A qnr-plasmid allows aminoglycosides to induce SOS in Escherichia coli
Figures
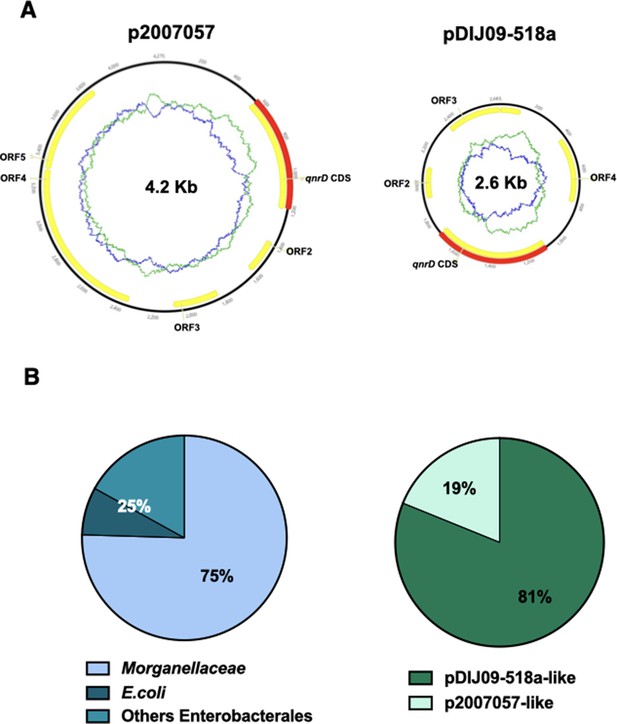
qnrD genes are carried by small plasmids.
(A) The two qnrD-plasmid archetypes: p2007057 and pDIJ09-518a. (B) Distribution of the qnrD-plasmids among the 53 qnrD fully sequenced plasmids available in GenBank.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
qnrD genes in small plasmids.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
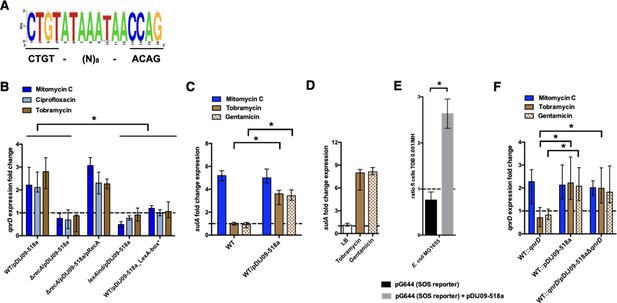
qnrD regulation is SOS-mediated and aminoglycosides induce the SOS in E. coli because of the qnrD-plasmid backbone.
(A) The qnrD SOS-box conservation by visualization of the consensus sequence logo generated from the 53 fully qnrD-plasmid sequences. The consensus sequence for E. coli is indicated below. (B) Relative expression of qnrD in E. coli MG1656 (WT) derived isogenic strains carrying pDIJ09-518a or pDIJ09-518a with a modified qnrD-SOS-box (LexA-box*), exposed to mitomycin C (dark blue), ciprofloxacin (blue), or tobramycin (brown) in comparison to expression in lysogeny broth (LB), normalized with dxs. (C) Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 (WT) with or without pDIJ09-518a, exposed to mitomycin C (dark blue), tobramycin (brown), or gentamicin (dotted brown) in comparison to expression in LB, normalized with dxs. (D) Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 (WT) with pDIJ09-518a, grown in LB, or either with tobramycin or with gentamicin, in comparison to the expression in E. coli MG1656, in the three culture conditions, and normalized with dxs. (E) Histogram bars show the ratio of green fluorescent protein (GFP) fluorescence in a E. coli MG1655 WT carrying or not the pDIJ09-518a plasmid in the presence of tobramycin (0.001 μg/ml) over fluorescence of the same strain grown in Mueller-Hinton (MH) reflecting induction of SOS. Black bars stand for strain with the SOS reporter vector and grey bars stand for strain carrying the qnrD-plasmid pDIJ09-518a and the SOS reporter vector. (F) Relative expression of qnrD in E. coli MG1656 with qnrD and its own promoter, or the native qnrD-plasmid inserted into the chromosome, or chromosomal qnrD complemented with pDIJ09-518aΔqnrD, exposed to mitomycin C (dark blue), tobramycin (brown), or gentamicin (dotted brown) in comparison to expression in LB, normalized with dxs. Data represent median values of six independent biological replicates, and error bars indicate upper/lower values. *p < 0.05. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Relative expression of qnrD in E. coli MG1656 (WT) and isogenic strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 (WT) and isogenic strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig2-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Relative expression of sulA in E. coli/pDIJ09-518a.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig2-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 4
GFP fluorescence in a E. coli MG1655 WT.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig2-data4-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 5
Relative expression of qnrD in E. coli MG1656 and isogenic strains with chormosomal complementation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig2-data5-v2.xlsx
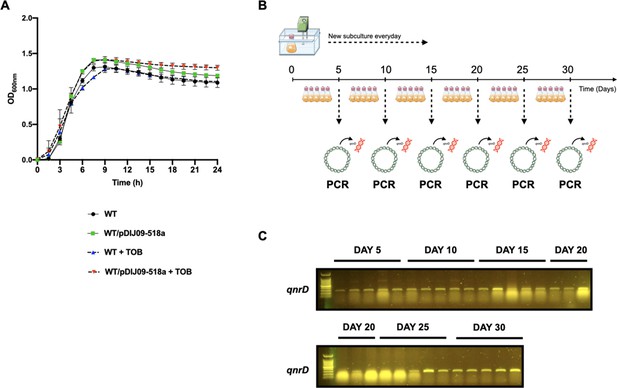
The viability of E. coli.
E. coli MG1656 carrying the qnrD-plasmid exposed to sub-minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of tobramycin is not impaired and the plasmid is stable in an antibiotic-free medium. (A) The curves represent the viability in the presence or in the absence of sub-MIC of tobramycin for 24 hr at 37°C, with shaking. The y-axis shows the OD at 600 nm measured at indicated hours on x-axis. Error bars represent standard deviation. Each strain was tested three times in triplicates. (B) The schematic approach for the stability of pDIJ09-518a plasmid under non-selective conditions. (C) PCR amplification of the qnrD gene from WT/pDIJ09-518a. Amplification of the predicted 150 bp fragment (including primers) from the 5′ end of the qnrD gene from different days isolated WT/pDIJ09-518a. In the left-most lane are molecular size markers (100 bp DNA ladder).
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
OD600 measured for E. coli MG1656 (WT) and isogenic strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
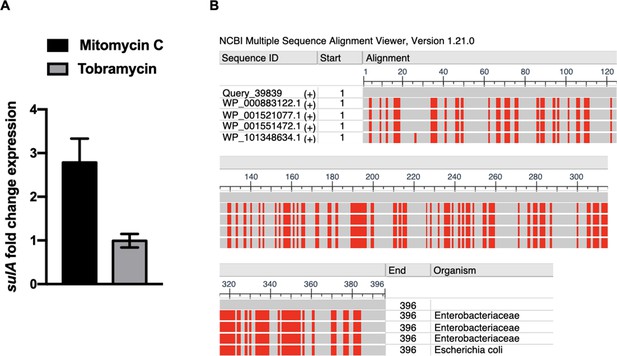
qnrD-plasmid carriage does not promote the SOS response induction by tobramycin in Providencia rettgeri.
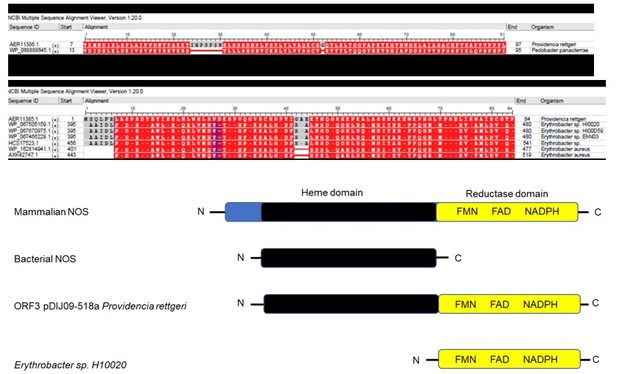
(A) Relative expression of sulA in P. rettgeri, carrying the pDIJ09-518a strains exposed to sub-minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of tobramycin or mitomycin C, in comparison to expression in lysogeny broth (LB), normalized with leuS. Data represent median values of two independent biological replicates, and error bars indicate upper/lower values. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. (B) Analyse of P. rettgeri Hmp protein (UniProt annotation D4C4 × 8_PRORE) in comparison to Hmp from E. coli str. K-12 substr MG1655 (sequence identity NP_4170471.1) using BLASTp showed 63,38% protein identity. Differences are shown in red in multiple sequence alignment viewer.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Relative expression of sulA in P. rettgeri/pDIJ09-518a.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
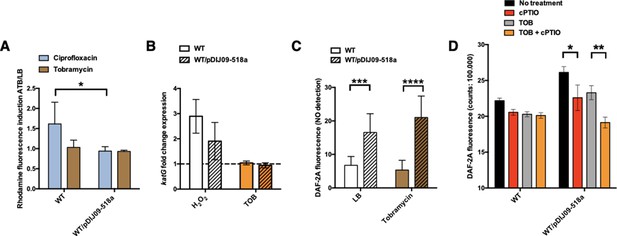
Small qnrD-plasmid promotes nitrosative stress in E.coli.
(A) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation for E. coli MG1656 (WT) and its derivative carrying pDIJ09-518a cultured in lysogeny broth (LB) or exposed to tobramycin. Production of ROS was calculated as the mean ratio of the dihydrorhodamine 123 (DHR-123) fluorescence of the treated samples to the control samples (n = 6). Data were analysed using a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with an p value <0.05 for strains as a source of variation in the overall ANOVA. *p < 0,05 using Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Mean difference for WT compared to WT/pDIJ09-518a exposed to ciprofloxacin was 0.6753; 95% confidence interval (CI) of difference [0.07565; 1.294]. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). (B) Relative expression of katG in E. coli MG1656 (WT) and in E. coli MG1656 carrying pDJJ09-518a, in comparison to expression in LB, normalized with dxs. Data represent median values of six independent biological replicates and error bars indicate upper/lower values. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. (C) Nitric oxide (NO) formation for E. coli MG1656 (WT) and its derivative carrying pDIJ09-518a culture in LB or exposed to tobramycin. Production of NO was calculated as the mean ratio of the DAF-2A fluorescence (n = 9). y-Axis represents arbitrary units of fluorescence. Data were analysed using a two-way ANOVA with a p value <0.0001 for strains as a source of variation in the overall ANOVA. ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001 using a Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The mean difference for WT compared to WT/pDIJ09-518a grown in LB was −9.790 [95% CI, −15.75; −3.825]. The mean difference for WT compared to WT/pDIJ09-518a exposed to tobramycin was −15.66 [95% CI, −21.62; −9.695]. Error bars represent the SD. Data represent median values of four independent biological replicates, and error bars indicate upper/lower values. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. (D) Histogram bars show the DAF-2A fluorescence, in E. coli WT and WT/pDIJ09-518a as a measure of intracellular in NO obtained using a FACS-based approach, with or without NO scavenger (carboxy-PTIO, cPTIO). Data were analysed using a two-way ANOVA with a p value <0.0001 for treatment as a source of variation in the overall ANOVA. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 using a Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The mean difference for WT/pDIJ09-518a grown in LB compared to WT/pDIJ09-518a grown in LB and cPTIO was 3.545 [95% CI, 0.4866; 6.603]. The mean difference for WT/pDIJ09-518a grown with tobramycin (TOB) compared to WT/pDIJ09-518a grown with TOB and cPTIO was 4.160 [95% CI, 1.163; 7.157]. Error bars represent the SD. Data represent median values of three independent biological replicates, and error bars indicate upper/lower values.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
DHR-123 fluorescence for ROS formation in E. coli MG1656 (WT) and isogenic strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Relative expression of katG in E. coli MG1656 (WT) and isogenic strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig3-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 3
DAF-2A fluorescence for NOS formation in E. coli MG1656 (WT) and isogenic strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig3-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 4
DAF-2A fluorescence obtained using a FACS-based approach, in E. coli WT and isogenic strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig3-data4-v2.xlsx
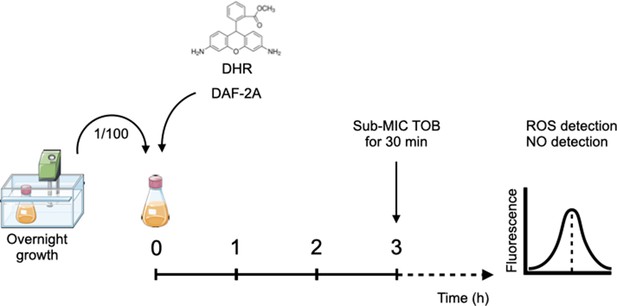
Schematic approach for fluorometric detection of free intercellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO).
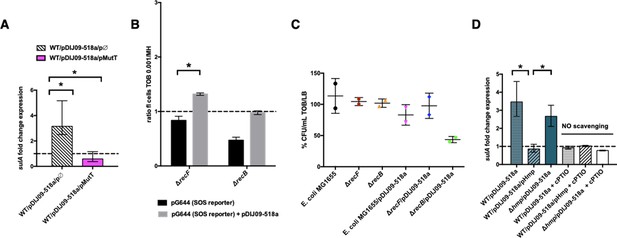
Aminoglycosides induce SOS in E. coli/pDIJ09-518a due to overwhelmed GO-repair pathway associated with inactivated Hmp.
(A, D) Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 (WT) isogenic strains carrying pDJJ09-518a, overexpressing the GO-repair system protein MutT and the hmp-deleted mutant, exposed to tobramycin, treated with the nitric oxide (NO) scavenger carboxy-PTIO (cPTIO) (for D), in comparison to expression in lysogeny broth (LB), normalized with dxs. Data represent median values of six independent biological replicates and error bars indicate upper/lower values. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. (B) Histogram bars show the ratio of GFP fluorescence in a E. coli MG1655 ΔrecB and ΔrecF in the presence of tobramycin (0.001 μg/ml) over fluorescence of the same strain grown in MH reflecting induction of SOS. Black bars stand for strain with the SOS reporter vector and grey bars stand for strain carrying the qnrD-plasmid pDIJ09-518a and the SOS reporter vector. (C) Impact of recB gene inactivation in E. coli harbouring the qnrD-plasmid on growth in sub-MIC tobramycin. Histogram bars represent the percentage of the ratio of colony-forming units (CFUs)/ml for each strain in tobramycin (0.001 µg/ml) over CFU/ml in LB. Data represent median values of two independent biological replicates, and error bars indicates the standard deviation (SD). Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. *p < 0.05.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656/ pDJJ09-518a overexpressing MutT.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
GFP fluorescence in a E. coli MG1655 ΔrecB and ΔrecF.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig4-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Ratio of colony-forming units.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig4-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 4
Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656/pDJJ09-518a with deleted hmp.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig4-data4-v2.xlsx
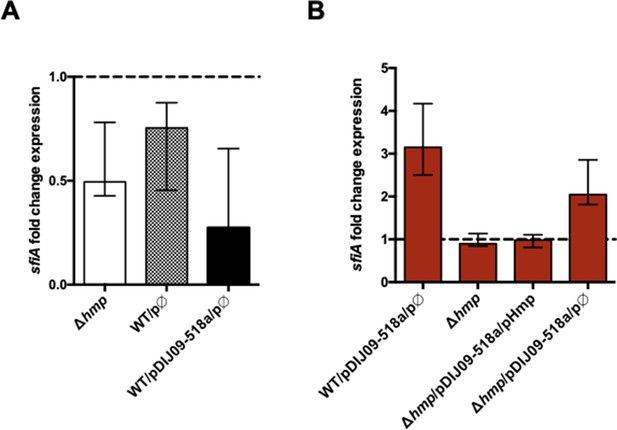
hmp deletion and empty vector carriage do not promote the SOS response induction.
(A) Relative expression of sulA in hmp-deleted E. coli MG1656, E. coli MG1656 carrying the empty vector, in comparison to expression in wild-type (WT) E. coli MG1656 strain and E. coli co-carrying pDIJ09-518a and the empty vector compared to E. coli WT-harbouring pDIJ09-518a, normalized with dxs. (B) Relative expression of sulA in hmp mutant and derivatives strains exposed to sub-MIC concentration of tobramycin, in comparison to expression in lysogeny broth (LB), normalized with dxs. Data represent median values of six independent biological replicates, and error bars indicate upper/lower values. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 Δhmp and E. coli MG1656 carrying empty vector.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Relative expression of sulA in hmp mutant and derivatives strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig4-figsupp1-data2-v2.xlsx
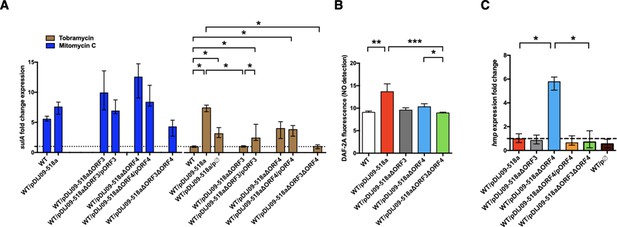
Deletion of ORF3 decreases the SOS response induction, after tobramycin treatment and ORF4 regulates the Hmp nitric oxide detoxification pathway.
(A) Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 (WT) derived isogenic strains carrying pDIJ09-518a with ORF3 and/or ORF4 deleted and complemented, exposed to mitomycin C (dark blue) or tobramycin (brown) in comparison to expression in lysogeny broth (LB), normalized with dxs. Data represent median values of six independent biological replicates, and error bars indicate upper/lower values. *p < 0.05. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. (B) Nitric oxide (NO) formation for the isogenic strains (n = 6). Data were analysed using a Kruskal–Wallis test, with a p value <0.0001 for the overall analysis of variance (ANOVA). NO formation for each strain was analysed using Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. Bars represent mean values and SD. (C) Relative expression of hmp in E. coli MG1656 (WT) derivative isogenic strains carrying pDIJ09-518a with ORF3 and/or ORF4 deleted and complemented, or the empty vector, grown in LB, in comparison to expression in E. coli MG1656 (WT), normalized with dxs. Data represent median values of six independent biological replicates, and error bars indicate upper/lower values. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. *p < 0.05.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 (WT) derived isogenic strains #1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 (WT) derived isogenic strains #2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig5-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Relative expression of sulA in E. coli MG1656 (WT) derived isogenic strains #3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig5-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 4
DAF-2A fluorescence in E. coli MG1656 (WT) and complemented strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig5-data4-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 5
Relative expression of hmp in E. coli MG1656 (WT) and isogenic strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig5-data5-v2.xlsx
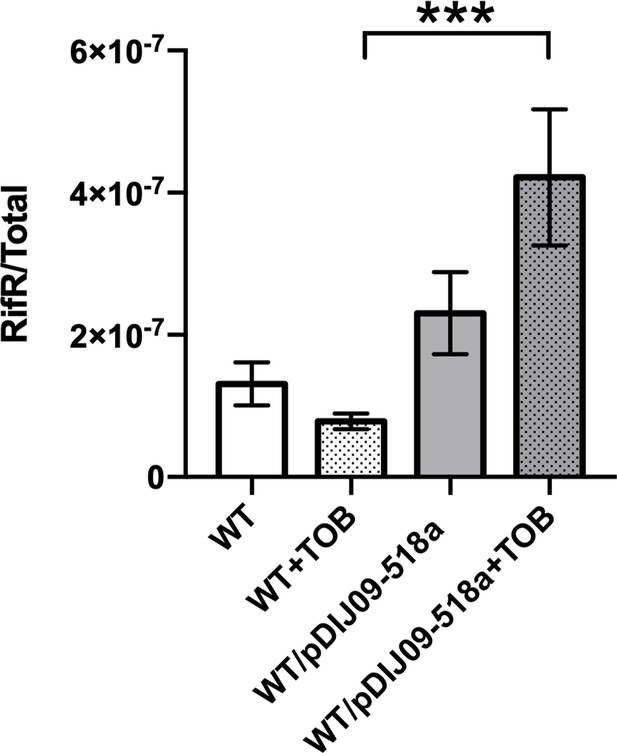
Spontaneous mutation ratio after treatment with sub-minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of tobramycin.
Bacteria were grown overnight in lysogeny broth (LB) supplemented or not with sub-MIC of tobramycin (0.001 µg/ml). Appropriate dilutions were plated on LB plate, and 1 ml of culture was centrifuged and plated on 200 μg/ml rifampin plates. The y-axis shows the ratio of the spontaneous mutations to rifampicin resistance correspond to the rifampin-resistant colony-forming unit (CFU) count over the total number of CFU in the presence or in the absence of sub-MIC of tobramycin. Error bars represent standard deviation (of the median). Two independent experiments with six independent cultures each were used. Results are shown as the average frequencies of all 12 cultures. ***p < 0.010. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
CFU counting after treatment of sub-MIC of tobramycin.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
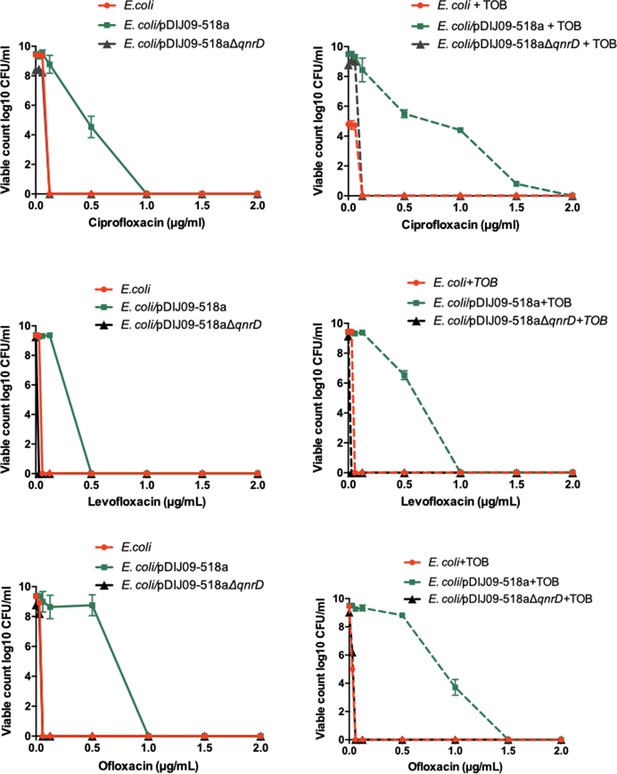
Aminoglycosides potentiate the selection of higher fluoroquinolone resistance in E.coli harbouring the small qnrD-plasmid.
Mutant prevention concentrations (MPCs) of isogenic E. coli ATCC25922 strains with or without exposure to sub-MIC of tobramycin. E. coli ATCC25922 (red circle), E. coli ATCC25922/pDIJ09-518a (green square), and E. coli ATCC25922/pDIJ09-518a∆qnrD (dark grey triangle).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
CFU counting for MPC assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
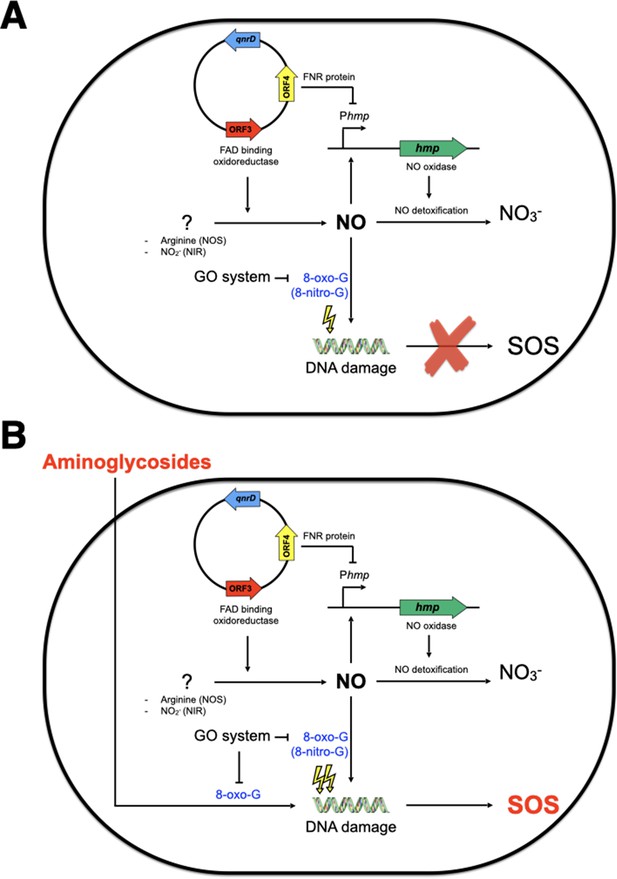
Model of SOS response induction by aminoglycosides in E. coli bearing the small qnrD-plasmid.
Schematic representation of the network leading to SOS induction in E. coli/pDIJ09-518a when not (A) or exposed (B) to sub-minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of aminoglycosides. NOS, nitric oxide species; NIR, nitrite reductase.
Tables
Minimal inhibitory concentration of quinolones.
| Strain* | MIC (μg/ml)† | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAL | LVX | OFX | CIP | ||||||||
| E. coli MG1656 | 3 | S | 0.023 | S | 0.006 | S | 0.004 | S | |||
| E. coli MG1656/pDIJ09-518a | >256 | R | 0.19 | S | 0.25 | S | 0.094 | S | |||
| E. coli MG1656 + CIP | 2 | S | 0.023 | S | 0.006 | S | 0.004 | S | |||
| E. coli MG1656/pDIJ09-518a + CIP | >256 | R | 0.25 | S | ×1.3 | 0.38 | I | x 1.5 | 0.19 | S | ×2 |
| E. coli MG1656 + TOB | 2 | S | 0.032 | S | 0.006 | S | 0.006 | S | |||
| E. coli MG1656/pDIJ09-518a + TOB | >256 | R | 0.38 | S | ×2 | 0.38 | I | x 1.5 | 0.25 | S | ×2.7 |
-
*
+CIP and +TOB stand for strains exposed to sub-MIC of ciprofloxacin and tobramycin, respectively, prior to MIC assessment.
-
†
Susceptibility testing categories according to EUCAST clinical breakpoints. Nalidixic acid: R > 16 μg/ml. Levofloxacin: S ≤ 0.5 μg/m, R > 1 μg/ml. Ofloxacin: S ≤ 0.25 μg/ml, R > 0.5 μg/ml. Ciprofloxacin: S ≤ 0.25 μg/ml, R > 0.5 μg/ml. Fold-change increases of MIC are shown in comparison to the QnrD-producing WT strain.
-
Similarly, the MICs increased for the qnrD-carrying E. coli exposed to sub-MIC of tobramycin as compared to growth in antibiotic-free medium (Table 1): 2-, 1.5-, and 2.7-fold higher for levofloxacin, ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin, respectively. These results showed that the aminoglycoside-induced SOS response increased quinolone (nalidixic acid and fluoroquinolones) MIC in line with the increased expression of qnrD in E. coli.
Quinolone resistance-determining region (QRDR) mutations and minimal inhibitory concentration of quinolones for surviving mutants obtained in the mutant prevention concentration (MPC) assay.
| Strain* | Mutant | MPC(μg/ml) | QRDR mutations | MIC (μg/ml)† | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GyrA | GyrB | ParC | ParE | NAL | CIP | OFX | LVX | |||||||
| E. coli ATCC25922/pDIJ09-518a | #1 | 1 | S83L | - | - | - | >256 | R | 0.125 | S | 0.38 | I | 0.19 | S |
| #2 | 1 | S83W | - | - | - | 24 | R | 0.25 | S | 0.5 | I | 0.38 | S | |
| #3 | 1 | S83W | - | - | - | >256 | R | 0.38 | I | 0.75 | R | 0.38 | S | |
| #4 | 1 | S83W | - | - | - | 24 | R | 0.19 | S | 0.5 | I | 0.25 | S | |
| #5 | 1 | S83W | - | - | - | >256 | R | 0.125 | S | 0.38 | I | 0.19 | S | |
| E. coli ATCC25922/pDIJ09-518a + TOB | #1 | 2 | S83W | - | - | - | >256 | R | 1 | R | 4 | R | 1 | I |
| #2 | 2 | S83W | - | G78D | - | >256 | R | 0.38 | I | 2 | R | 0.75 | I | |
| #3 | 2 | S83W | - | G78D | - | >256 | R | 1.5 | R | 4 | R | 0.75 | I | |
| #4 | 2 | S83W | - | G78D | - | >256 | R | 1 | R | 6 | R | 1 | I | |
| #5 | 2 | S83W | - | - | - | >256 | R | 1 | R | 4 | R | 1 | I | |
-
*
+TOB stands for strains exposed to sub-MIC of tobramycin prior to MPC assay.
-
†
Susceptibility testing categories according to EUCAST clinical breakpoints. Nalidixic acid: R > 16 μg/ml. Levofloxacin: S ≤ 0.5 μg/ml, R > 1 μg/ml. Ofloxacin: S ≤ 0.25 μg/ml, R > 0.5 μg/ml. Ciprofloxacin: S ≤ 0.25 μg/ml, R > 0.5 μg/ml.
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-transrepform1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 1
Genetic background of qnrD positive enterobacterial isolates.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Minimum-inhibitory concentrations for antibiotics used as SOS-response inducers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-supp2-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Strains and plasmids.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-supp3-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Primers used for this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69511/elife-69511-supp4-v2.docx