Translation inhibitory elements from Hoxa3 and Hoxa11 mRNAs use uORFs for translation inhibition
Figures
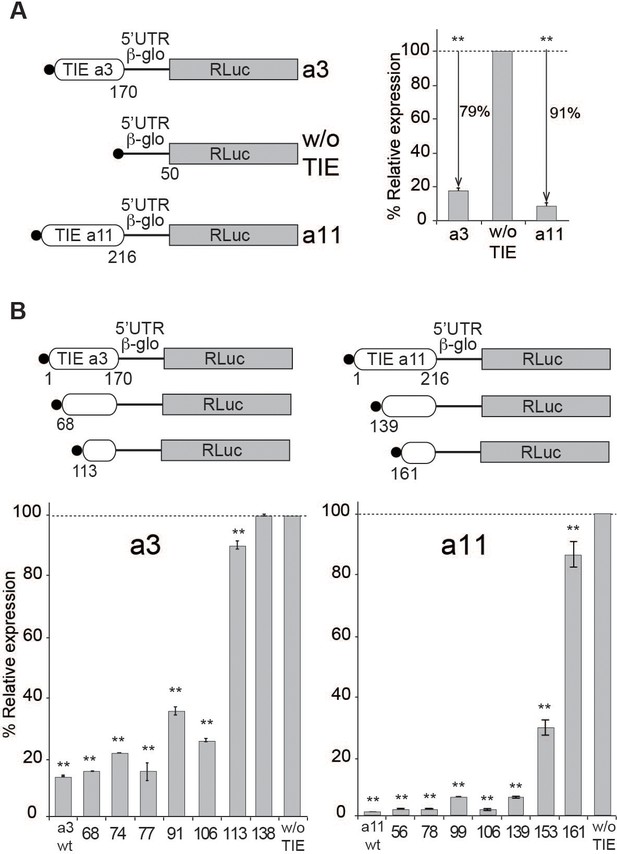
Translation inhibitory element (TIE)-mediated inhibition is recapitulated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) and does not require full-length TIEs.
(A) Three capped mRNAs were used to test TIE-mediated inhibition in vitro. Hoxa3 TIE and Hoxa11 TIE were placed upstream of the 5’UTR of Hbb-b1 and the Renilla luciferase coding sequence. Translation assays were performed in vitro using RRL at an mRNA concentration of 50 nM, which enables sub-saturating conditions. The relative expression of luciferase protein reflects the efficiency of translation inhibition by Hoxa3 TIE and Hoxa11 TIE. Values were normalized to that of the control (w/o TIE) which corresponds to normal expression without inhibition and was set to 100%. **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to w/o TIE). n = 3. Experiments were performed in triplicates. (B) Sequential deletions in the 5’ extremity of Hoxa3 TIE and Hoxa11 TIE constructs were performed to assay their effect on translation. Values of translation expression were normalized to that of the control (w/o TIE). Experiments were performed in triplicates. The percentages of inhibition for each TIE are indicated in the histogram. **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to w/o TIE). n = 3. Experiments were performed in triplicates.
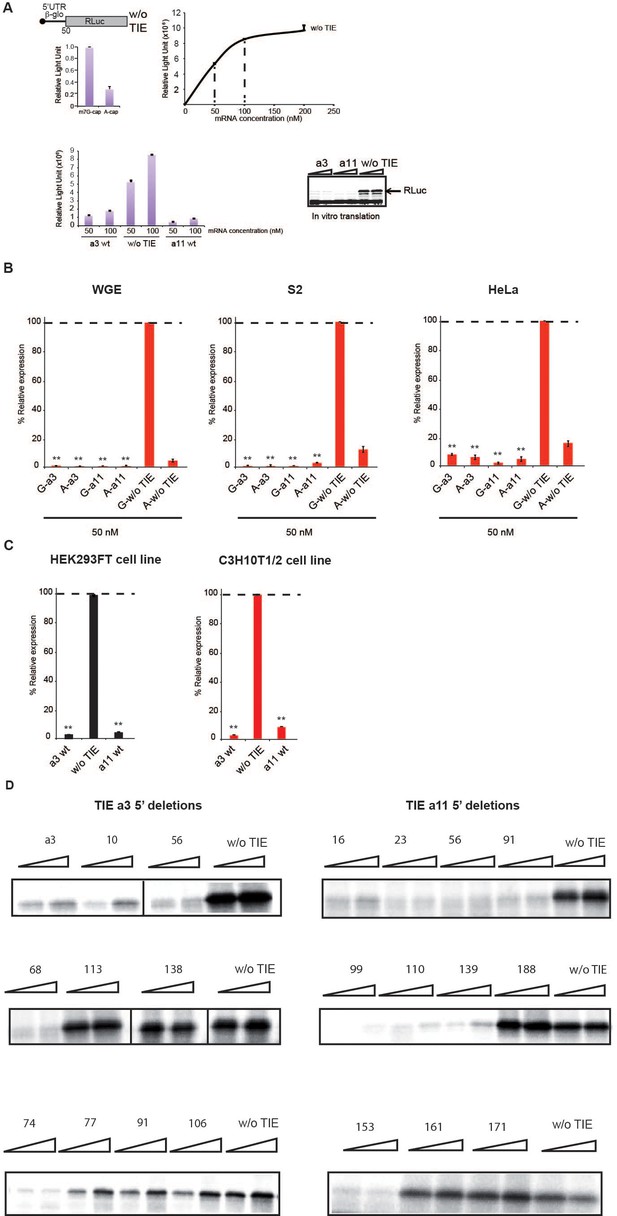
Translation inhibitory element (TIE)-mediated inhibition recapitulated in different in vitro and in vivo systems.
(A) Translation efficiency was measured with a 5’UTR Hbb-b1 Renilla luciferase (RLuc) reporter without TIE. A-capped and m7G-capped mRNAs were first used to assess cap dependency of the rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) extracts. Then, the translation efficiency was measured with increasing concentrations of m7G-capped 5’UTR Hbb-b1 Renilla. The intensity of light emitted by RLuc protein as a function of control mRNA (w/o TIE) concentration (nM). Emission of light was measured under sub-saturating conditions (50–100 nM mRNA concentration). (To the left) The intensity of light emission by RLuc protein relative to different concentrations (50 and 100 nM, respectively) of tested mRNA samples Hoxa3 TIE, Hoxa11 TIE, and control (w/o TIE). (To the right) Analysis of translation products after in vitro translation in RRL on 10% SDS-PAGE to monitor RLuc expression. Visualization of protein bands was achieved by incorporation of radiolabelled 35S-methionine, which are detected by autoradiography. (B) In vitro translation of Hoxa3 TIE and Hoxa11 TIE transcripts in the presence of m7GpppG cap or a non-functional analogue ApppG. Three in vitro systems were used: wheat germ extract (WGE), Drosophila embryonic cell extract (S2), and HeLa cell extract. All mRNAs were translated in vitro at 50 nM concentrations and RLuc expression was normalized to control (w/o TIE) in each condition. (C) Transfection of reporter plasmids with Hoxa3 TIE or Hoxa11 TIE in two embryonic cell lines, kidney HEK293FT, and mesenchymal C3H10T1/2 cell lines. RLuc expression was normalized to the control (w/o TIE). **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to construct w/o TIE). n = 3. Experiments were performed in triplicates. (D) SDS-PAGE of Renilla expression with 5’ deletions in Hoxa3 TIE and Hoxa11 TIE.
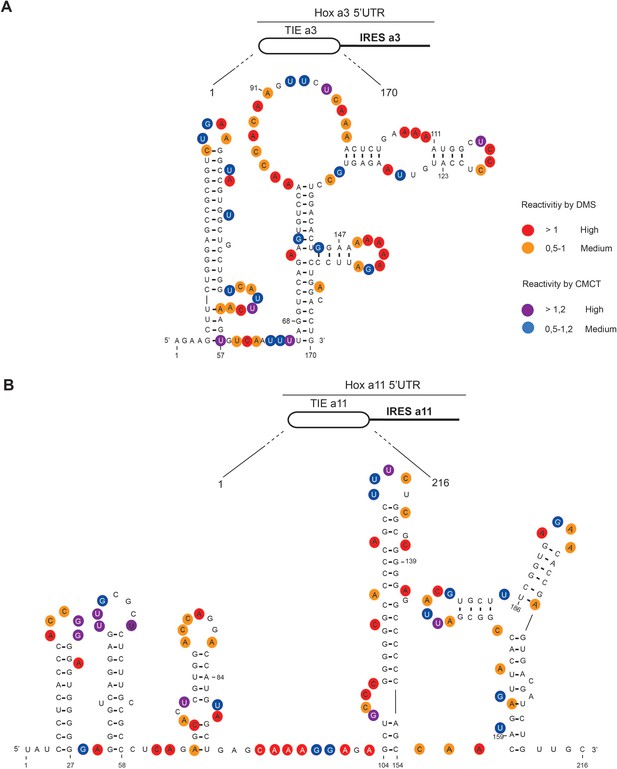
The secondary structural models of Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) and Hoxa11 TIE reveal distinct structures.
The structures of (A) Hoxa3 TIE (170 nucleotides) and (B) Hoxa11 TIE (216 nucleotides) were obtained by chemical probing using base-specific reagents, dimethyl sulfate (DMS) and 1-cyclohexyl-3-(2-morpholinoethyl) carbodiimide metho-p-toluene sulfonate (CMCT). After modifications, reverse transcription was performed using fluorescently labelled primers to determine the position of modified nucleotides. Experiments were performed in triplicates. Reactivities are shown as average reactivity from three independent experiments. A representation of reactivities is assigned as colour code depending on a range of values as shown in the figure legend on the right. Reactivity values for each nucleotide with corresponding standard deviations are shown in figure supplements (S2A, S2B, S2C, and S2D).
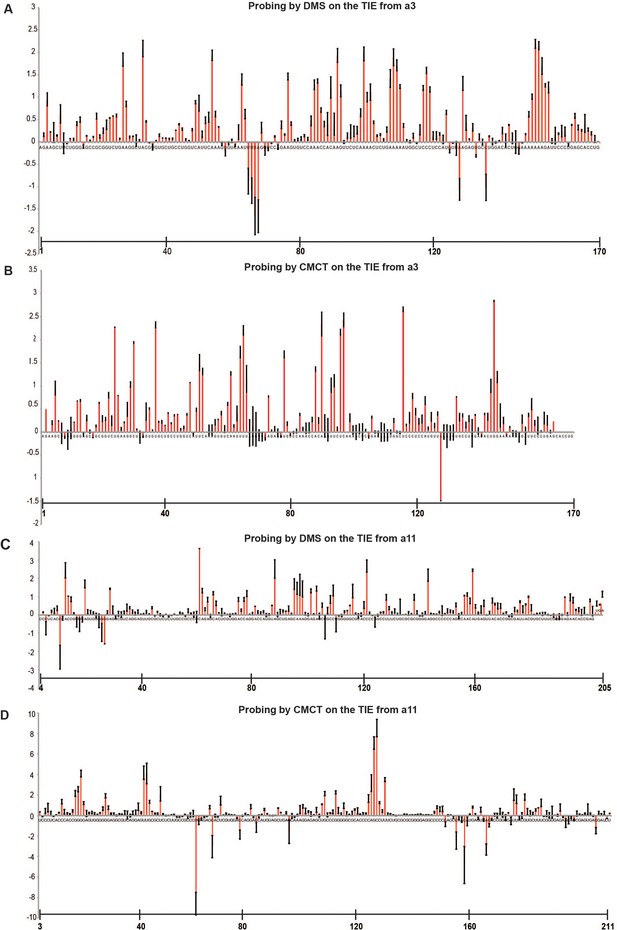
Average of reactivities of dimethyl sulfate (DMS) and 1-cyclohexyl-3-(2-morpholinoethyl) carbodiimide metho-p-toluene sulfonate (CMCT) for Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) and Hoxa11 TIE.
Probing experiments by DMS and CMCT were performed in triplicates. Figures S2A and S2B represent averages of reactivities of DMS and CMCT for Hoxa3 TIE, respectively. Figures S2C and S2D represent averages of reactivities of DMS and CMCT for Hoxa11 TIE, respectively. A scale of 40 nucleotides range was included to determine position of every nucleotide. Standard deviations are shown.
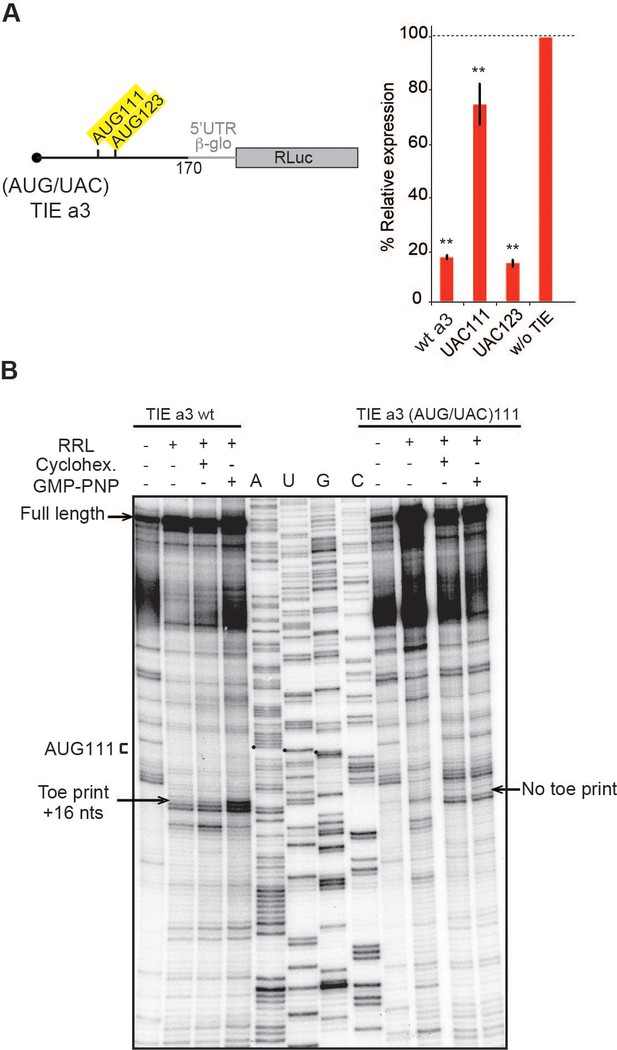
Upstream AUG111 in Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) is essential for inhibition.
(A) Substitution mutations in uAUG111and uAUG123 to UAC in Hoxa3 TIE were performed. Constructs with the corresponding mutations were translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) and luciferase assay was performed to evaluate the effect of mutation on translation efficiency as previously described. **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to construct w/o TIE). n = 3. Experiments were performed in triplicates. (B) Toe printing analysis of ribosomal assembly on two mRNAs, Hoxa3 TIE Wt and the mutant of upstream (AUG/UAC)111. Initiation complexes were assembled in RRL extracts in the absence or presence of translation inhibitors: cycloheximide and GMP-PNP. Reaction samples were separated on 8% denaturing PAGE together with the appropriate sequencing ladder. Toe print positions were counted starting on the A + 1 of the AUG codon at +16 position. A, U, and G nucleotides of the start codon are marked by black dots. Full-length cDNAs are indicated by an arrow at the top of the gel.
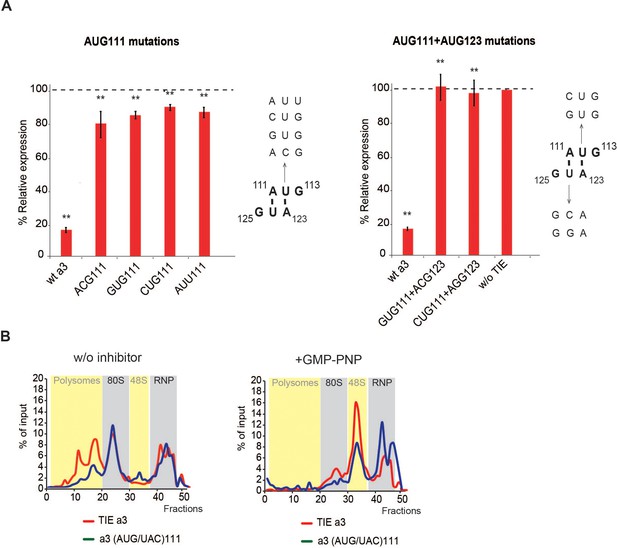
Upstream AUG111 in Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) is essential for inhibition.
(A) (To the left) AUG-like mutations (AUU, GUG, CUG, and ACG) were tested in vitro in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) compared to wt Hoxa3. (To the right) Representation of uAUG111 context in the secondary structure of Hoxa3 TIE is shown. A111 and U112 base pair with the A123 and U124 of the second AUG123. Mutants of the uAUG into CUG and GUG with the corresponding compensatory mutagenesis were tested. Renilla luciferase (RLuc) expression with different transcripts was normalized to control (w/o TIE). **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to construct w/o TIE). n = 3. Experiments were performed in triplicates. (B) Sucrose gradient analysis of Hoxa3 TIE and mutant of upstream (AUG/UAC)111. Ribosomal pre-initiation complexes were assembled and analysed on 7–47% sucrose gradient with radioactive m7G-capped Hoxa3 TIE and the mutants of upstream (AUG/UAC)111 in the absence (upper panel) or in the presence of GMP-PNP (lower panel). Heavy fractions correspond to polysomes while the lightest correspond to free RNPs.
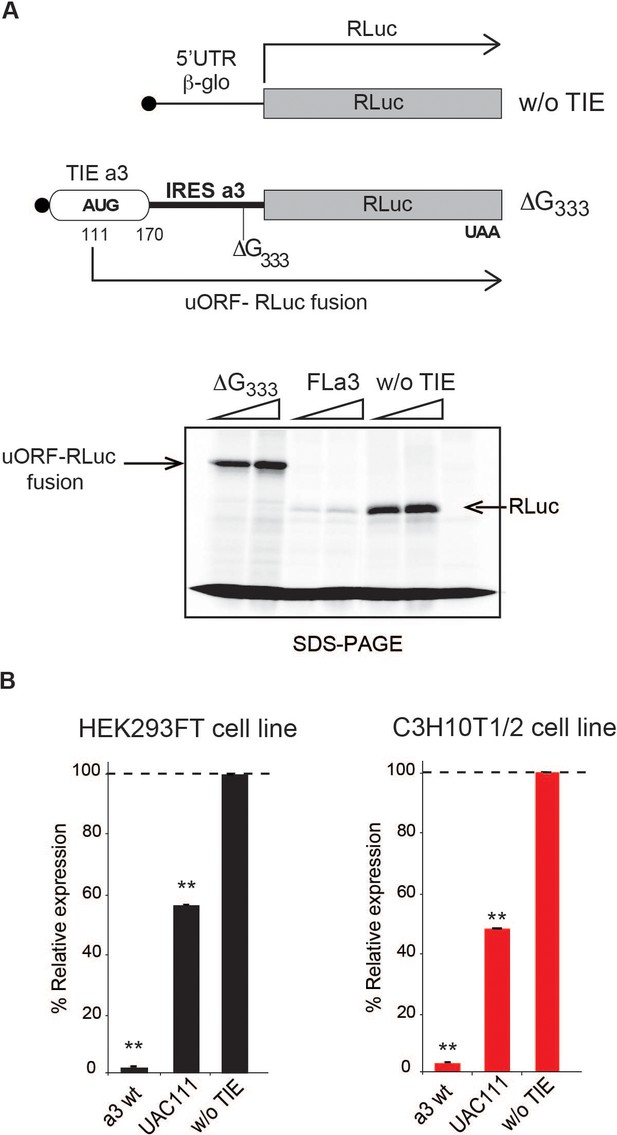
The uAUG111 in Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) is translated through 5’UTR of Hoxa3.
(A) Three transcripts were used for this experiment: full-length 5’UTR of Hoxa3, a deletion mutant at nucleotide G333 in Hoxa3 internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and a control transcript without TIE. To test the translation of upstream open reading frame (uORF) in Hoxa3 TIE starting form uAUG111, a deletion of G in Hoxa3 IRES at position 333 was performed to create a longer uORF that is in the same frame as the ORF of Renilla luciferase to create an N-terminally extended luciferase. FLa3 mRNA was used as a control to correspond to the full-length Hoxa3 5’UTR (TIE + IRES). Transcripts were translated in vitro in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) and products were loaded on 10% SDS-PAGE in the presence of 35S-methionine. (B) In vivo luciferase assays in two embryonic cells lines: HEK293FT (left) and C3H10T1/2 (right). Reporter constructs in pmirGlo containing Hoxa3 TIE, u(AUG/UAC)111, and without TIE were transfected in the two indicated cell lines. Renilla luciferase expression was normalized to the control (w/o TIE), which was set to 100%. **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to empty plasmid [w/o TIE]). Experiments were performed in triplicates. n = 3.
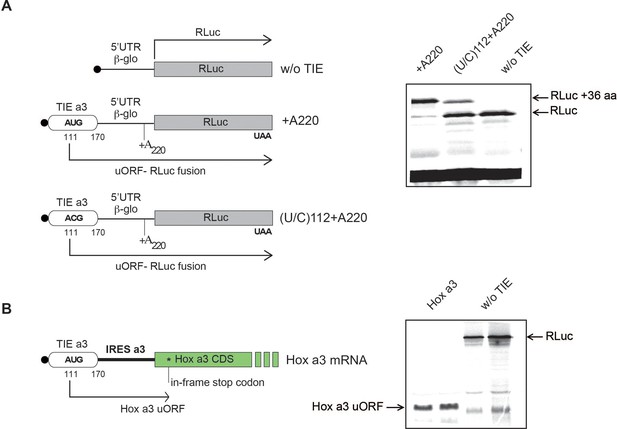
Translation of Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) upstream open reading frame (uORF) in different constructs.
(A) A single nucleotide deletion of A220 in Hoxa3 TIE is performed to frameshift the uORF frame to the same as the main Renilla luciferase (RLuc) ORF. Another mutation was performed combining this deletion with uAUG mutation of (U/C)112. Transcripts were in vitro translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) and products were loaded on 1-11S PAGE gel.ere in vitro translated in RRL and products were loaded on 1°111-113s. y. Figures 3 and 4s calculated and RLuc rib0% SDS-PAGE. (B) Translation of Hoxa3 TIE uORF in Hoxa3 mRNA. Hoxa3 mRNA (5’UTR + CDS) was translated in vitro to check uORF translation in this context. Products were analysed on 15% SDS-PAGE. The experiment was performed in duplicate samples.
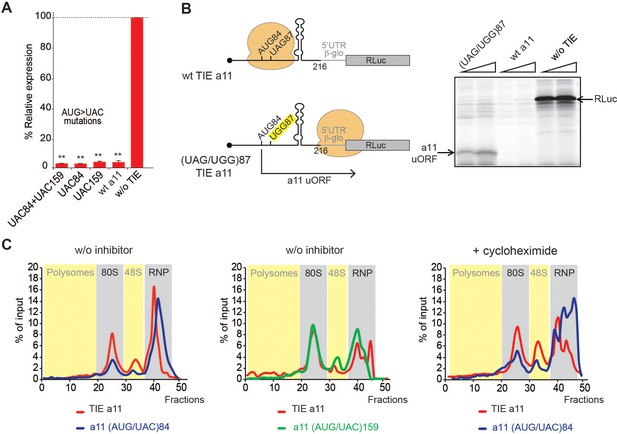
A start-stop upstream open reading frame (uORF) in Hoxa11 translation inhibitory element (TIE) stalls an 80S upstream of a highly stable structure.
(A) Mutational analysis of uAUGs in Hoxa11 TIE. Three transcripts with AUG/UAC mutations were used: M1: (AUG/UAC)84 + (AUG/UAC)159, M2: (AUG/UAC)84, and M3: AUG/UAC159. Transcripts were translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) at 50 nM concentrations and the luciferase expression was normalized to the control (w/o TIE) as previously described. **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to construct w/o TIE). n = 3. Experiments were performed in triplicates. (B) A single substitution (A/G)88 mutation destroys the stop codon UAG87 to UGG in Hoxa11 TIE, Hoxa11 TIE wt, and control (w/o TIE) were also translated as references in RRL. Translation products were loaded on 15% SDS-PAGE. (C) Ribosomal pre-initiation complexes were assembled and analysed on 7–47% sucrose gradient with [alpha-32P]GTP-radiolabelled Hoxa11 TIE as well as the two mutants of uAUG/UAC at the previously indicated positions in the absence or presence of cycloheximide. Heavy fractions correspond to polysomes and lighter fractions correspond to free RNPs. The coloured sections corresponding to RNP, 48S, 80S, and polysomes have been assigned according the the OD254nm profiles (see also Figure supplement S6).
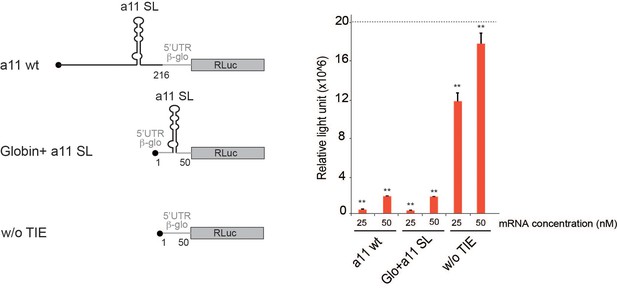
Transplanting Hoxa11 translation inhibitory element (TIE) stem loop structure in Hbb-b1 5’ UTR efficiently inhibits translation of Renilla luciferase (RLuc) mRNA.
The stem loop structure of Hoxa11 TIE (104–154) was transplanted in the 5’UTR of Hbb-b1 with 25 nucleotides spanning from each extremity. The three shown transcripts were in vitro translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) at two concentrations, 25 and 50 nM. Results are represented in relative light unit of RLuc expression.
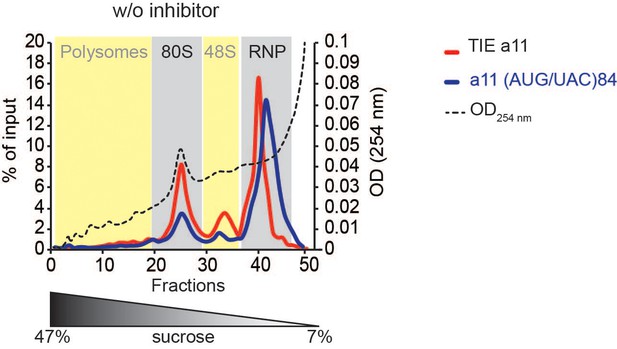
Polysome fractionation on 7–47% sucrose gradient of pre-initiation complexes.
Polysome fractionation of pre-initiation complexes programmed with m7G-capped radioactive mRNAs containing Wt Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) and the mutant (AUG/UAC)84 in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) previously treated with cycloheximide. The y-axis represent the percentage of radioactive RNA present in the fractions. The coloured sections corresponding to RNP, 48S, 80S, and polysomes are assigned according to the OD254 nm profile (dashed line).
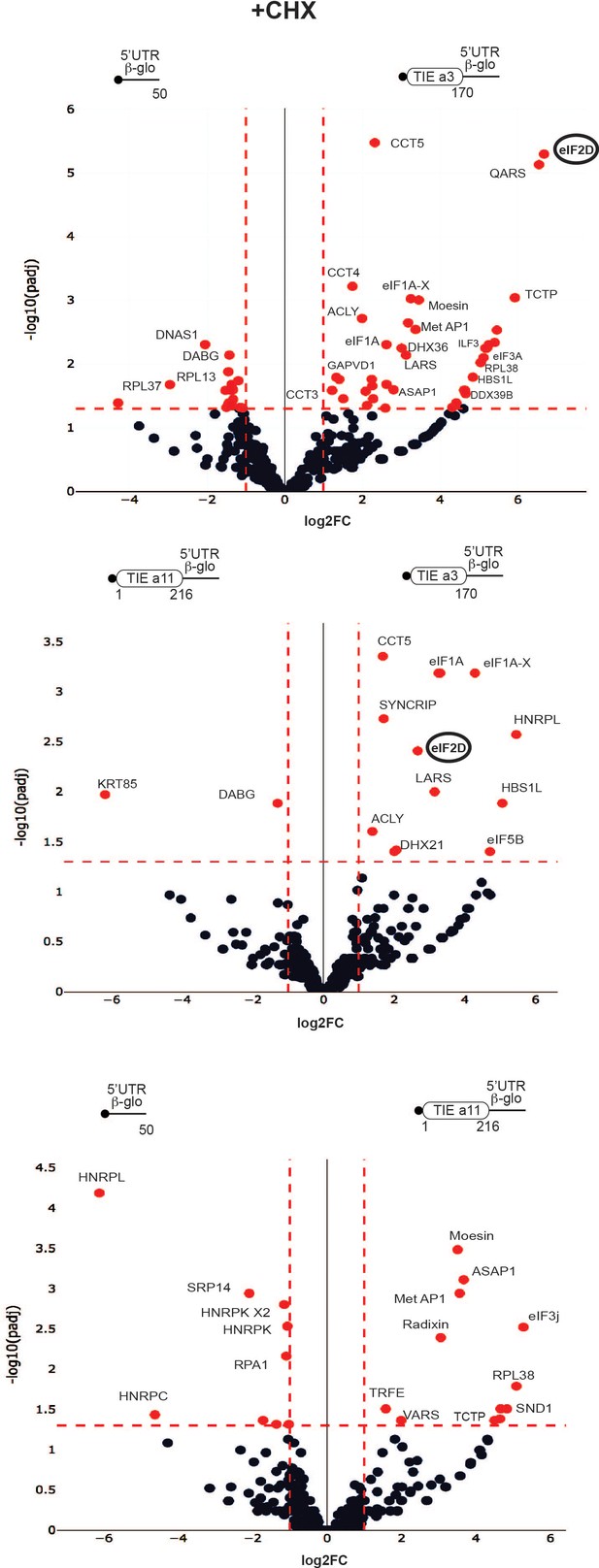
Distinct profiles for factors involved in translation inhibitory element (TIE)-mediated inhibition blocked with cycloheximide.
Mass spectrometry analysis of cycloheximide-blocked translation initiation complexes and on three transcripts: Hoxa3 TIE, Hoxa11 TIE placed upstream of 5’UTR of Hbb-b1, and the 5’UTR of Hbb-b1 (control). Graphical representation of proteomics data: protein log2 spectral count fold changes (on the x-axis) and the corresponding adjusted log10p-values (on the y-axis) are plotted in a pair-wise volcano plot. The significance thresholds are represented by a horizontal dashed line (p-value=1.25, negative binomial test with Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment) and two vertical dashed lines (−1.0-fold on the left and +1.0-fold on the right). Data points in the upper left and upper right quadrants indicate significant negative and positive changes in protein abundance. Protein names are labelled next to the off-centred spots and they are depicted according to the following colour code: red spots are significant hits and black are non-significant with <10 spectra. Data points are plotted based on the average spectral counts from triplicate analysis. Three profiles were produced by comparing the proteomics of two transcripts.
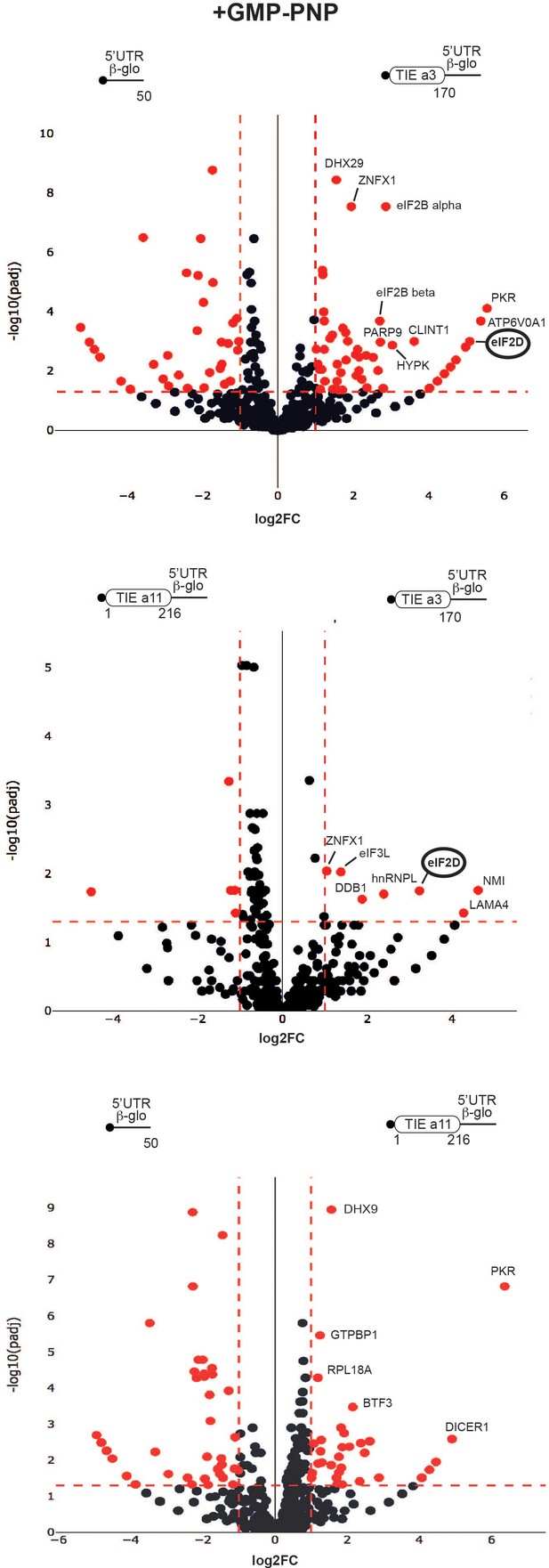
Distinct profiles for factors involved in translation inhibitory element (TIE)-mediated inhibition blocked with GMP-PNP.
Mass spectrometry analysis of GMP-PNP-blocked translation initiation complexes and on three transcripts: Hoxa3 TIE, Hoxa11 TIE placed upstream of 5’UTR of Hbb-b1, and the 5’UTR of Hbb-b1 (control). Graphical representation of proteomics data: protein log2 spectral count fold changes (on the x-axis) and the corresponding adjusted log10p-values (on the y-axis) are plotted in a pair-wise volcano plot. The significance thresholds are represented by a horizontal dashed line (p-value=1.25, negative binomial test with Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment) and two vertical dashed lines (−1.0-fold on the left and +1.0-fold on the right). Data points in the upper left and upper right quadrants indicate significant negative and positive changes in protein abundance. Protein names are labelled next to the off-centred spots and they are depicted according to the following colour code: red spots are significant hits and black are non-significant with <10 spectra. Data points are plotted based on the average spectral counts from triplicate analysis. Three profiles were produced by comparing the proteomics of two transcripts.
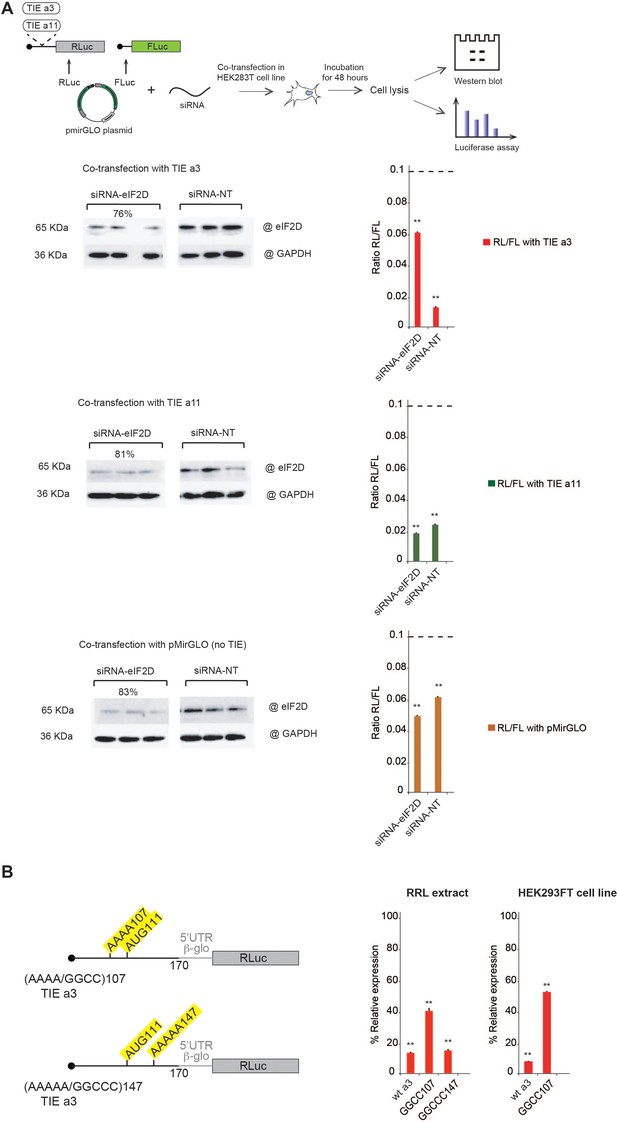
Co-transfection assay of translation inhibitory element (TIE) plasmids and siRNA against eIF2D confirms its implication in Hoxa3-mediated inhibition.
Mutational analysis of A-motif sequences in Hoxa3 TIE shows a requirement for an upstream A-motif for efficient inhibition. (A) Co-transfection assay was performed using pmirGLO plasmids with inserts of Hoxa3 TIE, Hoxa11 TIE, and w/o TIE (pmirGLO) with siRNA against eIF2D (siRNA-eIF2D), and non-target pool of siRNA (siRNA-NT) in HEK293 cell line. The plasmids harbour two reporter genes, Renilla luciferase for monitoring the impact of TIEs and Firefly luciferase for normalization. Plates were incubated for 48 hr followed by cell lysis. Cell lysate was analysed by western blot and luciferase assay. The histograms present the Renilla to Firelfly luciferase activity ratio. **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to construct w/o TIE). n = 3. Experiments were performed in triplicates. Efficiency of silencing of each protein was quantified by western blot analysis for Hoxa3 TIE and Hoxa11 TIE samples. (B) Two sets of mutations were performed on distinct A-motif sequences in Hoxa3 TIE. The first mutation is AAAA/GGCC107 and the second mutation AAAAA/GGCCC147. The transcripts were in vitro translated in RRL with Hoxa3 TIE Wt and control (w/o TIE). Results were confirmed in vivo in HEK293FT cell line. Luciferase activities were normalized to control (w/o TIE). **p<0.01 (t-test as compared to construct w/o TIE). n = 3. Experiments were performed in triplicates.
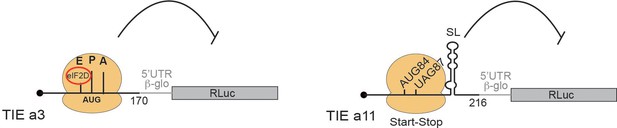
Two distinct models for translational inhibition by Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) and Hoxa11 TIE.
A model for Hoxa3 TIE suggests a ribosomal assembly on the uAUG111 with a requirement of eIF2D initiation factor. The model for Hoxa11 TIE suggests a stalled 80S ribosome on AUG-stop codons combination upstream of a highly stable structure.
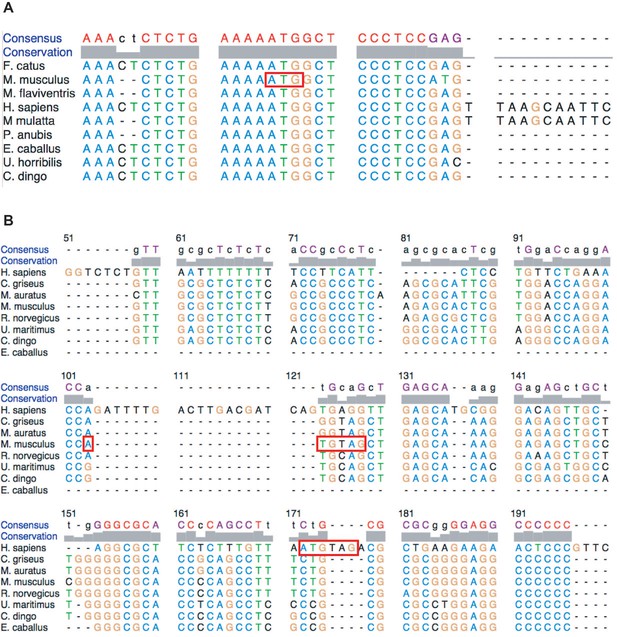
Alignment of Hoxa3 translation inhibitory element (TIE) and Hoxa11 TIE among different species shows variation in the conservation of the inhibitory elements.
(A) Nucleotides 1–170 from the mouse Hoxa3 TIE sequence were aligned with different species. The position of uAUG in Mus musculus is highlighted in a red box. Accession numbers: Felis catus: XR_002740526.1, M. musculus: NM_010452.3, Marmota flaviventris: XM_0279, Homo sapiens: XM_011515343.3, Macaca mulatta: XM_028845931.1, Papio anubis: XM_017956197.2, Equus caballus: XM_023639416.1, Ursus arctos horribilis: XM_026508219.1, Canis lupus dingo: XM_025464436.1. (B) Nucleotides 1–216 from the mouse Hoxa11 TIE sequence were aligned with different species. The position of uAUG-UAG in Mus Musculus and the insertion of AUG-UAG in H. sapiens are highlighted in red boxes. Accession numbers: H. sapiens: AF071164.1, M. mulata: XM_015133828.2, C. dingo: XR_003143092.1, Cricetulus griseus: XM_027436289.1, Rattus norvegicus: XM_008762951.2, E. caballus: XM_023639423.1, Melanochromis auratus: XM_00508585871.3, M. musculus: NM_010450.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Mass spectrometry analysis of pre-initiation complexes programmed with Hoxa3 TIE, Hoxa11 TIE, and 5’UTR Hbb-b1 in the presence of cycloheximide.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66369/elife-66369-supp1-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 2
Mass spectrometry analysis of pre-initiation complexes programmed with Hoxa3 TIE, Hoxa11 TIE, and 5’UTR Hbb-b1 in the presence of GMP-PNP.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66369/elife-66369-supp2-v1.xls
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/66369/elife-66369-transrepform-v1.docx





