Neuronal sequences during theta rely on behavior-dependent spatial maps
Figures
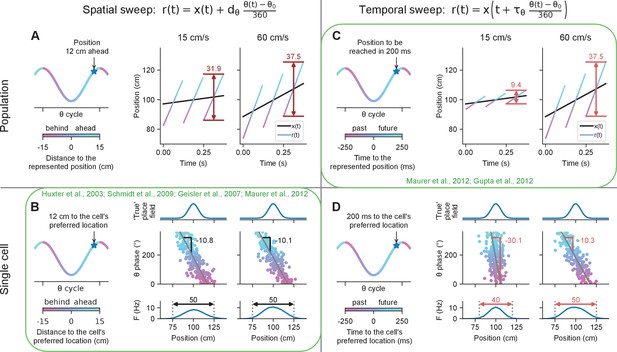
Simulated effect of running speed on population and single-cell properties in spatial sweep and temporal sweep models.
Certain findings in previous studies (green) paradoxically support the spatial sweep at the single-cell level, but the temporal sweep at the population level. (A) Left. At different phases of theta, the population represents positions shifted behind or ahead in space by fixed distances. Right. The black lines represents the rat’s actual location as it runs through a linear track; the color-coded lines indicate theta trajectories represented by the place cell population . Since each theta trajectory starts and ends at fixed distances behind and ahead of the animal’s current location, the length of a theta trajectory increases slightly with running speed (37.5 vs. 31.9 cm) to account for the animal’s motion during the span of the theta cycle. (B) Left. At the single-cell level, the phases at which a cell spikes reflect the distances to the cell’s preferred location. Right. The cell’s preferred location is defined by its underlying 'true' place field (top). The cell fires proportionally to the activation of its true place field at , generating a phase precession cloud (middle) and corresponding measured place field (bottom). Phase precession slopes and place field sizes remain constant with running speed since, e.g., the cell always starts firing at 12 cm from the cell’s preferred location. (C) Left. At different phases of theta, the population represents the positions that were or will be reached at fixed time intervals into the past or future, respectively. Right. A higher running speed leads to a proportionally increased theta trajectory length since, e.g., the position that will be reached in 200 ms is further ahead in space at higher speeds. (D) Left. At the single-cell level, the phase of theta reflects the time to reach the cell’s preferred location. Right. At higher speed, the phase precession slope becomes shallower (−10.3 vs. −30.1 °/cm) and the size of the measured place field increases (50 vs. 40 cm) since, e.g., the cell will start signaling arrival at the cell’s preferred location in 200 ms from an earlier position in space.
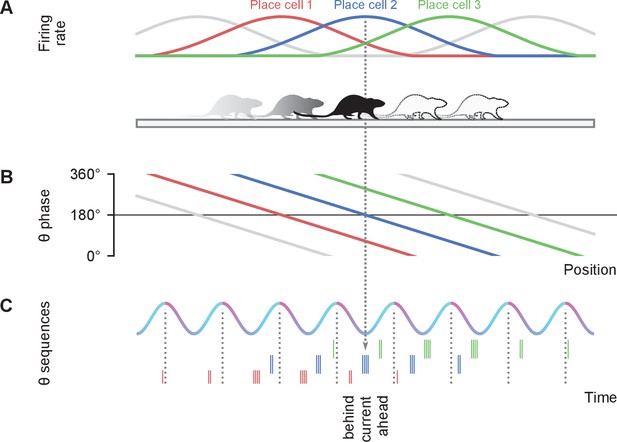
Schematic illustration of the relationship between place fields, theta phase precession, and theta sequences.
Illustration of theta phase coding in spatial navigation. (A) A rat is running from left to right on a linear track. The firing rate of three place cells are indicated in different colors. (B) The idealized theta phase vs. position relationship for the spikes emitted by each of the cells shows a decrease in phase as the animal crosses the field (theta phase precession). (C) At the population level, phase precession manifests as spike sequences that represent, in a temporally compressed fashion, the sequence of place fields being traversed. The falling edge of the oscillation holds spikes from place cells with fields centered behind the current position of the rat, followed by spikes from cells with fields centered at the current position of the rat at the trough of the oscillation, and place cells with fields centered ahead in the rising edge.
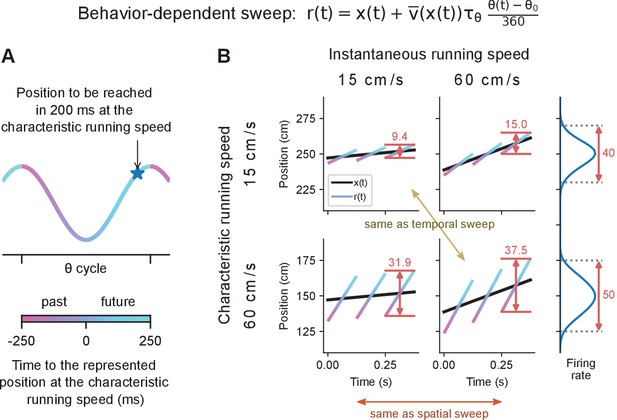
The behavior-dependent sweep integrates aspects of both spatial and temporal sweeps.
Simulated data plotted as in Figure 1A and C. (A) Different phases of theta represent positions reached at different time intervals into the past or future assuming the animal ran at the characteristic speed at that location. (B) Comparison of theta trajectory lengths in areas of low and fast characteristic running speed (rows) at low and fast instantaneous running speeds (columns). When both characteristic and instantaneous running speeds coincide, the behavior-dependent sweep model and the first-order approximation of the temporal sweep model agree (ochre arrow). On the other hand, when changing the instantaneous speed at a given location, the behavior-dependent and spatial sweeps agree (orange arrow). Theta trajectory length is primarily determined by characteristic running speed. Instantaneous running speed has a modest effect caused by the larger change in during the theta cycle at higher speeds. Place fields (right) are larger in areas of higher characteristic running speed, but do not change size with instantaneous running speed.
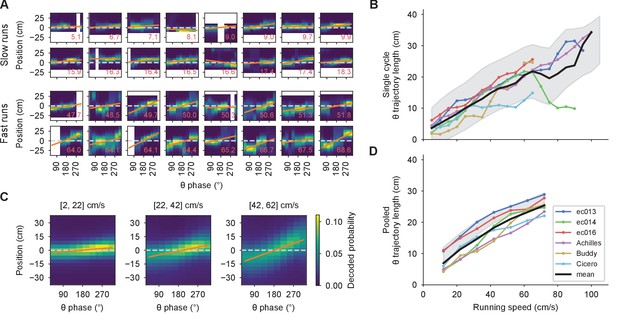
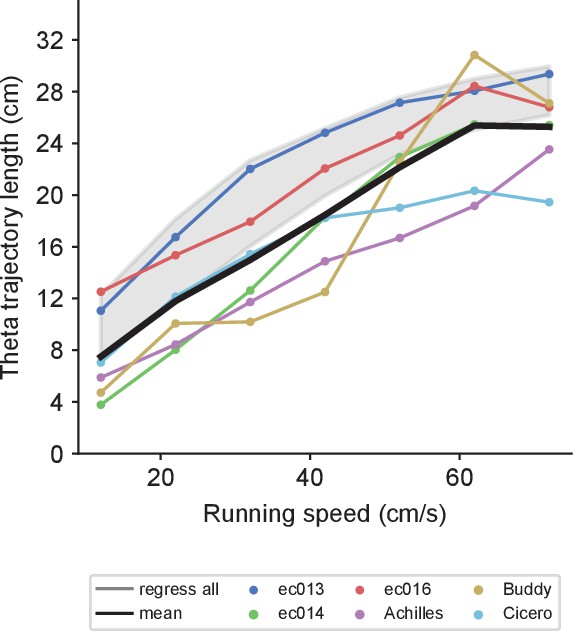
Theta trajectory lengths increase proportionally with running speed.
(A) A random sample of theta sequences from a representative experimental session, with position probabilities decoded from the population spikes. Zero corresponds to the actual position of the rat at the middle of the theta cycle; negative positions are behind and positive ones, ahead. Orange lines indicate linear fits, from which theta trajectory lengths are computed. White pixels correspond to positions outside of the track or phase bins with no spikes. The red number at the lower right corner indicates the running speed in cm/s. (B) Moving averages for theta trajectory length for each animal using a 10 cm/s wide sliding window (colored lines). These averages are averaged again (thick black line) to obtain a grand average that weighs all animals equally. Shaded region indicates a standard deviation around the mean of all data points pooled across animals, which weigh each theta sequence equally. This mean does not necessarily match the grand average since different animals contribute different numbers of theta sequences. (C) Similar to A, but averaging the decoded probabilities across theta cycles belonging to the same speed bin indicated above the panel. (D) Similar to B for the averaged cycles, confirming the observation in B.
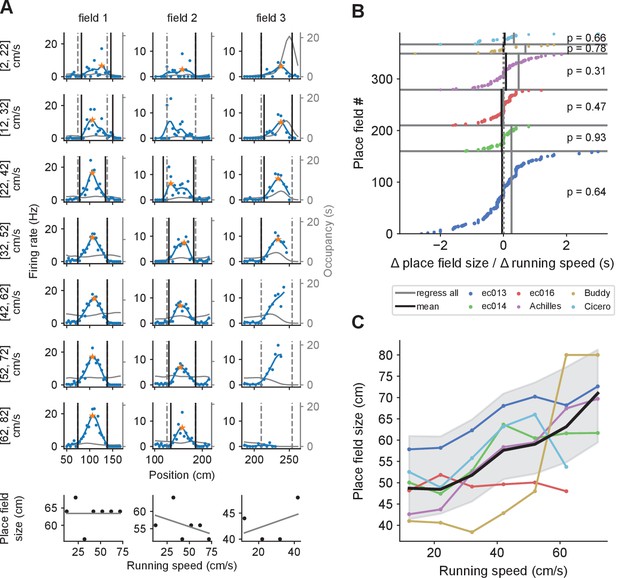
Place field size increases with running speed when combining data across fields, but not for individual fields.
(A) The size of a given place field remains roughly constant regardless of running speed in examples from three individual place fields (one per column). Dashed gray lines represent the extent of the place fields calculated from the complete set of spikes at all running speeds. Black lines mark the extent of the place field calculated for each speed bin. Where only one end of the place field could be determined (e.g., field 3, third and fourth rows), place field size was set to twice the distance from the field’s peak (orange star) to the detected field end (see Materials and methods). Thin gray lines represent the occupancy (time spent) per spatial bin (axis on the right). At the bottom, linear regressions on place field size versus running speed for each place field. Fields 2 and 3 belong to the same cell. (B) The slopes from linear regression of place field size vs. running speed for all place fields, sorted for each animal. Across the population of place fields, slopes were not significantly different from zero (indicated p values). The size of the dot reflects the number of data points that contributed to the regression. The black vertical lines indicate the weighted averages of these slopes for each animal. The gray lines indicate the slope of the regression calculated by first pooling together data points from all place fields for each animal. (C) Remarkably, when combining data across fields, the average field size generally increases as a function of running speed. Colored lines represent individual animals, and the thick black line averages over them. Shading represents the standard deviation around the mean of all data points pooled across animals.
Restricting the theta trajectory length analysis to areas covered by the place fields analyzed does not change the results meaningfully.
Theta trajectory lengths remain unchanged when restricting the analysis to theta cycles occurring in areas covered by place field analyses. Same analysis as in Figure 3D, but pooling only theta cycles occurring in portions of the track that are covered by place fields included in the place field size or phase precession slope analyses.
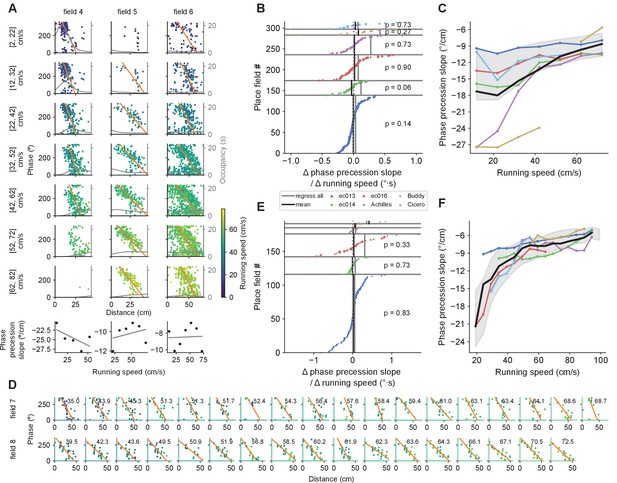
Phase precession slope increases with running speed when combining data across fields, but not for individual fields.
(A) Example phase precession slopes at different speeds for three fields. Instantaneous speeds when the spikes where emitted are color coded. Thin gray line displays the occupancy. At the bottom, linear regressions on phase precession slope versus running speed for each place field. (B) Similar to Figure 4B for the slopes of the linear regressions on phase precession slope vs. running speed for individual fields. (C) Similar to Figure 4C for phase precession slopes combined across fields for each speed bin. (D) Example phase precessions in single passes through two place fields (rows) sorted by running speed (upper right corner, in cm/s). Color code as in A. (E, F) Same as in B and C but for single-trial phase precession slopes. The means for each animal in F were calculated as a moving average on a 10 cm/s wide sliding window.
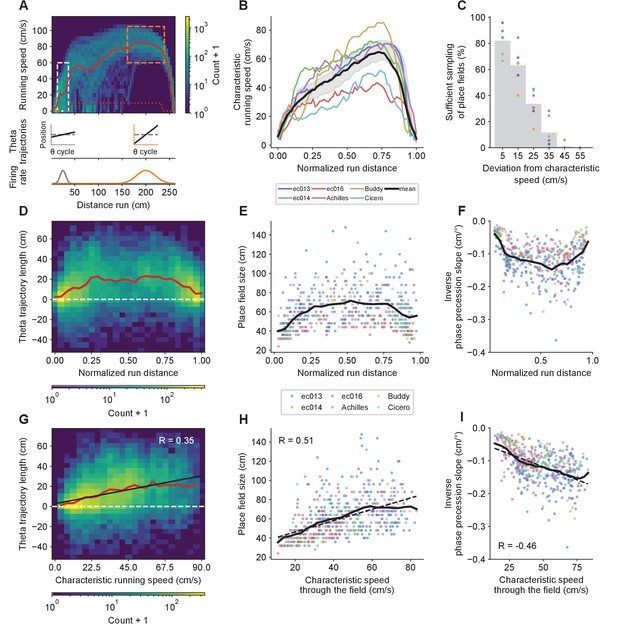
Structured place field and theta trajectory heterogeneity correlates with characteristic speed.
(A) Potential explanation for the increase in average theta trajectory length, place field size and phase precession slopes with speed despite the lack of systematic within-field changes. The histogram shows the distribution of running speeds by positions for rightward runs in one experimental session. The thick red line is the characteristic speed, defined as the mean speed after discarding trials with running speed < 10 cm/s in the center of the track (exclusion criteria indicated by dotted red line). Running speeds tend to cluster around the characteristic speed. (B) Average characteristic speed as a function of the normalized distance from the start of the run for each animal (colored lines) and the grand average across animals (thick black line). Shaded region as in Figure 3B. (C) The proportion of fields sufficiently sampled for place field analysis at a certain speed bin falls steeply with the deviation between the speed bin and the mean characteristic speed through the field. Grey bars indicate averages across animals. (D) Histogram of individual theta trajectory lengths across the track for all animals combined and their mean (red line). Negative values correspond to theta trajectories going in the opposite directional as running. (E) Place field sizes and (F) the inverse of phase precession slopes across the track for each animal (colored dots), and their moving average with a window size of 0.1 (normalized units; black lines). (G) Histogram of theta trajectory lengths (with mean [red line] and linear fit [black line]) versus characteristic running speed for locations where each trajectory was observed. (H) Place fields are larger and with (I) shallower phase precession slopes for fields with higher mean characteristic speed. Solid black lines represent moving averages with a window size of 15 cm/s, and dashed lines indicate linear fits.
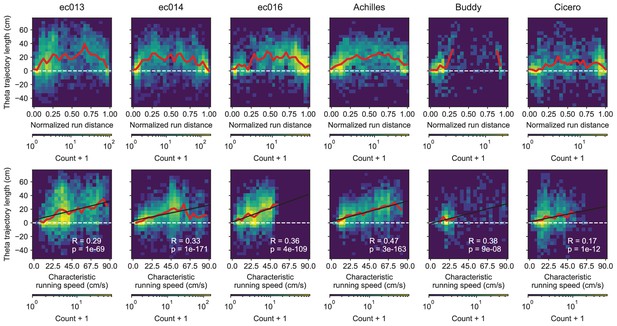
Like D, G, separated by animal.
Theta trajectory lengths vary across the track and correlate with characteristic running speed. Histograms of theta trajectory lengths as a function of normalized distance from the start of the run (first row) and characteristic running speed at the position where the theta trajectory occurred (second row). The red lines indicates mean values, and black lines, linear fits. p-Values are indicated for Kendall’s tests.
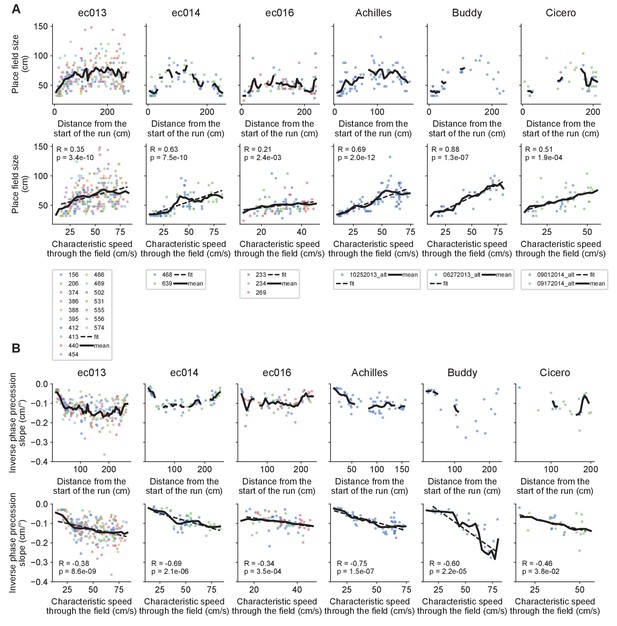
Like E, F, H, and I, separated by animal.
Place field sizes and phase precession slopes vary across the track and correlate with characteristic running speed. (A) Place field sizes as a function of distance from the start of the run (first row), and characteristic speed through the field (second row). Each column contains data for one animal. Different colors for each animal represent different experimental sessions. Each point is a place field. Thick black lines indicate moving averages with sliding windows of 15 cm and 15 cm/s for distance and speed, respectively (minimum three points per window). Dashed lines correspond to linear fits. p-Values are indicated for Kendall’s tests, null hypothesis: no association between place field size and characteristic speed. (B) Same as above but for the inverse of phase precession slopes.
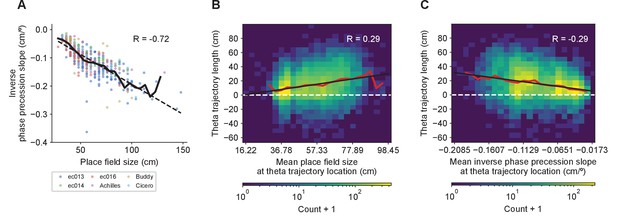
Linear relationships between place field sizes, phase precession slopes, and theta trajectory lengths.
Place field sizes, phase precession slopes, and theta trajectory lengths correlate with one another. (A) The inverse of phase precession slope correlates strongly with place field size. Colored dots indicate individual place fields from different animals. The solid line represents a moving average with a window size of 15 cm, and the dashed line, a linear fit. (B) Histogram of theta trajectory lengths as a function of the mean place field size or (C) mean inverse phase precession slope in 15 cm wide windows centered at the positions where the theta trajectories occurred (black lines in Figure 6—figure supplement 2). Changing the size of the moving average window to 10 cm/s or lower, or 20 cm/s or higher decreased the value of the correlations. The red lines indicates mean values, and black lines, linear fits.
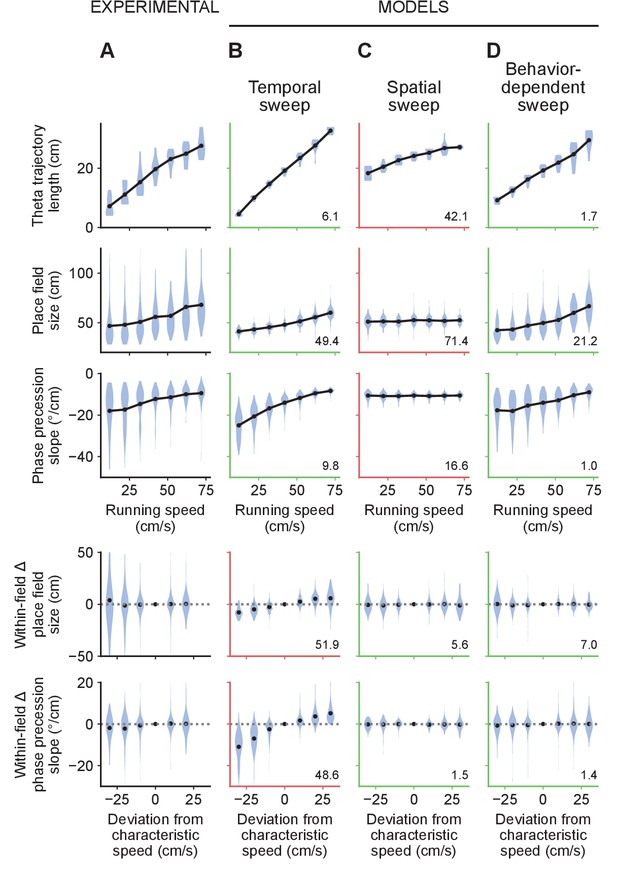
Only the behavior-dependent sweep model accounts for all experimental observations.
(A) Summary of experimental results from Figures 3–5. Results from all animals are combined. Only one animal featured more than three sessions. For this animal, we sub-selected three sessions at random so that it would not dominate the results. Top three rows: theta trajectory lengths, place field sizes and phase precession slopes combined across positions and fields based on instantaneous running speed. Bottom two rows: the changes in individual place fields’ sizes and phase precession slopes as a function of the difference between instantaneous running speed and the characteristic running speed. For this analysis, fields were assigned to the speed bins closest to the characteristic running speeds at their locations. Black dots represent average values. (B) Similar to A for data generated by the temporal sweep model. The temporal sweep model provides a qualitative fit to the average theta trajectory lengths, place field sizes and phase precession slopes, but incorrectly predicts increases in individual place field sizes and phase precession slopes. In this and other columns, green and red axes indicate good and bad qualitative fits, respectively (i.e. whether the model predicts the same type of change in the variables with speed as the experimental data exhibits) and the numbers in the lower right corners indicate the mean squared differences between the average values produced by the model and the experimental data across speed bins. (C) The spatial sweep model accounts for the lack of within-field increases in place field sizes and phase precession slopes. However, the increase in theta trajectory length with running speed is not nearly large enough and place field sizes and phase precession slopes remain flat with running speed. (D) The behavior-dependent sweep model captures both the population average and within-field effects, providing a good agreement with all experimental results.
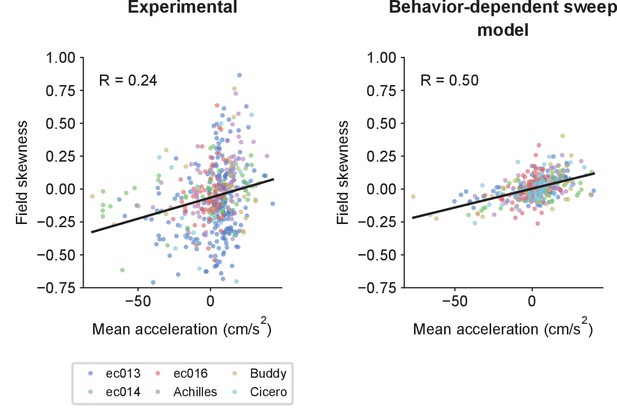
The behavior-dependent sweep model captures changes in place field skewness with acceleration.
The behavior-dependent sweep model captures changes in place field skewness with acceleration. Place field skewness is correlated with the mean acceleration through the field in the experimental data (left) and the model (right), although the experimental distribution is notably broader. Black lines represent linear fits. The correlations are significant ( and for the experimental and simulated data, respectively [Kendall’s test]).
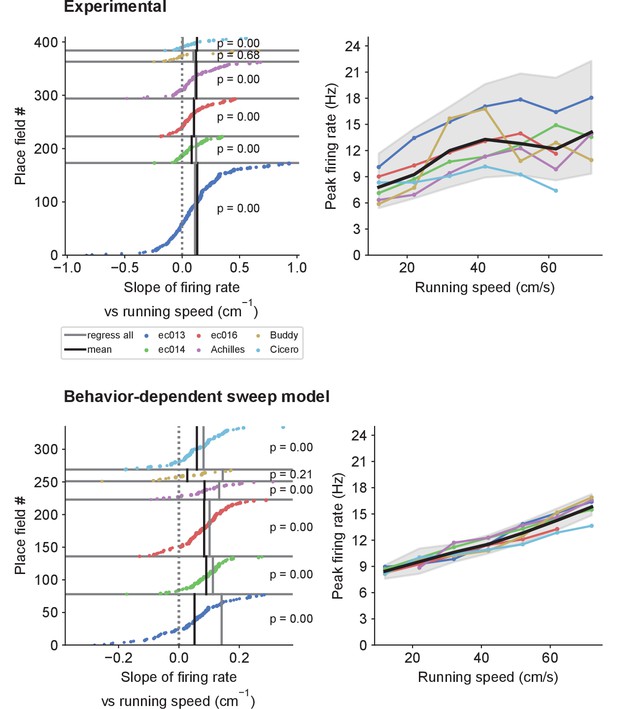
The behavior-dependent sweep model captures changes in peak firing rates with speed.
The behavior-dependent sweep model replicates the experimentally observed increase in firing rates with running speed. Analyses and plotting conventions as for Figure 4B & C, for the peak firing rate of place fields.
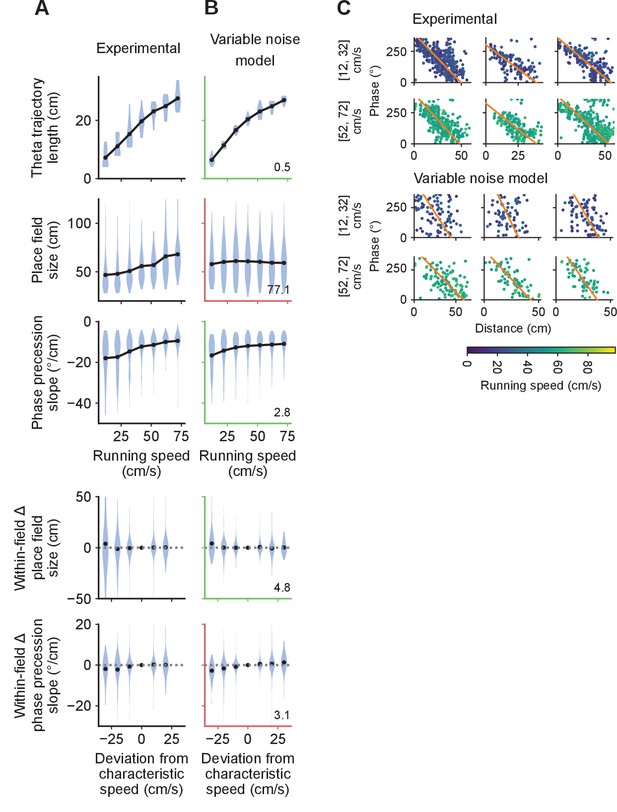
Variable theta phase locking fails to account for the combination of population and single-cell results.
(A, B) Comparison of experimental and simulated data produced by a model with constant but variable theta phase noise. Plotting conventions as in Figure 7. The variable noise model does a good job at capturing the increase in theta trajectory lengths and phase precession slopes with running speed, but it does so at the cost of modest within-field changes in phase precession slopes and without capturing any of the increase in place field sizes. (C) Example phase precession clouds at low and high speeds for experimental and modeled place fields. Each column corresponds to a cell. The variable noise model introduces an atypically large amount of noise at low speeds as compared to the experimental data.
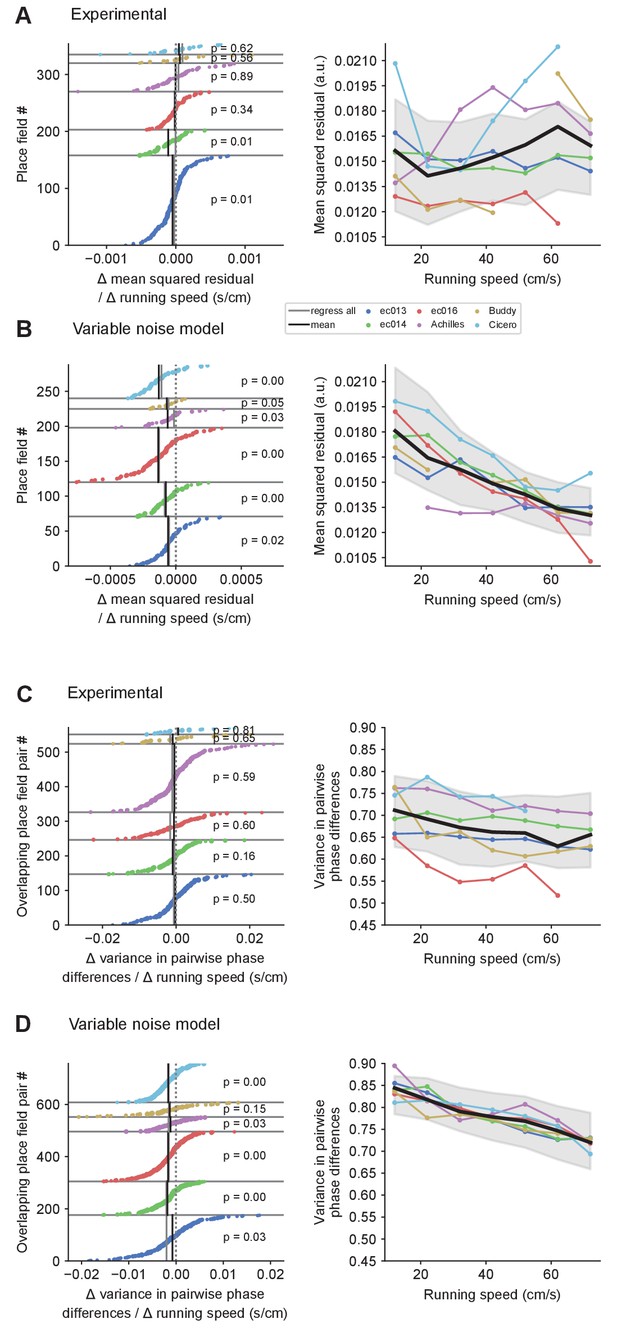
Theta phase locking and theta timescale coordination between cells vary with speed in the variable noise model but not in the experimental data.
(A, B) The effect of speed on the residuals of the phase precession cloud fits (i.e. mean squared orthogonal distances from the points to the fitting line). The fits are calculated after normalizing the place field size and the phase precession range (360°) to 1, so the residuals are dimensionless. In the variable noise model, the residuals decrease systematically with speed, as the phase vs. position relationship of spikes becomes sharper. This relationship, however, is not clear in the experimental data. Plotting conventions as for Figure 4B,C. (C, D) The effect of speed on the circular variance in phase differences between spikes emitted by pairs of cells with overlapping place fields. The variable noise model produces atypically high variance, and the variance tends to decrease with speed for individual cell pairs, which is not the case for the experimental data.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Summary of statistical tests.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70296/elife-70296-supp1-v2.ods
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70296/elife-70296-transrepform-v2.docx





