Functional CDKN2A assay identifies frequent deleterious alleles misclassified as variants of uncertain significance
Figures
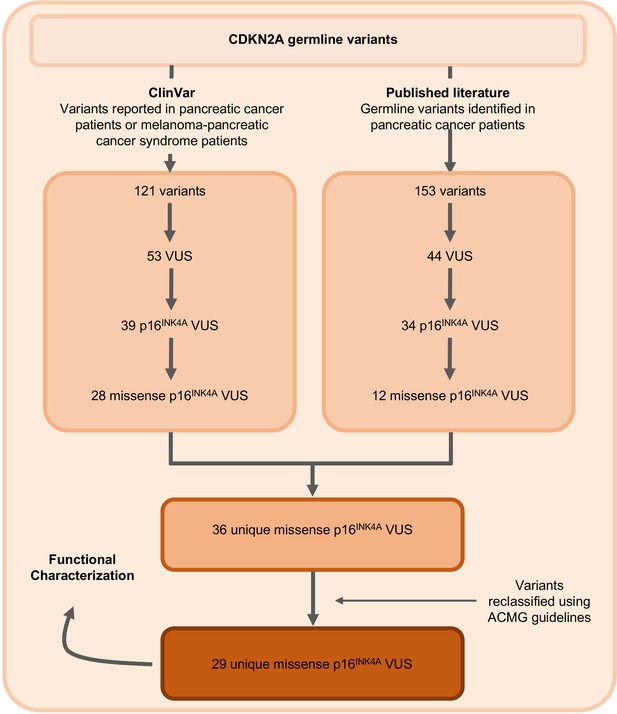
Identification of germline CDKN2A variant of uncertain significance (VUS) for functional characterization.
Workflow to identify the 29 germline CDKN2A VUS selected for characterization in our functional assay. CDKN2A VUSs were classified using American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) guidelines and either identified in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) from published literature or in ClinVar.
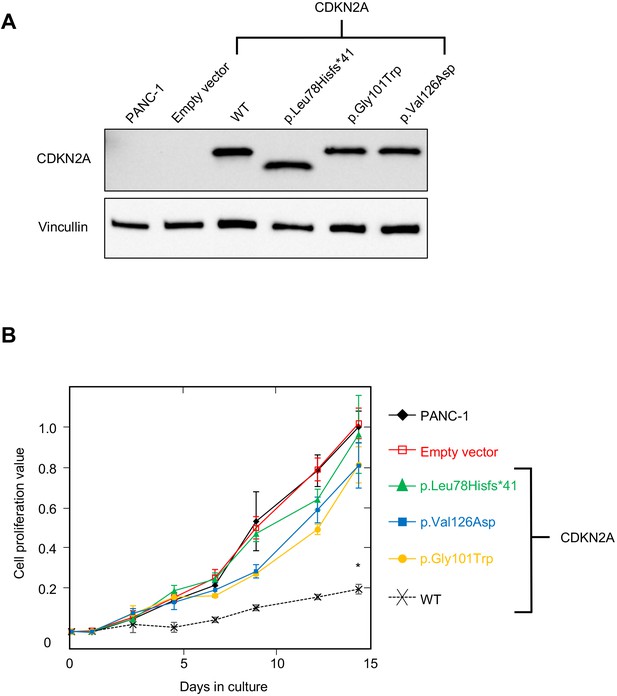
Development and validation of functional assay.
(A) Western blot of whole cell lysates from PANC-1 cells and PANC-1 cells stably expressing wild type CDKN2A (p16INK4A) or selected pathogenic variants using anti-CDKN2A and anti-vinculin antibodies as a loading control. No expression of CDKN2A (p16INK4A) detected in PANC-1 cells or PANC-1 cell stably expressing empty vector. CDKN2A (p16INK4A) expression detected in PANC-1 cells stably expressing pathogenic variants. (B) Growth of PANC-1 cell and PANC-1 cells stably expressing wild type CDKN2A cDNA (p16INK4A) or selected pathogenic variants over 14 days in culture. Cell proliferation values are shown as mean (n = 3) ± s.d. normalized to PANC-1 cell stably expressed with empty vector. Significant growth inhibition in PANC-1 cell stably expressing wild type CDKN2A (p16INK4A). *p < 0.01. Original files of the full raw unedited blots and the uncropped blots with the relevant CDKN2A and vinculin bands presented in Figure 2—source data 1, Figure 2—source data 2 and 3. For raw data in Figure 2, please refer to Figure 2—source data 4.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Original file of the full raw unedited CDKN2A blot.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig2-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Original file of the full raw unedited vinculin blot.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig2-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 3
The uncropped blots with the relevant CDKN2A and vinculin bands labelled.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig2-data3-v2.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 4
Raw data in Figure 2B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig2-data4-v2.xlsx
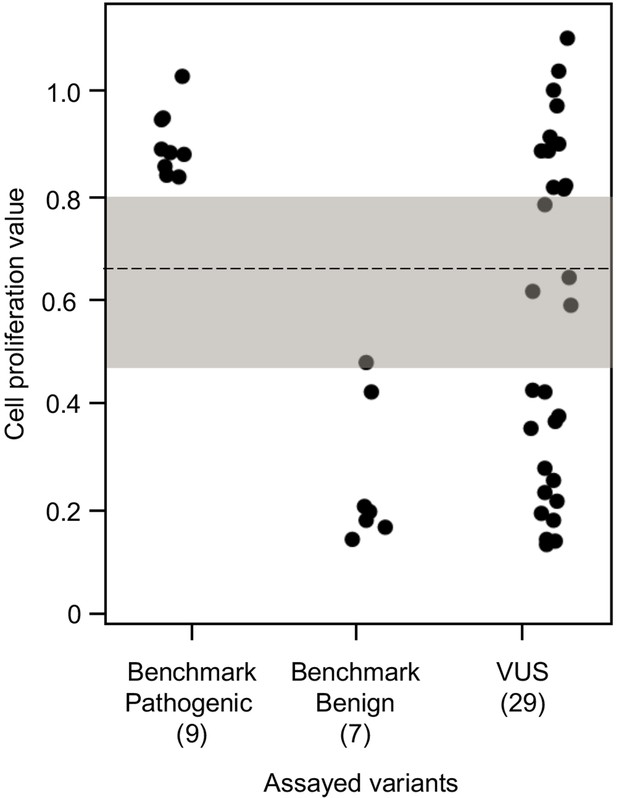
Functional characterization of CDKN2A variants.
Functional characterization of 45 CDKN2A variants (9 pathogenic variants, 7 benign variants, 29 variants of uncertain significance [VUSs]) in PANC-1 cells. Cell proliferation values are shown as mean (n = 3) ± s.d. normalized to PANC-1 cell stably expressed with empty vector. Assayed variants with mean cell proliferation values: (1) above the gray shaded area (>0.81) were classified as functionally deleterious, (2) below the gray shaded area (<0.44) were classified as functionally benign, (3) in the gray area above the threshold dotted line (≥0.66 but ≤0.81) were potentially functionally deleterious, and (4) in the gray area below the threshold dotted line (<0.66 but ≥0.44) were potentially functionally neutral. For raw data in this figure, please refer to Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw data in Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
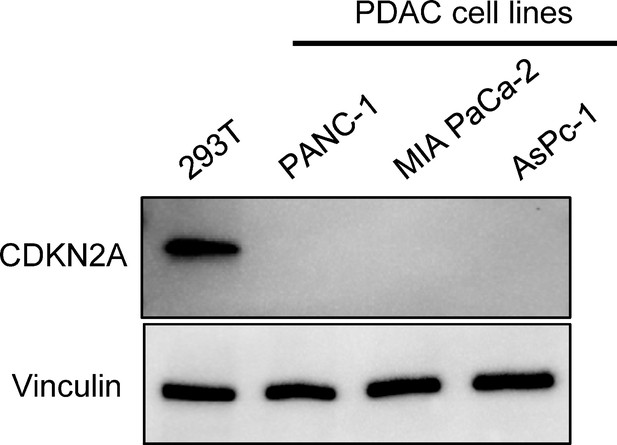
CDKN2A expression in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells.
Western blot of whole cell lysates from 293T cells, a human embryonic kidney cell line and PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, and AsPC-1 cells, human PDAC cell lines using anti-CDKN2A and anti-vinculin antibodies as a loading control. No expression of CDKN2A (p16INK4A) detected in human PDAC cells. CDKN2A (p16INK4A) expression detected in 293T cells. For the original files of the full raw unedited blots and figures with the uncropped blots with the relevant bands clearly labelled, please refer to Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1, Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 2, Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 3.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original file of the full raw unedited CDKN2A western blot.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Original file of the full raw unedited vinculin western blot.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig3-figsupp1-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 3
The uncropped western blots with the relevant CDKN2A and vinculin bands labelled.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig3-figsupp1-data3-v2.zip
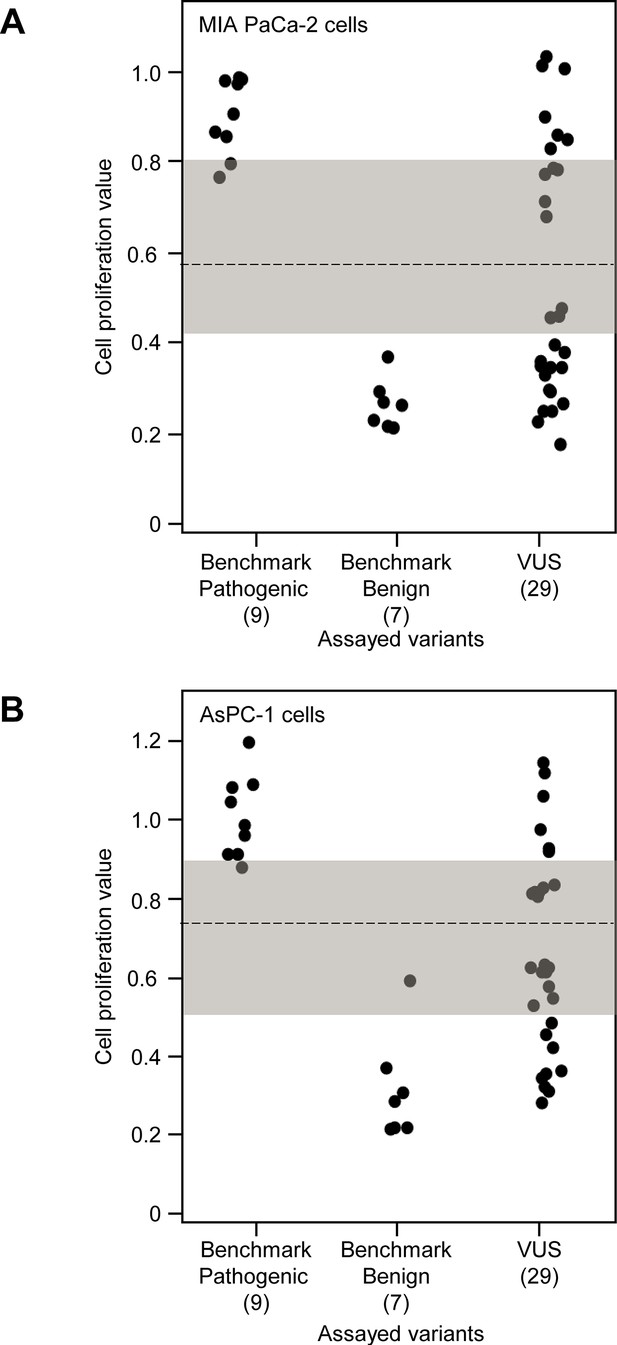
Functional characterization of CDKN2A variants in MIA PaCa-2 and AsPC-1 cells.
Functional characterization of 45 CDKN2A variants (9 pathogenic variants, 7 benign variants, 29 variants of uncertain significance [VUSs]). Cell proliferation values are shown as mean (n = 3) ± s.d. normalized to MIA PaCa-2 (A) or AsPc-1 (B) cell stably expressed with empty vector. Assayed variants with mean cell proliferation values: (1) above the gray shaded area (>0.80 for MIA PaCa-2 cells and 0.91 for AsPC-1 cells) were classified as functionally deleterious, (2) below the gray shaded area (<0.45 for MIA PaCa-2 cells and 0.51 for AsPC-1 cells) were classified as functionally benign, (3) in the gray area above the threshold dotted line (≥0.57 but ≤0.80 for MIA PaCa-2 cells and ≥0.74 but ≤0.91 for AsPC-1 cells) were potentially functionally deleterious, and (4) in the gray area below the threshold dotted line (<0.57 but ≥0.45 for MIA PaCa-2 cells and <0.74 but ≥0.51 for AsPC-1 cells) were potentially functionally neutral. For raw data in this figure, please refer to Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data in Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig3-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
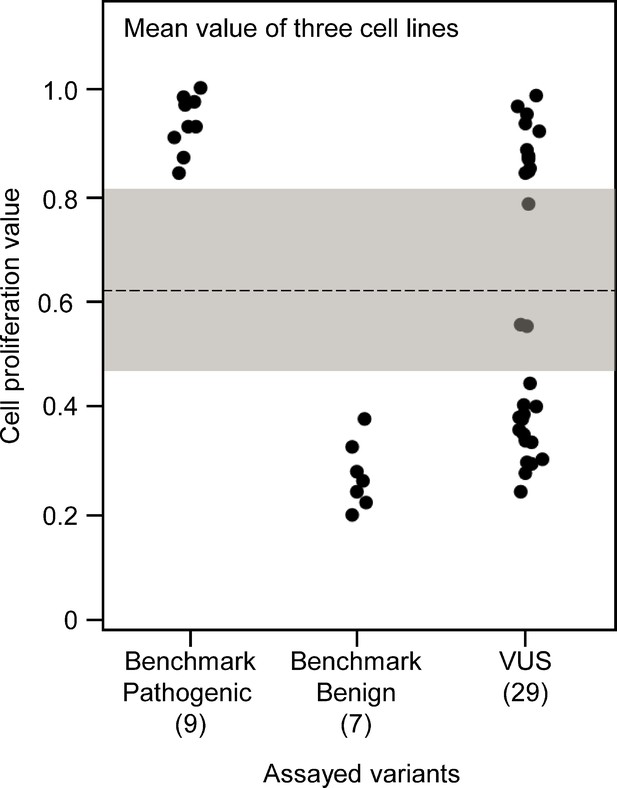
Functional characterization of CDKN2A variants.
Functional characterization of 45 CDKN2A variants (9 pathogenic variants, 7 benign variants, 29 variants of uncertain significance [VUSs]). Cell proliferation values are shown as mean of PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, and AsPc-1 cell values. Assayed variants with mean cell proliferation values: (1) above the gray shaded area (>0.83) were classified as functionally deleterious, (2) below the gray shaded area (<0.47) were classified as functionally benign, (3) in the gray area above the threshold dotted line (≥0.62 but ≤0.83) were potentially functionally deleterious, and (4) in the gray area below the threshold dotted line (<0.62 but ≥0.47) were potentially functionally neutral. For raw data in this figure, please refer to Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Raw data in Figure 3—figure supplement 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig3-figsupp3-data1-v2.xlsx
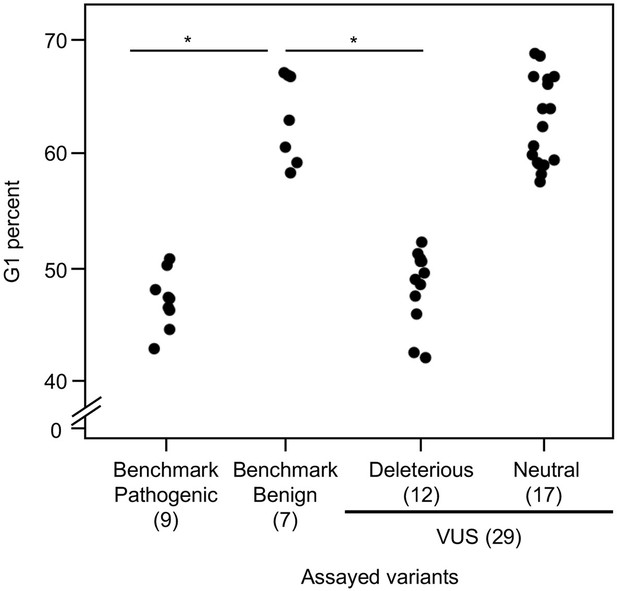
Cell cycle analysis of CDKN2A variants.
G1 percent for 45 CDKN2A variants (9 pathogenic variants, 7 benign variants, 29 variants of uncertain significance [VUSs]) in PANC-1 cells. Significant inhibition of G1 arrest function of CDKN2A by benchmark pathogenic variants and functionally deleterious or potentially functionally deleterious VUSs. *p < 0.01. For raw data in this figure, please refer to Figure 4 and Table 1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Raw data in Figure 4 and Figure 4—figure supplement 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
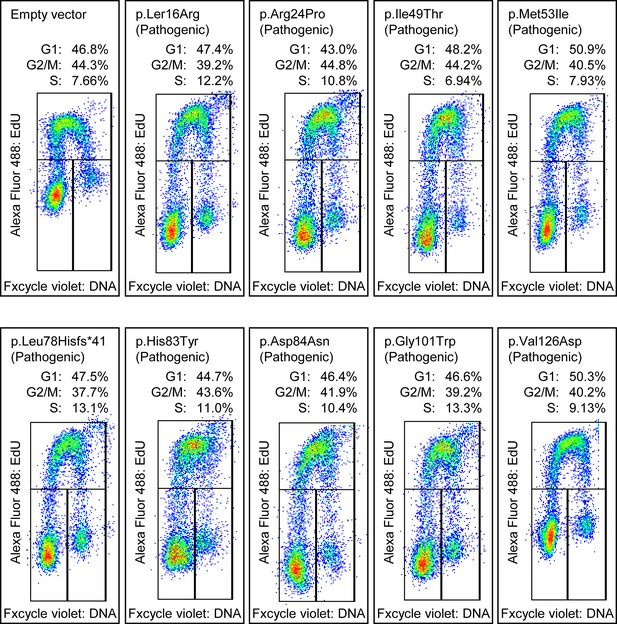
Cell cycle analysis of benchmark pathogenic CDKN2A variants.
Cell cycle analysis was performed with percentages of cells in each phase (G1, G2_M, and S) indicated. Flow cytometry analysis images for PANC-1 cell stably expressed with empty vector or benchmark pathogenic variants.
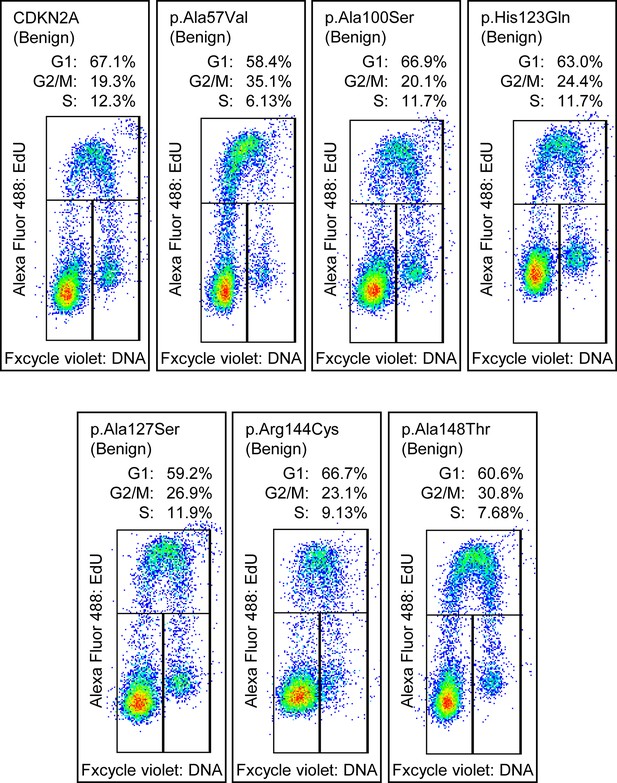
Cell cycle analysis of benchmark benign CDKN2A variants.
Cell cycle analysis was performed with percentages of cells in each phase (G1, G2_M, and S) indicated. Flow cytometry analysis images for PANC-1 cell stably expressed with empty vector or benchmark benign variants.
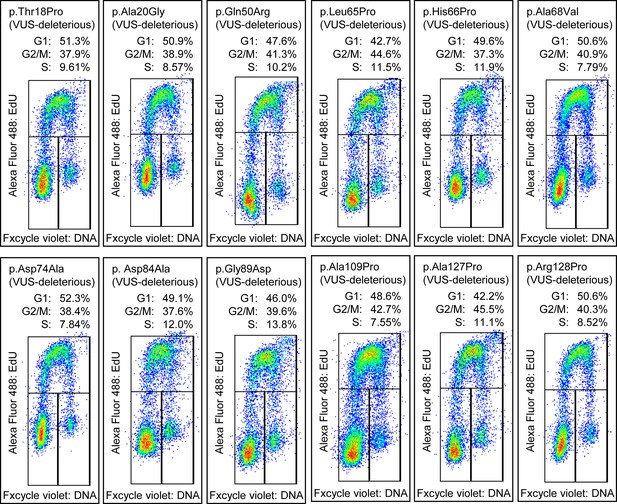
Cell cycle analysis of functionally deleterious and potentially functionally deleterious CDKN2A variants of uncertain significance (VUSs).
Cell cycle analysis was performed with percentages of cells in each phase (G1, G2_M, and S) indicated. Flow cytometry analysis images for PANC-1 cell stably expressed with empty vector or functionally deleterious and potentially functionally deleterious VUSs.
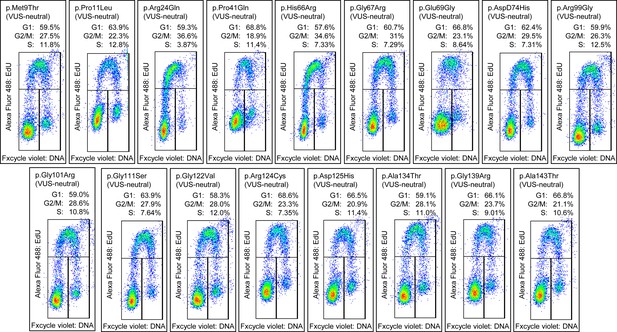
Cell cycle analysis of functionally neutral and potentially functionally neutral CDKN2A variants of uncertain significance (VUSs).
Cell cycle analysis was performed with percentages of cells in each phase (G1, G2_M, and S) indicated. Flow cytometry analysis images for PANC-1 cell stably expressed with empty vector or functionally neutral and potentially functionally neutral VUSs.
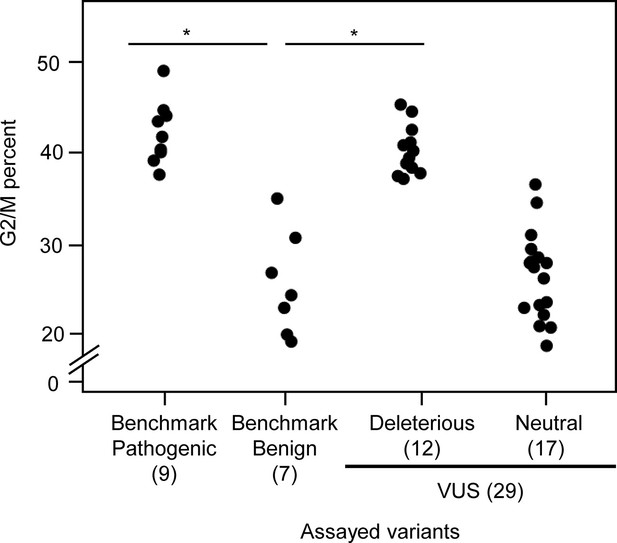
G2_M percent of CDKN2A variants expression cells.
G2_M percent for 45 CDKN2A variants (9 pathogenic variants, 7 benign variants, 29 variants of uncertain significance [VUS]) in PANC-1 cells. G2_M percent in benchmark pathogenic variants and functionally deleterious or potentially functionally deleterious VUSs expression cells were significantly higher than that in benchmark benign variants expression cells. *p < 0.01. For raw data in this figure, please refer to Figure 4 and 1.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 5—source data 1
Raw data in Figure 4 and Figure 4—figure supplement 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-fig4-figsupp5-data1-v2.xlsx
Tables
CDKN2A variants assayed.
| Classificationa | Variantb |
|---|---|
| Pathogenic | p.Leu16Arg, p.Arg24Pro, p.Met53Ile, p.Gly101Trp, p.Val126Asp |
| Likely pathogenic | p.Ile49Thr, p.Leu78Hisfs*41, p.His83Tyr, p.Asp84Asn |
| Likely benign | p.Ala57Val, p.Ala100Ser, p.His123Gln, p.Ala127Ser, p.Arg144Cys |
| Benign | p.Ala148Thr |
| VUS | p.Met9Thr, p.Pro11Leu, p.Thr18Pro, p.Ala20Gly, p.Arg24Gln, p.Pro41Gln, p.Gln50Arg, p.Leu65Pro, p.His66Pro, p.His66Arg, p.Gly67Arg, p.Ala68Val, p.GluE69Gly, p.Asp74Ala, p.Asp74His, p. Asp84Ala, p.Gly89Asp, p.Arg99Gly, p.Gly101Arg, p.Ala109Pro, p.Gly111Ser, p.Gly122Val, p.Arg124Cys, p.Asp125His, p.Ala127Pro, p.Arg128Pro, p.Ala134Thr, p.Gly139Arg, and p.Ala143Thr |
-
a. Classification using American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) variant classification guidelines.
-
b. Variant given as protein change with reference to NP_000068.1. Known pathogenic and benign variants used for benchmarking indicated in bold.
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-transrepform1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 1
CDKN2A variants assayed with genomic, transcript, and protein change.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Functional characterization.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Previously reported functional data for assayed CDKN2A variants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Primer sequences used for subconing and site directed mutagenesis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71137/elife-71137-supp4-v2.xlsx





