Thirst interneurons that promote water seeking and limit feeding behavior in Drosophila
Figures
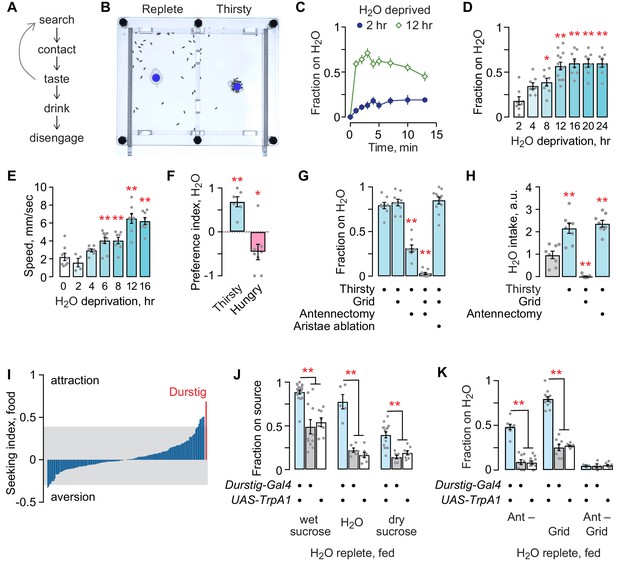
Thirst behavior in an open field; a forward screen uncovers Durstig thirst neurons.
(A) Thirst-induced sequence of behavior. (B) Two-chambered open field assay with a vertical divider at the center. Thirsty flies avidly seek and occupy a discrete water source (dyed blue for clarity). (C) Occupancy of an open water source over time by a group of 20 flies, n = 8 groups. (D) Occupancy increases with increasing water deprivation. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett’s compared to 2 hr water deprivation. Each dot represents one group of 20 flies. (E) Water deprivation increases locomotor activity. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett’s compared to 0 hr. (F) Two choice preference for water (1) and dry sucrose (−1) depends on deprivation state. One-sample t-test, compared to 0 (no preference). (G) Sensory systems in thirsty water seeking. A mesh grid atop the water source preserves humidity sensing and blocks water contact, taste, and ingestion. Antennectomy, removal of the third antennal segment and aristae, removes humidity and temperature sensors. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett’s compared to open/unoperated. (H) Sensory input in water intake. Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s compared to water replete (gray bar). (I) Screen for neurons that affect the occupancy of food, using a library of InSITE enhancer-Gal4 strains driving expression of the TrpA1 heat activated cation channel. Seeking index is enhancer-Gal4>TrpA1 minus enhancer-Gal4>+. Positive index indicates greater occupancy. Gray extends to two standard deviations from the mean. (J) Durstig neuron activation drives occupancy of food and water. (K) Durstig activation promotes water occupancy through hygrotaxis and contact-dependent mechanisms. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s, unless indicated otherwise.
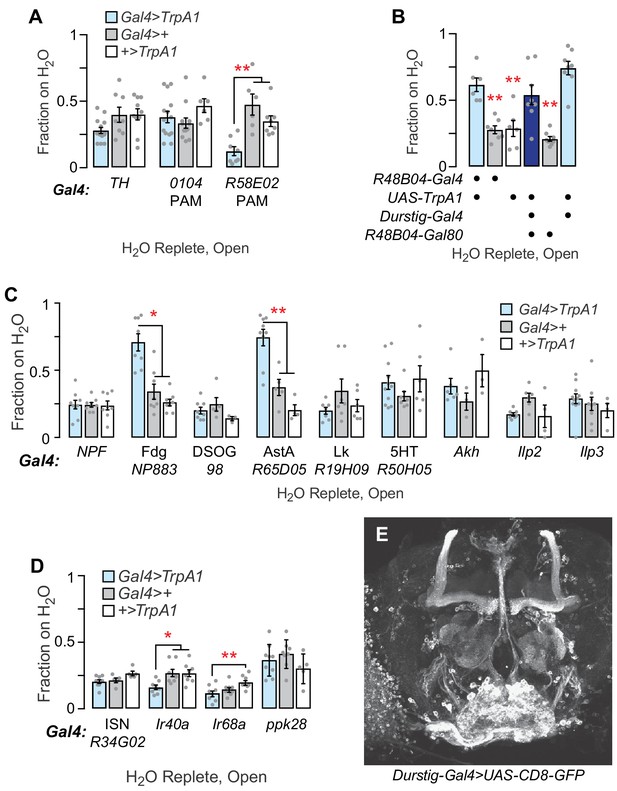
Effects of activating neurons implicated in feeding, reward, and water learning on water seeking.
(A) Dopaminergic neuron activation effect on water seeking. (B) R48B04-Gal4, previously implicated in thirsty humidity preference, contains water seeking neurons that are different from those in Durstig: subtraction of R48B04 neurons (R48B04-Gal80) from Durstig>TrpA1. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett's, compared to Durstig>TrpA1. (C) Effects on water seeking of activation of neurons implicated in water and food intake. (D) Osmosensory ISN, hygrosensory neuron (Ir40a-Gal4, Ir68a-Gal4), and water taste neuron (ppk28-Gal4) activation effects on water seeking. (E) Durstig neurons in the central brain, labeled with membrane tethered GFP. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s, unless indicated otherwise.
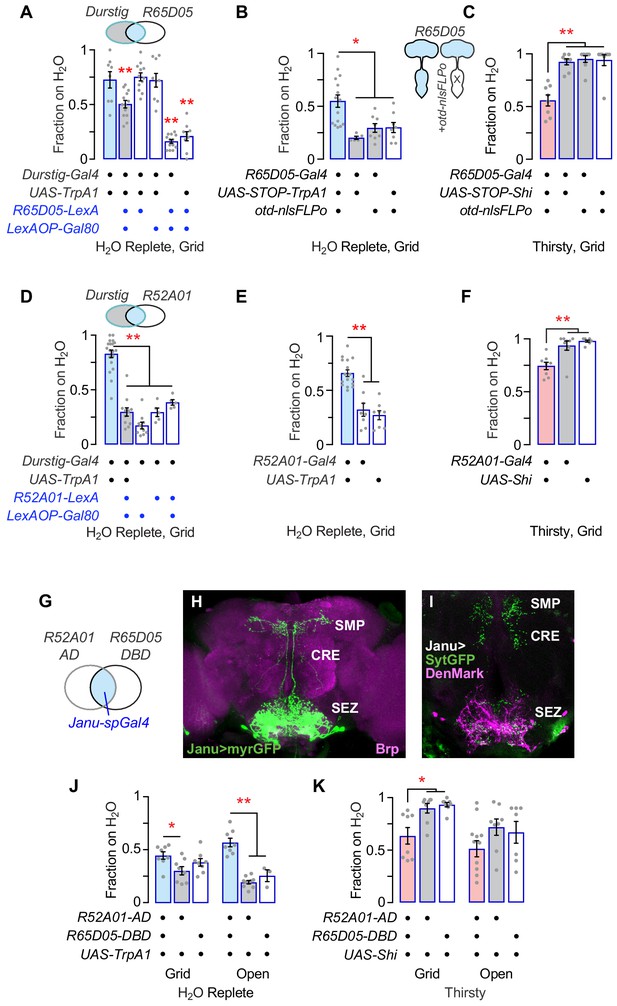
Isolation of Janu thirst neurons from the Durstig pattern.
(A) Subtraction of R65D05 neurons (R65D05>Gal80) from the Durstig pattern decreases Durstig activation water seeking. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett's compared to Durstig>TrpA1. (B) Activation of R65D05 neurons specifically in the central brain promotes water seeking. otd-nlsFLPo expresses Flippase in the central brain and not the ventral nervous system, to remove the STOP cassette from UAS-STOP-TrpA1, thus restricting TrpA1 expression to central brain R65D05 neurons. (C) Inactivation of R65D05 neurons specifically in the central brain inhibits thirsty water seeking. (D) Subtraction of R52A01 neurons (R52A01>Gal80) from the Durstig pattern decreases Durstig activation (Durstig>TrpA1) water seeking. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett's compared to Durstig>TrpA1. (E) R52A01 neuron activation increases water seeking. (F) R52A01 inactivation decreases thirsty water seeking. (G) A split-Gal4 (spGal4) with R52A01-AD and R65D05-DBD forms functional GAL4 (Janu-spGal4) selectively in the R52A01/R65D05 overlap. (H) Expression pattern of Janu-spGal4 in the brain, counterstained with the Brp synaptic marker. (I) Janu neuron polarity, revealed by presynaptic synaptotagmin-GFP (UAS-sytGFP, green) and dendrite localized UAS-DenMark (magenta). (J) Janu neuron activation increases water seeking. (K) Janu neuron inactivation decreases thirsty water seeking. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s, unless indicated otherwise.
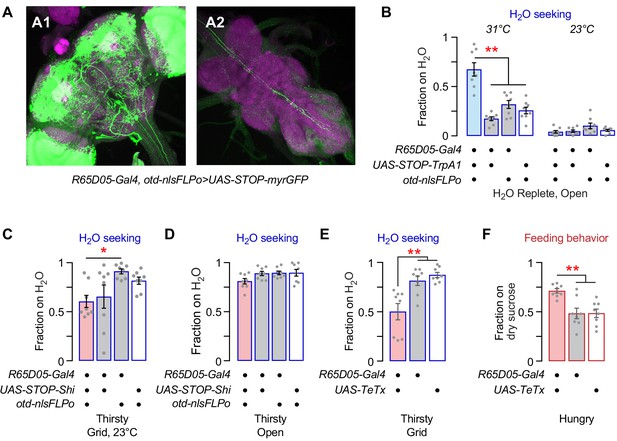
Characterization of R65D05-Gal4 neurons for thirst and hunger behaviors.
(A) Otd-nlsFLPo expresses Flippase predominantly in the central brain, effectively limiting R65D05-Gal4-driven GFP to the central brain. High gain to highlight absence of GFP positive neuron cell bodies in the ventral nervous system (A2). (B) Selective activation of R65D05 central brain neurons promotes water seeking. TrpA1 activation is necessary for increased occupancy (no effect at control 23°C). (C) Temperature control for Shi inactivation (23°C) has no effect on thirsty water seeking. (D) R65D05 neuron inactivation has no effect on thirsty water occupancy of an open water source. (E) R65D05 constitutive inactivation with tetanus toxin light chain blocks thirsty water seeking. (F) R65D05 inactivation increases dry sucrose seeking in hungry flies. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey's.
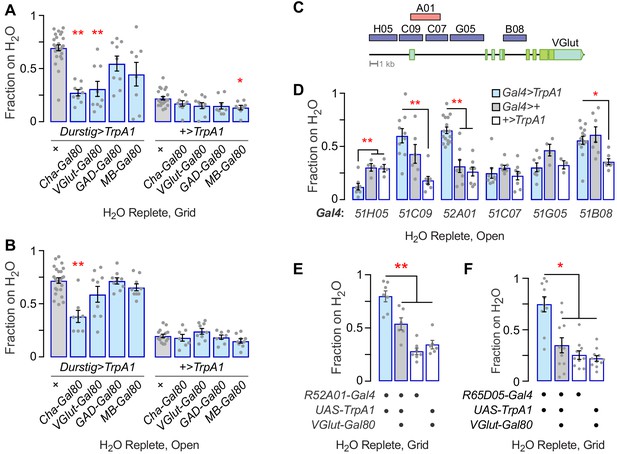
Characterization of R52A01-Gal4 neuron for thirst behaviors.
(A) Subtraction of subsets of neurons from Durstig>TrpA1 with patterns of GAL80 expression, occupancy of an inaccessible water source. Cha-Gal80: choline acetyltransferase enhancer, VGlut-Gal80: vesicular glutamate transporter enhancer, GAD-Gal80: Glutamic acid decarboxylase one enhancer, MB-Gal80: mushroom body neurons. Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s, compared to Durstig>TrpA1 (left) or +>TrpA1 (right). (B) As in (A), for water seeking to an open water source. (C) Map location of enhancer fragments in VGlut locus used to drive GAL4. (D) Activation of VGlut enhancer-Gal4 patterns, open source water occupancy. (E) VGlut-Gal80 neuron subtraction from R52A01-Gal4 decreases TrpA1 activation water seeking. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett’s, compared to R52A01>TrpA1,VGlut-Gal80. (F) VGlut-Gal80 neuron subtraction from R65D05-Gal4 decreases TrpA1 activation water seeking, compared to R65D05>TrpA1,VGlut-Gal80. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s, unless otherwise indicated.
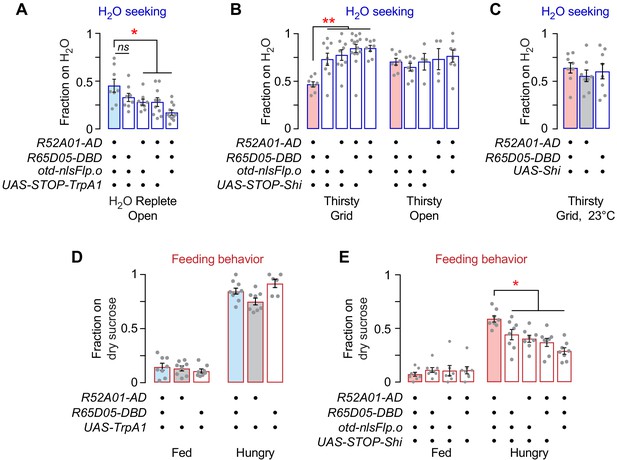
Janu neuron water seeking and feeding behavior characterization.
(A) Janu activation limited to central brain neurons promotes occupancy of open water source. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett's compared to Janu>UAS-STOP-TrpA1,otd-nlsFLPo. (B) Janu neuron inactivation limited to central brain neurons decreases thirsty water seeking to an inaccessible source. One-way ANOVA/Dunnett's compared to Janu>UAS-STOP-Shi,otd-nlsFLPo. (C) Temperature control for Janu neuron inactivation by Shibirets, thirsty water seeking. One-way ANOVA/Tukey’s. (D) Janu neuron activation has no effect on dry sucrose seeking. One-way ANOVA/Tukey’s. (E) Janu neuron pattern inactivation limited to the central brain increases hungry seeking of dry sucrose. One-way ANOVA/Dunnet's compared to Janu>UAS STOP-Shi,otd-nlsFLPo.
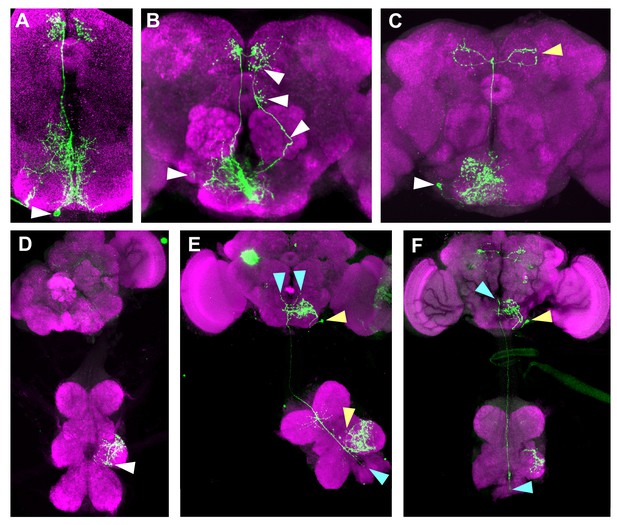
Anatomy of individual Janu neurons.
Stochastic labeling of Janu neurons using a flip-out technique, detected with anti-FLAG (green), and counterstained with anti-VGAT (magenta). (A) Janu-AstA, arrowhead points to cell body (micrograph also shown in Figure 5A). (B) Contralateral projecting neuron. Arrowhead on left points to cell body, and other arrowheads point to the axon and presynaptic endings. The neuron elaborates processes in the SEZ, partially hidden by a co-labeled Janu-AstA neuron. (C) Janu-GABA2 neuron (white arrowhead points to cell body), and the axon of a second neuron that elaborates presynaptic endings in the dorsal protocerebrum (yellow arrowhead). We were unable to locate the cell body for the latter neuron. (D) Local interneuron in the mesoneuromere, arrowhead points to the cell body. (E) An SEZ Janu-GABA1 interneuron (yellow arrowhead points to cell body). Ascending interneuron with cell body and bifurcated presynaptic endings indicated by blue arrowheads. A separate mesoneuromere local interneuron is also labeled (yellow arrowhead in the ventral nervous system). (F) Ascending interneuron with a single process ending is indicated with blue arrowheads, and a Janu-GABA1 SEZ interneuron (yellow arrowhead points to its cell body).
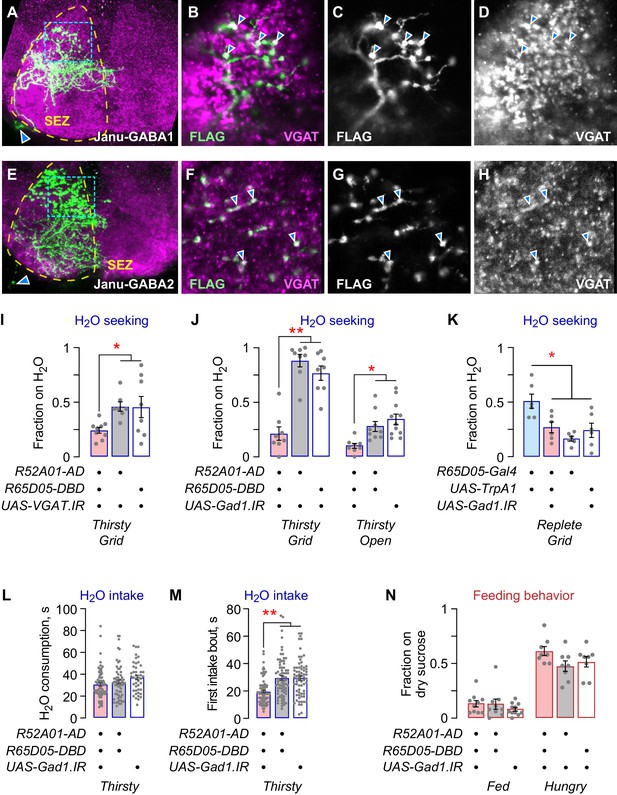
Janu-GABA SEZ local interneurons specifically promote water-seeking behaviors.
(A–D) Janu-GABA1 interneuron morphology in the SEZ of a Janu>multicolor flip-out brain, compressed z-stack. Arrowhead in (A) points to the cell body. Boxed area is enlarged in (B–D), showing colocalization of the Janu-GABA1 neuron (anti-FLAG) with immunoreactivity for VGAT (arrowheads in B–D). Single 1 μm confocal section. (E–H) Janu-GABA2 interneuron morphology in the SEZ of a Janu>multicolor flip-out brain, compressed z-stack. Arrowhead in (E) points to the cell body. Boxed area is enlarged in (F–H), showing colocalization of the Janu-GABA2 neuron (anti-FLAG) with immunoreactivity for VGAT (arrowheads in F–H). Single 1 μm confocal section. (I) VGAT knockdown in Janu neurons decreases thirsty water seeking. (J) Gad1 knockdown in Janu neurons decreases thirsty water seeking. (K) Simultaneous TrpA1 neuronal activation and Gad1 knockdown in R65D05 neurons blocked R65D05>TrpA1 increased water seeking in replete flies. (L) No effect on water consumption time with Gad1 knockdown in Janu neurons in thirsty flies. (M) Decreased time to termination of first drinking bout with Gad1 knockdown in Janu neurons in thirsty flies. (N) No effect on feeding behavior with Gad1 knockdown in Janu neurons. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s.
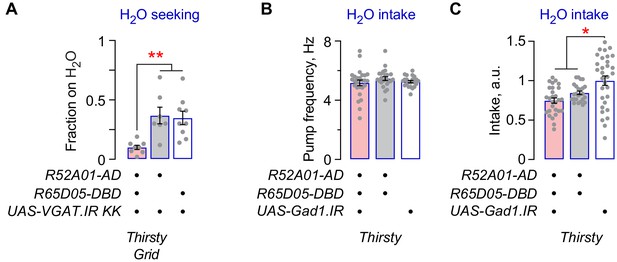
Additional characterization of Janu-GABA neuron function in thirst behaviors.
(A) Decreased thirsty water seeking when VGAT is knocked down by a second, independent RNAi in Janu neurons. (B) No change in pharyngeal pumping rate with Gad1 knockdown in Janu neurons in thirsty flies. (C) No effect on water intake in the open field arena in Janu>Gad1.IR thirsty flies. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s.
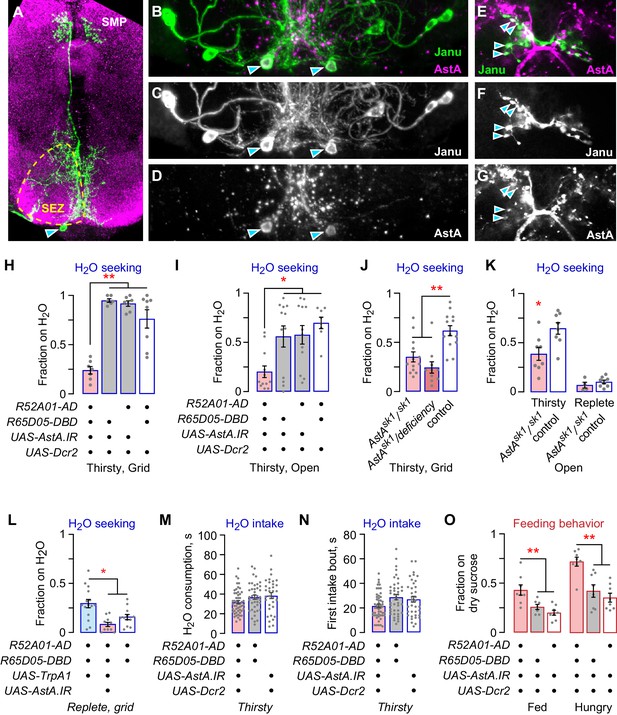
The Janu-AstA neuron reciprocally regulates thirst and feeding behaviors.
(A–G) Janu-AstA neuron morphology and AstA expression. (A) Janu-AstA neuron morphology obtained from a multicolor flip-out brain. Green: anti-FLAG; magenta: anti-VGAT. Arrowhead points to cell body. Process at bottom left is from a co-labeled Janu-GABA neuron. (B–D) The Janu-AstA neuron cell body is immunoreactive for AstA. Arrowheads points to the cell body. (E–G) Colocalization of AstA immunoreactivity with Janu-AstA presynaptic endings in the medial SMP. Arrowheads point to a subset of overlapping expression. Single 1 μm confocal section. (H, I) AstA knockdown in Janu neurons reduced thirsty water seeking and open water occupancy. (J, K) Flies lacking AstA showed reduced thirsty water seeking and open water occupancy. (K) t-test. (L) Simultaneous TrpA1 neuronal activation and AstA knockdown in Janu neurons blocked increased water seeking in replete flies. (M) No effect on water consumption time with AstA knockdown in Janu neurons in thirsty flies. (N) No effect on time to termination of first drinking bout with AstA knockdown in Janu neurons in thirsty flies. (O) AstA knockdown in Janu neurons increased food occupancy in well-fed and hungry flies. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s, unless indicated otherwise.
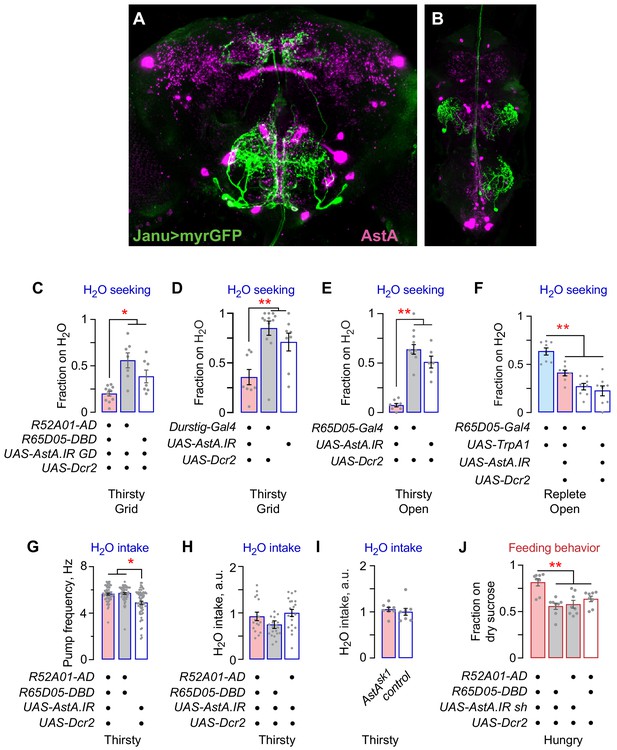
Additional characterization of Janu-AstA neurons.
(A, B) Colocalization of Janu>myrGFP with AstA immunoreactivity, in the central brain (A) and in the ventral nervous system (B). Colocalization is limited to the Janu-AstA neurons. (C) AstA knockdown with a second, independent RNAi reduced thirsty water seeking. (D) AstA knockdown in Durstig neurons reduced thirsty water seeking. (E) AstA knockdown in R65D05 neurons reduced open water source occupancy by thirsty flies. (F) Simultaneous TrpA1 neuronal activation and AstA knockdown in R65D05 neurons blocked increased open water source occupancy in replete flies. (G) No change in pharyngeal pumping rate in Janu>AstA.IR thirsty flies. (H) No change in water intake in open field assay for AstA knockdown in Janu neurons. (I) No effect on open field water intake in AstA loss-of-function mutant flies. t-test. (J) AstA knockdown with a second, independent RNAi increased occupancy of dry sucrose. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn’s, unless indicated otherwise.
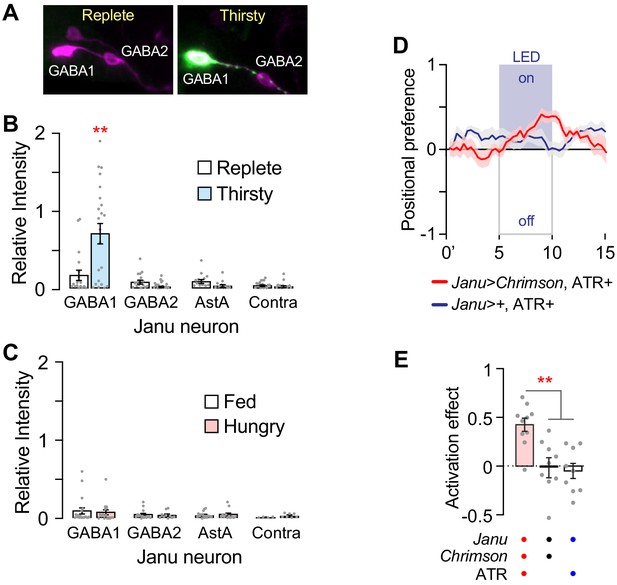
Thirst regulation of Janu neuron activity, and positive valuation of optogenetic activation of Janu.
(A) Examples of TRIC detection of neuronal activity (green) and the pattern of cells expressing the calcium indicator (magenta) under water replete and thirsty conditions in Janu neurons, detected with anti-GFP (green) and dsRed (magenta) antibodies. (B, C) Relative intensity of TRIC signal (green in A) to pattern (magenta in A) for the individual Janu neurons in replete and thirsty (B), and well-fed and hungry (C) flies. Multiple adjusted t-test, with FDR = 1%. (D) Positional preference of Janu>Chrimson (red) and Janu>+ (blue) water replete and well-fed flies that were fed all-trans retinal (ATR). Positive values indicate attraction to LED-ON half of the rectangular arena, controlled for arena side bias. (E) Quantification of D. Activation effect is the average positional preference for a 1 min bin at 4 min (activation lights off) subtracted from 9 min (activating LEDs on) (see also Figure 5—figure supplement 1A). One-way ANOVA/Tukey's.
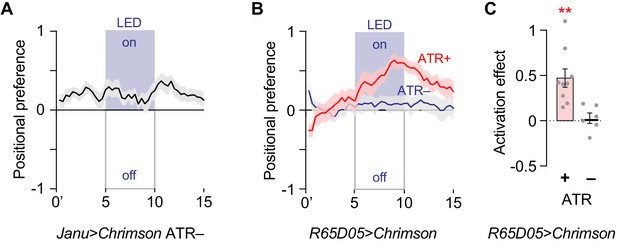
Flies prefer activation of water seeking neurons.
(A) Positional preference of Janu > Chrimson flies without ATR. Positive values indicate attraction to optogenetic stimulation. (B) Positional preference for R65D05>Chrimson with and without ATR. (C) Quantification of the activation effect in B, t-test.
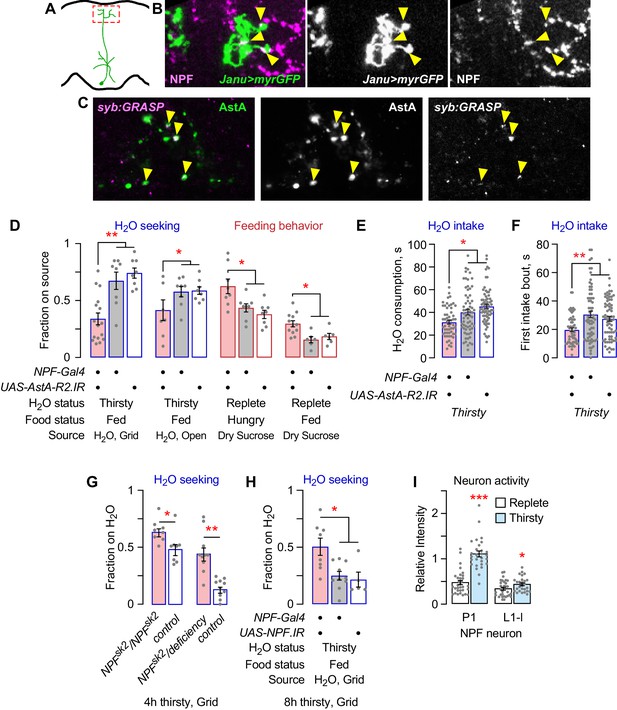
NPF neurons are postsynaptic to Janu-AstA neurons via the AstA-R2 receptor, and NPF inhibits water seeking.
(A) Janu-AstA presynaptic endings in boxed area imaged for immunohistochemistry. (B) Janu-AstA presynaptic endings partially overlap with NPF immunolabeling. Single 1 μm confocal section. Yellow arrowheads point to overlap. (C) Synaptic GRASP (syb:GRASP) between R65D05-Gal4>UAS-syb:spGFP1–10 and NPF-LexA>LexAOP-spGFP11 in thirsty flies. Single 1 μm confocal section. Yellow arrowheads point to GRASP GFP signal that overlaps with AstA immunoreactivity in the superior medial protocerebrum. (D) Behavioral effects of AstA-R2 RNAi in NPF neurons. (E) AstA-R2 knockdown in NPF neurons decreased total water consumption time. (F) AstA-R2 knockdown in NPF neurons decreased the length of the first water intake bout. (G) Flies mutant for NPF show increased water seeking when mildly water deprived (4 hr). Mann-Whitney t-test. (H) NPF knockdown in NPF neurons increased water seeking in mildly water deprived flies (8 hr). (I) NPF neuron activity in thirsty flies with TRIC. Activity was detected only in P1 and L1-l NPF neurons. t-test. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s or Kruskal/Wallis/Dunn's, unless indicated otherwise.
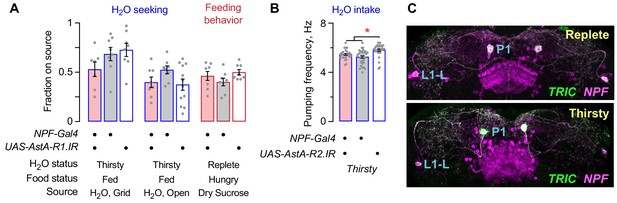
Additional characterization of the role of NPF neurons in thirst behaviors.
(A) AstA-R1 receptor RNAi in NPF neurons had no effect on thirst or feeding behavior. (B) No change in pharyngeal pumping rate in thirsty NPF>AstA-R2 RNAi flies. (C) Immunohistochemical detection of TRIC calcium indicator (green) in NPF-Gal4 (magenta) neurons in water replete and thirsty flies. Statistics are one-way ANOVA/Tukey’s.
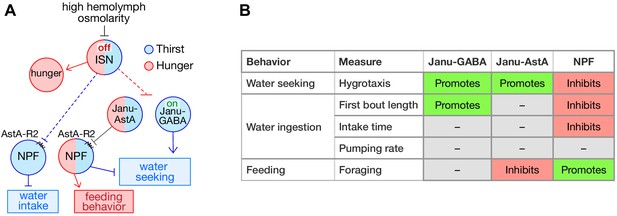
Thirst interneuron circuitry in Drosophila.
(A) Functional relationship for thirst and feeding behavior. The dotted lines represent putative connectivity between interoceptive sensory neurons (ISN) and targets neuropeptide F (NPF) and Janu neurons. (B) Functions of GABA, AstA, and NPF in their respective thirst interneurons.
Tables
| Figure | Question | Approach | Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3K | Are Janu-GABA neurons important for neural activation driven seeking? | We co-expressed a GABA neurotransmitter RNAi with TrpA1 activation. | Water seeking is suppressed. | Janu-GABA neuron activation drives replete water seeking. |
| 3L,M 3S1B,C | Are Janu-GABA neurons important for water ingestion? | We used well-established behavioral assays to specifically address ingestive behaviors. | Water ingestion does not change. But, the first bout of water intake decreases. Pumping rate is unchaged. | The first bout of water intake is mediated by Janu-GABA neurons. Other downstream neurons may be responsible for the maintenance of persistent ingestive behaviors. |
| 3N | Are Janu-GABA neurons important for fed and hungry feeding behavior? | We expressed a GABA neurotransmitter RNAi and assessed dry sucrose occupancy in fed and hungry flies. | Fed and hungry dry sucrose occupancy is unaltered. | Janu-GABA neurons are specific for thirst and do not contribute to feeding behavior. |
| 4L | Are Janu-AstA neurons important for neural activation driven seeking? | We co-expressed an AstA neurotransmitter RNAi with TrpA1 activation. | Water seeking is suppressed | Janu-AstA neuron activation drives replete water seeking. |
| 4M,N | Are Janu-AstA neurons important for water ingestion? | We used well-established behavioral assays to specifically address ingestive behaviors. | Water ingestion and first bout of water intake does not change. Pumping rate is unchanged. | Janu-AstA neurons are dispensable for thirsty water ingestion. |
| 5A,B,C | Are Janu-GABA and Janu-AstA activated by states of thirst and hunger? | We used TRIC, a calciumdependent fluorescent reporter, to assess neuronal activity. | Only the Janu-GABA1 subtype was highly active in thirsty flies. Janu-AstA was not active in thirsty or hungry states. | The Janu-GABA1 neuron is thirst activated. It may be regulated by the osmosensory ISNs. |
| 5D,E 5S1A,B,C | Does the activity of Janu and R65D05 neurons encode positive or negative valence? | We optogenetically activated Janu and R65D05 neurons to assess positional preference. | Flies exhibit positional preference for activation of Janu or R65D05 neurons. | Janu and R65D05 neurons encode positive valence. This is distinct from mammalian hunger and thirst neurons which encode negative valence. |
| 6EF 6S1B | Is AstA-R2 signaling on NPF neurons important for thirsty water ingestion? | We expressed an AstA-R2 RNAi in NPF neurons. We used well-established behavioral assays to specifically address ingestive behaviors. | Total water consumption and first bout water consumption are decreased. Pumping rate is unaffected | AstA signaling onto NPF neurons is important for water intake. |
| 6H | Is NPF signaling important for thirsty water seeking? | We expressed a NPF RNAi in thirsty flies to assess water seeking. | Water seeking is increased. | NPF released by NPF neurons suppresses water seeking. Thus, NPF can reciprocally modulate hunger and thirst. |
| 6I 6S1C | Are NPF neurons activated by thirst? | We used TRIC, a calcium-dependent fluorescent reporter, to assess neuronal activity. | Dorsomedial P1 and lateral L1 NPF neurons both are significantly activated in thirsty states. | NPF neurons encode thirst and are a critical convergence node for the integration of thirst and hunger signals. |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
InSITE strains and seeking index.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66286/elife-66286-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Strains and resources.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66286/elife-66286-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Experimental conditions and statistical analyses.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66286/elife-66286-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66286/elife-66286-transrepform-v1.docx





