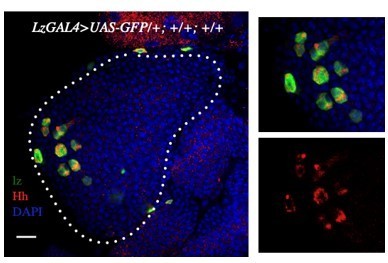
Relish plays a dynamic role in the niche to modulate Drosophila blood progenitor homeostasis in development and infection
Figures
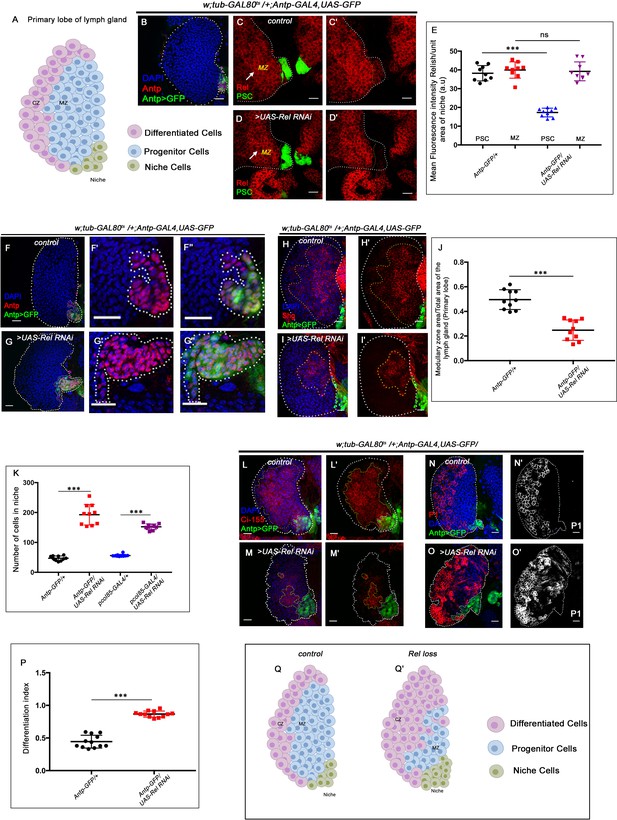
Relish expression and its function in hematopoietic niche of Drosophila larval lymph gland.
Genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A) Schematic representation of Drosophila larval lymph gland with its different cell types. (B) Hematopoietic niche in larval lymph gland visualized by Antp-Gal4,UAS-GFP and Antennapedia (Antp) antibody. (C–D') Expression of Relish (antibody: red) in larval lymph gland. (C) Relish is expressed in the hematopoietic niche of lymph gland and in the progenitor population. (C') Zoomed in view of the niche showing the expression of Relish in control niche. (D–D') Relish expression is abrogated in the niche upon RNAi mediated downregulation. (E) Quantitation of Relish expression in the niche. Significant reduction in Relish expression was observed in niche (n=10, p-value=7.4 × 10−9, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test), whereas progenitor-specific expression remained unchanged (n=10, p-value=0.764 , two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (F–G'') Effect of Relish loss from the niche on cell proliferation (F–F''), Antp expression marks the niche of wild-type lymph gland. (G–G'') Loss of Relish function from niche leads to increase in niche cell number. (H–I') Hematopoietic progenitors of larval lymph gland (red, reported by DE-Cadherin [Shg] immunostaining). Compared to control (H–H'), drastic reduction in progenitor pool was observed when Relish function was attenuated from niche (I–I'). (J) Quantitation of Shg-positive progenitor population upon Relish knockdown from the niche using Antp-GAL4 (n=10, p-value=8.47 × 10−6, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (K) Quantitation of niche cell number upon Relish knockdown from the niche using Antp-GAL4 (n=10, p-value=1.3 × 10−7, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) and pcol85-GAL4 (n=11, p-value=1.2 × 10−12, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (L–M') Hematopoietic progenitors of larval lymph gland (red, reported by Ci155 immunostaining) (L–L'). Loss of Relish from the niche resulted in reduction in Ci155-positive progenitor pool (M–M'). (N–O') Compared to control (N–N'), increase in the amount of differentiated cell population (red, P1 immunostaining) was observed upon niche-specific downregulation of Relish (O–O'). (P) Quantitative analysis of (N–O') reveals significant increase in the amount of differentiated cells in comparison to control (n=10, p-value=2.3 × 10−9, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (Q–Q') Scheme based on our observation. The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases and niche in (F–G''). Yellow dotted lines mark the progenitor zone in (H–I') and (L–M'). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Contains numerical data plotted in Figure 1C–D', Figure 1F–G'', Figure 1H–I', Figure 1N–O' and Figure 1—figure supplement 1C–D', Figure 1—figure supplement 1F–G'' and Figure 1—figure supplement 1K–L'.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67158/elife-67158-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx.xlsx
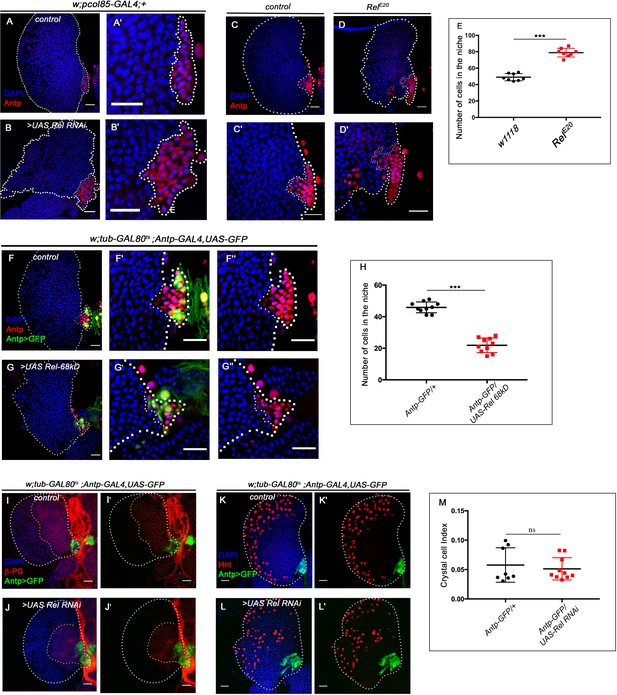
Relish negatively regulate niche cell proliferation.
Genotypes of the larvae are mentioned in respective panels. Scale bar: 20 µm. (A–B') Effect of Relish loss from the niche using an independent GAL4 line, pcol85-GAL4. Compared to control (A–A'), downregulation of Relish from the niche using pcol85-GAL4 (B–B') also leads to increased niche cell proliferation. (C–D') A substantial increase in niche number was observed in Relish mutant (RelE20) (D–D') when compared to control (C–C'). (E) Quantitation of niche cell number in RelE20 mutant in comparison to control (n=8, p-value=9.03 × 10−9, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (F– G'') In comparison to control (F–F''), overexpression of Relish in the niche resulted in a reduction in niche cell number (G–G''). (H) Quantitation of niche cell number in Relish overexpression in comparison to control (n=10, p-value=3.3 × 10−10, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (I–J') Lamellocytes were not observed in Relish loss scenario (red, integrin β-PS-immunostaining). Loss of β-PS-positive progenitor pool is further evident in Relish loss scenario compared to control (compare J- J' to I- I') (K–L') In comparison to the control (K–K'), no significant change in crystal cell index (number of crystal cells/total number of cells in the lobe) was observed in Relish downregulation scenario (L–L'). (M) Quantitative analysis of crystal cell index in both control and Relish loss condition (n=8, p-value=0.596, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases and niche in A' and B', C' and D', F'–F'', and G'–G''. Yellow dotted lines mark the progenitor zone in (I–J') The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). In all panels, the age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
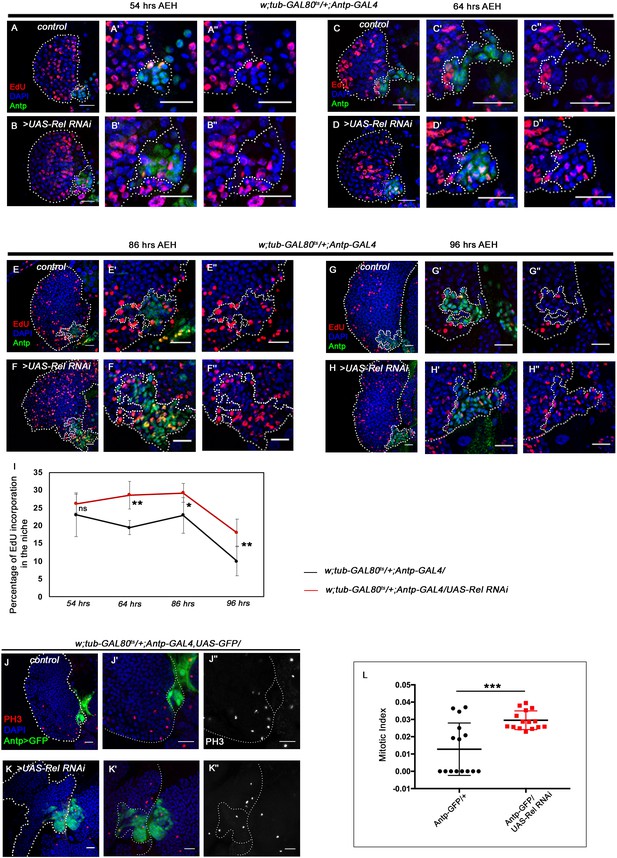
Loss of Relish from the niche causes niche cell hyperplasia. Genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels.
Scale bar: 20 μm. Niche is visualized by Antp antibody expression. (A–H'') EdU or 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine marks the cells in S-phase of the cell cycle. EdU profiling at 54 hr AEH (A–B''), 64 hr AEH (C–D''), 86 hr AEH (E–F''), and 96 hr AEH (G–H'') displayed EdU incorporation in the niche (green) in control and upon Relish downregulation. Control niches showed scanty EdU incorporation beyond 84 hr (E–E'' and G–G''), whereas loss of Relish induced niche cells to proliferate more (F–F'' and H–H''). (I) Graph representing percentage of EdU incorporation in the niche during the course of development in control (black line) and Relish loss (red line). Significant increase in the niche cell number is observed with development in Relish loss scenario. (54 hr, n=6, p-value=0.294), (64 hr, n=6, p-value=1.3 × 10−3), (86 hr, n=6, p-value=2.9 × 10−2), (96 hr, n=6, p-value=5.9 × 10−3); two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. (J–K'') Significant increase in the number of mitotic cells (phospho-histone 3 [PH3], red) was observed upon Relish loss from the niche (K–K'') compared to the control (J–J''). (L) Quantitation of the mitotic index of wild-type and Relish loss niche (n=15, p-value=8.1 × 10−4; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland and the niches. In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH, unless otherwise mentioned. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Contains numerical data plotted in Figure 2A–B'', Figure 2C–D'', Figure 2E–F'', Figure 2G–H'', Figure 2J–K'' and Figure 2—figure supplement 1H–I''''.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67158/elife-67158-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx.xlsx
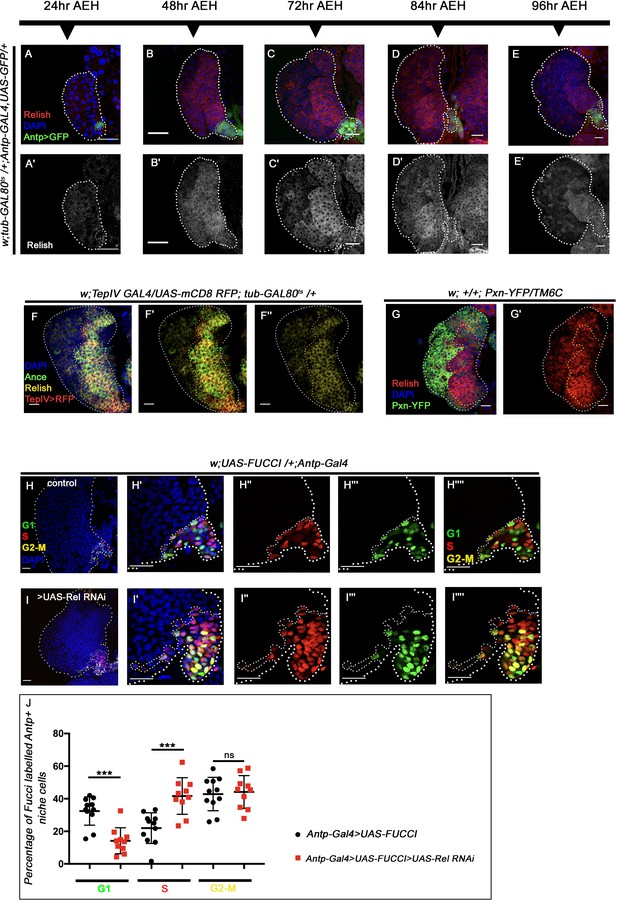
Relish expression starts beyond the second-instar stage in the hematopoietic niche. The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels.
Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–E') Expression of Relish (red, by antibody) at different developmental time points in the larval lymph gland (niche marked with AntpGAL4>UAS-GFP). Observations were made at 24 hr AEH (A–A'), 48 hr AEH (B–B'), 72 hr AEH (C–C'), 84 hr AEH (D–D'), and 96 hr AEH (E–E'). Relish expression in the niche can be detected around 48 hr AEH. (F–F'') Relish expression (yellow) in the progenitor cells co-localizes with prohemocyte markers Ance (green) and TepIV (red). (G–G') Relish expression (red) is restricted to progenitor cells, whereas it is downregulated in Pxn-YFP-positive differentiated cells (green). (H–I'''') Cell cycle status reported by Fly-FUCCI using niche-specific GAL4: Antp-Gal4. In control, niche cells are mostly in G1 (green, H''') and G2–M (yellow, H'''') phase, while few are in S phase (red, H''). Niche cells from where Relish function has been downregulated were mostly in S, (red, I'') and G2-M (yellow, I''''), and very less in G1 (green, I''') phase of the cell cycle. (J) Quantitative analyses of the cell cycle status of control and Relish loss niches (n=10, p-value for G1=7.3 × 10−5, p-value for S=4.2 × 10−4, p-value for G2-M = 0.657), two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland and the niches in (H–I''''). Yellow dotted lines mark the progenitor zone in (F–G'). In all panels. age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH, unless otherwise mentioned. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
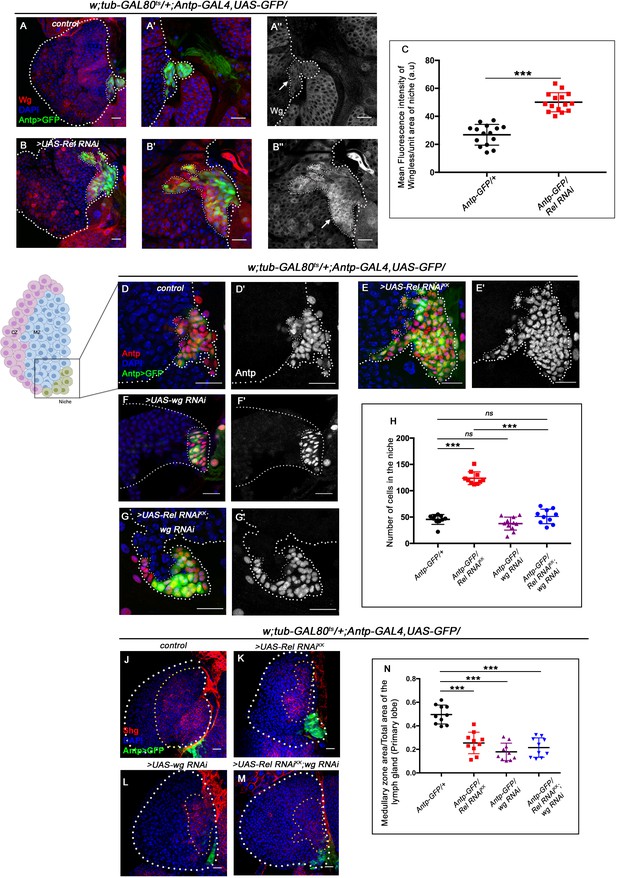
Upregulated Wingless signaling leads to increase in niche cell number. The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels.
Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–B'') Expression of Wingless (antibody) in the lymph gland. The hematopoietic niche is visualized by Antp-GAL4>UAS-GFP. (A'–A'') and (B'–B'') are higher magnifications of (A) and (B), respectively. In comparison to the wild-type niche (A–A''), Wingless protein levels were substantially high in Relish loss of function (B–B''). (C) Statistical analysis reveals elevated wingless expression upon Relish knockdown in niche (n=15; p-value=5.8 × 10−9, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.) (D–G') The increased niche number observed upon Relish loss (E–E') is rescued upon reducing Wingless level by the wg RNAi (F–F') in Relish loss genetic background (G–G'). The rescued niche cell number is comparable to control (D–D'). (H) Statistical analysis of the data in (D–G') (n=10, p-value=1.1 × 10−11 for control versus Rel RNAiKK, p-value=3.15 × 10−10 for Rel RNAiKK versus Rel RNAiKK; wg RNAi, n=10, p-value=0.10 for control versus wg RNAi, n=10, p-value=0.29 for control versus Rel RNAiKK; wg RNAi; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (J–M) Hematopoietic progenitors of larval lymph gland (red, reported by DE-Cadherin [Shg] immunostaining). Knocking down wingless function from the niche resulted in loss of Shg-positive progenitors (L). Downregulating wingless using wg RNAi in Relish loss genetic background was unable to restore the reduction in prohemocyte pool (M) observed in Relish loss (K) scenario in comparison to control (J). (N) Statistical analysis of the data in (J–M) (n=10, p-value=6.74 × 10−6 for control versus Rel RNAiKK, p-value=4.03 × 10−7 for control versus wg RNAi; Rel RNAiKK, p-value=3.42 × 10−8 for control versus wg RNAi; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland and the niches in (A–G') Yellow dotted lines mark the progenitor zone in (J–M). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Contains numerical data plotted in Figure 3A–B'', Figure 3D–G', Figure 3J–M and Figure 3—figure supplement 1A–D, Figure 3—figure supplement 1G–J, Figure 3—figure supplement 1L–O and Figure 3—figure supplement 1Q–T.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67158/elife-67158-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
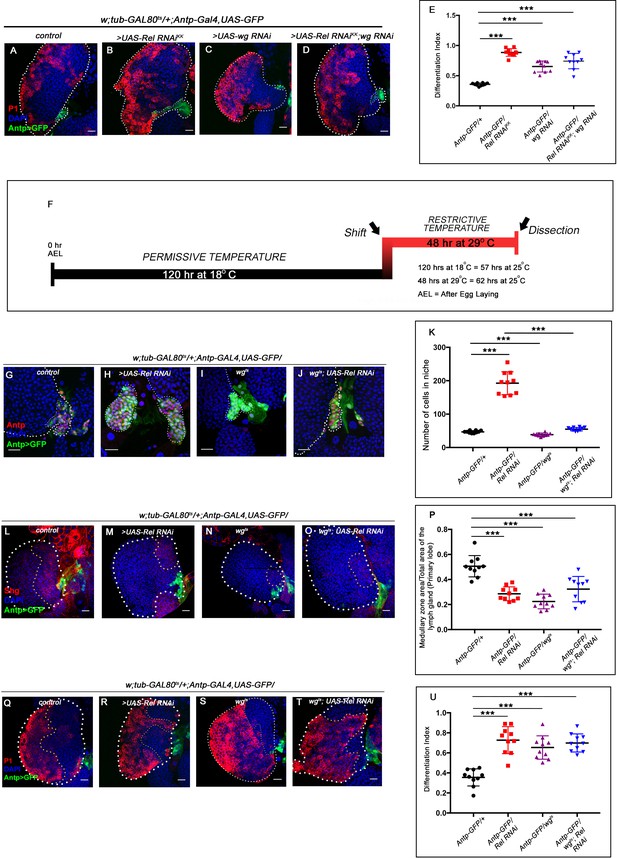
Downregulating wingless in Relish loss condition rescues niche cell proliferation, but not differentiation.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–D) Increase in plasmatocyte population (marked by P1, red) was observed upon Relish (B) and wingless downregulation (C) from the niche compared to the control (A). Simultaneous downregulation of wingless function in Relish loss genetic background did not rescue the increased differentiation (D). (E) Statistical analysis of the data in (A–D) (n=10, p-value=2.97 × 10−9 for control versus Rel RNAiKK, p-value = 4.18 × 10−5 for control versus wg RNAi; Rel RNAiKK, p-value=2.8 × 10−4 for control versus wg RNAi; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (F) Scheme depicting the temperature regime followed for the rescue experiments (G–U) for wingless mutant (wgts). (G–J) The increased niche number observed upon Relish loss (H) is rescued upon reducing Wingless level by the temperature-sensitive allele wgts (I) in Relish loss genetic background (J). The rescued niche cell number is comparable to control (G). (K) Statistical analysis of the data in (G–J) (n=10; p-value=2.4 × 10−7 for control versus Relish RNAi, p-value=4.3 × 10−4 for control versus wgts and p-value = 3.4 × 10−7 for wgts; Relish RNAi versus Relish RNAi; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (L–O) Hematopoietic progenitors of larval lymph gland (red, reported by DE-Cadherin [Shg] immunostaining). Knocking down wingless function using wgts resulted in loss of Shg-positive progenitors (N). Downregulating wg function in Relish loss genetic background was unable to restore the reduction in prohemocyte pool (O) observed in Relish loss (M) scenario in comparison to control (L). (P) Statistical analysis of the data in (L–O) (n=10; p-value=4.80 × 10−6 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=3.8×10−4 for wgts; Rel RNAi versus control, p-value=2.18 × 10−7 for control versus wgts; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (Q–T) Increase in plasmatocyte population (marked by P1, red) was observed upon wingless (S) and Relish down regulation from the niche (R) compared with the control (Q). Simultaneous downregulation of wingless function using wgts in Relish loss genetic background did not rescue the increased differentiation (T). (U) Statistical analysis of the data in (Q–T) (n=10, p-value=2.1 × 10−6 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=5.9 × 10−6 for control versus wgts, p-value=6.8 × 10−8 for control versus wgts; Rel RNAi; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland and the niches in (A–D) and (G–J). Yellow dotted lines mark the progenitor zone in (L–O) and (Q–T). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
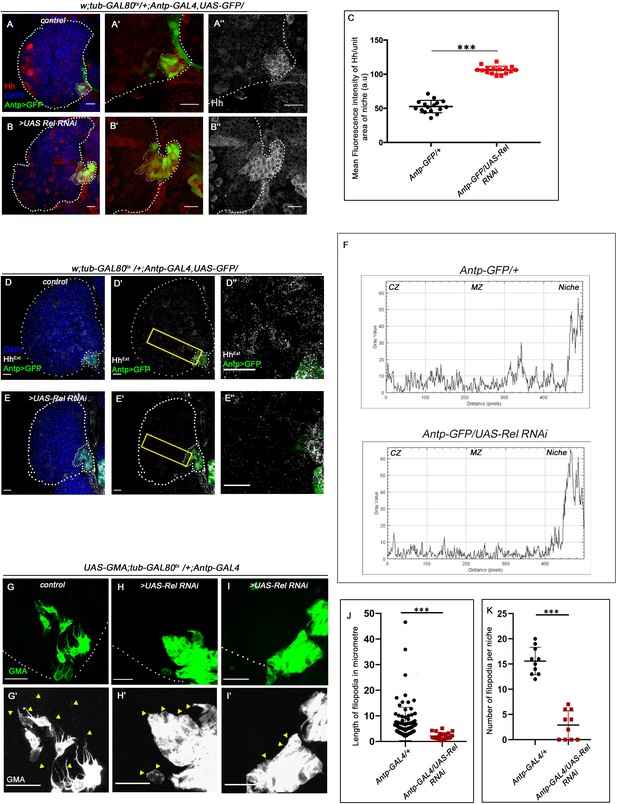
Hedgehog release from the niche is affected in Relish loss of function.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–B'') Hedgehog (Hh) antibody staining in the lymph gland shows Hh enrichment in the niche. The hematopoietic niche in Relish loss of function (B–B'') exhibits higher level of Hh in comparison to the control (A–A''). (C) Statistical analysis of fluorescence intensity revealed more than 2.5-fold increase in Hh levels compared to control (n=15, p-value=2.5 × 10−17, two-tailed Students t-test). (D–E'') Progenitors in Relish loss of function exhibits lower level of Extracellular Hh (HhExtra) (E–E'') in comparison to those of control (D–D''). (E'' and D'') are zoomed in view of niche and the neighboring progenitor cells of (E' and D'), respectively. The yellow box denotes the area quantified in (F). (F) The intensity profile of HhExtra in progenitors (along the rectangle drawn from PSC to cortical zone housing differentiated cells in D' and E') reflects a stark decline in the level of HhExtra in Relish loss scenario compared to control. (G–I') Cellular filopodia emanating from the niche cells were stabilized by using untagged phalloidin. The filopodia in Relish loss of function niches were found to be smaller in length and fewer in number (H–H', I–I') as compared to control (G–G'). (J–K) Significant reduction in filopodial length (J, n=10, p-value=6.64 × 10−9, two-tailed Student’s t-test) and number (K, n=6, p-value=9.19 × 10−10, two-tailed Student’s t-test) were observed in Relish loss scenario compared to control. The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland and niches in A–B'', D-E'. In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Contains numerical data plotted in Figure 4A–B'', Figure 4D–E'', Figure 4G–I', Figure 4—figure supplement 1A–B', Figure 4—figure supplement 1E–F, Figure 4—figure supplement 1H–I, Figure 4—figure supplement 1J–K, Figure 4—figure supplement 2A–B'', Figure 4—figure supplement 2D–E'', Figure 4—figure supplement 2G–H'', Figure 4—figure supplement 3A–C, Figure 4—figure supplement 3E–G and Figure 4—figure supplement 3I–K'.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67158/elife-67158-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
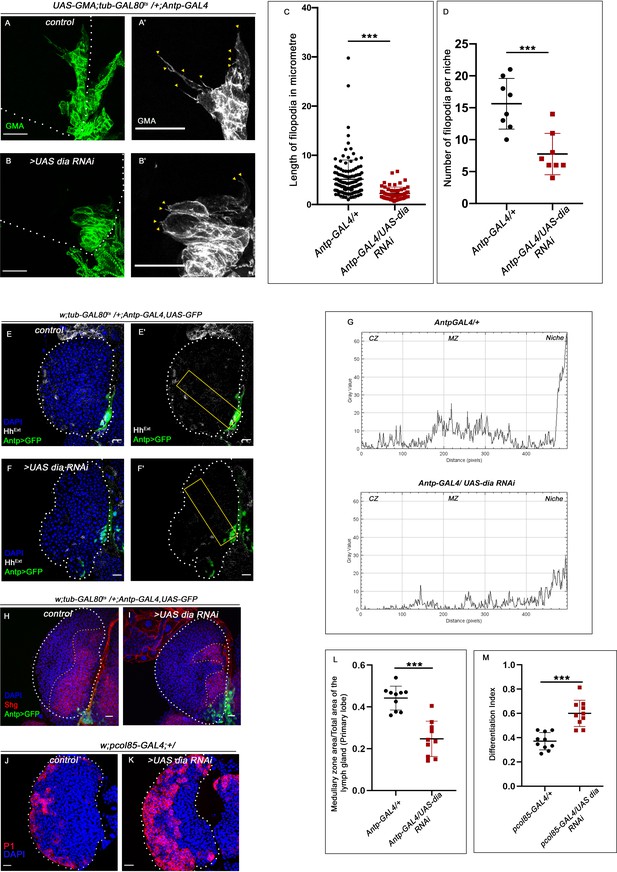
Loss of Diaphanous from the niche resulted in defect in filopodial formation and enhanced differentiation.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–B') The filopodia in dia loss of function niches were found to be smaller in length and fewer in number (B–B') as compared to control (A–A'). (C–D) Significant reduction in filopodial lengths (C, n=8, p-value=3.73 × 10−12, two-tailed Student’s t-test) and number (D, n=8, p-value=7.2 × 10−4, two-tailed Student’s t-test) was observed in dia loss scenario compared to control. (E–F') Progenitors in dia loss of function from niche exhibits lower level of extracellular Hh (HhExtra) (F–F') in comparison to those of control (E–E'). The yellow box denotes the area quantified in (G). (G) The intensity profile of HhExtra in progenitors (along the rectangle drawn from niche to Cortical zone housing differentiated cells in Figure 4E' and F') reflects a stark decline in the level of HhExtra in dia loss scenario compared to control. (H–I) Knocking down dia function resulted in loss of Shg-positive progenitors (I) compared to control (H). (L) Statistical analysis of the data in (H–I) (n = 10, p-value=1.8 × 10−5; two-tailed Student’s t-test). (J–K) Loss of dia, from the niche caused ectopic differentiation of progenitors (K) compared to control (J). (M) Differentiation index for dia loss niches compared to control (n=10, p-value=4.28 × 10−5; two-tailed Student’s t-test). The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases. Yellow dotted lines mark the progenitor zone in (H)–(I). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.

Loss of Relish from the niche resulted in upregulation of actin remodelers.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–B'') F-actin (visualized by Phalloidin, red) highly enriched in the plasma membrane of niche cells where Relish function is downregulated (B–B'') in comparison to that of control (A–A''). (C) Statistical analysis of fluorescence intensity showed significant increase in F-actin in Relish loss niches compared to control (n=10, p-value=5.6 × 10−9, two-tailed Student’s t-test). (D–E'') Expression of Singed, an actin-bundling protein, is significantly upregulated in Relish loss niches (E–E'') compared to control (D–D''). (F) Statistical analysis of fluorescence intensity showed significant increase in Singed expression in Relish loss niches compared to control (n=15, p-value=7.0 × 10−13, two-tailed Student’s t-test). (G–H'') Enabled an actin polymerase, which is normally absent from the niche cells of control (G–G'') is upregulated upon Relish downregulation (H–H''). (I) Statistical analysis of fluorescence intensity showed significant increase in Ena expression in Relish loss niches compared to control (n=15, p-value=8.1 × 10−20, two-tailed Student’s t-test). The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland and the niches in all cases. In all panels age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.

Downregulation of Ena in Rel loss genetic condition partially rescues the differentiation and HhExtra dispersal defects.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–C) Upon simultaneous knockdown of both Rel and Ena from the niche, the decrease in Shg-positive progenitors observed in Relish loss (B) was partially rescued (C) compared to control (A). (D) Statistical analysis of the data in (A–C) (n=10, p-value=6.8 × 10−5 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=3.4 × 10−2 for ena RNAiKK; Rel RNAi versus control; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (E–G) Differentiation defects observed in Rel loss (F) was partially rescued when both Rel and Ena was simultaneously downregulated from the niche (G) compared to the control (E). (H) Statistical analysis of the data in (E–G) (n=10, p-value=5.5 × 10−5 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=1.1 × 10−2 for ena RNAiKK; Rel RNAi versus control; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (I–K') Reduced extracellular Hh observed in the progenitors (HhExt) of Rel loss of function condition (J–J'), in comparison to those of control (I–I'), is partially rescued in simultaneous loss of both Rel and Ena from the niche (K–K'). The yellow box in I', J', and K' denotes the area quantified in L, M, and N, respectively. (L–N) The intensity profile of HhExtra in progenitors (along the rectangle drawn from niche to Cortical zone housing differentiated cells in I'–K') reflects a stark decline in the level of HhExtra in Rel loss scenario (M) compared to control (L) and a partial rescue when both Rel and Ena was downregulated simultaneously (N). The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases. Yellow dotted lines mark the progenitor zone in (A–C and E–G). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
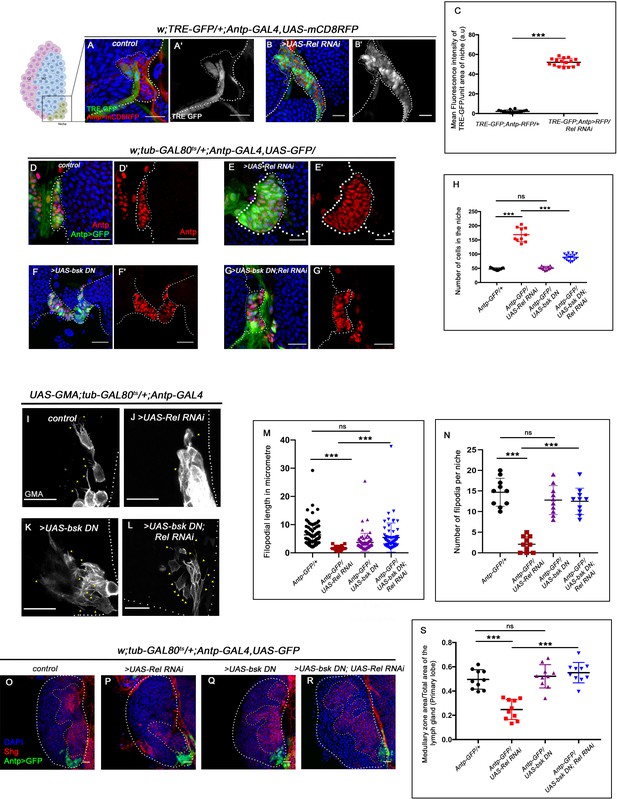
Loss of Relish from the niche activated JNK causing niche hyperplasia.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–B') Upregulation of JNK signaling visualized by its reporter TRE-GFP (green) in Relish knockdown (B–B') compared with WT niche (A–A'). (C) Statistical analysis of fluorescence intensity (A–B') revealed a significant increase in TRE-GFP levels compared to control (n=15, p-value=4.2 × 10−19, two-tailed Student’s t-test). (D–G') Upon niche-specific simultaneous knockdown of Rel and JNK, the niche hyperplasia observed upon loss of Relish (E–E') is rescued (G–G') and is comparable to control (D–D') whereas loss of bsk from the niche does not alter niche cell number (F–F'). (H) Statistical analysis of the data in (D–G') (n=10, p-value=5.6 × 10−8 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=8.0 × 10−7 for bsk DN; Rel RNAi versus Rel RNAi, p-value=0.10 control versus for bsk DN; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (I–N) Cellular filopodia from the niche cells in Rel loss of function is found to be smaller in length and fewer in numbers (J and M–N). Simultaneous loss of both JNK using bsk DN and Relish (L and M–N) rescued the stunted, scanty filopodia to control state (I and M–N), whereas loss of JNK did not affect filopodia formation (K and M–N). (M–N) Statistical analysis of the data in (I–L) (Filopodia number: n=10, p=6.96 × 10−8 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=8.11 × 10−7 for bsk DN; Rel RNAi versus Rel RNAi, p-value=0.153 for bsk DN versus control. Filopodia length: n=6, p-value=2.78 × 10−16 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=1.84 × 10−6 for bsk DN; Rel RNAi versus Rel RNAi, p-value=0.22 for bsk DN vs control; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (O–R) Knocking down JNK function from the niche did not have any effect on progenitors (visualized by Shg) (Q). Downregulating bsk function in Rel loss genetic background was able to restore the reduction in prohemocyte pool (R) observed in Relish loss (P) scenario in comparison to control (O). (S) Statistical analysis of the data in (O–R) (n=10, p-value=2.26 × 10−6 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=1.94 × 10−7 for bsk DN; Rel RNAi versus Rel RNAi, p-value=0.521 for control versus bsk DN; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test) The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland in all cases and niches in (A–G'). Yellow dotted lines mark the progenitor zone in (O–R). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Contains numerical data plotted in Figure 5A–B', Figure 5D–G', Figure 5I–L, Figure 5O–R, Figure 5—figure supplement 1A–B', Figure 5—figure supplement 1D–E', Figure 5—figure supplement 1G–H'', Figure 5—figure supplement 1J–M, Figure 5—figure supplement 2A–D, Figure 5—figure supplement 2F–H', Figure 5—figure supplement 3E–H, Figure 5—figure supplement 3J–M and Figure 5—figure supplement 3O–R.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67158/elife-67158-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx.xlsx
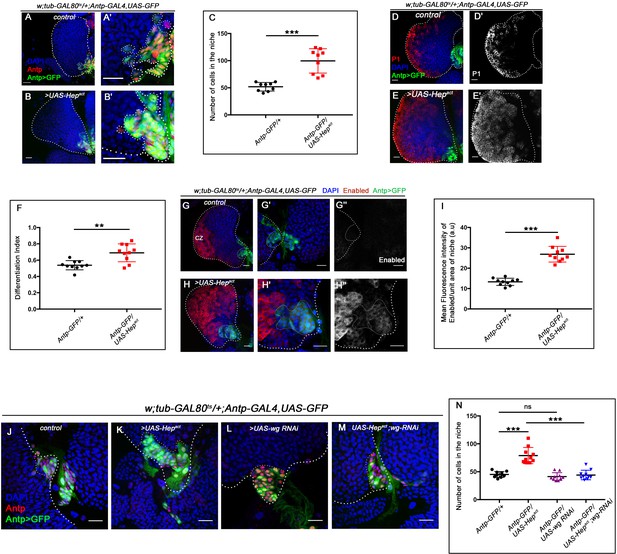
Ectopic activation of JNK signaling in the niche affects niche cell proliferation and progenitor maintenance.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–B') An increase in niche cell numbers observed upon upregulating JNK signaling using Hepact in the niche (B–B') compared to control (A–A'). (C) Statistical analysis of the data in (A–B') (n=10; p-value=2.2 × 10−4 for control versus Hepact, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (D–E') A significant increase in differentiation observed upon JNK overexpression using Hepact in the niche (E–E') compared to control (D–D'). (F) Statistical analysis of the data in (D–E') (n=10, p-value=1.7 × 10−3 for control versus Hepact, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test.) (G–H'') Robust increase in Enabled expression is observed when in Hepact (H–H'') compared to control (G–G''). (I) Statistical analysis of the data in (G–H'') (n=10; p-value=2.1 × 10−7 for control versus Hepact, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (J–M) Increase in niche cell numbers observed upon overexpressing Hep in the niche (K) is rescued to control levels (J) in a simultaneous loss of both Hep and wingless function from the niche (M). Loss of wingless using wg RNAi had milder effect on niche cell number compared to control (compare L and J). (N) Statistical analysis of the data in (J–M) (n=10; p-value=2.20 × 10−5 for control versus Hepact, p-value=1.08 × 10−5 for Hepact versus Hepact; wg RNAi, p-value=0.178 for control versus wg RNAi; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases and the niches in (A–B' and G'– H'' and J–M). In all panels age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (Blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
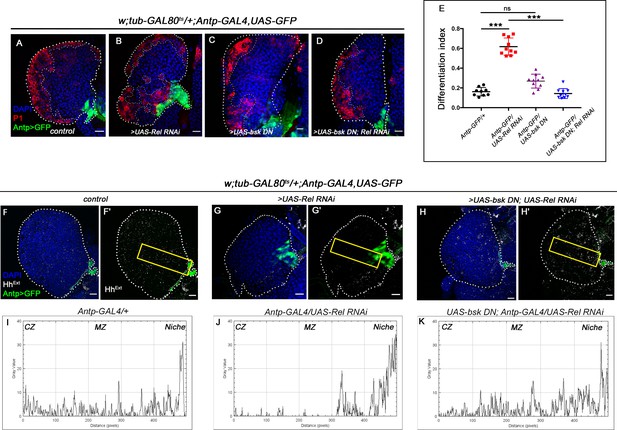
Downregulating JNK in Relish loss genetic background rescues progenitor loss and precocious differentiation.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–D) Differentiation defect observed in Relish loss (B) was reverted to control (A) in a simultaneous knockdown of both Relish and JNK (D) from the niche. Loss of JNK alone from the niche had no significant effect on differentiation (C). (E) Statistical analysis of the data in (A–D) (n = 10, p-value=1.5 × 10−9 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=1.79 × 10−8 for bsk DN; Rel RNAi versus Rel RNAi, p-value=0.392 for bsk DN versus control; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (F–H') Reduced Extracellular Hh observed in the progenitors (HhExt) of Relish loss of function condition (G–G') in comparison to those of control (F–F'), is significantly rescued in simultaneous loss of both Rel and JNK from the niche (H–H'). The yellow box in (F', G', and H') denotes the area quantified in (I, J, and K) respectively. (I–K) The intensity profile of HhExtra in progenitors (along the rectangle drawn from niche to Cortical zone housing differentiated cells in F', G', and H') reflects a stark decline in the level of HhExtr in Rel loss scenario (J) compared to control (I) which is rescued upon simultaneous loss of both Rel and JNK from the niche (K). The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases. Yellow dotted line indicates the boundary between CZ and MZ in (A)–(D). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: SD. Data are mean ± (SD). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
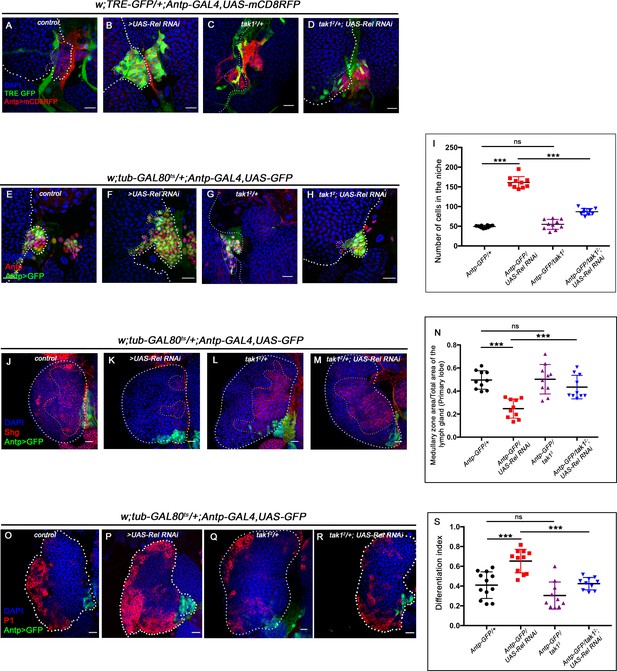
Relish inhibits JNK signaling by restricting tak1 activity in the niche during development.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–D) Up regulation of JNK signaling visualized by its reporter TRE-GFP (green) in Rel knockdown (B) compared with WT niche (A) is rescued in simultaneous loss of both the function of tak1 and Rel (D) whereas JNK activation was not observed in tak1 loss (C). (E–H) Increase in niche cell numbers observed upon loss of Rel from the niche (F) is rescued to control levels (E) in a simultaneous loss of both Rel and tak1 function from the niche (H) whereas no significant change in niche cell number was observed in tak1 loss (G). (I) Statistical analysis of the data in (E–H) (n=10, p-value=6.9×10−10 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value=1.9×10−9 for tak12; Rel RNAi versus Rel RNAi, p-value=0.201 for control versus tak12; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (J–M) Loss of tak1 function from the niche did not have any effect on progenitors (Shg) (L). Downregulating tak1 function in Rel loss genetic background could restore the reduction in prohemocyte pool (M) observed in Relish loss (K) scenario in comparison to control (J). (N) Statistical analysis of the data in (J–M) (n = 10, p-value=2.26×10−6 for control versus Rel RNAi, p-value = 3.1×10−4 for tak12; Rel RNAi versus Rel RNAi, p-value=0.891 for control versus tak12; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (O–R) Differentiation defects observed in Rel loss (P) was comparable to control (O) in simultaneous loss of both Rel and tak1 function (R) from the niche. No significant change in differentiation was observed in tak1 loss from the niche (Q). (S) Statistical analysis of the data in (O–R) (n=10; p-value=1.5×10−4 for control versus Relish RNAi, p-value = 4.7×10−5 for; Rel RNAi versus tak12; Rel RNAi, p-value=0.115 for control versus tak12; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases and niches in (A–D and E–H). Yellow dotted lines marks the progenitor zone in (J–M). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
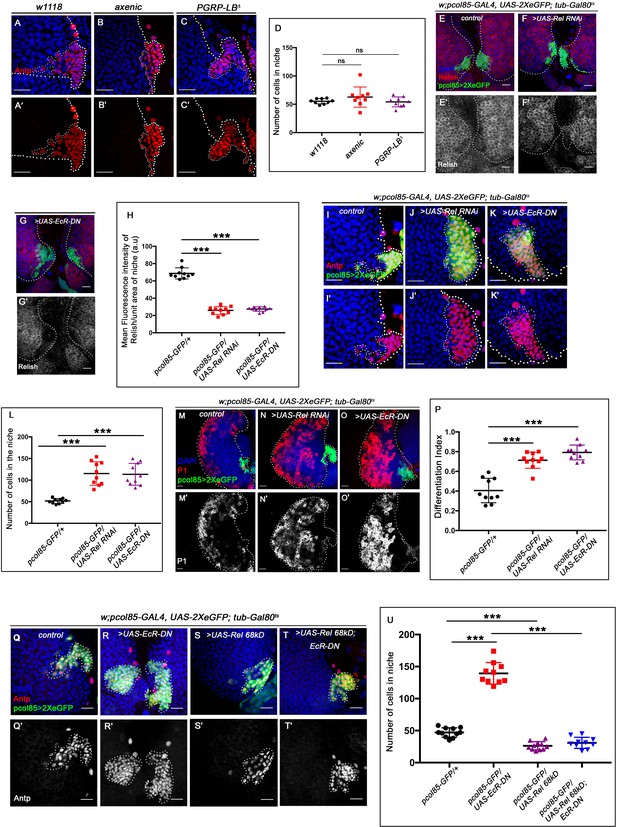
Ecdysone regulates Relish expression and functionality in the niche.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–C') Niche number remains comparable to control (A–A') both in axenic larval lymph gland (B–B') and in PGRP-LB mutant where there is upregulation in systemic peptidoglycan levels (C–C'). (D) Statistical analysis of the data in (A–C') (n=9; p-value = 0.262 for control versus germ free and 0.392 for control versus PGRP-LB mutant; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (E–G') Compared to that of control (E–E') Rel expression is significantly downregulated both in EcR loss (G–G') as well as in Rel loss from the niche (F–F'). (H) Statistical analysis of the data in (E–G') (n=10, p-value=7.81 × 10−12 for control versus Rel RNAi loss and p-value = 3.76 × 10−10 for control versus EcR-DN; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (I–K') Similar to Rel loss from the niche (J–J'), EcR loss also results in increase in niche cell numbers (K–K') compared to that of control (I–I'). (L) Statistical analysis of the data in I-K' (n=10, p-value=6.6 × 10−5 for control versus EcR-DN and p-value = 3.1x10−5 for control versus Rel RNAi; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (M–O') Compared to control (M–M'), both loss of Rel (N–N') and EcR (O–O') from the niche results in increase in differentiation. (P) Statistical analysis of the data in (M–O') (n=10, p-value=4.3 × 10−5 for control versus Rel RNAi and p-value=2.2 × 10−6 for control versus EcR-DN; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (Q–T') Increase in niche cell numbers observed upon EcR loss from the niche (R–R') is rescued to control levels (Q–Q') when Relish was overexpressed in an EcR loss genetic background (T–T'). Overexpression of Relish in the niche reduced the cell number compared to control (compare S–S' and Q–Q'). (U) Statistical analysis of the data in (Q–T') (n=10; p-value=1.7×10−9 for control versus EcR-DN, p-value=7.8 × 10−11 for Ecr-DN versus UAS-Rel 68kD; EcR-DN, p-value=3.63 × 10−6 for control versus UAS-Rel 68kD; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland and niches in all the cases. In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Contains numerical data plotted in Figure 6A–C', Figure 6E–G', Figure 6I–K', and Figure 6M–O', Figure 6Q–T', Figure 6—figure supplement 2F–G'', Figure 6—figure supplement 2I–L.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67158/elife-67158-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
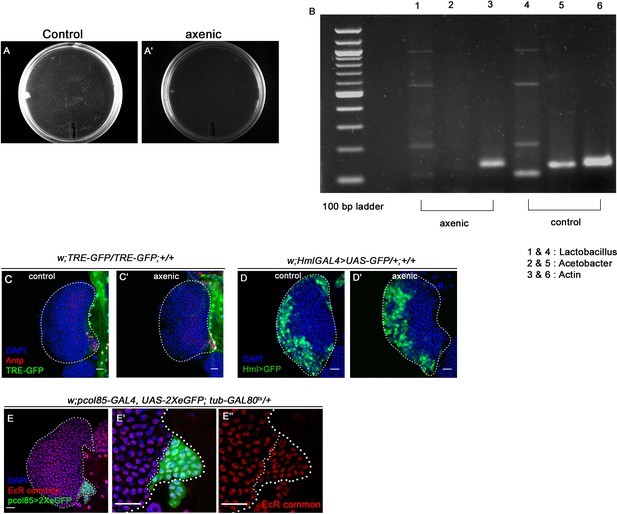
Ecdysone signaling is active in the hematopoietic niche.
Genotypes of the larvae are mentioned in respective panels. Scale bar: 20 µm (A–A') Larval homogenates were spread on LB Agar plates to check the presence of commensal gut microbiota. In control scenario (A) bacterial colonies were visible post incubation whereas in axenic condition no growth was observed on the plates (A'). (B) The efficacy of removal of gut microflora was further checked by performing PCR analysis on DNA isolated from larval guts using 16S rDNA primers. Drosophila actin was used as control. Significant reduction in the amount of both Lactobacillus (compare lane 1 (axenic) with 4 (control)) and Acetobacter (compare lane 2 [axenic] with 5 [control]) species was observed in axenic condition compared to control scenario (compare lane 3 [axenic] and 6 [control]). (C–C') TRE-GFP expression in the hematopoietic niche (visualized by Antp, red) in axenic condition (C') is comparable to that of control (C). (D–D') Differentiation status (visualized by Hml>GFP, pan plasmatocyte marker) in axenic condition (D’) is comparable to control (D). (E–E'') Nuclear expression of Ecdysone receptor (red, EcR common) in the hematopoietic niche (green). The white dotted line marks whole of the lymph gland and the niches in (E–E''). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue).
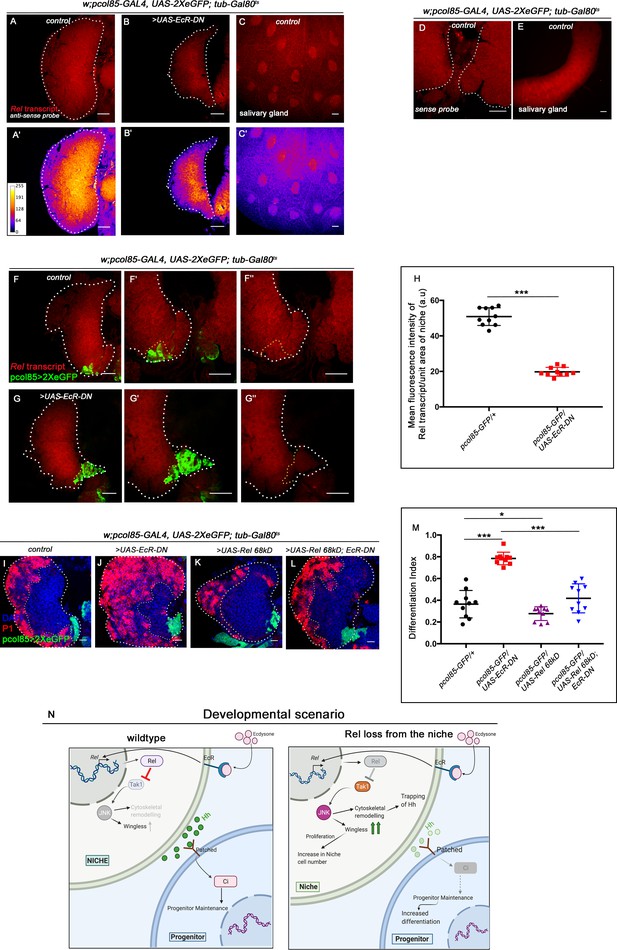
Relish expression is transcriptionally regulated by ecdysone signaling in the hematopoietic niche.
Genotypes of the larvae are mentioned in respective panels. Scale bar: 20 µm (A–C') Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis showing the expression of Rel transcript in the lymph gland of the control larvae (A–A'). Loss of EcR from the niche resulted in loss of Re-positive progenitors (B–B'). Rel transcripts were also detected in salivary gland of the control larvae (C–C'). (D–E) Sense probe (negative control) showing nonspecific background expression in the control lymph gland (D) and salivary gland (E). (F–G'') Whole-mount immunofluorescence (IF) and FISH on third-instar lymph gland. Compared to control (F–F''), drastic reduction of the Rel transcript was observed in the niche from where EcR levels were downregulated (G–G''). Please note the smaller size of the LG in G–G' reflects the peeling off of the cortical zone due to excessive differentiation around 96 hr AEH in EcR loss from the niche. The increased differentiation renders fragility to the LG, which is unable to withstand harsh in situ process. (H) Statistical analysis of the data in (F'–G'') (n=10, p-value=1.56 x 10−10 for control versus EcR-DN; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (I–L) Differentiation defects observed in EcR loss (J) was reverted to control (I) when Relish was overexpressed in EcR loss genetic background (L). Slight decrease in differentiation of progenitors were observed upon Relish overexpression in the niche (compare I and K). (M) Statistical analysis of the data in (I–L) (n=10; p=3.8 × 10−7 for control versus EcR-DN, p=3.3 × 10−6 for Ecr-DN versus UAS-Rel 68kD; EcR-DN, p=7.2 × 10−2 for control versus UAS-Rel 68kD; two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (N) Model depicting the developmental role of Relish in hematopoietic niche maintenance. Downregulation of Relish affects the proliferation and primary function of the niche by upregulated JNK signaling. Upregulated JNK disturbs niche homeostasis through wingless and cytoskeletal remodeling, thereby affecting progenitor maintenance. The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases. Yellow dotted line marks the niche in (F–G'') and the boundary between CZ and MZ in (I–L). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
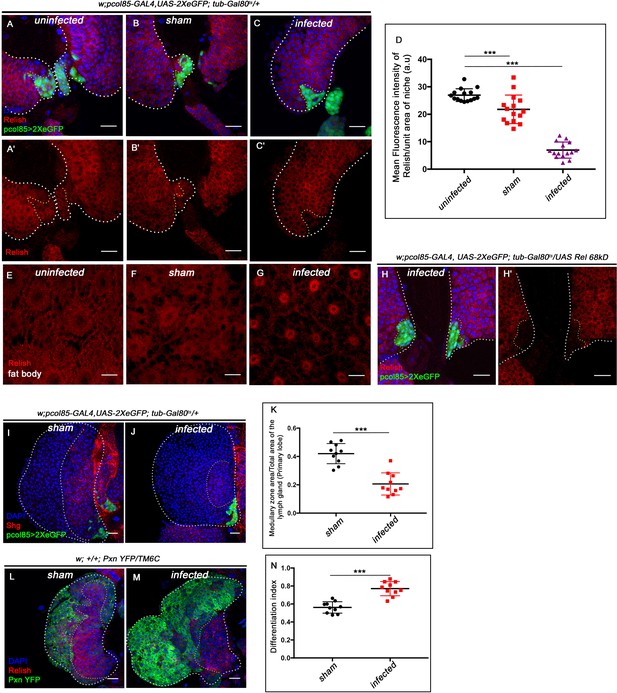
Niche-specific expression and function of Relish is susceptible to pathophysiological state of the organism.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–C') Compare to uninfected conditions (A–A') and sham (B–B'), significant reduction in Relish expression was observed in the hematopoietic niche 4 hr post-infection (C–C'). (D) Statistical analysis of the data in (A–C') (n=15; p=6.62×10−18 for unpricked versus infected, p=2.5×10−7 for sham versus infected, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (E–G) Nuclear expression of Relish was observed in infected (G) fat body cells 4 hr post in contrast to uninfected (E) and sham (F) larval fat body. (H–H') Overexpressing Relish N-terminus (UAS-Rel-68kD) could not rescue loss of Relish expression post-infection. (I–J) Compared to sham (I), significant reduction in Shg-positive progenitors (red) were observed in infected lymph glands (J). (K) Statistical analysis of the data in (I–J) (n=10; p-value=5.2 × 10−6 for sham versus infected, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (L–M) Drastic increase in differentiation (visualized by Pxn-YFP, green) was observed in infected lymph glands (M) compared to sham (L). (N) Statistical analysis of the data in (L-M) (n=10; p-value = 4.65×10−6 for sham versus infected, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland in all cases. Yellow dotted line marks the niche in (A– C' and H–H') and the boundary between CZ and MZ in (L–M). In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (Blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Contains numerical data plotted in Figure 7A–C', Figure 7I–J, Figure 7L–M, Figure 7—figure supplement 1C–D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/67158/elife-67158-fig7-data1-v2.xlsx
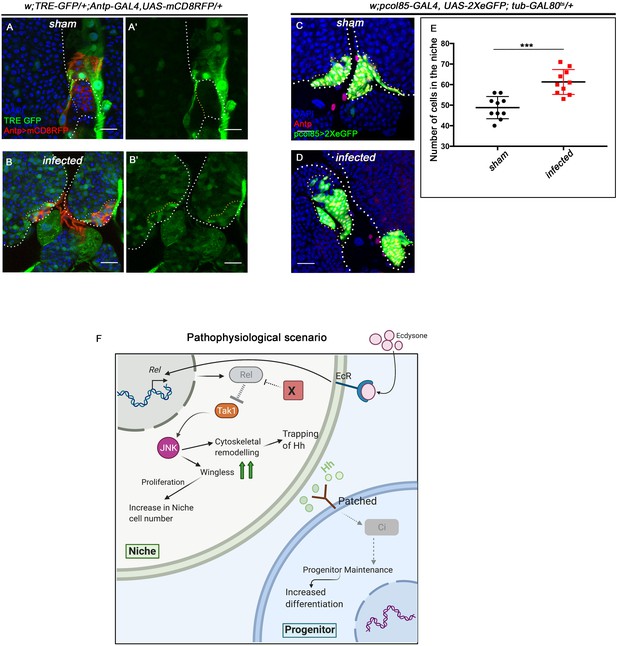
Upregulation in JNK signaling and increase in cell proliferation was observed in the niche during infection.
The genotypes are mentioned in relevant panels. Scale bar: 20 μm. (A–B') An overall up regulation in JNK signaling (visualized by its reporter TRE-GFP [green] was observed in infected lymph glands (B–B') compared to sham (A–A')). (C–D) Significant increase in niche proliferation was observed in infected lymph gland niches (D) compared to sham infected (C). (E) Statistical analysis of the data in (C–D) (n=10; p-value=1.1×10−4 for sham versus infected, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test). (F) Model based on current results depicting how upon bacterial challenge Relish expression is differentially modulated in the niche to bolster the cellular immune response by eliciting precocious differentiation of the lymph gland hemocytes. The white dotted line mark whole of the lymph gland and yellow doted lines marks the niches in all cases. In all panels, age of the larvae is 96 hr AEH. The nuclei are marked with DAPI (blue). Individual dots represent biological replicates. Error bar: standard deviation (S.D). Data are mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
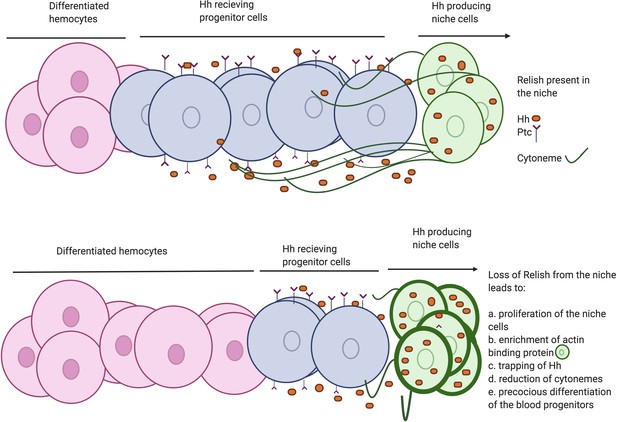
Developmental requirement of Relish in the niche for progenitor maintenance.
Scheme describing how loss of Relish from the niche alters cytoskeletal elements of the cells. The change in cytoskeletal architecture affects cytoneme-like filopodial formation thereby trapping Hedgehog within the niche. The failure of Hh delivery in turn interferes with progenitor maintenances and pushes them toward differentiation.

A-C: No significant change in Relish expression in the niche was observed at 72 hours (AEH) (B-B') compared to 60 hours (AEH) ( A-A').
Statistical analysis of the data from A-B' (n=29 P-value =.297 ; two tailed Students t-test).
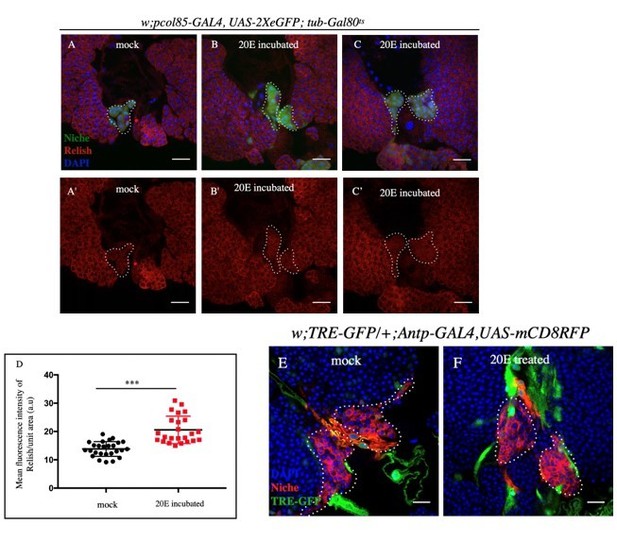
A-C': Post 20E incubation, slight increase in Relish expression was observed compared (B-C') to mock incubated samples (A-A').
D. Statistical analysis of the data from A-B' (n=24 P-value=6.19 x10-7; two tailed Students t-test). E-F. JNK expression remained unaltered in 20E incubated (F) and mock (E) incubated samples.
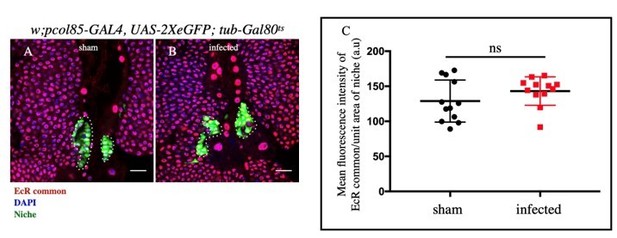
A-B: No significant change in EcR expression in the niche was observed upon infection and sham.
C. Statistical analysis of the data from A-B (n= 12 P-value=.364).
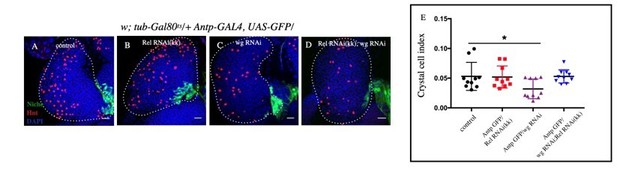
A-D.
Slight decrease in Crystal cell index was observed in wg-RNAi (C) compared to control (C) whereas no significant change was observed in Rel RNAi(KK) (B) and Rel RNAi(KK), wg RNAi (D). E. Statistical analysis of the data from A-D (n=11 P–value=3.4x10-2 for control versus wg-RNAi).
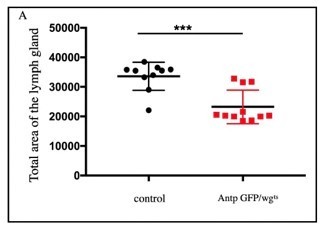
Significant decrease in LG area was observed in wgts compared to control (n=10, P-value = 2.
3x10-4 two tailed students t-test).
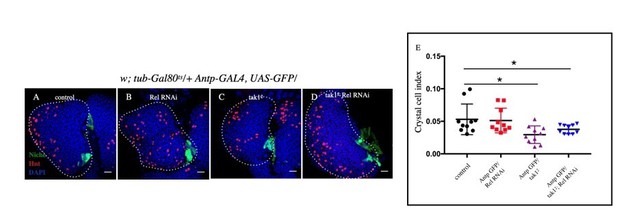
Slight decrease in Crystal cell index was observed in tak12 (C) and tak12; Rel RNAi (D) compared to control (A) whereas no significant change was observed in Rel RNAi (B).
E. Statistical analysis of the data from A-D (n=10 P-value=1.5 x10-2 for control versus tak12 and P-value=7.4x10-2 control versus tak12; Rel RNAi, two tailed students t-test).

Slight decrease in Crystal cell index was observed in bskDN (C) and bskDN; Rel RNAi (D) compared to control (A) whereas no significant change was observed in Rel RNAi (B).
E. Statistical analysis of the data from A-D (n=10 P-value=8.5 x10-2 for control versus bskDN and P-value=6.5x10-2 for control versus bskDN; Rel RNAi, two tailed students t-test).

A-D.
Compared to control (A) ectopic differentiation and peeling off of lymph glands was observed in infected (B) as well as Rel loss samples (C).

A-B: Rel expression in the niche was observed in control as well as in UAS-Rel68KD tissues.
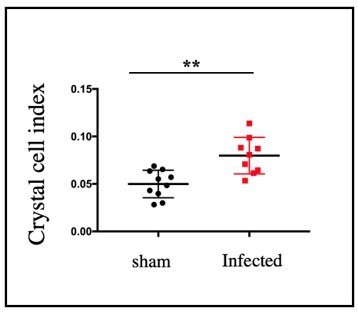
Significant increase in crystal cell index was observed in infected samples compared to sham (n=9, P-value =1.
8x10-3, two tailed students t-test).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | Antp | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn0260642 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | Hml | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn 0029167 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | Collier/kn | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn0001319 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | wg | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB: FBgn0284084 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | hep | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn0010303 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | EcR | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn0000546 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | PGRP-LB | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn0037906 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | Tak1 | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn0026323 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | bsk | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn 0000229 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | Ena | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FBgn0000578 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | Hh | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FBgn0004644 | |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | Dia | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FBgn0011202 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Antp-Gal4 | Emerald and Cohen, 2004 | FLYB:FBal0155891 | FlyBase symbol: GAL4Antp-21 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | P(col5-cDNA)/CyO-TM6B, Tb | Krzemień et al., 2007 | FLYB:FBti0077825 | FlyBase symbol: P{GAL4}col85 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Hml-GAL4.Δ | Sinenko and Mathey-Prevot, 2004 | FLYB:FBtp0040877 | FlyBase symbol:P{Hml-GAL4.Δ} |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Rel RNAiKK | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | VDRC:v108469; FLYB:FBti0116709; RRID:FlyBase_FBst0477227 | FlyBase symbol: P{KK100935}VIE-260B |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | w[1118] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:3605; FLYB:FBal0018186;RRID:BDSC_3605 | FlyBase symbol: w1118 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Rel RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:33661; FLYB:FBti0140134;RRID:BDSC33661 | FlyBase symbol: P{TRiP.HMS00070}attP |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-wg RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:33902; FLYB:FBal0263076; RRID:BDSC_33902 | FlyBase symbol: P{TRiP.HMS00844}attP2 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-dia RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:35479; FLYB:FBtp0068562; RRID:BDSC_35479 | FlyBase symbol: P{TRiP.GL00408} |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-hep.Act | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:9305; FLYB:FBti0074410; RRID:BDSC_9305 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-Hep.Act}1 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-FUCCI | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:55121; RRID:BDSC_55121 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-GFP.E2f1.1–230}32; P{UAS-mRFP1.NLS.CycB.1–266}19 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | TRE-GFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:59010; FLYB:FBti0147634; RRID:BDSC_59010 | FlyBase symbol: P{TRE-EGFP}attP16 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Pxn-YFP | Kyoto Stock Center | kyoto:115452; FLYB: FBti0143571; RRID:FlyBase_FBst0325439 | FlyBase symbol: PBac{802 .P.SVS-2}PxnCPTI003897 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | hhF4f-GFP | Tokusumi et al., 2012 | FBtp0070210 | FlyBase symbol:P{hhF4f-GFP} |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-GMA | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:31774; FLYB:FBti0131130; RRID:BDSC_31774 | FlyBase symbol:P{UAS-GMA}1 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Rel 68kD | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:55778; FLYB:FBti0160486; RRID:BDSC_55778 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-FLAG-Rel.68}i21-B |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-Rel 68kD | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:55777; FLYB:FBti0160484 RRID:BDSC_55777 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-FLAG-Rel.68} |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-EcR.B1Δ | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:6872; FLYB:FBti0026963; RRID:BDSC_6872 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-EcR.B1-ΔC655.W650A}TP1-9 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | PGRP-LB[Delta] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:55715; FLYB:FBti0180381; RRID:BDSC_55715 | FlyBase symbol: TI{TI}PGRP-LBΔ |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | wgl-12 cn1 bw1/CyO | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:7000; FLYB:FBal0018504; RRID:BDSC_7000 | FlyBase symbol: wgl-12 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Tak1(2) | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:26272; FLYB:FBal0131420; RRID:BDSC_26272 | FlyBase symbol: dTak12 |
| Gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | RelE20 | Flybase:FB2020_01 | FLYB:FBgn0014018 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-bsk[DN] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:6409; FLYB:FBti0021048; RRID:BDSC_6409 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-bsk.DN}2 |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-ena RNAiKK | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | VDRC: v106484 FBst0478308; RRID:v106484 | FlyBase symbol: P{KK107752}VIE-260B |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS-mCD8: RFP | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:27400; FLYB:FBti0115747; RRID:BDSC_27400 | FlyBase symbol: P{UAS-mCD8.mRFP.LG}28a |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | tubGAL80[ts20] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDSC:7109; FLYB:FBti0027796; RRID:BDSC_7109 | FlyBase symbol: P{tubP-GAL80ts}20 |
| Antibody | Anti-P1 (Mouse monoclonal) | Kurucz et al., 2007 | Cat# NimC1, RRID:AB_2568423 | IF(1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-c Rel (Mouse monoclonal) | Stöven et al., 2000 | Cat#21F3, RRID:AB_1552772 | IF (1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-Ci155 (Rat polyclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat# 2A1, RRID:AB_2109711 | IF(1:2) |
| Antibody | Anti-Wg (Mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat#4D4 RRID:AB_528512 | IF(1:3) |
| Antibody | Anti-Singed (Mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat# sn 7C RRID:AB_528239 | IF(1:20) |
| Antibody | Anti-Enabled (Mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat#5G2 RRID:AB_528220 | IF(1:30) |
| Antibody | Anti-PH3(Rabbit monoclonal) | Cell signaling Technology | Cat# 3642S RRID:AB_10694226 | IF(1:150) |
| Antibody | Anti-Hh (Rabbit monoclonal) | Forbes et al., 1993 | IF(1:500) | |
| Antibody | Anti-Hnt (Mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat#1G9 RRID:AB_528278 | IF(1:5) |
| Antibody | Anti-EcR common (Mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat#DDA2.7 RRID:AB_10683834 | IF(1:20) |
| Antibody | Anti-Ance (rabbit monoclonal) | Hurst et al., 2003 | IF(1:500) | |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell signaling Technology | Cat#2555 | IF(1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-shg (rat monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat#DCAD2 RRID:AB_528120 | IF(1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-β-PS (mouse monoclonal) | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat#CF.6G11 RRID:AB_528310 | IF(1:3) |
| Antibody | Anti-DIG-POD (sheep polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#11207733910 | IF(1:1000) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phalloidin from Amanita phalloides | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#P2141 | IF(1:500) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Rhodamine Phalloidin | Thermo Scientific | Cat# R415 RRID:AB_2572408 | IF(1:500) |
| Sequence-based reagent | Relish cDNA clone | DGRC | Clone id: GH01881 FLYB: FBcl0110737 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Actin_F | Elgart et al., 2016 | PCR primers | GGAAACCACGCAAATTCTCAGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Actin_R | Elgart et al., 2016 | PCR primers | CGACAACCAGAGCAGCAACTT |
| sequence-based reagent | Aceto_F | Elgart et al., 2016 | PCR primers | TAGTGGCGGACGGGTGAGTA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Aceto_R | Elgart et al., 2016 | PCR primers | AATCAAACGCAGGCTCCTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Lacto_F | Elgart et al., 2016 | PCR primers | AGGTAACGGCTCACCATGGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Lacto_R | Elgart et al., 2016 | PCR primers | ATTCCCTACTGCTGCCTCCC |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | Fiji | RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| Software, algorithm | Photoshop CC | Adobe | RRID:SCR_014199 | |
| Software, algorithm | Imaris | Bitplane | RRID:SCR_007370 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Click-iTEdU plus (DNA replication kit) | Invitrogen | Cat# C10639 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Alexa Fluor 594 Tyramide Reagent | Thermo Fischer | Cat# B40957 |