Recessive pathogenic variants in MCAT cause combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency
Figures
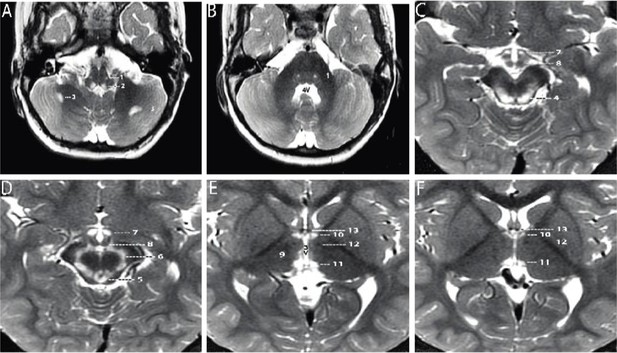
Axial T2-weighted MRI sections of the brain displayed from inferior to superior.
(A–B) Sections through the brainstem and cerebellum. Sections through the medulla (A) and mid pons (B) demonstrate well-defined, symmetrical signal increase in the central tegmental tracts (1) and the nuclei prepositus hypoglossi (2) with very limited, slightly asymmetrical involvement of the white matter of both cerebellar hemispheres (3). 4V=fourth ventricle. (C–D) Sections through the midbrain display intense symmetrical increase in signal in the tectum (4), peri-aqueductal gray matter (5), substantia nigra (6), and medial hypothalamus (7). The mammillary bodies (8) are spared. (E–F) Sections through the hypothalamus (E) and thalamus (F) display intense symmetrical increase in signal in the medial thalamus (9), anteromedial thalamus (10), and habenular nuclei (11), with sparing of the low signal mammillothalamic tracts (12) and anterior columns of the fornix (13). No abnormal signal was identified in any other portions of the brain. 3V=third ventricle.
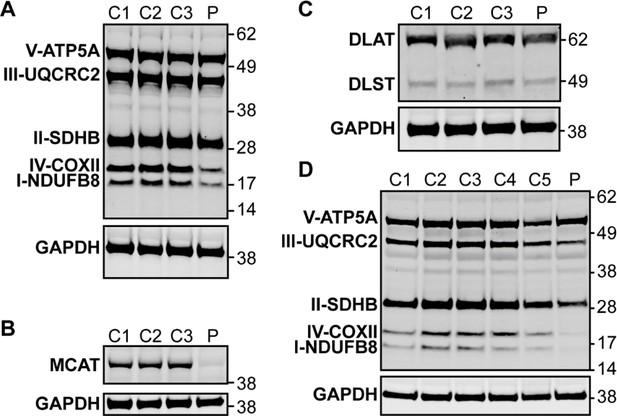
Western blot analysis in patient lymphoblasts (A–C) and fibroblasts (D).
(A) Western blot analysis to assess the expression level of one subunit of each of the five different oxidative phosphorylation complexes in the patient lymphoblast sample (P) compared to three control lymphoblast lines from healthy individuals (C1–3). Protein content of NDUFB8 and COXII, which are subunits of complexes I and IV, respectively, are decreased in the patient compared to healthy controls. (B) Western blot analysis to assess malonyl-CoA-acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT) levels reveals decreased expression of MCAT in patient lymphoblasts (P) compared to three controls (C1–3). (C) Western blot analysis to assess lipoylation with an anti-lipoic acid antibody in patient lymphoblasts (P) compared to controls (C1–3) reveals normal lipoylation of the PDH and OGDH E2 components (DLAT and DLST, respectively) in the patient sample. (D) Western blot analysis to assess the expression level of one subunit of each of the five different oxidative phosphorylation complexes in the patient fibroblast sample (P) compared to five fibroblast controls (C1–5). Protein content of NDUFB8, COXII, and SDHB, which are subunits of complexes I, IV, and II, respectively, are decreased in the patient compared to healthy controls.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Uncropped immunoblots for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig2-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Unlabeled immunoblots for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig2-data2-v1.zip
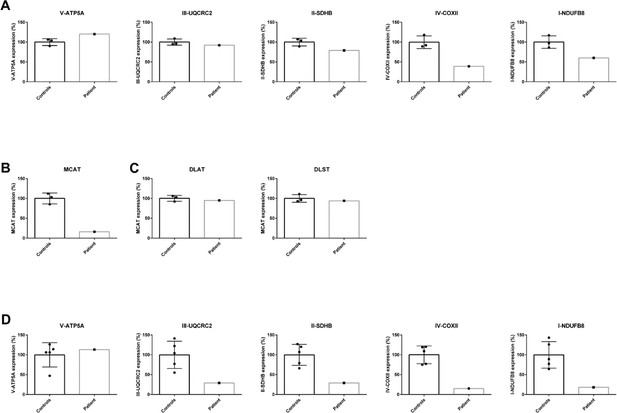
Quantification of western blot analysis in patient lymphoblasts (A–C) and fibroblasts (D).
The intensity of the protein of interest was normalized to GAPDH. The average of the controls was set to 100% and the individual values are expressed as a percentage.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Excel spreadsheet containing quantitative data for Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
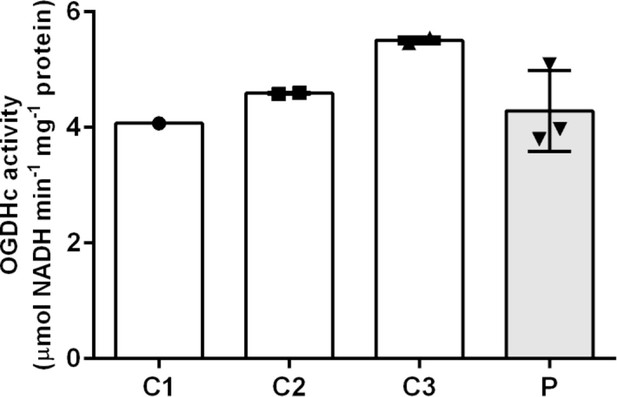
Measurement of 2-oxoglutaric acid dehydrogenase complex (OGDHc) activity.
Oxidative decarboxylation of 2-oxoglutaric acid by OGDHc is measured in cell lysates from lymphoblasts from the patient (P) and three healthy controls (C1–3). Control 1 (C1) was a single observation from one cell pellet, controls 2 and 3 (C2 and C3) were duplicate measurements from one cell pellet. For the patient (P), we analyzed two cell pellets, one measured in duplicate and the other measured as a single data point. Standard deviation is shown with the error bars. No deficit in OGDHc activity was identified in the patient sample (P).
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Excel spreadsheet containing quantitative data for Figure 2—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
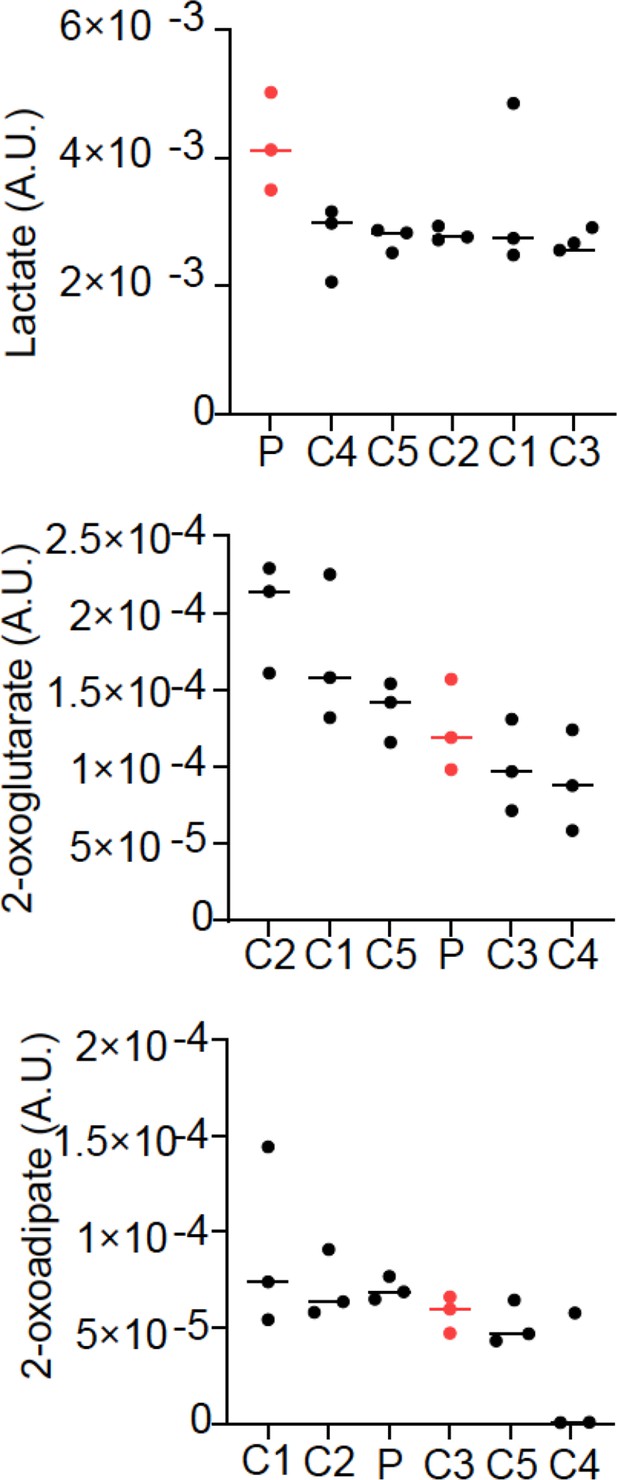
Relative abundance of lactate, 2-oxoglutarate, and 2-oxoadipate from quantitative metabolomics.
Three cell pellets were collected for the patient fibroblast cell line (P) and each of five control fibroblast lines (C1–5). Lactate was elevated in the patient line, while 2-oxoglutarate and 2-oxoadipate were normal.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Excel spreadsheet containing quantitative data for Figure 2—figure supplement 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig2-figsupp3-data1-v1.zip
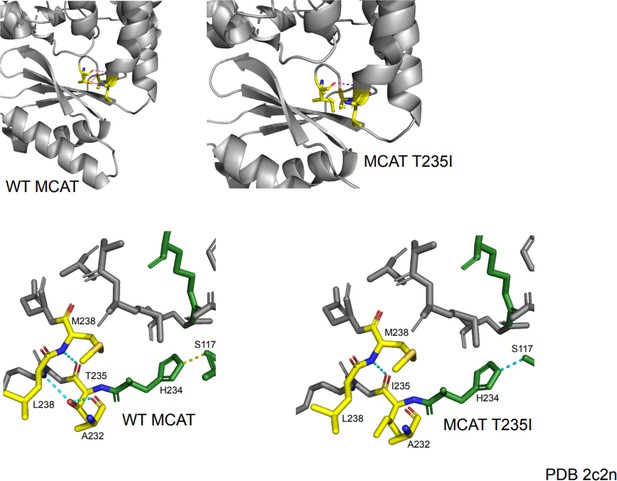
Protein modeling of malonyl-CoA-acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT) p.T271I mutation.
The T235 residue in the crystal structure corresponds to the residue at the site of the T271I mutation. This mutation occurs one residue away from the active site histidine (H234) and is located in a semi-structured region between the end of an alpha helix and a linker region between the alpha helix and a series of beta sheets. In the wild-type protein, the T235 residue makes several contacts with surrounding residues. The carboxy group of T235 makes contact with the amide nitrogen of M238. The hydroxyl group of T235 forms a hydrogen bond with the carboxyl group of A232 and the amide nitrogen of L238. The mutation of threonine to isoleucine results in a loss of polar contacts with A232 and L238 due to a loss of the hydroxyl moiety. This likely reduces the structure of the end of the alpha helix and may generate additional flexibility of the linker region. Although the mutant protein shows maintenance of a contact between the active site histidine and another active site residue (S117), the proximity of this mutation to the active site may suggest a negative impact on catalytic efficiency.
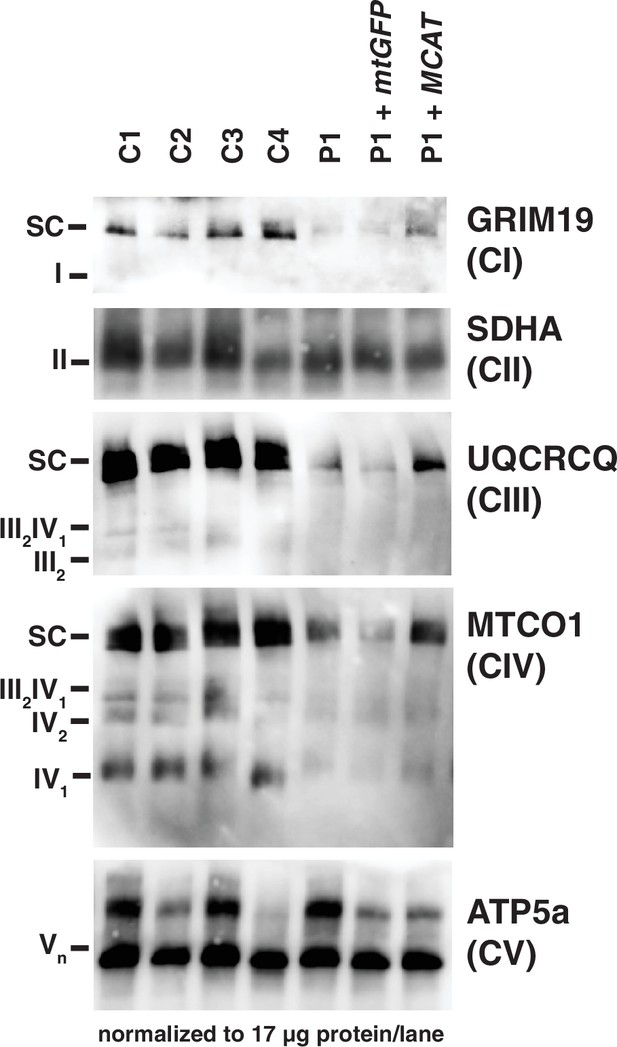
Mitochondrial respiratory supercomplexes visualized by blue-native PAGE.
Mitochondrial lysates generated from four control fibroblast lines (C1–4), the patient fibroblast line (P), the patient line expressing the control plasmid mtGFP (P+mtGFP), and the patient line with re-expression of wild-type malonyl-CoA-acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT) (P+MCAT). The lysates are separated by blue-native PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Expression of GRIM19, UQCRCQ, and MTCO1 delineating supercomplexes I, III, and IV respectively are decreased in the patient cells (P) compared to four controls, and improved with re-expression of wild-type MCAT (P+MCAT). For each immunoblot, at least two technical replicates were completed and one representative blot is shown. SC = supercomplex.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Uncropped immunoblots for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig3-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Unlabeled immunoblots for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig3-data2-v1.zip
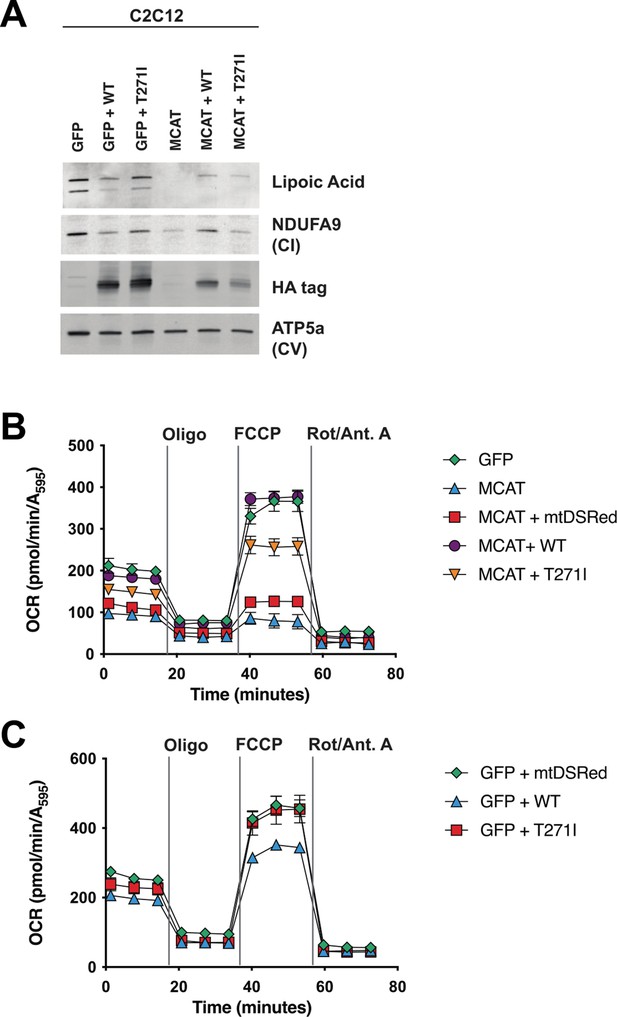
Rescue of hypomorphic malonyl-CoA-acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT) mutant C2C12 with wild-type (WT) and p.T271I mutant MCAT constructs.
(A) Mitochondrial lysates generated from MCAT hypomorphic CRISPR mutant C2C12 mouse skeletal myoblasts (MCAT) and isogenic controls (GFP), stably infected with either WT human MCAT or p.T271I mutant human MCAT (T271I) transgenes. Lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Protein lipoylation (lipoic acid) is undetectable in MCAT mutant C2C12 and rescued by both WT and p.T271I mutant MCAT, while complex I (NDUFA9, CI) is only rescued by expression of WT human MCAT. For each immunoblot, at least two technical replicates were completed and one representative blot is shown. (B–C) Cells from each of the indicated genotypes were seeded in eight wells of a 96-well seahorse plate and allowed to adhere overnight, then equilibrated and treated with the indicated drugs following standard mitochondrial stress test protocols from the manufacturer to determine oxygen consumption rate (OCR). Error bars are SEM. Oxygen consumption is fully rescued by WT human MCAT but only partially rescued by expression of the p.T271I patient mutation.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Uncropped immunoblots for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig4-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Unlabeled immunoblots for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig4-data2-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Excel spreadsheet containing quantitative data for Figure 4 Panel B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig4-data3-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 4
Excel spreadsheet containing quantitative data for Figure 4 Panel C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68047/elife-68047-fig4-data4-v1.xlsx
Tables
Clinical biochemical testing of respiratory chain enzyme activities in the proband’s fibroblasts.
| Proband | Reference range | |
|---|---|---|
| Complex I | 119 mU/U CS | 163–599 mU/U CS |
| Complex II | 286 mU/U CS | 335–888 mU/U CS |
| Complex III | 632 mU/U CS | 570–1383 mU/U CS |
| Complex IV | 103 mU/U CS | 288–954 mU/U CS |
| Complex V | 630 mU/U CS | 193–819 mU/U CS |
| CS | 412 mU/mg | 151–449 mU/mg |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (Mus musculus) | C2C12 | ATCC | #CRL-1772, RRID:CVCL_0188 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293T | ATCC | #CRL-11268, RRID:CVCL_1926 | |
| Antibody | Anti-human OXPHOS cocktail (mouse monoclonal) | MitoSciences | ab110411 | WB: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-GAPDH (rabbit monoclonal) | Abnova | H00002597-K | WB: (1:2500) |
| Antibody | Anti-MCAT (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | HPA035471, RRID: AB_10670590 | WB: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-MCAT (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc-390858, RRID:AB_2827536 | WB: (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-DLAT (rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | ab172617, RRID:AB_2827534 | WB: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-DLST (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | 5556, RRID:AB_106951 | WB: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-GRIM19 (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab110240, RRID:AB_10863178 | WB: (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-SDHA (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab14715, RRID:AB_301433 | WB: (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-UQCRQ (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab110255 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-MTCO1 (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab14705, RRID:AB_2084810 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-ATP5A (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab14748, RRID:AB_301447 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Lipoic Acid (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab58724, RRID:AB_880635 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-NDUFA9 (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab14713, RRID:AB_301431 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-HA (rabbit polyclonal) | BioLegend | PRB-101C | WB (1:1000) |





