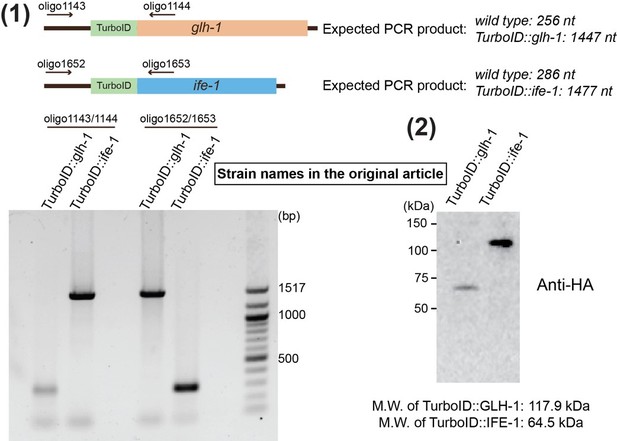
Proximity labeling identifies LOTUS domain proteins that promote the formation of perinuclear germ granules in C. elegans
Figures
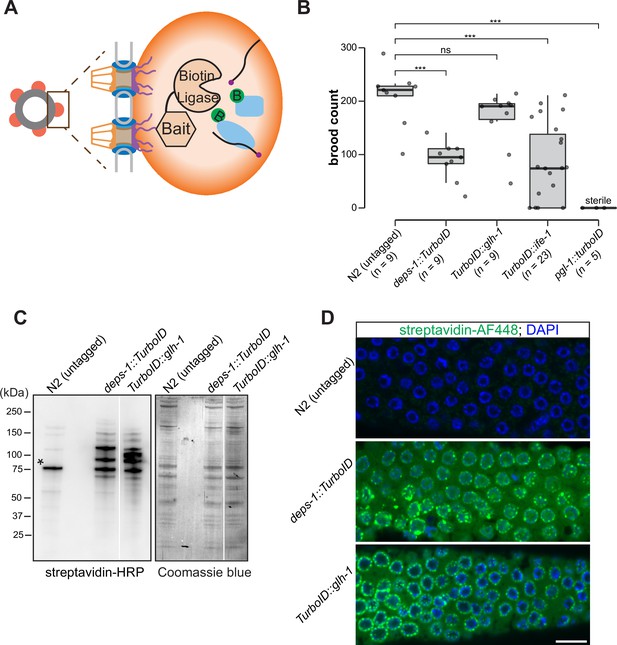
A proximity labeling system for specific biotin labeling of P granule proteins.
(A) Schematic of proximity-based labeling. Known P granule bait proteins are tagged with the promiscuous biotin ligase—TurboID—to label proteins present in P granules. (B) Brood sizes of strains endogenously tagged at the loci encoding deps-1, glh-1, ife-1, pgl-1, and N2 control. Five independent lines of pgl-1::TurboID heterozygotes are sterile. ns: not significant, *** p<0.0005, two-tailed Student’s t-test. (C) Streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase blotting. The left panel shows whole animal lysates prepared from N2 (untagged control), and strains expressing DEPS-1::TurboID or TurboID::GLH-1 blotted with streptavidin-HRP to visualize biotinylated proteins. The right panel shows Coomassie blue stain of the same membrane. An asterisk marks endogenously biotinylated protein (Based on its size, the protein likely is PCCA-1). (D) Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor 488 staining of gonad dissected from N2 (untagged control), and animals expressing DEPS-1::TurboID and TurboID::GLH-1. Scale bar=10 µm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Brood counts of N2(untagged) and TurboID-tagged strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Uncropped blots of Figure 1C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig1-data2-v2.zip
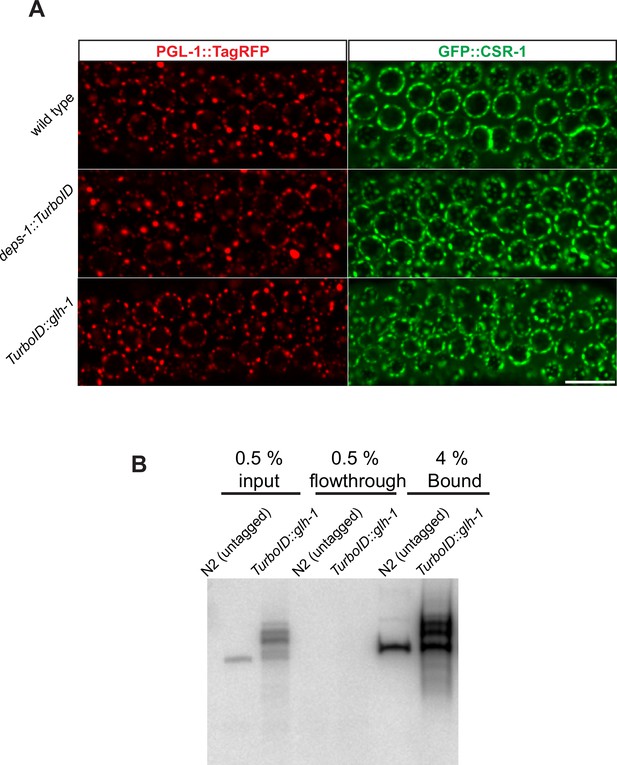
Streptavidin pull-down of biotinylated proteins.
(A) Fluorescence micrographs showing pachytene nuclei of wild-type, deps-1::TurboID, and TurboID::glh-1 animals expressing either PGL-1::TagRFP or GFP::CSR-1.Scale bar=10 µm. Animals were cultured at 25°C. (B) Streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase blotting showing pull-down efficiency. Biotinylated proteins are present in the input, depleted in the flow-through and enriched in the pull-down fraction.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Uncropped blots of Figure 1—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
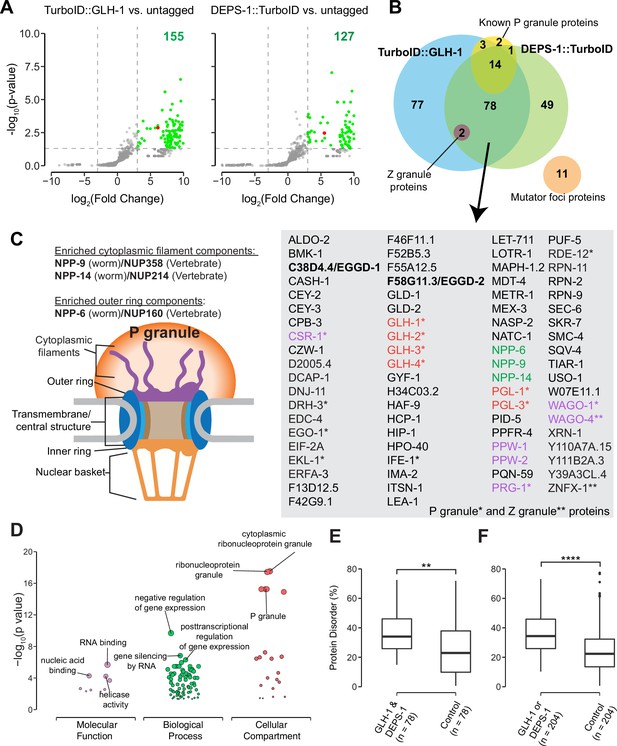
Proteomic analysis of P granules and properties of P granule proteome.
(A) Volcano plots showing statistically significant enriched proteins from strains expressing TurboID::GLH-1 and DEPS-1::TurboID in green. One-tailed Student’s t-test, p<0.05, log2(fold change)≥3. GLH-1 and DEPS-1 proteins are shown in red on the respective plots. (B) Venn diagram showing overlapping proteins recovered from strains expressing TurboID::GLH-1 and DEPS-1::TurboID, along with previously reported P granule, Z granule, and mutator foci proteins. The list shows proteins enriched by both pull-down experiments. Argonaute proteins (purple), nuclear pore proteins (NPPs, green), and core P granule components GLH and PGL-1 family proteins (red). P granule and Z granule proteins are marked with an asterisk and two asterisks, respectively. No reported mutator foci proteins were significantly enriched. (C) Schematic of nuclear pores and P granules. Pull-down experiments enrich NPPs (NPP-6, NPP-9, and NPP-14) composing either the cytoplasmic filaments or outer ring (purple). NPPs and their vertebrate homologs are shown. (D) Functional gene set enrichment analysis of proteins significantly enriched in both pull-down experiments organized by molecular function, biological processes, and cellular compartments. Top three enriched categories (based on p-value) are labeled. (E) Boxplot showing the average disorder of proteins enriched in both TurboID::glh-1 and deps-1::TurboID (n=78) as predicted using IUPRED compared to a random control set (n=78). The average disorder of proteins was derived by comparing the total IUPRED score of each protein to its length. Wilcoxon rank-sum test (p<0.01 **). (F) The same analysis as in (E), but with proteins labeled in either TurboID::glh-1 or deps-1::TurboID pull-down experiments (n=204). Wilcoxon rank-sum test (p<0.0001 ****).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Normalized spectral counts for N2 (untagged) and TurboID tagged strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig2-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Average IUPred disorder score for each Caenorhabditis elegans protein.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig2-data2-v2.zip
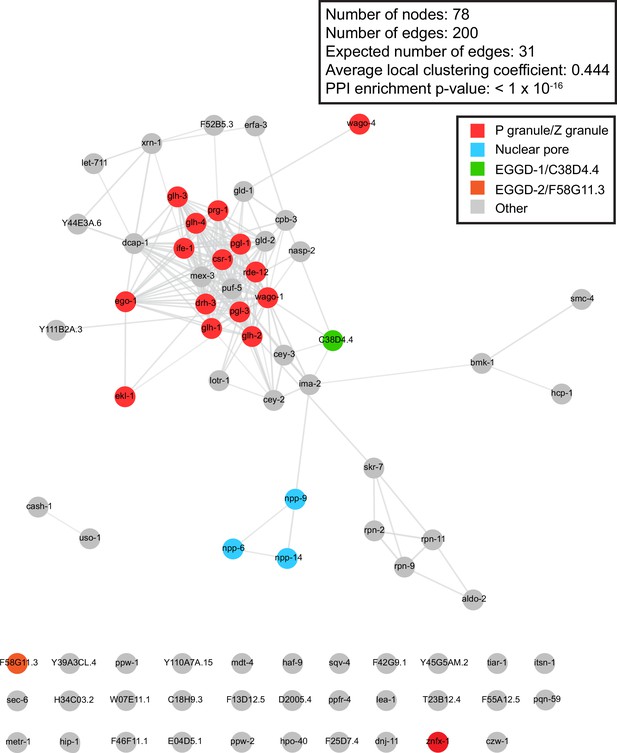
Network analysis of proteins enriched from TurboID.
STRING network analysis of proteins enriched in both pull-down experiments from strains expressing DEPS-1::TurboID and TurboID::GLH-1 (n=78). Known P granule and Z granule proteins are shown in red, nuclear pore proteins are shown in turquoise, EGGD-1 is shown in green, and EGGD-2 is shown in orange. Other proteins are shown in gray. Network was visualized in Cytoscape.
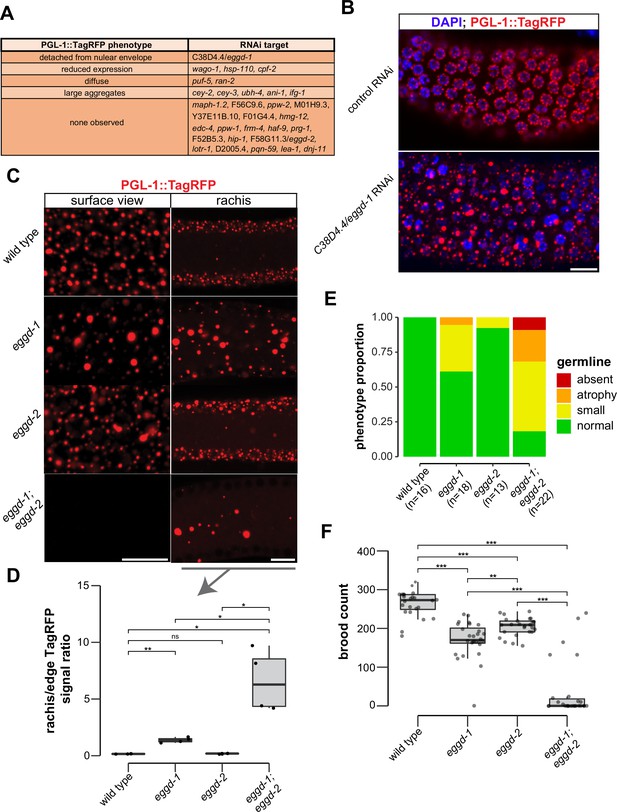
EGGD-1 and EGGD-2 promote perinuclear localization of P granules.
(A) PGL-1::TagRFP phenotypes. Summarized PGL-1::TagRFP phenotypes from an RNAi-based screen. RNAi targets are grouped by the observed PGL-1::TagRFP phenotypes in rrf-3; pgl-1::TagRFP adult germ lines. (B) Fluorescence micrographs of dissected gonads from pgl-1::TagRFP reporter animals after two successive generations of control RNAi or C38D4.4/eggd-1 RNAi. Scale bar=10 µm. (C) Single confocal slices of the edge and rachis of the germ line in live adult animals expressing PGL-1::TagRFP. Wild-type animals, and animals bearing mutations in eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 are shown. Scale bar=10 µm. Images are representative of at least four animals. (D) Boxplot of quantified rachis versus edge PGL-1::TagRFP signal intensity in eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 mutant backgrounds. ns: not significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.005, two-tailed Student’s t-test (n=4). (E) Germ line morphology in adult eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 mutants compared to wild-type animals. All strains express PGL-1::TagRFP. Representative images of absent, atrophy, small, and normal classifications are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1D. (F) Brood counts of wild-type, eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 animals. All strains express PGL-1::TagRFP. **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Gray value measurements used to quantify rachis/edge signal ratio.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig3-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Categorization of germ line atrophy in eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig3-data2-v2.zip
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Brood counts of eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig3-data3-v2.zip
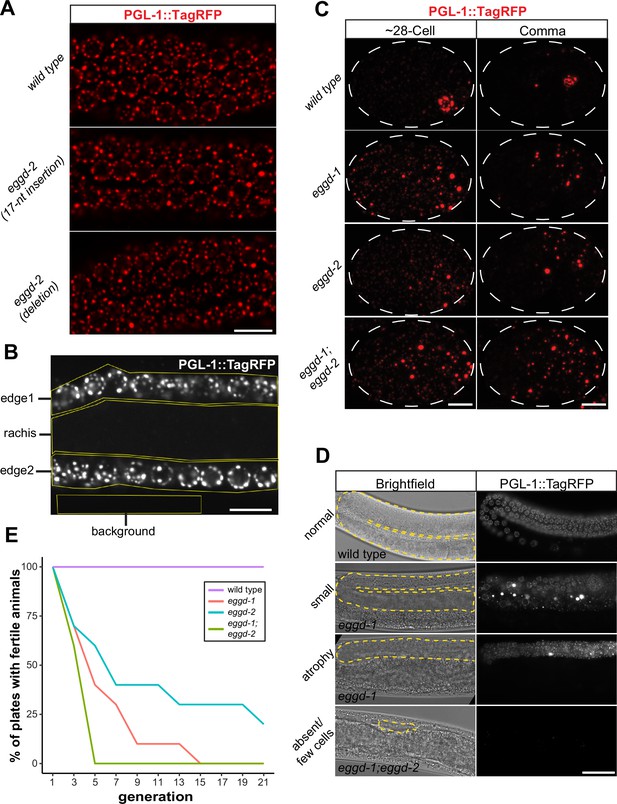
Embryonic PGL-1::TagRFP localization and images of diminutive germ line.
(A) Fluorescence micrographs of pachytene nuclei in adult wild-type, eggd-2 (17-nt insertion), and eggd-2 (deletion). All strains express PGL-1::TagRFP. Scale bar=10 µm. (B) One example of regions of interest drawn to quantify PGL-1::TagRFP signal intensity plotted in Figure 3D. The equation used to quantify rachis/edge signal intensity is located in the Materials and methods section. (C) Maximum intensity projections of confocal z stacks spanning the depth of embryos expressing PGL-1::TagRFP at the indicated stages in eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 mutants. Dashed line outlines the embryos. Images are representative of at least four embryos. (D) Brightfield and fluorescence images of adult animals with normal, small, atrophied, and absent germ lines. The gonad is outlined by a yellow dashed line in the brightfield images. The genotype of imaged animals is indicated at the bottom left of each brightfield image. Scale bar=20 µm. (E) Mortal germ line assay showing the percentage of plates with fertile wild-type, eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 animals over successive generations beginning the first generation that outcrossed homozygous animals were obtained. eggd-1, eggd-2, and eggd-1; eggd-2 mutants become sterile more rapidly over generations compared to wild-type animals. Log-rank test (p<0.0005).
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Percentage of plates with progeny over successive generations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
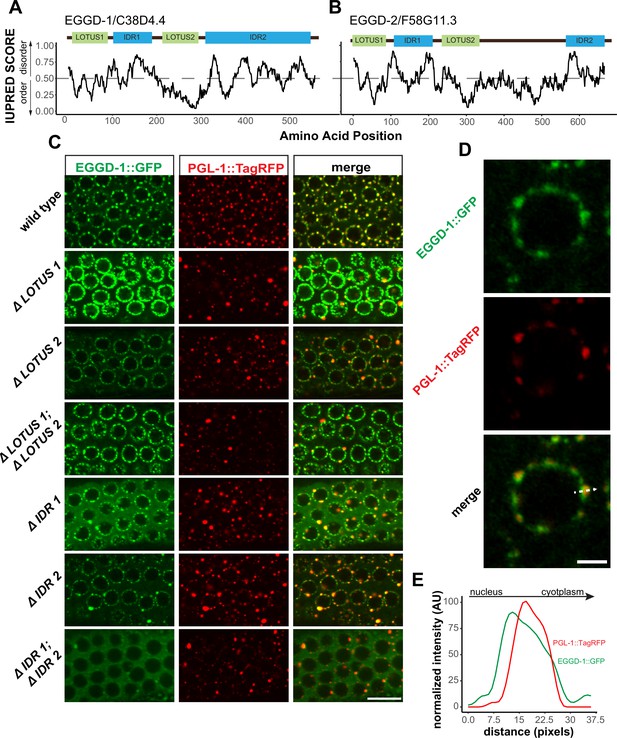
EGGD-1 and EGGD-2 contain IDRs and LOTUS domains.
(A, B). Domain architecture and IUPRED score for EGGD-1 (A) and EGGD-2 (B). Regions of proteins with an IUPRED score above 0.5 are predicted to be disordered, while regions below 0.5 are predicted to be ordered. Intrinsically disordered regions are shown in blue and abbreviated as ‘IDR.’ LOTUS domains are shown in green. (C) Spinning disc confocal images (100× objective) showing the localization of EGGD-1::GFP protein, and a series of EGGD-1::GFP domain deletion mutants in pachytene germ cells of live animals expressing PGL-1::TagRFP. Images are representative of over five animals. Scale bar=10 µm. (D) Super-resolution Zeiss Airyscan image of a single pachytene nucleus in animals co-expressing EGGD-1::GFP and PGL-1::TagRFP. Scale bar=2 µm. (E) Intensity profile of EGGD-1::GFP and PGL-1::TagRFP signals along the dotted arrow in panel (D). AU, arbitrary unit; IDR, intrinsically disordered region.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
IUPred score for each amino acid in EGGD-1 and EGGD-2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig4-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Gray value intensity along the dotted line in Figure 4D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-fig4-data2-v2.zip
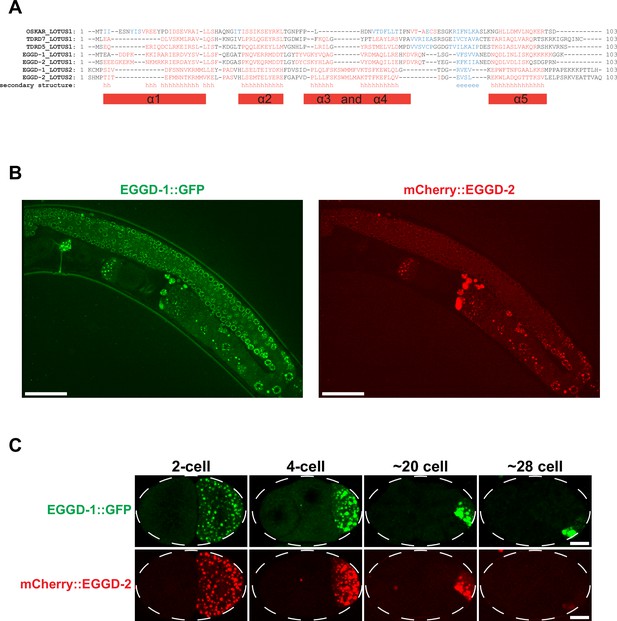
Localization of EGGD-1 and EGGD-2 proteins.
(A) Alignment between the extended LOTUS domains of Drosophila melanogaster Oskar mouse TDRD7, TDRD5, and the putative LOTUS domains present in EGGD-1 and EGGD-2. In the ‘secondary structure’ row, ‘h’ indicates a consensus prediction for an alpha-helical secondary structure, while ‘e’ indicates a prediction for a beta sheet. (B) Single confocal slices of EGGD-1::GFP and mCherry::EGGD-2 protein in the adult germ line. Scale bar=20 µm. (C) Maximum intensity projections made from confocal images spanning the depth of embryos, visualizing EGGD-1::GFP, and mCherry::EGGD-2 during embryonic development. Scale bar=5 µm.
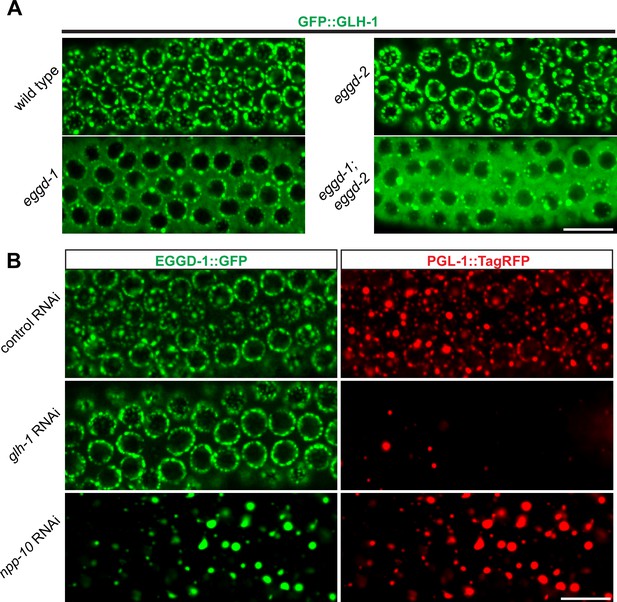
EGGD-1 acts upstream of GLH-1 in P granule assembly and localization.
(A) Micrographs showing pachytene nuclei of wild-type and mutant animals expressing GFP::GLH-1 (60× objective). The contrast of images in eggd-1, and eggd-1; eggd-2 mutants is manually adjusted to visualize localization of GFP::GLH-1. Images are representative of at least four animals. Scale bar=10 µm. (B) Fluorescence micrographs of pachytene nuclei from live animals expressing EGGD-1::GFP and PGL-1::TagRFP under the indicated RNAi conditions (60× objective). The contrast in images upon glh-1 RNAi and npp-10 RNAi is manually adjusted to visualize EGGD-1::GFP. Scale bar=10 µm.
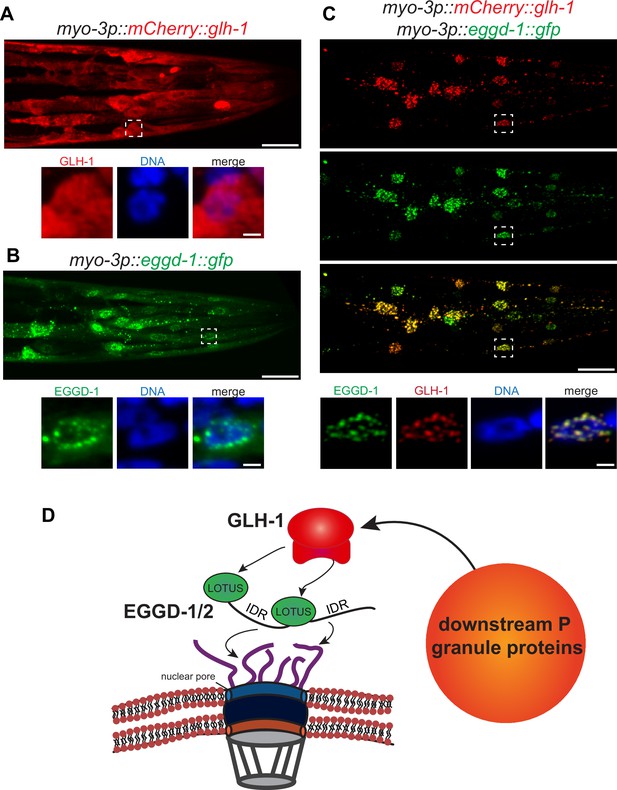
EGGD-1 intrinsically localizes to the nuclear envelope and is sufficient to recruit GLH-1 to the nuclear periphery.
(A–C) Maximum intensity projection of a z stack spanning the head of fixed adult animals ectopically expressing mCherry::GLH-1 (A), EGGD-1::GFP (B), or mCherry::GLH-1 and EGGD-1::GFP (C) under the muscle-specific myo-3 promoter. Top panel shows the entire head. Scale bar=20 µm. Bottom panel shows individual nuclei outlined by a dashed box in the top panel. Scale bar=2 µm. Images are representative of at least six animals (60× objective). (D) Model illustrating the proposed role of EGGD-1 in P granule assembly.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans) | N2 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | N2 | Wildtype C. elegans, RRID:WB-STRAIN:WBStrain00000001 |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | deps-1::TurboID | This study | WHY14 | deps-1(how1[deps-1::TurboID]) I |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | TurboID::ife-1 | This study | WHY12 | ife-1(how2[TurboID::ife-1]) III |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | TurboID::glh-1 | This study | WHY10 | glh-1(how3[TurboID::glh-1]) I |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pgl-1::TurboID | This study | N/A | pgl-1(how4[pgl-1::TurboID]) IV-- this strain is sterile and cannot be grown |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY100 | pgl-1(gg547[pgl1::3x flag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | rrf-3; pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY134 | rrf-3(pk1426)II; pgl-1 (gg547[pgl-1::3xflag::tag RFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | eggd-1; pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY219 | eggd-1(how5) III; pgl- 1(gg547[pgl-1::3x flag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | eggd-2(17nt insertion); pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY178 | pgl-1(gg547[pgl- 1::3xflag::tagRFP]) IV; eggd-2(how6) V |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | eggd-2(deletion);pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY297 | eggd-1(how7[eggd- 1::GFP::TEV::3x FLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547[pgl-1::3x flag::tagRFP]) IV; eggd-2(how14) V |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | eggd-1; eggd-2; pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY285 | eggd-1(how5) III; pgl-1 (gg547[pgl-1::3xflag::tag RFP]) IV; eggd-2(how6) V |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | eggd-1::GFP; pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY170 | eggd-1(how7[eggd- 1::GFP::TEV::3xFLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547[pgl-1::3x flag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | ΔLOTUS1 | This study | WHY203 | eggd-1(how8[eggd- 1(ΔLOTUS 1)::GFP::TEV::3x FLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547 [pgl-1::3xflag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | ΔLOTUS2 | This study | WHY180 | eggd-1(how9[eggd- 1(ΔLOTUS 2)::GFP::TEV::3x FLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547 [pgl-1::3xflag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | ΔLOTUS1; ΔLOTUS2 | This study | WHY182 | eggd-1(how10[eggd- 1(ΔLOTUS 1&2)::GFP::TEV::3x FLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547 [pgl-1::3xflag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | ΔIDR1 | This study | WHY186 | eggd-1(how11[eggd- 1(ΔIDR 1)::GFP::TEV::3x FLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547 [pgl-1::3xflag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | ΔIDR2 | This study | WHY216 | eggd-1(how12[eggd- 1(ΔIDR 2)::GFP::TEV::3x FLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg 547[pgl-1::3xflag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | ΔIDR1; ΔIDR2 | This study | WHY282 | eggd-1(how13[eggd- 1(ΔIDR 1&2)::GFP::TEV::3x FLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547 [pgl-1::3xflag::tagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::glh-1 | Gift from Craig Mello | WM704 | glh-1(ne4816[GFP::glh-1]) I |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::glh-1; eggd-1 | This study | WHY273 | glh-1(ne4816[GFP::glh-1]) I; eggd-1(how5) III |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::glh-1; eggd-2 | This study | WHY274 | glh-1(ne4816[GFP::glh-1]) I; eggd-2(how6) V |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | gfp::glh-1; eggd-1; eggd-2 | This study | WHY275 | glh-1(ne4816[GFP::glh-1]) I; eggd-1(how5) III; eggd-2(how-6) V |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | unc-119 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | EG4322 | ttTi5605 II; unc-119(ed9) III |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myo-3p::mCherry::glh-1 | This study | WHY276 | ttTi5605 II; unc-119(ed9) III; howEx1[myo- 3p::mCherry::glh- 1::unc-54 3'UTR+ Cbr-unc-119(+)] |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myo-3p::eggd-1::GFP | This study | WHY277 | ttTi5605 II; unc-119(ed9) III; howEx2[myo-3p::eggd- 1::GFP::unc-54 3'UTR+ Cbr-unc-119(+)] |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | myo-3p::mCherry::glh-1; myo-3p::eggd-1::GFP | This study | WHY278 | ttTi5605 II; unc-119(ed9) III; howEx3[myo-3p::mCherry::glh- 1::unc-54 3'UTR+ myo-3p::eggd- 1::gfp::unc-54 3'UTR+ Cbr-unc-119(+)] |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | GFP::csr-1 | Gift from Craig Mello | WM343 | csr-1(GFP::csr-1) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | TurboID::deps-1; GFP::csr-1 | This study | WHY304 | deps-1(how1[deps- 1::TurboID]) I; csr-1 (GFP::csr-1) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | TurboID::deps-1; pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY305 | deps-1(how1[deps- 1::TurboID]) I; eggd-1(how7[eggd- 1::GFP::TEV::3X FLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547[pgl- 1::3xFLAG::TagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | glh-1::TurboID; GFP::csr-1 | This study | WHY312 | glh-1(how3[TurboID::glh-1]) I; csr-1(GFP::csr-1) IV |
| Strain, strain background (C. elegans) | glh-1::TurboID; pgl-1::TagRFP | This study | WHY313 | glh-1(how3[TurboID::glh-1]) I; eggd-1(how7[eggd-::GFP::TEV::3XFLAG::AID]) III; pgl-1(gg547[pgl-1::3x FLAG::TagRFP]) IV |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | OP50 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | OP50 | Bacteria. Uracil auxotroph. E. coli B. |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | HT115 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | HT115 | E. coli [F-, mcrA, mcrB, IN(rrnD-rrnE)1, rnc14::Tn10(DE3 lysogen: lacUV5 promoter) -T7 polymerase]., RRID:WB-STRAIN:WBStrain00041080 |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | Control RNAi | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | L4440 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | C38D4.4 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00008005 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | wago-1 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00011061 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | hsp-110 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00016250 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | cpf-2 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00000774 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | puf-5 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00004241 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | ran-2 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00004303 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | cey-2 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00000473 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | cey-3 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00000474 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | ubh-4 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00006724 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | ani-1 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00013038 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | ifg-1 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00002066 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | maph-1.2 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00009113 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | F56C9.6 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00018950 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | ppw-2 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00004094 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | M01H9.3 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00019719 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | Y37E11B.10 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00021381 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | F01G4.4 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00008503 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | hmg-12 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00001977 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | edc-4 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00021551 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | ppw-1 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00004093 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | frm-4 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00001491 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | haf-9 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00001819 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | prg-1 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00004178 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | F52B5.3 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00009922 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | hip-1 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00010281 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | F58G11.3 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00008385 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | lotr-1 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00008399 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | D2005.4 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00004143 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | pqn-59 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00002263 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | lea-1 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00001029 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | dnj-11 | DOI: 10.1101/gr.2505604 | WBGene00011735 | Vidal RNAi Library |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | npp-10 | DOI: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00050–1 | WBGene00003796 | (C. elegans RNAi Collection (Ahringer), RRID:SCR_017064) |
| Genetic reagent (E. coli) | glh-1 | doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.083469 | WBGene00001598 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Plasmid) | TurboID HDR donor template | DOI: 10.1038/nbt.4201 | pAS31 | RRID:Addgene_118220 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Plasmid) | pCFJ104 | DOI: 10.1038/ng.248 | pCFJ104 | RRID:Addgene_19328 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Plasmid) | pCFJ151 | DOI: 10.1038/ng.248 | pCFJ151 | RRID:Addgene_19330 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Plasmid) | myo-3p::eggd-1::gfp | This study | pIP1 | myo-3p::eggd- 1::gfp::unc-54 3′ UTR |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Plasmid) | myo-3p::mCherry::glh-1 | This study | pIP12 | myo-3p::mCherry::glh- 1::unc-54 3′ UTR |
| Commercial assay or kit | 18×18 Cover Glass # 1 | MedSupply Partners | Cat# G07-140110 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Microscope Slides, Diamond White Glass, 25×75 mm2, 90° Ground Edges, Plain | MedSupply Partners | Cat# G07-1380-10 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Fisherbrand Fluorescent Antibody Microscope Slides w/ two 10 mm diameter circles | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 22-339408 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Nail Polish | Electron Microscopy Sciences | Cat# 72180 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | cOmplete, Mini EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 11836170001 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate | Life Technologies | Cat# S11223 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Streptavidin-Horseradish Peroxidase conjugate | Life Technologies | Cat# S911 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Streptavidin magnetic beads | NEB | Cat# S1421S | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NuPAGE 4–12% Bis-Tris Gel | Invitrogen | cat# NP0323BOX | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Immobilon-FL PVDF membrane | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# IPFL00010 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Vectashield antifade mounting medium with DAPI | Vector Labs | Cat# H-1200-10 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NOVEX colloidal blue staining kit | Invitrogen | Cat# LC6025 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lysing Matrix D | mpbio | Cat# 6913100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Agarose | Genesee Scientific | Cat# 20-102GP | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Paraformaldehyde | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# O4042-500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Methanol | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A408-4 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Acetone | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A929-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium Chloride | VWR | Cat# BDH9286 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Agar | Genesee Scientific | Cat# 20-248 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Chloesterol | VWR | Cat# 0433-250 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Magnesium Chloride | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# M35-500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Potassium Phosphate Monobasic | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP362-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Potassium Phosphate Dibasic | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP363-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium Citrate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# S297-500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# H4034-500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Potassium Hydroxide | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# P250-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Urea | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# AC140750010 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trition X-100 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP151-500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tween 20 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP337-500 | |
| Software, algorithm | R version 4.0.3 | The R Project for Statistical Computing | https://www.r-project.org/ | RRID:SCR_001905 |
| Software, algorithm | ggplot2 version 3.3.2 | Tidyverse | https://www.tidyverse.org/ | RRID:SCR_019186 |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | National Institutes of Health | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ | RRID:SCR_003070 |
| Software, algorithm | Adobe Illustrator | Adobe | https://www.adobe.com/products/illustrator.html | RRID:SCR_010279 |
| Software, algorithm | HHPRED | DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.12.007 | https://toolkit.tuebingen.mpg.de/tools/hhpred | RRID:SCR_010276 |
| Software, algorithm | Zen Blue 3.0 | Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH | https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/int/home.html | RRID:SCR_013672 |
| Software, algorithm | MetaMorph Premier Acquisition version 7.8.1.0 | Molecular Devices | https://www.moleculardevices.com/ | RRID:SCR_002368 |
| Software, algorithm | g:Profiler | doi:10.1093/nar/gkz369 | https://biit.cs.ut.ee/gprofiler/gost | RRID:SCR_006809 |
| Software, algorithm | IUPred2A | DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti541 | https://iupred2a.elte.hu/ | RRID:SCR_014632 |
| Software, algorithm | STRING | DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki005 | https://string-db.org/ | RRID:SCR_005223 |
| Software, algorithm | PROMALS3D | doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn072 | http://prodata.swmed.edu/promals3d/promals3d.php | RRID:SCR_018161 |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 Cat# 1081058 | Integrated DNA Technologies | Cat# 1081058 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Alt-R CRISPR-Cas9 tracrRNA, 20 nmol | Integrated DNA Technologies | Cat# 1072533 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | ife-1 5′ guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | TTGAGAAGCTGAAAATCTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | deps-1 3′ guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | gtatatatttaaTTAGACCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | glh-1 5′ guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | ttttctgcgaaaATGTCTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | pgl-1 3′ guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | tagaaattattaaaggcgcA |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1 5′ guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | GACATTCACTTGGCAAATGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1 3′ guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | CACCAACTATCCTTATCCGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-2 5′ guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | TGAAAAATGTCTGAAGAAGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-2 3′ guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | GCACTGCTTCAACTACGCCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1 5′ ΔLOTUS1 guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | CGACCCCAAATCAAGTAGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1 3′ ΔLOTUS1 guide RNA, 5′ ΔIDR1 guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | GCTTTGAGATCAGATTGATT |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1 5′ ΔLOTUS2 guide RNA, 3′ ΔIDR1 guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | TGGCTGCAACTCGGAACAGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1 3′ ΔLOTUS2 guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | ATACACTTCGAGTCAATCCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1 5′ ΔIDR2 guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | GGAACTCCAAAAGATCTTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1 3′ ΔIDR2 guide RNA | Integrated DNA Technologies | Guide RNA oligo | CTCCAGCTGTCTTTGTCTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | turboID::ife-1 5′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 5′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | cacgattagttggcgttttccccagttgtt ctcggcttctcagatcagtcctgtttttgcc ttgccagttgtcgaggtgc gaaaatttta agcgcaaATG tacccatacga CgtCccaga |
| Sequence-based reagent | turboID::ife-1 3′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 3′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | tgaataatttatagtactcaaacga taatgaaaaagggaatggctcac CTTCTTTCTCTCCAGAG ATTTTCAGCTTCTCAAAT GCTATTTCAGAATCTGA CTTCTCGGCGGAACGAAGGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | deps-1::turboID 5′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 5′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | CAGTGAGCTCAAACgtaag tttatttttaaggttggaagatgataaaa acaagtttttcagCGATTCGTT GGCCCTTCAA GCCGCA GAACTCCATCTGGTACTC CACAAAGCTCAACATCTT CCAGGGTC tacccatacga CgtCccaga |
| Sequence-based reagent | deps-1::turboID 3′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 3′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | gaatgggatggtggtggaacttga agtttaaataaataaatgtttggttg gataacgggtagattaaaaatga gcagaacatttgaaacacaaat acgggggaaaacgggatgcgt atatatttaaTTA CTTCTCG GCGGAACGAAGGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | turboID::glh-1 5′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 5′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | acctcgacacactcatctacta aattttgggacagttcctaattctt tttgctgttttcaactcaattttctg gaaaaat cttaattttctgcgaa aATG tacccatacga CgtCccaga |
| Sequence-based reagent | turboID::glh-1 3′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 3′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | CTACCGAATCCAGT TTTGGctgaaataaagtttt taatcaaaataaaaccggtgg aaagttcaaaataaaactcac CCTTAGCAGCACTTT CGCTATCACTCCAAC CATCAGA CTTCTCG GCGGAACGAAGGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | pgl-1::turboID 5′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 5′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | tctataaaatctataacaagt taaacatattatttaattataa aaccccgcattgattaaacat attttgatttgaaaaa aaaaac tagaaaataggtaaaataaatc tggaaatagttcagaaac ttagaaattattaaaggcgc ATGtacccatacgaCgtCccaga |
| Sequence-based reagent | pgl-1::turboID 3′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 3′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | ttcgagattagaattcaaaaa aacgcaaaatttacCCAAA AAAGTAAGAAAACGG AAAAGAAAATTGGG ACGAGATCGAAA TTGCAACTTCCG CGTTCGCGTCGAG TTGTTCGTTTCGAGA CCCGTAGATC TGAAACTTC CTTCTCGGCG GAACGAAGGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1::FLAG::AID::GFP::TEV 5′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 5′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | TACAAAAGTGCCAT CCACGACTAGAAG TGTAGTTCTCCCAC CAATGTCAAAAGGA CCAGGATTGGCAC GTTCTCGTAACT TTTCACCACAACAA TCGACTACATCTTCA ATTGATAATGAGTGT CTAGAAGCTATCAAT GCTGCGTTGCCG TCaGAcAAa GAcAGc TGGAGATCCAGTAA AGGAGAAGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | eggd-1::FLAG::AID::GFP::TEV 5′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 3′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | tgaatgactcgcatccaaa atataaaaaaaacaatgtt actattaaaactaattaaa aaataattttacaaaaac acata aacaggatatttt aaagcacgtaaaatttcga TCActtcacgaacgccgccgcct |
| Sequence-based reagent | mCherry::eggd-2 5′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 5′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | acttctgccacgattttgac atttttaagttttaaatcatttt tttgtattcgttatttcagatt tccgttttctgaata tttaa agtcattcaactgattgttttac tgtttccagcatttgcctgaaaa ATGGTCTCAAAGG GTGAAGAAGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | mCherry::eggd-2 3′ homology arm | Integrated DNA Technologies | 3′ primer to amplify dsDNA donor | AAGAAGAACACTATA AGCGTCCCGTTCGA TGCGCTTACGCATTT TGTTCATTTTTTCTTT GCCcTCcTCcTCtGAA GCTC CACCTCCACCTCCCTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | ΔLOTUS1 single strand donor | Integrated DNA Technologies | Single-stranded repair template | AGAAAATACGCGCG CGCATCGAGCGCGA CGTGTACAGTGTTCT GCTATCAAAGAAAAAA AAGAAAGGTGGAAA AGGTGCA AAGCCCA TTCGTGCAGCTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | ΔLOTUS2 single-strand donor | Integrated DNA Technologies | Single-stranded repair template | TTGTTCAAAGACTGT CGTCTACAGTGGCTGT TCCAGTTTTGCAACCCG GGAAGGAACCCTGGTTC ACAAATTTTGGAGCT GC GTTAAAGAAATCAATGCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | ΔIDR1 single strand donor | Integrated DNA Technologies | Single-stranded repair template | caatacattcgttttcagCGCA AATGAGGACAATCA AGAtCTAATtAAcCTtA TtTCtAAACAaAAaA AgAAgAAaAAgG GaGGAAAgGGaACaG TcGTgCAgAGACTtTC tTCaACtGTtGCaGTgC CgGTcTTaCAgCCaG GaATcGAtTCaAAaTGc ATGCCTTCGATCGTT GATTTTTCGAACAA CGTTAAGCGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | ΔIDR2 single strand donor | Integrated DNA Technologies | Single-stranded repair template | ttttagGACTCACAGTG AGTGCCCGTAGCGTA ATGAGATCCAGTAAA GGAGAAGAACTTT TCACTGGAGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | 5′ amplify eggd-1::GFP for cloning | Integrated DNA Technologies | PCR primer | CTTCTT CCTAGG ATG ACGGAAGCTGA CGATCCCAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | 3′ amplify eggd-1::GFP for cloning | Integrated DNA Technologies | PCR primer | CTTCTT GAGCTC TCA CGATTGG AAGTAGAGGTTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | 5′ amplify mCherry::GLH-1 for cloning | Integrated DNA Technologies | PCR primer | CTTCTT CCTAGG ATGGTCTCAAAGG GTGAAGAAGATAACATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | 3′ amplify mCherry::GLH-1 for cloning | Integrated DNA Technologies | PCR primer | CTTCTT GAGCTC CTACCAGCCTT CTTCATCTTGA |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
P granule proteins revealed by TurboID and their IUPRED score.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Known components of P granules, Z granules and Mutator foci in hermaphrodite germ line.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Nuclear pore complex proteins that are enriched by proximity labeling.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Significantly enriched gene ontology terms for TurboID hits.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72276/elife-72276-transrepform1-v2.docx