Developmental change in prefrontal cortex recruitment supports the emergence of value-guided memory
Figures
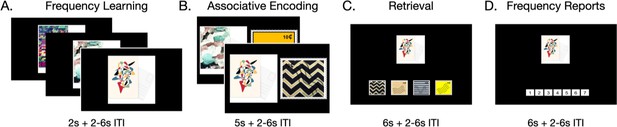
Task structure.
Participants first learned the frequencies of each item (A) by viewing them in a continuous stream. They then were shown the information associated with each item (B). During retrieval, participants had to report the information associated with each item (C) as well as the item’s original frequency (D).
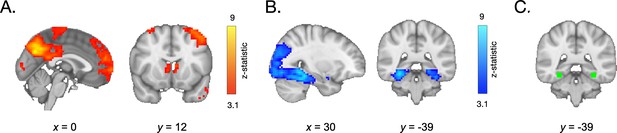
Neural activation during frequency learning.
(A) During frequency learning, participants demonstrated increased recruitment of regions in the frontal cortex, angular gyrus, and striatum on the last vs. first appearance of high-frequency items. (B) They demonstrated decreased activation in the lateral occipital cortex, temporal occipital cortex, and parahippocampal cortex. (C) Within a parahippocampal ROI (shown in green), the decrease in responses to each stimulus on its last vs. first appearance was greater in older participants.
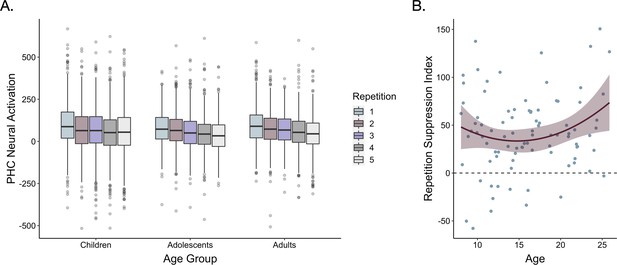
Repetition suppression during frequency learning.
(A) Neural activation within a bilateral parahippocampal cortex ROI decreased across stimulus repetitions both linearly, F(1, 5015.9) = 30.64, p < 0.001, and quadratically, F(1, 9881.0) = 7.47, p = 0.006. Repetition suppression increased with linear age, F(1, 7267.5) = 7.2, p = 0.007, and quadratic age F(1, 7260.8) = 6.9, p = 0.009. The horizontal black lines indicate median neural activation values. The lower and upper edges of the boxes indicate the first and third quartiles of the grouped data, and the vertical lines extend to the smallest value no further than 1.5 times the interquartile range. Grey dots indicate data points outside those values. (B) The decrease in neural activation in the bilateral PHC ROI from the first to fifth repetition of each item also increased with both linear age, F(1, 78.32) = 3.97, p = 0.05, and quadratic age, F(1, 77.55) = 4.8, p = 0.031. The line on the scatter plot represents the best-fitting regression line from the model including both linear and quadratic age terms. The shaded region represents 95% confidence intervals.
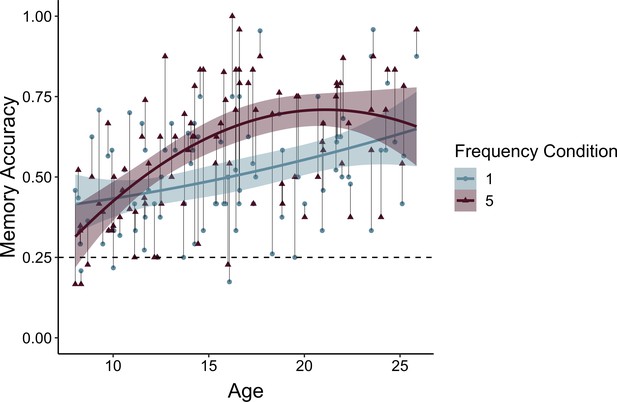
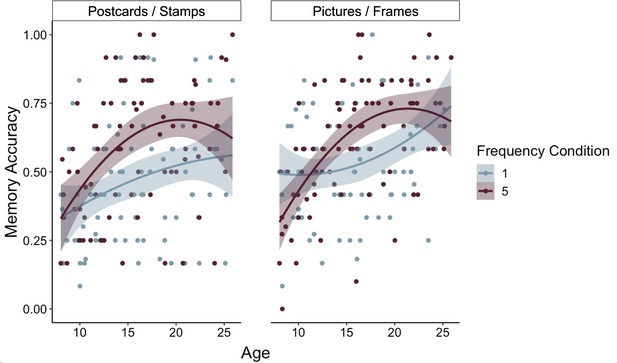
Memory accuracy by age and frequency condition.
Participants demonstrated prioritization of memory for high-value information, as indicated by higher memory accuracy for associations involving items in the five- relative to the one-frequency condition (χ2(1) = 19.73, p < 0.001). The effects of item frequency on associative memory increased throughout childhood and into adolescence (linear age x frequency condition: χ2(1) = 10.74, p = 0.001; quadratic age x frequency condition: χ2(1) = 9.27, p = 0.002). The thin grey lines connect each dots representing each participant's memory accuracy for items in the one- and five-frequency condition. The thicker colored lines represent the best-fitting regression lines from models including linear and quadratic age terms. The shaded regions represent 95% confidence intervals.
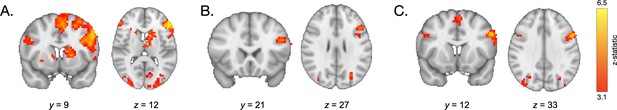
Neural activation during encoding.
(A) During encoding of associations involving high- vs. low-frequency items, participants demonstrated greater engagement of the lateral PFC and caudate. (B) Participants who demonstrated the greatest value-based modulation of memory also demonstrated the greatest modulation of left prefrontal cortical activation during encoding of high- vs. low-value associations. (C) During encoding of both high- and low-value pairs, older participants demonstrated greater recruitment of the PFC relative to younger participants.
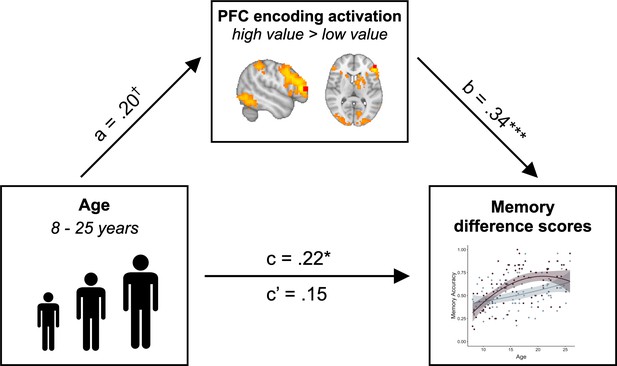
PFC activation mediates the relation between age and value-guided memory.
The increased engagement of left lateral PFC (ROI depicted in red) during encoding of high- vs. low-value information mediated the relation between age and memory difference scores (standardized indirect effect: .07, 95% confidence interval: [0.01, 0.15], p = 0.017; standardized direct effect: .15, 95% confidence interval: [−0.03, 0.33], p = 0.108). Path a shows the regression coefficient of the relation between age and PFC modulation. Path b shows the regression coefficient of the relation between PFC activation and memory difference scores, while controlling for age. Paths c and c’ show the regression coefficient of the relation between age and memory difference scores without and while controlling for PFC activation, respectively. † denotes p<0.06, * denotes p<0.05, ** denotes p<0.01.
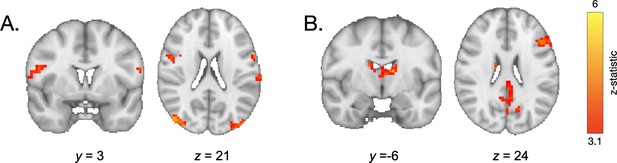
Neural activation during retrieval.
(A) During retrieval, older participants demonstrated greater recruitment of the inferior frontal cortex relative to younger participants. (B) During retrieval of associations involving high- vs. low-frequency items, participants demonstrated greater engagement of the left lateral PFC and bilateral caudate.
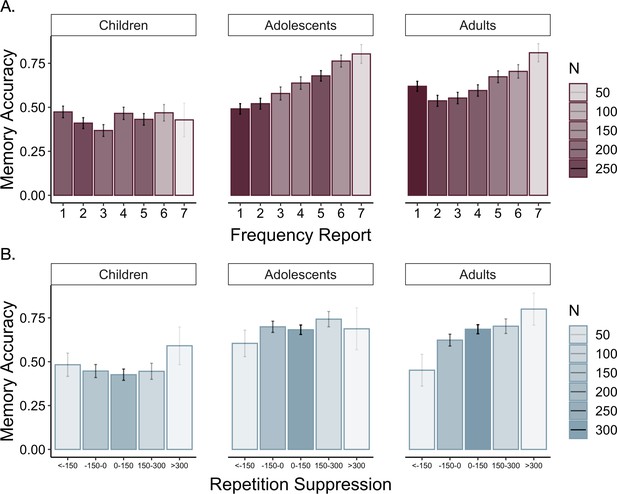
Memory accuracy by reported frequency.
(A) Participants demonstrated increased associative memory accuracy for items that they reported as being more frequent (χ2(1) = 31.20, p < 0.001). This effect strengthened with increasing age (frequency report x linear age: χ2(1) = 10.37, p = 0.001; frequency report x quadratic age: χ2(1) = 9.50, p = 0.002). (B) Participants also demonstrated better memory for associations involving high-frequency items to which they demonstrated the greatest repetition suppression during frequency learning (χ2(1) = 11.21, p < 0.001). In both panels, the shading of the bars represents the number of trials included in each bin.
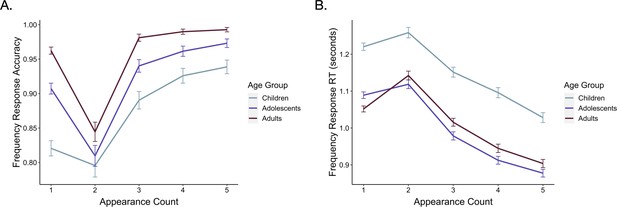
Frequency learning accuracy and reaction times.
(A) During frequency learning, older participants were more accurate in identifying items as new (χ2(1) = 25.54, p < 0.001) and as repeated (χ2(1) = 33.81, p < 0.001). All participants became more accurate in identifying items as repeated as the number of repetitions increased (χ2 = 138.20, p < 0.001), though younger participants demonstrated a greater increase in accuracy throughout learning (χ2(1) = 17.52, p < 0.001). (B) Older participants also responded to both new (F(1, 85.99) = 32.51, p < 0.001) and repeated (F(1, 87.55) = 21.82, p < 0.001) items more quickly than younger participants. Reaction times to old items became faster as the a function of item repetition number (F(1, 69.94) = 282.21, p < 0.001).
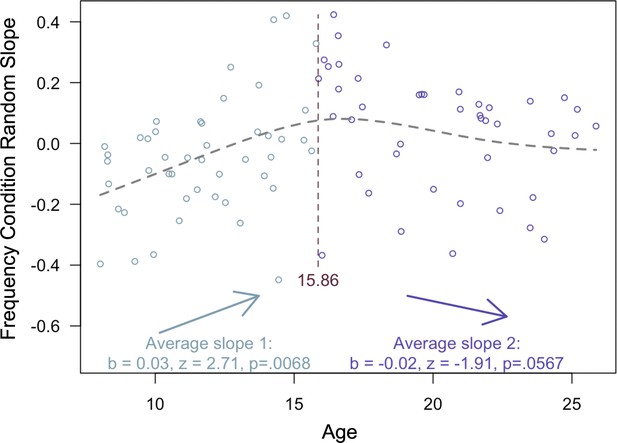
Relation between age and associative memory.
Results from the two-lines test (Simonsohn, 2018) revealed that the influence of frequency condition on memory accuracy increased throughout childhood and early adolescence, and did not significantly decrease from adolescence into early adulthood.
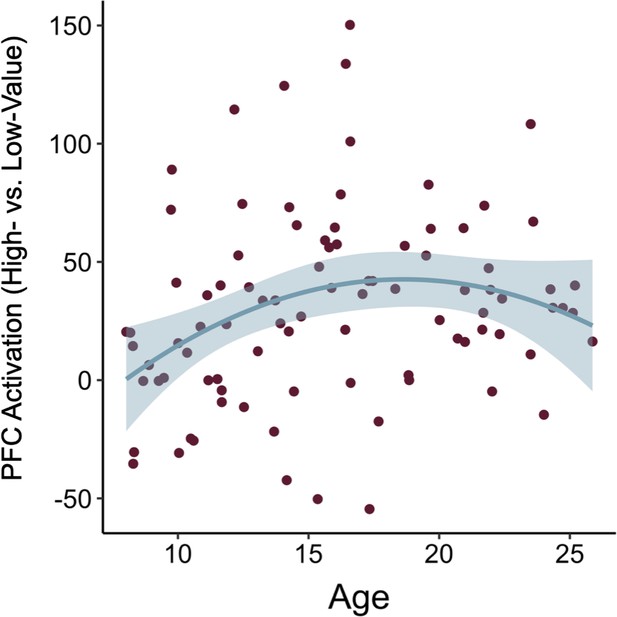
Prefrontal cortex activation during encoding.
Mean beta weights averaged over voxels within a prefrontal cortex ROI (see ‘methods’ in main text) during encoding of associations involving high- vs. low-frequency items increased with age. The increase was greatest in childhood before leveling out into late adolescence and early adulthood. The line represents the best-fitting regression line from the model including both linear and quadratic age. The shaded region represents 95% confidence intervals.
Tables
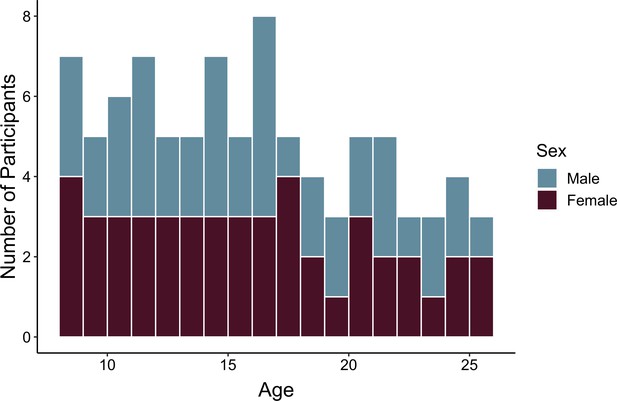
Number of participants included in each analysis.
| Block | Data type | Frequency- learning | Associative encoding | Retrieval | Frequency reports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Behavioral | 89 | NA | 90 | 90 |
| 1 | Neural | 88 | 90 | 90 | NA |
| 2 | Behavioral | 86 | NA | 85 | 85 |
| 2 | Neural | 84 | 81 | 81 | NA |
Associative memory accuracy by frequency condition with block order.
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.26 | 0.12–0.40 | ||
| Age | 1.42 | 0.52–2.33 | 8.97 | 0.003 |
| Age2 | −0.97 | −1.87 - −0.08 | 4.39 | 0.036 |
| WASI | 0.28 | 0.14–0.41 | 15.09 | <0.001 |
| Frequency Condition | −0.22 | −0.31 - −0.13 | 19.47 | <0.001 |
| Block Order | −0.02 | −0.11–0.07 | 0.18 | 0.676 |
| Age x WASI | 0.15 | −0.80–1.10 | 0.10 | 0.756 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.10 | −1.00–0.80 | 0.04 | 0.833 |
| Age x Block Order | −0.23 | −0.85–0.39 | 0.53 | 0.468 |
| Age2 x Block Order | 0.13 | −0.48–0.75 | 0.18 | 0.675 |
| Age x Frequency Condition | −1.05 | −1.68 - −0.43 | 10.31 | 0.001 |
| Age2 x Frequency Condition | 0.97 | −0.35–1.59 | 8.94 | 0.003 |
| WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.04 | −0.13–0.05 | 0.65 | 0.419 |
| Block Order x Frequency Condition | −0.03 | −0.10–0.05 | 0.76 | 0.384 |
| Block Order x WASI | −0.05 | −0.15–0.04 | 1.13 | 0.288 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.53 | −1.19–0.13 | 2.43 | 0.119 |
| Age2 x WASI x Frequency Condition | 0.54 | −0.08–1.17 | 2.83 | 0.092 |
| Age x Block Order x Frequency Condition | −0.35 | −0.86–0.16 | 1.80 | 0.180 |
| Age2 x Block Order x Frequency Condition | 0.27 | −0.23–0.77 | 1.10 | 0.294 |
| WASI x Block Order x Frequency Condition | −0.05 | −0.12–0.03 | 1.35 | 0.246 |
| WASI x Age x Block Order | 0.05 | −0.61–0.70 | 0.02 | 0.887 |
| WASI x Age2 x Block Order | −0.01 | −0.63–0.62 | 0.00 | 0.985 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Condition x Block Order | 0.35 | −0.19–0.89 | 1.61 | 0.205 |
| Age2 x WASI x Frequency Condition x Block Order | −0.33 | −0.85–0.18 | 1.62 | 0.203 |
Associative memory accuracy by frequency condition with block type.
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.26 | 0.12–0.40 | ||
| Age | 1.40 | 0.49–2.31 | 8.61 | 0.003 |
| Age2 | −0.95 | −1.85 - −0.05 | 4.16 | 0.041 |
| WASI | 0.27 | 0.14–0.40 | 14.46 | <0.001 |
| Frequency Condition | −0.22 | −0.31 - −0.13 | 20.07 | <0.001 |
| Block Type | −0.10 | −0.20–0.00 | 3.52 | 0.061 |
| Age x WASI | 0.17 | −0.79–1.12 | 0.12 | 0.734 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.10 | −1.01–0.80 | 0.05 | 0.822 |
| Age x Block Type | 0.23 | −0.39–0.85 | 0.53 | 0.465 |
| Age2 x Block Type | −0.28 | −0.89–0.33 | 0.79 | 0.375 |
| Age x Frequency Condition | −1.05 | −1.68 - −0.42 | 10.06 | 0.002 |
| Age2 x Frequency Condition | 0.96 | 0.34–1.59 | 8.64 | 0.003 |
| WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.04 | −0.13–0.05 | 0.65 | 0.419 |
| Block Type x Frequency Condition | −0.08 | −0.15 - −0.01 | 4.40 | 0.036 |
| Block Type x WASI | 0.01 | −0.08–0.10 | 0.03 | 0.866 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.51 | −1.18–0.15 | 2.24 | 0.135 |
| Age2 x WASI x Frequency Condition | 0.52 | −0.11–1.15 | 2.56 | 0.109 |
| Age x Block Type x Frequency Condition | 0.31 | −0.19–0.82 | 1.44 | 0.230 |
| Age2 x Block Type x Frequency Condition | −0.29 | −0.79–0.21 | 1.28 | 0.258 |
| WASI x Block Type x Frequency Condition | −0.03 | −0.10–0.05 | 0.44 | 0.505 |
| WASI x Age x Block Type | 0.62 | −0.03–1.27 | 3.44 | 0.064 |
| WASI x Age2 x Block Type | −0.60 | −1.22–0.02 | 3.57 | 0.059 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Condition x Block Type | −0.31 | −0.84–0.23 | 1.28 | 0.258 |
| Age2 x WASI x Frequency Condition x Block Type | 0.34 | −0.17–0.85 | 1.68 | 0.195 |
High- vs. low-value encoding PFC activation by age with block type.
| Estimate | 95% CI | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.01 | −0.17–0.15 | |||
| Age | 1.60 | 0.47–2.73 | 1, 79.46 | 7.76 | 0.007 |
| Age2 | −1.39 | −2.50 - −0.28 | 1, 79.24 | 6.04 | 0.016 |
| WASI | 0.15 | −0.02–0.32 | 1, 86.82 | 3.06 | 0.084 |
| Block Type | −0.04 | −0.19–0.11 | 1, 80.30 | 0.30 | 0.585 |
| Age x WASI | 0.45 | −0.79–1.69 | 1, 87.35 | 0.50 | 0.479 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.53 | −1.69–0.63 | 1, 86.03 | 0.79 | 0.376 |
| Age x Block Type | 0.11 | −0.94–1.16 | 1, 78.81 | 0.04 | 0.843 |
| Age2 x Block Type | −0.12 | −1.16–0.91 | 1, 78.59 | 0.05 | 0.818 |
| WASI x Block Type | −0.06 | −0.22–0.10 | 1, 86.37 | 0.54 | 0.462 |
| Age x WASI x Block Type | −0.73 | −1.89–0.44 | 1, 86.58 | 1.49 | 0.226 |
| Age2 x WASI x Block Type | 0.68 | −0.41–1.77 | 1, 85.26 | 1.48 | 0.227 |
Memory difference scores by PFC activation and age with block type.
| Estimate | 95% CI | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.09 | 0.05–0.13 | |||
| PFC Activation | 0.06 | 0.02–0.10 | 1, 153.78 | 9.85 | 0.002 |
| Age | 0.02 | −0.01–0.06 | 1, 84.35 | 1.52 | 0.221 |
| WASI | −0.00 | −0.04–0.04 | 1, 86.86 | 0.04 | 0.836 |
| Block Type | 0.03 | −0.00–0.07 | 1, 82.48 | 2.92 | 0.091 |
| PFC Activation x Age | 0.01 | −0.03–0.06 | 1, 153.53 | 0.28 | 0.598 |
| PFC Activation x WASI | 0.03 | −0.01–0.08 | 1, 154.29 | 2.13 | 0.147 |
| Age x WASI | −0.01 | −0.05–0.03 | 1, 86.37 | 0.22 | 0.642 |
| PFC Activation x Block Type | −0.01 | −0.04–0.03 | 1, 151.41 | 0.09 | 0.770 |
| Age x Block Type | 0.01 | −0.03–0.04 | 1, 82.91 | 0.13 | 0.718 |
| WASI x Block Type | 0.02 | −0.02–0.05 | 1, 85.40 | 0.76 | 0.385 |
| PFC Activation x Age x WASI | −0.01 | −0.06–0.04 | 1, 152.59 | 0.14 | 0.711 |
| PFC Activation x Age x Block Type | 0.03 | −0.02–0.08 | 1, 152.38 | 1.56 | 0.214 |
| PFC Activation x WASI x Block Type | −0.04 | −0.09–0.00 | 1, 151.64 | 3.49 | 0.064 |
| Age x WASI x Block Type | −0.02 | −0.05–0.01 | 1, 85.20 | 1.23 | 0.270 |
| PFC Activation x Age x WASI x Block Type | 0.05 | −0.01–0.10 | 1, 154.25 | 3.00 | 0.085 |
Frequency-learning accuracy: new items.
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 3.08 | 2.73–3.44 | ||
| Age | 0.92 | 0.58–1.25 | 25.52 | <0.001 |
| WASI | 0.43 | 0.09–0.77 | 6.18 | 0.013 |
| Age x WASI | 0.25 | −0.08–0.57 | 2.25 | 0.134 |
Frequency-learning accuracy: repeated item appearances.
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 3.83 | 3.46–4.20 | ||
| Appearance | 1.53 | 1.28–1.78 | 138.03 | <0.001 |
| Age | 0.97 | 0.64–1.29 | 33.43 | <0.001 |
| WASI | 0.46 | 0.13–0.79 | 7.58 | 0.006 |
| Appearance x Age | 0.45 | 0.24–0.67 | 17.41 | <0.001 |
| Appearance x WASI | 0.05 | −0.17–0.26 | 0.18 | 0.672 |
| Age x WASI | 0.12 | −0.20–0.45 | 0.57 | 0.449 |
| Appearance x Age x WASI | 0.04 | −0.17–0.25 | 0.14 | 0.707 |
Frequency-learning reaction times: new items.
| Estimate | 95% CI | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.12 | 1.09–1.15 | |||
| Age | −0.08 | −0.11 - −0.05 | 1, 85.99 | 32.51 | <.001 |
| WASI | −0.01 | −0.04–0.02 | 1, 82.34 | 0.56 | .457 |
| Age x WASI | −0.02 | −0.05 - −0.01 | 1, 83.14 | 2.12 | .149 |
Frequency-learning reaction times: repeated items.
| Estimate | 95% CI | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.03 | 1.00–1.06 | |||
| Age | −0.07 | −0.10 – −0.04 | 1, 87.55 | 21.82 | <0.001 |
| WASI | −0.03 | −0.06 – −0.01 | 1, 86.27 | 2.65 | 0.108 |
| Appearance | −0.08 | −0.09 – −0.07 | 1, 69.94 | 282.21 | <0.001 |
| Age x WASI | −0.01 | −0.03–0.02 | 1, 84.97 | 0.22 | 0.641 |
| Age x Appearance | −0.01 | −0.01–0.00 | 1, 77.06 | 1.26 | 0.265 |
| WASI x Appearance | 0.00 | −0.01–0.01 | 1, 75.79 | 0.00 | 0.992 |
| Age x WASI x Appearance | 0.00 | −0.01–0.01 | 1, 74.96 | 0.68 | 0.413 |
Parahippocampal cortex neural activation by stimulus repetition and age.
| Estimate | 95% CI | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 65.70 | 52.23–79.17 | |||
| Age | −78.41 | −164.25–7.43 | 1, 82.78 | 3.21 | 0.077 |
| Age2 | 82.54 | −2.27–167.35 | 1, 82.77 | 3.64 | 0.060 |
| Repetition | −30.20 | −40.89 – −19.50 | 1, 5015.94 | 30.64 | <0.001 |
| Repetition2 | 14.52 | 4.10–24.93 | 1, 9881.00 | 7.47 | 0.006 |
| WASI | −1.11 | −13.49–11.27 | 1, 83.31 | 0.03 | 0.861 |
| Age x Repetition | 101.65 | 27.40–175.90 | 1, 7267.46 | 7.20 | 0.007 |
| Age x Repetition2 | −88.18 | 161.49 - −14.87 | 1, 9857.85 | 5.56 | 0.018 |
| Age2 x Repetition | 97.99 | −171.28 - −24.71 | 1, 7260.70 | 6.87 | 0.009 |
| Age2 x Repetition2 | 82.76 | 10.40–155.11 | 1, 9854.92 | 5.03 | 0.025 |
| WASI x Age | 28.87 | −61.72–119.47 | 1, 83.51 | 0.39 | 0.534 |
| WASI x Age2 | −20.73 | −106.34–64.88 | 1, 83.47 | 0.23 | 0.636 |
| WASI x Repetition | −7.56 | −18.46–3.35 | 1, 7402.99 | 1.84 | 0.175 |
| WASI x Repetition2 | 7.40 | −3.38–18.18 | 1, 7857.10 | 1.81 | 0.178 |
| WASI x Age x Repetition | −52.32 | −130.26–25.61 | 1, 7243.45 | 1.73 | 0.188 |
| WASI x Age x Repetition2 | 42.15 | −34.79–119.08 | 1, 9868.65 | 1.15 | 0.283 |
| WASI x Age2 x Repetition | 45.97 | −27.58–119.53 | 1, 7235.30 | 1.50 | 0.221 |
| WASI x Age2 x Repetition2 | −38.01 | −110.62–34.59 | 1, 9867.59 | 1.05 | 0.305 |
Repetition suppression indices.
| Estimate | 95% CI | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 45.54 | 35.63–55.45 | |||
| Age | −61.34 | −8.56–10.77 | 1, 78.32 | 3.97 | 0.050 |
| Age2 | 66.52 | −121.70 - −0.98 | 1, 77.55 | 4.80 | 0.031 |
| WASI | 1.11 | 7.01–126.03 | 1, 58.06 | 0.05 | 0.823 |
| Age x WASI | 60.90 | −2.53–124.34 | 1, 77.38 | 3.54 | 0.064 |
| Age2 x WASI | −51.17 | −111.03–8.70 | 1, 77.16 | 2.81 | 0.098 |
Frequency report error magnitudes.
| Estimate | 95% CI | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.21 | 1.12–1.30 | |||
| Age | −0.18 | −0.27 - - 0.10 | 1, 94.30 | 17.57 | <0.001 |
| WASI | −0.11 | −0.19 - −0.02 | 1, 83.80 | 6.47 | 0.014 |
| Frequency Condition | −0.00 | −0.11–0.11 | 1, 93.81 | 0.00 | 0.993 |
| Age x WASI | −0.07 | −0.15–0.01 | 1, 86.35 | 3.24 | 0.075 |
| Age x Frequency Condition | −0.05 | −0.17–0.06 | 1, 85.48 | 0.95 | 0.332 |
| WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.03 | −0.14–0.09 | 1, 86.55 | 0.20 | 0.652 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.07 | −0.17–0.03 | 1, 85.94 | 1.77 | 0.187 |
Frequency reports by repetition suppression.
| Estimate | 95% CI | df | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 4.44 | 4.26–4.63 | |||
| Age | 0.26 | 0.09–0.42 | 1, 82.87 | 8.93 | 0.004 |
| WASI | 0.19 | 0.02–0.36 | 1, 85.19 | 4.77 | 0.032 |
| Repetition Suppression | 0.00 | −0.06–0.07 | 1, 1360.74 | 0.01 | 0.903 |
| Age x WASI | 0.09 | −0.07–0.25 | 1, 84.13 | 1.34 | 0.251 |
| Age x Repetition Suppression | 0.06 | −0.00–0.12 | 1, 938.87 | 3.61 | 0.058 |
| WASI x Repetition Suppression | 0.04 | −0.02–0.10 | 1, 58.81 | 1.52 | 0.222 |
| Age x WASI x Repetition Suppression | −0.03 | −0.08–0.03 | 1, 313.72 | 1.10 | 0.296 |
Associative memory accuracy by frequency condition.
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.26 | 0.12–0.40 | ||
| Age | 1.38 | 0.49–2.28 | 8.68 | 0.003 |
| Age2 | −0.95 | −1.83 – −0.06 | 4.24 | 0.039 |
| WASI | 0.26 | 0.13–0.39 | 14.18 | <0.001 |
| Frequency Condition | −0.21 | −0.30 – −0.13 | 19.73 | <0.001 |
| Age x WASI | 0.18 | −0.76–1.12 | 0.14 | 0.704 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.12 | −1.01–0.77 | 0.07 | 0.789 |
| Age x Frequency Condition | −1.06 | −1.68 – −0.45 | 10.74 | 0.001 |
| Age2 x Frequency Condition | 0.98 | 0.37–1.59 | 9.27 | 0.002 |
| WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.04 | −0.13–0.05 | 0.86 | 0.355 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.50 | −1.15–0.15 | 2.26 | 0.133 |
| Age2 x WASI x Frequency Condition | 0.52 | −0.10–1.13 | 2.65 | 0.104 |
Associative memory accuracy by frequency condition (below-chance subjects excluded).
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.30 | 0.16–0.44 | ||
| Age | 1.19 | 0.29–2.09 | 6.48 | 0.011 |
| Age2 | −0.79 | −1.68–0.10 | 2.98 | 0.084 |
| WASI | 0.24 | 0.11–0.37 | 12.44 | <0.001 |
| Frequency Condition | −0.22 | −0.31 – −0.13 | 20.04 | <0.001 |
| Age x WASI | 0.31 | −0.62–1.24 | 0.43 | 0.513 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.23 | −1.11–0.66 | 0.25 | 0.615 |
| Age x Frequency Condition | −1.07 | −1.70 - −0.43 | 10.25 | 0.001 |
| Age2 x Frequency Condition | 0.99 | 0.36–1.61 | 8.97 | 0.003 |
| WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.04 | −0.14–0.05 | 0.81 | 0.368 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.50 | −1.16–0.16 | 2.17 | 0.141 |
| Age2 x WASI x Frequency Condition | 0.52 | −0.11–1.15 | 2.54 | 0.111 |
Associative memory accuracy by frequency condition (with frequency-learning covariates).
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.25 | 0.12–0.38 | ||
| Age | 0.59 | −0.31–1.49 | 1.62 | 0.203 |
| Age2 | −0.30 | −1.17–0.56 | 0.47 | 0.491 |
| WASI | 0.16 | 0.03–0.29 | 6.02 | 0.014 |
| Frequency Condition | −0.21 | −0.30 – −0.13 | 19.65 | <0.001 |
| Mean Frequency Report Error Magnitude | −0.26 | −0.39 – −0.12 | 13.05 | <0.001 |
| Frequency-learning Accuracy | 0.17 | −0.04–0.38 | 2.36 | 0.125 |
| Frequency-learning Accuracy (last item appearance) | −0.10 | −0.30–0.09 | 1.06 | 0.304 |
| Age x WASI | 0.11 | −0.75–0.96 | 0.06 | 0.807 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.08 | −0.89–0.72 | 0.04 | 0.843 |
| Age x Frequency Condition | −1.06 | −1.67 - −0.44 | 10.59 | 0.001 |
| Age2 x Frequency Condition | 0.97 | 0.36–1.58 | 9.15 | 0.002 |
| WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.04 | −0.13–0.05 | 0.83 | 0.362 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Condition | −0.50 | −1.15–0.15 | 2.22 | 0.136 |
| Age2 x WASI x Frequency Condition | 0.51 | −0.10–1.13 | 2.61 | 0.106 |
High vs. low-value encoding caudate activation by age.
| Estimate | SE | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.07 | .104 | ||
| Age | 0.16 | .107 | 1.55 | 0.126 |
| WASI | 0.18 | .110 | 1.64 | 0.105 |
| Age x WASI | −0.29 | .101 | −2.86 | 0.005 |
High vs. low-value encoding PFC activation by age.
| Estimate | SE | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.00 | .105 | ||
| Age | 1.97 | .743 | 2.65 | 0.009 |
| Age2 | −1.73 | .734 | −2.35 | 0.021 |
| WASI | 0.26 | .109 | 2.34 | 0.022 |
| Age x WASI | 0.93 | .789 | 1.18 | 0.240 |
| Age2 x WASI | −1.02 | .745 | −1.37 | 0.174 |
Associative memory accuracy by frequency report.
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.26 | 0.12–0.40 | ||
| Age | 1.46 | 0.55–2.38 | 9.25 | 0.002 |
| Age2 | −1.01 | −1.92 – −0.11 | 4.64 | 0.031 |
| WASI | 0.27 | 0.13–0.40 | 13.94 | <0.001 |
| Frequency Report | 0.28 | 0.19–0.37 | 31.20 | <0.001 |
| Age x WASI | 0.15 | −0.81–1.12 | 0.09 | 0.759 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.10 | −1.01–0.82 | 0.04 | 0.838 |
| Age x Frequency Report | 1.13 | 0.46–1.79 | 10.37 | 0.001 |
| Age2 x Frequency Report | −1.07 | −1.73 – −0.41 | 9.50 | 0.002 |
| WASI x Frequency Report | 0.02 | −0.08–0.11 | 0.10 | 0.754 |
| Age x WASI x Frequency Report | 0.37 | −0.35–1.09 | 1.00 | 0.316 |
| Age2 x WASI x Frequency Report | −0.33 | −1.01–0.35 | 0.89 | 0.345 |
Associative memory accuracy by repetition suppression.
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.51 | 0.32–0.69 | ||
| Age | 2.63 | 1.43–3.83 | 16.87 | <0.001 |
| Age2 | −2.13 | −3.31 – −0.94 | 11.55 | <0.001 |
| WASI | 0.31 | 0.14–0.49 | 11.47 | <0.001 |
| Repetition Suppression | 0.23 | 0.10–0.37 | 11.21 | <0.001 |
| Age x WASI | 0.78 | −0.49–2.05 | 1.44 | 0.230 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.75 | −1.95–0.45 | 1.47 | 0.225 |
| Age x Repetition Suppression | −0.42 | −1.32–0.49 | 0.79 | 0.374 |
| Age2 x Repetition Suppression | 0.64 | −0.28–1.57 | 1.79 | 0.181 |
| WASI x Repetition Suppression | 0.00 | −0.13–0.14 | 0.00 | 0.954 |
| Age x WASI x Repetition Suppression | −0.17 | −1.02–0.68 | 0.15 | 0.700 |
| Age2 x WASI x Repetition Suppression | 0.27 | −0.57–1.10 | 0.37 | 0.541 |
Associative memory accuracy by repetition suppression and frequency reports.
| Estimate | 95% CI | Χ2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.51 | 0.32–0.69 | ||
| Repetition Suppression | 0.23 | 0.09–0.36 | 10.25 | 0.001 |
| WASI | 0.26 | 0.08–0.44 | 7.59 | 0.006 |
| Frequency Report | 0.3 | 0.17–0.42 | 21.16 | <0.001 |
| Age | 2.47 | 1.25–3.69 | 14.4 | <0.001 |
| Age2 | −2.02 | −3.23 – −0.81 | 9.98 | 0.002 |
| Repetition Suppression x WASI | 0.00 | −0.13–0.14 | 0.00 | 0.968 |
| Repetition Suppression x Frequency Report | −0.11 | −0.25–0.04 | 2.18 | 0.140 |
| WASI x Frequency Report | −0.05 | −0.18–0.08 | 0.48 | 0.488 |
| Repetition Suppression x Age | −0.12 | −1.05–0.81 | 0.06 | 0.804 |
| Repetition Suppression x Age2 | 0.33 | −0.62–1.27 | 0.45 | 0.503 |
| WASI x Age | 0.92 | −0.36–2.21 | 1.96 | 0.161 |
| WASI x Age2 | −0.89 | −2.12–0.33 | 2.04 | 0.153 |
| Frequency Report x Age | 0.12 | −0.74–0.99 | 0.08 | 0.783 |
| Frequency Report x Age2 | −0.09 | −0.97–0.79 | 0.04 | 0.843 |
| RS x WASI x Frequency Report | −0.04 | −0.19–0.11 | 0.27 | 0.603 |
| RS x WASI x Age | −0.28 | −1.16–0.61 | 0.36 | 0.550 |
| RS x WASI x Age2 | 0.39 | −0.49–1.26 | 0.71 | 0.400 |
| RS x Frequency Report x Age | 0.13 | −0.78–1.03 | 0.07 | 0.786 |
| RS x Frequency Report x Age2 | −0.12 | −1.09–0.85 | 0.06 | 0.809 |
| WASI x Frequency Report x Age | −0.33 | −1.31–0.65 | 0.44 | 0.509 |
| WASI x Frequency Report x Age2 | 0.44 | −0.52–1.40 | 0.79 | 0.374 |
| RS x WASI x Frequency Report x Age | −0.73 | −1.68–0.22 | 2.29 | 0.130 |
| RS x WASI x Frequency Report x Age2 | 0.83 | −0.14–1.80 | 2.86 | 0.091 |
Mean repetition suppression indices by age.
| Estimate | SE | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 44.76 | 4.53 | ||
| Age | −59.00 | 31.82 | −1.85 | 0.067 |
| Age2 | 64.93 | 31.37 | 2.07 | 0.042 |
| WASI | 1.86 | 4.72 | 0.39 | 0.695 |
| Age x WASI | 57.06 | 33.89 | 1.68 | 0.096 |
| Age2 x WASI | −48.02 | 31.93 | −1.50 | 0.136 |
Caudate activation by repetition suppression indices.
| Estimate | SE | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 8.23 | 1.54 | ||
| Repetition Suppression | 2.31 | 1.60 | 1.44 | 0.153 |
| Age | 1.48 | 1.64 | 0.91 | 0.367 |
| WASI | 1.93 | 1.64 | 1.17 | 0.244 |
| Repetition Suppression x Age | 1.29 | 1.42 | 0.91 | 0.366 |
| Repetition Suppression x WASI | 0.26 | 1.54 | 0.17 | 0.864 |
| Age x WASI | −4.40 | 1.50 | −2.94 | 0.004 |
| Repetition Suppression x Age x WASI | −0.09 | 1.22 | −0.07 | 0.945 |
PFC activation by repetition suppression indices.
| Estimate | SE | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 28.66 | 4.51 | ||
| Repetition Suppression | −6.78 | 4.83 | −1.40 | 0.165 |
| Age | 103.36 | 35.33 | 2.93 | 0.004 |
| Age2 | −94.25 | 35.13 | −2.68 | 0.009 |
| WASI | 13.59 | 4.74 | 2.87 | 0.005 |
| Repetition Suppression x Age | −54.15 | 34.13 | −1.59 | 0.112 |
| Repetition Suppression x Age2 | 53.85 | 32.79 | 1.64 | 0.105 |
| Repetition Suppression x WASI | −3.28 | 4.49 | −0.73 | 0.467 |
| Age x WASI | 30.43 | 34.44 | 0.88 | 0.380 |
| Age2 x WASI | −38.59 | 32.41 | −1.91 | 0.237 |
| Repetition Suppression x Age x WASI | −41.33 | 29.80 | −1.39 | 0.169 |
| Repetition Suppression x Age2 x WASI | 41.46 | 27.58 | 1.50 | 0.137 |
Frequency distance by age.
| Estimate | SE | T | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 2.23 | .09 | ||
| Age | 2.75 | .67 | 4.10 | <0.001 |
| Age2 | −2.28 | .66 | −3.44 | <0.001 |
| WASI | 0.38 | .10 | 3.89 | <0.001 |
| Age x WASI | 0.33 | .71 | 0.46 | 0.646 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.12 | .67 | −0.18 | 0.857 |
Caudate activation by frequency distance.
| Estimate | SE | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 7.00 | 1.78 | ||
| Frequency Distance | 2.55 | 1.86 | 1.37 | 0.175 |
| Age | 1.39 | 1.89 | 0.74 | 0.463 |
| WASI | 1.13 | 1.77 | 0.64 | 0.526 |
| Frequency Distance x Age | 2.27 | 1.77 | 1.29 | 0.202 |
| Frequency Distance x WASI | −1.50 | 1.77 | −0.85 | 0.399 |
| Age x WASI | −5.49 | 1.64 | −3.43 | 0.001 |
| Frequency Distance x Age x WASI | 1.71 | 1.40 | 1.22 | 0.227 |
PFC activation by frequency distance.
| Estimate | SE | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.02 | 0.12 | ||
| Frequency Distance | 0.42 | 0.12 | 3.36 | 0.001 |
| Age | −0.03 | 0.13 | −0.22 | 0.824 |
| WASI | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.64 | 0.522 |
| Frequency Distance x Age | −0.18 | 0.12 | −1.51 | 0.136 |
| Frequency Distance x WASI | 0.15 | 0.12 | 1.23 | 0.223 |
| Age x WASI | −0.17 | 0.11 | −1.52 | 0.132 |
| Frequency Distance x Age x WASI | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.52 | 0.607 |
Memory difference scores by PFC activation and frequency distance.
| Estimate | SE | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.07 | |||
| Frequency Distance | −0.02 | 0.03 | −0.55 | 0.582 |
| Age | 0.56 | 0.2 | 2.83 | 0.006 |
| Age2 | −0.51 | 0.2 | −2.6 | 0.012 |
| WASI | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.85 | 0.398 |
| PFC Activation | 0.08 | 0.04 | 1.95 | 0.055 |
| Frequency Distance x Age | 0.29 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 0.139 |
| Frequency Distance x Age2 | −0.27 | 0.2 | −1.36 | 0.178 |
| Frequency Distance x WASI | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.38 | 0.709 |
| Age x WASI | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.866 |
| Age2 x WASI | −0.05 | 0.18 | −0.25 | 0.800 |
| Frequency Distance x PFC Activation | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.800 |
| Age x PFC Activation | −0.15 | 0.34 | −0.43 | 0.672 |
| Age2 x PFC Activation | 0.21 | 0.34 | 0.62 | 0.538 |
| WASI x PFC Activation | −0.04 | 0.04 | −0.84 | 0.406 |
| Frequency Distance x Age x WASI | −0.36 | 0.22 | −1.66 | 0.102 |
| Frequency Distance x Age2 x WASI | 0.33 | 0.2 | 1.62 | 0.111 |
| Frequency Distance x Age x PFC Activation | −0.07 | 0.27 | −0.24 | 0.809 |
| Frequency Distance x Age2 x PFC Activation | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.778 |
| Frequency Distance x WASI x PFC Activation | −0.05 | 0.03 | −1.49 | 0.142 |
| Age2 x WASI x PFC Activation | 0.46 | 0.36 | 1.29 | 0.202 |
| Age2 x WASI x PFC Activation | −0.46 | 0.36 | −1.28 | 0.204 |
| Frequency Distance x Age2 x WASI x PFC Activation | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.99 | 0.324 |
| Frequency Distance x Age2 x WASI x PFC Activation | −0.28 | 0.27 | −1.07 | 0.288 |
Frequency-learning: Last vs. first item appearance cluster table.
| Region | x | y | z | Cluster size | z-max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal pole | −42 | 51 | 0 | 2419 | 6.33 |
| Precuneus | 0 | −66 | 33 | 1322 | 8.99 |
| Left lateral occipital cortex / angular gyrus | −57 | −66 | 30 | 1319 | 7.2 |
| Right lateral occipital cortex / angular gyrus | 51 | −63 | 33 | 637 | 6.03 |
| Right middle temporal gyrus | 66 | −33 | −12 | 304 | 5.48 |
| Right cerebellum | 15 | −87 | −27 | 164 | 5.33 |
| Precentral gyrus | 3 | −18 | 75 | 124 | 4.53 |
| Left cerebellum | −42 | −75 | −42 | 92 | 4.72 |
| Left middle temporal gyrus | −57 | -3 | −27 | 73 | 4.44 |
| Left caudate | -6 | 12 | 9 | 62 | 4.91 |
| Right caudate | 9 | 24 | 6 | 60 | 5.04 |
| Occipital pole | -3 | −96 | 12 | 46 | 4.81 |
Frequency-learning: First vs. last item appearance cluster table.
| Region | x | y | z | Cluster size | z-max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right temporal fusiform cortex / lateral occipital cortex / parahippocampal gyrus | 30 | −39 | −15 | 2137 | 8.62 |
| Left temporal fusiform cortex / lateral occipital cortex / parahippocampal gyrus | −33 | −63 | −15 | 1858 | 7.53 |
| Cingulate gyrus | 9 | 9 | 42 | 100 | 6 |
| Right precuneus | 18 | −51 | 9 | 80 | 6.05 |
| Left postcentral gyrus | −51 | −15 | 57 | 74 | 4.73 |
| Right precentral gyrus | 42 | 3 | 33 | 73 | 5.54 |
| Juxtapositional lobule cortex | 6 | 6 | 57 | 24 | 4.11 |
| Left amygdala | −24 | -6 | −15 | 22 | 4.23 |
| Cingulate gyrus | 3 | -3 | 33 | 22 | 4.68 |
| Central opercular cortex | 39 | -3 | 15 | 21 | 4.8 |
Encoding: Encoding vs. baseline by linear age cluster table.
| Region | x | y | z | Cluster size | z-max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right lateral occipital cortex | 45 | −81 | 21 | 132 | 5 |
| Left precentral gyrus / middle frontal gyrus | −54 | 12 | 33 | 120 | 5.9 |
| Left lateral occipital cortex | −45 | −84 | 21 | 54 | 4.69 |
| Left lateral occipital cortex | −27 | −72 | 42 | 50 | 4.32 |
| Right lateral occipital cortex | 30 | −69 | 45 | 44 | 4.17 |
| Left cerebellum | −18 | −45 | −48 | 39 | 4.55 |
| Superior frontal gyrus | -3 | 12 | 60 | 39 | 4.35 |
| Left supramarginal gyrus | −36 | −45 | 36 | 37 | 4.57 |
| Left middle frontal gyrus | −33 | 3 | 63 | 33 | 4.6 |
| Right superior parietal lobule | 33 | −45 | 42 | 31 | 3.76 |
| Right inferior frontal gyrus | 48 | 12 | 30 | 24 | 3.97 |
Encoding: High- vs. low-value cluster table.
| Region | x | y | z | Cluster size | z-max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superior parietal lobule / lateral occipital cortex / temporal occipital fusiform cortex / cerebellum | −33 | −54 | 51 | 4262 | 6.23 |
| Left frontal pole / inferior frontal gyrus / middle frontal gyrus | −51 | 42 | 9 | 1765 | 6.92 |
| Left caudate / thalamus | −18 | 12 | 6 | 232 | 5.67 |
| Right caudate | 18 | 18 | 12 | 54 | 4.17 |
| Right precentral gyrus | 51 | 9 | 33 | 50 | 4.26 |
| Right precentral gyrus | 24 | -9 | 54 | 47 | 4.79 |
| Left cerebellum | -3 | −51 | 0 | 38 | 4.73 |
| Right frontal pole | 51 | 39 | 12 | 35 | 4.53 |
| Right postcentral gyrus | 42 | −36 | 51 | 28 | 4.32 |
| Right putamen | 27 | 15 | -3 | 26 | 4.52 |
| Left thalamus | -3 | −24 | -3 | 23 | 4.65 |
| Left putamen | −30 | −15 | -6 | 20 | 5.7 |
Encoding: High- vs. low-value by memory difference scores cluster table.
| Region | x | y | z | Cluster size | z-max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left lateral occipital cortex | −45 | −69 | -6 | 377 | 4.78 |
| Left middle frontal gyrus / inferior frontal gyrus | −48 | 21 | 27 | 232 | 4.95 |
| Right lateral occipital cortex (inferior) | 39 | −90 | 3 | 189 | 4.89 |
| Right temporal occipital fusiform cortex | 42 | −57 | -9 | 87 | 4.45 |
| Right lateral occipital cortex (superior) | 27 | −66 | 33 | 61 | 4.83 |
Encoding: Remembered vs. not remembered cluster table.
| Region | x | y | z | Cluster size | z-max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right lateral occipital cortex / temporal occipital fusiform gyrus | 48 | −75 | -9 | 1296 | 5.75 |
| Left lateral occipital cortex / temporal occipital fusiform gyrus / inferior temporal gyrus | −48 | −72 | -6 | 1273 | 5.97 |
| Left inferior frontal gyrus | −48 | 9 | 27 | 103 | 4.22 |
| Left inferior frontal gyrus | −57 | 21 | -3 | 40 | 3.81 |
| Right hippocampus / amygdala | 24 | -6 | −21 | 21 | 4.06 |
Retrieval: Retrieval vs. baseline by linear age cluster table.
| Region | x | y | z | Cluster size | z-max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right lateral occipital cortex | 45 | −81 | 21 | 147 | 5.28 |
| Left lateral occipital cortex | −39 | −87 | 21 | 59 | 4.25 |
| Right precentral gyrus / inferior frontal gyrus | 51 | 3 | 21 | 42 | 4.21 |
| Right precentral gyrus | 39 | −12 | 39 | 41 | 4.4 |
| Left postcentral gyrus / supramarginal gyrus | −63 | −24 | 48 | 38 | 4.45 |
| Left precentral gyrus | −60 | 6 | 21 | 36 | 4.39 |
| Right lateral occipital cortex | 27 | −60 | 57 | 34 | 3.76 |
| Cingulate gyrus / left thalamus | 3 | −33 | 0 | 30 | 4.74 |
| Left supramarginal gyrus | −69 | −24 | 24 | 28 | 4.33 |
Retrieval: High- vs. low-value cluster table.
| Region | x | y | z | Cluster size | z-max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precuneus cortex | 0 | −72 | 39 | 299 | 4.81 |
| Left lateral occipital cortex | −33 | −69 | 51 | 236 | 5.28 |
| Left caudate / thalamus | −12 | -6 | 15 | 128 | 5.15 |
| Right cerebellum | 3 | −81 | −30 | 125 | 6.12 |
| Left inferior frontal gyrus / middle frontal gyrus | −48 | 21 | 24 | 116 | 4.57 |
| Left frontal orbital cortex | −30 | 30 | -3 | 88 | 4.82 |
| Right cerebellum | 39 | −69 | −36 | 85 | 4.65 |
| Right caudate | 15 | -3 | 21 | 77 | 4.96 |
| Left middle frontal gyrus | −45 | 12 | 48 | 74 | 4.31 |
| Cerebellum | -3 | −60 | −36 | 60 | 4.57 |
| Left inferior temporal gyrus | −57 | −60 | −15 | 60 | 4.33 |
| Cingulate gyrus | 0 | −33 | 3 | 25 | 4.09 |
| Right frontal orbital cortex | 33 | 33 | 3 | 21 | 4.69 |
| Left frontal pole | −36 | 57 | 3 | 20 | 3.79 |
| Right lateral occipital cortex | 27 | −66 | 42 | 20 | 4.24 |