iMyoblasts for ex vivo and in vivo investigations of human myogenesis and disease modeling
Figures
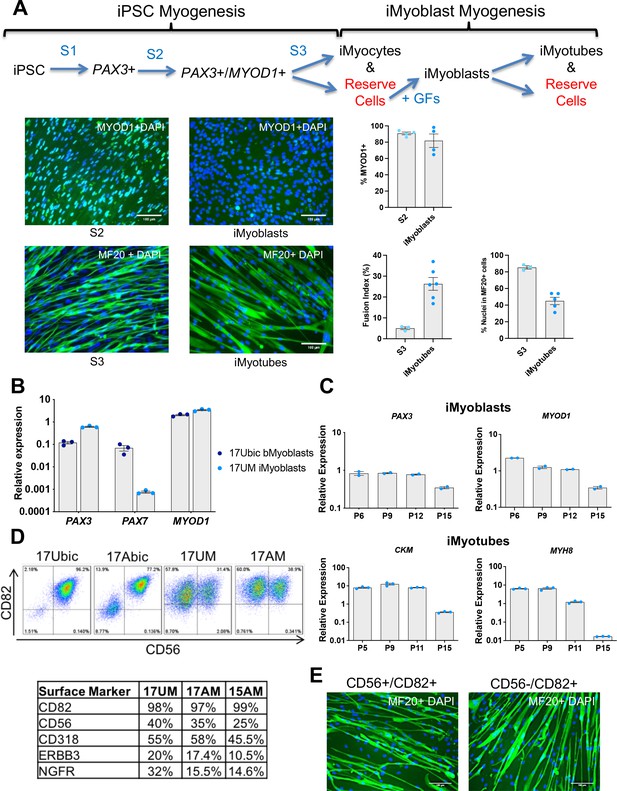
Isolation and characterization of iMyoblasts.
(A) Schematic of a three-stage transgene-free iPSC induction, iMyoblast reserve cell isolation, and iMyotube differentiation protocol. Images of S2 cells and iMyoblasts immunostained with MYOD1 antibody, and S3 iMyocytes and iMyotubes immunostained with MF20 myosin antibody. Nuclei are stained with DAPI. Scale bars=100 µm. Quantification of % MYOD1+ S2 cells and iMyoblasts, fusion index (the percentage of nuclei within MF20+ cells containing ≥2 nuclei ) and % nuclei within MF20+ cells for S3 cells and iMyotubes are shown on the right. For quantification, each dot corresponds to the % MYOD1+ cells or fusion index in an individual image. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each condition. (B) qPCR assays of PAX3, PAX7, and MYOD1 in bMyoblasts (17Ubic) and iMyoblasts (17UM) normalized to RPL13A. (C) qPCR assays normalized to RPL13A of proliferating (top, iMyoblasts) or Day 7 differentiated (bottom, iMyotubes) Ctrl 17UM iMyotubes with increasing passage (P) numbers. (D) Flow cytometry of CD56 and CD82 cell surface markers for bMyoblasts (17Ubic, 17Abic) and iMyoblasts (17UM, 17AM). Table below summarizes flow cytometry assays of iMyoblast surface markers in Ctrl (17UM) and FSHD1 (17AM, 15AM) cell lines. (E) MF20 immunostaining of CD56+/CD82+ or CD56-/CD82+ Ctrl (17UM) iMyotubes after 7 days of differentiation. Scale bars=100 µm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx

Transgene-free myogenic induction of FSHD1 and Ctrl iPSC and ESC and FKRP LGMDR9 and LGMDR7 iPSCs.
(A) Three-stage transgene-free myogenic induction (Caron et al., 2016). (B) Normalized qPCR assays of PAX3, PAX7, MYOD1, and MYH8 RNAs during myogenic induction of FSHD1 (pink) and Ctrl (teal) ESCs, FSHD1 (red) and Ctrl (blue) iPSCs, and FKRP LGMDR9 (dark green) and LGMDR7 iPSCs (light green). Expression relative to RPL13A. Symbols: 17 cohort=circle, 15 cohort=square, 30 cohort=diamond. iPSCs reprogrammed from bMyoblasts have colored symbols. iPSC reprogrammed from primary fibroblasts (15AF, 15VF, and 17AF) have black symbols. For ESC lines: Genea 002=filled, up triangle, Genea 015=filled, down triangle, Genea 019=filled hexagon, Genea 049=open, up triangle, Genea 050=open, down triangle, and Genea 096=open hexagon.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
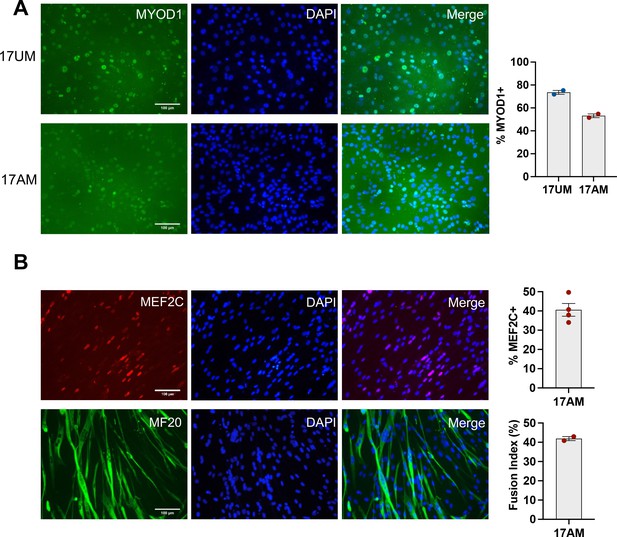
Reserve cell isolation of induced tertiary Myoblasts.
(A) Ctrl (17UM) and FSHD1 (17AM) tertiary iMyoblast cell lines isolated from iMyotube cultures using reserve cell selection and cultured for three passages in bMyoblast growth medium followed by MYOD1 immunostaining. Quantification of % MYOD1+ cells is shown on the right. Each dot represents the percentage of MYOD1 expressing nuclei in an individual image. (B) FSHD1 (17AM) tertiary iMyotube cultures cultured for 4 days in N2 serum-free differentiation medium followed by MEF2C and MF20 immunostaining. Scale bar=100 µm. Quantification of % MEF2C+ cells and fusion index for 17AM tertiary iMyotubes is shown on the right.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
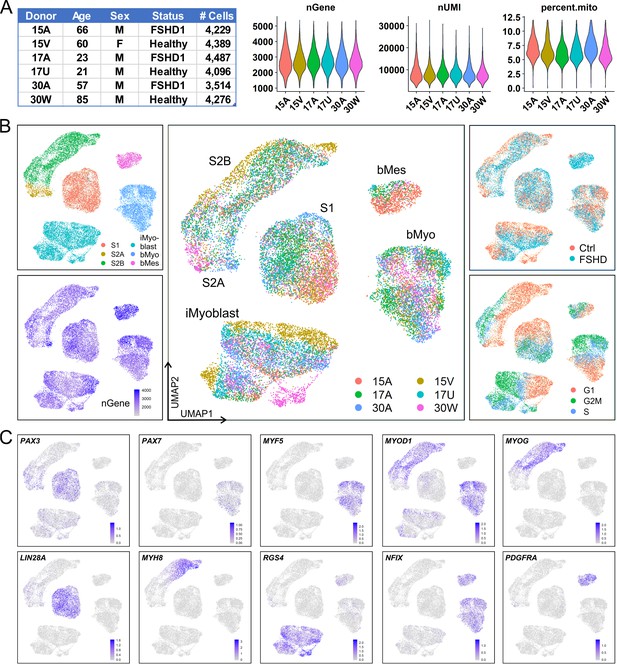
iMyoblasts have a distinct gene expression signature compared to S1, S2, and muscle biopsy cells.
(A) Single-cell transcriptome sequencing (scRNA-Seq) was performed on S1, S2, iMyoblasts and bMyoblasts from three FSHD1 and three healthy (Ctrl) donors. A total of 24,991 cells satisfied criteria that included 1000–5500 genes detected per cell (nGene), <40,000 UMI detected per cell (nUMI), and <12% of total reads from mitochondrial genes. (B) iPSC-induced S1 and S2 cultures, iMyoblasts and primary biopsy cultures segregated into distinct clusters in UMAP plot (upper left panel). S2 cells were segregated into S2A and S2B subclusters. Biopsy cells were segregated into a myogenic cell cluster (bMyo) and a non-myogenic mesodermal cell cluster (bMes). UMAP plots with color-scales indicating nGene, donor identities, disease group, and estimation of cell cycle state for each cell are also shown. (C) Expression of representative myogenesis and cluster marker genes in UMAP plots.
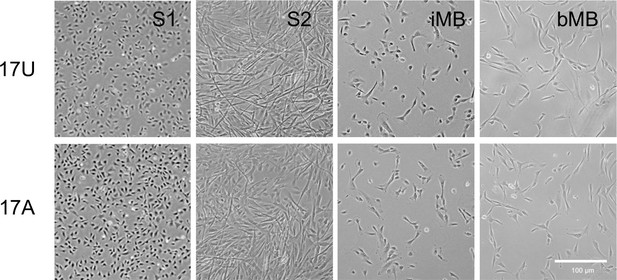
Morphology of different cell classes used in scRNA-Seq.
Phase images of S1, S2, iMyoblast (iMB), and bMyoblast (bMB) of cohort 17. Scale bar=100 µm.

scRNA-seq transcriptome signatures of iMyoblasts from FSHD1 and Ctrl subjects compared to S1, S2A, S2B, bMyo, and bMes myogenic cell classes.
Dot plot of manually curated genes in cells from six different subjects for each of the six cell classes (bottom row). Purple to orange colors define the low to high average expression of each gene (vertical row) in cells of each subject in each of the six cell classes (columns), centered to have mean=0 and scaled to have SD=1; positive values indicate upregulation and negative values indicate downregulation compared to the average expression across all cell groups. Dot sizes indicate the fraction of cells expressing each gene.
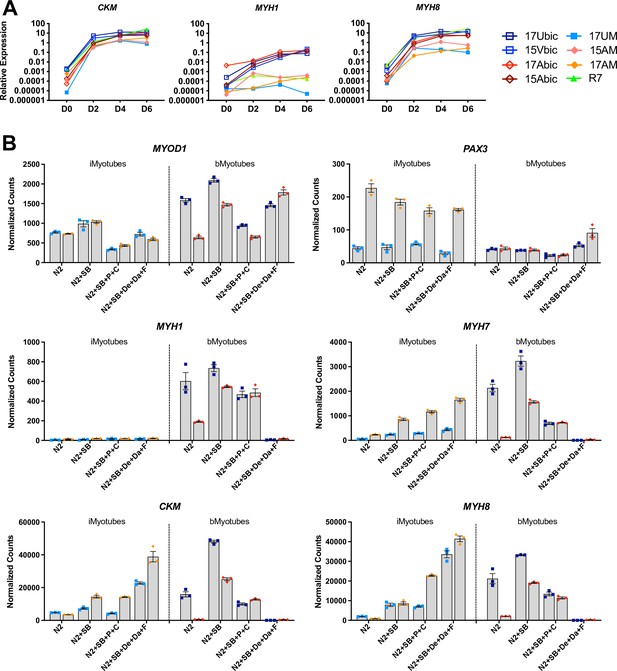
iMyoblasts upregulated muscle genes during ex vivo differentiation in response to specialized differentiation media.
(A) Normalized qPCR assays of muscle RNAs CKM, MYH1, and MYH8 in cultures of bMyoblasts and iMyoblasts from FSHD1, Ctrl, and LGMDR7 iPSCs during their differentiation for 6 days (D) in N2 serum-free medium. (B) NanoString digital RNA assays comparing the expression of MYOD1, PAX3, MYH1, MYH7, MYH8, and CKM in FSHD1 and Ctrl iMyotubes and bMyotubes of cohort 17 in response to N2 serum-free culture medium and N2 medium supplemented with signaling regulators as described in the text. NanoString digital counts were normalized to RPL13A and are shown on a linear scale. Each dot corresponds to an individual culture. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each condition.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
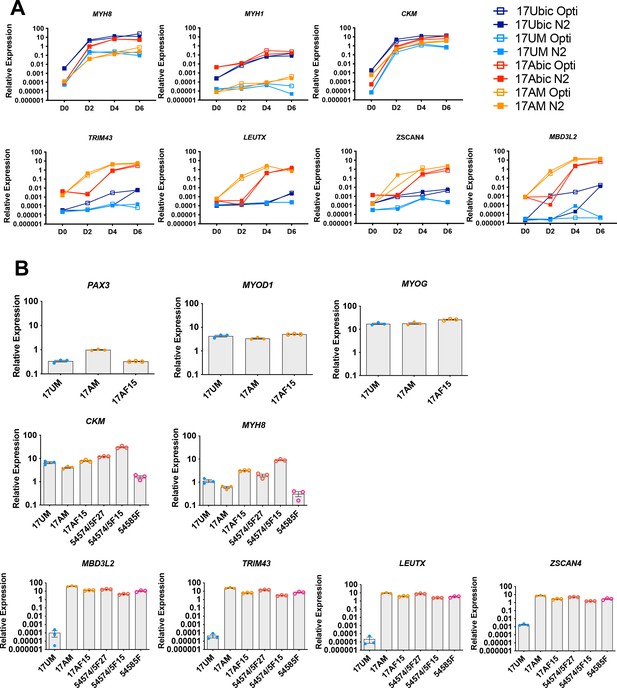
Effects of serum-free media and iPSC reprogramming on muscle and DUX4 target gene expression.
(A) Normalized qPCR assays of the expression of muscle and DUX4 target genes during the myotube differentiation of FSHD1 and Ctrl bMyoblasts and iMyoblasts at Days 0, 2, 4, and 6, comparing Opti-MEM and N2 serum-free differentiation media. The N2 medium results are also shown in Figure 4A, Opti-MEM is shown here to provide a comparison to N2 medium. (B) qPCR assays comparing muscle and DUX4 target gene expression in FSHD and Ctrl iMyotubes generated from iPSC lines derived by reprogramming CD56+ muscle biopsy bMyoblasts (17UM, 17AM), CD56− muscle biopsy fibroblasts (17AF15), and skin fibroblasts (54574/5F, 54585F).
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
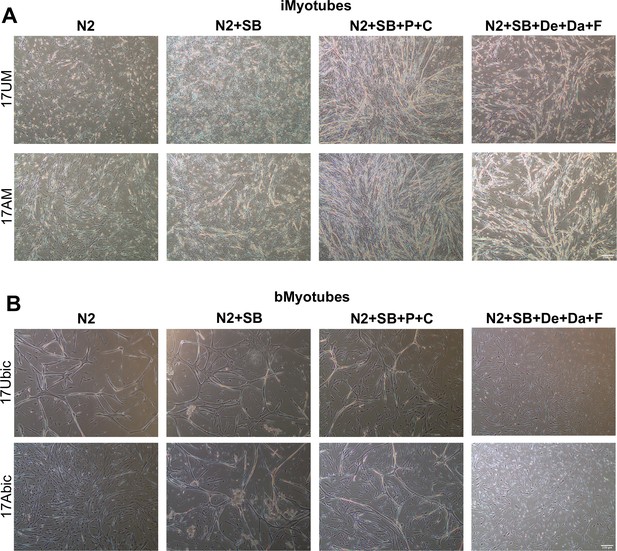
iMyotubes and bMyotubes respond differently to specialized differentiation media.
Phase images of Ctrl and FSHD1 (A) iMyotubes and (B) bMyotubes after differentiation in designated specialized differentiation media cocktails described in text. Scale bar=250µm.
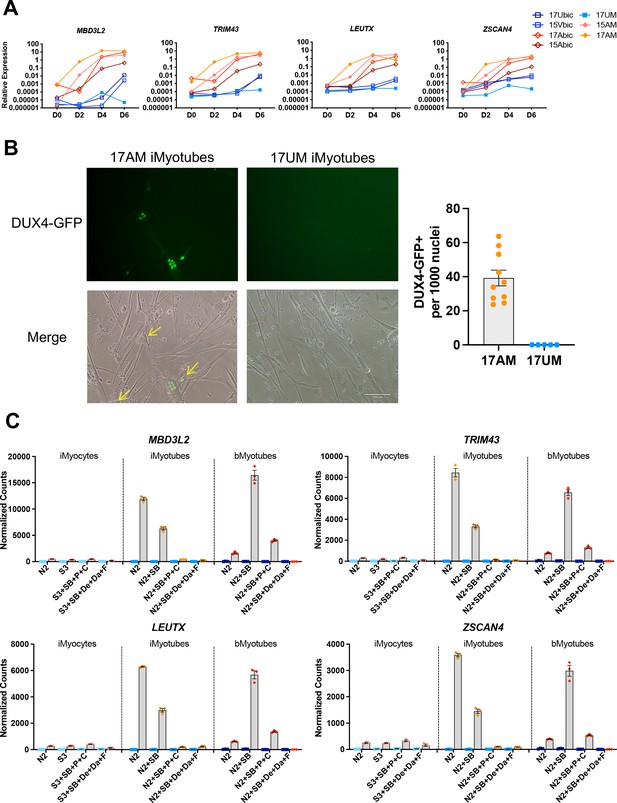
DUX4 and DUX4 target gene expression by iMyotubes, bMyotubes, and S3 iMyocytes in response to differentiation media.
(A) Normalized qPCR assays of DUX4 target genes MBD3L2, TRIM43, LEUTX, and ZSCAN4 in cultures of bMyoblasts and iMyoblasts of family cohorts 17 and 15 during differentiation for 6 days (D) in N2 serum-free medium. (B) DUX4-GFP reporter expression in FSHD1 bMyotubes (17Abic), FSHD1 iMyotubes (17AM), and Ctrl iMyotubes (17UM) after 7 days of differentiation. Scale bar=100 µm and quantification of DUX4 GFP+ nuclei/1000 nuclei/field is shown to the right. (C) NanoString digital RNA assays comparing the expression of DUX4 target gene RNAs in FSHD1 and Ctrl S3 iMyocytes, iMyotubes, and bMyotubes of cohort 17 in response to N2 serum-free culture medium and N2 medium supplemented with signaling regulators, as described in the text. NanoString digital counts were normalized to RPL13A and are shown on a linear scale. Each dot corresponds to an individual culture. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each condition.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
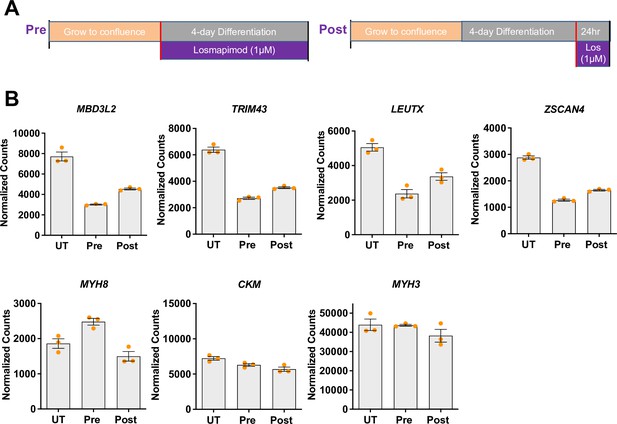
Losmapimod treatment decreases DUX4 target gene expression in FSHD1 iMyotubes.
(A) Schematic of Losmapimod treatment protocols for Pre-drug administration at the initiation of iMyotube differentiation and Post-drug administration after 4 days of iMyotube differentiation in N2 differentiation medium. (B) NanoString digital assays of DUX4 target gene and muscle gene expression in carrier treated (UT) FSHD1 iMyoblasts and treated iMyotube cultures Pre- or Post-drug treatment with 1µM Losmapimod. Normalized counts of expression are on linear scale with each dot corresponding to an individual culture. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each condition.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
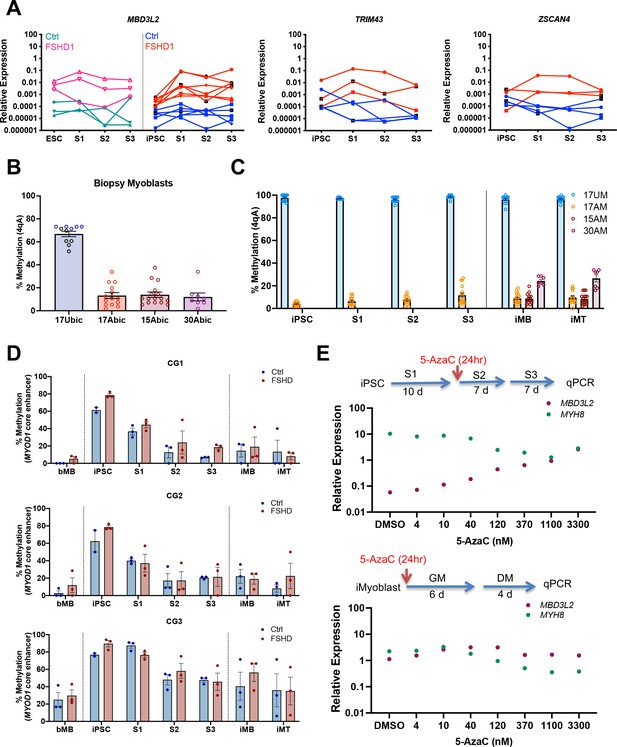
Epigenetic regulation of DUX4 and MYOD1 during iPSC reprogramming and iMyocyte and iMyotube differentiation.
(A) Normalized qPCR assays of DUX4 target genes MBD3L2, ZSCAN4, and TRIM43 during myogenic induction of FSHD1 and Ctrl ESC or iPSC. (B) Bisulfite sequencing of the DUX4 4qA locus in bMyoblasts from Ctrl (17Ubic) and FSHD1 subjects (15Abic, 17Abic, and 30Abic), shown as % 4qA CpG sites methylated. Each dot corresponds to the % CpG methylation of an individually sequenced DNA clone. (C) Bisulfite sequencing of DUX4 4qA alleles of iPSCs reprogrammed from parental bMyoblasts of Ctrl (17UM) and FSHD1 (17AM, 15AM, and 30AM) subjects, shown as % CpG methylation of DUX4 4qA alleles in iPSC, S1, S2, S3, and in iMyoblasts (iMB) and iMyotube (iMT) derived from these iPSC lines. (D) Bisulfite sequencing of MYOD1 Core Enhancer, showing the % methylation of the three MYOD1 core enhancer CpG sites (CG1, CG2, and CG3) from parental bMyoblasts (bMB) (15A, 17A, 30A, 15V, 17U, and 30W), reprogrammed iPSCs, cells at S1, S2, and S3 stages of primary myogenic induction, and iMyoblast (iMB) cell lines derived from these iPSC lines. Each dot corresponds to the average methylation of 10 sequenced DNA clones for each cell stage. (E) Normalized qPCR assays of the DUX4 target gene MBD3L2 and the MYH8 muscle RNA in S3 cultures (top panel) and iMyotube cultures (bottom panel) following treatment with increasing doses of 5-AzaC. Proliferating S2 cultures treated for 24 hr with 5-AzaC were cultured for 6 days in S2 growth medium followed by culture for 7 days in S3 differentiation medium for RNA isolation and qPCR. Proliferating cultures of iMyoblasts were treated for 24 hr with 5-AzaC and then cultured for 6 days in bMyoblast growth medium followed by culture for 4 days in Opti-MEM differentiation medium for RNA isolation and qPCR.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Source data for Figure 6.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
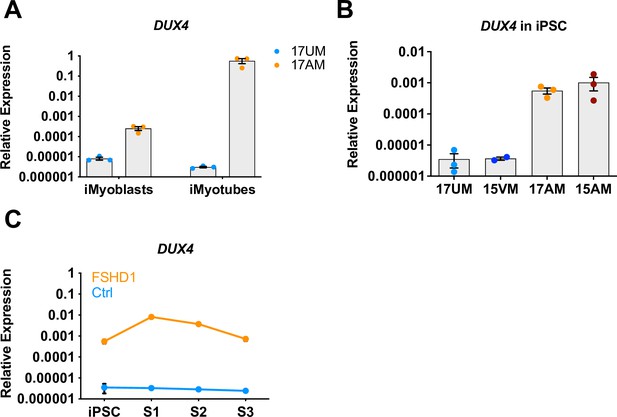
DUX4 expression by FSHD1 and Ctrl iPSCs and iMyoblasts and bMyoblasts.
(A) Normalized qPCR assays of DUX4 RNA expressed by Ctrl (17UM) and FSHD (17AM) in proliferating iMyoblasts and iMyotubes after 7 days in serum-free Opti-MEM differentiation medium. (B) Normalized qPCR assays of DUX4 expressed by Ctrl (17UM and 15VM) and FSHD1 (17AM and 15AM) iPSC lines. (C) Normalized qPCR assays of DUX4 RNA expression during myogenic induction in FSHD1 and Ctrl iPSC. All qPCR data are shown relative to RPL13A.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
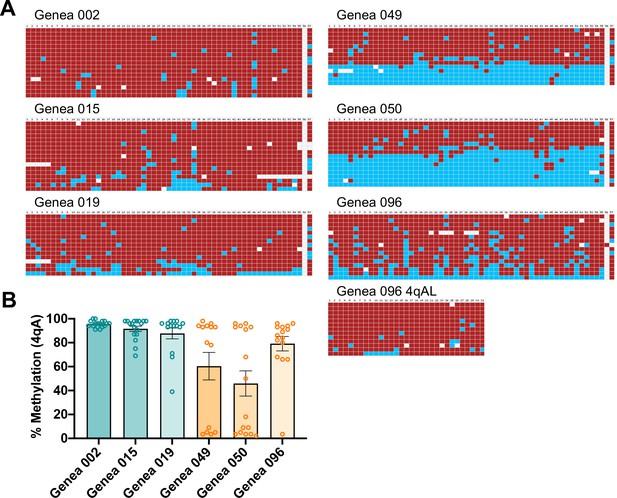
CpG methylation of the 4qA allele of FSHD1 and Ctrl ESCs.
Bisulfite sequencing of the DUX4 4qA alleles of Genea Biocells' three Ctrl and three FSHD1 ESCs. (A) Bisulfite sequencing showing CpG methylated (red) and unmethylated (blue) CpG sites in DNA molecules amplified from the DUX4 4qA or 4qAL alleles for each ESC line. Each row represents CpG sites along the DUX4 4qA DNA sequence. Note that if contracted and non-contracted alleles from an ESC line both have a 4qA haplotype, the DNA clones would be recovered and sequenced from either allele in roughly equal proportions and would result in a bimodal distribution of DNA sequences with hypo- and hyper-methylation, as seen for Genea 049 and 050. Because Genea 096 showed neither hypomethylation nor clear bimodality (excluding one outlier clone, an unlikely split of sampling from two alleles with equal probability), a 4qA-L methylation assay was also performed for this sample, as this haplotype can also be permissive for FSHD1. Neither the 4qA nor the 4qA-L assay of Genea 096 showed evidence of a hypomethylated allele, consistent with the lower level expression of DUX4 in this ESC line (Figure 6A). (B) Graphical representation of the CpG methylation data in (A) where each dot represents the % CpG methylation of the sequence of one DNA clone. Teal are Ctrl and orange are FSHD1. Data are shown as mean ± SEM for each cell line.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 6—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
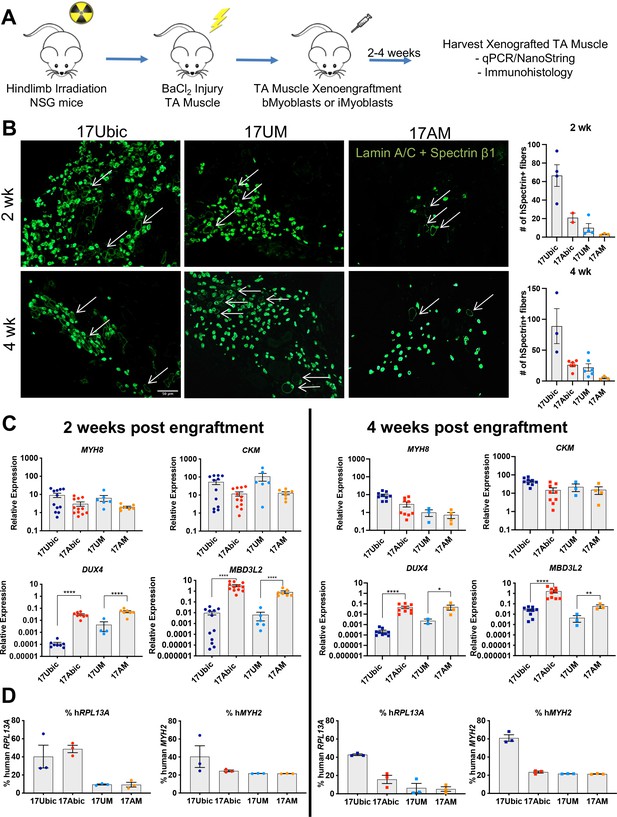
In vivo differentiation of FSHD1 and Ctrl iMyoblasts in muscle xenografts.
(A) Schematic of muscle xenograft protocol. (B) Representative cryosections of 2 and 4 weeks Ctrl bMyoblasts (17Ubic) and Ctrl and FSHD1 iMyoblasts (17UM and 17AM) xenoengrafted TA muscles were immunostained with human-specific lamin A/C and spectrin-β1. Quantification for # of spectrin+ fibers for each condition is shown on the right. White arrows highlight human spectrin+ fibers. Scale bar=100 µm. (C) Normalized qPCR assays of the expression of DUX4, MBD3L2, MYH8, and CKM. *=p<0.05, **=p<0.01, ****=p<0.0001. (D) Percentage of human RPL13A and MYH2 NanoString counts was calculated for each condition. Each dot corresponds to RNA from one xenografted mouse TA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each xenoengrafted condition.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Source data for Figure 7.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig7-data1-v1.xlsx
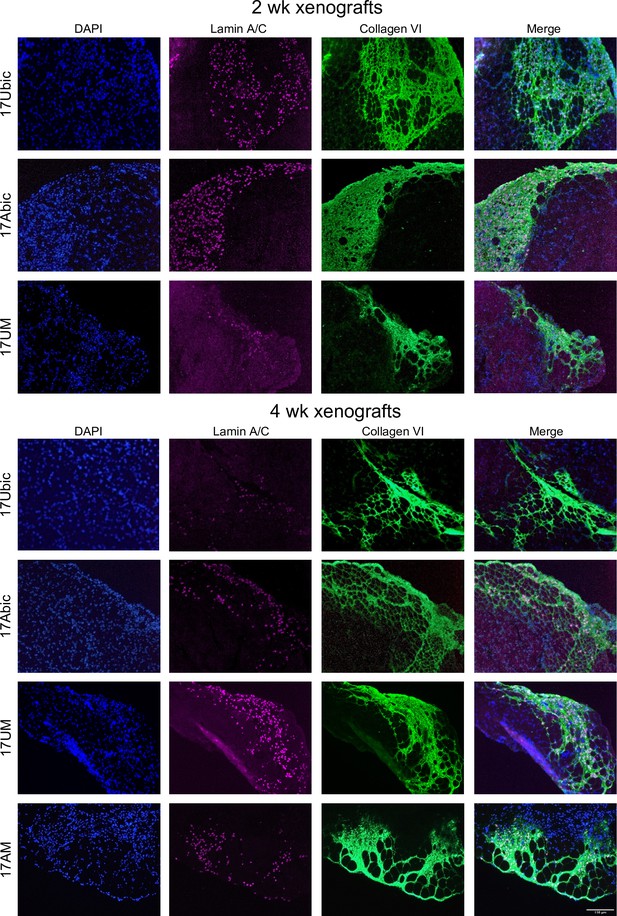
bMyoblasts and iMyoblasts efficiently xenoengraft into irradiated and injured TA muscle of NSG mice.
Cryosections of TA muscles were xenoengrafted with Ctrl (17Ubic) and FSHD (17Abic) bMyo and Ctrl (17UM) and FSHD (17AM) iMyoblasts. Xenografted TAs recovered 2 weeks (top panel) or 4 weeks (bottom panel) after muscle xenoengraftment and immunostained with human-specific lamin A/C and collagen VI antibodies. Scale bar=150 µm.
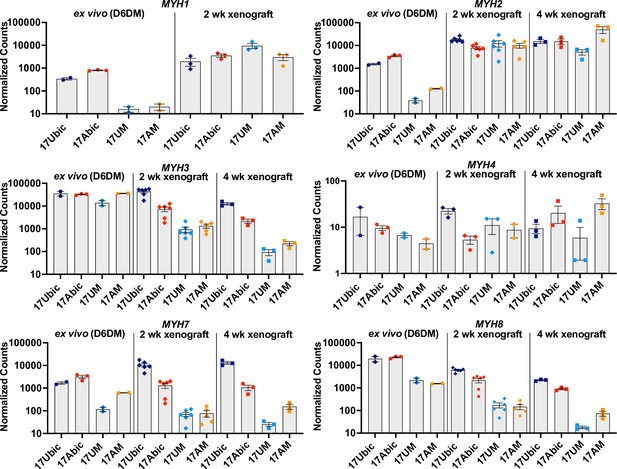
Embryonic/adult MYH isoform switching during maturation of iMyoblast and bMyoblast muscle xenografts.
NanoString digital assays of the expression of MYH isoforms in cultures of FSHD1 (17Abic) and Ctrl (17Ubic) bMyotubes and FSHD1 (17AM) and Ctrl (17UM) iMyotubes at Day 6 differentiation in Opti-MEM (D6DM), compared to MYH isoform expression in 2 and 4 weeks TA muscle xenografts of these same cell-lines. Digital counts were normalized to a panel of four human-specific housekeeping genes and plotted on a log10 scale. Each dot corresponds to RNA from one xenoengrafted mouse TA muscle (2 and 4 weeks xenograft) or one ex vivo bMyotube or iMyotube culture. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each cell or xenograft sample.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Source data for Figure 8.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig8-data1-v1.xlsx
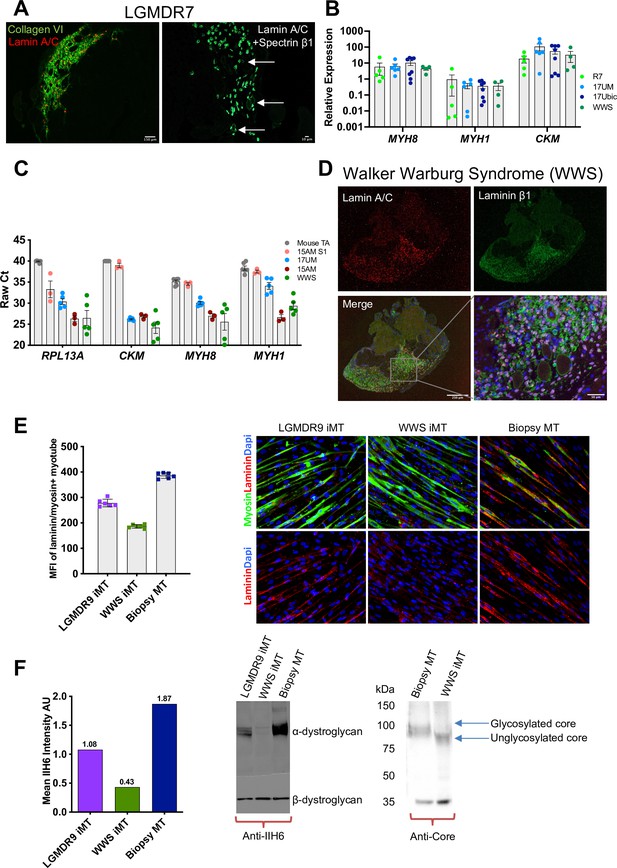
iMyoblast modeling LGMDR7 and FKRP dystroglycanopathies.
(A) Representative images from LGMDR7 muscle xenograft cryosections immunostained with human-specific antibodies (left) lamin A/C (red) and collagen VI (green) or (right) lamin A/C and spectrin β1 (green). Scale bar=150 µm and 10 µm. Arrows identify spectrin+ fibers. (B) Normalized qPCR assays of muscle RNAs 3 weeks after engraftment of bMyoblasts (17Ubic) or iMyoblasts (17UM, LGMDR7, WWS). Each dot corresponds to RNA from one xenografted mouse TA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (C) Raw Ct values comparing engraftment of S1 cells to Ctrl, FSHD1, LGMDR7, and WWS iMyoblasts and control unengrafted mouse TA using human-specific RPL13A, CKM, MYH8, and MYH1. (D) Representative images of cryosections of WWS iMyoblast engrafted TA xenograft muscles immunostained with human lamin A/C and human laminin β1. Scale bar=250 µm, inset scale bar=50 µm. (E) Representative images from bMyotube (biopsy MT) or FKRP disease iMyotube cultures (LGMDR9 iMT and WWS iMT) immunostained with laminin (red) and myosin (green) antibodies, and DAPI (blue). The mean fluorescent intensity averaged from multiple fields of view for each condition is shown on the left. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (F) Western blot assays of the expression of α-DG and β-DG in biopsy MTs, WWS, and LGMDR9 iMyotubes (iMT) using glycosylation-specific IIH6 antibody and Core Dystroglycan antibody. Mean intensity of α-DG for IIH6 is shown on the left.
-
Figure 9—source data 1
Source data for Figure 9.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig9-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 9—source data 2
Source data for Figure 9F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig9-data2-v1.pptx
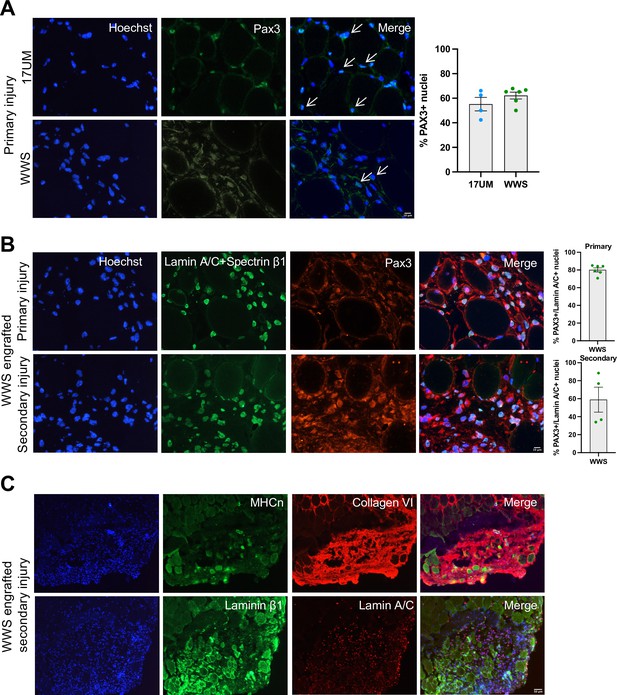
iMyoblasts have regenerative potential after secondary muscle injury.
(A) Representative images from 17UM and WWS muscle xenograft cryosections immunostained with PAX3 and stained with Hoechst. The percentage of PAX3+ nuclei is shown on the right. N=4, 17UM engrafted sections and 6, WWS engrafted sections. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each engraftment condition. Scale bar=10 µm. (B) Representative images from primary and secondary injury WWS muscle xenograft cryosections immunostained with PAX3 (red), lamin A/C and spectrin-β1 (green), and stained with Hoechst. N=6, primary injury WWS engrafted sections and 4, secondary injury WWS engrafted sections. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each engraftment condition. Scale bar=10 µm. (C) Representative images from secondary injury WWS muscle xenograft cryosections immunostained with human-specific (TOP) neonatal myosin heavy chain (MHCn) (green), collagen VI (red) and stained with Hoechst or (BOTTOM) laminin β1 (green), lamin A/C (red) and stained with Hoechst. Scale bar=50 µm.
-
Figure 10—source data 1
Source data for Figure 10.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-fig10-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIL2rγtmiWjl/SzJ | Jackson Lab | Stock No: 005557 | |
| Cell line(Homo sapiens) | 15Abic biopsy myoblast | Homma et al., 2012; Jones et al., 2012 | ||
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 15Vbic biopsy myoblast | Homma et al., 2012; Jones et al., 2012 | ||
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 17Abic biopsy myoblast | Jones et al., 2012 | ||
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 17Ubic biopsy myoblast | Jones et al., 2012 | ||
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 30Abic biopsy myoblast | Jones et al., 2012 | ||
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 30Wbic biopsy myoblast | University of Massachusetts Medical School https://www.umassmed.edu/wellstone/ | ||
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 15AM iPSCs | This paper | 15AM iPSCs were reprogrammed from 15Abic biopsy CD56+ myoblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 15VM iPSCs | This paper | 15VM iPSCs were reprogrammed from 15Vbic biopsy CD56+ myoblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 17AM iPSCs | This paper | 17AM iPSCs were reprogrammed from 17Abic biopsy CD56+ myoblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 17AF iPSCs | This paper | 17UM iPSCs were reprogrammed from 17Abic biopsy CD56- fibroblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 17UM iPSCs | This paper | 17UM iPSCs were reprogrammed from 17Ubic biopsy CD56+ myoblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 30AM iPSCs | This paper | 30AM iPSCs were reprogrammed from 30Abic biopsy CD56+ myoblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 30WM iPSCs | This paper | 30WM iPSCs were reprogrammed from 30Wbic biopsy CD56+ myoblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 54574/75 iPSCs | This paper | 54574/75 iPSCs were reprogrammed from skin fibroblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 54585 iPSCs | This paper | 54585 iPSCs were reprogrammed from skin fibroblast at UMMS | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | LGMDR7 iPSCs | Formerly LGMD2G (Iyer et al., 2019) | ||
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | LGMDR9 FP iPSCs | This paper | FP iPSCs were reprogrammed from skin fibroblast at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | WWS iPSCs | This paper | WWS iPSCs were reprogrammed from skin fibroblast at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 15AM iMyoblasts | This paper | 15AM iMyoblasts were made from 15AM iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 15VM iMyoblasts | This paper | 15VM iMyoblasts were made from 15VM iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 17AM iMyoblasts | This paper | 17AM iMyoblasts were made from 17AM iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 17AF iMyoblasts | This paper | 17AF iMyoblasts were made from 17AF iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 17UM iMyoblasts | This paper | 17UM iMyoblasts were made from 17UM iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 30AM iMyoblasts | This paper | 30AM iMyoblasts were made from 30AM iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 30WM iMyoblasts | This paper | 30WM iMyoblasts were made from 30WM iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 54574/75 iMyoblasts | This paper | 54574/75 iMyoblasts were made from 30WM iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | 54585 iMyoblasts | This paper | 54585 iMyoblasts were made from 54585 iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | LGMDR7 iMyoblasts | This paper | LGMDR7 iMyoblasts were made from LGMDR7 iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | LGMDR9 FP iMyoblast | This paper | LGMDR9 FP iMyoblasts were made from LGMDR9 iPSCs | |
| Cell line(H. sapiens) | WWS iMyoblasts | This paper | WWS iMyoblasts were made from WWS iPSCs | |
| Antibody | MyoD1 (Clone: 5.8A) (Mouse Monoclonal) | Dako | Cat #: M3512 | IF (1:50) |
| Antibody | MF20 (Mouse Monoclonal) | DSHB | Cat #: AB_2147781 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | MEF2C (Rabbit polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat #: HPA005533 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Collagen Type VI (Mouse Monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat #: MAB1944 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Lamin A/C (Mouse Monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat #: MA3-1000 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Laminin β1 (clone 4E10) | MilliporeSigma | Cat #: MAB1921P | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Myosin heavy chain, neonatal | Leica Biosystems | Cat #: NCL-MHCn | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | PAX3 | Abcam | Cat #: Ab180754 | IF (1:50) |
| Antibody | Spectrin β1 (Mouse Monoclonal) | Leica Biosystems | Cat #: NCL-SPEC1 | IF (1:50) |
| Antibody | APC Mouse Anti-Human CD56 (Mouse Monoclonal) | BD Biosciences | Cat #: 555518 | Flow (100 μl per million cells) |
| Antibody | PE anti-human CD82 (Mouse Monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat #: 342103 | Flow (3 μl per million cells) |
| Antibody | FITC anti-human CD318 (Mouse Monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat #: 324004 | Flow (5 μl per million cells) |
| Antibody | APC anti-human ERBB3 (Mouse Monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat #: 324708 | Flow (5 μl per million cells) |
| Antibody | FITC anti-human NGFR (Mouse Monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat #: 345104 | Flow (5 μl per million cells) |
| Antibody | PE anti-human CD18 (Mouse Monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat #: 373407 | Flow (5 μl per million cells) |
| Sequence-based reagent | RT-qPCR primers | This paper | Supplementary file 4 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | StemMACS iPS-Brew XF, human | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat #: 130-104-368 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Skeletal Muscle Differentiation Kit | Amsbio | Amsbio Skeletal Muscle Differentiation Kit | SKM01, SKM02, and SKM03 were used for human iPSCs skeletal muscle differentiation |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNeasy Plus Mini Kit | QIAGEN | Cat #: 74136 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Mouse on Mouse (M.O.M.) Basic Kit | Vectorlab | Cat #: BMK-2202 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis System | Invitrogen | Cat #: 18080051 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Emerson lab custom muscle NanoString panel | NanoString Technologies | NanoString Technologies developed the muscle NanoString panel based a gene list provided by Emerson lab | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Chromium Single Cell 3' GEM, Library &Gel Bead Kit v2, 4 rxns | 10× Genomics | Cat #: 120267 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Chromium Chip A Single Cell Kit, 16 rxns | 10× Genomics | Cat #: 1000009 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Chromium i7 Multiplex Kit, 96 rxns | 10× Genomics | Cat #: 120262 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ROCK Inhibitor Y-27632 | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat #: 72307 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SB431542 | SelleckChem | Cat #: S1067 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CHIR99021 | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat #: 72052 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Prednisolone | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat #: P6004 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DAPT | SelleckChem | Cat #: S2215 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dexamethasone | SelleckChem | Cat #: S1322 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Forskolin | SelleckChem | Cat #: S2449 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Prism, RRID:SCR_002798 | https://www.graphpad.com/ | |
| Software, algorithm | nSolver 4.0 Analysis Software | nSolver Analysis Software, RRID:SCR_003420 | http://www.nanostring.com/products/nSolver | |
| Software, algorithm | Bisulfite Sequencing DNA Methylation Analysis | BISMA, RRID:SCR_000688 | http://services.ibc.uni-stuttgart.de/BDPC/BISMA/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Cell Ranger | Cell Ranger, RRID:SCR_017344 | https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/pipelines/latest/what-is-cell-ranger | Version 3.1.0 |
| Software, algorithm | STAR 2.5.1b | Implemented in Cell Ranger version 3.1.0 | https://github.com/alexdobin/STAR (Dobin, 2022) | Version 2.5.1b |
| Software, algorithm | Python | Python Programming Language, RRID:SCR_008394 | http://www.python.org/ | Version 2.7.9 |
| Software, algorithm | Opossum 0.2 | Oikkonen and Lise, 2017 | https://github.com/BSGOxford/Opossum (BSG Oxford, 2022) | Version 0.2 |
| Software, algorithm | Platypus | Platypus, RRID:SCR_005389 | https://www.rdm.ox.ac.uk/research/lunter-group/lunter-group/all-platypus-and-stampy-versions | Version 0.8.1 |
| Software, algorithm | Demuxlet | Kang et al., 2018 | https://github.com/statgen/demuxlet (The Center for Statistical Genetics at the University of Michigan School of Public Health, 2021) | Version 08/03/2018 |
| Software, algorithm | Seurat | SEURAT, RRID:SCR_007322 | http://seurat.r-forge.r-project.org/ | Version 3.1.4 |
| Software, algorithm | R Project for Statistical Computing | R Project for Statistical Computing, RRID:SCR_001905 | http://www.r-project.org/ | Version 3.6.2 |
| Software, algorithm | edgeR | edgeR, RRID:SCR_012802 | http://bioconductor.org/packages/edgeR/ | Version 3.30.3 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Differential expression for pairwise cell type comparisons from edgeR analysis.
For each of the 15 pairwise comparisons (shown in separate tabs), genes with differential expression (in either up or down directions) were ranked by p-value if the P-value < 1.0E-06 and |log2(FC)| > 1. The table includes columns for p-values, log2(FC), log2(CPM), QL F-test (F), and false discovery rate (FDR) from edgeR, and several columns for gene annotations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-supp1-v1.xlsb
-
Supplementary file 2
Top 20 Up and Down GO terms (BP, CC, MF) and KEGG pathways for pairwise cell type comparisons.
For each of the 15 pairwise comparisons (shown in separate tabs), the goana and kegga functions in edgeR were used to rank the top 20 Gene Ontology (GO) terms from each of the biological process (BP), cellular component (CC) and molecular function (MF) branches of GO, and the top 20 KEGG pathways, based on overrepresentation among the DE genes. Terms comprising N ( < 500) genes are sorted by P.Up and P.Down. For each term, the top DE Genes.Up and Genes.Down (ordered by P Value) are listed, up to a maximum of 30 genes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Pseudobulk counts for 36 samples based on scRNA-Seq data.
Raw single-cell counts were summed for each of the 6 cell types or subclusters of interest (S1, S2A, S2B, iMyoblast, bMyo, bMes) in each of the six donors (15 A, 15 V, 17 A, 17 U, 30 A, 30 W).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Primer sequences.
Table lists all primers for qPCR and bisulfite sequencing.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-supp4-v1.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/70341/elife-70341-transrepform1-v1.pdf





