A vibrissa pathway that activates the limbic system
Figures
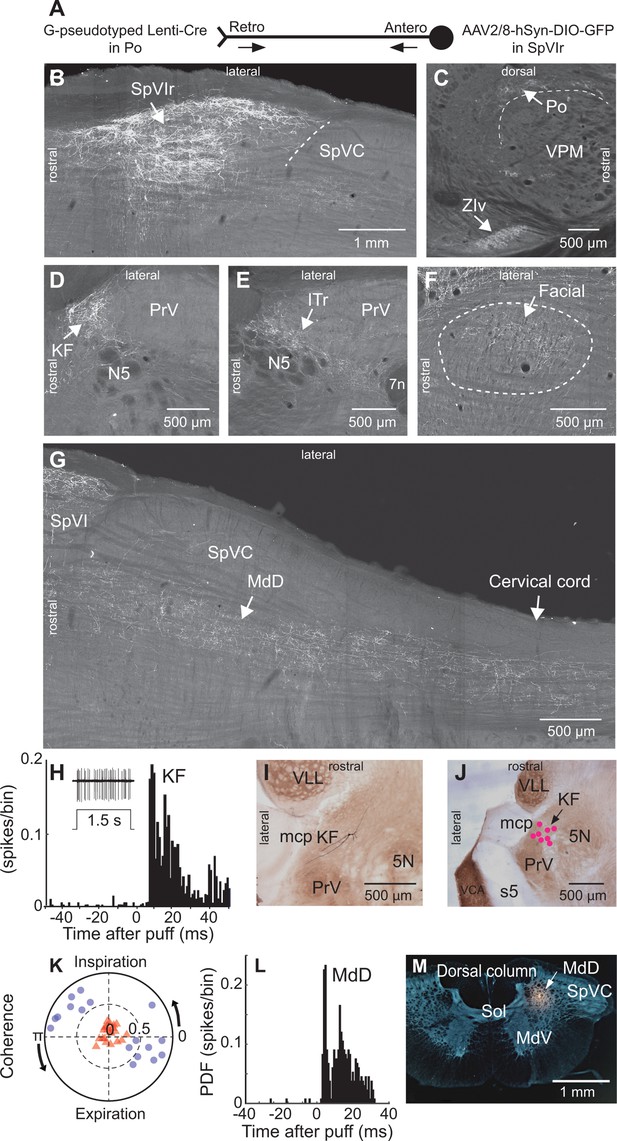
Anatomical and electrophysiological evidence that vibrissa-responsive interpolaris cells have widespread axonal projections.
(A) Viral method used for labeling paralemniscal projections. (B) Labeling of interpolaris cells after injection of G-pseudotyped Lenti-Cre virus in Po thalamus, and a Cre-dependent AAV that expresses GFP in the vibrissa-responsive sector of SpVIr. Horizontal section. (C) Anterograde labeling of terminal fields in Po thalamus and zona incerta. Sagittal section. (D) Anterograde labeling in the KF/PBc. Horizontal section. (E) Anterograde labeling in the ITr. Horizontal section. (F) Anterograde labeling in the dorsal sector of the facial nucleus. Horizontal section. (G) Anterograde labeling in the MdD and cervical cord. Horizontal section. (H) Population peristimulus time histogram of spike discharges evoked in KF (22 cells) by air puff deflection of the vibrissae in the anesthetized rat. A representative response is shown in the insert. (I) Example of a vibrissa responsive KF cell labeled by juxtacellular delivery of Neurobiotin. Horizontal section. (J) Location of eight juxtacellularly labeled KF cells. Horizontal brainstem sections in (I) and (J) were counterstained for cytochrome oxidase. Horizontal section. (K) Spectral coherence of spontaneous discharges of KF cells with the respiratory cycle at the respiratory frequency; 1–3 Hz. Note that, in contrast with the respiratory units (blue dots), spontaneous discharges of vibrissa-responsive cells (red triangles) display low coherence with respiration. (L) Population peristimulus time histogram of spike discharges evoked in MdD (33 cells) by air puff deflection of the vibrissae. (M) Recording site in the MdD labeled by an iontophoretic injection of Chicago Sky Blue. This coronal section was counterstained for cytochrome oxidase and a negative image was generated. Coronal section. See Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for additional anatomical data. Abbreviations for all anatomy: 5n, root of the trigeminal motor nucleus; 5N, trigeminal motor nucleus; 5t, trigeminal tract; 7n, facial nerve tract; 7N, facial nucleus; Amb, ambiguus nucleus; APT, anterior pretectal nucleus; BSTL, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; CeA, central amygdala; Cerv Cord, cervical cord; CM/PC, central medial/paracentral thalamic nuclei; CPu, caudate putamen; DR, dorsal raphe; EW, Edinger-Westphal; Hab, habenula; IML, intermedio-lateral column of the spinal cord; ITr, intertrigeminal region; KF, Kölliker-Fuse nucleus; KF/PBc, Kölliker-Fuse/parabrachial complex; mcp, middle cerebellar peduncle; MdD, dorsal part of the medullary reticular formation; MdV, ventral part of the medullary reticular formation; mt, mammillothalamic tract; NA, nucleus ammbiguus; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; opt, optic tract; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PB, parabrachial nuclei; PC, paracentral thalamic nucleus; PCRt, parvicellular reticular formation; PLH, posterior lateral hypothalamus; Po, posterior nuclear group of the thalamus; PrV, principal trigeminal nucleus; RN, red nucleus; Rt, reticular thalamic nucleus; s5, sensory root of the trigeminal nerve; SC, superior colliculus; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle; SpVC, caudalis division of the spinal trigeminal complex; Sol, nucleus of the solitary tract; SpVIc, caudal sector of the interpolaris trigeminal nucleus; SpVIr, rostral division of the interpolaris nucleus; TG, trigeminal ganglion; VLL, ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus; VPL, ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus; VPM, ventral posterior medial nucleus; VPCc, parvicellular sector of the ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus; VPPc, parvocellular part of the ventral posterior thalamic nucleus; VRG, ventral respiratory group; vsc, ventral spinocerebellar tract; ZIv, ventral division of zona incerta.
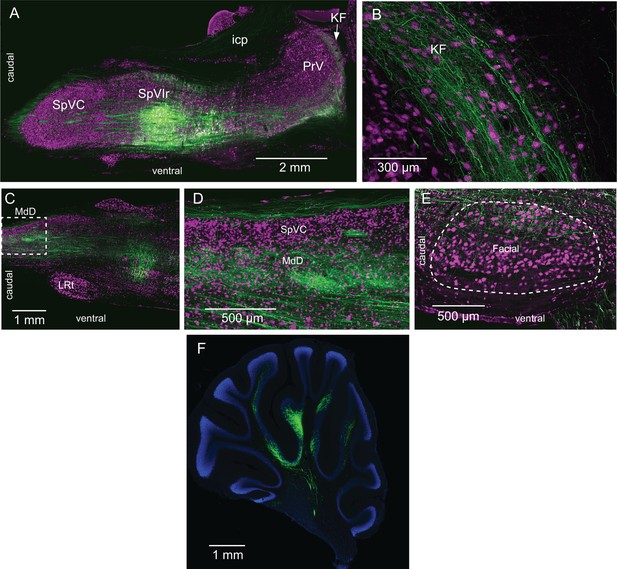
Interpolaris cells project to the KF/PBc and MdD (Supplementary Information related to Figure 1).
(A) Injection site of AAV1-hSyn-eGFP-WPRE-hgh in SpVIr. Sagittal section. (B) Anterograde labeling in the KF/PBc. Sagittal section. (C, D) Anterograde labeling in the MdD. The framed region is enlarged in (D). Sagittal section. (E) Terminal field in the dorsal lateral sector of the facial nucleus. Sagittal section. (F) Anterograde labeling in the cerebellum. Sagittal section. Sections were immunostained for NeuN (A–E) or counterstained with DAPI (F). Abbreviations: icp, inferior cerebellar peduncle; KF, Kölliker-Fuse nucleus; LRT, lateral reticular nucleus; MdD, dorsal part of the medullary reticular formation; PrV, principal trigeminal sensory nucleus; SpIr, rostral sector of the interpolaris trigeminal nucleus; SpVC, caudalis division of the spinal trigeminal complex.
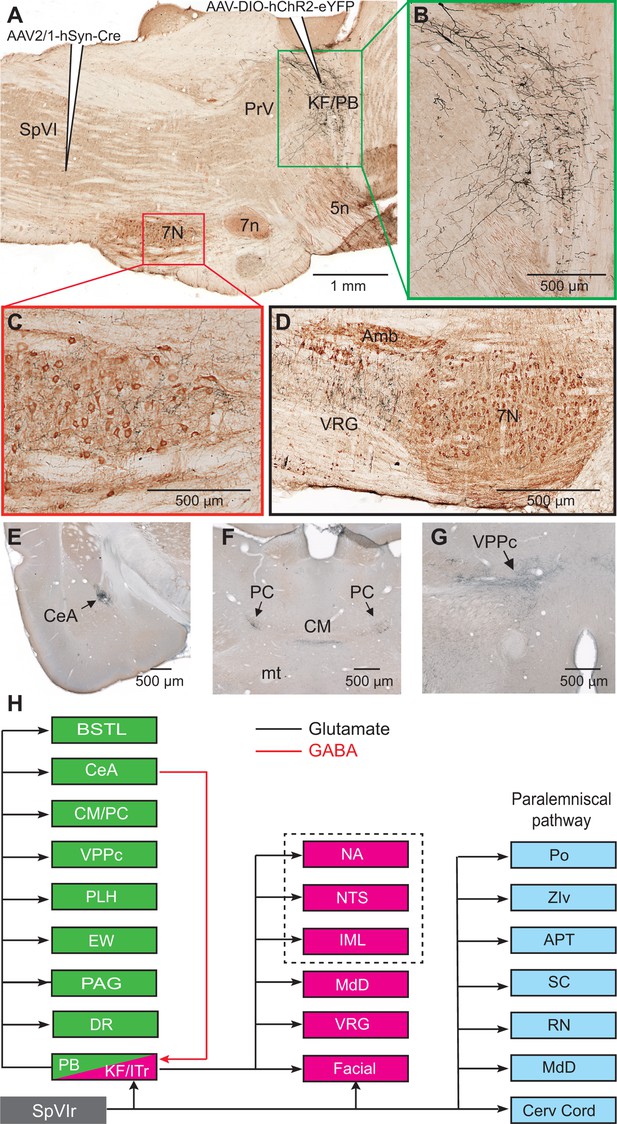
Axonal projections of KF/PBc cells that receive interpolaris input.
See Figure 1 for abbreviations. (A–C) AAV2/1-hSyn-Cre-WPRE was injected in the vibrissa-responsive sector of the SpVIr, and AAV2/1-EF1a-DIO-hChR2-eYFP was injected in the KF/PBc. This parasagittal section shows labeling in the KF/PBc. The section was immunostained for choline acetyltransferase (A). The green and red framed areas are enlarged in (B) and (C). Sagittal section. (D) Terminal labeling in the ventral respiratory group underneath the ambiguous nucleus. Sagittal section. (E) Anterograde labeling in the central amygdala. Coronal section. (F) Anterograde labeling in the paracentral and central medial thalamic nuclei. Coronal section. (G) Anterograde labeling in the parvocellular division of the ventral posterior medial nucleus of the thalamus (see Figure S2 for additional projection sites). Coronal section. (H) Summary of the first-order axonal projections of interpolaris cells and the second-order projections that derive from the KF/PBc. Projection sites in the framed area are from prior studies (see review by Saper and Stornetta, 2015). The classical paralemniscal pathway, that is, structures that receive input from SpVI, is in cyan. Magenta is the brainstem target of KF and green is the target of PG. MdD appears twice as it received input from both SpVI and the KF/PBc. We have added this to the legend.
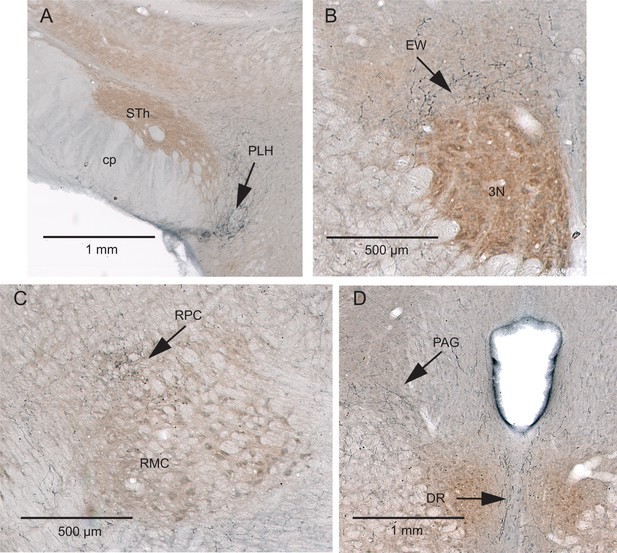
Additional projection sites of KF/PBc cells that receive interpolaris input (Supplementary Information related to Figure 2).
(A–D) AAV2/1-hSyn-Cre-WPRE was injected in the vibrissa-responsive sector of the SpVIr, and AAV2/1-EF1a-DIO-hChR2-eYFP was injected in the KF/PBc. Anterograde labeling is present in the posterior lateral hypothalamus (A), the Edinger-Westphal nucleus (B), the parvocellular division of the red nucleus (C), and in the dorsal raphe and ventral lateral periaqueductal gray (D). Sections were counterstained for cytochrome oxidase. Coronal sections. Abbreviations: 3N, oculomotor nucleus; cp, cerebral peduncle; DR, dorsal raphe; EW, Edinger-Westphal nucleus; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PLH, posterior lateral hypothalamus; RMC, red nucleus magnocellular part; RPC, red nucleus parvocellular part; STh, subthalamic nucleus.
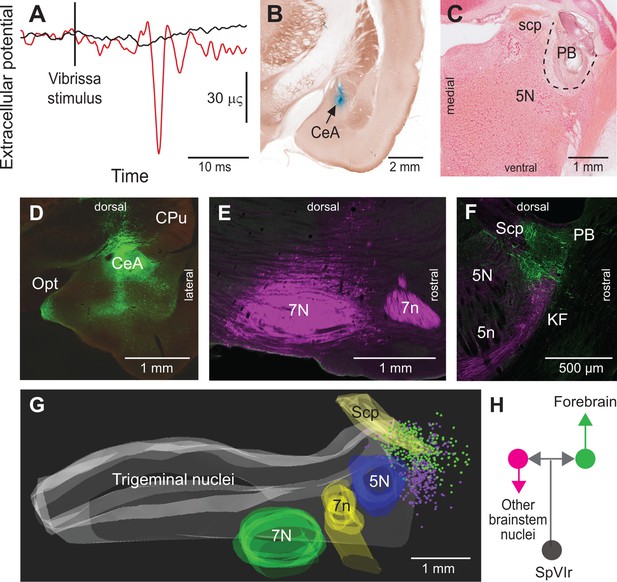
Vibrissa-evoked responses in central amygdala and anatomical evidence that separate cellular populations in the KF/PBc project to the CeA as compared to the facial nucleus.
See Figure 1 for abbreviations. (A) Average response (50 trials) evoked in the CeA by air puff stimulation of the vibrissae before (red trace) and after (black trace) an electrolytic lesion of the PB complex. (B) Recording site in the amygdala labeled by an iontophoretic injection of Chicago Sky Blue (cytochrome oxidase counterstaining). Coronal section. (C) Electrolytic lesion of the PB complex. Coronal section. (D) Injection site of retroAAV-CAG-eGFP in the CeA. Coronal section. (E) Injection site of retroAAV-CAG-mCherry in the facial nucleus. Sagittal section. (F) Retrogradely labeled cells in the KF/PBc. Sagittal section. (G) Sagittal view of a three-dimensional reconstruction showing the distribution of amygdala-projecting cells (green dots) in the medial and lateral PB, and facial-projecting neurons in the KF (magenta dots). Note that a few cells in lateral PB project to the facial nucleus; yet, none of the KF/PBc cells are doubly labeled. (H) Wiring diagram of the projections of KF and PB cells that receive vibrissa input from the interpolaris nucleus (see also Figure S3 for additional evidence).
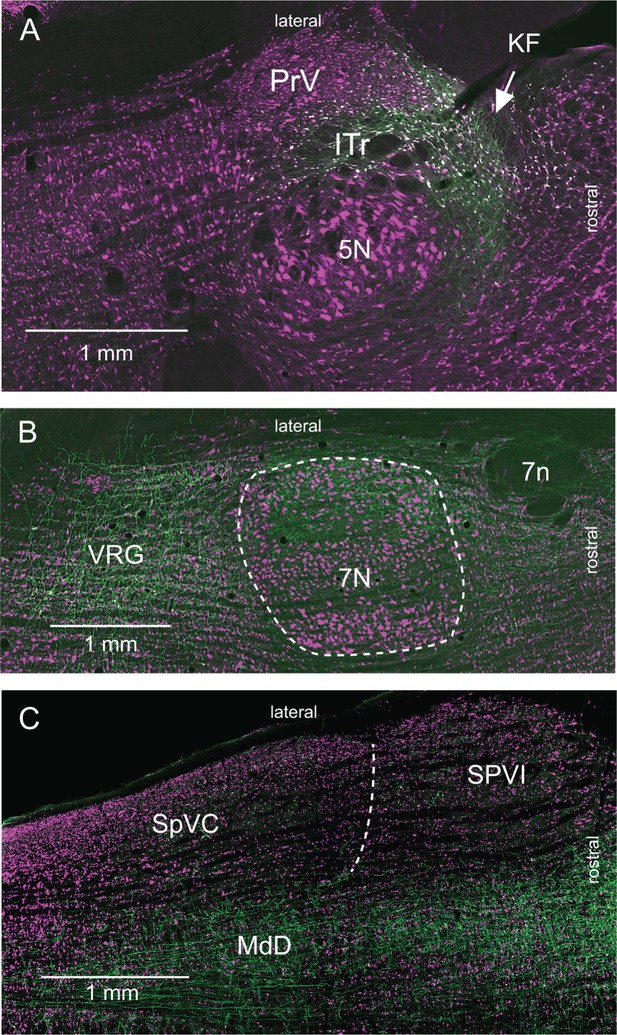
Labeling of KF cells that project to lower brainstem (Supplementary Information related to Figure 3).
Horizontal sections were immunostained for NeuN (magenta). (A) Labeling of KF cells (green) after injection of retroAAV-hSyn-Cre in the ventral respiratory group and AAV2/8-hSyn-DIO-GFP in the KF/PBc. Note the absence of anterograde labeling in the sensory trigeminal nuclei. (B) Anterograde labeling in the lateral part of the facial nucleus and in the ventral respiratory group; labeling as in (A). No anterograde labeling is observed in midbrain or forebrain regions. (C) Anterograde labeling in the MdD; labeling as in (A). Note the absence of labeling in trigeminal subnuclei SpVC and SpVI. Abbreviations: 5N, trigeminal motor nucleus; 7N, facial nucleus; 7n, facial nerve tract; Amb, ambiguous nucleus; ITr, intertrigeminal region; PrV, principal trigeminal sensory nucleus; SpVC, caudalis division of the spinal trigeminal complex. SpVI, interpolaris division of the spinal trigeminal complex; VRG, ventral respiratory group.
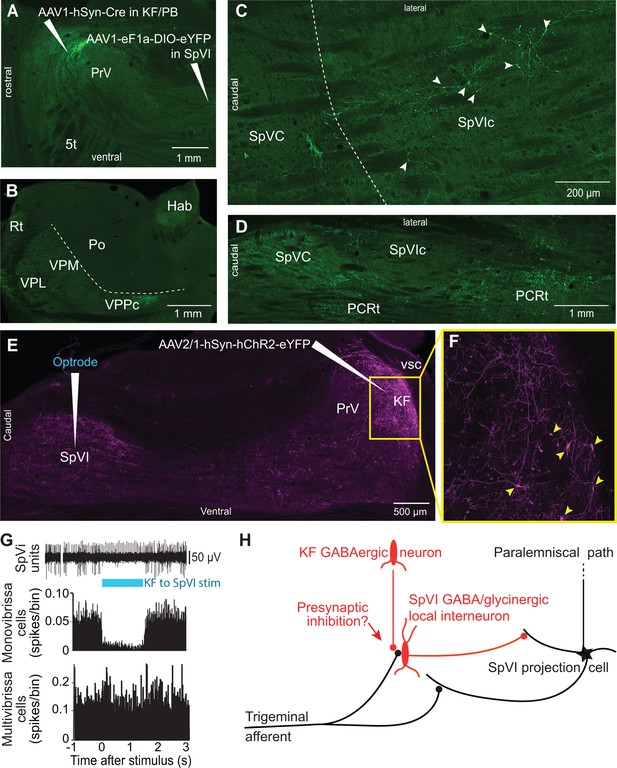
Postsynaptic targets of KF projections to the SPVI.
See Figure 1 for abbreviations. (A) The viral method used for transsynaptic labeling of brainstem cells that receive input from the KF. Sagittal section. (B–D) Transsynaptic labeling in SpVI is restricted to a small population of cells (C) that project to VPCC (B). Yet, numerous cells are transsynaptically labeled in the parvicellular reticular formation (D). Panel (B) in a coronal section while (C) and (D) are horizontal sections. (E, F) Viral labeling method for optogenetic stimulation of KF axons. Injection of AAV2/1-hSyn-hChR2-eYFP in KF results in anterograde labeling in SpVI. The framed region in (E) is shown in (F); arrowheads point to labeled cell bodies. Note the dense network of axon collaterals within the KF/PBc. Sagittal section. (G) Representative responses of a monovibrissa-responsive cell (biphasic unit) and a multivibrissa-responsive cell (positive unit) upon optogenetic stimulation of KF axons labeled as in (E). Population peristimulus time histogram shows the responses of 26 monovibrissa-responsive units upon optogenetic stimulation of KF axons along with 10 multivibrissa-responsive units to optogenetic stimulation of KF axons. Only mono-vibrissa and not multi-vibrissa cells are responsive to KF input. (H) Summary of the effect of KF projections on the flow of sensory input through SpVI.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (chicken polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat#: ab13970 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Anti-Chicken IgY (IgG) (H+L) (donkey polyclonal)(Alexa Fluor 488) | Jackson ImmunoResearch Labs | Cat#: 703-545-155; RRID: AB_2340375 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-NeuN (mouse monoclonal (A60)) | MilliporeSigma | Cat#: MAB377 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit IgG – H&L (Goat polyclonal)(Alexa Fluor 594) | Abcam | Cat#: ab150080 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (rabbit polyclonal) | Novus Biologicals | Cat#: NB600-308 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) (horse)(Biotynilated) | Vector Laboratories | Cat#: BA-1100 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | Anti-Choline- acetyltransferase (Goat polyclonal) | MilliporeSigma | Cat#: SAB2500236 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Anti-Goat IgG H&L (Rabbit polyclonal)(Horseradish peroxidase) | Abcam | Cat#: ab6741 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-GFP (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat#: ab1218 | 1:2000 |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG (H+L) (Goat)(Biotynilated) | Vector Laboratories | Cat#: BA-9200 | 1:200 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | G-pseudotyped- Lenti-Cre | Fan Wang(MIT McGovern Institute) | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAAV-hSyn-DIO- eGFP (AAV8) | Addgene | Addgene ID: 50457 | Depositor: Bryan Roth |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAAV-Ef1a-DIO- hChR2-eYFP- WPRE-HGHpA (AAV1) | Addgene | Addgene ID: 20298 | Depositor: Karl Deisseroth.New version of this virus is pAAV- EF1a-double floxed- hChR2(H134R)- EYFP-WPRE-HGHpA |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pENN.AAV.hSyn. Cre.WPRE.hGH (AAV1) | Addgene | Addgene ID: 105553UPenn ID: AV- 1-PV-2676 | Depositor: James M. Wilson |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAAV.hSyn.eGFP.WPRE.bGH (AAV5) | Addgene | Addgene ID: 105539UPenn ID: AV- 5-PV-1696 | Viral service discontinued |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAAV-CAG-tdTomato (AAV retrograde) | Addgene | Addgene ID: 59462 | Depositor: Edward Boyden |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAAV-CAG-eGFP (AAV retrograde) | Addgene | Addgene ID: 37825 | Depositor: Edward Boyden |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Horseradish Peroxidase Streptavidin (HRP- Streptavidin conjugate) | Vector Laboratories | Cat#: SA-5704-100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Vectastain Elite ABC-HRP Kit, Peroxidase (Standard) | Vector Laboratories | Cat#: PK-6100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ImmPACT SG Substrate, Peroxidase (HRP) | Vector Laboratories | Cat#: SK-4705 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ImmPACT DAB Substrate, Peroxidase (HRP) | Vector Laboratories | Cat#: SK-4105 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Chicago Sky Blue 6B | MilliporeSigma | Cat#: C8679 | Powder |
| Chemical compound, drug | Neutral Red | MilliporeSigma | Cat#: 861251 | |
| Software, algorithm | Neurolucida | MBF Bioscience | RRID:SCR_001775 | http://mbfbioscience.com/neurolucida |
| Software, algorithm | LabChart 8.0 Spike Histogram Module | AD Instruments Data Acquisition Systems for Life Science | RRID:SCR_001620 | https://www.adinstruments.com/ |
| Software, algorithm | Matlab Chronux Toolbox | Chronux (MATLAB) | RRID:SCR_005547 | http://chronux.org |
| Other | Neurobiotin Tracer | Vector Laboratories | Cat#: SP-1120 | |
| Other | Cytochrome c oxidase (from bovine heart) | MilliporeSigma | Cat#: C5499 |





