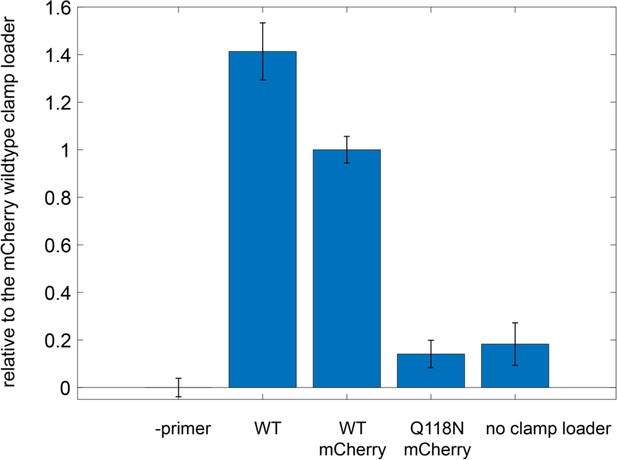
Ability of mCherry-tagged clamp loader variants to carry out DNA replication with M13 phage ssDNA as template.
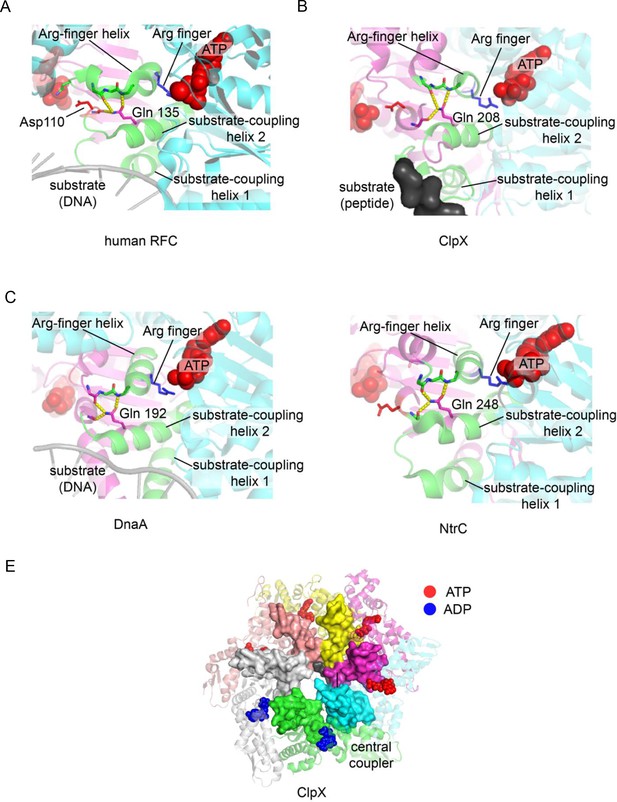
The central-coupler unit in different AAA+ proteins.
The central-coupler unit of subunit C is shown in green for (A) the human RFC structure (PDB ID: 6vvo [Gaubitz et al., 2020]), (B) the ClpX structure (PDB ID: 6vfs [Ripstein et al., 2020]), (C) the DnaA structure (PDB ID: 3r8f Duderstadt et al., 2011) and of (D) the structure of NtrC1 (PDB ID: 3m0e [Chen et al., 2010]). (E) The central coupler in each of the subunits of ClpX form a contiguous surface lining the central channel of ClpX (PDB ID: 6vfs [Ripstein et al., 2020]) and contacts the peptide substrate.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Bacteriophage T4) | T4del | This paper | https://benchling.com/s/seq-Vg4DZh83BOrbx3RgpaaC | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CRISPR plasmid | This paper | https://benchling.com/s/seq-abaKV7JgTgAghRyR9ZIY | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Donor plasmid | This paper | https://benchling.com/s/seq-Z2Bo2vnShDbLtji83VHm | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Helper plasmid | This paper | https://benchling.com/s/seq-KdFkydUFMBrlRkdpORA3 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Recombination plasmid | This paper | https://benchling.com/s/seq-bRQ2OUu39lSrs6I0gfmu | |
| Commercial assay or kit | MiSeq 500 cycles kit | Illumina | Cat. #: MS-102–2003 | |
| Software, algorithm | FLASH | doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507 | ||
| Software, algorithm | Analysis scripts | This paper | https://github.com/kuriyan-lab/cl1 |
Additional files
-
Source data 1
Relative enrichment values of single mutants of the ATPase subunit of the clamp loader.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66181/elife-66181-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Source data 2
Relative enrichment values of single mutants of the sliding clamp.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66181/elife-66181-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Source data 3
Relative enrichment values of single mutants of the clasp subunit of the clamp loader.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66181/elife-66181-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66181/elife-66181-transrepform-v2.pdf





